Hyperoside Promotes Mitochondrial Autophagy Through the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Thereby Improving UVB-Induced Photoaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Compounds, Reagents, and Laboratory Instruments
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.4. Functional Assays
2.4.1. Cell Migration Assay
2.4.2. Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.4.3. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase (SA-β-gal) Staining
2.4.4. 5-Ethynyl-2′-Deoxyuridine (EdU) Proliferation Assay
2.4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Detection of ROS and Mitochondrial Superoxide
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
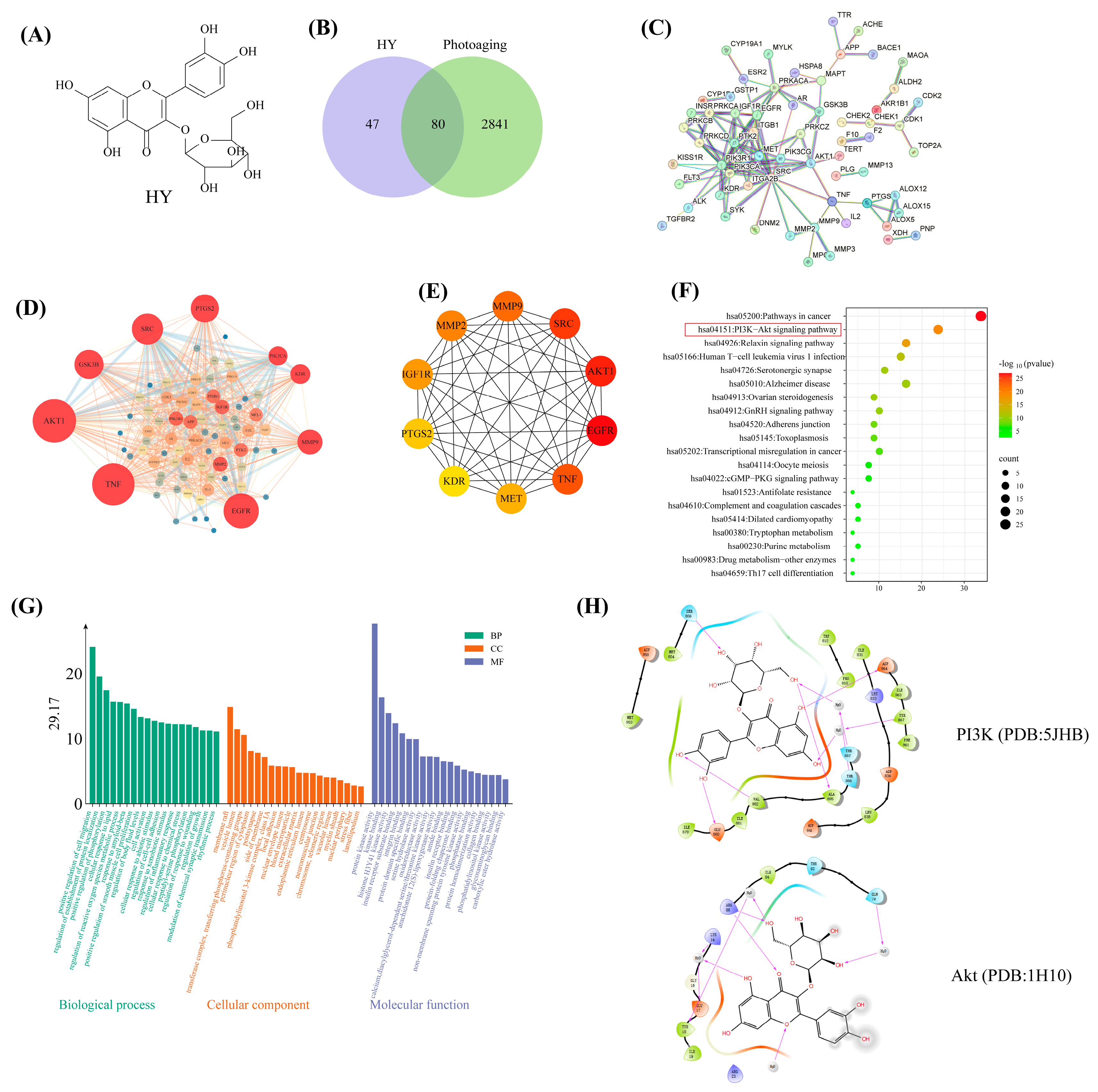
2.10. Network Pharmacology Analysis
2.11. Transfection
2.12. Animal Experiments
2.13. Histopathological Analysis
2.14. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
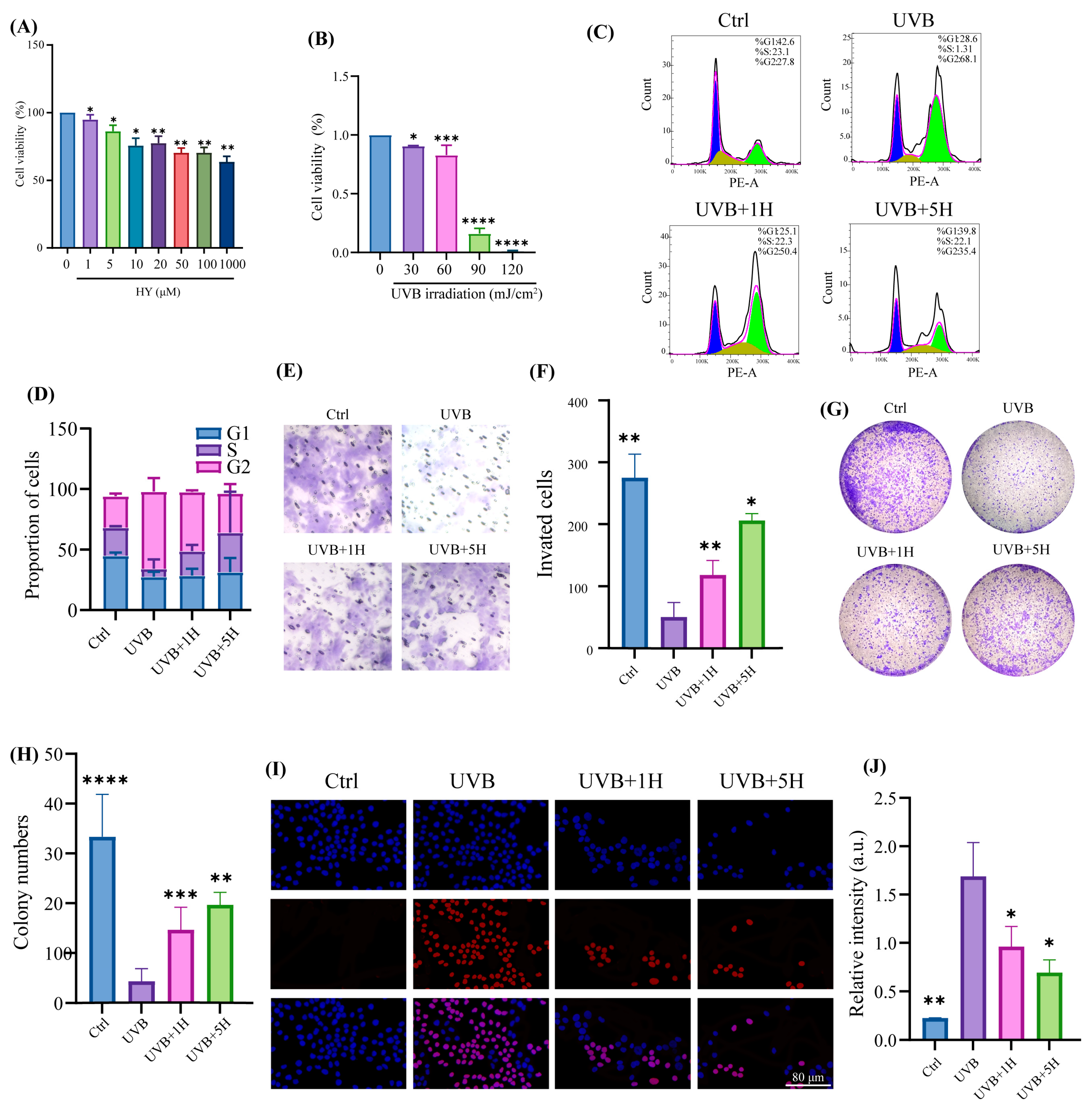
3.1. Protective Effect of HY Against UVB-Induced Skin Damage In Vitro
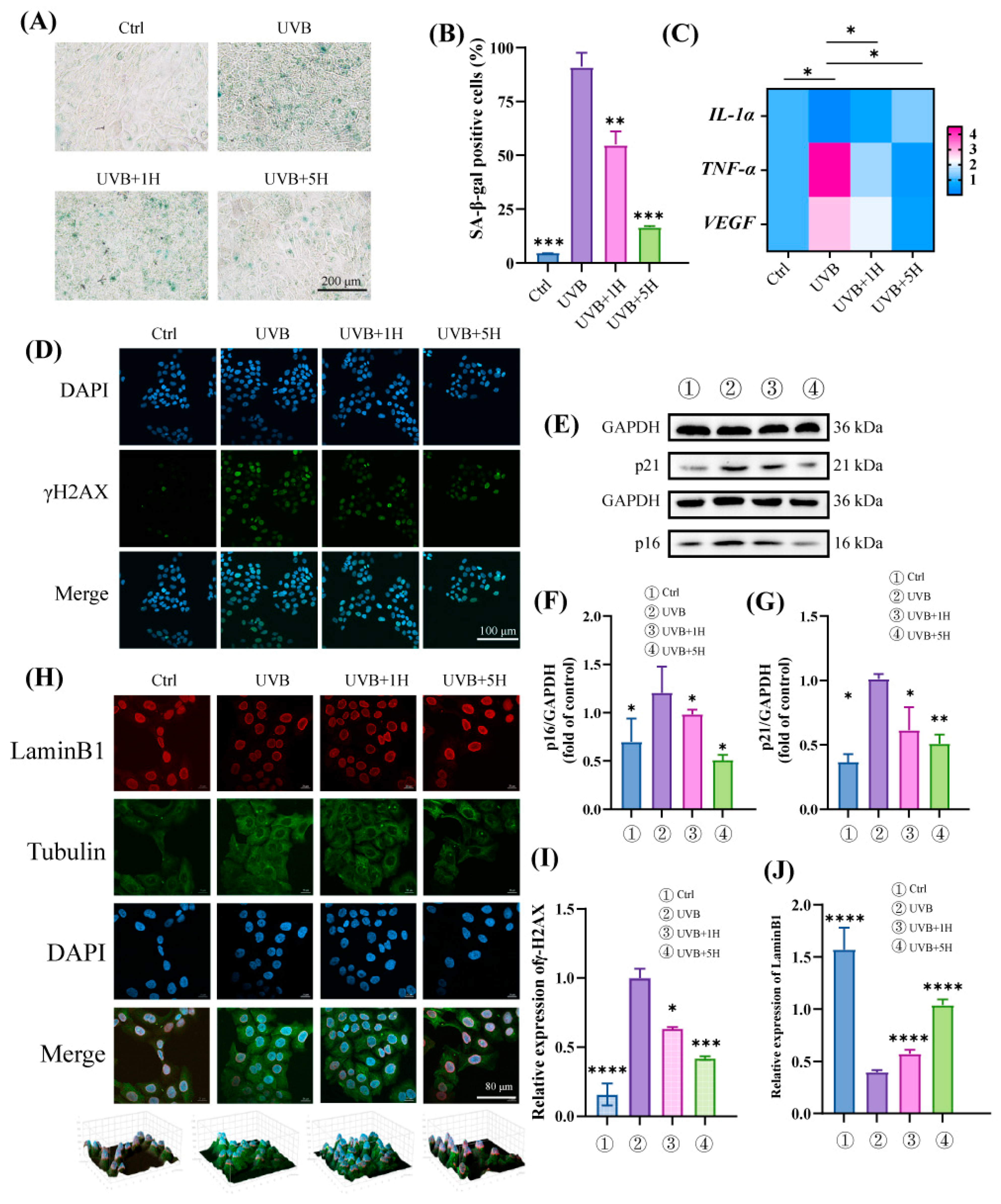
3.2. HY Protects HaCaT from UVB-Induced Cellular Senescence
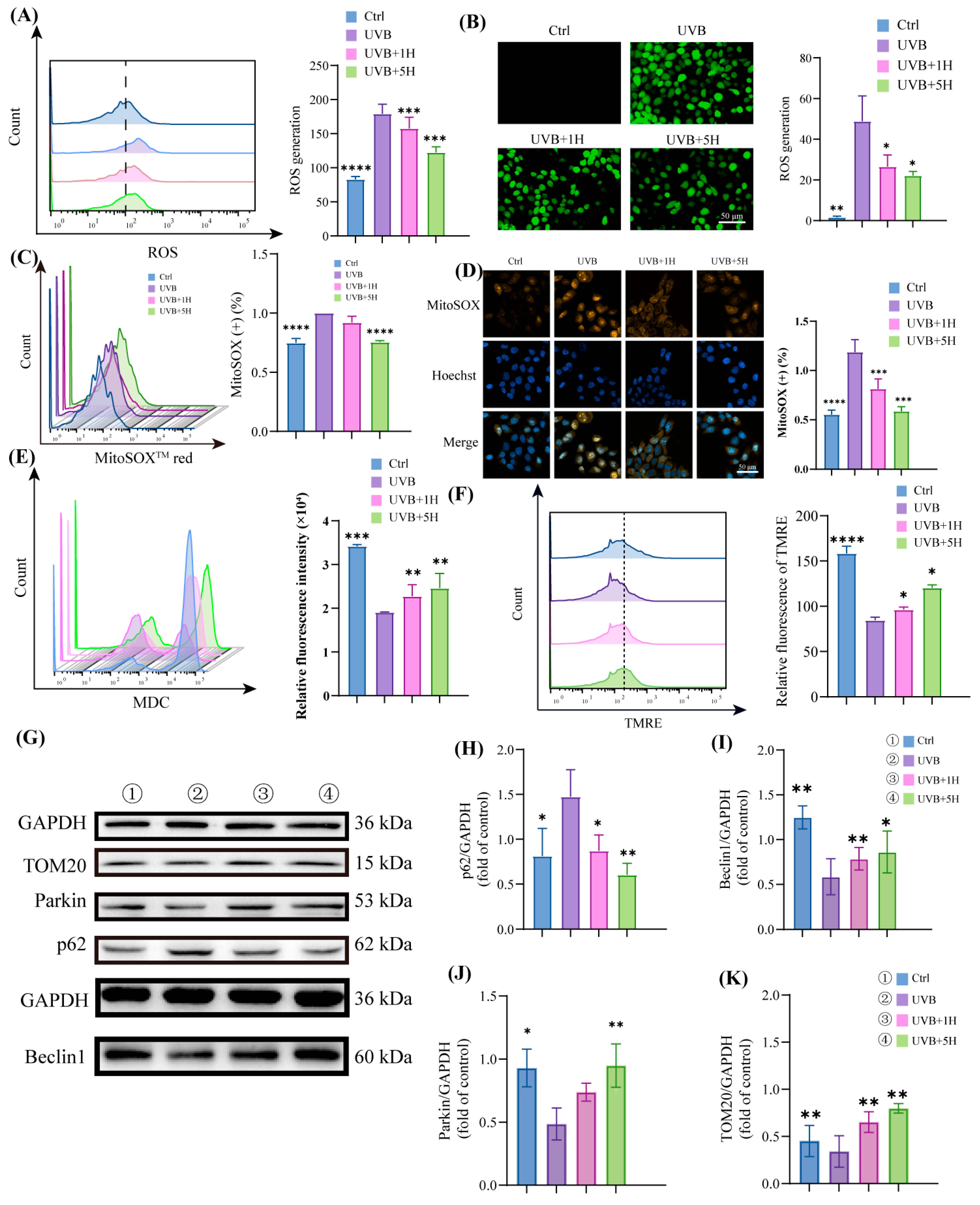
3.3. HY Induce Autophagy and Attenuate Mitochondrial Damage
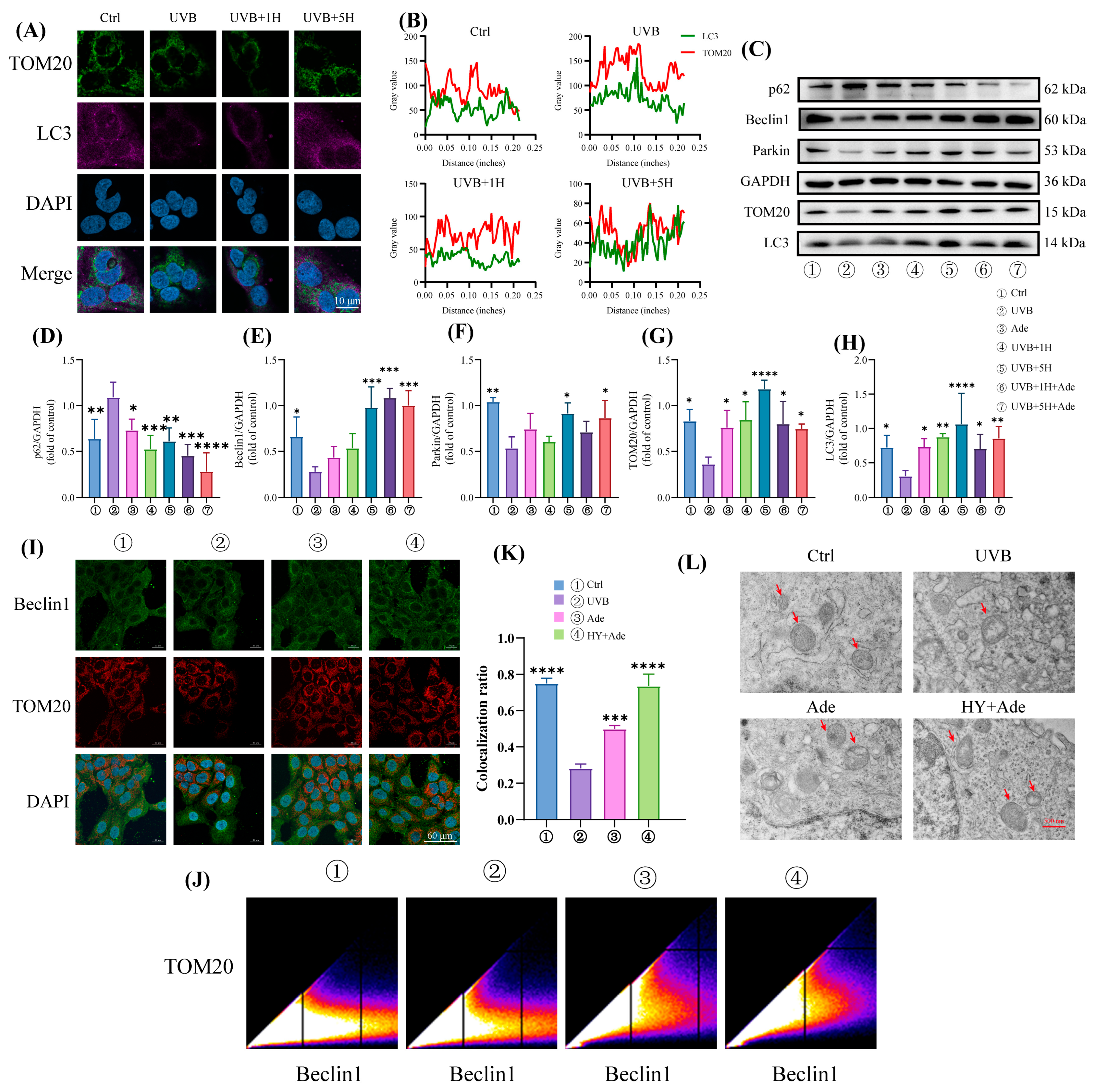
3.4. HY Promotes Mitophagy
3.5. Network Pharmacology Predicts the Molecular Mechanisms of HY in the Prevention of Photoaging
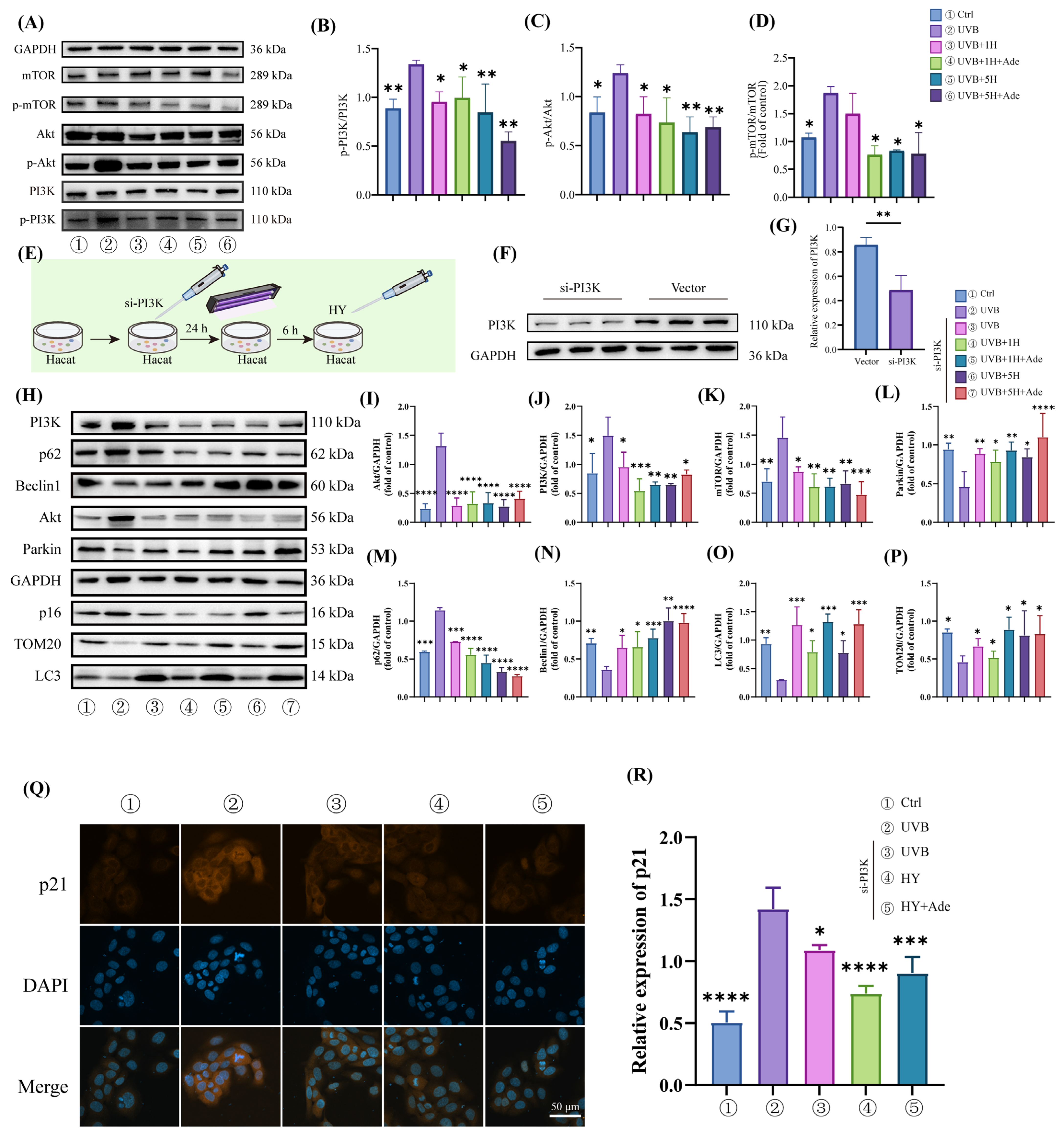
3.6. HY Activates Mitophagy by Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
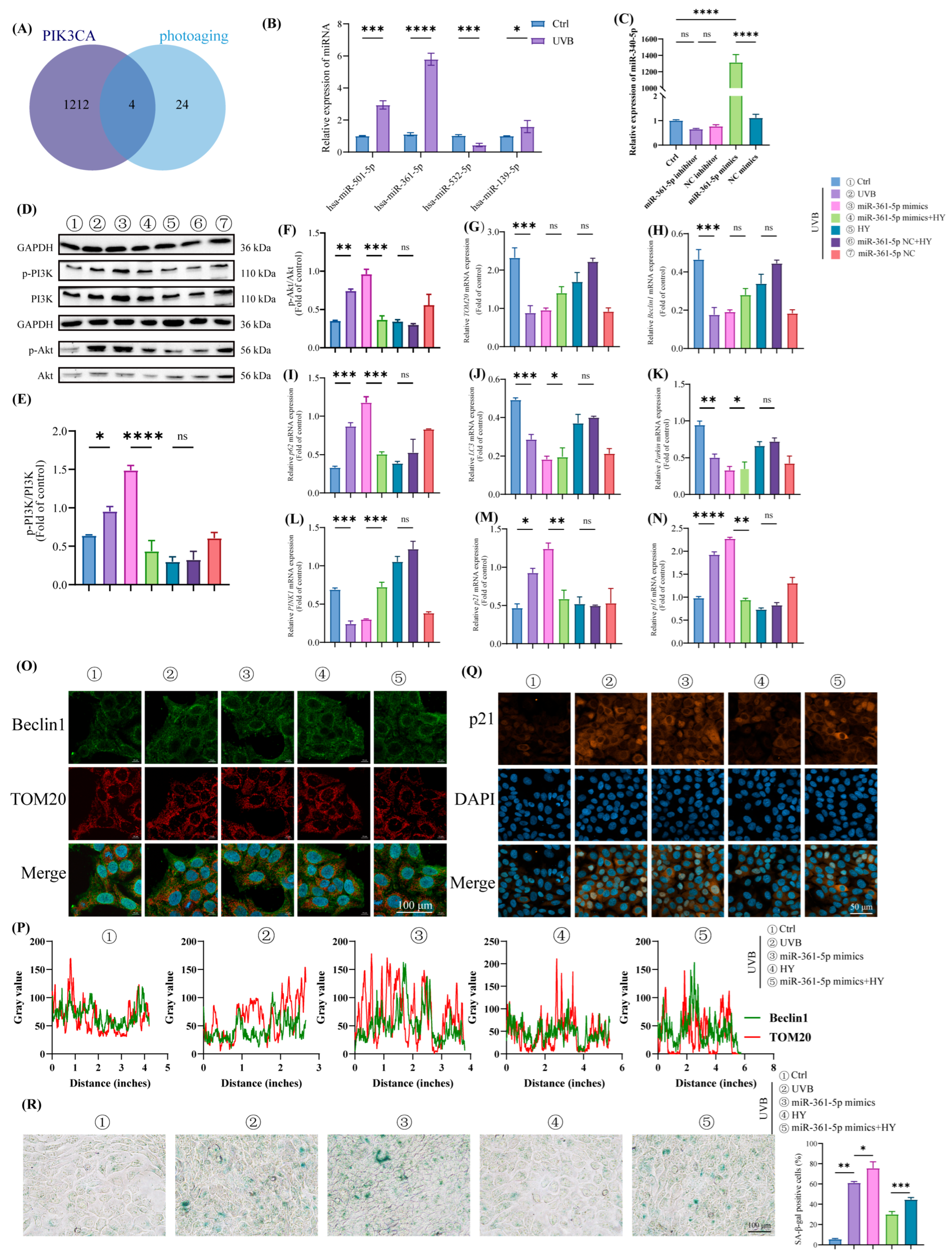
3.7. HY Attenuates Cellular Senescence in HaCaT Cells by Inhibiting the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
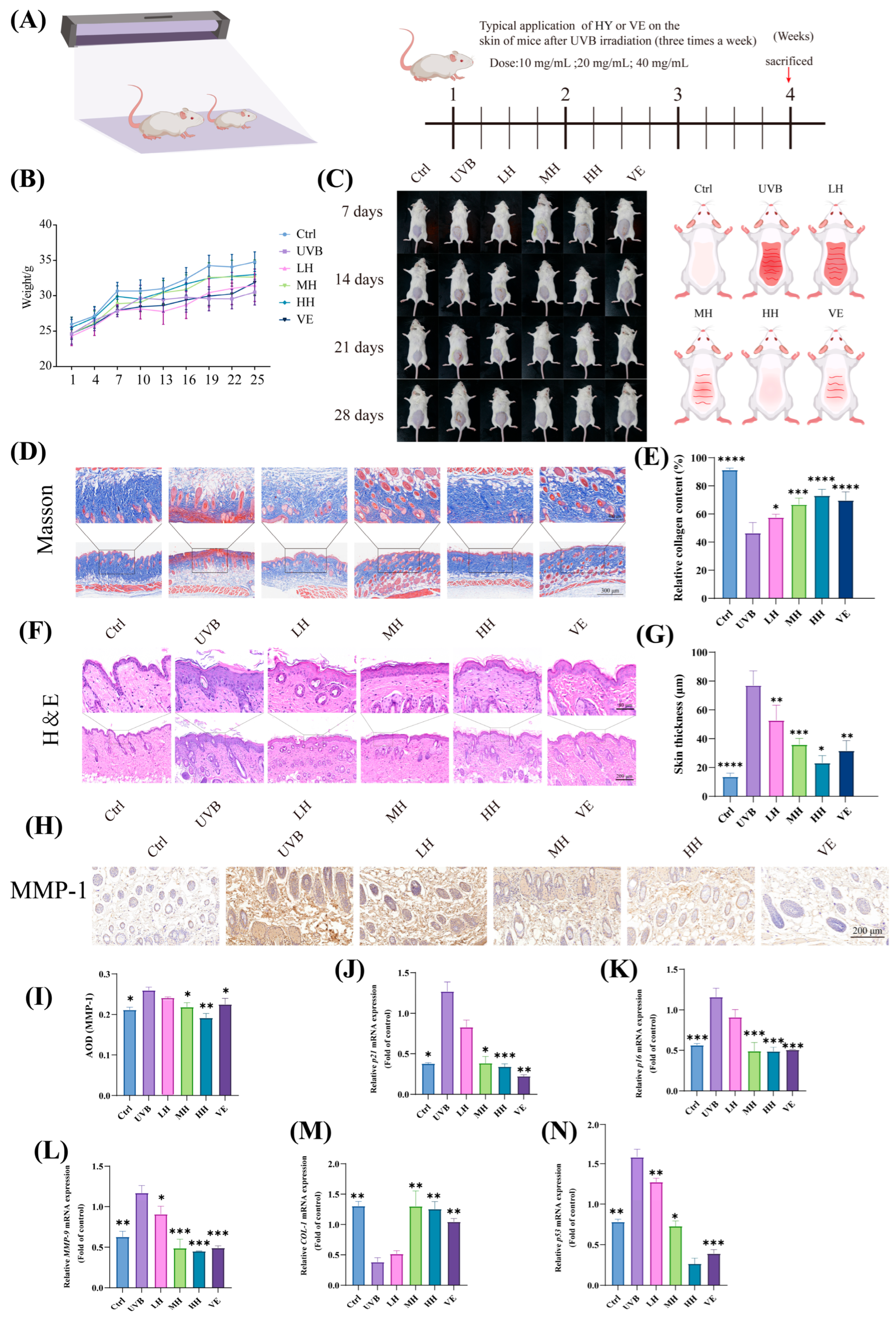
3.8. HY Exhibits Potential in Inhibiting Skin Photoaging and Cellular Damage in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UVB | ultraviolet radiation b |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| UVR | ultraviolet radiation |
| VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| VEGFR | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| FOXM1 | forkhead box protein M1 |
| PI3K | phosphatidyqinositol-3 kinase |
| HY | hyperoside |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| HaCaT | human keratinocytes |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| miR | microRNA |
| MMP-1 | matrix metalloproteinase-1 |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| COL-1 | collagen I |
