Time Course of Plasma Proteomic and Oxylipin Changes Induced by LPS Challenge and Modulated by Antioxidant Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Plasma Proteomics
2.3. Plasma Lipidomics
2.4. 3 Data Sharing Statement
3. Results
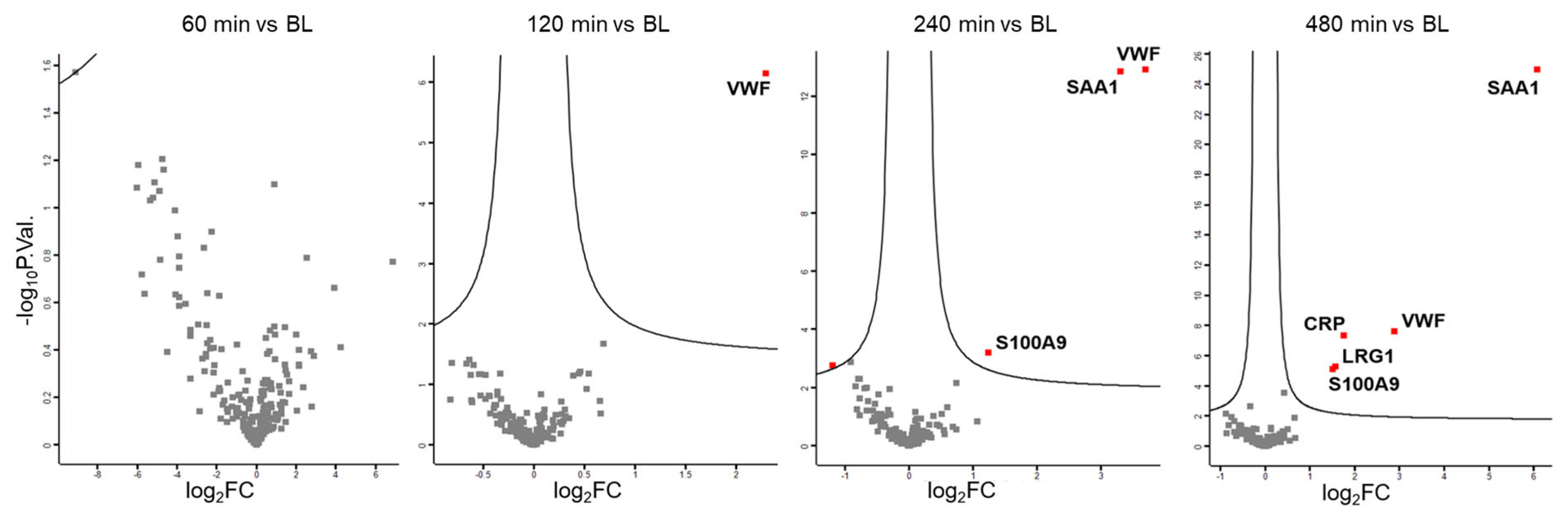
3.1. Plasma Proteome Profiling Indicates the Involvement of Endothelial Cells, Platelets, Innate Immune Cells, and the Liver During LPS-Induced Inflammation
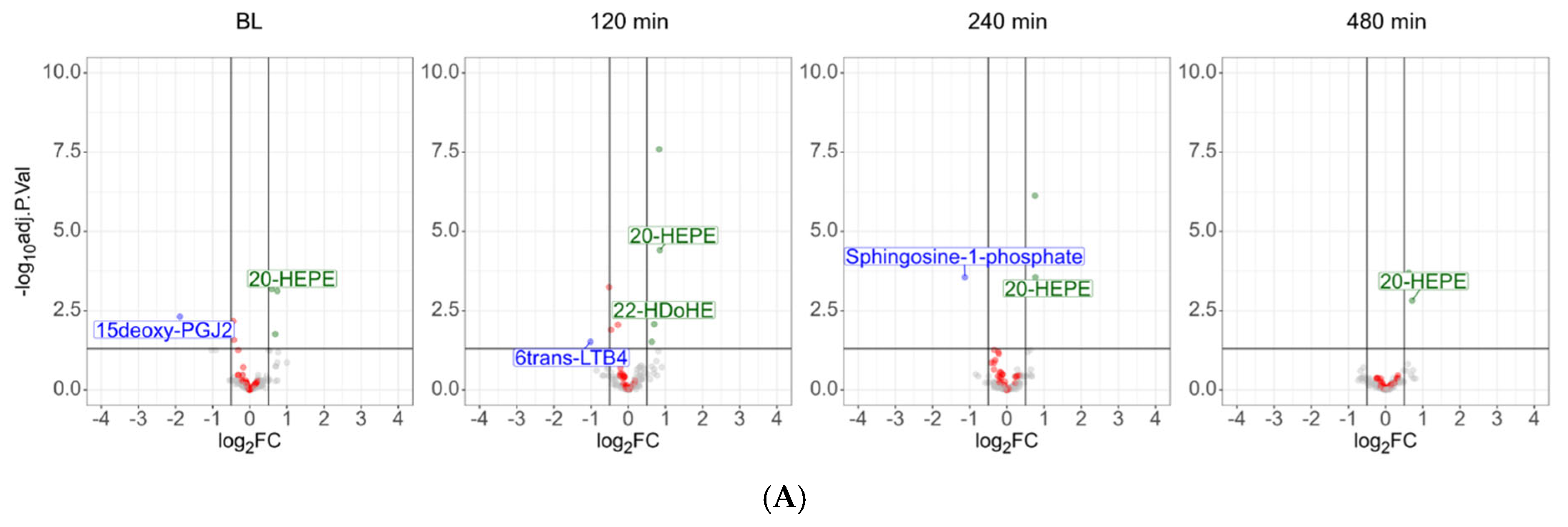
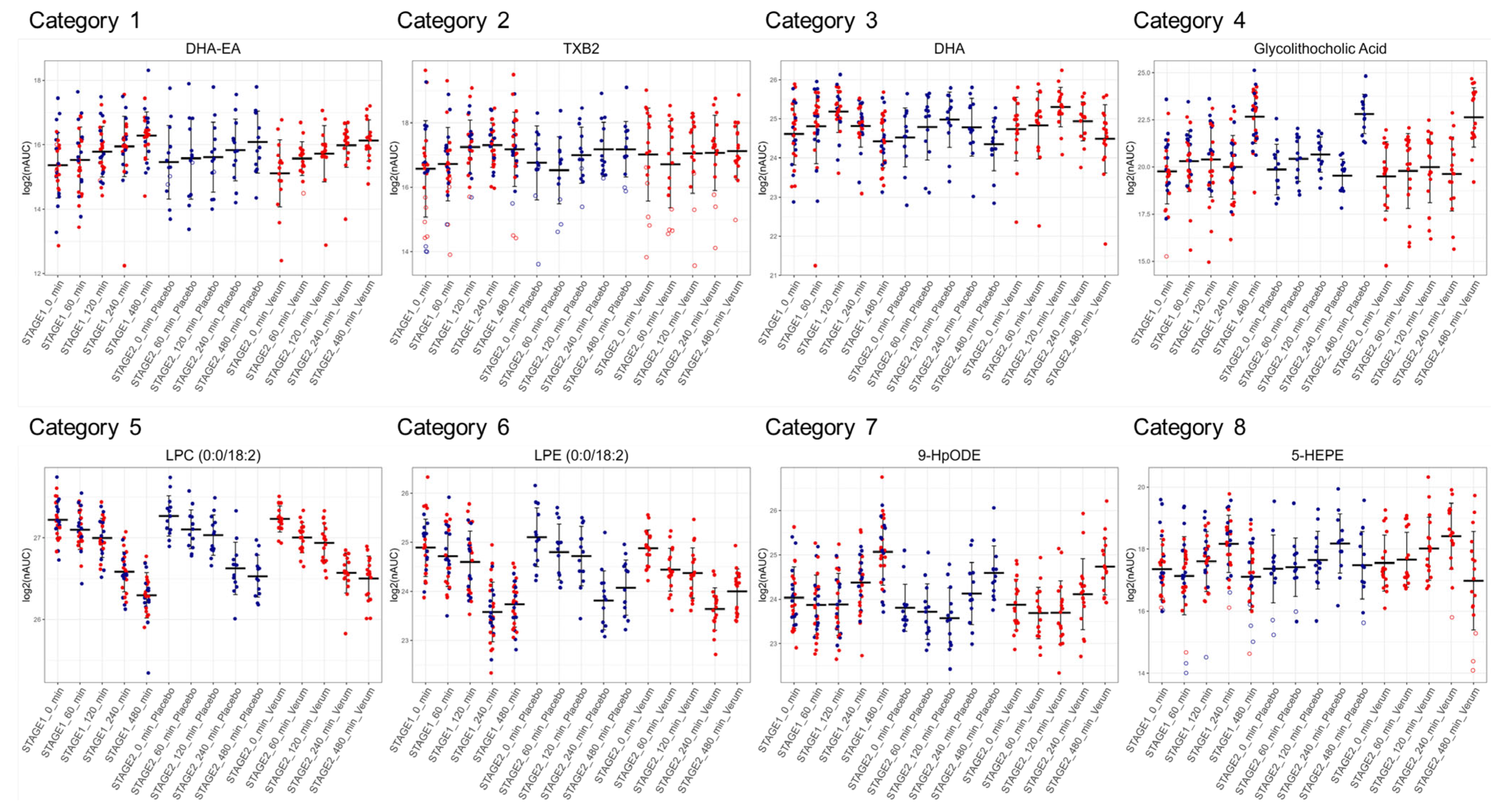
3.2. Plasma Lipidomics Demonstrates Immediate Adaptive Response Involving Oxylipins, Bile Acids, and the Lands Cycle in Response to LPS Challenge
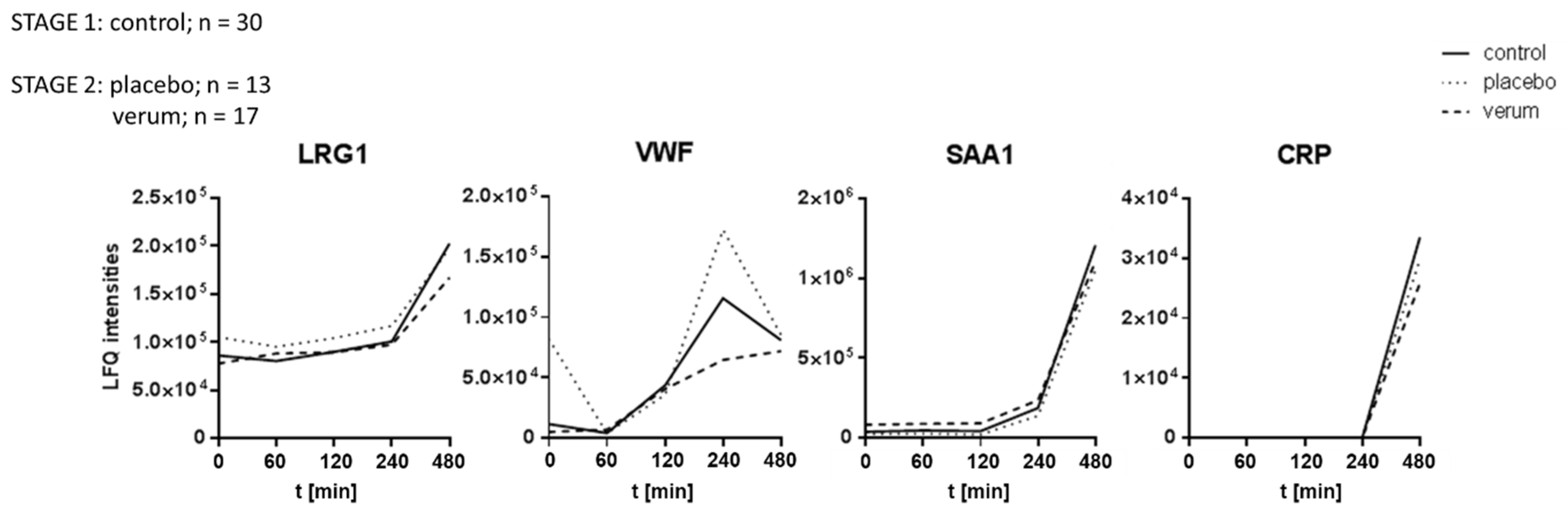
3.3. Dietary Antioxidant Supplementation Does Not Affect the Kinetics of Inflammatory Marker Proteins Within Eight Hours After LPS Challenge
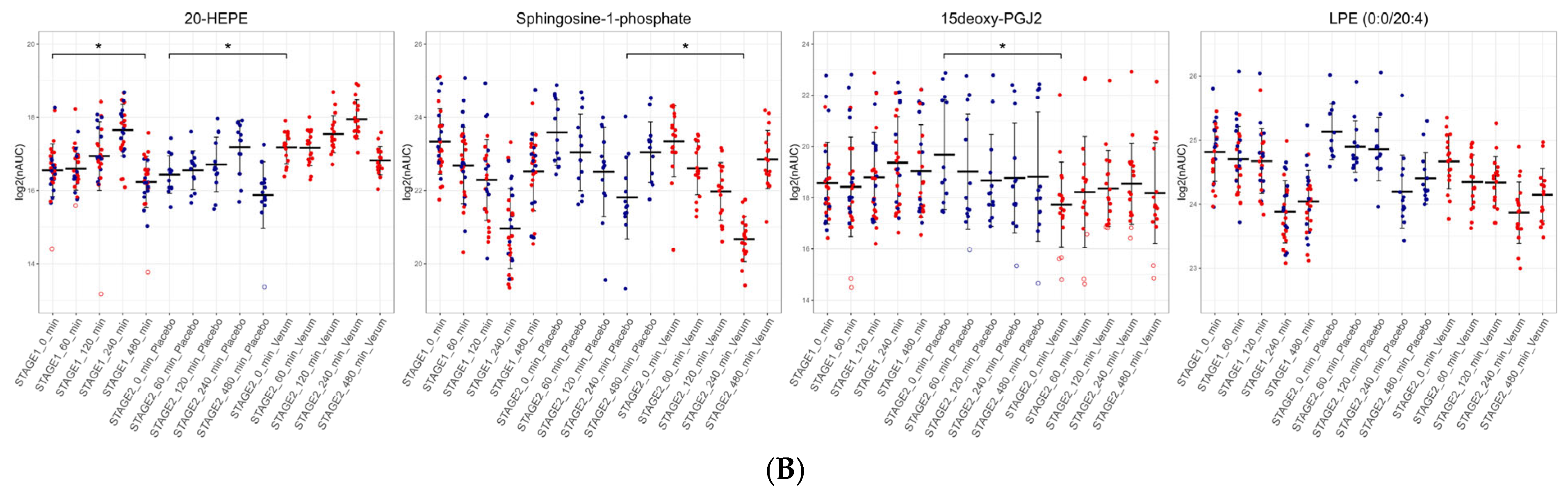
3.4. Dietary Antioxidant Supplementation Increases Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators and Downregulates Sphingosine-1-Phosphate After the LPS Challenge
3.5. Similar Kinetics After LPS Challenge Suggests Common Biosynthetic Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Told, R.; Palkovits, S.; Schmidl, D.; Boltz, A.; Gouya, G.; Wolzt, M.; Napora, K.J.; Werkmeister, R.M.; Popa-Cherecheanu, A.; Garhofer, G.; et al. Retinal hemodynamic effects of antioxidant supplementation in an endotoxin-induced model of oxidative stress in humans. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Told, R.; Schmidl, D.; Palkovits, S.; Boltz, A.; Gouya, G.; Wolzt, M.; Witkowska, K.J.; Popa-Cherecheanu, A.; Werkmeister, R.M.; Garhofer, G.; et al. Antioxidative capacity of a dietary supplement on retinal hemodynamic function in a human lipopolysaccharide (LPS) model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 56, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slany, A.; Bileck, A.; Kreutz, D.; Mayer, R.L.; Muqaku, B.; Gerner, C. Contribution of Human Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells to the Hallmarks of Inflammation as Determined by Proteome Profiling. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 1982–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennike, T.B. Advances in proteomics: Characterization of the innate immune system after birth and during inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1254948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Chu, Y.; Qin, X.; Yang, P.; Yu, H. Lipid metabolism in inflammation-related diseases. Analyst 2018, 143, 4526–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimessi, A.; Previati, M.; Nigro, F.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Pinton, P. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and inflammation: Molecular mechanisms, diseases and promising therapies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F.; Sono, Y.; Ito, T. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Lipid Peroxidation as a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress: Oxidative Stress in Diabetes, Atherosclerosis, and Chronic Inflammation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.T.; Aziz, F.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Arguelles, S. Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.P.; Carmody, R.J. NF-kappaB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 335, 41–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadina, M.; Hilton, D.; Johnston, J.A.; Morinobu, A.; Lighvani, A.; Zhou, Y.J.; Visconti, R.; O’Shea, J.J. Signaling by type I and II cytokine receptors: Ten years after. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2001, 13, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarczak, D.; Nierhaus, A. Cytokine Storm-Definition, Causes, and Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorino, G.; Ananthakrishnan, A.; Cohen, R.D.; Cross, R.K.; Deepak, P.; Farraye, F.A.; Halfvarson, J.; Steinhart, A.H. Accelerating Earlier Access to Anti-TNF-alpha Agents with Biosimilar Medicines in the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, P.; Golia, E.; Yeh, E.T. CRP and the risk of atherosclerotic events. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maile, R.; Willis, M.L.; Herring, L.E.; Prevatte, A.; Mahung, C.; Cairns, B.; Wallet, S.; Coleman, L.G., Jr. Burn Injury Induces Proinflammatory Plasma Extracellular Vesicles That Associate with Length of Hospital Stay in Women: CRP and SAA1 as Potential Prognostic Indicators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.; Van Hoovels, L.; Benucci, M.; De Luca, R.; Coccia, C.; Bernardini, P.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; Guiducci, S.; Grossi, V.; et al. Circulating Calprotectin (cCLP) in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.M. Biochemistry and pharmacology of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Bull. N. Y. Acad. Med. 1989, 65, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pergola, C.; Werz, O. 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors: A review of recent developments and patents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2010, 20, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misheva, M.; Johnson, J.; McCullagh, J. Role of Oxylipins in the Inflammatory-Related Diseases NAFLD, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, M.; Yurdagul, A., Jr.; Tabas, I.; Oorni, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: Mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiu, V.; Leuti, A.; Maccarrone, M. Bioactive Lipids and Chronic Inflammation: Managing the Fire Within. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.A.; Norris, P.C. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002, 21, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, M.; Victor, V.M. Anti-oxidants as modulators of immune function. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Dietetic, A. Position of the American Dietetic Association: Fortification and nutritional supplements. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinder, M.; Boyd, J.H.; Brunham, L.R. Molecular regulation of plasma lipid levels during systemic inflammation and sepsis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019, 30, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.; Samouda, H.; Dohet, F.; Loap, S.; Ellulu, M.S.; Bohn, T. Common and Novel Markers for Measuring Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Ex Vivo in Research and Clinical Practice-Which to Use Regarding Disease Outcomes? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. The Role of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Signalling in Chronic Inflammation. Chronic Stress 2022, 6, 24705470221076390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoergenhofer, C.; Schwameis, M.; Gelbenegger, G.; Buchtele, N.; Thaler, B.; Mussbacher, M.; Schabbauer, G.; Wojta, J.; Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Jilma, B. Inhibition of Protease-Activated Receptor (PAR1) Reduces Activation of the Endothelium, Coagulation, Fibrinolysis and Inflammation during Human Endotoxemia. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Kliegel, T.; Kantner-Schlifke, I.; Strasser-Marsik, C.; Mayr, F.B.; Jilma, B. Upregulation of cytokine mRNA in circulating leukocytes during human endotoxemia. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2017, 28, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janker, L.; Schuster, D.; Bortel, P.; Hagn, G.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Mohr, T.; Mader, J.C.; Slany, A.; Bileck, A.; Brunmair, J.; et al. Multiomics-Empowered Deep Phenotyping of Ulcerative Colitis Identifies Biomarker Signatures Reporting Functional Remission States. J. Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarik, J.J.; Bileck, A.; Hagn, G.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Frey, T.; Kaempf, A.; Hollenstein, M.; Shoumariyeh, T.; Skos, L.; Reiter, B.; et al. A multi-omics based anti-inflammatory immune signature characterizes long COVID-19 syndrome. iScience 2023, 26, 105717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagn, G.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Plessl-Walder, G.; Mitra, G.; Mohr, T.; Preindl, K.; Schlatter, A.; Schmidl, D.; Gerner, C.; Garhofer, G.; et al. Plasma Instead of Serum Avoids Critical Confounding of Clinical Metabolomics Studies by Platelets. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 3064–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougman, A.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Suspension trapping (STrap) sample preparation method for bottom-up proteomics analysis. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1006-1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. 1D and 2D annotation enrichment: A statistical method integrating quantitative proteomics with complementary high-throughput data. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. S16), S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Sud, M.; Cotter, D.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W606–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, C.; Burger, T.; Wieczorek, S. imputeLCMD: A Collection of Methods for Left-Censored Missing Data Imputation, Version 2.1. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=imputeLCMD (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, Y.; Benjamini, Y. More powerful procedures for multiple significance testing. Stat. Med. 1990, 9, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.; Edison, A.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, B.; Hegedus, D.; Szapary, L.; Marton, Z.; Alexy, T.; Koltai, K.; Czopf, L.; Wittmann, I.; Juricskay, I.; Toth, K.; et al. Measurement of von Willebrand factor as the marker of endothelial dysfunction in vascular diseases. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 9, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Compartmentalized regulation of lipid signaling in oxidative stress and inflammation: Plasmalogens, oxidized lipids and ferroptosis as new paradigms of bioactive lipid research. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 89, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yang, L.; Chang, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Dong, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Li, L. Macrophage Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 2 Blockade Attenuates Liver Inflammation and Fibrogenesis Triggered by NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, A.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: Lipid signaling in pathology and therapy. Science 2019, 366, eaar5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolksdorf, C.; Moritz, E.; Wolf, R.; Meyer, U.; Marx, S.; Bien-Moller, S.; Garscha, U.; Jedlitschky, G.; Rauch, B.H. Platelet-Derived S1P and Its Relevance for the Communication with Immune Cells in Multiple Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, F.; Guo, L.; Hou, Y.; Hu, H.; Yan, S.; Zhou, X.; Liao, L.; Allen, T.D.; et al. Plasma von Willebrand factor level is transiently elevated in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Dana, R.; Hazan, I.; Levy, I.; Weber, G.; Smoliakov, R.; Pesach, I.; Riesenberg, K.; Schlaeffer, F. Elevated cytosolic phospholipase A(2) expression and activity in human neutrophils during sepsis. Blood 2000, 95, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.C.; Hagn, G.; Niederstaetter, L.; Bileck, A.; Plessl-Walder, K.; Horvath, M.; Kolovratova, V.; Tanzmann, A.; Tolios, A.; Rabitsch, W.; et al. INTERCEPT Pathogen Reduction in Platelet Concentrates, in Contrast to Gamma Irradiation, Induces the Formation of trans-Arachidonic Acids and Affects Eicosanoid Release during Storage. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Kampoli, A.M.; Tentolouris, C.; Papageorgiou, N.; Stefanadis, C. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.M.; Ishizu, A.N.; Foo, J.C.; Toh, X.R.; Zhang, F.; Whee, D.M.; Torta, F.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Matsumura, T.; Kim, S.; et al. Mfsd2b is essential for the sphingosine-1-phosphate export in erythrocytes and platelets. Nature 2017, 550, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.S.; Nierhaus, A.; Holzmann, M.; Mudersbach, E.; Bauer, A.; Robbe, L.; Zahrte, C.; Geffken, M.; Peine, S.; Schwedhelm, E.; et al. Decreased serum concentrations of sphingosine-1-phosphate in sepsis. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xie, S.; Chi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Xia, D.; Ke, Y.; et al. Bile Acids Control Inflammation and Metabolic Disorder through Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome. Immunity 2016, 45, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, N.; Comiskey, S.M.; Dudeja, P.K.; Saksena, S.; Gill, R.K.; Alrefai, W.A. Bile acids as inflammatory mediators and modulators of intestinal permeability. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, V.B. New appreciation for an old pathway: The Lands Cycle moves into new arenas in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederstaetter, L.; Neuditschko, B.; Brunmair, J.; Janker, L.; Bileck, A.; Del Favero, G.; Gerner, C. Eicosanoid Content in Fetal Calf Serum Accounts for Reproducibility Challenges in Cell Culture. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Ramesh, T.; Toh, X.R.; Nguyen, L.N. Emerging roles of lysophospholipids in health and disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 2020, 80, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, R.C.; Duff, R.; Lawrence, P.; Kakinami, L.; Brenna, J.T.; Shearer, G.C.; Meednu, N.; Mousa, S.; Friedman, A.; Harris, W.S.; et al. The effects of EPA, DHA, and aspirin ingestion on plasma lysophospholipids and autotaxin. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2010, 82, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagace, T.A.; Ridgway, N.D. The role of phospholipids in the biological activity and structure of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouilloz, A.; Bourgeois, T.; Diedisheim, M.; Pilot, T.; Jalil, A.; Le Guern, N.; Bergas, V.; Rohmer, N.; Castelli, F.; Leleu, D.; et al. Impaired unsaturated fatty acid elongation alters mitochondrial function and accelerates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis progression. Metabolism 2025, 162, 156051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz-Santos, R.; Lucieri-Costa, G.; de Almeida, M.A.P.; Moraes-de-Souza, I.; Brito, M.; Silva, A.R.; Goncalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F. Lipid oxidation dysregulation: An emerging player in the pathophysiology of sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1224335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, P.N.