Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading global health concern, responsible for substantial morbidity and mortality. In recent years, as our understanding of the multifaceted nature of CVDs has increased, it has become increasingly evident that traditional risk factors alone do not account for the entirety of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Environmental toxins, a heterogeneous group of substances ubiquitous in our surroundings, have now entered the spotlight as offenders in the development and progression of CVDs. Environmental toxins include heavy metals, air pollutants, pesticides, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals, among others. Upon exposure, they can elicit oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to detoxify and repair the resulting damage. Oxidative stress triggers a cascade of events, including inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, lipid peroxidation, and vascular remodeling, which can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, hypertension, and other cardiovascular pathologies. This article delves into the molecular mechanisms underpinning oxidative stress-mediated cardiovascular damage induced by environmental toxins, emphasizing the role of specific toxins in this process. Further research is necessary to understand how individual susceptibility and genotype influence the impact of environmental toxins on oxidative stress and the risk of CVD.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, the growth of large-scale industrial processing and increasing reliance on fossil fuels have contributed to a boom in the ambient levels of known environmental toxins [1]. These toxins and their byproducts are defined as poisonous substances that adversely impact human well-being and are now released into the environment at almost 220 billion tons per annum [2]. Levels of toxins, such as particulate matter in the air and toxic metals, are continually rising and are now considered key contributors to human mortality. For example, pollution-associated diseases accounted for nearly 16% of all deaths worldwide in 2015 [3]. Research into the mechanism of exposure to these hazardous agents has shown that exposure predominantly occurs via inhalation, ingestion, and absorption through the skin [4]. Environmental toxins have an impact not only on physical health but are also deeply intertwined with human social issues. Research into the distribution of environmental toxins from around the world has shown that low- and middle-income communities are disproportionately exposed to environmental pollution [1], further contributing to lowered health equity. This is of dire concern as demographic shifts predict that by 2050, nearly 50% of the global population will reside in crowded urban locations, potentially exacerbating this crisis [5]. Within the multitude of harmful effects caused by these toxins, several epidemiological studies have linked environmental toxin exposure with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) [6].
Since CVD remains the number one cause of death amongst developed nations, substantial work has been undertaken to elucidate the causal mechanisms driving this cardiotoxicity [7]. This research has implicated environmental toxins with a variety of harmful pathologies, ranging from increased oxidative stress, increased systemic inflammation, increased risk of atherosclerosis, and impaired cardiomyocyte contractility [6,8]. Although previous studies have elucidated some key mechanisms that can contribute to CVD, a comprehensive understanding, particularly relating to the detailed molecular changes involved and the interactions of pollutants found in the environment, is lacking [9,10].
Despite significant improvements in addressing established cardiovascular risks, environmental toxins remain underrecognized yet are substantial contributors to the global CVD burden. As such, understanding this multifaceted link between CVD and environmental toxins is of utmost importance, as only through a comprehensive understanding can effective, comprehensive public health solutions be devised to minimize toxin exposure. Knowledge about how environmental toxins drive oxidative stress and contribute to CVD risk is not only a scientific pursuit but also a pressing public health imperative.
The purpose of this review is to synthesize current evidence on the critical relationship between environmental toxins and CVDs, with a specific focus on oxidative stress as a central mechanistic pathway.
2. Methodology
PubMed and Web of Science were systematically searched to identify applicable studies. Search terms included combinations of “environmental toxins”, “heavy metals”, “air pollutants”, “particulate matter (PM2.5/PM10)”, “tobacco smoke”, “radiation”, “pesticides”, “endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs)”, “bisphenol A (BPA)”, “mold”, “pharmaceuticals”, “personal care products”, “dioxin”, “asbestos”, “arsenic”, “cadmium”, “lead”, and “mercury”. For cardiovascular outcomes, the following search terms were used in combination with the other search terms above: “cardiovascular diseases”, “atherosclerosis”, “hypertension”, “myocardial infarction”, and “endothelial dysfunction”. To determine the mechanistic pathways involved, the search terms “oxidative stress”, “reactive oxygen species (ROS)”, “lipid peroxidation”, “inflammation”, and “antioxidant” were used in combination with the other terms listed above. Boolean operators (AND/OR) linked these terms, and MeSH headings were applied in PubMed [1]. Studies published from inception to January 2025 were included to find former and recent advances in environmental toxins and cardiovascular disease.
The inclusion criteria included peer-reviewed articles that explored the role of environmental toxins in CVDs via oxidative stress pathways and human and animal studies, both in vitro, in vivo, and observational studies, as well as studies reporting quantitative associations between toxin exposure and cardiovascular outcomes (e.g., biomarker levels). The exclusion criteria included studies focusing solely on traditional CVD risk factors (e.g., hypertension and diabetes) without environmental toxin linkages, research lacking a clear analysis of oxidative stress mechanisms, and non-English articles, editorials, and conference abstracts. To ensure reproducibility and rigor, all systematic reviews and meta-analyses from 2022 to 2024 were hand-searched to identify overlooked studies. This methodology aligns with PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [2].
3. Common Environmental Toxins
The most common environmental toxins include the following:
Air Pollutants: These include particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ground-level ozone (smog), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds. Sources of air pollutants include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and combustion processes.
Heavy Metals: Lead is found in older paints, pipes, and contaminated soil. Mercury is present in certain fish species due to water contamination. Arsenic is found in some drinking water and foods.
Pesticides: Chemicals used in agriculture and pest control, such as organophosphates and chlorpyrifos, can find their way into the food supply.
Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs): These chemicals can interfere with hormone function and include substances like bisphenol A (BPA) found in some plastics and phthalates found in personal care products.
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): PCBs were historically used in electrical equipment but are now banned mainly due to health concerns. However, they persist in the environment.
Dioxins: Dioxins are released into the environment through industrial processes like waste incineration and can accumulate in the food chain.
Asbestos: Asbestos is a fibrous mineral that, when disturbed, can release harmful airborne fibers. In the past, it was often used for building materials.
Radon: Radon is a naturally present radioactive gas that can leak into homes from beneath the ground.
Tobacco Smoke: Tobacco smoke contains numerous toxins, including nicotine, carbon monoxide, and various carcinogens.
Mold and Indoor Air Contaminants: Mold spores and indoor allergens can pose health risks, especially to individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Residues from medications and personal care products can enter water supplies and affect aquatic ecosystems.
Radiation: Exposure to ionizing radiation from sources like nuclear power plants, medical procedures, and certain industrial activities can be harmful.
Chemical Waste and Spills: Accidental spills of hazardous chemicals, like oil spills or chemical plant accidents, can have significant environmental and health impacts.
Microplastics: Microplastics are tiny plastic particles found in the environment, including in water and food sources.
Importantly, all of these environmental toxins cause oxidative stress (Table 1).

Table 1.
Effect of environmental toxins on oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease.
4. Oxidative and Antioxidative Stress
The balance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the presence of antioxidant systems within cells dictates the cell’s antioxidant status (Figure 1). Three related but distinct concepts in the field of redox biology are oxidative stress, antioxidative stress, and redox-balanced cells [115]. Under normal conditions, low ROS levels act as signaling molecules supporting cardiovascular function or are removed by the cellular antioxidant systems, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH), resulting in a redox-balanced cell. However, environmental toxins such as air pollutants and heavy metals can disrupt this equilibrium, resulting in excess ROS that overwhelm antioxidant systems, referred to as antioxidative stress. Environmental toxins such as PM cause oxidative stress, which occurs when there is an excess production of ROS that the intrinsic antioxidant systems in cells cannot adequately neutralize.
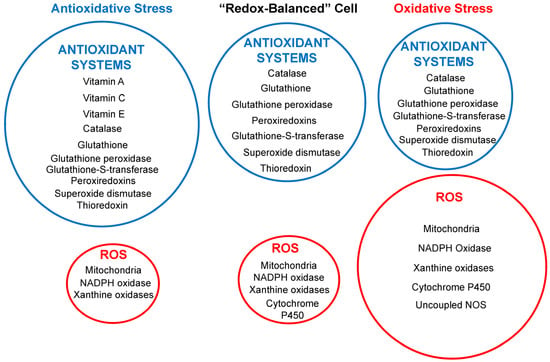
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram illustrating the relative contributions between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), shown in the red circles, and the presence of antioxidant systems (in blue circles) within cells in three different potential intracellular environments. The circle sizes correspond to the antioxidant system’s protective power relative to ROS generation levels. NOS, nitric oxide synthase.
A redox-balanced cell can adjust its antioxidant capacity according to the changing redox environment and can cope with mild or transient oxidative stress without compromising its viability or performance [115]. However, an often overlooked antioxidant status is antioxidative stress, whereby under conditions of overconsumption of synthetic antioxidants, the levels of ROS can become lower than required to support some cardiovascular function, leading to harmful effects [99,116,117]. Antioxidative stress can be achieved by upregulating the endogenous antioxidant systems, such as glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase, or peroxiredoxin, or by supplementing with exogenous antioxidants, such as antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, or polyphenols. It may be the cause of some of the adverse effects of antioxidant therapy discussed in the clinical implications.
Enzymes present in several organelles can produce ROS, including xanthine oxidases (XO) in peroxisomes, NADPH oxidase (NOX) in the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membranes, cytochrome P450 (CYP) in the endoplasmic reticulum, XO in the peroxisomes, and the electron transport chain (ETC) in mitochondria (Figure 2). Intracellular ROS dynamically interacts with mitochondria, cytoplasm, and the nucleus, creating a bidirectional regulatory network.
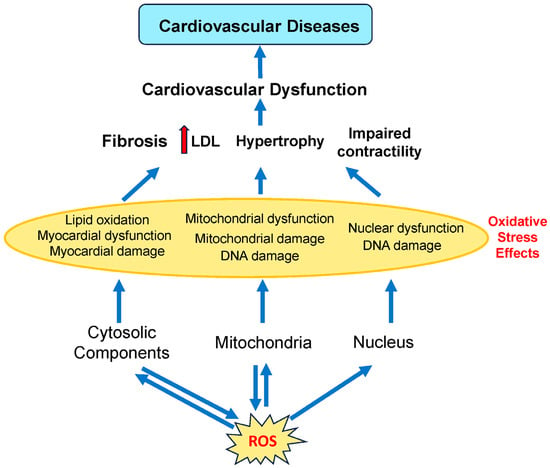
Figure 2.
Involvement of different subcellular components of cardiovascular cells in cardiovascular diseases. ROS is produced by the mitochondria and other organelles found in the cytoplasm (such as the endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes). ROS produced by the mitochondria and other organelles act on both mitochondrial and cytosolic components. Cardiovascular diseases are caused by mitochondrial, myocardial, and nuclear dysfunction. LDL, low-density lipoprotein. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
High ROS levels damage lipids, proteins, and DNA, driving endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Lipid peroxidation byproducts, such as 4-HNE (4-hydroxynonenal) and MDA (malondialdehyde), disrupt cell membranes, promoting cardiomyocyte death and compensatory fibrosis [118]. Environmental exposures amplify these effects by directly increasing ROS generation and impairing antioxidant capacity. While the mitochondria are a major source of ROS from complexes I and III, ROS also damages mitochondrial proteins, causing mitochondrial damage and dysfunction. ROS overproduction from dysfunctional mitochondria induces oxidative damage to proteins and DNA, impairing ATP synthesis and contractility [119]. Cytoplasmic ROS, such as from NOX, activate signaling pathways but also induce oxidative damage to proteins and lipids. Excessive cytosolic ROS can cause DNA damage, resulting in nuclear dysfunction.
Though mitochondria, cytoplasm, and the nucleus exhibit compartment-specific mechanisms for redox homeostasis, they engage in dynamic interorganellar cross-talk via ROS-mediated signaling. ROS from the mitochondria can go to the cytoplasm. Similarly, ROS produced in the cytoplasm can travel back to mitochondria and affect their energy production. Cells maintain healthy ROS levels by having specific control systems in each compartment, all working together like a coordinated team.
