Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Indomethacin-Derivative (ATB-344) Prevents the Development of Oxidative Gastric Mucosal Injuries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design, Chemicals and Drugs
2.2. I/R-Induced Gastric Lesions, Macro-and Microscopic Assessment of Gastric Damage, Tissue Collection and Storage
2.3. Assessment of H2S Release in Gastric Mucosa by Modified Zinc Trapping Assay and Methylene-Blue Method
2.4. Determination of PGE2 Concentration in Gastric Mucosa and Serum by ELISA Test
2.5. Evaluation of 8-Hydroxyguanozine (8-OHG) Concentration in Gastric Mucosa
2.6. Determination of mRNA Expression for Selected Genes by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
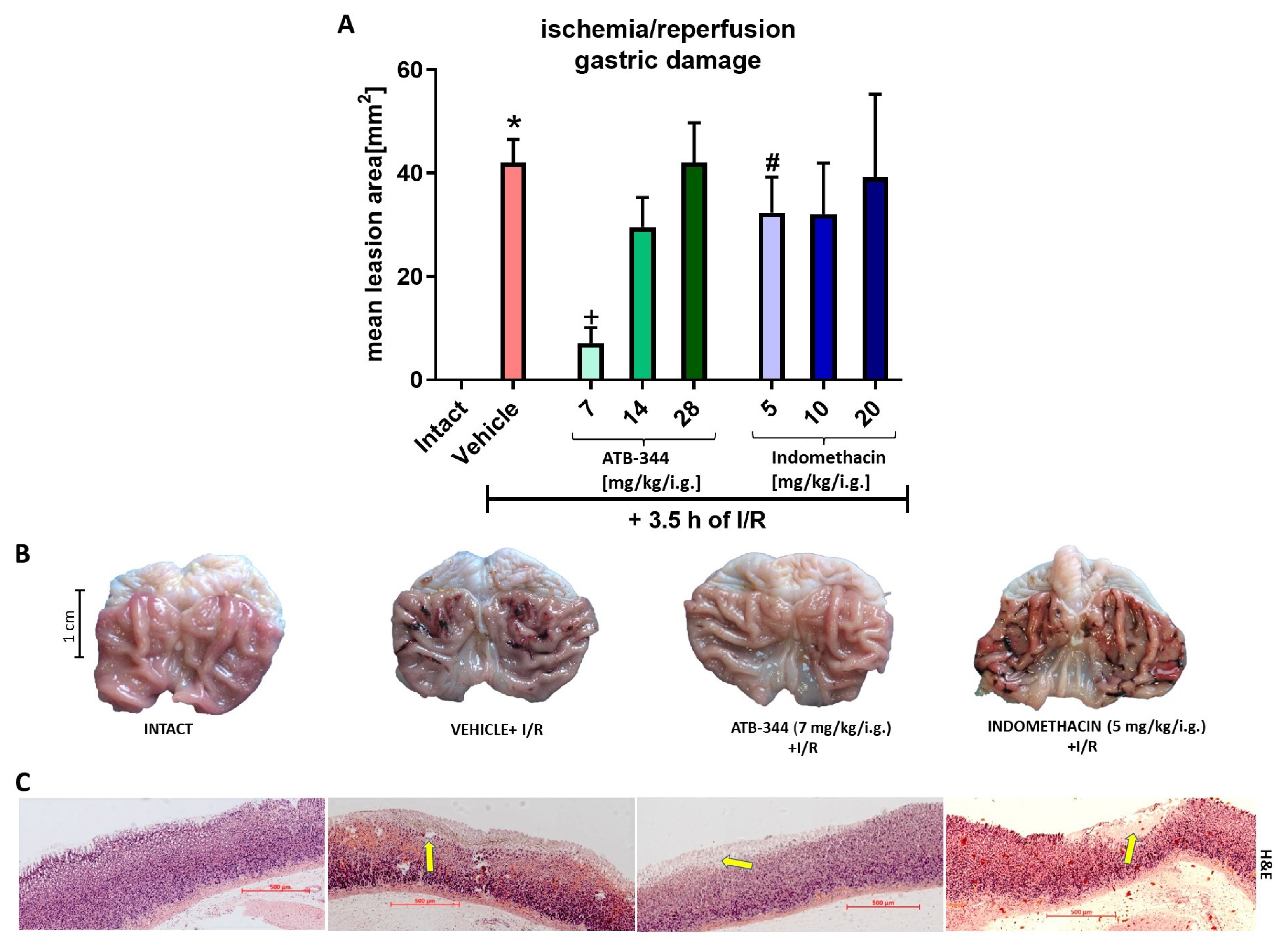
3. Results
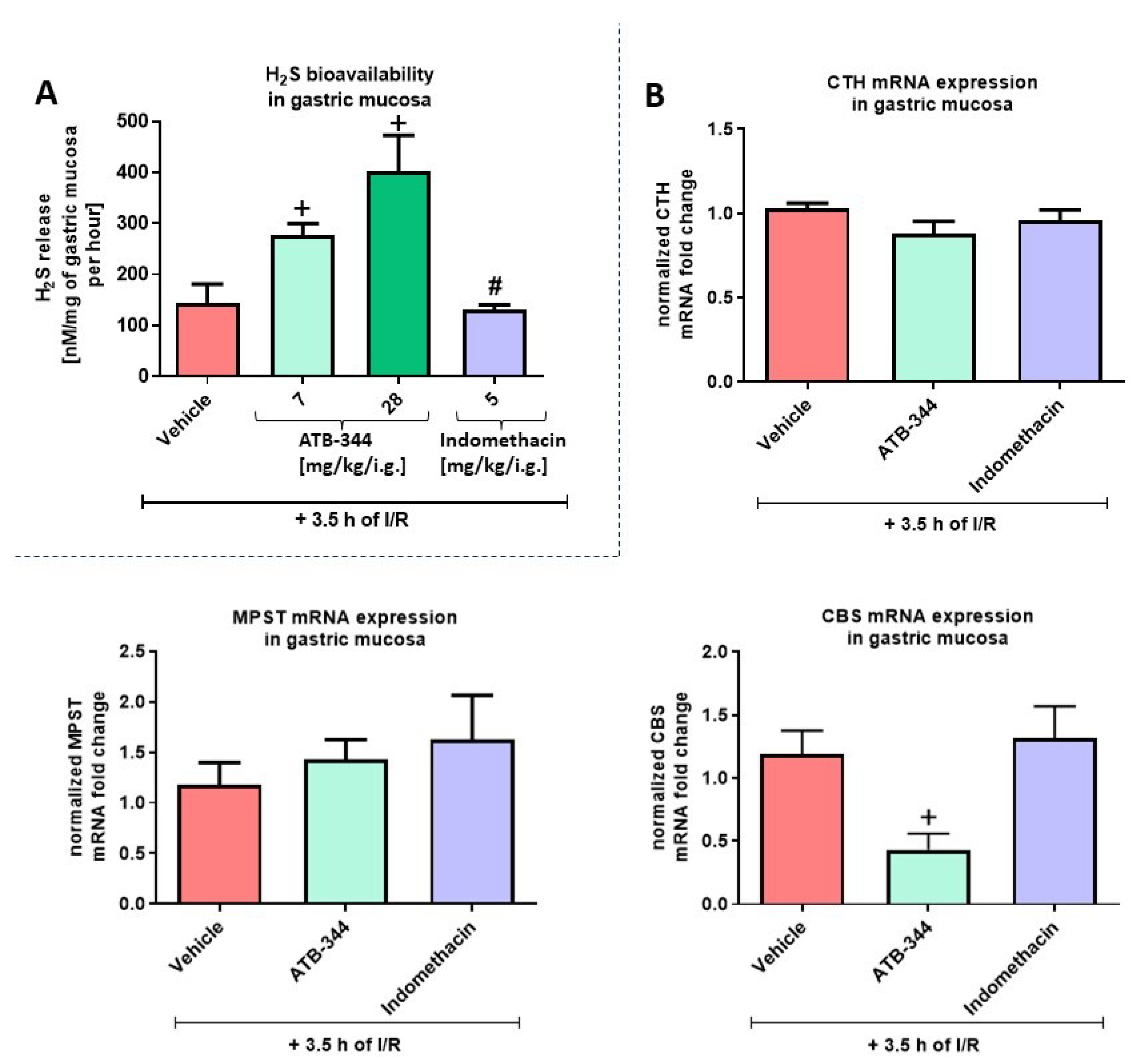
3.1. Dose-Dependent Impact of H2S-Releasing ATB-344 and Indomethacin on Gastric Mucosal Integrity and H2S Production in Gastric Mucosa under Oxidative Stress
3.2. Impact of H2S-Releasing ATB-344 and Indomethacin on Gastric Mucosal and Serum PGE2 Concentration and Gastric Mucosal mRNA Expression of COX-1 and COX-2
3.3. Gastric Mucosal Oxidation- and Hypoxia-Sensitive Markers
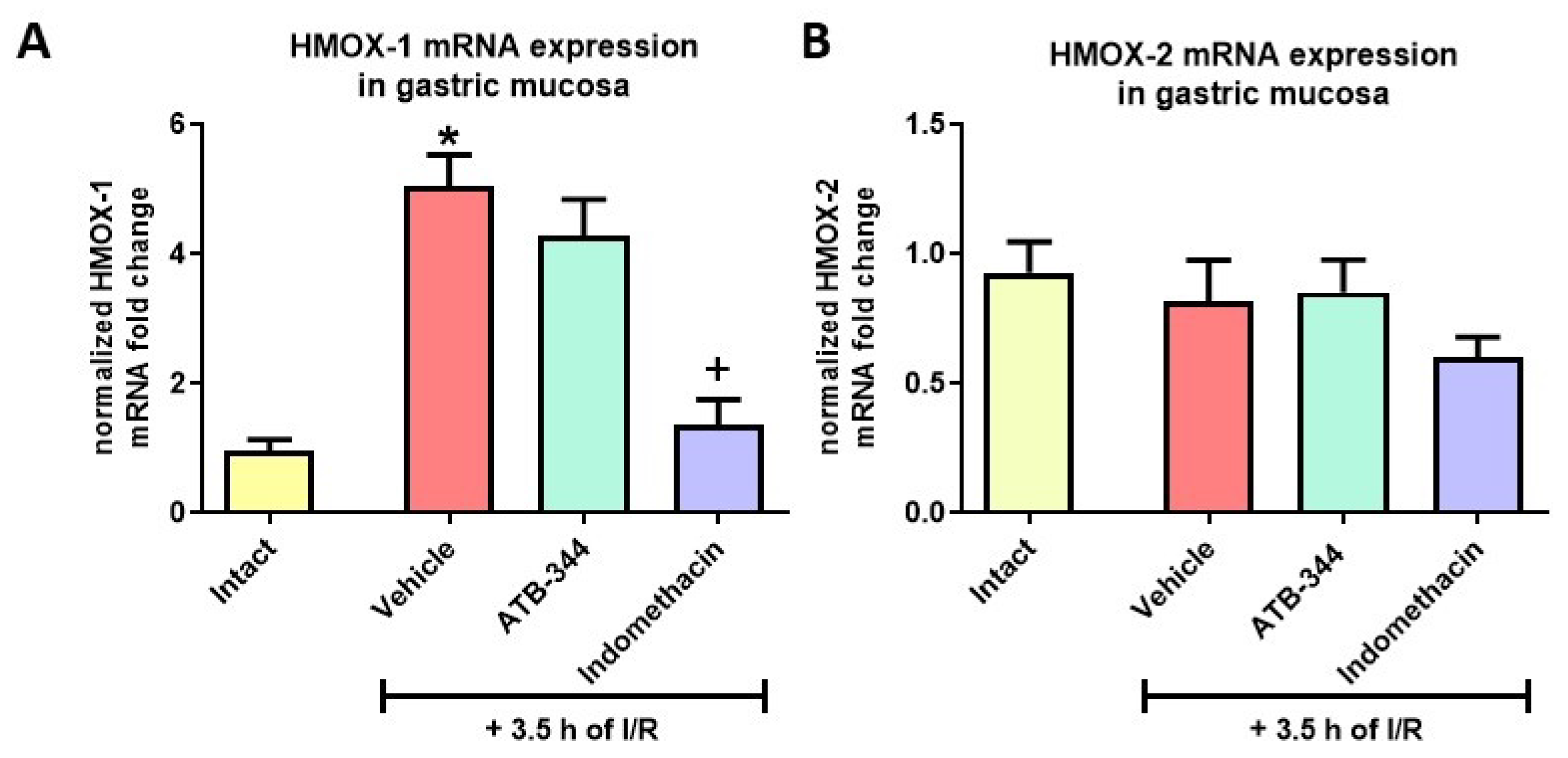
3.4. Heme Oxygenase-1 as the Inducible Anti-Oxidative Marker of Gastric Mucosal Redox Imbalance and Inflammation
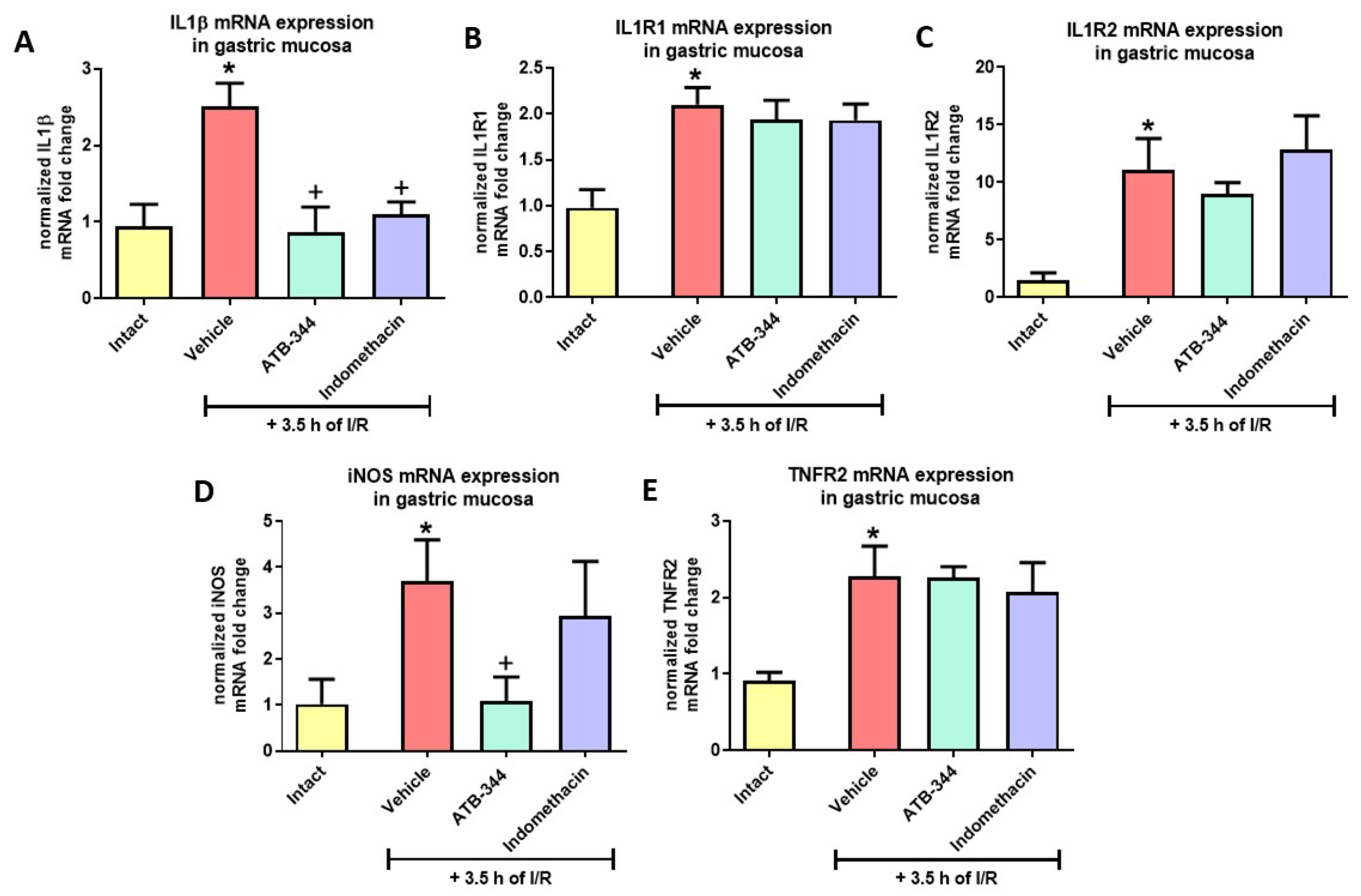
3.5. Gastric Mucosal Markers of I/R-Related Inflammation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nalamachu, S.; Wortmann, R. Role of indomethacin in acute pain and inflammation management: A review of the literature. Postgrad. Med. 2014, 126, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Martínez, M.D.; Moreno-Ajona, D.; Chan, C.; Goadsby, P.J. Indomethacin-responsive headaches—A narrative review. Headache 2021, 61, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleyman, H.; Albayrak, A.; Bilici, M.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z. Different mechanisms in formation and prevention of indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers. Inflammation 2010, 33, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashmawy, N.E.; Khedr, E.G.; El-Bahrawy, H.A.; Selim, H.M. Nebivolol prevents indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats. J. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 13, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Gaddam, R.R. Hydrogen Sulfide in Inflammation: A Novel Mediator and Therapeutic Target. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, B.; Wallace, J.L. Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective properties of hydrogen sulfide. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R. H2S and polysulfide metabolism: Conventional and unconventional pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ding, L.; Xie, Z.Z.; Yang, Y.; Whiteman, M.; Moore, P.K.; Bian, J.S. A Review of Hydrogen Sulfide Synthesis, Metabolism, and Measurement: Is Modulation of Hydrogen Sulfide a Novel Therapeutic for Cancer? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.V.; Wallace, J.L. Hydrogen sulfide-based therapeutics and gastrointestinal diseases: Translating physiology to treatments. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G467–G473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pajdo, R.; Ginter, G.; Kwiecien, S.; Brzozowski, T. Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Protects Gastric Mucosa against the Formation and Time-Dependent Development of Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lesions Progressing into Deeper Ulcerations. Molecules 2017, 22, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Plays an Important Role Through Regulating Autophagy in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 681676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xue, M.; Ji, A.; Li, Y. Role of hydrogen sulfide in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 186908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Qiao, W.; Liu, H.; Qi, Y.; Yan, C. Protective effect of endogenous hydrogen sulfide against oxidative stress in gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyrukluyildiz, U.; Delen, L.A.; Onk, D.; Yazici, G.N.; Gulaboglu, M.; Suleyman, H. The effect of dexmedetomidine on gastric ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Biochemical and histopathological evaluation. Acta Cir. Bras. 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; DeLeo, C.J. RNA damage and surveillance under oxidative stress. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen Sulfide and Cellular Redox Homeostasis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6043038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsello, T.; Komaravelli, N.; Casola, A. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magierowska, K.; Korbut, E.; Wójcik-Grzybek, D.; Bakalarz, D.; Sliwowski, Z.; Cieszkowski, J.; Szetela, M.; Torregrossa, R.; Whiteman, M.; Magierowski, M. Mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide donors versus acute oxidative gastric mucosal injury. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielak, A.; Wallace, J.L.; Brzozowski, T.; Magierowski, M. Gaseous Mediators as a Key Molecular Targets for the Development of Gastrointestinal-Safe Anti-Inflammatory Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 657457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Caliendo, G.; Santagada, V.; Cirino, G. Markedly reduced toxicity of a hydrogen sulphide-releasing derivative of naproxen (ATB-346). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Nagy, P.; Feener, T.D.; Allain, T.; Ditrói, T.; Vaughan, D.J.; Muscara, M.N.; de Nucci, G.; Buret, A.G. A proof-of-concept, Phase 2 clinical trial of the gastrointestinal safety of a hydrogen sulfide-releasing anti-inflammatory drug. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, W.; Blackler, R.W.; Flannigan, K.L.; Wallace, J.L. Enhanced chemopreventive effects of a hydrogen sulfide-releasing anti-inflammatory drug (ATB-346) in experimental colorectal cancer. Nitric Oxide 2014, 41, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacka, U.; Magierowska, K.; Wójcik, D.; Hankus, J.; Szetela, M.; Cieszkowski, J.; Korbut, E.; Danielak, A.; Surmiak, M.; Chmura, A.; et al. Microbiome Profile and Molecular Pathways Alterations in Gastrointestinal Tract by Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (ATB-352): Insight into Possible Safer Polypharmacy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, R.; Björne, H.; Omoto, Y.; Siemiatkowska, A.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Lindblad, M.; Holm, L. Sex differences and effects of oestrogen in rat gastric mucosal defence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Drozdowicz, D.; Kwiecieñ, S.; Pajdo, R.; Bielanski, W.; Hahn, E.G. Role of gastric acid secretion in progression of acute gastric erosions induced by ischemia-reperfusion into gastric ulcers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 398, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Ginter, G.; Pajdo, R.; Chmura, A.; Kwiecien, S.; Brzozowski, T. Carbon monoxide released from its pharmacological donor, tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer, accelerates the healing of pre-existing gastric ulcers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalarz, D.; Surmiak, M.; Yang, X.; Wójcik, D.; Korbut, E.; Śliwowski, Z.; Ginter, G.; Buszewicz, G.; Brzozowski, T.; Cieszkowski, J.; et al. Organic carbon monoxide prodrug, BW-CO-111, in protection against chemically-induced gastric mucosal damage. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 456–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, K.L.; Agbor, T.A.; Blackler, R.W.; Kim, J.J.; Khan, W.I.; Verdu, E.F.; Ferraz, G.J.P.; Wallace, J.L. Impaired hydrogen sulfide synthesis and IL-10 signaling underlie hyperhomocysteinemia-associated exacerbation of colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13559–13564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannigan, K.L.; Agbor, T.A.; Motta, J.P.; Ferraz, J.G.; Wang, R.; Buret, A.G.; Wallace, J.L. Proresolution effects of hydrogen sulfide during colitis are mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Dicay, M.; McKnight, W.; Martin, G.R. Hydrogen sulfide enhances ulcer healing in rats. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 4070–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, K.L.; Ferraz, J.G.P.; Wang, R.; Wallace, J.L. Enhanced Synthesis and Diminished Degradation of Hydrogen Sulfide in Experimental Colitis: A Site-Specific, Pro-Resolution Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magierowska, K.; Korbut, E.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Surmiak, M.; Chmura, A.; Bakalarz, D.; Buszewicz, G.; Wójcik, D.; Śliwowski, Z.; Ginter, G.; et al. Oxidative gastric mucosal damage induced by ischemia/reperfusion and the mechanisms of its prevention by carbon monoxide-releasing tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S: A Novel Gasotransmitter that Signals by Sulfhydration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, J.; Kouroussis, E.; Kohl, J.B.; Paul, B.D.; Carroll, K.S.; Filipovic Correspondence, M.R. Selective Persulfide Detection Reveals Evolutionarily Conserved Antiaging Effects of S-Sulfhydration. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1152–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibli, S.I.; Hu, J.; Looso, M.; Weigert, A.; Ratiu, C.; Wittig, J.; Drekolia, M.K.; Tombor, L.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Leisegang, M.S.; et al. Mapping the Endothelial Cell S-Sulfhydrome Highlights the Crucial Role of Integrin Sulfhydration in Vascular Function. Circulation 2021, 143, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovinazzo, D.; Bursac, B.; Sbodio, J.I.; Nalluru, S.; Vignane, T.; Snowman, A.M.; Albacarys, L.M.; Sedlak, T.W.; Torregrossa, R.; Whiteman, M.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide is neuroprotective in Alzheimer’s disease by sulfhydrating GSK3β and inhibiting Tau hyperphosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017225118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouda, A.; Valakos, D.; Dionellis, V.S.; Bibli, S.I.; Akoumianakis, I.; Karaliota, S.; Zuhra, K.; Fleming, I.; Nagahara, N.; Havaki, S.; et al. MPST sulfurtransferase maintains mitochondrial protein import and cellular bioenergetics to attenuate obesity. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Sliwowski, Z.; Drozdowicz, D.; Stachura, J.; Pajdo, R.; Hahn, E.G. Role of prostaglandins generated by cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in healing of ischemia–reperfusion-induced gastric lesions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 385, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Shimokawa, O.; Kaneko, T.; Nagano, Y.; Rai, K.; Hyodo, I. The pathophysiology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced mucosal injuries in stomach and small intestine. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K. Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhao, C.S.; Shen, M.F.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. The role of hydrogen sulfide in gastric mucosal damage. Med. Gas Res. 2019, 9, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedre, B.; Talwar, D.; Barayeu, U.; Schilling, D.; Luzarowski, M.; Sokolowski, M.; Glatt, S.; Dick, T.P. 3-Mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase is a protein persulfidase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domán, A.; Dóka, É.; Garai, D.; Bogdándi, V.; Balla, G.; Balla, J.; Nagy, P. Interactions of reactive sulfur species with metalloproteins. Redox Biol. 2023, 60, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, P.; Dóka, É.; Ida, T.; Akaike, T. Measuring Reactive Sulfur Species and Thiol Oxidation States: Challenges and Cautions in Relation to Alkylation-Based Protocols. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic, M.R.; Zivanovic, J.; Alvarez, B.; Banerjee, R. Chemical Biology of H2S Signaling through Persulfidation. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1253–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, D.; Ditrói, T.; Barayeu, U.; Jurányi, P.; Nagy, P.; Dick, T.P. The influence of alkylating agents on sulfur-sulfur bonds in per-and polysulfides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 2023, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Sbodio, J.I.; Xu, R.; Vandiver, M.S.; Cha, J.Y.; Snowman, A.M.; Snyder, S.H. Cystathionine γ-lyase deficiency mediates neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. Nature 2014, 508, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.S.; Rodrigues, L.d.O.C.P.; Martins, V.; Petrosino, M.; Zuhra, K.; Ascenção, K.; Anand, A.; Abdel-Kader, R.M.; Gad, M.Z.; Bourquin, C.; et al. Role of Cystathionine β-Synthase and 3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase in the Regulation of Proliferation, Migration, and Bioenergetics of Murine Breast Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagaki, T.; Lozano-Montes, L.; Janickova, L.; Zuhra, K.; Szabo, M.P.; Majtan, T.; Rainer, G.; Maréchal, D.; Herault, Y.; Szabo, C. Overproduction of hydrogen sulfide, generated by cystathionine β-synthase, disrupts brain wave patterns and contributes to neurobehavioral dysfunction in a rat model of down syndrome. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, S.; Goeller, M.; Baar, W.; Wollborn, J.; Buerkle, H.; Schlunck, G.; Lagrèze, W.; Goebel, U.; Ulbrich, F. Hydrogen Sulfide Reduces Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Neuronal Cells in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Surmiak, M.