Potential Antioxidant Compounds from the Spores of Dicranopteris linearis and the Branches of Averrhoa bilimbi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Extraction and Isolation Procedure
2.4. Structural Elucidation
2.5. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.6. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.7. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.8. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Ability
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. HPLC Analysis for Extracts and Selected Compounds
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents, and Antioxidant Activity in A. bilimbi and D. linearis Extracts
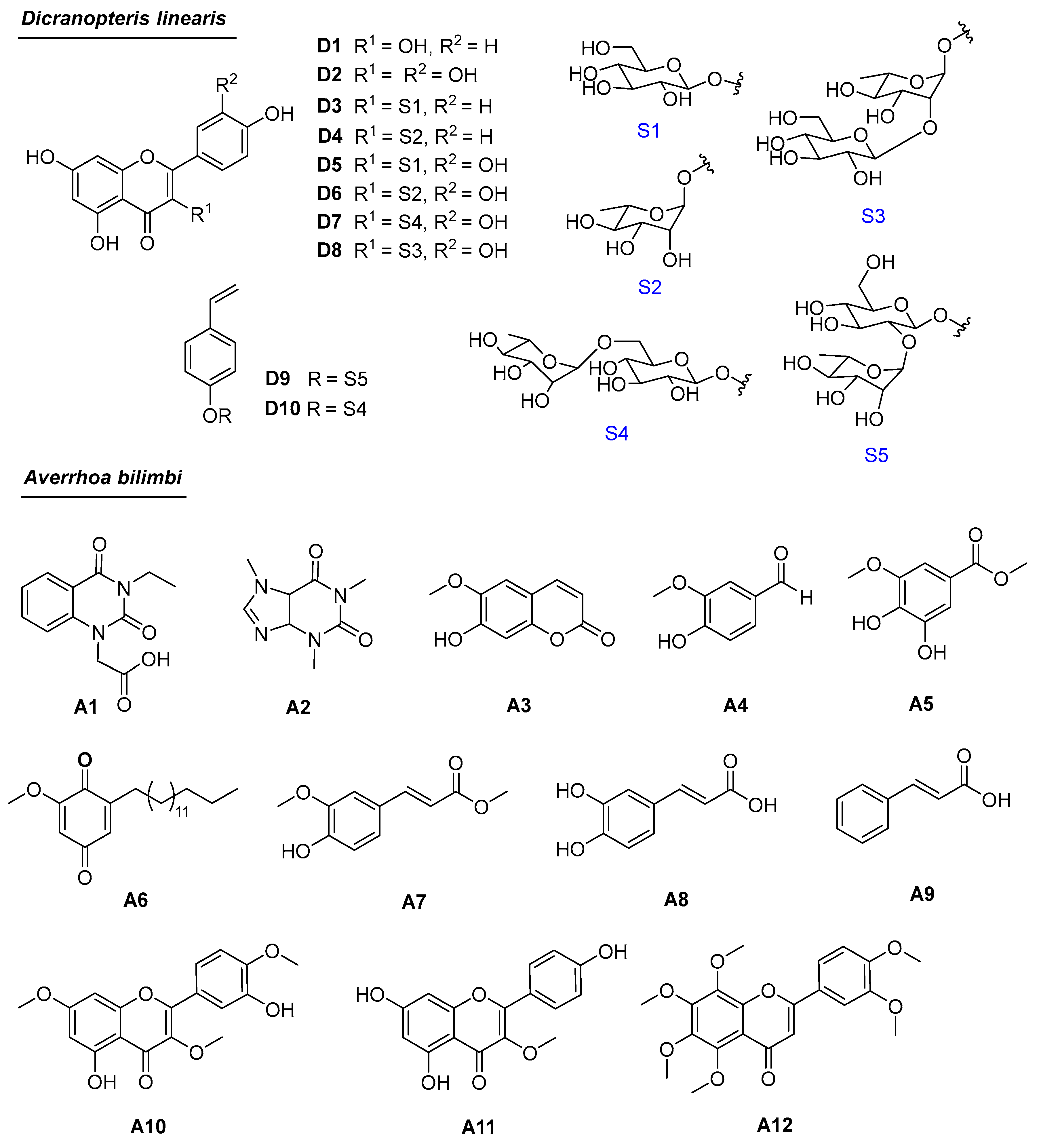
3.2. Phytochemical Investigations of A. bilimbi and D. linearis
3.3. Antioxidant Activities of Compounds D3–D5, D8–D10, and A1–A11
3.4. HPLC-DAD Analysis of A. bilimbi and D. linearis Extracts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, H.; Chai, T.-T.; Wang, X.; Morais-Braga, M.F.B.; Yang, J.-H.; Wong, F.-C.; Wang, R.; Yao, H.; Cao, J.; Cornara, L.; et al. Phytochemicals from fern species: Potential for medicine applications. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 379–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Fernández, H.; Revilla, M.A. (Eds.) Working with Ferns: Issues and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kamisan, F.H.; Yahya, F.; Mamat, S.S.; Kamarolzaman, M.F.F.; Mohtarrudin, N.; Kek, T.L.; Salleh, M.Z.; Hussain, M.K.; Zakaria, Z.A. Effect of methanol extract of Dicranopteris linearis against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, Y.; Chear, N.J.-Y.; Ramanathan, S.; Lai, C.-S. Polyphenols rich fraction of Dicranopteris linearis promotes fibroblast cell migration and proliferation in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.-J.; Gao, K. Chemical constituents and biological activities of Dicranopteris linearis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 49, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Sahmat, A.; Azmi, A.H.; Nur Zainol, A.S.; Omar, M.H.; Balan, T.; Sulistyorini, L.; Azizah, R.; Abdullah, M.N.H. Polyphenolics and triterpenes presence in chloroform extract of Dicranopteris linearis leaves attenuated paracetamol-induced liver intoxication in rat. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Kamisan, F.H.; Omar, M.H.; Mahmood, N.D.; Othman, F.; Abdul Hamid, S.S.; Abdullah, M.N.H. Methanol extract of Dicranopteris linearis L. leaves impedes acetaminophen-induced liver intoxication partly by enhancing the endogenous antioxidant system. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Kamisan, F.H.; Mohd Nasir, N.; Teh, L.K.; Salleh, M.Z. Aqueous partition of methanolic extract of Dicranopteris linearis leaves protects against liver damage induced by paracetamol. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Chowdhury, A.S.; Nawrin, K.; Mostaq, S.; Rayhan, M.A.; Tushar, R.R. Serotonergic and noradrenergic response of ethanol extract; opioidergic response of ethyl acetate extract of Dicranopteris linearis L. leaf. Clin. Phytosci. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.-H.; Vu, Y.T.; Long, N.P.; Phan, N.-H.-N.; Pham, N.-K.-T.; Sichaem, J.; Kieu, N.-K.-D.; Duong, C.-B.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Dang, V.-S.; et al. Bioactive-guided phytochemical investigations, in vitro and in silico alpha-glucosidase inhibition of two Vietnamese medicinal plants Dicranopteris linearis and Psychotria adenophylla. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Mohamed, A.M.; Jamil, N.S.M.; Rofiee, M.S.; Somchit, M.N.; Zuraini, A.; Arifah, A.K.; Sulaiman, M.R. In vitro cytotoxic and antioxidant properties of the aqueous, chloroform and methanol extracts of Dicranopteris linearis leaves. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Kamisan, F.H.; Kek, T.L.; Salleh, M.Z. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Dicranopteris linearis leaf extract against paracetamol-induced liver intoxication in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurup, S.B.; S, M. Protective potential of Averrhoa bilimbi fruits in ameliorating the hepatic key enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebaluck-Sandoram, R.; Lall, N.; Fibrich, B.; Blom van Staden, A.; Saleem, H.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic evaluation of two underutilised food plants: Averrhoa bilimbi L. (Oxalidaceae) and Phyllanthus acidus L. Skeels (Phyllanthaceae). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, A.; Ahmed, Q. Averrhoa bilimbi Linn.: A review of its ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioall. Sci. 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Auw, L.; Subehan; Sukrasno; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Constituents of Indonesian medicinal plant Averrhoa bilimbi and their cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2D6 inhibitory activities. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, A.J.; Geetha, G.; Thavamani, B.S. Isolation and characterisation of an isolated flavonoid from Averrhoa bilimbi. AJOCS 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.P.; Muthusamy, M.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Kuppusamy, S. Optimization of extraction and quantification of flavonoids from Averrhoa bilimbi fruits using RP-HPLC and its correlation between total flavonoids content against antimicrobial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyada, F.F.A.; Agustina, E.; Faizah, H. The effect of fermentation on the characteristics and antioxidant activity of Wuluh starfruit leaf kombucha tea (Averrhoa bilimbi Linn.). Indo. J. Chem. Res. 2023, 11, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidrianny, I.; Rahmawati, A.; Hartati, R. Comparison profile of different extracts of Averrhoa bilimbi L. in antioxidant properties and phytochemical content. Rasayan J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Q.U.; Alhassan, A.M.; Khatib, A.; Shah, S.A.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Sarian, M.N. Antiradical and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity evaluations of Averrhoa bilimbi L. leaves and tentative identification of bioactive constituents through LC-QTOF-MS/MS and molecular docking approach. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Atiyah, M.; Shnawa Jasim, H.; Mohammed Atiyah, H. Phytochemical screening and anti-bacterial activities aqueous & alcoholic extracts of Averrhoa bilimbi leaf against bacteria isolated from oral cavity. Arch. Razi Inst. 2022, 70, 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Iwansyah, A.C.; Desnilasari, D.; Agustina, W.; Pramesti, D.; Indriati, A.; Mayasti, N.K.I.; Andriana, Y.; Kormin, F.B. Evaluation on the physicochemical properties and mineral contents of Averrhoa bilimbi L. leaves dried extract and its antioxidant and antibacterial capacities. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, K.I.; Uddin, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Parvin, S.; Shahriar, M. Phytochemical screenings, thrombolytic activity and antimicrobial properties of the bark extracts of Averrhoa bilimbi. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Suluvoy, J.K.; Sakthivel, K.M.; Guruvayoorappan, C.; Berlin Grace, V.M. Protective effect of Averrhoa bilimbi L. fruit extract on ulcerative colitis in Wistar rats via regulation of inflammatory mediators and cytokines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molole, G.J.; Gure, A.; Abdissa, N. Determination of total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Commiphora mollis (Oliv.) Engl. resin. BMC Chem. 2022, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yue, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z. One-step high efficiency separation of prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus niger and its application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.-N.; Nguyen, T.-V.-A.; Mai, D.-T.; Tran, N.-M.-A.; Nguyen, N.-H.; Vo, G.V.; Duong, T.-H.; Truong Nguyen, H. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from Nervilia concolor, Tecoma stans, and Bouea macrophylla. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 29, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Mai, T.T.; Minh, P.N.; Phat, N.T.; Duong, T.H.; Minh An, T.N.; Dang, V.S.; Van Hue, N.; Tri, M.D. Antimicrobial and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory flavonoid glycosides from the plant Mussaenda recurvata: In vitro and in silico approaches. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 9326–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J. Purification and characterization of flavonoids from the leaves of Zanthoxylum bungeanum and correlation between their structure and antioxidant activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, J.G.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.; Pauli, G.F. Complete 1H NMR spectral analysis of ten chemical markers of Ginkgo biloba. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2012, 50, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, T.V.; Ninh, P.T.; Luu, N.T.; Chien, T.V.; Anh, T.T.; Dung, N.T.; Thao, T.T.P. Chemical composition of Euphorbia hirta L. collected in Dan Phuong, Hanoi. Nat. Sci. Technol. 2022, 38, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, A.; Gross, G.-A.; Meier, B.; Sticher, O. Complex flavonol glycosides from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Tomè, F.; Vitalini, S.; Agradi, E.; Innocenti, G. In vitro estrogenic activity of Asplenium trichomanes L. extracts and isolated compounds. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmonsef, A.H. Design, synthetic approach, in silico molecular docking and antibacterial activity of quinazolin-2,4-dione hybrids bearing bioactive scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshta, N.M.; El-Essawy, F.A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Noreldein, S.G.; Darwesh, O.M. Discovery of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione derivatives as potential antibacterial agent: Design, synthesis, and their antibacterial activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitkowski, J.; Webb, G.A. Complete assignments of the 1H, 13C and 15N NMR spectra of caffeine. Spectrochim. Acta 1995, 51A, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octaviana, L.; Hakim, E.H. Two arylpropanoid derivatives from the leaves of Morus cathayana. In Proceedings of the International Seminar on Chemistry 2008, Jatinangor, Indonesia, 30–31 October 2008; pp. 