| IL-1α | interleukin-1α |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| p16 | multiple tumor suppressor 1 |
| p21 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| p53 | tumor protein 53 |
| p62 | sequestosome 1 |
| LC3 | microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 |
| TOM20 | translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 20 |
| γ-H2AX | phosphorylated histone 2AX |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| BCA | bicinchoninic acid |
| MTT | methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide |
| EdU | 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine |
| RT-qPCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate—polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| ICR | Institute of Cancer Research |
| VE | vitamin E |
| ARRIVE | Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments |
| IHC | immunohistochemical |
| DAB | 3,3-N-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride |
| LH | low-dose HY |
| MH | medium-dose HY |
| HH | high-dose HY |
References
- Pellacani, G.; Lim, H.W.; Stockfleth, E.; Sibaud, V.; Brugués, A.O.; Saint Aroman, M. Photoprotection: Current developments and controversies. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38 (Suppl. 5), 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.L.; Lim, H.W.; Mohammad, T.F. Sunscreens and Photoaging: A Review of Current Literature. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xin, Y.; Chen, C.; Luo, J. The extract of buds of Chrysanthemum morifolium ramat alleviated UVB-induced skin photoaging by regulating MAPK and Nrf2/ARE pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 332, 118352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavinato, M.; Martic, I.; Wedel, S.; Pittl, A.; Koziel, R.; Weinmmüllner, R.; Schosserer, M.; Jenewein, B.; Bobbili, M.R.; Arcalis, E.; et al. Elimination of damaged mitochondria during UVB-induced senescence is orchestrated by NIX-dependent mitophagy. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, J.; Suomalainen, A. Mitochondria: In sickness and in health. Cell 2012, 148, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Zang, K.; Gao, X.; Shi, Y.; Ye, X.; Dang, Y. P2RY6 deletion promotes UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis by activating the PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Cancer Sci. 2025, 116, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yan, F.