Anti-Oxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory In Vitro Activity of Amino Acids and Small Peptides: New Hints for the Multifaceted Treatment of Neurologic and Metabolic Disfunctions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Studies
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| ACE | Acarbose equivalents |
| AChE | acetylcholinesterase |
| AcOEt | Ethyl acetate |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ATCI | Acetylthiocholine iodide |
| BChE | Butyrylcholinesterase |
| BTCI | Butyrylthiocholine chloride |
| CECC | Carnosine Equivalent Iron Chelation Capacity |
| ChE | Cholinesterase |
| 13C-NMR | Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance |
| CUPRAC | Cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| DTNB | 5,5-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| EECC | EDTA Equivalent Iron Chelation Capacity |
| EGT | L-ergothioneine |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing ability of plasma |
| GALAE | Galantamine equivalents |
| GSH | Gluthatione |
| HAT | Hydrogen atom transfer |
| 1H-NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance |
| KAE | Kojic acid |
| L-DOPA | Levo-dihydroxy-phenylalanine |
| LPA | Lipid peroxidation assay |
| NEAC | Non enzymatic antioxidant capacity |
| ORAC | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
| OS | Oxidative strees |
| PM | Phosphomolybdenum |
| PNPG | p-nitrophenol-alfa-D-glucopyranoside |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SET | Single electron transfer |
| TAC | Total anti-oxidant capacity |
| Tau | Taurine |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| TEAC | Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity |
| TLC | Thin layer chromatography |
| TPTZ | 2,4,6-tris(2-pyridyl)-S-triazine |
| TRAP | Total radical trapping antioxidant parameter |
References
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: Oxidants and antioxidants. Exp. Physiol. 1997, 82, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Cerretani, L.; Bendini, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Del Carlo, M.; Gallina-Toschi, T.; Lercker, G.; Compagnone, D.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A. Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of individual phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8918–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbo, H.; Batthyany, C.; Radi, R. Nitric Oxide: Oxygen Radical Interactions in Atherosclerosis. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, A.; Anadón, A.; Rodríguez, J.-L.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Yuan, Z.; Martínez, M.-A. Paracetamol: Overdose-induced oxidative stress toxicity, metabolism, and protective effects of various compounds in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 395–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, G.; Abdallah, H.H.; Dogan, A.; Mollica, A.; Aumeeruddy-Elalfi, Z.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Phenolic components and assessment of biological properties of Tchihatchewia isatidea Boiss. extracts: Docking and functional approaches for designing novel products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droge, W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjendirane, V.; Joseph, P.; Jaiswal, A.K. Oxidative Stress and Signal Transduction; Cadenas, E., Forman, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 1997; pp. 441–469. [Google Scholar]