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Vrabas, I.S.; Kyparos, A.; D’Alessandro, A.; Nikolaidis, M.G. Erythrocyte metabolism. Acta Physiol. 2024, 240, e14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaginuma, S.; Omi, J.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Lysophospholipids and their producing enzymes: Their pathological roles and potential as pathological biomarkers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 246, 108415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, R.R. The prowess of platelets in immunity and inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukijan, F.; Chandrakanthan, M.; Nguyen, L.N. The signalling roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate derived from red blood cells and platelets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3741–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, C.; Peng, Z.; Brown, B.C.; Reisz, J.A.; Xu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Song, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bogdanov, M.V.; et al. Erythrocyte Metabolic Reprogramming by Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapies. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Song, A.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Adebiyi, M.; Huang, A.; Wen, Y.E.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes erythrocyte glycolysis and oxygen release for adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Amati, A.L.; Padberg, W.; Grau, V. Negative regulation of ATP-induced inflammasome activation and cytokine secretion by acute-phase proteins: A mini review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 981276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, S. Serum amyloid protein A in inflammatory bowel disease: From bench to bedside. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppedisano, F.; Macri, R.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Bosco, F.; Nucera, S.; Caterina Zito, M.; Guarnieri, L.; et al. The Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of n-3 PUFAs: Their Role in Cardiovascular Protection. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, O.; Ganguly, D. Endocannabinoids in immune regulation and immunopathologies. Immunology 2021, 164, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Huang, S.; Ren, C.; Zhao, L. Taurocholic Acid and Glycocholic Acid Inhibit Inflammation and Activate Farnesoid X Receptor Expression in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish and Macrophages. Molecules 2023, 28, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihlan, M.; Glaser, K.M.; Epple, M.W.; Lammermann, T. Neutrophils: Amoeboid Migration and Swarming Dynamics in Tissues. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 871789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.A.; Peskar, B.A.; Sinzinger, H. Defects in the prostaglandin system—What is known? Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 71, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biringer, R.G. The enzymology of human eicosanoid pathways: The lipoxygenase branches. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7189–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgi, C.A.; Peti, A.P.F.; Petta, T.; Meirelles, A.F.G.; Fontanari, C.; Moraes, L.A.B.; Faccioli, L.H. Comprehensive high-resolution multiple-reaction monitoring mass spectrometry for targeted eicosanoid assays. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, S.; Suzuki, K.; Castell, L. A Short Overview of Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in Response to Physical Activity and Antioxidant Supplementation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Konkel, A.; Mehling, H.; Blossey, K.; Gapelyuk, A.; Wessel, N.; von Schacky, C.; Dechend, R.; Muller, D.N.; Rothe, M.; et al. Dietary omega-3 fatty acids modulate the eicosanoid profile in man primarily via the CYP-epoxygenase pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppe, A.E.F.; Edelmann, M.J. Roles of Eicosanoids in Regulating Inflammation and Neutrophil Migration as an Innate Host Response to Bacterial Infections. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0009521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagn, G.; Bileck, A.; Mohr, T.; Schmidl, D.; Baron, D.M.; Jilma, B.; Schmetterer, L.; Garhöfer, G.; Gerner, C. Time Course of Plasma Proteomic and Oxylipin Changes Induced by LPS Challenge and Modulated by Antioxidant Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050536
Hagn G, Bileck A, Mohr T, Schmidl D, Baron DM, Jilma B, Schmetterer L, Garhöfer G, Gerner C. Time Course of Plasma Proteomic and Oxylipin Changes Induced by LPS Challenge and Modulated by Antioxidant Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagn, Gerhard, Andrea Bileck, Thomas Mohr, Doreen Schmidl, David M. Baron, Bernd Jilma, Leopold Schmetterer, Gerhard Garhöfer, and Christopher Gerner. 2025. "Time Course of Plasma Proteomic and Oxylipin Changes Induced by LPS Challenge and Modulated by Antioxidant Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050536
APA StyleHagn, G., Bileck, A., Mohr, T., Schmidl, D., Baron, D. M., Jilma, B., Schmetterer, L., Garhöfer, G., & Gerner, C. (2025). Time Course of Plasma Proteomic and Oxylipin Changes Induced by LPS Challenge and Modulated by Antioxidant Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants, 14(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050536









