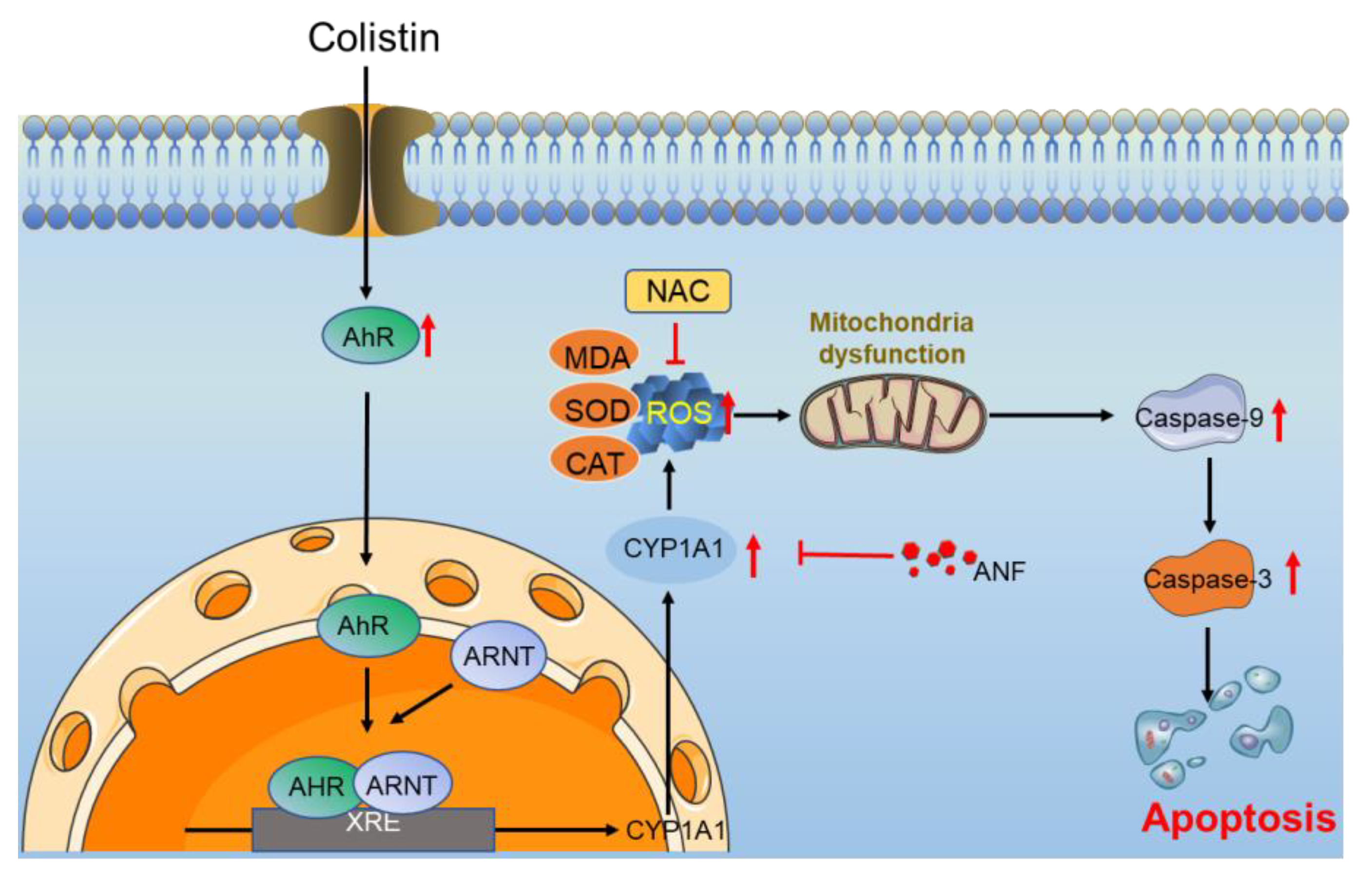
Colistin Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death through the Activation of the AhR/CYP1A1 Pathway in PC12 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
2.4. Measurement of Apoptosis
2.5. Assessment of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.7. Levels of Caspases-9 and -3 Activities Measurement
2.8. Gene Knockdown by Short Interfering RNAs (SiRNA)
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. Quantitative RT–PCR
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
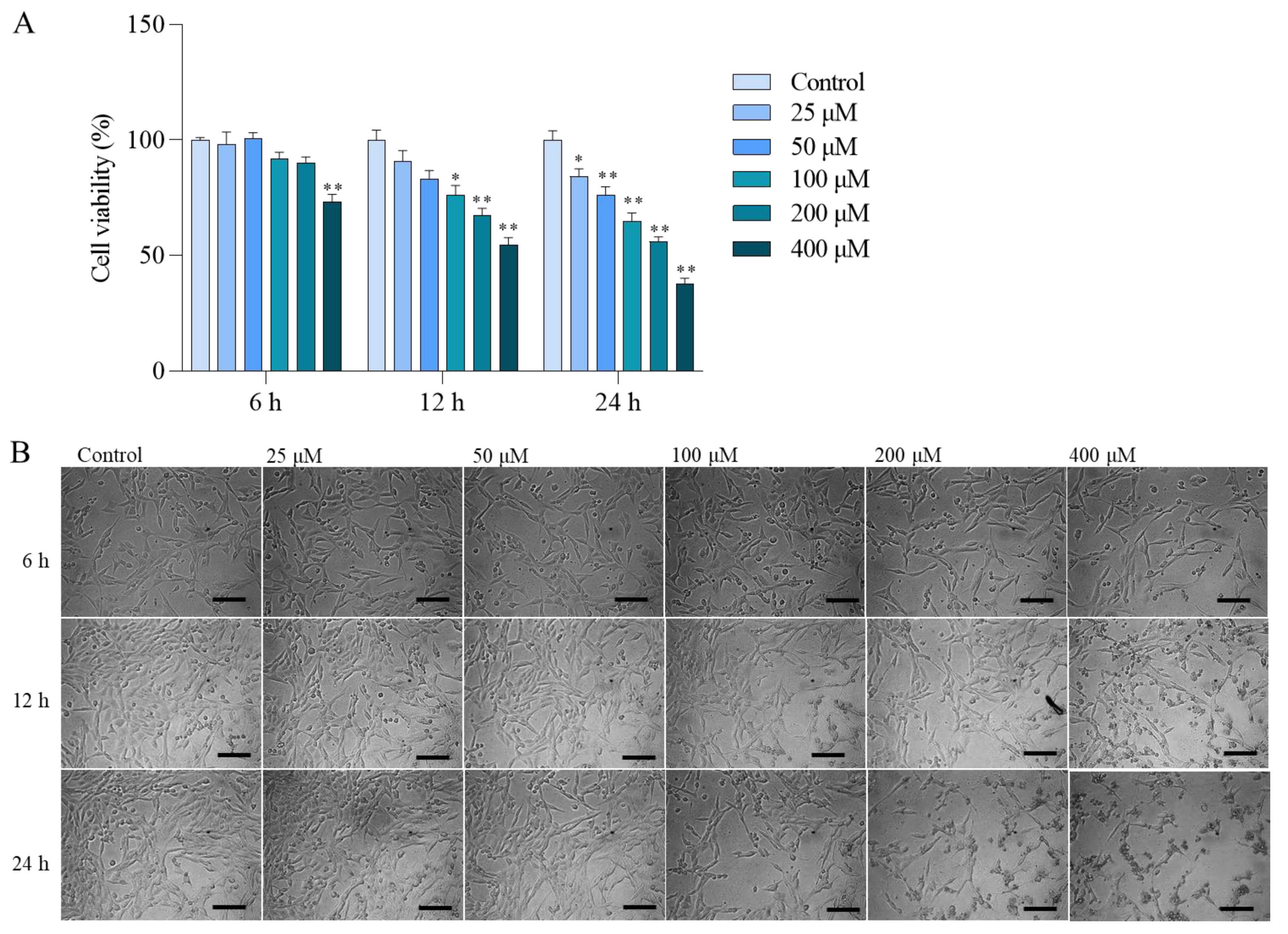
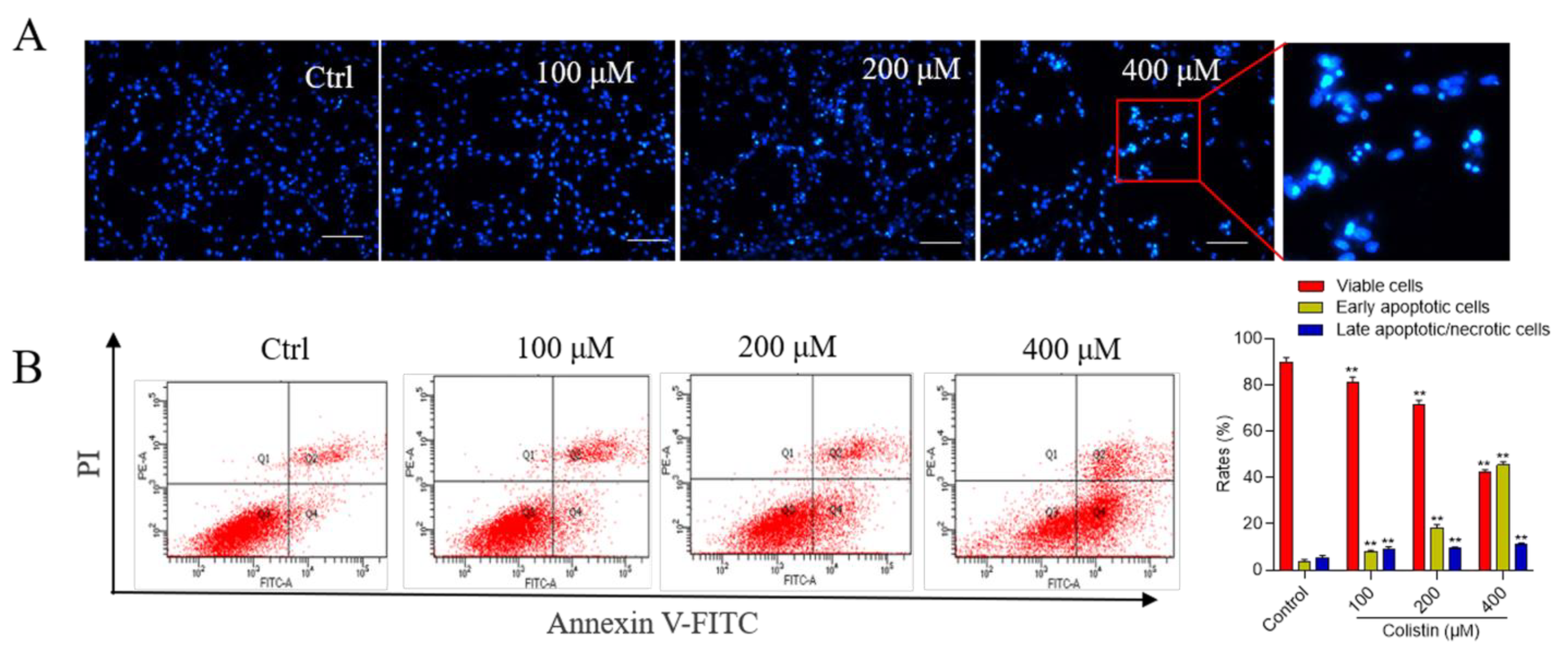
3.1. Colistin Induces Cytotoxicity and Apoptotic Cell Death in PC12 Cells
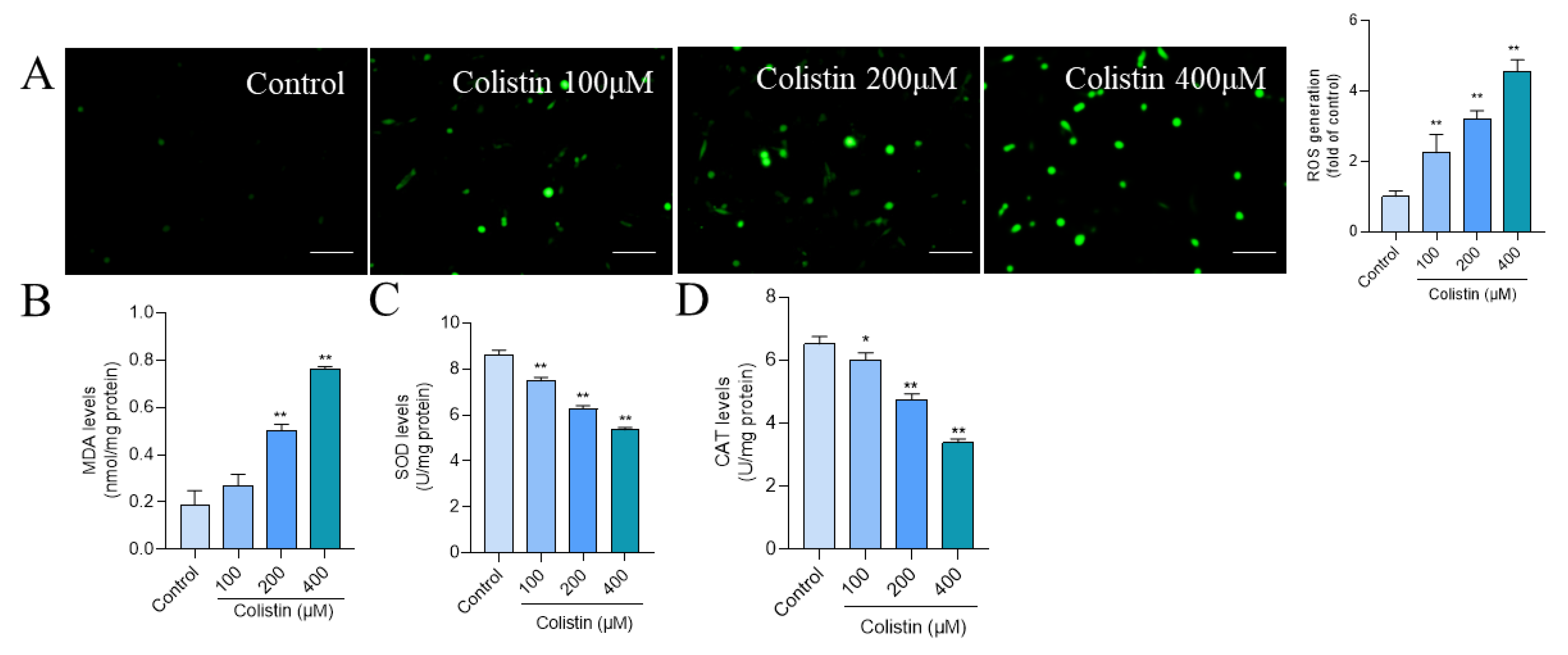
3.2. Colistin Treatment Induces Oxidative Stress in PC12 Cells
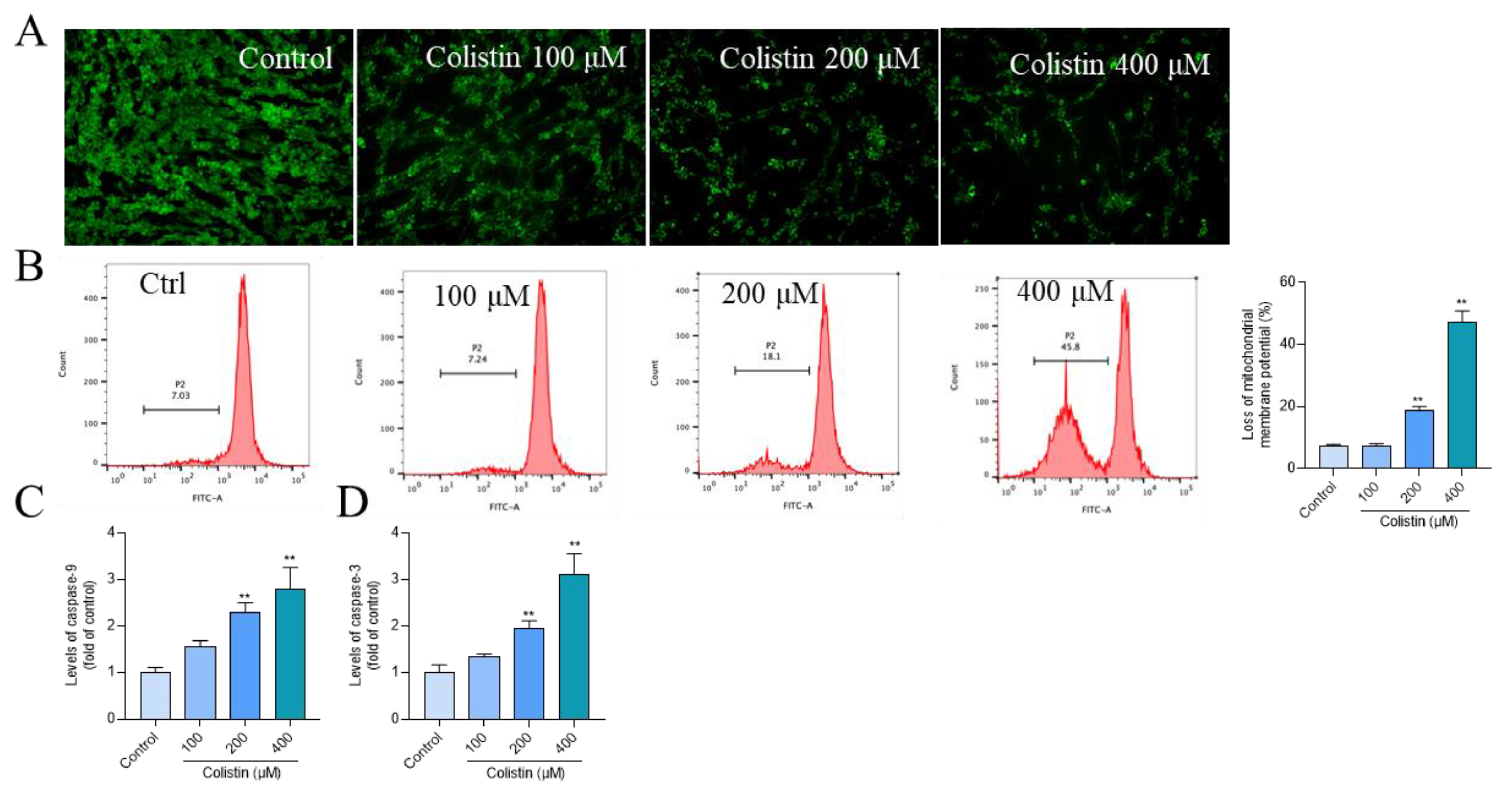
3.3. Colistin Treatment Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Caspase Activation in PC12 Cells
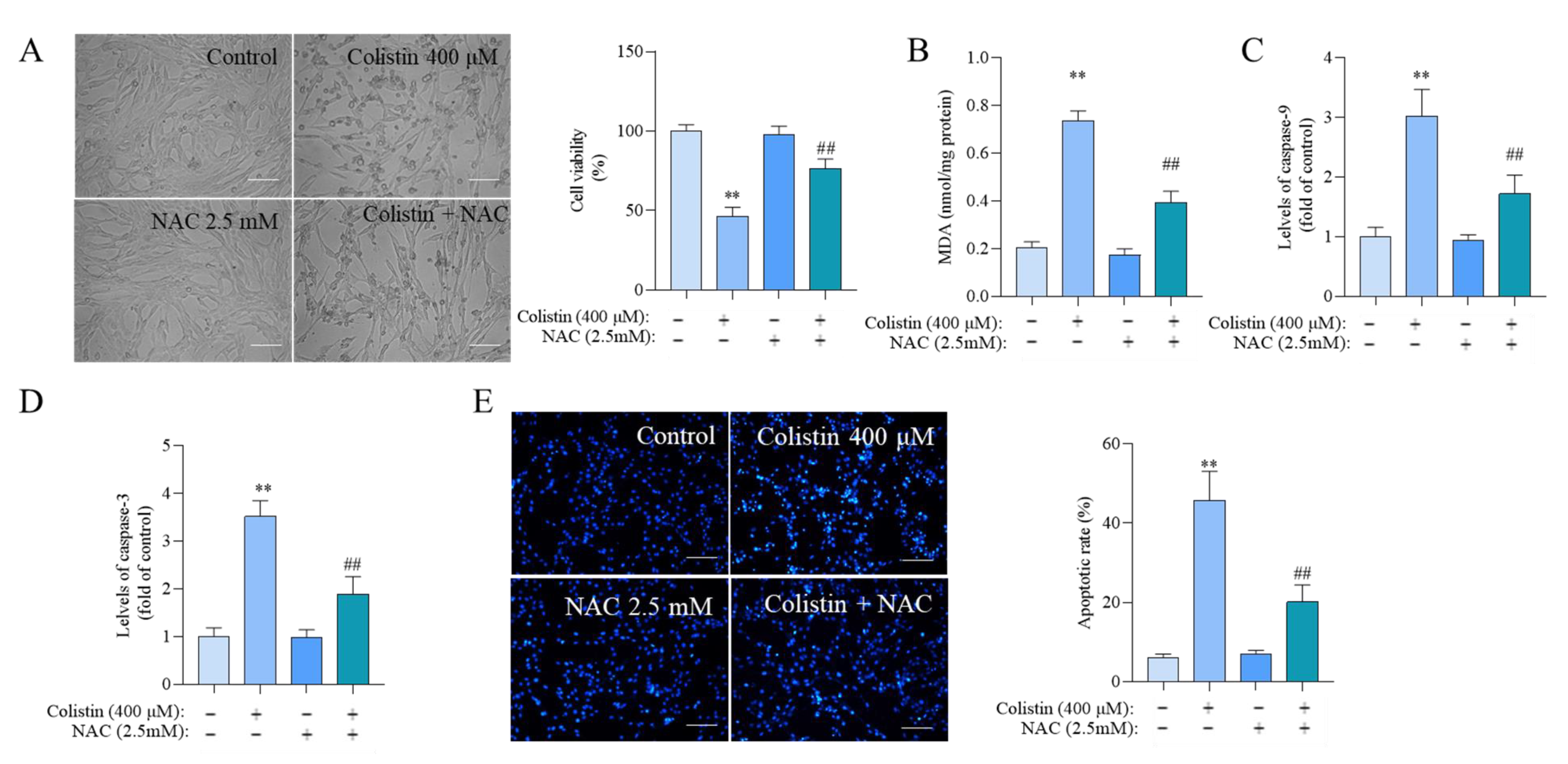
3.4. NAC Antioxidant Supplementation Attenuates Colistin-Induced Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in PC12 Cells
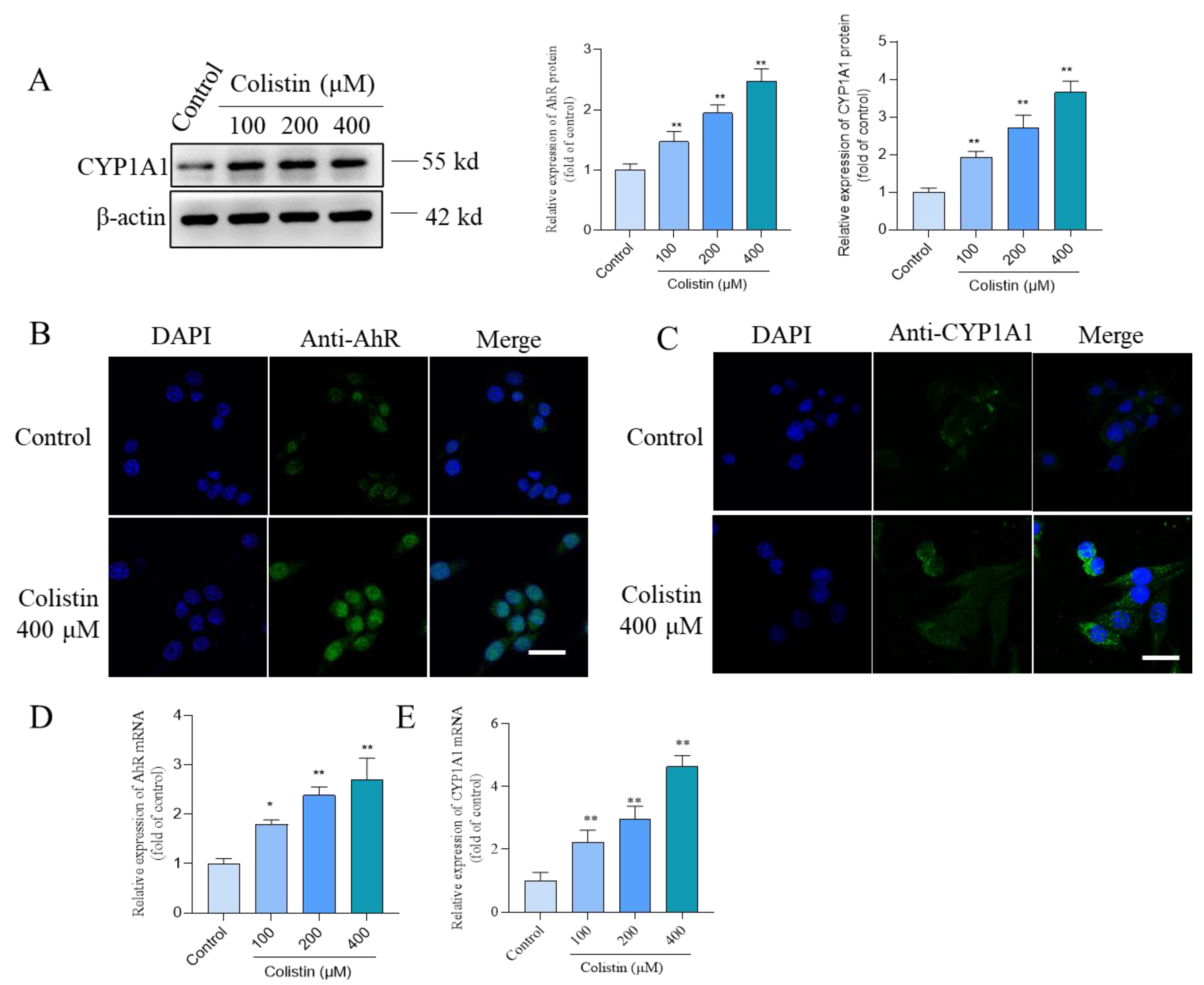
3.5. Colistin Treatment Triggers the Upregulation of AhR and CYP1A1 Proteins in PC12 Cells
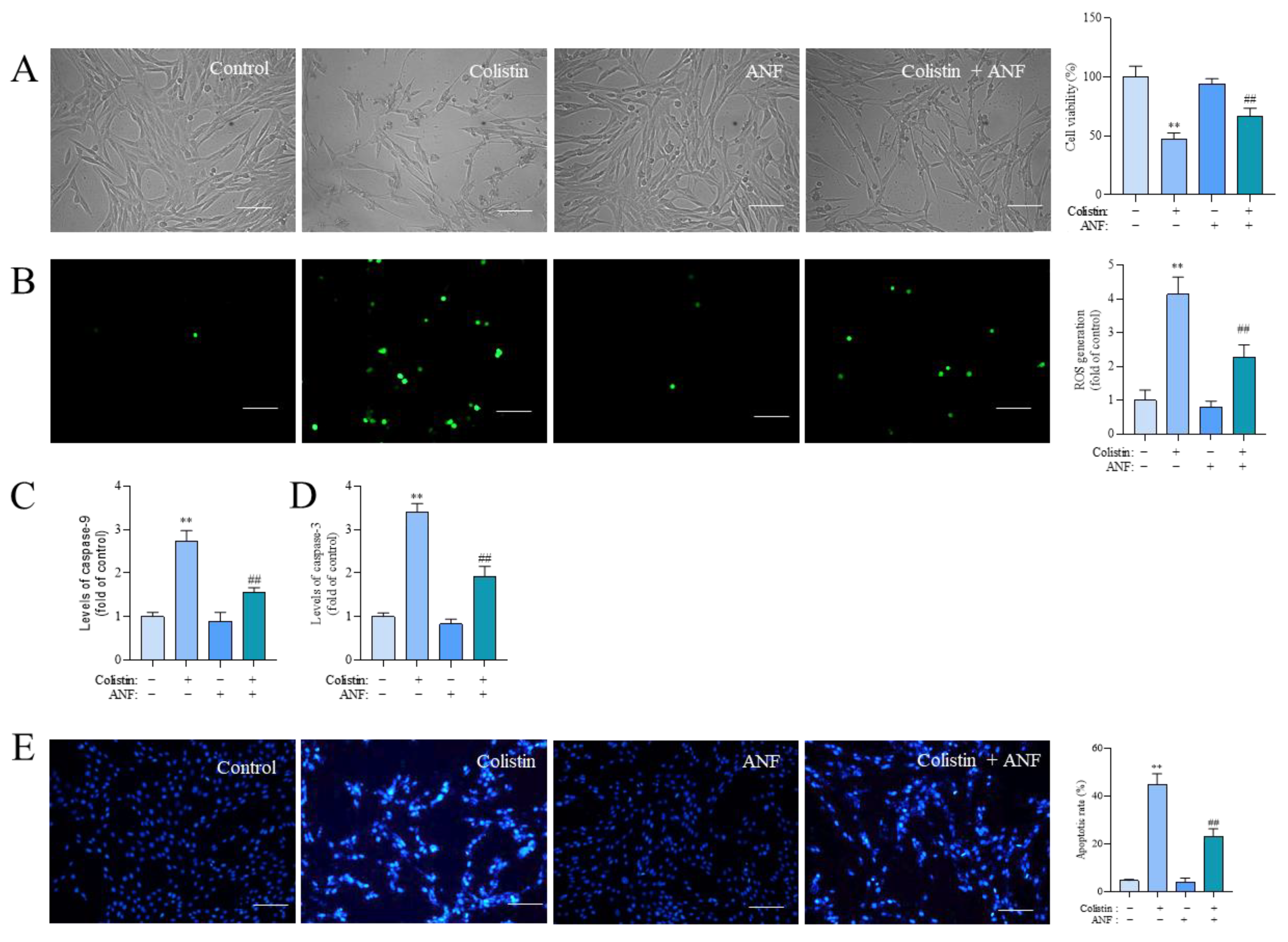
3.6. Pharmacological Intervention of CYP1A1 Attenuates Colistin Treatment-Induced Loss of Cell Viability, the Production of ROS, Caspase Activation, and Apoptosis
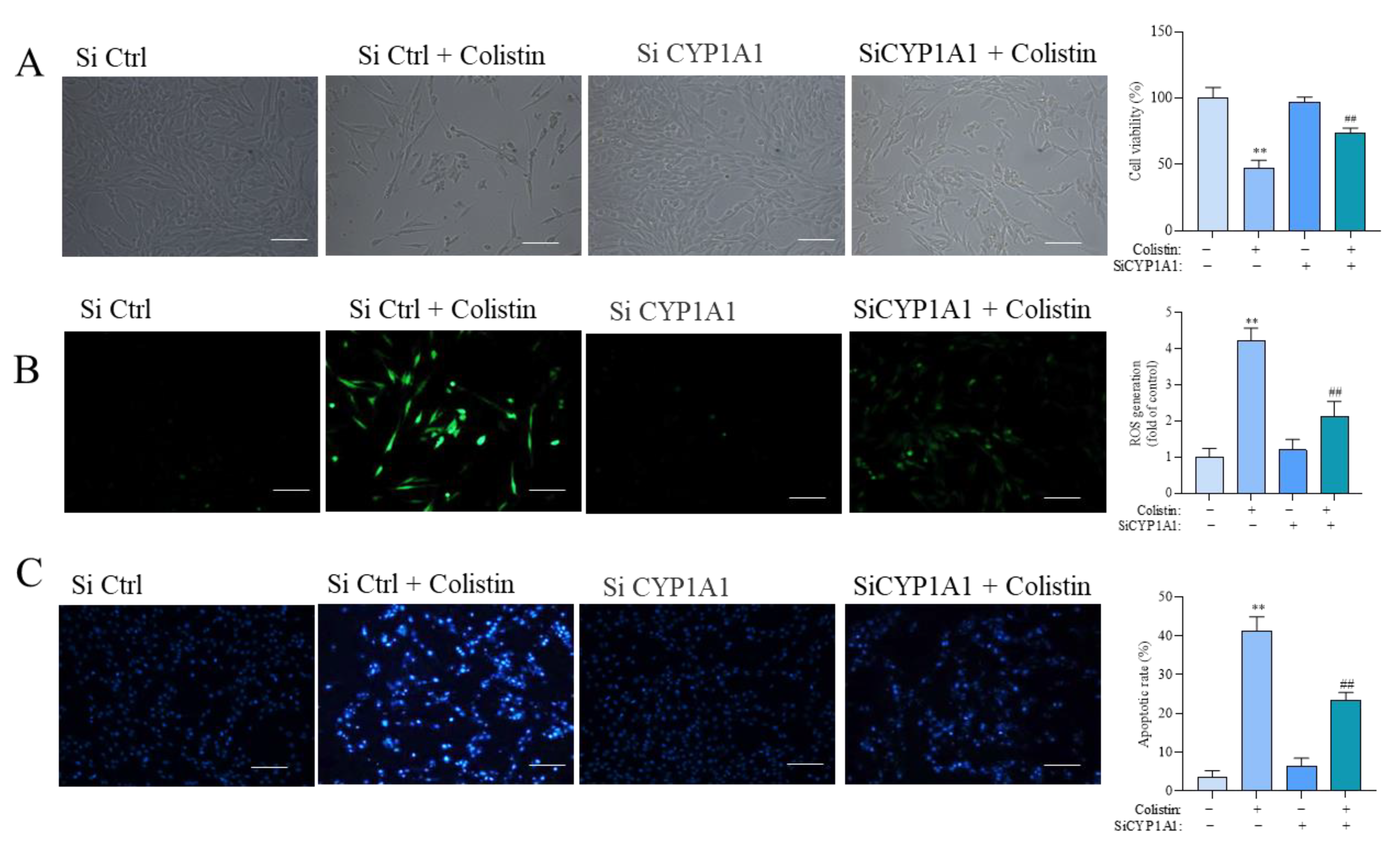
3.7. CYP1A1 Knockdown Attenuates Colistin-Induced Cytotoxicity, the Production of ROS, and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castañeda-Barba, S.; Top, E.M.; Stalder, T. Plasmids, a molecular cornerstone of antimicrobial resistance in the One Health era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Rayner, C.R.; Paterson, D.L. Colistin: The re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, T.M.; Forrest, G.N.; Messmer, K.J. Polymyxin antibiotics for gram-negative infections. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2007, 64, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.J.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Rayner, C.R.; Taylor, D.; Middleton, D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Turnidge, J.D. Subacute toxicity of colistin methanesulfonate in rats: Comparison of various intravenous dosage regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogue, J.M.; Tam, V.H. Toxicity in Patients. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroudi, S.; Mousavi, G.; Jafari, F.; Elyasi, S. Prevention of colistin-induced neurotoxicity: A narrative review of preclinical data. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 3709–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K. Toxicity of polymyxins: A systematic review of the evidence from old and recent studies. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Li, J.; Li, J. New insight in colistin induced neurotoxicity with the mitochondrial dysfunction in mice central nervous tissues. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Cappai, R.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Hoyer, D.; Schneider, E.K.; Velkov, T.; Xiao, X. Rapamycin Confers Neuroprotection against Colistin-Induced Oxidative Stress, Mitochondria Dysfunction, and Apoptosis through the Activation of Autophagy and mTOR/Akt/CREB Signaling Pathways. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Cappai, R.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Xie, S.; Xiao, X.; Velkov, T. Curcumin Attenuates Colistin-Induced Neurotoxicity in N2a Cells via Anti-inflammatory Activity, Suppression of Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.F.; Ragab, D.; Ibrahim, S.G.; Abd El-Galil, M.M.; Hassan Abd-El-Hamid, A.; Hamed, D.M.; Magdy William, M.; Salem, M.A. The potential role of Tirzepatide as adjuvant therapy in countering colistin-induced nephro and neurotoxicity in rats via modulation of PI3K/p-Akt/GSK3-β/NF-kB p65 hub, shielding against oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress, and activation of p-CREB/BDNF/TrkB cascade. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xiang, D.; Yuan, F.; Tong, H.; Yang, R.; Zhou, L.; Xu, B.; Deng, C.; Li, X. Piceatannol-3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside attenuates colistin-induced neurotoxicity by suppressing oxidative stress via the NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Miao, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Tian, E.; Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, R.; Li, J. Colistin-induced autophagy and apoptosis involves the JNK-Bcl2-Bax signaling pathway and JNK-p53-ROS positive feedback loop in PC-12 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 277, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Velkov, T.; Xiao, X. Nerve Growth Factor Confers Neuroprotection against Colistin-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, D.; Chen, X.; Hughes, M.L.; Jiang, G.; Lu, Z.; Xia, C.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; et al. p53 Mediates Colistin-Induced Autophagy and Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5294–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, E.; Hu, W.; Miao, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Zhang, L.; Xia, C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Chen, C.; et al. Preventive effects of nerve growth factor against colistin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in PC12 cells. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Ravichandran, K.; Gil, H.W.; Song, H.Y.; Hong, S.Y. P-Glycoprotein Induction Ameliorates Colistin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Cultured Human Proximal Tubular Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, B.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, N.; Yang, X.; Ma, P. Ferroptosis participates in dibutyl phthalate-aggravated allergic asthma in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Hesperetin protects hippocampal neurons from the neurotoxicity of Aflatoxin B1 in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 269, 115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Wnuk, A.; Kajta, M.; Wójtowicz, A.K. Triclosan activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-dependent apoptosis and affects Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 expression in mouse neocortical neurons. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stading, R.; Chu, C.; Couroucli, X.; Lingappan, K.; Moorthy, B. Molecular role of cytochrome P4501A enzymes inoxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 20–21, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, N.R.; Pimpão, A.B.; Correia, M.J.; Rodrigues, T.C.; Monteiro, E.C.; Morello, J.; Pereira, S.A. Pharmacological blockage of the AHR-CYP1A1 axis: A call for in vivo evidence. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Jin, Y. Alpha-naphthoflavone attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in oleic acid-treated HepG2 hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassa, Z.E.; Myrianthefs, P.M.; Boutzouka, E.G.; Tsakris, A.; Baltopoulos, G.J. Monotherapy with inhaled colistin for the treatment of patients with ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis due to polymyxin-only-susceptible Gram-negative bacteria. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Sideri, G.; Korbila, I.P.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Papadatos, J.H.; Kafetzis, D.A. Inhaled colistin for the treatment of tracheobronchitis and pneumonia in critically ill children without cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nang, S.C.; Azad, M.A.K.; Velkov, T.; Zhou, Q.T.; Li, J. Rescuing the Last-Line Polymyxins: Achievements and Challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.T. Tobramycin Reduces Pulmonary Toxicity of Polymyxin B via Inhibiting the Megalin-Mediated Drug Uptake in the Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Shi, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhu, B.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. A pharmacovigilance study of adverse events associated with polymyxins based on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, W.; Jiang, G.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, J. Autophagy regulates colistin-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaushal, N.; Saleth, L.R.; Ghavami, S.; Dhingra, S.; Kaur, P. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy: Balancing the contrary forces in spermatogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.X.; Sun, Z.; Lin, X.F.; Tan, C.; Lu, R.R. Curcumin protects mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2A cells against hydrogen-peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrees, N.E.; Galal, A.A.A.; Abdel Monaem, A.R.; Beheiry, R.R.; Metwally, M.M.M. Curcumin alleviates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Park, S.R.; Cho, S.; Yu, S.L.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, C.G.; Kang, J.; Jung, D.Y.; Park, M.H.; Hwang, W.M.; et al. TGF-β-mediated NADPH oxidase 4-dependent oxidative stress promotes colistin-induced acute kidney injury. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, J.; Ago, T.; Matsushima, S.; Zhai, P.; Schneider, M.D.; Sadoshima, J. NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a major source of oxidative stress in the failing heart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15565–15570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Ji, C.; Aniagu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR/ROS-mediated mitochondria apoptosis contributes to benzo[a]pyrene-induced heart defects and the protective effects of resveratrol. Toxicology 2021, 462, 152965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Sun, X.; Che, S.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, J. AhR-mediated CYP1A1 and ROS overexpression are involved in hepatotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 352, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Shi, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. Polychlorinated diphenyl sulfides can induce ROS and genotoxicity via the AhR-CYP1A1 pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Duan, J.; Huang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, F. Inhibition of CYP1A1 Alleviates Colchicine-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Toxins 2024, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bi, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Deng, N.; Pan, H.; Li, D.; Xiao, B. α- and β-Naphthoflavone synergistically attenuate H(2)O(2)-induced neuron SH-SY5Y cell damage. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Lv, P.