To discuss all 14 environmental toxin groups in significant depth would result in a review of over 20,000 words, which would be too extensive for a single article. A more focused review of five toxins (air pollutants, heavy metals, PPCPs, mycotoxins, and microplastics) was selected based on their widespread exposure, diverse mechanisms of inducing oxidative stress, and the strongest mechanistic evidence for ROS production specifically linked to cardiovascular outcomes. Other toxins, while important, either have more specialized effects or overlap with these primary categories in terms of oxidative stress mechanisms. For example, while radiation and radon cause oxidative stress through ionization, these effects are more related to DNA damage and cancer rather than cardiovascular diseases. While pesticides induce oxidative stress, their mechanisms are somewhat similar to those of heavy metals and mycotoxins, involving mitochondrial disruption and antioxidant suppression.
5. Air Pollutants—Particulate Matter (PM)
A major environmental toxin implicated in increasing the risk for CVD is air pollution based on ambient PM. Specifically, ambient PM is defined as the minute solid particles or liquid droplets suspended in the air that can be produced because of human or natural activities [68]. In most cases, ambient PM consists of a heterogeneous mixture of particles of multiple sizes and chemical compositions, including compounds such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. Due to their varied nature, PM is classified in terms of its particulate sizes. PM10 refers to particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter (AD) ranging from 2.5 to 10 μm and typically includes coarse particles originating from various sources such as road and agricultural dust, construction, and mining operations [69]. PM2.5, which includes fine particles with an AD less than 2.5 μM, is predominantly from power plant fuel combustion and mobile brake emissions. The last category of PM is ultrafine particles (UFPs), which include particles with diameters less than 0.1 μM. These mainly come from tailpipe emissions from mobile sources. Primary exposure to PM occurs via the respiratory system and eye conjunctiva, with some contribution to the gastrointestinal tract. Beyond direct air contact, certain pollutants can enter the human body through food (Figure 3) [70]. Presently, it is estimated that around 4.2 million deaths can be attributed to ambient air pollution and 2.9 million to household air pollution [3,71]. Furthermore, rapid urbanization has played a role in exposing over 90% of the world’s population to air pollution levels that exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines [72].
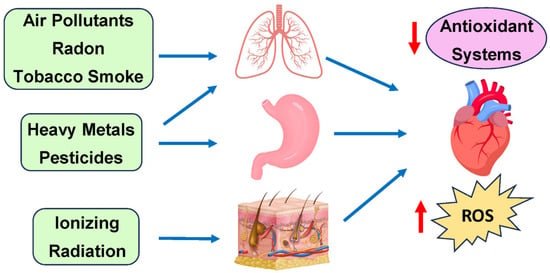
Figure 3.
Primary exposure routes of environmental toxins and their cardiovascular effects.
Environmental toxins initially affect different tissues: ionizing radiation impacts the skin (low/moderate doses) or the heart (high doses); air pollutants, radon, and tobacco smoke target the lungs; while heavy metals and pesticides enter through digestion. Systemic effects from these exposures indirectly drive cardiovascular diseases, primarily through increased ROS production and decreased antioxidant defenses in heart tissue.
In terms of cardiovascular pathologies specifically, PM has been associated with conditions such as increased risks of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, arrhythmia, and heart failure exacerbation [73]. Numerous epidemiological sources have attributed PM2.5 to the key group responsible for cardiovascular incidents. For example, several epidemiological studies have implicated PM2.5 in cases of CVDs, such as coronary artery disease [74,75,76], acute MI [76,77,78], cardiac arrhythmias [79,80], and hypertension [81]. This vast amount of evidence has led the American Heart Association (AHA) to claim a causal link between PM2.5 exposure and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [73,82]. Furthermore, both short- and long-term exposure to PM2.5 has been associated with increased rates of cardiovascular damage [73].
While the exact mechanisms through which particulate matter contributes to CVD are not fully understood, research suggests that much of their effect stems from their ability to generate ROS [83,84,85]. Several studies have demonstrated PM’s ability to increase markers of cellular oxidative stress [74,86,87]. This effect is also seen in a wide range of cells, including nasal, airway, and lung epithelial cells [88], macrophages [89], and cardiomyocytes [90]. For example, PM exposure in alveolar macrophages has been associated with the transcriptional upregulation of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and GM-CSF [91,92]. These markers indicate increased systemic inflammation, which can lead to subclinical responses such as increased vasoconstriction and cardiac electrical changes (Figure 4). These subclinical pathologies then contribute to an increased risk of acute ischemic or thrombotic events, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and chronic heart failure [93]. Altering the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, can affect the recruitment and activation of immune cells, the secretion of chemokines, and the regulation of apoptosis and tissue repair. Another possible mechanism is via the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX), which is a key contributor to cellular ROS and atherosclerosis (Figure 4). Furthermore, a study by Kampfrath et al. demonstrated that chronic exposure to PM2.5 increased NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide in monocytes and aortic tissue [94]. Other sources of PM-induced ROS include increased leaking of electrons from the mitochondrial ETC, and reductions in catalase (CAT), glutathione S transferase (GST), and SOD activity, and glutathione (GSH) levels [11,12].
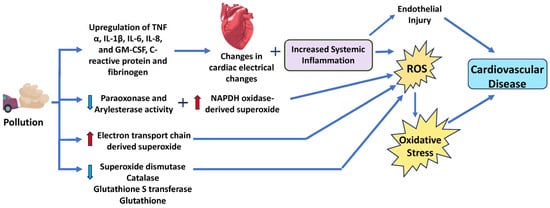
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism and signaling pathways by which particulate matter increases cardiovascular disease risk. Particulate matter induces ROS and reduces antioxidant systems, resulting in oxidative stress. IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component, while light blue arrows show decreased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
Lin et al. also demonstrated that traveling from Los Angeles (a less polluted area) to Beijing (a more polluted area) lowered the antioxidative activities of paraoxonase and aryl esterase as well as increased proinflammatory C-reactive protein and fibrinogen (Figure 2) [95]. Thus, there is strong support to suggest that the cardiotoxic activity of PM, especially PM2.5, stems from its ability to increase systemic inflammation. Additionally, Su et al. exposed C57BL/6 mice to PM2.5 or filtered air for 8 or 16 weeks and found that cardiac hypertrophy developed in PM2.5-exposed mice might be regulated by the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway [13]. In cardiomyocytes, the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway led to hypertrophic growth and net protein accumulation due to growth factors secreted [96]. Therefore, PI3K/Akt can trigger its downstream protein FoxO, regulate cardiac cell catabolism, and inhibit cell growth by specifically targeting hypertrophy signal molecules [96]. Previous studies have indicated that FoxO plays a role in the development of different kinds of heart diseases [97]. This implies that the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway might be responsible for cardiac hypertrophy due to exposure to particulate matter, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk. PI3K is a key enzyme that mediates cellular responses to growth factors, hormones, and cytokines and can be activated by oxidative stress [98].
6. Common Heavy Metal Pollutants
6.1. Lead
Lead is one of the most persistent environmental toxins implicated in cardiovascular toxicity today [120]. While public policy changes since the 1970s banning the use of lead in motor fuels, paints, and other common construction materials have meant an overall reduction in exposure to this harmful metal, the levels of lead in the environment still remain troublingly high [4]. Specifically, over 26 million people globally are still at risk of lead toxicity, leading to a loss of an estimated 9 million combined years [1]. In high-income countries like the US, lead exposure primarily occurs via sources such as aging lead piping, unreplaced lead paint in older houses, and leaded gasoline. For low-income countries, the exposure mainly comes through occupational hazards in industries within these countries, such as battery manufacturing, mining, and recycling plants. Beyond occupational exposure, lead is also heavily found in the soil and water supplies of these countries, adding risk to citizens [1,32]. Specifically, in terms of the methods of action, lead is absorbed via the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts as well as occasionally through the skin. Once in the blood, almost 99% of the lead is rapidly bound by erythrocytes, after which 95% is moved into the bones [32]. This increases the stability of the lead significantly and serves as a consistent reservoir of toxicity even decades after exposure.
In terms of its specific cardiovascular effects, increased lead levels have been implicated in a variety of physiological changes, such as the impaired regulation of cardiac excitability and contractility, damaged endothelial and vascular function, dyslipidemia, impaired mitochondrial function, and increased inflammation [8]. These mechanistic changes can then significantly increase the risk of clinical pathologies such as hypertension, ischemic heart disease, stroke, congenital heart disease, and peripheral vascular disease [121,122,123,124,125]. A recent study used approximately 40,000 participants’ data from the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 1999 to 2021 as representative of the US population. Tsoi et al. uncovered that doubling blood lead levels, even within the range considered acceptable, was associated with higher blood pressure when controlling for factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, waist circumference, poverty to income ratio, education, ever cigarette smoking, diabetes and stage 3–5 chronic kidney diseases [126]. This is especially concerning since just an increase of 2 mmHg in systolic blood pressure is associated with an increased risk of stroke [127]. Several other studies have corroborated this association, suggesting that high blood lead levels are associated with an increased risk of hypertension [128,129,130,131,132,133,134].
While the exact mechanism by which increased lead exposure causes hypertension is not well understood, researchers have suggested several physiological pathways may be involved. Chief amongst these is lead’s role in producing ROS through various mechanisms, including ETC complexes, NOX, and XO [30,31]. Lead also reduces SOD, CAT, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities. Furthermore, lead elevates cytosolic Ca2+, activating protein kinase C (PKC) and phospholipases that amplify ROS generation [30].
Specifically, ROS, like superoxide (O2−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), are unstable, highly reactive molecules usually created during the process of oxygen metabolism. When excessive generation of ROS happens, significant physiological tissue damage, such as tissue breakdown and activation of redox-sensitive transcription factors, occurs. Several prior studies have also implicated ROS in the pathogenesis of hypertension and other CVDs [135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142]. Research has demonstrated that lead participates in Fenton- and Haber-Weiss-type reactions, which promote the generation of ROS (Figure 5). Specifically, lead upregulates the Fenton and Haber–Weiss reactions, in which H2O2 is the substrate. During the reaction, H2O2 is converted to ·OH, which is highly toxic. Overproduction of ROS can then lead to significant oxidative stress within the cell [57,143]. Increased oxidative stress acts by limiting the bioavailability of active NO (a known vasodilator) via the inactivation/sequestration of NO by ROS, depletion of the NO synthase (NOS) cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin, and uncoupling of endothelial NOS (eNOS) [144]. Diminished NO in the heart results in the development of hypertension and CVDs. Furthermore, most actions of NO require the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC). Courtois et al. demonstrated that incubating normal rat aorta in a lead-containing medium for 24 h leads to a concentration-dependent downregulation of sGC expression, elevation of O2− production, and upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression [32,145]. Additionally, oxidative stress also leads to the generation of peroxynitrite (ONOO−), which is a highly toxic reactive nitrogen species and can contribute to cardiovascular, renal, and neurological damage [32]. Beyond direct oxidative stress, previous studies have also demonstrated that lead exposure caused protein kinase C activation, NF-κB activation, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity as a possible means of increasing the risk for hypertension [32]. Figure 5 shows the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways by which lead and cadmium increase cardiovascular disease risk.
