Dichloromethane Extract from Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Sm. Seeds and Its Coumarin Reduce ROS Production and Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Extracts of A. cearensis Seeds (EDAC)
2.2. PC12 Cell Culture
2.3. Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Treatment with EDAC and Isolated Coumarin
2.4. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation (OGD) and Treatment with EDAC and Isolated Coumarin
2.5. Cell Viability by Propidium Iodide (PI)
2.6. Cell Viability by MTT
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Quantitative Assay of Reactive Oxygen Species
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
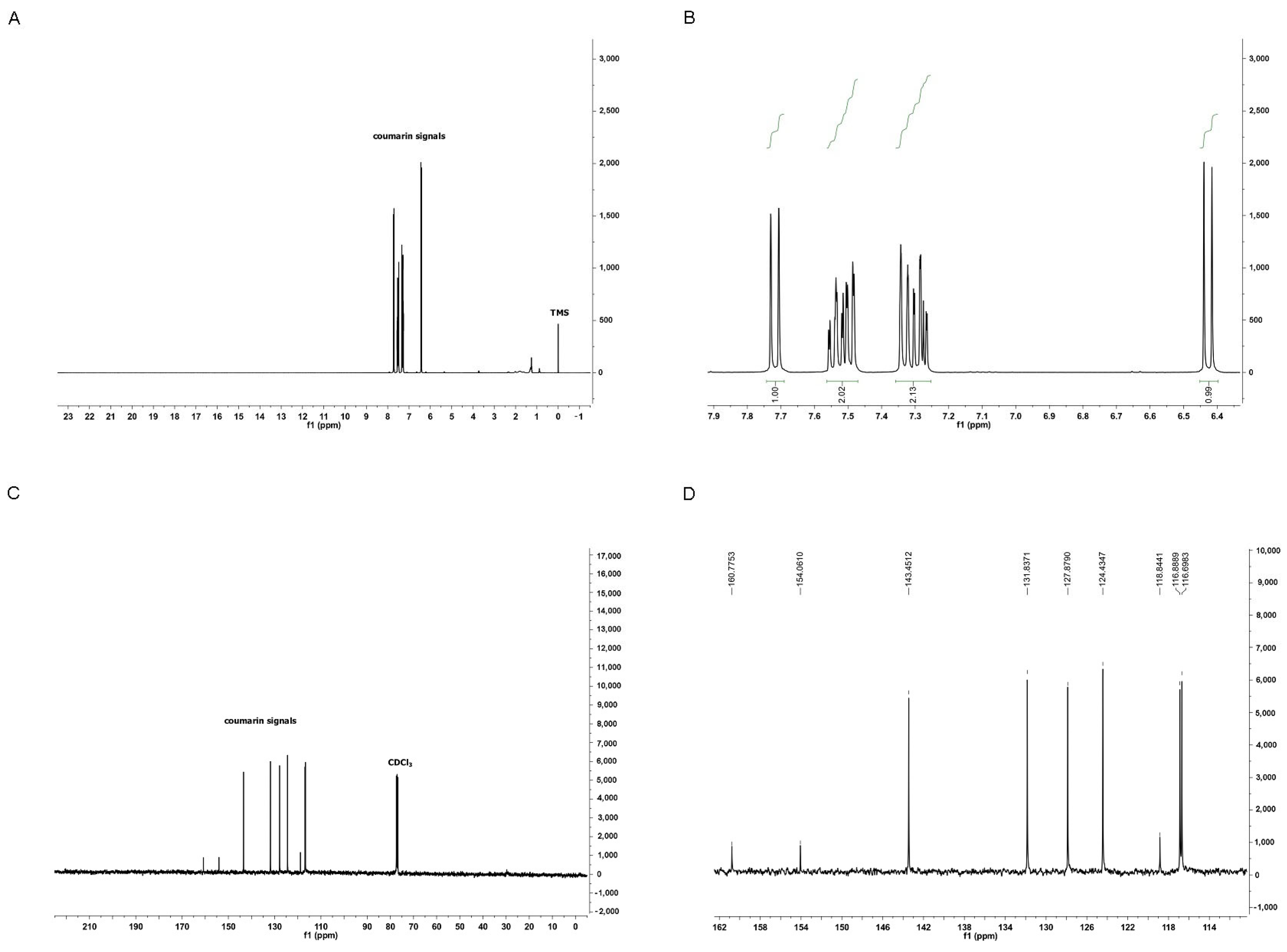
3.1. Characterization of Coumarin
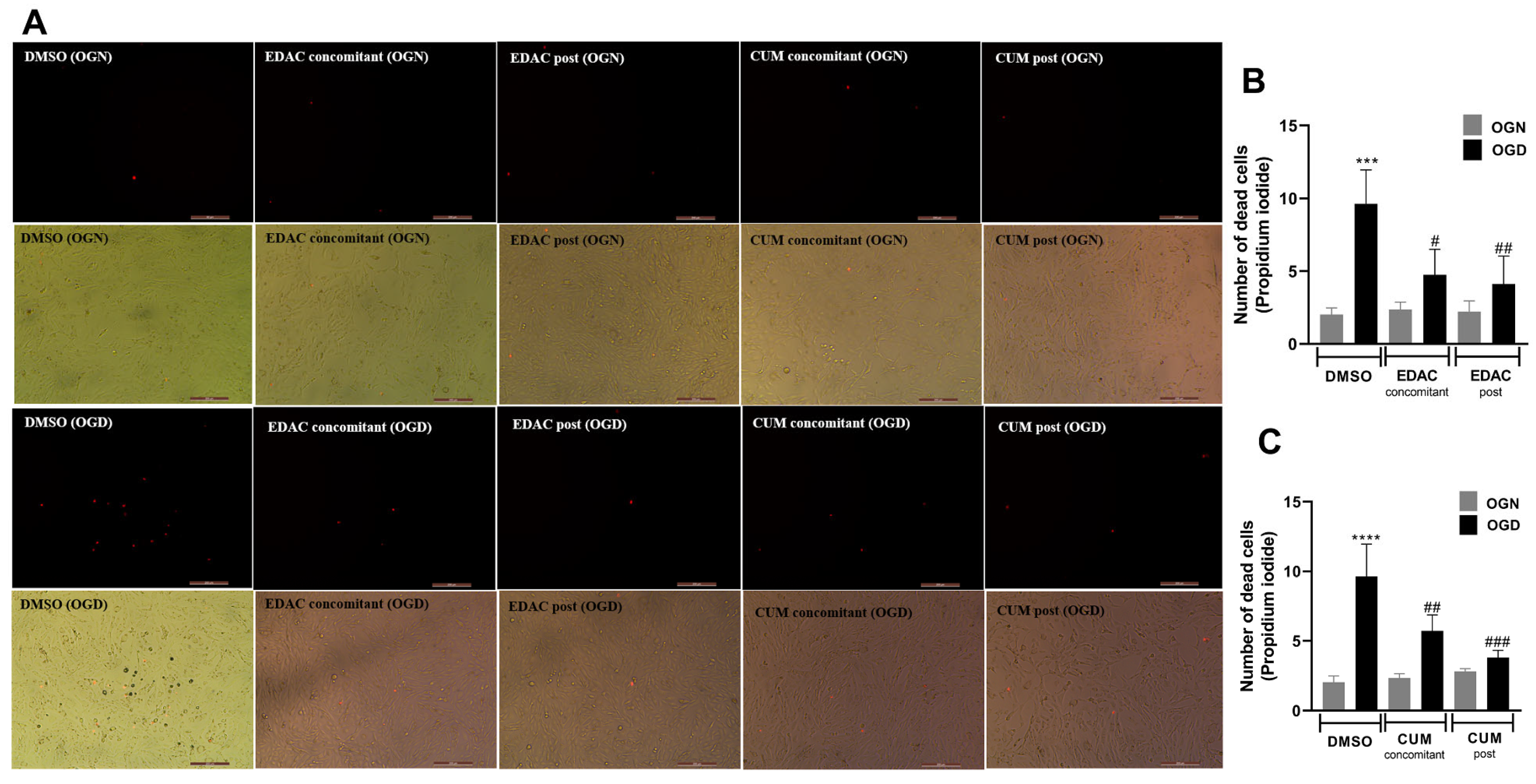
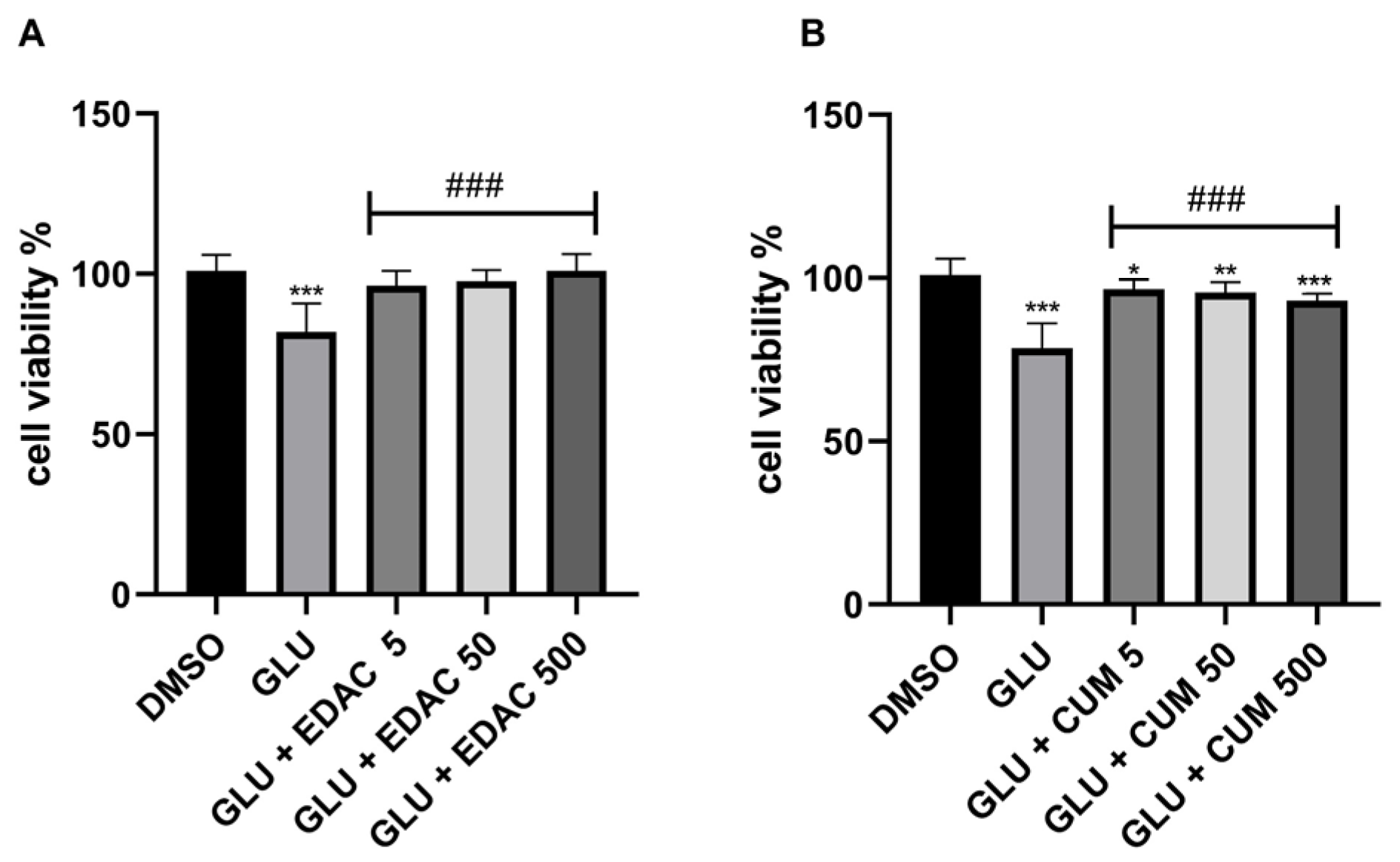
3.2. EDAC and Coumarin Protect PC12 Cells Against Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation (OGD)
3.3. EDAC and Coumarin Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity
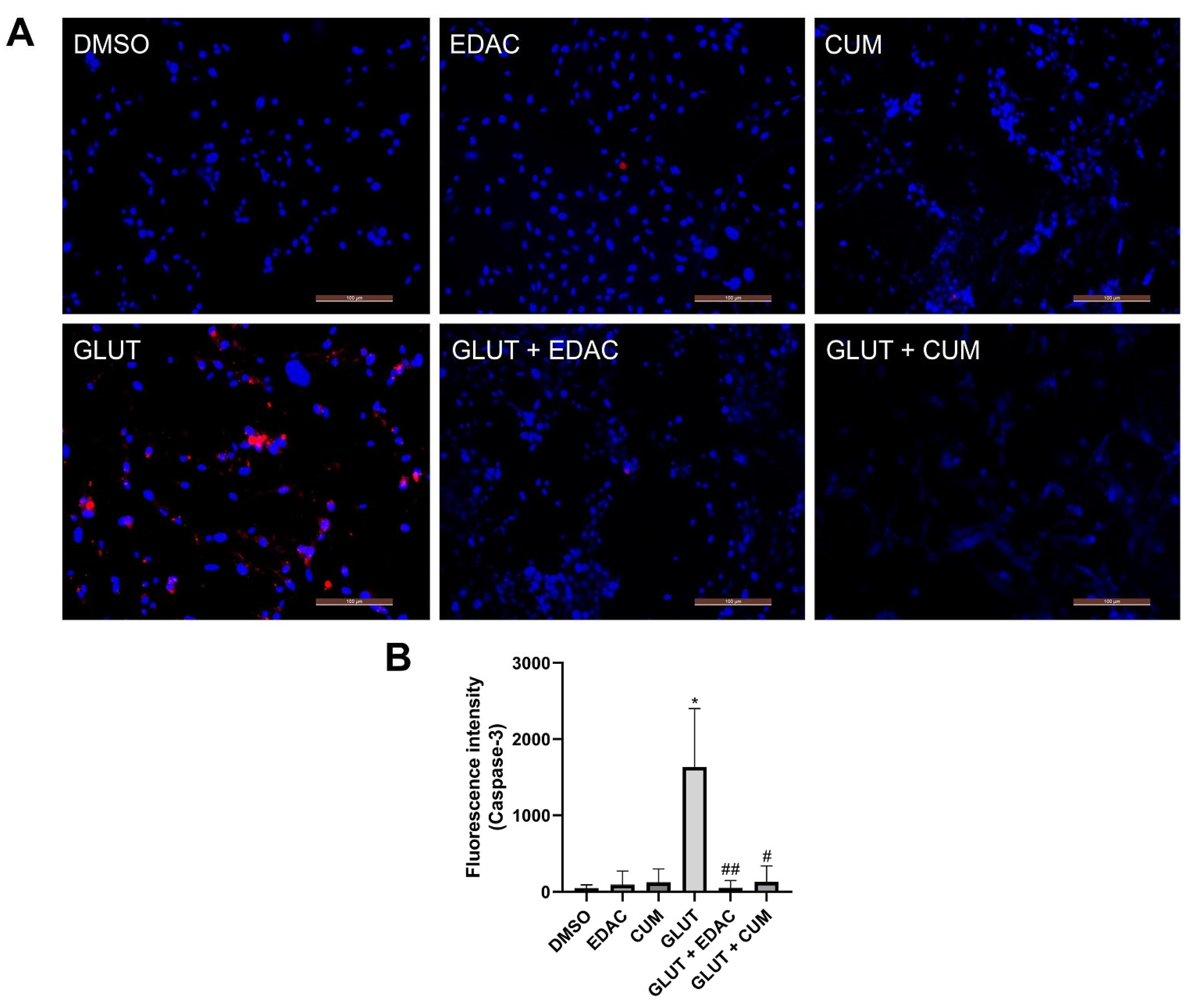
3.4. EDAC and Coumarin Prevent Cysteinyl Aspartate Specific Proteinase-3 (Caspase-3) Activation in PC12 Cells Induced by Glutamate Excitotoxicity
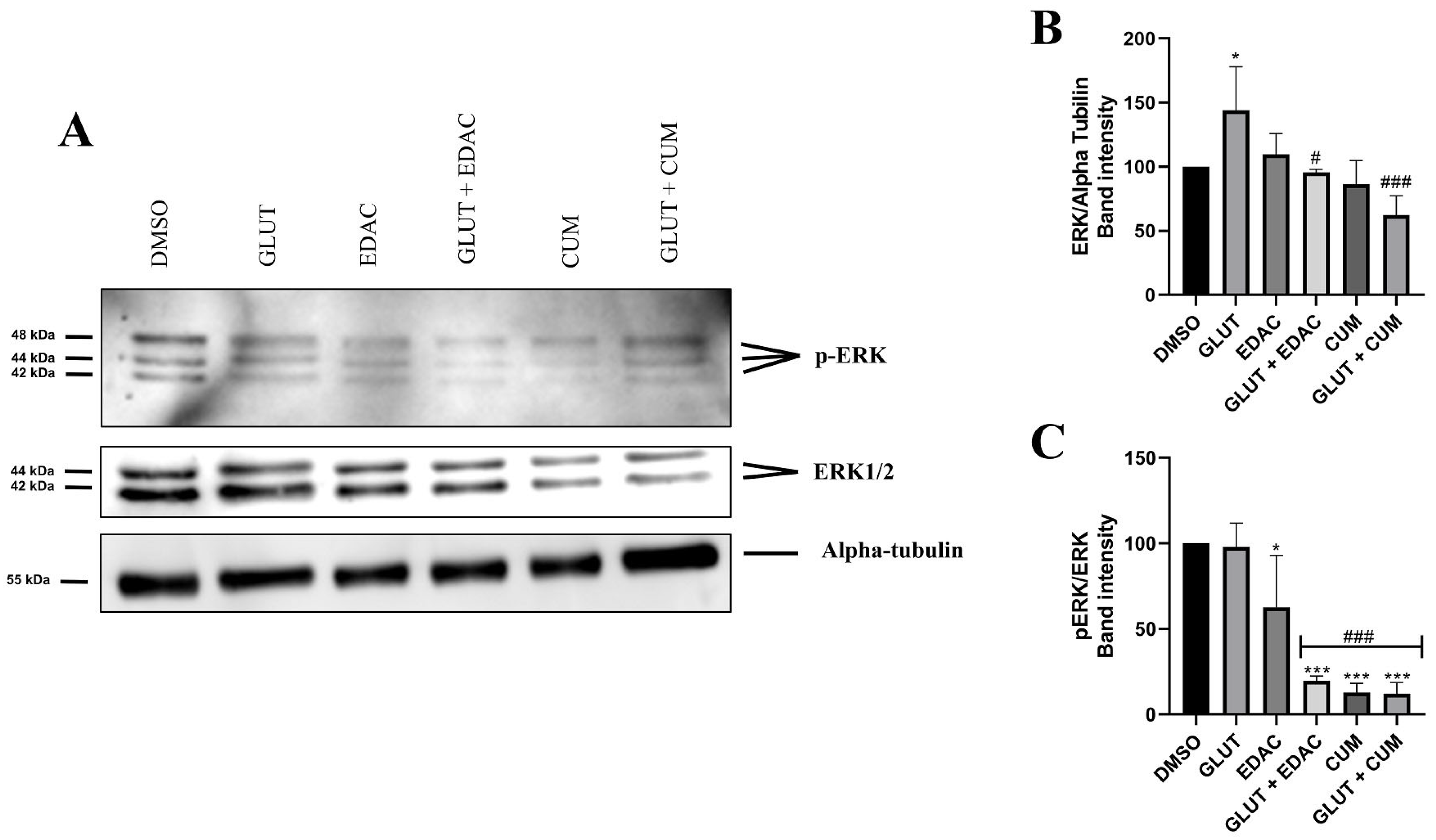
3.5. EDAC and Coumarin Reduced the Expression of ERK and p-ERK in PC12 Cells
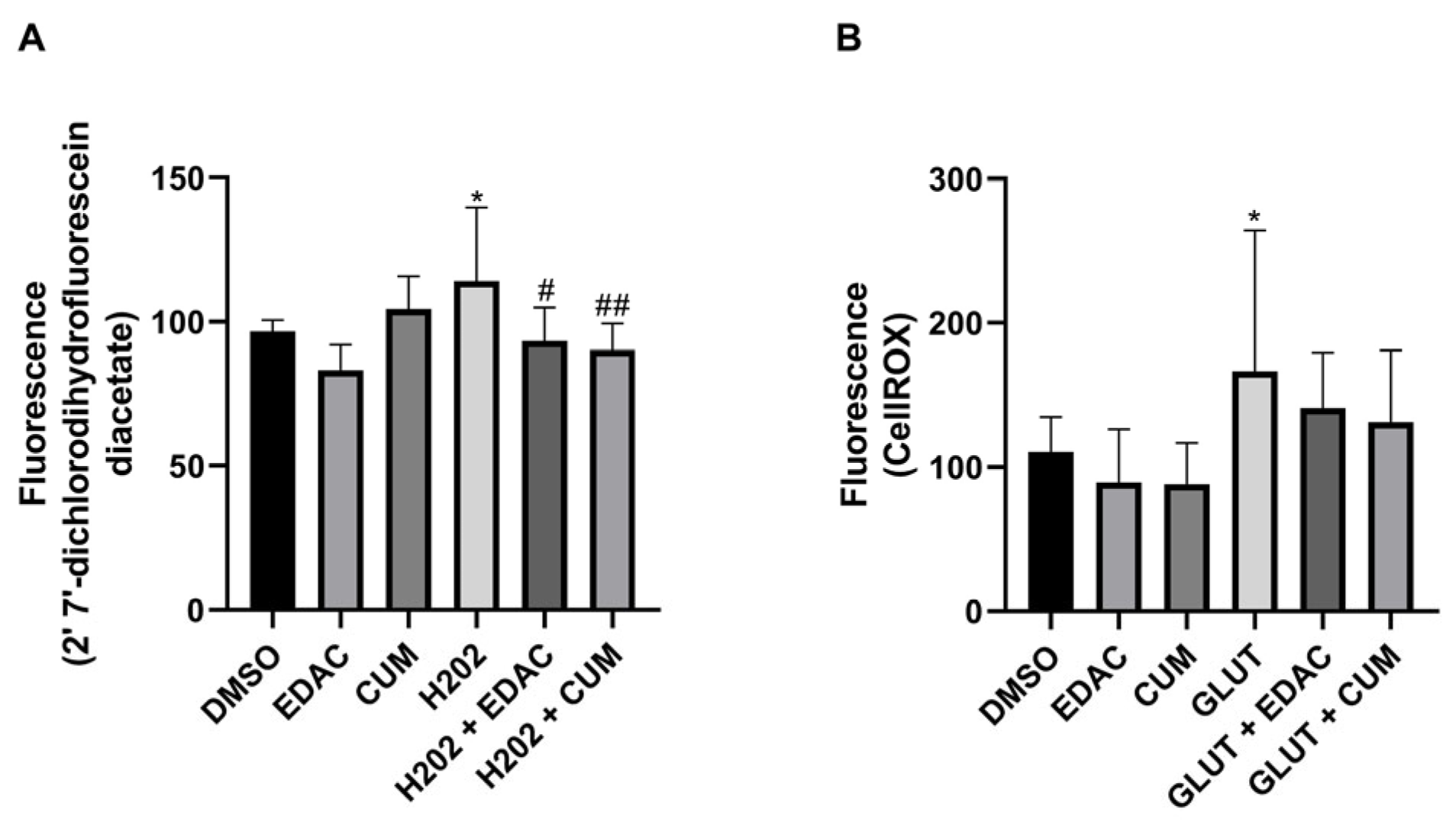
3.6. EDAC and Coumarin Decrease the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in PC12 Cells Treated with Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) or Glutamate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, S.L.; Silva, V.D.A.; dos Santos Souza, C.; Santos, C.C.; Paris, I.; Muñoz, P.; Segura-Aguilar, J. Impact of Plant-Derived Flavonoids on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, L.M.G.; Carreira, R.B.; de Oliveira, J.V.R.; do Nascimento, R.P.; dos Santos Souza, C.; Trias, E.; da Silva, V.D.A.; Costa, S.L. Impact of Plant-Derived Compounds on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurotox. Res. 2023, 41, 288–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.-P.; Wan, Q. Therapeutic Targets of Neuroprotection and Neurorestoration in Ischemic Stroke: Applications for Natural Compounds from Medicinal Herbs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; De Silva, D.