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Lin, W. Baicalin inhibits colistin sulfate-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Colistin-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells: Involvement of the mitochondrial apoptotic and death receptor pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, G.Z.; Li, J.C. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against colistin sulfate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; Miao, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Ding, L.; Tian, E.; Hu, W.; Ni, H.; Li, R.; et al. A Dual Role of P53 in Regulating Colistin-Induced Autophagy in PC-12 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Perspective of structural flexibility on selective inhibition towards CYP1B1 over CYP1A1 by α-naphthoflavone analogs. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 20230–20246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.T.; Li, C.H.; Dai, T.T.; Song, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.; Han, Z.L.; Sun, N.X.; Wang, D.L. Effect of allyl isothiocyanate on oxidative stress in COPD via the AhR/CYP1A1 and Nrf2/QO1 pathways and the underlying mechanism. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 114, 154774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvonen, R.O.; Jokinen, E.M.; Javaid, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Raunio, H.; Pentikäinen, O.T. Inhibition of human CYP1 enzymes by a classical inhibitor α-naphthoflavone and a novel inhibitor N-(3, 5-dichlorophenyl)cyclopropanecarboxamide: An in vitro and in silico study. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 95, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha, P.; Lee, D.A. The role of AhR in transcriptional regulation of immune cell development and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, L.; Sharma, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Shen, J. Quercetin Attenuates Quinocetone-Induced Cell Apoptosis In Vitro by Activating the P38/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway and Inhibiting the ROS/Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.B.; Brannick, K.E.; Raetzman, L.T. Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor activity modulates prolactin expression in the pituitary. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 265, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Velkov, T.; Tang, S.; Shen, J.; Dai, C. Colistin Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death through the Activation of the AhR/CYP1A1 Pathway in PC12 Cells. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070827
Xie B, Liu Y, Chen C, Velkov T, Tang S, Shen J, Dai C. Colistin Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death through the Activation of the AhR/CYP1A1 Pathway in PC12 Cells. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(7):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070827
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Baofu, Yue Liu, Chunhong Chen, Tony Velkov, Shusheng Tang, Jianzhong Shen, and Chongshan Dai. 2024. "Colistin Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death through the Activation of the AhR/CYP1A1 Pathway in PC12 Cells" Antioxidants 13, no. 7: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070827
APA StyleXie, B., Liu, Y., Chen, C., Velkov, T., Tang, S., Shen, J., & Dai, C. (2024). Colistin Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death through the Activation of the AhR/CYP1A1 Pathway in PC12 Cells. Antioxidants, 13(7), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070827