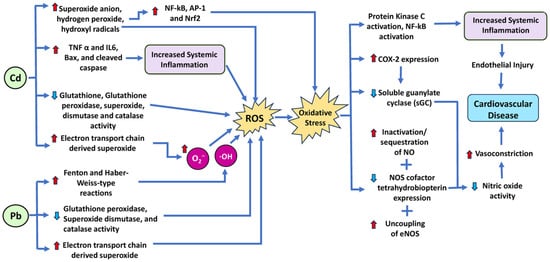
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism and signaling pathways by which the heavy metals lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) increase cardiovascular disease risk. Both lead and cadmium induce ROS by various mechanisms, resulting in oxidative stress. IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Nrf2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; AP1, activator protein-1; NF-kβ, nuclear factor-kappa B. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component, while light blue arrows show decreased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
6.2. Cadmium
Another key environmental determinant of cardiovascular risk is cadmium (Cd). Cadmium is a toxic heavy metal that has been linked with a variety of pathologies, including cancer, reproductive damage, and renal damage. Exposure to this toxin can occur through a variety of sources, including contaminated air and water, as well as the byproducts of fossil fuels. Leaking sewage waste containing cadmium compounds is absorbed by plants, introducing them into the food chain, where they proceed to accumulate in various organs [146]. Presently, tobacco smoke is seen as the primary source of cadmium exposure, with research demonstrating that smokers have 4–5 times higher Cd levels in their blood compared with non-smokers [146]. Further industrial sources of cadmium include nickel–cadmium batteries, pigments in paint production, electroplating, and polyvinyl chloride plastic [146]. A central reason for concern with cadmium is its long retention times in human systems. Specifically, cadmium demonstrates a clearance half-life of 25 years and can be retained in organs such as the kidneys [147], bone, liver, lung, central nervous system, and cardiovascular system [148]. The primary means of entry for cadmium include inhalation and ingestion. Approximately 10–50% of inhaled Cd dust is absorbed, and 5–10% of ingested Cd is absorbed into the body [148].
In terms of CVD, Cd has been implicated in several pathologies, including hypertension, promotion of atherosclerosis, and impaired cardiac function [51]. While causal links have not been established between Cd exposure and certain pathologies, epidemiological evidence has shown that people living in areas of greater Cd exposure have a higher risk of cardiovascular mortality [149,150]. Furthermore, amongst the various CVDs in which Cd is implicated, the most common are cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy. A cohort study of 3348 American Indian adults aged 45–74 years in the US measured urine Cd levels using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to determine the association of urine Cd levels with CVD occurrence and mortality. The authors identified 1084 cardiovascular events, including 400 deaths, in their cohort study and demonstrated a significant association between urinary Cd and increased incidence of heart failure [151,152]. The exact pathway of Cd-induced cardiotoxicity remains unclear. However, ROS is a key mediator of cardiotoxicity [153,154]. Previous reports highlighted that Cd exposure induces oxidative stress in cells due to the accumulation of ROS and increases in lipid peroxidation and malondialdehyde (MDA), causing oxidative damage [155,156].
It is known that Cd leads to the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, possibly by interacting with the Q-site of Complex I or other NADH-dependent enzymes, lowering their activity [157]. Prior work by Hirst has also demonstrated that inhibition of the Q-site significantly increases ROS production by Complex I [158]. This Complex I activity also leads to electrons accumulating in the Q-site, which can then be transferred to molecular oxygen, resulting in O2•− generation [159]. In addition to ROS production via ETC complexes, Cd also induces ROS through NOX and increases ROS levels via the suppression of SOD, CAT, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and GST activities (Figure 5) [47,48,49,160]. Cd also increases cytosolic Ca2+, activating phospholipases and ROS overproduction [50].
Furthermore, Cd causes changes in mitochondrial membrane permeability, releases cytochrome C, and induces mitochondrial caspase-dependent apoptotic protein expression through a cascade reaction, which can lead to apoptosis [161]. A study conducted in rat hearts showed that Cd treatment upregulated the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) and IL-6 (interleukin 6)), and apoptotic stimulants (Bax and cleaved caspase-3) in cardiac tissue [160]. Studies have also shown evidence of Cd-generated superoxide anion, H2O2, and hydroxyl radicals, which also activate sensitive transcription factors like NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells), AP-1 (activator protein-1), and Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2), thereby altering ROS-related gene expression [31]. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of many antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase, catalase, SOD, heme oxygenase-1, and NAD(P)H/quinone oxidoreductase 1 [162]. Nrf2 can contribute to cardiovascular disease by inducing undesirable effects on vascular function and remodeling, such as by increasing the expression of xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH), which converts hypoxanthine and xanthine into uric acid and superoxide anion. Uric acid can induce vasoconstriction and inflammation, while superoxide anion can react with NO and impair its vasodilatory and antiplatelet effects [163].
Both lead and cadmium can bind to the heme group of eNOS, inhibiting it and decreasing NO production, resulting in impaired vasodilation and increased blood pressure. ROS can also deplete the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which is essential for eNOS function and stability [164]. When BH4 levels are low, eNOS becomes uncoupled and produces more O2− instead of NO, further exacerbating oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Therefore, lead and cadmium can impair the NO pathway and cause oxidative stress by both direct and indirect mechanisms.
7. Household Toxins
Parabens are preservatives that are rampant in households and found in haircare products, cosmetics, foods, and even drinking water due to their ubiquity in products [165]. There is ample evidence that parabens are endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), demonstrated by parabens’ alteration of estrogen receptors, thereby modifying estrogens’ actions. Estrogen receptors regulate cardiac gene expression. Therefore, efforts were previously performed to explore the relationship between CVD and paraben exposure. Zhou et al. found that single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in estrogen receptor genes 1 and 2 interacted with paraben to increase hypertension risk. Men were more susceptible to the hypertensive effect of paraben exposure than women, even though women had higher urinary concentrations of parabens from their hospital-based case–control study involving 396 hypertension cases and 396 controls in Wuhan, China [165]. The authors found a positive association between parabens and hypertension, with an additive and interactive effect contributed by SNPs on estrogen receptor genes [165].
Fan et al. found that ethyl paraben exposure caused abnormal cardiac function and heart morphology, mainly manifested as pericardial effusion and abnormal heart rate in the early-stage development of zebrafish embryos. Another interesting finding was that zebrafish heart rates showed a compensatory change in response to ethyl paraben in the early stage of cardiac function decline, where it first increased, then decreased, or stopped. Surprisingly, RNA-seq analysis performed to explore the molecular mechanism underlying the toxic effects of ethyl paraben in zebrafish uncovered that retinoic acid signaling, cardiac muscle contraction, and cell apoptosis pathways in ethyl paraben-exposed larvae were significantly influenced [98].
Parabens appear to contribute to the development of oxidative stress in plasma and erythrocytes [166]. Pollack et al. found that several parabens were associated with modestly reduced levels of erythrocyte GPx, while other parabens were associated with a decrease in SOD. Interestingly, they found that three parabens were related to increases in antioxidant enzymes. A review article of 27 studies from 2008 to 2019 examining the association between bisphenol-A (BPA) exposure and oxidative stress biomarkers found a positive association with the biomarker 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), an indicator of DNA/RNA damage [167]. Another common household toxin is BPA, found in epoxy resins that coat water supply pipes and metal food cans, and polycarbonate plastics used to make water bottles or plastic containers. Moon et al. conducted a population-based analysis to find an association between BPA and CVD. When accounting for differences in urine dilution between 9265 participants using the natural log ratio of BPA to creatine (ln-BPA/Cr), higher levels of ln-BPA/Cr were associated with an increased risk of CVD, including ischemic heart disease and congestive heart failure [168]. Several in vivo studies in rats suggest that BPA-induced arrhythmia disrupts intracellular calcium signaling in cardiomyocytes and triggers atherosclerosis [63,64].
Oxidative stress has been suggested to be a contributing factor in paraben and bisphenol association with CVD. A case–control study of patients from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in Guangzhou, China, found that butylparaben, BPA, and BPF significantly increased the risk of coronary heart disease [169]. Moreover, reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and oxidative DNA damage mediated the increased CHD risk when exposed to bisphenols. Though HDL was a more significant mediator than oxidative stress, HDL is a scavenger of ROS, hinting at another relationship between oxidative stress and CHD. To draw any robust conclusions, further research is needed.
Another ubiquitous group of phenols is chlorophenols, which are used in industrial products and are formed as degradation byproducts from sewage and drinking water chlorination [170]. 2,5-dichlorophenol (DCP) is often used in room and toilet deodorizers and for the synthesis of resins and dyes. Using data from a nationally representative survey, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Rooney et al. found that higher urinary concentrations of 2,5-DCP were associated with higher rates of CVD and all forms of cancer in a sample of 3617 adult participants [171]. Mechanistically, Li et al. found that 2,4-DCP decreased ATP production and mitochondrial respiration in fathead minnow embryos, causing developmental toxicity, while heart rate was significantly decreased [172].
Phthalates are also a common group of domestic toxins. According to the FDA’s 2010 Survey of Cosmetics for Phthalate Content, phthalates were found in some nail polishes, body lotions, fragrances, deodorants, hair care products, body washes, and more (U.S Food and Drug Administration, 2022 [173]). Also of note is that the FDA does not require cosmetic products and ingredients to be approved and does not currently suggest that phthalates in such products pose a health risk. A common phthalate, Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), is found in plastic products such as tablecloths, shower curtains, garden hoses, toys, and swimming pool liners.
When mice were treated with DEHP daily for 28 days, DEHP induced cardiac mitochondrial damage [174]. In another study, mice were injected via an intragastric route with DEHP daily for 28 days, leading to cardiomyocyte mitochondrial damage and thus oxidative stress [175]. A review of studies on the relationship between DEHP and CVD found that DEHP increases the development and severity of CVD due to oxidative stress and inflammation [176]. Alongside BPA and phthalates, perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are added to plastics during processing and make their appearance in the food chain, namely, via plastic degradation [177]. The perfluorinated compound perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) has been detected in drinking water, soil, air, dust, and sediment, and due to its high chemical stability, humans ingest it in food and water often enough to result in measurable blood serum levels [178]. It has been previously shown that PFOS might be linked to the development of CVD, particularly atherosclerosis, leading Wang et al. to treat mice with the dose-equivalent of the human tolerable daily intake of PFOS. They found that chronic PFOS exposure increases atherosclerosis progression by polarizing M1 macrophages, inducing proinflammatory cytokines, and contributing to the progression and instability of arterial plaques, making them more likely to rupture [178]. In line with these findings, Xu et al. found that rats that were injected intraperitoneally with PFOS suffered from significant myocardial injury, myocardial apoptosis, and cardiac inflammation [179]. Cardiovascular damage from PFOS extends beyond the immune system, additionally impairing the structure and function of mitochondria in mouse embryonic stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes [180]. PFOS disrupted calcium fluxes and the mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum structure and decreased ATP production and cardiomyocyte differentiation. Furthermore, the Rictor/mTORC2 signaling pathway was activated by PFOS and found to be responsible for the mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) structure impairment, altered fatty acid metabolism and glycolysis, and disrupted mitochondrial physiology [180]. In zebrafish larvae, the PFC perfluorotetradecanoic acid (PFTeDA) induced the upregulation of several antioxidant enzymes and genes associated with Complex I and IV of the electron transport chain to combat ROS production and maintain oxidative respiration [181]. In contrast, when Liu et al. treated zebrafish with significantly higher concentrations of perfluorononanoic acid, ROS generation increased, and mitochondrial- and oxidative stress-related genes were downregulated [182]. This indicates a dose-dependent relationship as well as a significance in the minor chemical structure differences between PFCs, where, for instance, mitochondrial membrane permeability and proton leak were observed with perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) but not with PFTeDA [183]. Similar findings of ROS generation in response to exposure to PFCs have been demonstrated in human cells. When immortalized primary human microvascular endothelial cells were treated with both high and low concentrations of PFOS, ROS production increased [184]. The low concentrations of PFOS used were both occupationally and environmentally relevant, indicating that ROS generation may occur at typical human exposure ranges.
8. Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites produced by mold and fungi that can contaminate many kinds of food and sprout in buildings damaged by water [185,186]. Even animal byproducts, such as milk and eggs, can also be contaminated with mycotoxins through animals ingesting feed contaminated with mycotoxins [187]. Exposure to mycotoxins can lead to increased amounts of ROS in the body, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage (Figure 6). This increase in ROS levels is due to enhanced ROS production by NOX, CYP, and ETC complexes. Reduced GSH levels and SOD and CAT activity further raise ROS levels [93,94,95].
