Rutaecarpine Protects Human Endothelial Cells from Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis via TRPV1- and AhR-Mediated Nrf2 Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assessment
2.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. ROS Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Annexin V and Dead Cell Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
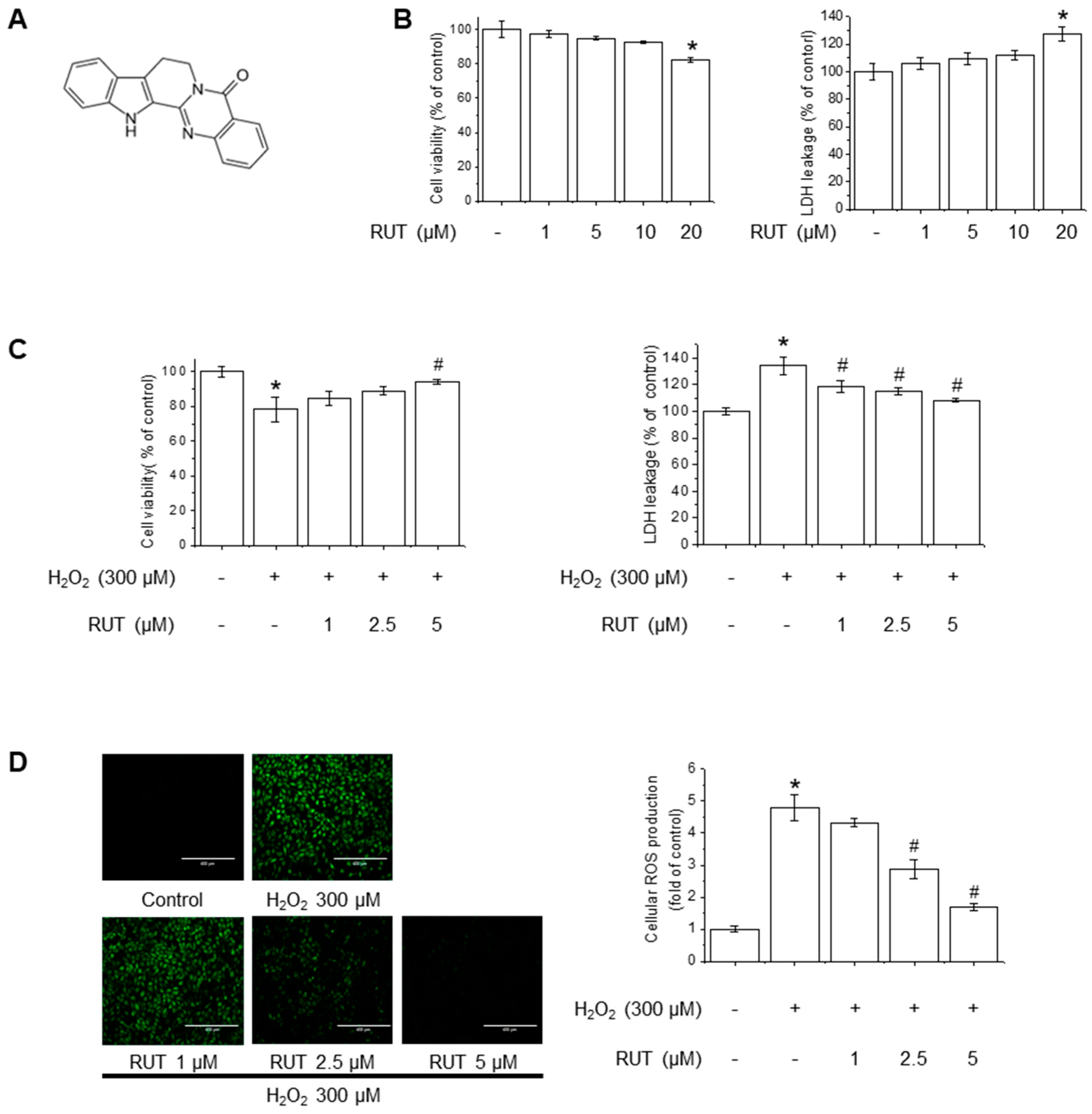
3.1. RUT Exerts a Protective Effect on Endothelial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress
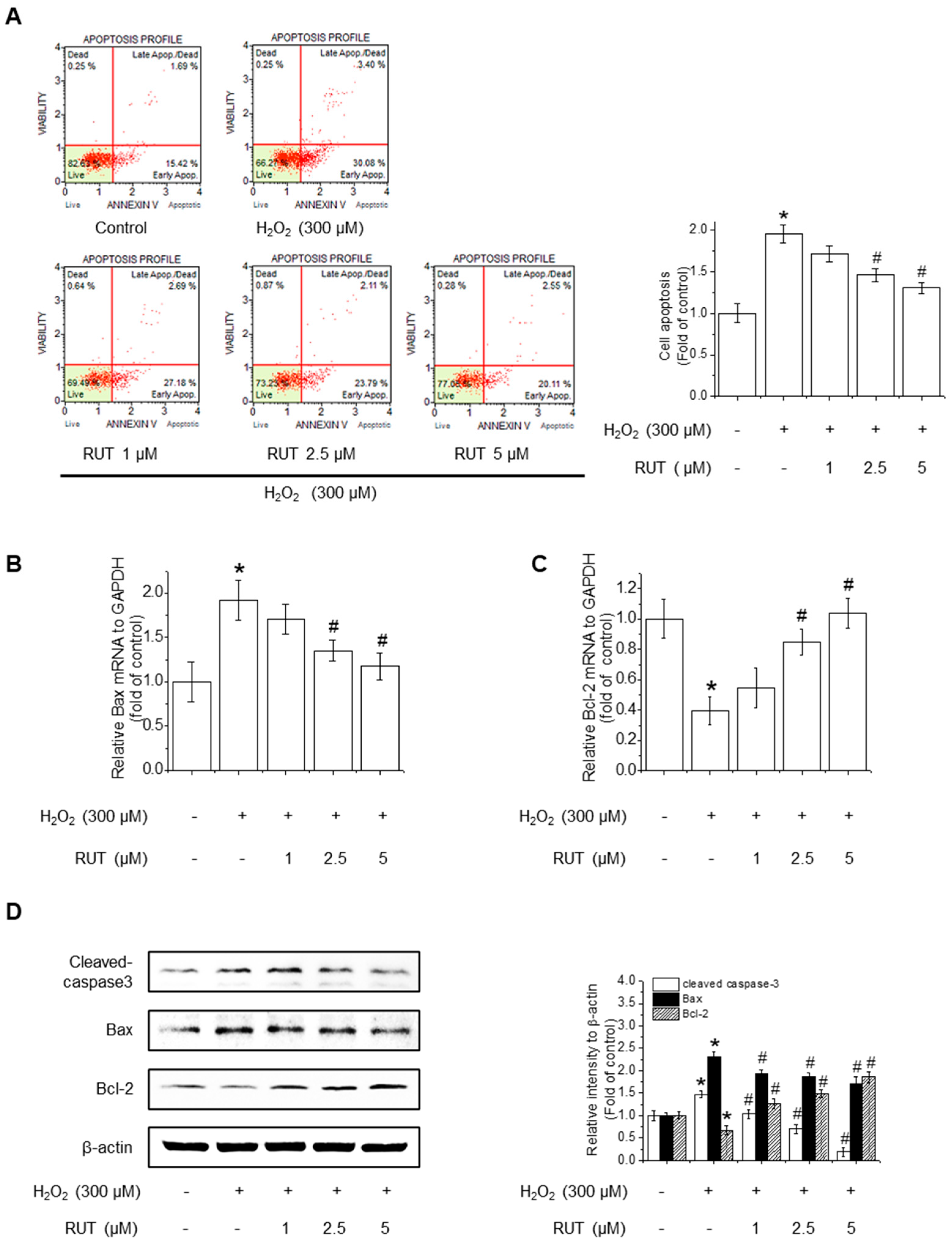
3.2. RUT Ameliorates H2O2-Induced Apoptosis by Regulating Apoptotic Pathways
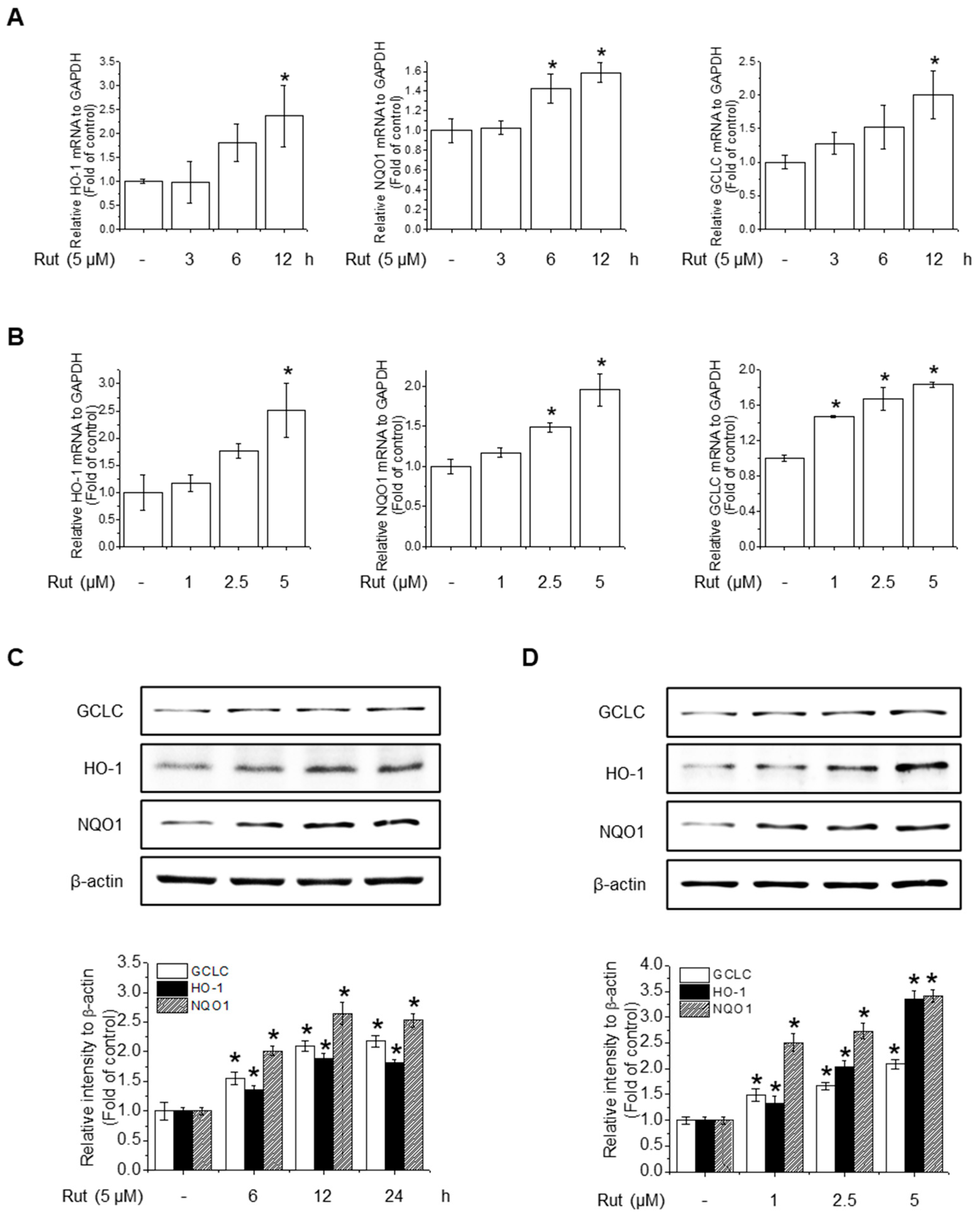
3.3. RUT Enhances Antioxidant Activity Through Nrf2 Activation via the PI3K/Akt and PKCδ Signaling Pathways
3.4. TRPV1-Mediated Calcium Influx Regulates Akt/PKCδ Signaling to Promote Nrf2 Activation
3.5. RUT Induces Nrf2 Expression by Activating the AhR Signaling Pathway
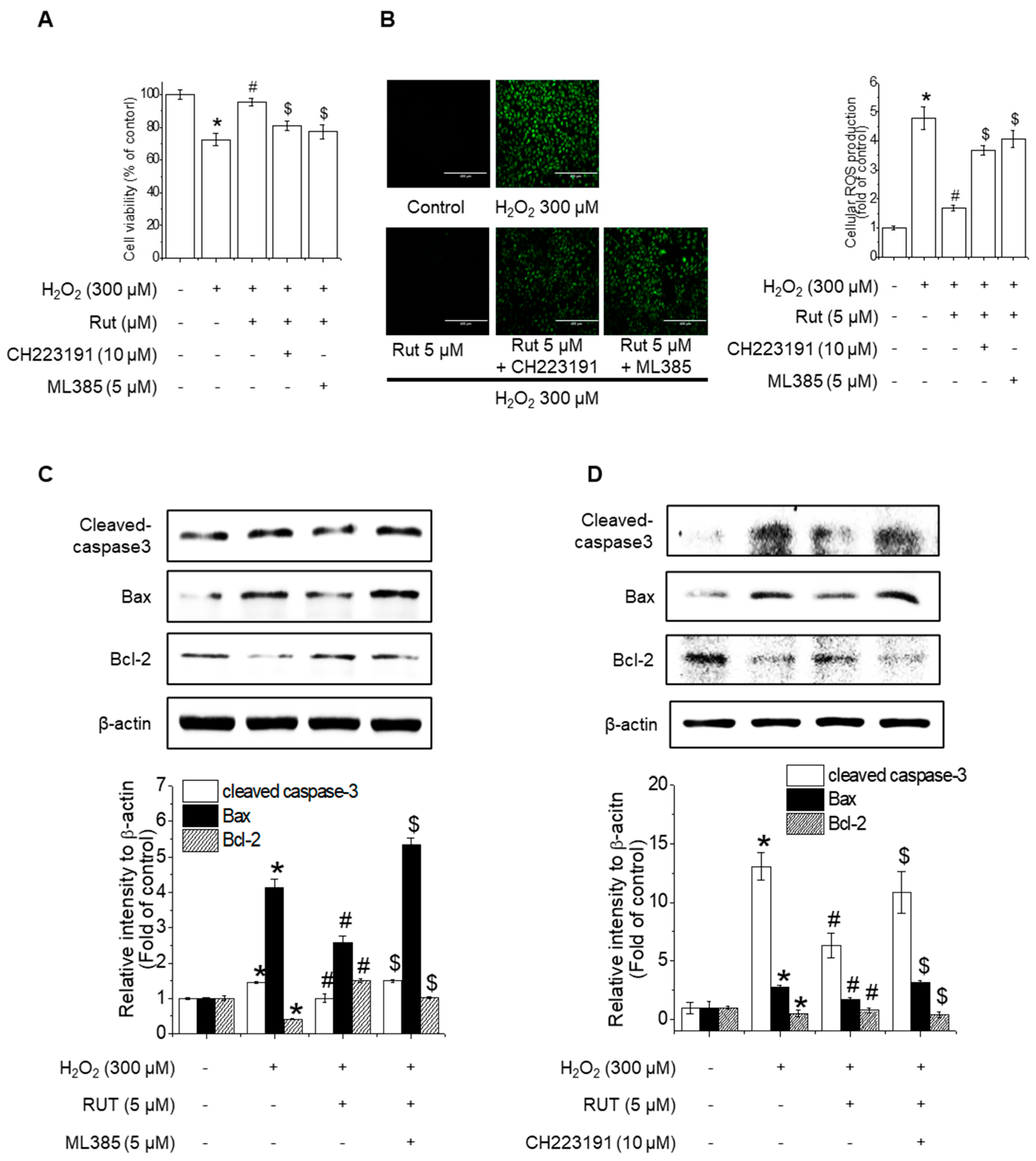
3.6. Nrf2 and AhR Inhibition Counteracts RUT-Mediated Protection Against Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AhR | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| ARE | Antioxidant response element |
| BAPTA | 1,2-Bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| CYP1A1 | Cytochrome P450 Family 1 Subfamily A Member 1 |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| GCLC | Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit |
| Hsp90 | Heat shock protein 90 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| IAPs | Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1 |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NQO1 | NADPH dehydrogenase quinone 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RUT | Rutaecarpine |