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ren, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Ying, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; et al. Urolithin A protects human dermal fibroblasts from UVA-induced photoaging through NRF2 activation and mitophagy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2022, 232, 112462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ponandai-Srinivasan, S.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Fabre, S.; Xu Landén, N.; Mavon, A.; Khmaladze, I. Targeting microRNA for improved skin health. Health Sci. Rep. 2021, 4, e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, E.; Jeffery, N.; Chambers, D.; Slade, L.; Etheridge, T.; Harries, L.W. An evaluation of the role of miR-361-5p in senescence and systemic ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 174, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitz, A.; Imig, J.; Dziunycz, P.J.; Primorac, A.; Galgano, A.; Hofbauer, G.F.L.; Gerber, A.P.; Detmar, M. The expression levels of microRNA-361-5p and its target VEGFA are inversely correlated in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekan, M.; Haass, N.K.; Rokni, G.R.; Gholizadeh, N.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Kazeminejad, A. VEGF/VEGFR axis and its signaling in melanoma: Current knowledge toward therapeutic targeting agents and future perspectives. Life Sci. 2024, 345, 122563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhu, J. MiR-361-5p suppresses chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells by targeting FOXM1 via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4886–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, M.; Nawaz, J.; Duan, X. Regulatory Mechanisms of Natural Active Ingredients and Compounds on Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Mitigating Skin Photoaging. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1943–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanveer, M.A.; Rashid, H.; Tasduq, S.A. Molecular basis of skin photoaging and therapeutic interventions by plant-derived natural product ingredients: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, P.; Piao, M.J.; Herath, H.; Kang, K.A.; Hyun, C.L.; Kim, E.T.; Koh, Y.S.; Hyun, J.W. Hyperoside reduced