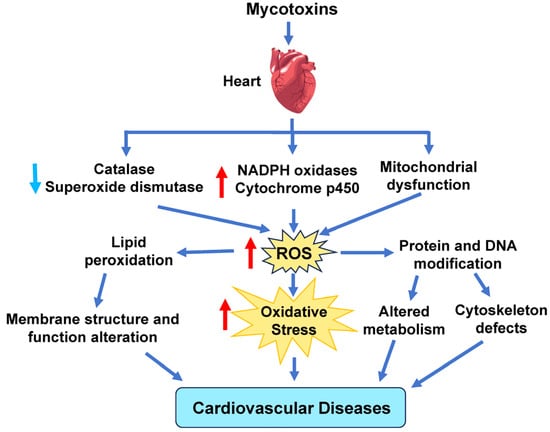
Figure 6.
Effect of mycotoxins on cardiovascular disease. Mycotoxins can cause elevated ROS production by decreasing catalase and superoxide dismutase activity and increasing ROS derived from NADPH oxidases, cytochrome P450, and the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component, while light blue arrows show decreased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
Even low levels of mycotoxins can result in inflammation of the vasculature, disruption of lipid metabolism, breakdown of osteocytes for calcium, and obstruction of the arteries. Prolonged inflammation can lead to more adverse effects, such as endothelial dysfunction, vascular oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation injury, and vascular lesions [185].
Aflatoxin is a well-recognized type of mycotoxin known for being the most toxic and abundant carcinogen [186]. The presence of aflatoxin in the body causes activation of cytochrome P450, leading to increased ROS production and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) regulation. The increased upregulation of TLR-4, an inflammatory mediator, results in an intensified immune response. Aflatoxin is also capable of disrupting metabolism, including the dysfunction of the Krebs cycle, glycolysis, and mitochondria [185]. This effect, in combination with the high NO concentration from the endothelial dysfunction and the increased inflammatory response, can result in apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. This effect was observed during an experiment that involved exposing rats to low concentrations of aflatoxin. The rats’ myocardium exhibited areas of necrosis, inflammation, and a decrease in cardiomyocytes, resulting in cardiac damage [185,188].
9. Pharmaceutical Products
Pharmaceuticals are generally used for their therapeutic, preventive, and diagnostic properties since they play a vital role in human health outcomes. There has been a continuous increase in the global use of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the last decade due to advances in research and development, the growing world population, and increased accessibility to healthcare and pharmaceuticals [189]. Approximately 100,000 over-the-counter (OTC) medicines and personal care products are sold in pharmacies and convenience stores in the US alone [189]. Inevitably, PPCPs are released into the environment at different phases of their lifecycle, like many other man-made chemicals. In recent years, PPCPs have been of great concern due to their detection, even at low concentrations (picograms per liter, pg/L), in sewage, surface waters, groundwater, drinking water, soil, and aquatic organisms [189]. The toxicity and concentration of PPCPs in waste treatment plants (WTPs) and water bodies are increasing day by day due to the increased rate of indiscriminate and mass consumption of these organic compounds [190]. Surprisingly, one of the most used pharmaceuticals that few think about with respect to causing cardiotoxicity is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen [97,191]. Therefore, this section explores the potential health implications of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen exposure, to the cardiovascular system.
9.1. Ibuprofen
NSAIDs (notably ibuprofen) are among the top 10 persistent pollutants, accounting for more than 15% of all pharmaceuticals detected in aquatic environments [192]. Ibuprofen metabolites (carboxy-ibuprofen, hydroxy-ibuprofen, and ibuprofen–acyl-glucuronide conjugates) are more toxic and may potentially pose a greater risk than its parent molecule [190,193]. Ibuprofen concentrations in influent wastewater have been recorded to reach between 5.78 and 1673 mg/L [194]. Due to the presence of ibuprofen or its metabolites in the environment, they are consumed by plants and aquatic organisms, allowing ibuprofen and its metabolites to enter the food chain [190]. The bioaccumulation of ibuprofen and other NSAIDs in aquatic organisms, like fish, mollusks, and crustaceans, can also lead to their transfer and concentration further up the trophic chain [190,195]. The concentrations of ibuprofen and its metabolites in wastewater signify an ecological hazard and can act as a source of adverse environmental effects because ibuprofen’s stable chemical structure and biological activity make it highly resistant to biodegradation, thereby resulting in its toxic and persistent presence in human and animal food chains [194,196].
Even though the direct effects of these pharmaceutical pollutants on aquatic organisms are certain, their resulting impact on human health and well-being is challenging to measure accurately. Nevertheless, orally and topically administered NSAIDs have the potential to cause a wide range of direct negative side effects on human health, including increasing the risk of adverse events in the cardiovascular system (MI, heart failure, and hypertension) [97]. An ecological risk assessment study conducted in a French national survey found that the estimated real risk ratio of ibuprofen was ≤1, suggesting that it was an environmentally risky substance [197]. Moreover, the effects of ibuprofen are most likely dose-dependent and rely on the degree of exposure—acute or chronic. Female B6C3F1 mice treated with 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg of ibuprofen for 2 weeks had significantly increased liver weights. Tiwari et al. found that ibuprofen resulted in sex-specific changes in energy metabolism and protein degradation pathways in livers of mice treated with a moderate daily dose of ibuprofen for 7 days [198]. This implies that ibuprofen has the potential to affect males and females differently.
9.2. Mechanism and Signaling Pathways by Which NSAIDs Increase Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Several clinical studies have been conducted in the past few years to ascertain the safety and effectiveness of NSAIDs in CVD. It was found that the risk of atrial fibrillation, heart failure, MI, and other cardiovascular conditions increased in patients with a history of these pathological conditions [97,199]. Both nonselective NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) and selective NSAIDs result in the development of hypertension in both normotensive and hypertensive individuals, and NSAIDs use interferes with antihypertensive medications except for calcium channel blockers [97]. Additionally, the authors reported that the use of NSAIDs with other antiplatelet drugs (except aspirin) increased the rate of cardiovascular events like cardiovascular death, MI, and stroke [97,200].
The biological mechanism for the NSAID-associated risk of MI has primarily emphasized pro-thromboembolic effects, but NSAIDs have also been found to influence renal function and the regulation of fluid balance, causing fluid retention and worsening of heart failure, all of which contribute to the risk of MI [201]. Furthermore, NSAIDs have been found to interact with antihypertensive drugs, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, through mechanisms related to the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, which interferes with the renal vasculature and the regulation of blood pressure [202]. Moreover, NSAIDs can increase serum aldosterone levels, leading to sodium retention and hypertension [191,203]. NSAIDs have also been associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation [191]. The biological mechanism involved is not well understood, but it is suggested to involve adverse effects on fluid retention, serum electrolytes, and blood pressure [201,204,205].
The main players implicated by several studies in NSAID-induced cardiotoxicity are the generation of ROS in the mitochondrial ETC, NOX, XO, and lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenases, NOS, and cytochrome P450-based enzymes [97]. ROS levels are further elevated due to decreased CAT and GPx activities [97]. As a result, several other cell signaling pathways (p53, Vax, Bcl-2, mitochondrial Cyt C, NF-KB, apoptosis-inducing factor, Akt, and ubiquitin–proteasome system) that can increase the production of ROS occur, leading to platelet aggregation and thrombosis, acute MI, apoptosis, reperfusion injury, and heart failure due to prolonged oxidative stress in the heart (Figure 7) [97]. Specifically, Li et al. found that four different types of NSAIDs, diclofenac, naproxen, rofecoxib, and celecoxib increased NADPH oxidase expression, eNOS expression, and nitrite levels in the aorta and heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats model, concluding that the aorta and heart of the NSAID-treated rats showed increased O2•− production and oxidative stress [206]. In vitro studies by Ghosh et al. showed that at pharmacological levels, the NSAID meclofenamate sodium induced ROS and inhibited mitochondrial respiratory complexes [207]. Several studies have also shown that ibuprofen increased ROS levels which induce lipid peroxidation and DNA damage and increased expression of endogenous antioxidant systems such as SOD, catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) [208,209].
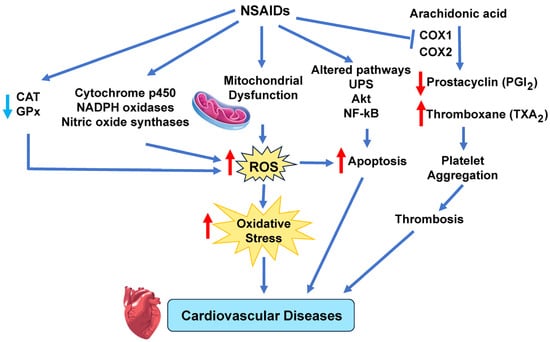
Figure 7.
NSAID induce cardiovascular disease. NSAIDs induce mitochondrial dysfunction and alterations in several enzymes that increase ROS. Elevated ROS levels disrupt cellular redox balance, overwhelming antioxidant systems, and creating oxidative stress. Prolonged oxidative stress damages blood vessels and heart tissue, leading to different cardiovascular diseases. Akt, protein kinase B; CAT, catalase; COX, cyclooxygenase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; UPS, ubiquitin–proteasome system. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component, while light blue arrows show decreased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
One potential way that NSAIDs may be causing cardiovascular disease is via decreased proteasomal activity in cardiac cells. Our laboratory has found that NSAIDs and pesticides decrease proteasome activity [57,207,210]. Proteasome dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury, hypertrophy, heart failure, and arrhythmias [211]. The decreased proteasome activity observed will likely result in an accumulation of damaged or misfolded proteins in cardiac cells, which can trigger cellular stress responses, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis. However, since the proteasome is so fundamental to survival, many signaling pathways are likely to be involved (such as the NF-κB pathway) that need to be investigated.
Endothelial cells play a critical role in maintaining vascular homeostasis, which is essential for the control of many cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis and thrombosis [97,212]. Interestingly, Liou et al. [213] found that 160 μM sulindac (an NSAID) induced endothelial apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), as evident by an increase in annexin V-positive cells. Both sulindac and indomethacin significantly increased cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) levels, as well as increased the level of the apoptotic activating factor caspase-3 [213]. The apoptosis in HUVECs induced by the NSAIDs was associated with reduced PPARδ and 14-3-3-ε expression. Under normal conditions, 14-3-3-ε binds phosphorylated Bad, inhibiting the translocation of Bad to the mitochondria and preventing apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. However, sulindac, through the suppression of 14-3-3-ε expression, increased Bad translocation to mitochondria, thereby inducing apoptosis [97,213].
10. Microplastics
Plastic is a globally produced material used in many common industries, such as the automobile and home goods industries. The high amounts of plastics present throughout the world lead to a higher accumulation of plastic in the environment, which then degrades into microplastics and nanoplastics. Recent studies show that higher exposure to microplastics and nanoplastics leads to harmful effects in human and animal cell models, which include the cardiovascular system phenotype [214]. Several CVD risk factors are associated with higher microplastic and nanoplastic exposure, mainly through the skin, mouth, and lungs. In a review by Zhu et al., the associated risk factors found were myocardial fibrosis, altered heart rate, abnormal blood velocity, decreased cardiac output, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiometabolic disease phenotype [214]. The degraded microplastics and nanoplastics can result in particles small enough to pass through the intestinal epithelium blood vessels, the pulmonary blood–air barrier, and macrophage cells. It was found that microplastics and nanoplastics can cause multiple adverse cardiovascular effects through various means, including oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, pyroptosis, and cellular interaction, leading to the risk of CVD. Several studies found that, depending on the size of the plastic, nanoplastics can accumulate in the blood, and microplastics can accumulate in various organs in rodent models [214].