- Bartosz, G. Non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity assays: Limitations of use in biomedicine. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.A.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant activity/capacity measurement. 2. Hydrogen atom transfer (HAT)-based, mixed-mode (electron transfer (ET)/HAT), and lipid peroxidation assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1028–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metodiewa, D.; Kośka, C. Reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species: Relevance to cyto (neuro) toxic events and neurologic disorders. An overview. Neurotox. Res. 1999, 1, 197–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, X.; Li, X. Cardiovascular diseases: Oxidative damage and antioxidant protection. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Tota, S.; Nath, C.; Tyagi, N. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress and Synapse Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding the Therapeutics Strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramutola, A.; Lanzillotta, C.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress, protein modification and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 133, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.S.I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagni, A.; Lucente, G.; Luisi, G.; Pinnen, F.; Rossi, D. Novel glutathione analogues containing the dithiol and disulfide form of the Cys-Cys dyad. Amino Acids 1999, 17, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, A.; Leboffe, L.; Agamennone, M.; Di Pizio, A.; Fiocchetti, M.; Marino, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Luisi, G. Ac-tLeu-Asp-H is the minimal and highly effective human caspase-3 inhibitor: Biological and in silico studies. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Mirzaie, S.; Costante, R.; Carradori, S.; Macedonio, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Dvoracsko, S.; Novellino, E. Exploring the biological consequences of conformational changes in aspartame models containing constrained analogues of phenylalanine. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdei, A.I.; Borbély, A.; Magyar, A.; Szűcs, E.; Ötvös, F.; Gombos, D.; Al-Khrasani, M.; Stefanucci, A.; Dimmito, M.P.; Luisi, G.; et al. Biochemical and pharmacological investigation of novel nociceptin/OFQ analogues and N/OFQ-RYYRIK hybrid peptides. Peptides 2018, 99, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Noor, J. Natural Products as a Potential Enzyme Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants, Enzyme Inhibitors and Activators, Murat Senturk. IntechOpen. 2017. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/enzyme-inhibitors-and-activators/natural-products-as-a-potential-enzyme-inhibitors-from-medicinal-plants (accessed on 29 March 2017). [CrossRef]
