Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress in Human Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer: Evidence from 4-Hydroxyneonal Detection and Its Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Generation of Macrophage-Conditioned Media and Treatment of PZ-HPV7 Cells
2.3. Total Cell Lysates Collection and Immunoblotting
2.4. Human Prostate Tissue Samples
2.5. Immunohistochemistry and Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
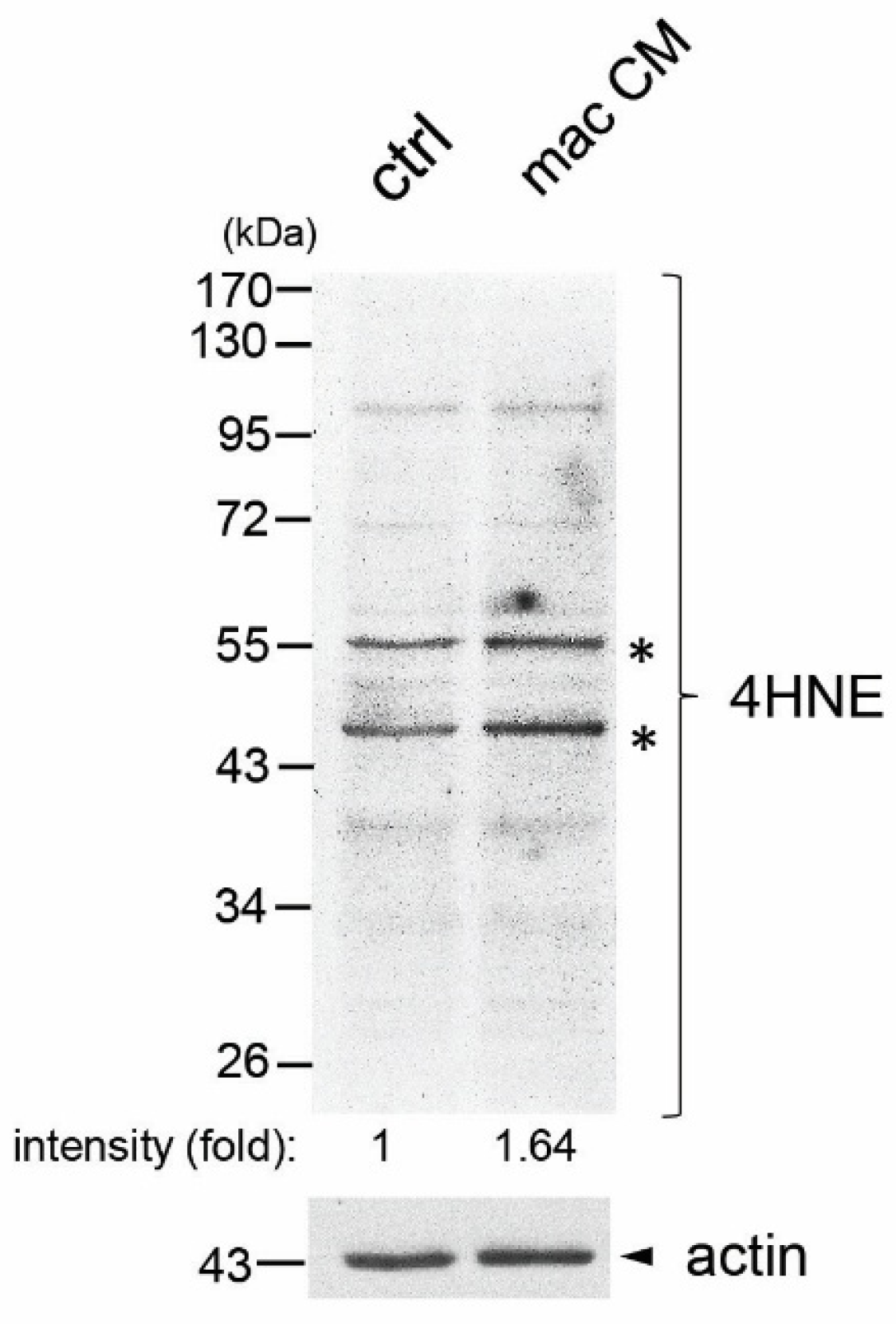
3.1. Macrophage-Conditioned Media Increased Formation of 4HNE Protein Adducts in Immortalized Human Normal Prostate Epithelial Cell Line PZ-HPV7
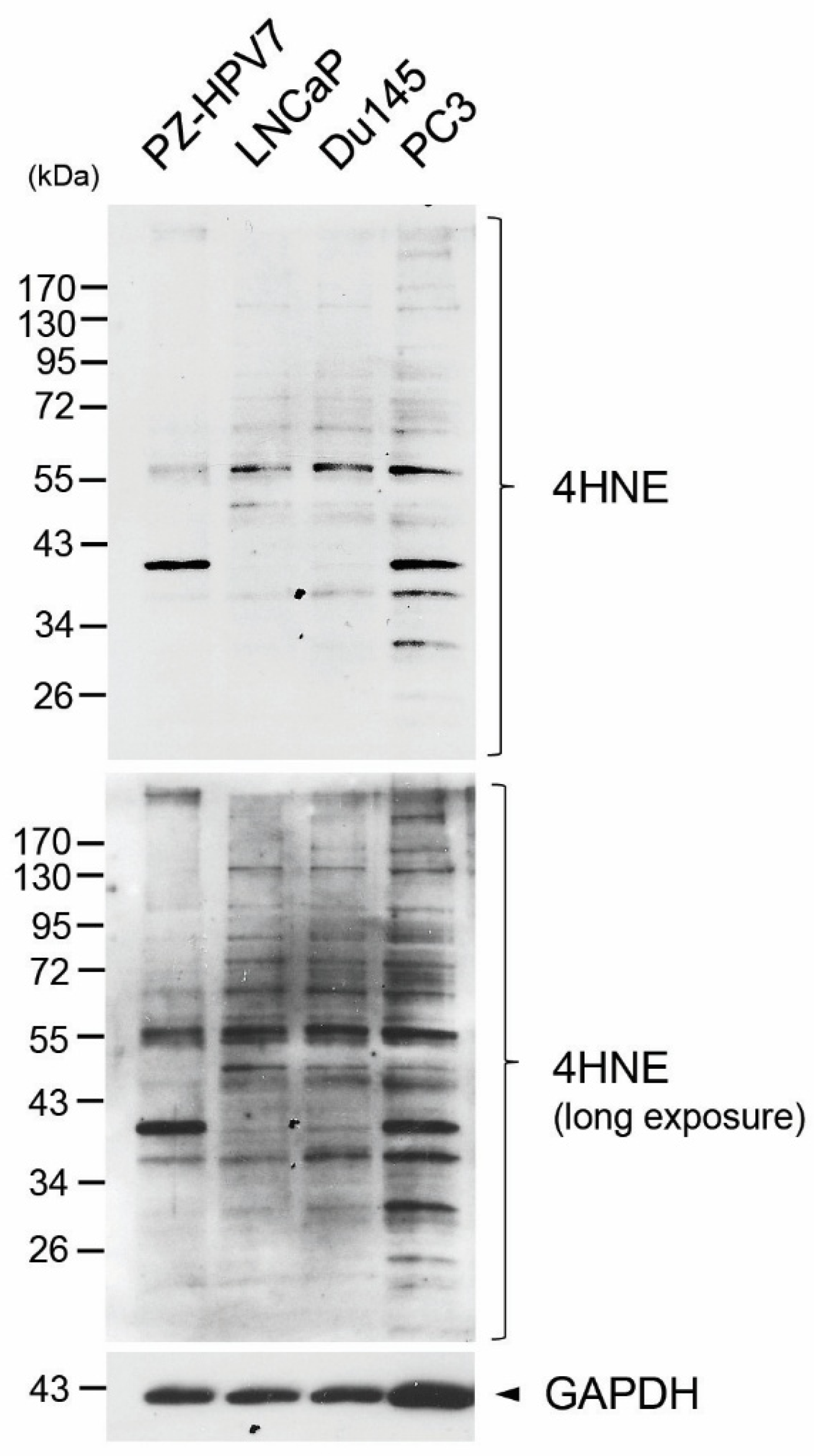
3.2. Elevated Production of 4HNE Protein Adducts in Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
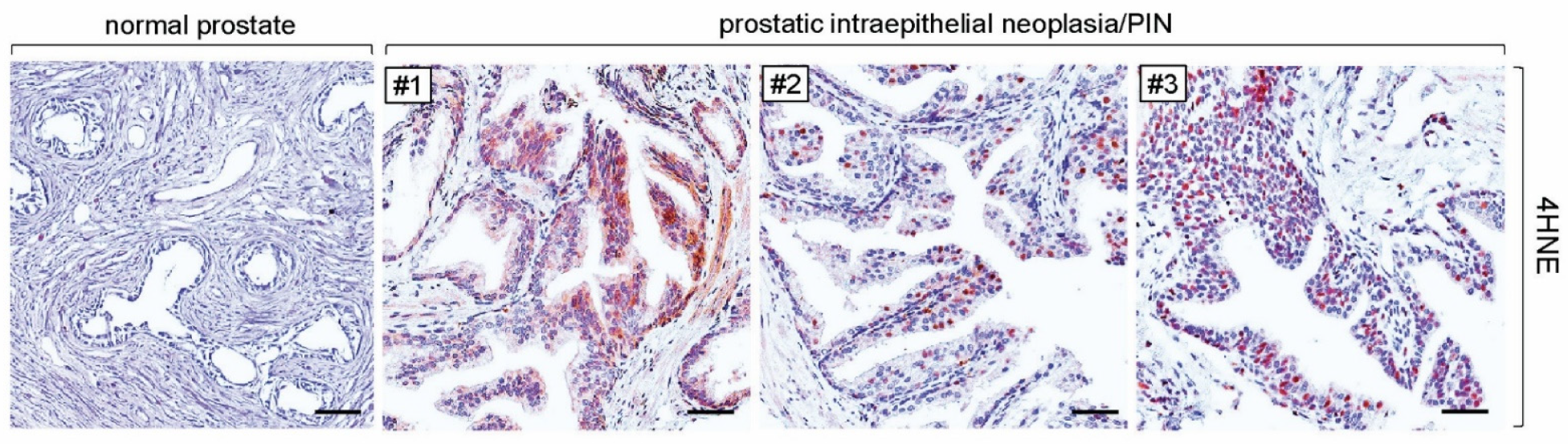
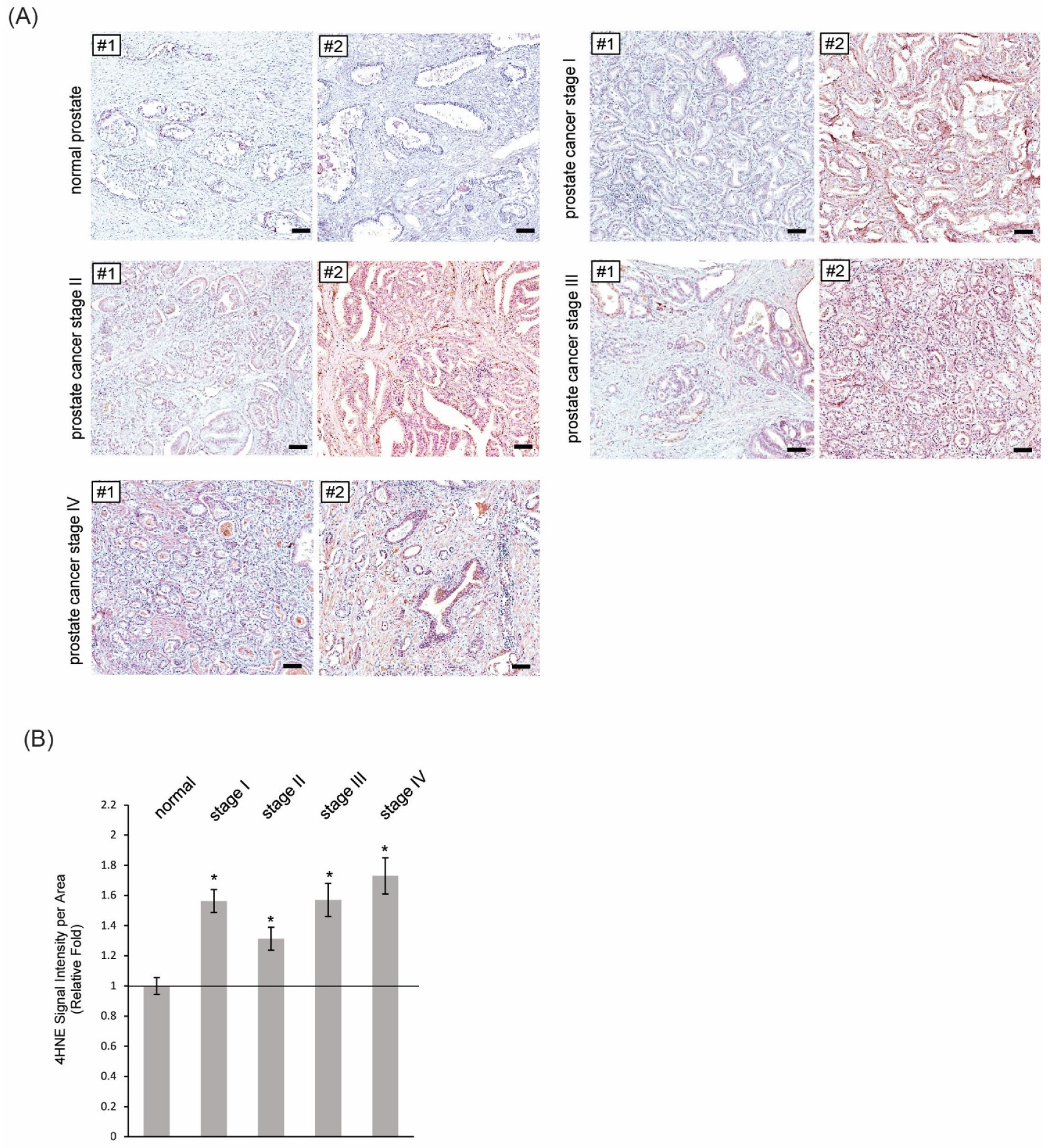
3.3. More Formations of 4HNE Adducts Were Present in Human Tissues of PIN and Prostate Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Deruy, E.; Peugnet, V.; Turkieh, A.; Pinet, F. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierengarten, M.B. Cancer Statistics 2024: Deaths drop, incidences increase, prevention needed. Cancer 2024, 130, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Perez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Perez-Lebena, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catala, A. Lipid peroxidation of membrane phospholipids generates hydroxy-alkenals and oxidized phospholipids active in physiological and/or pathological conditions. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalleau, S.; Baradat, M.; Gueraud, F.; Huc, L. Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress: 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitzig, M.; Bhimineni, C.; Lockey, R.; Kolliputi, N. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal: A critical target in oxidative stress? Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 311, C537–C543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalas, B.P.; De Iuliis, G.N.; Redgrove, K.A.; McLaughlin, E.A.; Nixon, B. The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal contributes to oxidative stress-mediated deterioration of the ageing oocyte. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Yin, H. Role of lipid peroxidation derived 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in cancer: Focusing on mitochondria. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wu, G.; Wu, Z. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal induces apoptosis by activating ERK1/2 signaling and depleting intracellular glutathione in intestinal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeb, M.; Ansari, N.H.; Srivastava, S.K.; Ramana, K.V. 4-Hydroxynonenal in the pathogenesis and progression of human diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Y.; Cohen, G.; Shamni, O.; Sasson, S. Signaling and cytotoxic functions of 4-hydroxyalkenals. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E879–E886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Liou, G.Y. Macrophage Cytokines Enhance Cell Proliferation of Normal Prostate Epithelial Cells through Activation of ERK and Akt. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, G.Y.; Byrd, C.J.; Storz, P.; Messex, J.K. Cytokine CCL9 Mediates Oncogenic KRAS-Induced Pancreatic Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia by Promoting Reactive Oxygen Species and Metalloproteinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messex, J.K.; Adams, K.L.A.; Hawkins, W.G.; DeNardo, D.; Bardeesy, N.; Billadeau, D.D.; Liou, G.Y. Oncogenic Kras-Mediated Cytokine CCL15 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through ROS. Cancers 2022, 14, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messex, J.K.; Byrd, C.J.; Thomas, M.U.; Liou, G.Y. Macrophages Cytokine Spp1 Increases Growth of Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia to Promote Prostate Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.U.; Messex, J.K.; Dang, T.; Abdulkadir, S.A.; Jorcyk, C.L.; Liou, G.Y. Macrophages expedite cell proliferation of prostate intraepithelial neoplasia through their downstream target ERK. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 1871–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkahwaji, J.E.; Hauke, R.J.; Brawner, C.M. Chronic bacterial inflammation induces prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in mouse prostate. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Koul, S.; Khandrika, L.; Meacham, R.B.; Koul, H.K. Oxidative stress is inherent in prostate cancer cells and is required for aggressive phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.K.; Gemin, A.; Singh, G. High activity of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and glycerophosphate-dependent ROS production in prostate cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.K.; Raha, S.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Singh, G. Increased expression of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and antioxidant enzymes in prostate cancer cell lines/cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amamoto, R.; Uchiumi, T.; Yagi, M.; Monji, K.; Song, Y.; Oda, Y.; Shiota, M.; Yokomizo, A.; Naito, S.; Kang, D. The Expression of Ubiquitous Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase Is Downregulated as Prostate Cancer Progression. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schopf, B.; Weissensteiner, H.; Schafer, G.; Fazzini, F.; Charoentong, P.; Naschberger, A.; Rupp, B.; Fendt, L.; Bukur, V.; Giese, I.; et al. OXPHOS remodeling in high-grade prostate cancer involves mtDNA mutations and increased succinate oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, L.; Morandi, A.; Taddei, M.L.; Parri, M.; Comito, G.; Iscaro, A.; Raspollini, M.R.; Magherini, F.; Rapizzi, E.; Masquelier, J.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote prostate cancer malignancy via metabolic rewiring and mitochondrial transfer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5339–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsova-Sarafinovska, Z.; Eken, A.; Matevska, N.; Erdem, O.; Sayal, A.; Savaser, A.; Banev, S.; Petrovski, D.; Dzikova, S.; Georgiev, V.; et al. Increased oxidative/nitrosative stress and decreased antioxidant enzyme activities in prostate cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.M.; Oberley, L.W.; Cohen, M.B. Expression of antioxidant enzymes in human prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate 1997, 32, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Alexander, E.E.; Singh, R.; Shan, A.; Qian, J.; Santella, R.M.; Oberley, L.W.; Yan, T.