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Coutts, S.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Ischaemic Stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekker, M.S.; Boot, E.M.; Singhal, A.B.; Tan, K.S.; Debette, S.; Tuladhar, A.M.; de Leeuw, F.E. Epidemiology, Aetiology, and Management of Ischaemic Stroke in Young Adults. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Y.; Huang, B.Y.; Nie, H.F.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, T.; Cheng, S.W.; Mei, Z.G.; Ge, J.W. The Interplay Between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Ferroptosis During Ischemia-Associated Central Nervous System Diseases. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, D.; Salazar, I.L.; Almeida, R.D.; Silva, R.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Ischemia and Glutamate Excitotoxicity. Life Sci. 2023, 328, 121814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekerdag, E.; Solaroglu, I.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y. Cell Death Mechanisms in Stroke and Novel Molecular and Cellular Treatment Options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1396–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Sarmah, D.; Mounica, L.; Kaur, H.; Kesharwani, R.; Verma, G.; Veeresh, P.; Kotian, V.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; et al. Cell Death Pathways in Ischemic Stroke and Targeted Pharmacotherapy. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolugbo, P.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Thrombus Composition and Efficacy of Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2021, 52, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, R.B.; dos Santos, C.C.; de Oliveira, J.V.R.; da Silva, V.D.A.; David, J.M.; Butt, A.M.; Costa, S.L. Neuroprotective Effect of Flavonoid Agathisflavone in the Ex Vivo Cerebellar Slice Neonatal Ischemia. Molecules 2024, 29, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, A.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yan, W.; Pan, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Cao, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Natural Compounds Modulate the Autophagy with Potential Implication of Stroke. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yao, M.; Qi, J.