- Revadigar, V.; Ghalib, R.M.; Murugaiyah, V.; Embaby, M.A.; Jawad, A.; Mehdi, S.H.; Hashim, R.; Sulaiman, O. Enzyme Inhibitors Involved in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Drug Design and Discovery in Alzheimer’s Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 142–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kandiah, N.; Pai, M.-C.; Senanarong, V.; Looi, I.; Ampil, E.; Park, K.W.; Karanam, A.K.; Christopher, S. Rivastigmine: The advantages of dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase and its role in subcortical vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Baek, N.; Nam, T.-G. Natural, semisynthetic and synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tief, K.; Schmidt, A.; Beermann, F. New evidence for presence of tyrosinase in substantia nigra, forebrain and midbrain. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 53, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Peng, J. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollica, A.; Zengin, G.; Durdagi, S.; Ekhteiari, S.R.; Macedonio, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Dimmito, M.P.; Novellino, E. Combinatorial peptide library screening for discovery of diverse α-glucosidase inhibitors using molecular dynamics simulations and binary QSAR models. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisi, G.; Mollica, A.; Carradori, S.; Lenoci, A.; De Luca, A.; Caccuri, A.M. Nitrobenzoxadiazole-based GSTP1-1 inhibitors containing the full peptidyl moiety of (pseudo) glutathione. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colantonio, P.; Leboffe, L.; Bolli, A.; Marino, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Luisi, G. Human caspase-3 inhibition by Z-tLeu-Asp-H: TLeu (P2) counterbalances Asp (P4) and Glu (P3) specific inhibitor truncation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowski, D.M.; Uysal, S.; Aktumsek, A.; Granica, S.; Zengin, G.; Ceylan, R.; Locatelli, M.; Tomczyk, M. In vitro enzyme inhibitory properties, antioxidant activities, and phytochemical profile of Potentilla thuringiaca. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagni, A.; Duprè, S.; Lucente, G.; Luisi, G.; Pinnen, F.; Rossi, D.; Spirito, A. Synthesis and Activity of the Glutathione Analogue γ-(L-γ-Oxaglutamyl)-L-cysteinyl-glycine. Arch. Pharm. 1996, 329, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, I.K.; Halliwell, B. Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.A.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant activity/capacity measurement. 1. Classification, physicochemical principles, mechanisms, and electron transfer (ET)-based assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 4, 997–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, N.; Mori, I.; Sugiura, Y.; Tanaka, H. Metal complexes of ergothioneine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1974, 22, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Pandya, K.; Clark, G.J.; Parikh, M.C.; Lau-Cam, C.A. Comparison of taurine and pantoyltaurine as antioxidants in vitro and in the central nervous system of diabetic rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bold, G.; Fässler, A.; Capraro, H.