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, X.; et al. Antioxidant enzyme expression and reactive oxygen species damage in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer. Cancer 2000, 89, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiswing, L.; Zhong, W.; Oberley, T.D. Increasing discordant antioxidant protein levels and enzymatic activities contribute to increasing redox imbalance observed during human prostate cancer progression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 67, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, N.; Oberley, T.D.; Oberley, L.W.; Zhong, W. Overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase in DU145 human prostate carcinoma cells has multiple effects on cell phenotype. Prostate 1998, 35, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Jiang, H.; Thapa, P.; Hao, Y.; Alshahrani, A.; Allison, D.; Izumi, T.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Liu, X.; Wei, Q. Peroxiredoxin IV plays a critical role in cancer cell growth and radioresistance through the activation of the Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury-Paulino, I.M.; Ericsson, C.; Vince, R., Jr.; Spratt, D.E.; George, D.J.; Mucci, L.A. Racial disparities in prostate cancer among black men: Epidemiology and outcomes. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinata, N.; Fujisawa, M. Racial Differences in Prostate Cancer Characteristics and Cancer-Specific Mortality: An Overview. World J. Mens. Health 2022, 40, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, M.; Xie, Y.; Nawrocki, S.; Morze, J.; Ran, X.; Shan, T.; Xia, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; et al. Racial/ethnic disparities in the cause of death among patients with prostate cancer in the United States from 1995 to 2019: A population-based retrospective cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 62, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Berglund, A.; Abraham-Miranda, J.; Rounbehler, R.J.; Kensler, K.; Serna, A.; Vidal, A.; You, S.; Freeman, M.R.; Davicioni, E.; et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals Distinct Immune-oncologic Pathways in African American Men with Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, S.H.; Holwerda, S.W.; Keller, D.M.; Fadel, P.J. Elevated peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived superoxide production in healthy young black men. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 308, H548–H552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feairheller, D.L.; Park, J.Y.; Sturgeon, K.M.; Williamson, S.T.; Diaz, K.M.; Veerabhadrappa, P.; Brown, M.D. Racial differences in oxidative stress and inflammation: In vitro and in vivo. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2011, 4, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, G.Y.; C’Lay-Pettis, R.; Kavuri, S. Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species in Prostate Cancer and Its Disparity in African Descendants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liou, G.-Y.; Kim, W.; Hobbs, T.M. Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress in Human Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer: Evidence from 4-Hydroxyneonal Detection and Its Implications. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091060
Liou G-Y, Kim W, Hobbs TM. Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress in Human Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer: Evidence from 4-Hydroxyneonal Detection and Its Implications. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(9):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiou, Geou-Yarh, Woojung Kim, and Tamiya M. Hobbs. 2025. "Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress in Human Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer: Evidence from 4-Hydroxyneonal Detection and Its Implications" Antioxidants 14, no. 9: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091060
APA StyleLiou, G.-Y., Kim, W., & Hobbs, T. M. (2025). Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress in Human Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer: Evidence from 4-Hydroxyneonal Detection and Its Implications. Antioxidants, 14(9), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091060