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Chang, D.; Huang, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Puerarin Inhibited Oxidative Stress and Alleviated Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1134380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, M.; Li, L.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X.; Jing, W.; Nie, S. Aloe-Emodin Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Microglial Polarization and Pyroptosis Through Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, T.-A.; Zhang, W.Y.; Huang, S.R.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J. Rhein Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of Ferroptosis through NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 369, 114541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, A.B.; Azul, F.V.C.S.; Silva, F.R.M.; De Almeida, T.S.; Oliveira, J.V.N.; Pimenta, A.T.Á.; Bezerra, A.M.E.; Machado, N.J.; Leal, L.K.A.M. Antineuroinflammatory Effect of Amburana cearensis and Its Molecules Coumarin and Amburoside A by Inhibiting the MAPK Signaling Pathway in LPS-Activated BV-2 Microglial Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6304087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.P.L.; Braga-de-Souza, S.; Santos, C.C.; Santos, L.O.; Cerqueira, M.D.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Fernandez, L.G.; Silva, V.D.A.; Costa, S.L. Amburana cearensis Seed Extracts Protect PC-12 Cells against Toxicity Induced by Glutamate. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.S.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Silva, J.H.C.E.; Hoppe, J.B.; de Almeida, M.M.A.; de Lima Ferreira, B.C.; Andrade, G.B.; de Souza, S.B.; Ferdandez, L.G.; de Fátima Dias Costa, M.; et al. Amburana cearensis Seed Extract Stimulates Astrocyte Glutamate Homeostatic Mechanisms in Hippocampal Brain Slices and Protects Oligodendrocytes Against Ischemia. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.K.A.M.; Nobre Junior, H.V.; Cunha, G.M.A.; Moraes, M.O.; Pessoa, C.; Oliveira, R.A.; Silveira, E.R.; Canuto, K.M.; Viana, G.S.B. Amburoside A, a Glucoside from Amburanacearensis, Protects Mesencephalic Cells against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 388, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Macedo, J.G.