Studies also found that offspring in animal models could be exposed to microplastics and nanoplastics through the placenta and the mother’s milk [214,215]. There were also studies that analyzed the effect of microplastics and nanoplastics on other environmental hazards. One study found that a combination of micro- and nanoplastic exposure with chloroauric acid hydrate resulted in an increase in the rate of mortality, underdevelopment of the heart, and development of yolk edema in a zebrafish model [214,216]. Another study using zebrafish found that the combined effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (a flame retardant) and microplastics and nanoplastics caused a decreased heart rate and pericardial edema. However, micro- and nanoplastics also resulted in protective effects against some environmental toxins. Zebrafish larvae that were exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), a type of carcinogenic pollutant, and micro- and nanoplastics displayed a protective effect from the plastic against the toxic cardiovascular effects of the PAHs. Micro- and nanoplastics exhibited a protective response when zebrafish larvae were subjected to PAHs, mitigating the detrimental cardiovascular effects of the PAHs. The main contributor to these protective effects from micro- and nanoplastics seems to be that the plastics and the other environmental toxins compete against each other, reducing the amount of toxins able to enter and accumulate in the embryos [214]. It should be noted that many microplastic studies test doses of micro- and nanoplastics that were much higher than the concentrations found in the environment, making it difficult to determine whether the effects noted are realistic for actual situations [214,217].
A study by Li et al. exposed rats to various concentrations of polystyrene microplastics in their drinking water for ninety days [112]. Researchers found that when the microplastics are small enough, they can pass through the epithelial cells in the stomach and enter the circulation, where the microplastics can then enter other organs in the body. Two essential markers of myocardial damage were found to be significantly elevated in rat hearts: creatine kinase-MB and troponin I. The lipid peroxidation marker, malondialdehyde (MDA), was significantly elevated in the rat hearts. This is likely due to the microplastics-induced elevated ROS production by mitochondrial ETC complexes [110,111]. Additionally, several antioxidants, CAT, GPx, and SOD, were also significantly decreased, demonstrating that oxidative stress occurred in the hearts of the rats that ingested microplastics (Figure 8). In these treated mice, Bcl-2, a protein that inhibits apoptosis, was downregulated, and Bax, a protein that stimulates apoptosis, was upregulated, suggesting that cardiomyocyte apoptosis occurs in rat hearts due to oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage [112].
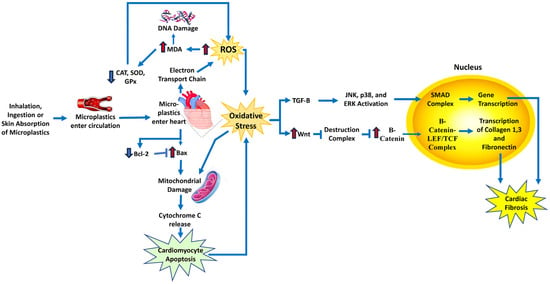
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism and signaling pathways by which microplastics increase cardiovascular disease risk. Microplastics induce ROS in heart tissue, leading to oxidative stress and activation of pathways involved in cardiac fibrosis. Bax, BCL2-associated X, apoptosis regulator; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2; LEF/TCF, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor/T-cell factor; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SMADs, sma- and MAD-related proteins; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β. Red arrows indicate increased levels of that component. The dark blue arrows indicate the direction of signaling.
Oxidative stress can also trigger the Wnt pathway, which is responsible for the production of myofibroblasts, leading to the development of cardiac fibrosis. In the rat hearts, there was an increase in Wnt, the first molecule in the pathway that activates signals in the cell, and an increase in β-catenin, which forms a complex once in the nucleus of the cell to activate gene transcription. This resulted in the increased production of collagen 1, collagen 3, and fibronectin, which leads to fibrosis (Figure 8). The myofibroblast marker α-SMA and the cardiac fibrosis marker TGF-β were also significantly increased in the rat hearts, showing that oxidative stress, which was caused by the ingestion of polystyrene microplastics, resulted in the development of cardiac fibrosis in the rat hearts [112].
11. Clinical Implications of Oxidative Stress
Antioxidant therapy: The administration of exogenous antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, coenzyme Q10, resveratrol, or polyphenols, that can scavenge ROS and protect biomolecules from oxidative damage has been significantly investigated. However, the efficacy and safety of antioxidant therapy for cardiovascular diseases are controversial, as some studies have shown beneficial effects, while others have shown no effect or even adverse effects [218,219,220]. These controversial effects of antioxidant therapy are not exclusive to cardiovascular diseases [221]. Moreover, antioxidant therapy may interfere with the physiological roles of ROS, such as cell signaling and adaptation, and may reduce the endogenous antioxidant defense systems, resulting in a paradoxical increase in oxidative stress. An example of antioxidant therapy that had no effects is the HOPE and HOPE-TOO trials, which investigated the effects of vitamin E on the prevention of cardiovascular events and cancer in high-risk patients with vascular disease or diabetes [218]. The trial enrolled 9541 patients and randomly assigned them to receive either vitamin E (400 IU/day) or placebo for a mean duration of 7 years. The results showed that vitamin E had no significant effect on the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death, nor the secondary endpoints of cancer, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or revascularization. Moreover, vitamin E was associated with a higher risk of heart failure and hospitalization for heart failure. The authors concluded that vitamin E does not prevent cardiovascular events or cancer in high-risk patients and may be harmful.
Studies that show more beneficial effects include mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants and Nrf2 activators. Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants have been shown to protect against atherosclerosis [222], ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, heart failure, and diabetic cardiomyopathy in animal models and may offer a novel strategy for cardiovascular protection [223,224,225]. Nrf2 activators, such as sulforaphane, curcumin, or dimethyl fumarate, can enhance the cellular antioxidant capacity and protect against oxidative stress-induced cardiovascular injury [226]. Nrf2 activators and modulators have been shown to attenuate atherosclerosis, I/R injury, hypertension, and cardiac hypertrophy in animal models and may have therapeutic potential for human cardiovascular diseases [227,228].
While some antioxidant therapies seem to have beneficial effects with respect to CVDs, some studies in mice models revealed that supplements with antioxidants, such as NAC, vitamin E, and the soluble form of vitamin E called Trolox, encouraged the growth and spread of tumors [229,230] (Le Gal et al., 2015, Zou et al., 2021). As more clinical trials are performed to understand the nuances associated with antioxidant therapy, individuals should be encouraged to eat more food rich in antioxidants. A study of the relationship between non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity (NEAC) from food and death from any cause or specific causes found that eating foods with higher NEACs was linked to a lower risk of death from any cause and death from CVD in Japanese adults [231]. None of the 42,520 men and 50,207 women who participated in this study had ever had cancer, stroke, ischemic heart disease, or chronic liver disease before. Figure 9 illustrates some of the key intracellular signaling pathways that are implicated in oxidative stress-induced CVD caused by environmental toxins.
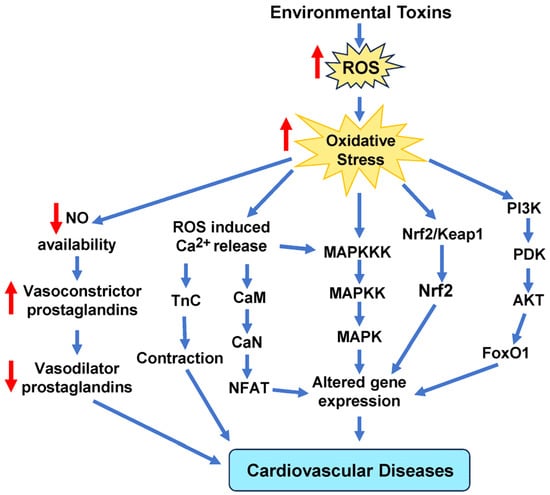
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the main signaling cascades in cells due to oxidative stress induced by environmental toxins. These signaling pathways include MAPKs, calcium, Nrf2, and NO signaling molecules that mediate signal transduction to alter gene expression that ultimately leads to cardiovascular disease. AKT, protein kinase B; CaM, calmodulin; CaN, calcineurin; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; MAPKKK, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase kinase; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NO, nitric oxide; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TnC, troponin c.
12. Conclusions
The interplay between environmental toxins and oxidative stress is an expanding area of research that sheds light on previously underappreciated factors contributing to the burden of CVDs. While the mechanisms of action of different environmental toxins may partly depend on other factors, such as genetic susceptibility, nutritional status, or lifestyle habits, there is substantial evidence that oxidative stress is a common pathway through which many environmental toxins can cause cellular damage and dysfunction, leading to various diseases and disorders. A comprehensive understanding of CVD-related pathways altered by environmental toxins has the potential to inform public health policies, clinical interventions, and preventive measures aimed at reducing cardiovascular risks associated with environmental exposures.
13. Future Directions
Emerging research has unveiled a significant link between the gut microbiome and ROS production [232,233]. Certain bacterial species within the gut microbiome, particularly those involved in the fermentation of dietary components like fiber, produce metabolites that can modulate oxidative stress. Short-chain fatty acids, for instance, are byproducts of microbial fermentation and have been shown to possess antioxidant properties. They can help regulate ROS levels in the gut and influence systemic oxidative stress. When the gut microbiome experiences an imbalance in composition and function, it can lead to a proinflammatory state, which is linked to CVD. An imbalanced microbiota can promote the production of proinflammatory cytokines and other molecules that exacerbate oxidative stress in the vascular system. This chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are key contributors to atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of most CVDs. As such, understanding the intricate relationship between the microbiome, ROS, and CVD will likely offer new therapeutic avenues. In-depth research exploring the intricate interplay between an individual’s unique susceptibility and their genetic makeup is needed to unravel the nuanced mechanisms that underlie how environmental toxins exert their influence on oxidative stress and increase the risk of CVD. Such research will advance our understanding of the complex relationship between genetics, environmental factors, oxidative stress, and cardiovascular health.