particulate matter 2.5-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and senescence in skin cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 99, 105870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Yao, F.; Fang, D.; Chen, L.; Zou, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, T.; Wei, P.; Li, P.; et al. Hyperoside alleviates photoreceptor degeneration by preventing cell senescence through AMPK-ULK1 signaling. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, W.; Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Xie, N.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Hyperoside Protects Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Activating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2025, 39, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.P.; Zheng, Y.F.; Sun, P.; Yao, M.Y.; Xie, L.X.; Dou, X.W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.S. The pro-tumorigenic activity of p38γ overexpression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Ling, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.R.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, M.B.; Yang, S.; et al. The histone acetyltransferase HBO1 functions as a novel oncogenic gene in osteosarcoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4599–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.J.; Wijshake, T.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Childs, B.G.; van de Sluis, B.; Kirkland, J.L.; van Deursen, J.M. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 2011, 479, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; He, J.; Long, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Xu, K.; Cao, Y. Orientin attenuates UVB-induced skin photodamage by inhibiting ROS generation via the AMPK/Nrf2 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 155, 114655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, M.; Bai, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X. Doxercalciferol alleviates UVB-induced HaCaT cell senescence and skin photoaging. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Z. Resveratrol Treats UVB-Induced Photoaging by Anti-MMP Expression, through Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antiapoptotic Properties, and Treats Photoaging by Upregulating VEGF-B Expression. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6037303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basisty, N.; Kale, A.; Jeon, O.H.; Kuehnemann, C.; Payne, T.; Rao, C.; Holtz, A.; Shah, S.; Sharma, V.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. A proteomic atlas of senescence-associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hickson, L.J.; Eirin, A.; Kirkland, J.L.; Lerman, L.O. Cellular senescence: The good, the bad and the unknown. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, L.J.; El-Osta, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. gammaH2AX: A sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia 2010, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.S.; Ong, P.F.; Chojnowski, A.; Clavel, C.; Dreesen, O. Loss of lamin B1 is a biomarker to quantify cellular senescence in photoaged skin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, H. Metformin Attenuates UVA-Induced Skin Photoaging by Suppressing Mitophagy and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.P.; Reddy, H.; Caivano, M.; Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersahin, T.; Tuncbag, N.; Cetin-Atalay, R. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Rao, S.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Cao, J.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, J.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, W.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Xie, H. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics 2018, 8, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Cores, J.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Dinh, P.U.; Cheng, K. Needle-Free Injection of Exosomes Derived from Human Dermal Fibroblast Spheroids Ameliorates Skin Photoaging. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11273–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.H.; Williams, J.; Smith, F.; Bhatti, J.S.; Kumar, S.; Vijayan, M.; Kandimalla, R.; Kuruva, C.S.; Wang, R.; Manczak, M.; et al. MicroRNAs, Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 146, 127–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Jin, X.