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Kwiecien, S.; Wallace, J.L.; Brzozowski, T. The effect of hydrogen sulfide-releasing naproxen (ATB-346) versus naproxen on formation of stress-induced gastric lesions, the regulation of systemic inflammation, hypoxia and alterations in gastric microcirculation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy, L.; Carr, D.F.; Pirmohamed, M. Pharmacogenomics of NSAID-Induced Upper Gastrointestinal Toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Fan, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Positive acceleration adaptive training attenuates gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury through COX-2 and PGE2 expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.N.; Kvietys, P.R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 524–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapca, O.E.; Borekci, B.; Suleyman, H. Ischemia-Reperfusion Damage. Eurasian J. Med. 2013, 45, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapalidis, K.; Papavramidis, T.S.; Gialamas, E.; Deligiannidis, N.; Tzioufa, V.; Papavramidis, S. The role of allopurinol’s timing in the ischemia reperfusion injury of small intestine. J. Emergencies Trauma Shock 2013, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peglow, S.; Toledo, A.H.; Anaya-Prado, R.; Lopez-Neblina, F.; Toledo-Pereyra, L.H. Allopurinol and xanthine oxidase inhibition in liver ischemia reperfusion. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2011, 18, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, S.; Tsekhmistrenko, S.; Polishchuk, V.; Tsekhmistrenko, O.; Zdorovtseva, L.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Kazimierz, T.; Yulia, I.; Taras, H. Status of prooxidant and antioxidant systems in the sperm and seminal plasma of breeding boars of large white breed and SS23 synthetic line. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 73, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.X.; Wu, Z.Z.; Liao, X.Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Lin, J.D. Remifentanil reduces multiple organ and energy metabolism disturbances in a rat sepsis model. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 73, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.M.; Melovn, S. SOD2 in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, E. SOD2 overexpression in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, F.R.; He, C.; Danes, J.M.; Paviani, V.; Coelho, D.R.; Gantner, B.N.; Bonini, M.G. Mitochondrial Superoxide Dismutase: What the Established, the Intriguing, and the Novel Reveal About a Key Cellular Redox Switch. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, C.; Fontana, S. Hypoxia and HIF Signaling: One Axis with Divergent Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)α: Its protein stability and biological functions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2004, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loor, G.; Schumacker, P.T. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor in cell survival during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Mailabaram, R.P.; Al-Jaidi, B.; Saadh, M.J. Molecular Basis of Binding Interactions of NSAIDs and Computer-Aided Drug Design Approaches in the Pursuit of the Development of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Selective Inhibitors. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflamm. Drugs 2017, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, B.; Tan, R.; Öngüt, G.; Nimet Izgüt-Uysal, V. Expressions of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Gastric Ischemia-Reperfusion: Role of Angiotensin II. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 161, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mard, S.A.; Nikraftar, Z.; Farbood, Y.; Mansouri, E. A preliminary study of the anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of crocin against gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martemucci, G.; Costagliola, C.; Mariano, M.; D’andrea, L.; Napolitano, P.; D’Alessandro, A.G. Free Radical Properties, Source and Targets, Antioxidant Consumption and Health. Oxygen 2022, 2, 48–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Iadecola, C. iNOS and COX-2 in ischemic stroke. In Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology: Acute Ischemic Injury and Repair in the Nervous System; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.K.; Patel, N.S.A.; Sivarajah, A.; Kvale, E.O.; Dugo, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Brown, P.A.J.; Stewart, K.N.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Britti, D.; et al. GW274150, a potent and highly selective inhibitor of iNOS reduces experimental renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisen, W.P.; Evans, W.R.; Sure, V.N.; Sperling, J.A.; Sakamuri, S.S.; Mostany, R.; Katakam, P.V. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor is an effective therapy for ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. FASEB J. 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Cao, H.J. The protective effect of high heme oxygenase-1 expression induced by propofol on the alveolar ii type epithelial cells of rats with acute lung injury induced by oleic acid. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 72, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyller, J.; Bil-Lula, I. Heat Shock Proteins in Oxidative Stress and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Benefits from Physical Exercises: A Review to the Current Knowledge. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6678457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Maulik, N.; Ho, Y.S.; Alam, J.; Das, D.K. Hmox-1 constitutes an adaptive response to effect antioxidant cardioprotection: A study with transgenic mice heterozygous for targeted disruption of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. Circulation 2001, 103, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Adamski, J.; Bakalarz, D.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pajdo, R.; Kwiecien, S.; Brzozowski, T. Interaction between endogenous carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide in the mechanism of gastroprotection against acute aspirin-induced gastric damage. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 114, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Głowacka, U.; Magierowski, M.; Śliwowski, Z.; Cieszkowski, J.; Szetela, M.; Wójcik-Grzybek, D.; Chmura, A.; Brzozowski, T.; Wallace, J.L.; Magierowska, K. Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Indomethacin-Derivative (ATB-344) Prevents the Development of Oxidative Gastric Mucosal Injuries. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081545
Głowacka U, Magierowski M, Śliwowski Z, Cieszkowski J, Szetela M, Wójcik-Grzybek D, Chmura A, Brzozowski T, Wallace JL, Magierowska K. Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Indomethacin-Derivative (ATB-344) Prevents the Development of Oxidative Gastric Mucosal Injuries. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(8):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081545
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłowacka, Urszula, Marcin Magierowski, Zbigniew Śliwowski, Jakub Cieszkowski, Małgorzata Szetela, Dagmara Wójcik-Grzybek, Anna Chmura, Tomasz Brzozowski, John L. Wallace, and Katarzyna Magierowska. 2023. "Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Indomethacin-Derivative (ATB-344) Prevents the Development of Oxidative Gastric Mucosal Injuries" Antioxidants 12, no. 8: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081545
APA StyleGłowacka, U., Magierowski, M., Śliwowski, Z., Cieszkowski, J., Szetela, M., Wójcik-Grzybek, D., Chmura, A., Brzozowski, T., Wallace, J. L., & Magierowska, K. (2023). Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Indomethacin-Derivative (ATB-344) Prevents the Development of Oxidative Gastric Mucosal Injuries. Antioxidants, 12(8), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081545