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Alves Ribeiro, D.; de Oliveira Santos, M.; Gonçalves de Mâcedo, D.; Ferreira Macêdo, M.J.; Vilar de Almeida, B.; Souza de Oliveira, L.G.; Pereira Leite, C.; de Almeida Souza, M.M. Analysis of the Variability of Therapeutic Indications of Medicinal Species in the Northeast of Brazil: Comparative Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 6769193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.H.; Ferreira, R.S.; Pereira, E.P.; Braga-de-Souza, S.; Almeida, M.M.; Santos, C.C.; Butt, A.M.; Caiazzo, E.; Capasso, R.; Silva, V.D.; et al. Amburana cearensis: Pharmacological and Neuroprotective Effects of Its Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.P.L.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Loureiro, M.B.; Castro, R.D.; Fernandez, L.G. Effect of water restriction on total phenolics and antioxidant properties of Amburana cearensis (Fr. Allem) A.C. Smith cotyledons during seed imbibition. Acta Physiol. Plant 2014, 36, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Pereira, E.P.; Santos Souza, C.; Amparo, J.; Short Ferreira, R.; Nuñez-Figueredo, Y.; Gonzaga Fernandez, L.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Braga-de-Souza, S.; Amaral da Silva, V.D.; Lima Costa, S. Amburana cearensis seed extract protects brain mitochondria from oxidative stress and cerebellar cells from excitotoxicity induced by glutamate. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 14, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.T.A.; de Alencar, M.V.O.B.; de Paulo Dos Anjos Landim, V.; Moura, G.M.M.; da Cruz, J.I.O.; Dos Santos, E.A.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Andrade, J.C.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Ribeiro, P.R.V.; et al. UPLC-MS-QTOF analysis and antifungal activity of Cumaru (Amburana cearensis). 3 Biotech 2020, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, B.B.; Barberino, R.S.; Menezes, V.G.; Monte, A.P.O.; Silva, R.L.S.; Palheta, R.C., Jr.; Rolim, L.A.; Pereira, E.C.V.; Oliveira, R.G., Jr.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; et al. Amburana cearensis leaf extract protects against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage through regulation of p-PTEN and p-Akt proteins in mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 6, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veras, B.O.; Moura, G.M.M.; Barros, A.V.; Vanusa da Silva, M.; Assis, P.A.C.; Aguiar, J.C.R.O.F.; Navarro, D.M.D.A.F.; Ximenes, R.M.; Wanderley, A.G.; Oliveira, M.B.M. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of essential oil of the leaves of Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Smith. from the semi-arid region of Northeastern Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrak, B.; Kubis-Kubiak, A.; Piwowar, A.; Barg, E. PC12 Cell Line: Cell Types, Coating of Culture Vessels, Differentiation and Other Culture Conditions. Cells 2020, 9, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Vanzulli, I.; Papanikolaou, M.; De La Rocha, I.C.; Hawkins, V.E. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Protect Oligodendrocytes from Acute Ischemia in the Mouse Optic Nerve. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 9, 2468–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 1, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. HMDB: A Knowledgebase for the Human Metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chopp, M. Astrocytes, Therapeutic Targets for Neuroprotection and Neurorestoration in Ischemic Stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 144, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Zhou, R.; Qi, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; Yu, J. Protective Effects of Aloin on Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation-Induced Injury in PC12 Cells; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 0086951408. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.H.C.; Lee, M.H.H.; Wu, C.Y.C.; Couto e Silva, A.; Possoit, H.E.; Hsieh, T.H.; Minagar, A.; Lin, H.W. Cerebral Ischemia and Neuroregeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xie, X.; Xing, X.; Sun, X. Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Ischemic Stroke: A New Outlet for Classical Neuroprotective Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.H.C.; Couto e Silva, A.; Possoit, H.L.E.; Lerner, F.M.; Chen, P.Y.; Azizbayeva, R.; Citadin, C.T.; Wu, C.Y.C.; Neumann, J.T.; Lin, H.W. Palmitic Acid Methyl Ester Is a Novel Neuroprotective Agent Against Cardiac Arrest. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019, 147, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, J.D.