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Yi, E.J.; Park, S.J.; Yi, G.S.; Yang, S.J.; Yi, T.H. Autophagy-Enhancing Properties of Hedyotis diffusa Extracts in HaCaT Keratinocytes: Potential as an Anti-Photoaging Cosmetic Ingredient. Molecules 2025, 30, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, A.; Chen, I.P.; Henning, S.; Faust, A.; Volkmer, B.; Atkinson, M.J.; Moertl, S.; Greinert, R. UVA and UVB irradiation differentially regulate microRNA expression in human primary keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Ye, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Mu, L. A non-bactericidal cathelicidin with antioxidant properties ameliorates UVB-induced mouse skin photoaging via intracellular ROS scavenging and Keap1/Nrf2 pathway activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 224, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dong, J.; Du, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, P. Collagen study advances for photoaging skin. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2024, 40, e12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, J.; He, L.; Guo, X.; Ye, H.; Yin, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, H. Beneficial Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Preventing Skin Photoaging: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, X.; Xie, X.L.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Yu, F.L. Phytocosmetic potential of Blumea balsamifera oil in mitigating UV-induced photoaging: Evidence from cellular and mouse models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 334, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhai, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, R.; Sun, L. Panax ginseng Meyer cv. Silvatica phenolic acids protect DNA from oxidative damage by activating Nrf2 to protect HFF-1 cells from UVA-induced photoaging. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, K.; Tigges, J.; Sass, S.; Schütze, A.; Florea, A.M.; Fender, A.C.; Theis, F.J.; Krutmann, J.; Boege, F.; Fritsche, E.; et al. miR-23a-3p causes cellular senescence by targeting hyaluronan synthase 2: Possible implication for skin aging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swahari, V.; Nakamura, A.; Hollville, E.; Hung, Y.H.; Kanke, M.; Kurtz, C.L.; Caravia, X.M.; Roiz-Valle, D.; He, S.; Krishnamurthy, J.; et al. miR-29 is an important driver of aging-related phenotypes. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B. Activation of the miR-34a-Mediated SIRT1/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Urolithin A Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging in Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Karlsson, M.; Marionnet, C.; Bernerd, F.; Gueniche, A.; Rawadi, C.E.L.