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- König, W.A.; Faasch, H.; Heitsch, H.; Colberg, C.; Hausen, B.M. Synthesis of side-chain-modified analogues of the allergen primin. Z. Naturforsch. B 1993, 48, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.M.A.; Zidan, S.A.H.; Shehata, R.M.; El-Sheikh, H.H.; Ameen, F.; Stephenson, S.L.; Al-Bedak, O.A.-H.M. Antioxidant, antibacterial, and molecular docking of methyl ferulate and oleic acid produced by Aspergillus pseudodeflectus AUMC 15761 utilizing wheat bran. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3183–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, D.T.B.; Dieu, N.T.H.; Huy, D.T. Some flavonoids from the leaves of Combretum quadrangulare growing in Vietnam. HCMC Univ. Educ. J. Sci. 2021, 18, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H. Preparative separation of 3-O-methylkaempferol from Caragana leucophloea by high-speed counter-current chromatography and its antimicrobial activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.; Duong, T.; Truong Nguyen, H.; Vu, Y.T.; Tran, T.; Ho, T.; Mai, C.; Mai, D.; Nguyen, H.; Thuy Le, H.; et al. New halogenated flavonoids from Adenosma bracteosum and Vitex negundo and their α-glucosidase inhibition. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakır, D.K.; Zannou, O.; Koca, I. Scopoletin contents and antioxidant properties of some edible plants of Black Sea regions. Discov. Food 2022, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antika, L.D.; Tasfiyati, A.N.; Hikmat, H.; Septama, A.W. Scopoletin: A review of its source, biosynthesis, methods of extraction, and pharmacological activities. Z. Naturforsch. C 2022, 77, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakthong, S.; Chiraphan, C.; Jundee, C.; Chaowalit, P.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Alkyl phenols from the wood of Averrhoa carambola. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Kamat, J.P.; Mukherjee, T. Free radical scavenging reactions and antioxidant activity of embelin: Biochemical and pulse radiolytic studies. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2007, 167, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Mai, T.T.; Minh, P.N.; Phat, N.T.; Chi, M.T.; Duong, T.H.; Nhi Phan, N.H.; Minh An, T.N.; Dang, V.S.; Van Hue, N.; Hong Anh, N.T.; et al. In vitro and in silico docking and molecular dynamic of antimicrobial activities, alpha-glucosidase, and anti-inflammatory activity of compounds from the aerial parts of Mussaenda saigonensis. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12081–12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.T.N.; Minh, P.N.; Phat, N.T.; Thanh Chi, M.; Chi Hien, D.; Nguyen, V.-K.; Duong, T.H.; Nha, T.T.; Minh An, T.N.; Huyen Tran, N.N.; et al. In vitro and in silico studies of alpha-glucosidase inhibition and antifungal activity of Coffea canephora husk. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 27252–27264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biosource | Extract | TPC | TFC | DPPH | ABTS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg GAE/g) | (mg QE/g) | %I | IC50 (µg/mL) | %I | IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
| D. linearis spores | Crude | 62.35 f ± 0.04 | 8.09 g ± 0.10 | 98.8 a ± 0.2 | 35.5 b ± 0.2 | 69.8 ± 0.4 d | 132.2 ± 0.7 a |
| HEA | 51.09 g ± 0.03 | 15.53 f ± 0.08 | 41.0 e ± 0.3 | 12.0 ± 0.3 c | |||