-G.; Cozens, R.; Klimkait, T.; Lazdins, J.; Mestan, J.; Poncioni, B.; Rösel, J.; Stover, D. New aza-dipeptide analogues as potent and orally absorbed HIV-1 protease inhibitors: Candidates for clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3387–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommarius, A.S.; Schwarm, M.; Stingl, K.; Kottenhahn, M.; Huthmacher, K.; Drauz, K. Synthesis and use of enantiomerically pure tert-leucine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1995, 6, 2851–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.C.; Sherman, J.C.; Chen, A.; Kallenbach, N.R. Alpha-helix stabilization by natural and unnatural amino acids with alkyl side chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5317–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, A.K.; Easton, C.J.; Radom, L. Design of radical-resistant amino acid residues: A combined theoretical and experimental investigation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanimuthu, D.; Wu, Z.; Jansson, P.J.; Braidy, N.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R.; Kalinowski, D.S. Novel chelators based on adamantane-derived semicarbazones and hydrazones that target multiple hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7190–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mechanisms of Assays | Type of Assay | pH | Solvent | Anti-Oxidant Character |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assays involving Single Electron Transfer (SET) reactions ● Non-competitive reduction-based assays | FRAP (Ferric ion Reducing Anti-oxidant Power) ● The assay does not sufficiently responds to thiols due to the kinetic inertness of high-spin Fe(III) in the TPTZ complex | acid | water | hydrophilic |
| CUPRAC (CUPric Reducing Anti-oxidant Capacity) ● The reagent rapidly oxidizes thiol-containing anti-oxidants | neutral | alcohols, acetone, DCM, alcohol-water mixtures | lipophilic and hydrophilic | |
| PM (Phosphomolybdenum assay) | 4–5 | water | hydrophilic | |
| Assays involving mixed-mode Hydrogen Atom Transfer (HAT) /SET reactions ● Non-competitive scavenging and reduction-based assays | DPPH (2,2-Di-Phenyl-1-Picryl-Hydrazyl) | 3–7.5 | methanol, ethanol alcohol-water mixtures | lipophilic and hydrophilic |
| ABTS (2,2-Azino-Bis(3-ethylbenzo-Thiazoline)-6-Sulphonic acid ● Thiols are oxidized by ABTS.+ radical cation to higher oxidation levels (sulfenic and sulfinic acids) | acid | water, ethanol | lipophilic and hydrophilic |
| Compounds | DPPH (mgTE/g Sample) | ABTS (mgTE/g Sample) | CUPRAC (mgTE/g Sample) | FRAP (mgTE/g Sample) | Phosphomolybdenum (mmolTE/g Sample) | Metal Chelating (mgEDTAE/g Sample) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-cysteine (1) | 102.50 ± 1.43 a | 245.14 ± 0.21 a | 939.97 ± 2.96 a | 761.90 ± 16.69 a | 2.28 ± 0.02 b | not active |
| GSH (2) | 65.48 ± 2.81 b | 196.89 ± 0.38 b | 389.74 ± 7.88 c | 143.03 ± 6.68 c | 2.50 ± 0.11 a | not active |
| H-Glo(Cys-Gly-OH)-OH (3) | 106.07 ± 0.54 a | not active | 69.36 ± 0.97 f | 41.44 ± 0.86 c | 0.21 ± 0.04 e | 70.91 ± 0.17 b |
| L-cystine (4) | 100.79 ± 0.40 a | 1.20 ± 0.08 f | 124.72 ± 4.13 d | 41.59 ± 0.35 e | 0.11 ± 0.01 f | 84.77 ± 0.11 a |
| Ergothioneine (5) | 73.23 ± 0.13 c | 123.88 ± 0.24 c | 534.55 ± 7.87 b | 114.94 ± 1.75 d | 2.46 ± 0.02 a | 1.35 ± 0.27 f |