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Breton, L.; Pivarcsi, A. Identification of chronological and photoageing-associated microRNAs in human skin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, W.; Sui, H.; Fu, X. Hyperoside: A Review of Its Structure, Synthesis, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Tang, C.; Gao, M.; Rui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Yan, B.C. Hyperoside alleviates epilepsy-induced neuronal damage by enhancing antioxidant levels and reducing autophagy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, L.; Wen, F.; Guo, G.; Zhang, Z. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide ameliorates skeletal muscle aging and mitochondrial dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Kuo, W.W.; Baskaran, R.; Kuo, C.H.; Chen, Y.A.; Chen, W.S.; Ho, T.J.; Day, C.H.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Huang, C.Y. Swimming exercise stimulates IGF1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α survival signaling to suppress apoptosis and inflammation in aging hippocampus. Aging 2020, 12, 6852–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Fu, L.Q.; Teng, Y.; He, J.J.; Shen, Y.Y.; Bian, Q.; Wang, T.Z.; Wang, M.X.; Pang, X.W.; Lin, Z.W.; et al. Human Hair Follicle Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate UVB-Induced Photoaging via the miR-125b-5p/TGF-β1/Smad Axis. Biomater. Res. 2025, 29, 0121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, D.N.; Khan, M.I.; Shabbir, M.; Mukhtar, H. MicroRNAs in skin response to UV radiation. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Jinnin, M.; Wang, Z.; Hirano, A.; Tomizawa, Y.; Kira, T.; Igata, T.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Ihn, H. The expression of miR-124 increases in aged skin to cause cell senescence and it decreases in squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci. Trends 2017, 10, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| mRNA | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| interleukin-1α (IL-1α) | AGATGCCTGAGATACCCAAAACC | CCAAGCACACCCAGTAGTCT |
| tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) | CCTCTCTCTAATCAGCCCTCTG | GAGGACCTGGGAGTAGATGAG |
| VEGF | GAGATGTCCCTGGAAGAACACA | GAGTGGGATGGGTGATGTCAG |
| glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21) | CCTGTCACTGTCTTGTACCCT | GCGTTTGGAGTGGTAGAAATCT |