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Gallego, R.; Fagundes, M.B.; Valdés, A.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibañez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Neuroprotective Potential of Terpenoid-Rich Extracts from Orange Juice by-Products Obtained by Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Fan, J.T.; Gu, X.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Han, J.; Du, S.H.; Zhang, A.X. Neuroprotective Activity of Cerebrosides from Typhonium giganteum by Regulating Caspase-3 and Bax/Bcl-2 Signaling Pathways in PC12 Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yao, W. Salidroside Inhibits H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in PC 12 Cells by Preventing Cytochrome c Release and Inactivating of Caspase Cascade. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Shrestha, R.M.; Yadav, P.N. Anticancer Mechanism of Coumarin-Based Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 267, 116179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-H.; Li, S.H.; Li, H.Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J.X. Osthole Protects Bone Marrow-Derived Neural Stem Cells from Oxidative Damage Through PI3K/Akt-1 Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sui, S.; Huang, J.; Bai, J.P.; Ren, T.S.; Zhao, Q.C. Neuroprotective Effects of Arctium lappa L. Roots Against Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Stress by Inhibiting Phosphorylation of P38, JNK and ERK 1/2 MAPKs in PC12 Cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; He, W.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, X.; Gao, N.; Wu, G.; Jin, H.; et al. Astragaloside IV Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells through Raf-MEK-ERK Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.M.; Oliveira, C.R. Glutamate toxicity on a PC12 cell line involves glutathione (GSH) depletion and oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 4, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, E.; Barluzzi, R.; Bocchini, V.; Mazzolla, R.; Bistoni, F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 2–3, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, R.J.; Nutile-McMenemy, N.; Alkaitis, M.S.; Deleo, J.A. Differential migration, LPS-induced cytokine, chemokine, and NO expression in immortalized BV-2 and HAPI cell lines and primary microglial cultures. J. Neurochem. 