| Taurine (6) | not active | 5.47 ± 0.14 e | 26.19 ± 0.53 g | 13.47 ± 0.63 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 g | 20.45 ± 2.08 d |
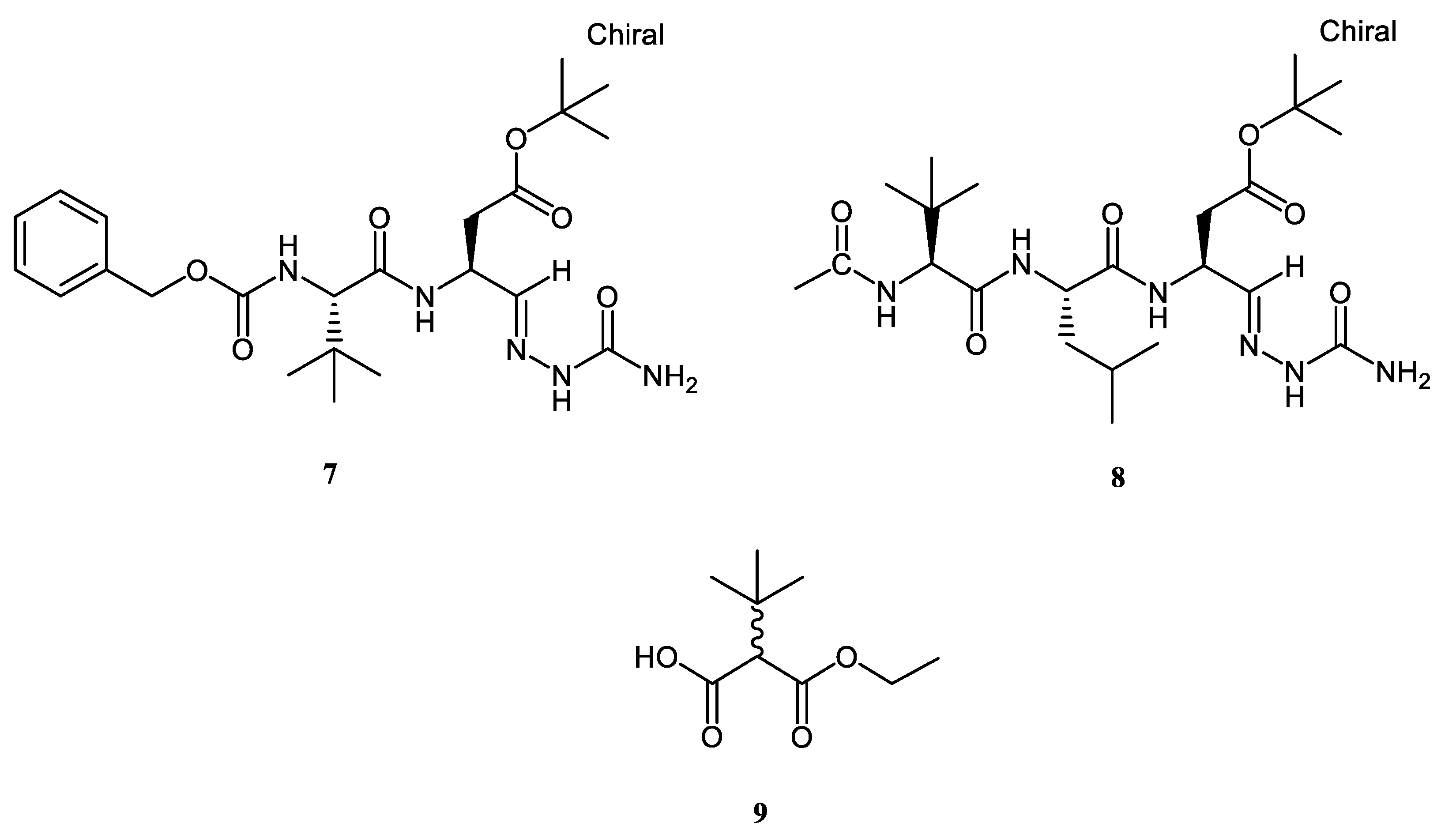
| Z-tleu-Asp (OtBu)-Sc (7) | not active | not active | 84.30 ± 1.39 e | 30.33 ± 1.44 f | 0.36 ± 0.01 d | 43.69 ± 3.40 c |
| Ac-tLeu-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Sc (8) | not active | 48.01 ± 1.41 d | 81.31 ± 1.85 e | 170.47 ± 5.50 b | 2.62 ± 0.13 a | 82.70 ± 3.01 a |
| Ethyl 2-tBu-(DL)-mono-malonate (9) | not active | not active | 27.41 ± 3.53 g | 14.29 ± 0.36 g | 0.54 ± 0.01 c | 13.76 ± 3.27 e |
| Compounds | AChE Inhibition (mgGALAE/g) | BChE Inhibition (mgGALAE/g) | Tyrosinase Inhibition (mgKAE/g) | Amylase Inhibition (mmolACAE/g) | Glucosidase Inhibition (mmolACAE/g Sample) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-cysteine (1) | 5.12 ± 0.15 a | 6.14 ± 0.08 ab | 216.40 ± 0.17 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 e | not active |
| GSH (2) | 3.62 ± 0.04 b | 6.13 ± 0.12 ab | 45.60 ± 0.15 e | 0.03 ± 0.01 f | not active |
| H-Glo(Cys-Gly-OH)-OH (3) | not active | 6.39 ± 0.01 a | 216.95 ± 0.17 a | 1.37 ± 0.03 b | 1.69 ± 0.01 b |
| L-cystine (4) | 5.24 ± 0.02 a | 6.38 ± 0.01 a | 217.16 ± 0.55 a | 1.95 ± 0.04 a | 1.68 ± 0.02 b |
| Ergothioneine (5) | 3.01 ± 0.01 c | 0.18 ± 0.05 d | 100.97 ± 1.71 d | 0.07 ± 0.01 e | not active |
| Taurine (6) | 0.45 ± 0.03 e | 0.07 ± 0.01 e | 33.87 ± 1.59 f | 0.07 ± 0.01 e | 3.96 ± 0.95 a |
| Z-tleu-Asp (OtBu)-Sc (7) | not active | 6.37 ± 0.01 a | 163.87 ± 0.90 b | 0.31 ± 0.06 c | 1.69 ± 0.01 b |
| Ac-tLeu-Leu-Asp(OtBu)-Sc (8) | 5.17 ± 0.07 a | 6.33 ± 0.01 a | 152.69 ± 1.19 c | 0.39 ± 0.08 c | not active |
| ethyl 2-tBu-(DL)-mono-malonate (9) | 2.61 ± 0.01 d | 2.96 ± 0.08 c | 45.37 ± 0.52 e | 0.20 ± 0.02 d | 0.84 ± 0.01 c |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luisi, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Zengin, G.; Dimmito, M.P.; Mollica, A. Anti-Oxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory In Vitro Activity of Amino Acids and Small Peptides: New Hints for the Multifaceted Treatment of Neurologic and Metabolic Disfunctions. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8010007
Luisi G, Stefanucci A, Zengin G, Dimmito MP, Mollica A. Anti-Oxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory In Vitro Activity of Amino Acids and Small Peptides: New Hints for the Multifaceted Treatment of Neurologic and Metabolic Disfunctions. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuisi, Grazia, Azzurra Stefanucci, Gokhan Zengin, Marilisa Pia Dimmito, and Adriano Mollica. 2019. "Anti-Oxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory In Vitro Activity of Amino Acids and Small Peptides: New Hints for the Multifaceted Treatment of Neurologic and Metabolic Disfunctions" Antioxidants 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8010007
APA StyleLuisi, G., Stefanucci, A., Zengin, G., Dimmito, M. P., & Mollica, A. (2019). Anti-Oxidant and Tyrosinase Inhibitory In Vitro Activity of Amino Acids and Small Peptides: New Hints for the Multifaceted Treatment of Neurologic and Metabolic Disfunctions. Antioxidants, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8010007