| multiple tumor suppressor 1 (p16) | GGCACCAGAGGCAGTAACCAT | GCGCTACCTGATTCCAATTCG |
| tumor protein 53 (p53) | CAGCACATGACGGAGGTTGT | TCATCCAAATACTCCACACGC |
| translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 20 (TOM20) | CTGCGTCGTGTTCCACTT | CTCCGCAACCTGACCATCT |
| Beclin1 | GCTGGAAGATGCTCCTGACC | CAGTTGTTCTGGGAGGACCA |
| sequestosome 1 (p62) | GCACCCCAATGTGATCTGC | CGCTACACAAGTCGTAGTCTGG |
| Parkin | TGGATGGCTTCTCCGACTAC | AAGGTCCTGCCACTGCTC |
| PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) | CGCGGGAGTCAATGAGAAAA | GGCAGCAGAGGAAGGTGAAG |
| microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) | AGCAGCATCCAACCAAAATC | CTGTGTCCGTTCACCAACAG |
| Collagen I (COL-1) | GAGGGCCAAGACGAAGACATC | CAGATCACGTCATCGCACAAC |
| matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) | TGTACCGCTATGGTTACACTCG | GGCAGGGACAGTTGCTTCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Le, J.; Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, W.; Otsuki, K.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Feng, F.; Zhang, J. Hyperoside Promotes Mitochondrial Autophagy Through the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Thereby Improving UVB-Induced Photoaging. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121401
Yang D, Le J, Xiao S, Cui Y, Zhu W, Otsuki K, Li W, Xu J, Feng F, Zhang J. Hyperoside Promotes Mitochondrial Autophagy Through the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Thereby Improving UVB-Induced Photoaging. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(12):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121401
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Danni, Jiayi Le, Shuyun Xiao, Yulin Cui, Wanfang Zhu, Kouharu Otsuki, Wei Li, Jian Xu, Feng Feng, and Jie Zhang. 2025. "Hyperoside Promotes Mitochondrial Autophagy Through the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Thereby Improving UVB-Induced Photoaging" Antioxidants 14, no. 12: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121401
APA StyleYang, D., Le, J., Xiao, S., Cui, Y., Zhu, W., Otsuki, K., Li, W., Xu, J., Feng, F., & Zhang, J. (2025). Hyperoside Promotes Mitochondrial Autophagy Through the miR-361-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Thereby Improving UVB-Induced Photoaging. Antioxidants, 14(12), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121401