| TRPV | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V |
| XRE | Xenobiotic response element |
References
- Higashi, Y.; Noma, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Kihara, Y. Endothelial function and oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Oever, I.A.; Raterman, H.G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Simsek, S. Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and apoptosis in diabetes mellitus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 792393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Gori, T.; Münzel, T. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaito, A.; Aramouni, K.; Assaf, R.; Parenti, A.; Orekhov, A.; Yazbi, A.E.; Pintus, G.; Eid, A.H. Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, N.; Alam, J.; Venkatesan, M.I.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Schmitz, D.; Stefano, E.D.; Slaughter, N.; Killeen, E.; Wang, X.; Huang, A.; et al. Nrf2 is a key transcription factor that regulates antioxidant defense in macrophages and epithelial cells: Protecting against the proinflammatory and oxidizing effects of diesel exhaust chemicals. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3467–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.O.; Kensler, T.W. Nrf2 signaling: An adaptive response pathway for protection against environmental toxic insults. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, M.; Covi, V.; Tabaracci, G.; Malatesta, M. The role of Nrf2 in the antioxidant cellular response to medical ozone exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osama, A.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Fang, J. Nrf2: A dark horse in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, C.P.; Glass, C.A.; Montgomery, M.B.; Lindl, K.A.; Ritson, G.P.; Chia, L.A.; Hamilton, R.L.; Chu, C.T.; Jordan-Sciutto, K.L. Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.N.; Jeon, W.K.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, B.C. Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through CaMKII-ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of bisdemethoxycurcumin in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizuka, Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature 1984, 308, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Itoh, K.; Yoshida, E.; Miyagishi, M.; Fukamizu, A.; Yamamoto, M. Two domains of Nrf2 cooperatively bind CBP, a CREB binding protein, and synergistically activate transcription. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, P.; Rojo, A.I.; Evrard-Todeschi, N.; Innamorato, N.G.; Cotte, A.; Jaworski, T.; Tobón-Velasco, J.C.; Devijver, H.; García-Mayoral, M.F.; Van Leuven, F.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by the glycogen synthase kinase 3/beta-TrCP axis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 3486–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Hu, L.; Scrivens, P.J.; Batist, G. Transcriptional regulation of NF-E2 p45-related factor (NRF2) expression by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-xenobiotic response element signaling pathway: Direct cross-talk between phase I and II drug-metabolizing enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20340–20348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.S.; Oh, H.; Rhee, S.G.; Yoo, Y.D. Regulation of reactive oxygen species generation in cell signaling. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Zheng, C.; Jin, S.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Han, E.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Jeong, H.G. Rutaecarpine increases nitric oxide synthesis via eNOS phosphorylation by TRPV1-dependent CaMKII and CaMKKbeta/AMPK signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.H.; Kim, H.G.; Im, J.H.; Jeong, T.C.; Jeong, H.G. Up-regulation of CYP1A1 by rutaecarpine is dependent on aryl hydrocarbon receptor and calcium. Toxicology 2009, 266, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.W.; Hwang, Y.P.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Chung, Y.C.; Lee, K.J.; Jeong, T.C.; Jeong, H.G. Protective effect of rutaecarpine against t-BHP-induced hepatotoxicity by upregulating antioxidant enzymes via the CaMKII-Akt and Nrf2/ARE pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.Q.; Yang, G.L.; Ren, L.; Chen, W.N.; Feng, Y.Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.T.; Lei, P. Tanshinone IIA reduces apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide in the human endothelium-derived EA.hy926 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, X.W.; Qui, Z.; Li, J.J. Aspirin Eugenol Ester Reduces H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress of HUVECs via Mitochondria-Lysosome Axis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8098135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silambarasan, T.; Manivannan, J.; Priya, M.K.; Suganya, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Raja, B. Sinapic Acid Prevents Hypertension and Cardiovascular Remodelling in Pharmacological Model of Nitric Oxide Inhibited Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.X.; Liu, G.Y.; Lei, H.; Li, Z.L.; Feng, Q.P.; Huang, W. Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 protects the heart against apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion injury through upregulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, L.; Hernández-García, D.; Schnabel, D.; Salas-Vidal, E.; Castro-Obregón, S. Function of reactive oxygen species during animal development: Passive or active? Dev. Biol. 2008, 320, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, X.Y.; He, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.W.; Liu, P.Q.; Gu, L.Q.; Ye, J.M.; et al. Rutaecarpine analogues reduce lipid accumulation in adipocytes via inhibiting adipogenesis/lipogenesis with AMPK activation and UPR suppression. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Ahn, H.; Nam, K.W.; Kim, K.H.; Mar, W. Effects of rutaecarpine on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in murine hepa-1c1c7 cells. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.K.; Chang, H.W.; Jahng, Y. Progress in studies on rutaecarpine. II.–Synthesis and Structure-Biological Activity Relationships. Molecules 2015, 20, 10800–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Liu, R. Evodiamine and rutaecarpine from Tetradium ruticarpum in the treatment of liver diseases. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, H.S.; Yang, D.; Park, E.Y.; Jun, H.S. EX4 stabilizes and activates Nrf2 via PKCdelta, contributing to the prevention of oxidative stress-induced pancreatic beta cell damage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 315, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Pan, T.; Yu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, P.; Yang, H.; Li, P. Activated PKB/GSK-3beta synergizes with PKC-delta signaling in attenuating myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via potentiation of NRF2 activity: Therapeutic efficacy of dihydrotanshinone-I. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munjuluri, S.; Wilkerson, D.; Sooch, G.; Chen, X.; White, F.A.; Obukhov, A.G. Capsaicin and TRPV1 Channels in the Cardiovascular System: The Role of Inflammation. Cells 2021, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.H.; Kim, I.K.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, H.Y.; Im, J.H.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, S.H. The effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia in bleomycin-induced lung injury on pulmonary fibrosis via regulating the NF-kappaB/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2020, 83 (Suppl. S1), S63–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Bui, A.T.N.; Jeong, H.G. Rutaecarpine Protects Human Endothelial Cells from Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis via TRPV1- and AhR-Mediated Nrf2 Activation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050616
Kim CY, Lee GH, Lee SY, Bui ATN, Jeong HG. Rutaecarpine Protects Human Endothelial Cells from Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis via TRPV1- and AhR-Mediated Nrf2 Activation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050616
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chae Yeon, Gi Ho Lee, Seung Yeon Lee, Anh Thi Ngoc Bui, and Hye Gwang Jeong. 2025. "Rutaecarpine Protects Human Endothelial Cells from Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis via TRPV1- and AhR-Mediated Nrf2 Activation" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050616
APA StyleKim, C. Y., Lee, G. H., Lee, S. Y., Bui, A. T. N., & Jeong, H. G. (2025). Rutaecarpine Protects Human Endothelial Cells from Oxidative-Stress-Induced Apoptosis via TRPV1- and AhR-Mediated Nrf2 Activation. Antioxidants, 14(5), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050616