| EA | 120.13 d ± 0.04 | 21.94 c ± 0.30 | 96.3 b ± 0.3 | 39.4 a ± 0.3 | 86.0 ± 0.2 b | 88.9 ± 0.7 a | |
| A. bilimbi branches | Crude | 213.34 a ± 0.06 | 31.56 a ± 0.03 | 38.9 f ± 1.2 | 37.2 ± 0.1 a | 539.5 ± 15.2 c | |
| n-Hexane | 125.30 c ± 0.01 | 19.12 d ± 0.03 | 18.2 g ± 1.4 | - | - | ||
| HEA | 165.21 b ± 0.24 | 26.20 b ± 0.01 | 89.6 c ± 0.7 | 39.7 a ± 1.9 | 44.5 ± 0.2 a | 130.8 ± 1.4 b | |
| EA | 112.72 e ± 0.21 | 18.38 e ± 0.19 | 48.9 d ± 0.7 | 12.8 ± 0.4 b | - | ||
| Ascorbic acid (positive control) | 2.1 c ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.1 b | |||||
| Compound | DPPH | ABTS |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | IC50 (µg/mL) | |
| D3 | 14.1 d ± 1.4 | 30.4 ± 0.1 e |
| D4 | 48.0 a ± 1.9 | 133.5 ± 1.2 a |
| D5 | 27.4 c ± 2.1 | >300 |
| D8 | 7.3 ± 0.8 | 26.9 ± 0.1 f |
| D9 | 39.4 b ± 0.3 | - |
| D10 | 12.3 d ± 0.5 | - |
| A1 | >100 | - |
| A2 | >100 | - |
| A3 | 7.1 e ± 0.1 | 14.8 ± 0.1 g |
| A4 | >100 | >300 |
| A5 | >100 | >300 |
| A6 | 39.7 a ± 1.9 | 37.3 ± 0.1 d |
| A7 | >100 | >300 |
| A8 | >100 | >300 |
| A9 | >100 | 131.4 ± 0.7 b |
| A10 | >100 | >300 |
| A11 | >100 | >300 |
| Ascorbic acid (positive control) | 2.1 b ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.1 h |
| Biosource | Extract | TPC (mg GAE/g) | TFC (mg QE/g) | DPPH (%I) | IC50 (µg/mL) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. linearis leaves | Crude CHCl3 | 0.148 ± 0.002 | 15.2 ± 0.0 (200 µg/mL) | [12] | ||
| Crude aqueous | 31.12 ± 0.06 | 61.4 ± 2.1 (100 µg/mL) | [6] | |||
| Crude CHCl3 | 10.12 ± 0.05 | 22.6 ± 0.7 (100 µg/mL) | [11] | |||
| Crude MeOH | 34.17 ± 0.05 | 85.2 ± 0.6 (100 µg/mL) | [11] | |||
| A. bilimbi leaves | Crude MeOH | 10.53 ± 0.72 | [21] | |||
| n-Hexane | >1000 | [21] | ||||
| CHCl3 | 13.44 ± 1.00 | [21] | ||||
| n-Butanol | 4.14 ± 0.21 | [21] | ||||
| A. bilimbi fruits | Crude EtOH | 0.851 ± 0.0025 | [18] | |||
| A. bilimbi fruits | Crude MeOH | 79.09 | [14] | |||
| A. bilimbi leaves | EtOAc | 91.41 | [14] | |||
| Crude MeOH | 34.85 | [14] | ||||
| A. bilimbi leaves | Crude EtOH | 53.55 ± 5.11 | 8.88 ± 1.14 | [23] | ||
| Crude aqueous | 35.68 ± 4.87 | 29.71 ± 4.66 | [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duong, T.-H.; Tran, T.-M.-D.; To, P.-M.; Phan, N.-H.-N.; Nguyen, T.-P.; Le, H.T.; Sichaem, J. Potential Antioxidant Compounds from the Spores of Dicranopteris linearis and the Branches of Averrhoa bilimbi. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13111319
Duong T-H, Tran T-M-D, To P-M, Phan N-H-N, Nguyen T-P, Le HT, Sichaem J. Potential Antioxidant Compounds from the Spores of Dicranopteris linearis and the Branches of Averrhoa bilimbi. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(11):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13111319
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuong, Thuc-Huy, Thi-Minh-Dinh Tran, Phuong-Mai To, Nguyen-Hong-Nhi Phan, Thi-Phuong Nguyen, Huong Thuy Le, and Jirapast Sichaem. 2024. "Potential Antioxidant Compounds from the Spores of Dicranopteris linearis and the Branches of Averrhoa bilimbi" Antioxidants 13, no. 11: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13111319
APA StyleDuong, T.-H., Tran, T.-M.-D., To, P.-M., Phan, N.-H.-N., Nguyen, T.-P., Le, H. T., & Sichaem, J. (2024). Potential Antioxidant Compounds from the Spores of Dicranopteris linearis and the Branches of Averrhoa bilimbi. Antioxidants, 13(11), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13111319