2008, 2, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 4, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, L.A.; Tischler, A.S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 7, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.A.; Rein, G. Synthesis, storage and release of acetylcholine by a noradrenergic pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature 1977, 5618, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritis, A.A.; Stamoula, E.G.; Paniskaki, K.A.; Vavilis, T.D. Researching glutamate—Induced cytotoxicity in different cell lines: A comparative/collective analysis/study. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.S.; Fanoudi, S.; Hosseini, A.; Jalili-Nik, M.; Bagheri, A.; Sadeghnia, H.R. Everolimus attenuates glutamate-induced PC12 cells death. Int. J. Neurosci. 2023, 4, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pang, B.; Wen, J.; Zhou, T. Predicting a Potential Link to Antidepressant Effect: Neuroprotection of Zhi-zi-chi Decoction on Glutamate-induced Cytotoxicity in PC12 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 625108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljabouri, I.; Rostami, M.; Mirzavi, F.; Kakhki, M.K.; Alalikhan, A.; Gheybi, E.; Hakimi, A.; Soukhtanloo, M. Urolithin B protects PC12 cells against glutamate-induced toxicity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 1, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Li, C.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liao, Y.; Pan, R. Longistyline C acts antidepressant in vivo and neuroprotection in vitro against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity by regulating NMDAR/NR2B-ERK pathway in PC12 cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 9, e0183702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Chen, H.X.; Yü, G.; Peng, C.C.; Peng, R.Y. Curcumin-Protected PC12 Cells Against Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Toxicity. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 4, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | Compounds (Extracts or Isolated Compounds) | Experimental Models | Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pereira et al. [23] |
|
Water restriction: PEG 8000 solution at −1.2 and −1.4 MPa
|
|