Author Contributions
A.V.G. conceived the aims and outline of the review. A.V.G., R.O.S., G.D.T.R., T.V. and E.G. wrote the manuscript, prepared the figures, and generated the tables. A.V.G., R.O.S. and G.D.T.R. performed the final review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support for this study was provided by the NIEHS/Superfund Research Program (P42 ES004699).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank members of the Gomes laboratory for their proofreading and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CD | Cadmium |
| CHD | Coronary heart disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| EDCs | Endocrine-disrupting chemicals |
| ETC | Mitochondrial electron transport chain |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| Gst | Glutathione S-transferase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PFCs | Perfluorinated compounds |
| PFOS | Perfluorinated compound perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TrxR | Thioredoxin reductase |
| XO | Xanthine oxidase |
References
- Burroughs Peña, M.S.; Rollins, A. Environmental Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease: A Challenge for Health and Development in Low-and Middle-Income Countries. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, R.; Biswas, B.; Willett, I.R.; Cribb, J.; Kumar Singh, B.; Paul Nathanail, C.; Coulon, F.; Semple, K.T.; Jones, K.C.; Barclay, A.; et al. Chemical pollution: A growing peril and potential catastrophic risk to humanity. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosselman, K.E.; Navas-Acien, A.; Kaufman, J.D. Environmental factors in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Mehndiratta, M.M.; Wasay, M.; Garg, D. Environmental Toxins and Brain: Life on Earth is in Danger. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2022, 25, S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.-M.; Lo, K.; Zheng, T.-Z.; Yang, J.-L.; Bai, Y.-N.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Cheng, N.; Liu, S.-M.; Cui, Y. Environmental heavy metals and cardiovascular diseases: Status and future direction. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2020, 6, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissa, E.M.; Ferns, G.A. Heavy Metal Poisoning and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 870125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Araujo, J.A.; Barchowsky, A.; Belcher, S.; Berridge, B.R.; Chiamvimonvat, N.; Chiu, W.A.; Cogliano, V.J.; Elmore, S.; Farraj, A.K.; et al. Key Characteristics of Cardiovascular Toxicants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimeca, M.; Palumbo, V.; Giacobbi, E.; Servadei, F.; Casciardi, S.; Cornella, E.; Cerbara, F.; Rotondaro, G.; Seghetti, C.; Scioli, M.P.; et al. Impact of the environmental pollution on cardiovascular diseases: From epidemiological to molecular evidence. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; He, K.; Peng, Z.; Niu, X.; Xu, H.; et al. New mechanisms of PM2.5 induced atherosclerosis: Source dependent toxicity and pathogenesis. Environ. Res. 2025, 266, 120535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibanez-Andrade, M.; Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Rivera-Pineda, A.; Chirino, Y.I.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M.; Sanchez-Perez, Y. The Road to Malignant Cell Transformation after Particulate Matter Exposure: From Oxidative Stress to Genotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.Y.; Kim, G.D. Particulate Matter-Induced Emerging Health Effects Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzis, C.; Godleski, J.J.; Gonzalez-Flecha, B.; Wolfson, J.M.; Koutrakis, P. Ambient particulate matter exhibits direct inhibitory effects on oxidative stress enzymes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuszka-Bulaga, A.; Tkacz, K.; Weglarczyk, K.; Siedlar, M.; Baran, J. Air pollution induces pyroptosis of human monocytes through activation of inflammasomes and Caspase-3-dependent pathways. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, K.; Song, L.; Zhou, J.; Kan, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, J.; et al. Fine particulate matter-induced cardiovascular injury is associated with NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Apo E−/− mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Xie, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Morishita, M.; Sun, Q.; Rajagopalan, S. Exposure to concentrated ambient particulate matter induces reversible increase of heart weight in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tian, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Kang, H.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Ambient PM2.5 caused cardiac dysfunction through FoxO1-targeted cardiac hypertrophy and macrophage-activated fibrosis in mice. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, R.; Sang, N. Ambient fine particulate matter exposure induces reversible cardiac dysfunction and fibrosis in juvenile and older female mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Ma, W.M.; Yuan, J.L.; Cui, L.Q. PM2.5 exposure aggravates left heart failure induced pulmonary hypertension. Acta Cardiol. 2019, 74, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Ku, T.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Ambient fine particulate matter exposure induces cardiac functional injury and metabolite alterations in middle-aged female mice. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, V.; Adelstein, J.M.; Grimmer, J.A.; Youtz, D.J.; Sugar, B.P.; Wold, L.E. PM2.5 exposure in utero contributes to neonatal cardiac dysfunction in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Nie, H.; Tian, L.; Shi, Y.; Lai, W.; Xi, Z.; Lin, B. Oil mist particulate matter induces myocardial tissue injury by impairing fatty acid metabolism and mitochondrial bioenergetics function via inhibiting the PPAR alpha signaling pathway in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 365, 125340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, T.; Magnani, N.; Garces, M.; Kelly, J.; Paz, M.; Caceres, L.; Calabro, V.; Lasagni Vitar, R.; Caltana, L.; Contin, M.; et al. Chronic exposure to polluted urban air aggravates myocardial infarction by impaired cardiac mitochondrial function and dynamics. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodovici, M.; Bigagli, E. Oxidative stress and air pollution exposure. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 487074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Bevan, G.H.; Palanivel, R.; Das, L.; Rajagopalan, S. Oxidative stress pathways of air pollution mediated toxicity: Recent insights. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease outcomes following exposure to ambient air pollution. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V.; Valacchi, G.; Corradeschi, F.; Aldinucci, C.; Silvestri, S.; Paccagnini, E.; Gerli, R. Studies on the biological effects of ozone: 7. Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) after exposure of human blood to ozone. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 1998, 12, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hazari, M.S.; Stratford, K.M.; Krantz, Q.T.; King, C.; Krug, J.; Farraj, A.K.; Gilmour, M.I. Comparative Cardiopulmonary Effects of Particulate Matter-and Ozone-Enhanced Smog Atmospheres in Mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Sharma, B. Biochemical and Molecular Bases of Lead-Induced Toxicity in Mammalian Systems and Possible Mitigations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, R.C.; Rautray, A.K.; Swarup, D. Oxidative stress in lead and cadmium toxicity and its amelioration. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 457327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H454–H465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Guallar, E.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Rothenberg, S.J. Lead exposure and cardiovascular Disease—A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Schwartz, J.; Vokonas, P.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Aro, A.; Hu, H. Electrocardiographic conduction disturbances in association with low-level lead exposure (the Normative Aging Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J. Lead, blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease in men and women. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 91, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Lin, C.Y.; Farmand, F.; Sindhu, R.K. Superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and NADPH oxidase in lead-induced hypertension. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.N.; Koren, S.A.; Wojtovich, A.P. Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.L.; Posser, T.; Dunkley, P.R.; Dickson, P.W.; Mattos, J.J.; Martins, R.; Bainy, A.C.; Marques, M.R.; Dafre, A.L.; Farina, M. Methylmercury neurotoxicity is associated with inhibition of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, N.B.; Angeli, J.K.; Faria Tde, O.; Ribeiro Junior, R.F.; Vassallo, D.V.; Padilha, A.S.; Stefanon, I. Low mercury concentration produces vasoconstriction, decreases nitric oxide bioavailability and increases oxidative stress in rat conductance artery. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes Dos Santos, A.; Ferrer, B.; Marques Goncalves, F.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Renieri, E.A.; Skalny, A.V.; Farina, M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Aschner, M. Oxidative Stress in Methylmercury-Induced Cell Toxicity. Toxics 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omanwar, S.; Fahim, M. Mercury Exposure and Endothelial Dysfunction: An Interplay Between Nitric Oxide and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Huang, S.F. Lipid peroxidation in liver of rats administrated with methyl mercuric chloride. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 54, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobal, A.B.; Horvat, M.; Prezelj, M.; Briski, A.S.; Krsnik, M.; Dizdarevic, T.; Mazej, D.; Falnoga, I.; Stibilj, V.; Arneric, N.; et al. The impact of long-term past exposure to elemental mercury on antioxidative capacity and lipid peroxidation in mercury miners. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2004, 17, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A. Mercury Exposure and Heart Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, M.C. Role of mercury toxicity in hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Lowe, M.; Chan, H.M. Mercury exposure, cardiovascular disease, and mortality: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Pacini, A.; Gulisano, M.; Taddei, N.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-Induced Cytotoxicity: Effects on Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 604377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, T.; Han, X.; Kontos, C.D.; Huang, S. Cadmium induction of reactive oxygen species activates the mTOR pathway, leading to neuronal cell death. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, A.; Nagpure, N.S.; Kumar, R.; Kushwaha, B.; Kumar, P.; Lakra, W.S. Assessment of tissue-specific effect of cadmium on antioxidant defense system and lipid peroxidation in freshwater murrel, Channa punctatus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, T.; Han, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Calcium signaling is involved in cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis via induction of reactive oxygen species and activation of MAPK/mTOR network. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, A.; Gabet, A.; Grave, C.; Blacher, J.; Olié, V. Associations between urinary cadmium levels, blood pressure, and hypertension: The ESTEBAN survey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10748–10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Guallar, E. Cadmium Exposure and Hypertension in the 1999–2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, C.J.; Frithsen, I.L. Association of urinary cadmium and myocardial infarction. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagerberg, B.; Bergström, G.; Borén, J.; Barregard, L. Cadmium exposure is accompanied by increased prevalence and future growth of atherosclerotic plaques in 64-year-old women. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, J.N.; Patel, M. The role of oxidative stress in organophosphate and nerve agent toxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1378, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorke, D.E.; Oz, M. A review on oxidative stress in organophosphate-induced neurotoxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2025, 180, 106735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress—The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Z.; Yang, H.J.; Li, Y.F.; Lin, C.L.; Chang, S.Y.; Sung, F.C.; Tai, S.C. The Long-Term Effects of Organophosphates Poisoning as a Risk Factor of CVDs: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, B.; Song, C.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y. Bisphenol A Promotes the Progression of Colon Cancer Through Dual-Targeting of NADPH Oxidase and Mitochondrial Electron-Transport Chain to Produce ROS and Activating HIF-1alpha/VEGF/PI3K/AKT Axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 933051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kwon, J.S.; Ahn, C.; Jeung, E.B. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Their Adverse Effects on the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, F.; Franco, G.A.; Tranchida, N.; Di Paola, R.; Cordaro, M. Molecular Mechanism of Action of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on the Respiratory System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shao, S.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, P.; Duan, H.; Zhou, K.; et al. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A induces congenital heart disease through mitochondrial dysfunction. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Hou, L.; Li, Z.; Ju, J.; Li, Q.; Qin, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Bisphenol A, an environmental estrogen-like toxic chemical, induces cardiac fibrosis by activating the ERK1/2 pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 250–251, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, M.; Marquez, S.; Reventun, P.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Arenas, M.I.; Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Gómez-Parrizas, M.; Muñóz-Moreno, C.; González-Santander, M.; Zaragoza, C.; et al. Oral administration of bisphenol A induces high blood pressure through angiotensin II/CaMKII-dependent uncoupling of eNOS. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4719–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, L.; Sarsour, E.H.; Kalen, A.L.; Aykin-Burns, N.; Spitz, D.R.; Goswami, P.C. Polychlorinated biphenyl induced ROS signaling delays the entry of quiescent human breast epithelial cells into the proliferative cycle. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Song, E.; Song, Y. A Critical Review of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Metabolism, Metabolites, and Their Correlation with Oxidative Stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2022–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, J.T.; Petriello, M.C.; Newsome, B.J.; Hennig, B. Polychlorinated biphenyls and links to cardiovascular disease. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, L.; Clark, A.; Hougaard, K.S.; Meyer, H.W.; Frederiksen, M.; Pedersen, E.B.; Petersen, K.U.; Flachs, E.M.; Bonde, J.P.E.; Tøttenborg, S.S. Risk of cardiovascular diseases following residential exposure to airborne polychlorinated biphenyls: A register-based cohort study. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, A.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Berglund, M.; Glynn, A.; Wolk, A.; Kippler, M. Dietary exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and risk of heart failure—A population-based prospective cohort study. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D. Exposure to Polychlorinated Biphenyls Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease. Epidemiology 2011, 22, S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhai, J.; Zhong, C.; Zeng, H.; Feng, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, M.; Luan, T.; et al. Effect of oxidative stress induced by 2,3,7,8- tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on DNA damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senft, A.P.; Dalton, T.P.; Nebert, D.W.; Genter, M.B.; Hutchinson, R.J.; Shertzer, H.G. Dioxin increases reactive oxygen production in mouse liver mitochondria. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 178, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.H.; Sutter, C.H.; Leon Carrion, S.; Tran, Q.T.; Bodreddigari, S.; Kensicki, E.; Mohney, R.P.; Sutter, T.R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-mediated production of reactive oxygen species is an essential step in the mechanism of action to accelerate human keratinocyte differentiation. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokinen, M.P.; Walker, N.J.; Brix, A.E.; Sells, D.M.; Haseman, J.K.; Nyska, A. Increase in cardiovascular pathology in female Sprague-Dawley rats following chronic treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2003, 3, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, P.G.; Huwe, J.K.; Walker, M.K. Hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy, and impaired vascular relaxation induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin are associated with increased superoxide. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2008, 8, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, T.P.; Kerzee, J.K.; Wang, B.; Miller, M.; Dieter, M.Z.; Lorenz, J.N.; Shertzer, H.G.; Nerbert, D.W.; Puga, A. Dioxin exposure is an environmental risk factor for ischemic heart disease. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2001, 1, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humblet, O.; Birnbaum, L.; Rimm, E.; Mittleman, M.A.; Hauser, R. Dioxins and cardiovascular disease mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivnitski-Steele, I.D.; Friggens, M.; Chavez, M.; Walker, M.K. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) inhibition of coronary vasculogenesis is mediated, in part, by reduced responsiveness to endogenous angiogenic stimuli, including vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2005, 73, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A. Perspectives on the Potential Involvement of the Ah Receptor-Dioxin Axis in Cardiovascular Disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 120, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, A.C.; Kopf, P.G.; Campen, M.J.; Huwe, J.K.; Walker, M.K. In utero and lactational 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure: Effects on fetal and adult cardiac gene expression and adult cardiac and renal morphology. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackaberry, E.A.; Nunez, B.A.; Ivnitski-Steele, I.D.; Friggins, M.; Walker, M.K. Effect of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin on Murine Heart Development: Alteration in Fetal and Postnatal Cardiac Growth, and Postnatal Cardiac Chronotropy. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, D.W.; Graceffa, P.; Pryor, W.A.; Weitzman, S.A. The role of free radicals in asbestos-induced diseases. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1992, 12, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Jung, M.; Stern, M.; Fukagawa, N.K.; Taatjes, D.J.; Sawyer, D.; Van Houten, B.; Mossman, B.T. Asbestos induces mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction linked to the development of apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L1018–L1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W. Occupational exposure to asbestos and cardiovascular related diseases: A meta-analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Field, R.W.; Kahe, K. Radon exposure and risk of cerebrovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis in occupational and general population studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45031–45043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, L.; Sun, J.; Zhai, X.; Chen, X.; Wan, J.; Tian, H. Repeated radon exposure induced lung damage via oxidative stress-mediated mitophagy in human bronchial epithelial cells and mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Nejad, H.A.; Kargarfard, M.; Mohseni, S.; Suzuki, K.; Carmelo Adsuar, J.; Perez-Gomez, J. The Effect of Acute Intense Exercise on Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes in Smokers and Non-Smokers. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.Y. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Formation: A Concise Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emma, R.; Caruso, M.; Campagna, D.; Pulvirenti, R.; Li Volti, G. The Impact of Tobacco Cigarettes, Vaping Products and Tobacco Heating Products on Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahdy, M.A.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Hemann, C.; Ewees, M.G.; Mahgoup, E.M.; Eid, M.S.; Shalaan, M.T.; Alzarie, Y.A.; Zweier, J.L. Chronic cigarette smoke exposure triggers a vicious cycle of leukocyte and endothelial-mediated oxidant stress that results in vascular dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H51–H65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, E.M.; Fagerberg, B.; Sallsten, G.; Borné, Y.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Barregard, L. Partial Mediation by Cadmium Exposure of the Association Between Tobacco Smoking and Atherosclerotic Plaques in the Carotid Artery. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 187, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockene, I.S.; Miller, N.H. Cigarette Smoking, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke. Circulation 1997, 96, 3243–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, Q. T-2 Toxin Induces Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Cytoprotective Autophagy in Chicken Hepatocytes. Toxins 2020, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, T.; Chen, Y.; Song, W.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X. Nrf2: A Main Responsive Element of the Toxicity Effect Caused by Trichothecene (T-2) Mycotoxin. Toxics 2023, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Uetsuka, K. Mechanisms of mycotoxin-induced neurotoxicity through oxidative stress-associated pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5213–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.; Xiang, R.; Zhan, J.; Deng, F.; Bao, M.; He, H.; Wen, X.; Deng, H.; et al. T-2 toxin induces cardiac fibrosis by causing metabolic disorders and up-regulating Sirt3/FoxO3alpha/MnSOD signaling pathway-mediated oxidative stress. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Alajbegovic, A.; Gomes, A.V. NSAIDs and Cardiovascular Diseases: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 536962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hu, P.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Hu, R.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. Molecular mechanism of ethylparaben on zebrafish embryo cardiotoxicity based on transcriptome analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Radiation-Induced Normal Tissue Damage: Oxidative Stress and Epigenetic Mechanisms. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3010342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Seo, D.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, E.; Kang, J.; Seong, K.M.; Youn, H.; Youn, B. Cellular Stress Responses in Radiotherapy. Cells 2019, 8, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile-Dugas, E.; Eisenberg, M.J. Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: Review of an Underrecognized Pathology. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Yin, X.; Jiang, X. Radiation-induced heart disease: A review of classification, mechanism and prevention. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.N.; Hussain, K.; Richards, J.R. Radiation-Induced Coronary Artery Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ellahham, S.; Khalouf, A.; Elkhazendar, M.; Dababo, N.; Manla, Y. An overview of radiation-induced heart disease. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2022, 40, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa, J.; Aran, J.M. Reactive Oxygen Species: Drivers of Physiological and Pathological Processes. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzma, N.; Kumar, B.S.; Hazari, M.A. Exposure to benzene induces oxidative stress, alters the immune response and expression of p53 in gasoline filling workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alfaro, M.; Alcaraz-Contreras, Y.; Carabez-Trejo, A.; Leo-Amador, G.E. Oxidative stress effects of thinner inhalation. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 15, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordiano, R.; Papa, V.; Cicero, N.; Spatari, G.; Allegra, A.; Gangemi, S. Effects of Benzene: Hematological and Hypersensitivity Manifestations in Resident Living in Oil Refinery Areas. Toxics 2022, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abplanalp, W.; DeJarnett, N.; Riggs, D.W.; Conklin, D.J.; McCracken, J.P.; Srivastava, S.; Xie, Z.; Rai, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; O’Toole, T.E. Benzene exposure is associated with cardiovascular disease risk. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Osko, J.; Knez, E.; Grembecka, M. Microplastics and Oxidative Stress-Current Problems and Prospects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.; Sarker, D.B.; Jocelyn, J.A.; Sang, Q.A. Molecular and Cellular Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Focus on Inflammation and Senescence. Cells 2024, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on cardiomyocytes pyroptosis through NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway and oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persiani, E.; Cecchettini, A.; Ceccherini, E.; Gisone, I.; Morales, M.A.; Vozzi, F. Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System). Biomedicines 2023, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.P.; Sies, H.; Klaunig, J.E. Redox biology: The old and the new. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zong, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Ning, S. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in pulmonary fibrosis: Current perspectives, opportunities and challenges. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbner, B.; Tavakoli-Rouzbehani, O.M.; Fatahian, A.N.; Boudina, S. The dynamic interplay between cardiac mitochondrial health and myocardial structural remodeling in metabolic heart disease, aging, and heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2023, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, T.; Xuan, H.C.; Li, X.Q.; Shi, X.X.; Dai, F.; Chen, J.H.; Li, D.Y.; Xu, T.D. Association of low-level lead exposure with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in US adults with hypertension: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2010. Arch. Public Health 2023, 81, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.B.; Potula, V.; Schwartz, J.; Vokonas, P.S.; Sparrow, D.; Wright, R.O.; Nie, H.; Hu, H. Lead Levels and Ischemic Heart Disease in a Prospective Study of Middle-Aged and Elderly Men: The VA Normative Aging Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; Jain, N.; Nie, H.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.; Schwartz, J.; Hu, H. A Prospective Study of Bone Lead Concentration and Death From All Causes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Cancer in the Department of Veterans Affairs Normative Aging Study. Circulation 2009, 120, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Selvin, E.; Sharrett, A.R.; Calderon-Aranda, E.; Silbergeld, E.; Guallar, E. Lead, Cadmium, Smoking, and Increased Risk of Peripheral Arterial Disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Park, S.K.; Hu, H.; Lee, S. Cadmium exposure and cardiovascular disease in the 2005 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Res. 2011, 111, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, R.; McMullen, H.; Beqaj, H.; Kalfa, D. Environmental Exposures and Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2021, 149, e2021052151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, M.F.; Lo, C.W.H.; Cheung, T.T.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Blood lead level and risk of hypertension in the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2016. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, S.; Rodgers, A. Blood pressure, antihypertensive treatment and stroke risk. J. Hypertens. 1994, 12, S5–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Croft, J. Review of the Relation between Blood Lead and Blood Pressure. Epidemiol. Rev. 1993, 15, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, T.S.; Thijs, L.; Den Hond, E.M.; Roels, H.A.; Staessen, J.A. An epidemiological re-appraisal of the association between blood pressure and blood lead: A meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Lead, Blood Pressure, and Cardiovascular Disease in Men. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1995, 50, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.A.; Bulpitt, C.J.; Fagard, R.; Lauwerys, R.R.; Roels, H.; Thijs, L.; Amery, A. Hypertension Caused by Low-Level Lead Exposure: Myth or Fact? Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 1994, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.A.; Roels, H.; Lauwerys, R.R.; Amery, A. Low-level lead exposure and blood pressure. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1995, 9, 303–328. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, M.H.; Khandker, S.; Sarwar, A.F.M.; Yasmin, N.; Faruquee, M.H.; Yasmin, R. Blood Lead Levels and Health Problems of Lead Acid Battery Workers in Bangladesh. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 974104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiue, I. Higher urinary heavy metal, arsenic, and phthalate concentrations in people with high blood pressure: US NHANES, 2009–2010. Blood Press. 2014, 23, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Harrison, D.G. Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases: The Role of Oxidant Stress. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, and Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.K. Mechanisms of plaque vulnerability and rupture. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, S15–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, B. Mechanisms of Disease: Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2006, 2, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, D.; Spartalis, M.; Spartalis, E.; Karachaliou, G.S.; Karaolanis, G.I.; Tsourouflis, G.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Tzatzaki, E.; Theocharis, S. The role of reactive oxygen species in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases and the clinical significance of myocardial redox. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panth, N.; Paudel, K.R.; Parajuli, K. Reactive Oxygen Species: A Key Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease. Adv. Med. 2016, 2016, 9152732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoples, J.N.; Saraf, A.; Ghazal, N.; Pham, T.T.; Kwong, J.Q. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverne, Y.J.H.J.; Bogers, A.J.J.C.; Duncker, D.J.; Merkus, D. Reactive Oxygen Species and the Cardiovascular System. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 862423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Münzel, T. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Vascular Disease. Circulation 2006, 113, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, E.; Marques, M.; Barrientos, A.; Casado, S.; Lopez-Farre, A. Lead-Induced Downregulation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase in Isolated Rat Aortic Segments Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species and Cyclooxygenase-2. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafati Rahimzadeh, M.; Rafati Rahimzadeh, M.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S. Dietary Cadmium Intake and Its Effects on Kidneys. Toxics 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-C.; Hao, W.-M.; Chu, P.-H. Cadmium and cardiovascular disease: An overview of pathophysiology, epidemiology, therapy, and predictive value. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2021, 40, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, A.; Muntner, P.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Platz, E.A.; Guallar, E. Cadmium Levels in Urine and Mortality among U.S. Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, K.E.; Callan, A.C.; Prince, R.L.; Lim, W.H.; Thompson, P.L.; Lewis, J.R.; Hinwood, A.L.; Devine, A. Low-level cadmium exposure and cardiovascular outcomes in elderly Australian women: A cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Weng, C.H.; Lee, C.C.; Lin-Tan, D.T.; Chu, P.H.; Chen, K.H.; Yen, T.H.; Huang, W.H. Urinary cadmium levels predict mortality of patients with acute heart failure. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Guallar, E.; Howard, B.V.; Umans, J.G.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Devereux, R.B.; Navas-Acien, A. Cadmium exposure and incident cardiovascular disease. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.; Ferreira de Oliveira, J.M.P.; Pinho, F.; Bastos, V.; Oliveira, H.; Peixoto, F.; Santos, C. Biochemical and transcriptional analyses of cadmium-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in human osteoblasts. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2018, 81, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharashi, N.A.O.; Periasamy, V.S.; Athinarayanan, J.; Alshatwi, A.A. Cadmium triggers mitochondrial oxidative stress in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes: Analysis using in vitro and system toxicology approaches. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 42, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Sánchez, C.; Egido, J.; Sánchez-González, P.D.; Pérez-Barriocanal, F.; López-Novoa, J.M.; Morales, A.I. Effect of the flavonoid quercetin on cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Ding, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Alleviating effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis by activating the Nrf2-keap1 pathway in BRL-3A cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 969892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.E.; Jacob, M.; Sanadi, D.R.; Bradley, L.B. Uncoupling of Oxidative Phosphorylation by Cadmium Ion. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 223, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.; King, M.S.; Pryde, K.R. The production of reactive oxygen species by complex I. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughan, A.K.; Harrison, D.G.; Dikalov, S.I. Molecular Mechanisms of Angiotensin II–Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, Ç.; Doğan, E.; Comakli, S. Cardiovascular disease and toxic metals. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Akter, M.; Corpus Bondad, S.E.; Saito, T.; Hosokawa, T.; Kurasaki, M. Carvacrol inhibits cadmium toxicity through combating against caspase dependent/independent apoptosis in PC12 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Rainbow, R.D.; Sharma, P. Mitigation of Cardiovascular Disease and Toxicity through NRF2 Signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cracowski, J.L.; Durand, T.; Bessard, G. Isoprostanes and their products as biomarkers of oxidative stress in humans. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Qiu, W.Y.; Huo, Y.N.; Yao, Y.F.; Lou, M.F. Low levels of hydrogen peroxide stimulate corneal epithelial cell adhesion, migration, and wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Jiang, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, Q. Paraben exposures and their interactions with ESR1/2 genetic polymorphisms on hypertension. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, A.Z.; Mumford, S.L.; Krall, J.R.; Carmichael, A.; Andriessen, V.C.; Kannan, K.; Schisterman, E.F. Urinary levels of environmental phenols and parabens and antioxidant enzyme activity in the blood of women. Environ. Res 2020, 186, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, I.L.; Dirven, H.; Couderq, S.; David, A.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Fernández, M.F.; Mustieles, V.; Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Hofer, T. Bisphenols and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers-Associations Found in Human Studies, Evaluation of Methods Used, and Strengths and Weaknesses of the Biomarkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Yu, S.H.; Lee, C.B.; Park, Y.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, D.S. Effects of bisphenol A on cardiovascular disease: An epidemiological study using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003-2016 and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Han, L.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Co-Exposure to Bisphenols, Parabens, and Antimicrobials and Association with Coronary Heart Disease: Oxidative Stress as a Potential Mediating Factor? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.L.; Hayes, K.P.J.W.R. Drinking water disinfection by-products: An Australian perspective. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, M.R.; Lutsey, P.L.; Bhatti, P.; Prizment, A. Urinary 2,5-dicholorophenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol concentrations and prevalent disease among adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 76, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Bolser, D.G.; Kroll, K.J.; Brockmeier, E.K.; Falciani, F.; Denslow, N.D. Comparative toxicity of three phenolic compounds on the embryo of fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 201, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics/cosmetic-ingredients/phthalates-cosmetics (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Cui, J.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.-N.; Li, J.-L. Lycopene regulates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response to prevent DEHP-induced cardiac mitochondrial damage in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4527–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, M.Z.; Wang, H.R.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.L. Lycopene prevents Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced mitophagy and oxidative stress in mice heart via modulating mitochondrial homeostasis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 115, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Li, T. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Mortality in U.S. Adults: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 67007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Potential adverse health effects of ingested micro- and nanoplastics on humans. Lessons learned from in vivo and in vitro mammalian models. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2020, 23, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Perfluorooctane sulfonate promotes atherosclerosis by modulating M1 polarization of macrophages through the NF-κB pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Li, L.; Tang, L.; Guo, M.; Yang, J. Perfluorooctane sulfonate induces heart toxicity involving cardiac apoptosis and inflammation in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.L.; Wang, J.D.; Xu, T.T.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, J.J.; Ge, R.S.; Zhu, D.Y. Mitochondrial toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicology 2017, 382, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Ivantsova, E.; Konig, I.; Souders, C.L., 2nd; Martyniuk, C.J. Perfluorotetradecanoic Acid (PFTeDA) Induces Mitochondrial Damage and Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos/Larvae. Toxics 2022, 10, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sheng, N.; Zhang, W.; Dai, J. Toxic effects of perfluorononanoic acid on the development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenaars, A.; Vergauwen, L.; De Coen, W.; Knapen, D. Structure-activity relationship assessment of four perfluorinated chemicals using a prolonged zebrafish early life stage test. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ducatman, A.; Ward, R.; Leonard, S.; Bukowski, V.; Lan Guo, N.; Shi, X.; Vallyathan, V.; Castranova, V. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in human microvascular endothelial cells: Role in endothelial permeability. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2010, 73, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvandi, A.M.; Shahba, S.; Mehrzad, J.; Lombardi, G. Metabolic Disruption by Naturally Occurring Mycotoxins in Circulation: A Focus on Vascular and Bone Homeostasis Dysfunction. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 915681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, J. A review of the mechanism of injury and treatment approaches for illness resulting from exposure to water-damaged buildings, mold, and mycotoxins. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 767482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Yu, C.; Xu, X.H. Effects of aflatoxin B1 on mitochondrial respiration, ROS generation and apoptosis in broiler cardiomyocytes. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Taylor, A.A.; Zenobio, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Salawu, O.A.; Zhu, Y. Abundance, fate, and effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schjerning, A.-M.; McGettigan, P.; Gislason, G. Cardiovascular effects and safety of (non-aspirin) NSAIDs. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Callejón, M.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceutically active compounds during 1-year period in wastewaters from four wastewater treatment plants in Seville (Spain). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Lee, D.S. Significance of metabolites in the environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals consumed by human. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Maric, F. Mitigating the environmental impact of NSAIDs—Physiotherapy as a contribution to One Health and the SDGs. Eur. J. Physiother. 2021, 25, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambosi, J.; Yamanaka, L.; Humberto, J.; José, H.; De, R.; Moreira, R.; Moreira, M.; Schröder, H. Recent research data on the removal of pharmaceuticals from sewage treatment plants (STP). Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyumina, E.A.; Bazhutin, G.A.; Cartagena Gómez, A.d.P.; Ivshina, I.B.J.M. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs as Emerging Contaminants. Microbiology 2020, 89, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouissou-Schurtz, C.; Houeto, P.; Guerbet, M.; Bachelot, M.; Casellas, C.; Mauclaire, A.-C.; Panetier, P.; Delval, C.; Masset, D. Ecological risk assessment of the presence of pharmaceutical residues in a French national water survey. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Mishra, M.; Salemi, M.R.; Phinney, B.S.; Newens, J.L.; Gomes, A.V. Gender-specific changes in energy metabolism and protein degradation as major pathways affected in livers of mice treated with ibuprofen. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfè, A.; Scotti, L.; Varas-Lorenzo, C.; Nicotra, F.; Zambon, A.; Kollhorst, B.; Schink, T.; Garbe, E.; Herings, R.; Straatman, H.; et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of heart failure in four European countries: Nested case-control study. BMJ 2016, 354, i4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, P.; Steg, P.G.; Cannon, C.P.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Eagle, K.A.; Ohman, E.M.; Alberts, M.J.; Hoffman, E.; Guo, J.; Simon, T.; et al. NSAID use and association with cardiovascular outcomes in outpatients with stable atherothrombotic disease. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 53–60.e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, T.J.; Haas, S.J.; Liew, D.; Krum, H. Meta-analysis of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and their effects on blood pressure. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Kent, J.; Taylor, A.; Verburg, K.M.; Lefkowith, J.B.; Whelton, A. Effects of celecoxib on ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients on ACE inhibitors. Hypertension 2002, 39, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Swee, M.L. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Use in a Patient With Hypertension: A Teachable Moment. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 892–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kömhoff, M.; Grone, H.J.; Klein, T.; Seyberth, H.W.; Nüsing, R.M. Localization of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in adult and fetal human kidney: Implication for renal function. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, F460–F468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, M.D.; Hao, C.; Qi, Z. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors and the kidney. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2001, 7, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hortmann, M.; Daiber, A.; Oelze, M.; Ostad, M.A.; Schwarz, P.M.; Xu, H.; Xia, N.; Kleschyov, A.L.; Mang, C.; et al. Cyclooxygenase 2-selective and nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induce oxidative stress by up-regulating vascular NADPH oxidases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Hwang, S.M.; Cui, Z.; Gilda, J.E.; Gomes, A.V. Different effects of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs meclofenamate sodium and naproxen sodium on proteasome activity in cardiac cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 94, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.A.; Sarwar, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Ishqi, H.M.; Tabish, M. Ibuprofen causes photocleavage through ROS generation and intercalates with DNA: A combined biophysical and molecular docking approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 13837–13850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, E.J.; Lim, K.M. Ibuprofen Increases the Hepatotoxicity of Ethanol through Potentiating Oxidative Stress. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Phinney, B.S.; Salemi, M.R.; Gomes, A.V. Mitochondrial and Proteasome Dysfunction Occurs in the Hearts of Mice Treated with Triazine Herbicide Prometryn. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilda, J.E.; Gomes, A.V. Proteasome dysfunction in cardiomyopathies. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4051–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, C. Endothelial cell functions. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, B.R.; Yen, L.B.; Wu, K.K. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induced endothelial apoptosis by perturbing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta transcriptional pathway. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, X.; Liang, B.; Genbo Xu, E.; Huang, Z. Micro- and nanoplastics: A new cardiovascular risk factor? Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshanzadeh, A.; Oyunbaatar, N.E.; Ganjbakhsh, S.E.; Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kanade, P.P.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, E.S. Exposure to nanoplastics impairs collective contractility of neonatal cardiomyocytes under electrical synchronization. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, J. Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonn, E.; Bosch, J.; Yusuf, S.; Sheridan, P.; Pogue, J.; Arnold, J.M.; Ross, C.; Arnold, A.; Sleight, P.; Probstfield, J.; et al. Effects of long-term vitamin E supplementation on cardiovascular events and cancer: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2005, 293, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfowiris, A.; Banigesh, A. Evaluation of Antioxidant Therapeutic Value of Ace Inhibitor as Adjunct Therapy on T2dm Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 310. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Nerune, S.M.; Das, K.K. Antioxidant therapy for hepatic diseases: A double-edged sword. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 35, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Role of oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1381–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukreja, R.C.; Salloum, F.N. Pharmacological preconditioning with natural compounds. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 51, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, L.L.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Huynh, N.N.; Hamilton, C.A.; Beattie, E.; Smith, R.A.; Cocheme, H.M.; Murphy, M.P.; Dominiczak, A.F. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ10 improves endothelial function and attenuates cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension 2009, 54, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G.; Bai, Y.; Liu, P.; Meng, L.; Jiang, X.; Xin, Y. Sulforaphane prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiomyopathy by activation of Nrf2 through epigenetic modification. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4408–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Rera, M.; Walker, D.W. Parkin overexpression during aging reduces proteotoxicity, alters mitochondrial dynamics, and extends lifespan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8638–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ichikawa, T.; Janicki, J.S.; Cui, T. Targeting the Nrf2 pathway against cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2009, 13, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, K.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Wiel, C.; Sayin, V.I.; Akula, M.K.; Karlsson, C.; Dalin, M.G.; Akyürek, L.M.; Lindahl, P.; Nilsson, J.; et al. Antioxidants can increase melanoma metastasis in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.V.; Le, G.K.; El Zowalaty, A.E.; Pehlivanoglu, L.E.; Garellick, V.; Gul, N.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Bergh, P.O.; Henricsson, M.; Wiel, C.; et al. Antioxidants Promote Intestinal Tumor Progression in Mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashino, I.; Mizoue, T.; Serafini, M.; Akter, S.; Sawada, N.; Ishihara, J.; Kotemori, A.; Inoue, M.; Yamaji, T.; Goto, A.; et al. Higher Dietary Non-enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity Is Associated with Decreased Risk of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in Japanese Adults. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, H. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Atherosclerosis and Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A.L.; Backhed, F. Role of gut microbiota in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).