| Lima Pereira et al. [18] | Seed extracts of Amburana cearensis:
|
|
|
| Lima Pereira et al. [24] | Seed extracts of Amburana cearensis:
|
|
|
| Oliveira et al. [25] |
|
|
|
| de Araújo et al. [17] |
|
|
|
| Gouveia et al. [26] |
|
Histological analysis Immunohistochemistry Fluorescence analysis Protein immunoexpression evaluation |
|
| Ferreira et al. [19] |
| Hippocampal brain slices from:
|
|
| de Veras et al. [27] |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanches, F.S.; Ramos, F.d.S.; Costa, C.C.d.O.S.; Nascimento, R.P.d.; Souza, B.S.d.F.; Costa, M.d.F.D.; Costa, S.L.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Ferreira, R.S.; Silva, V.D.A.d. Dichloromethane Extract from Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Sm. Seeds and Its Coumarin Reduce ROS Production and Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040440
Sanches FS, Ramos FdS, Costa CCdOS, Nascimento RPd, Souza BSdF, Costa MdFD, Costa SL, Ribeiro PR, Ferreira RS, Silva VDAd. Dichloromethane Extract from Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Sm. Seeds and Its Coumarin Reduce ROS Production and Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(4):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040440
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanches, Flávia Santos, Florisvaldo da Silva Ramos, Cinthia Cristina de O. S. Costa, Ravena Pereira do Nascimento, Bruno Solano de Freitas Souza, Maria de Fátima Dias Costa, Silvia Lima Costa, Paulo R. Ribeiro, Rafael Short Ferreira, and Victor Diogenes Amaral da Silva. 2025. "Dichloromethane Extract from Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Sm. Seeds and Its Coumarin Reduce ROS Production and Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation" Antioxidants 14, no. 4: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040440
APA StyleSanches, F. S., Ramos, F. d. S., Costa, C. C. d. O. S., Nascimento, R. P. d., Souza, B. S. d. F., Costa, M. d. F. D., Costa, S. L., Ribeiro, P. R., Ferreira, R. S., & Silva, V. D. A. d. (2025). Dichloromethane Extract from Amburana cearensis (Allemão) A.C. Sm. Seeds and Its Coumarin Reduce ROS Production and Protect PC12 Cells Against Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation. Antioxidants, 14(4), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040440







