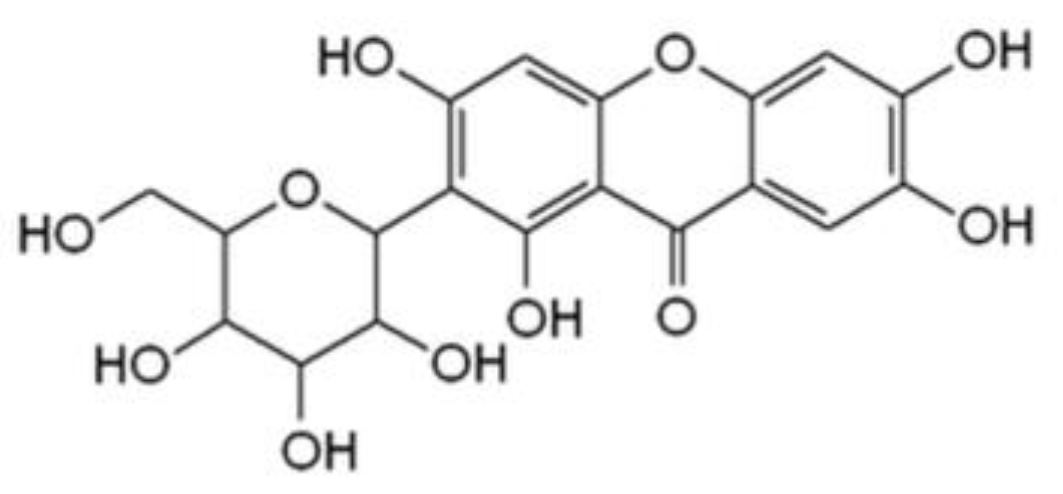
Mangiferin Affects Melanin Synthesis by an Influence on Tyrosinase: Inhibition, Mechanism of Action and Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
2.3. Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
2.4. Molecular Docking: Methods and Materials
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
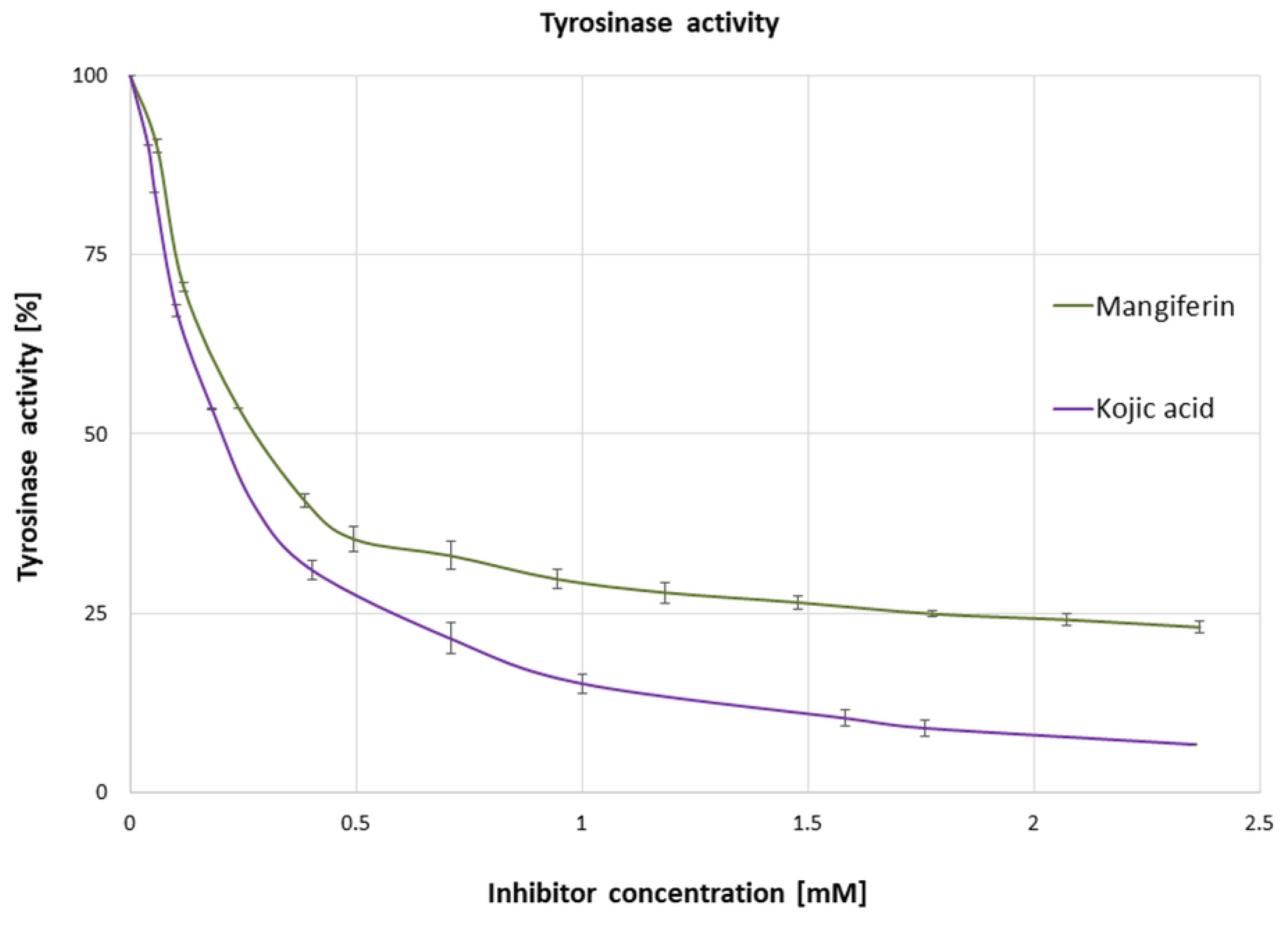
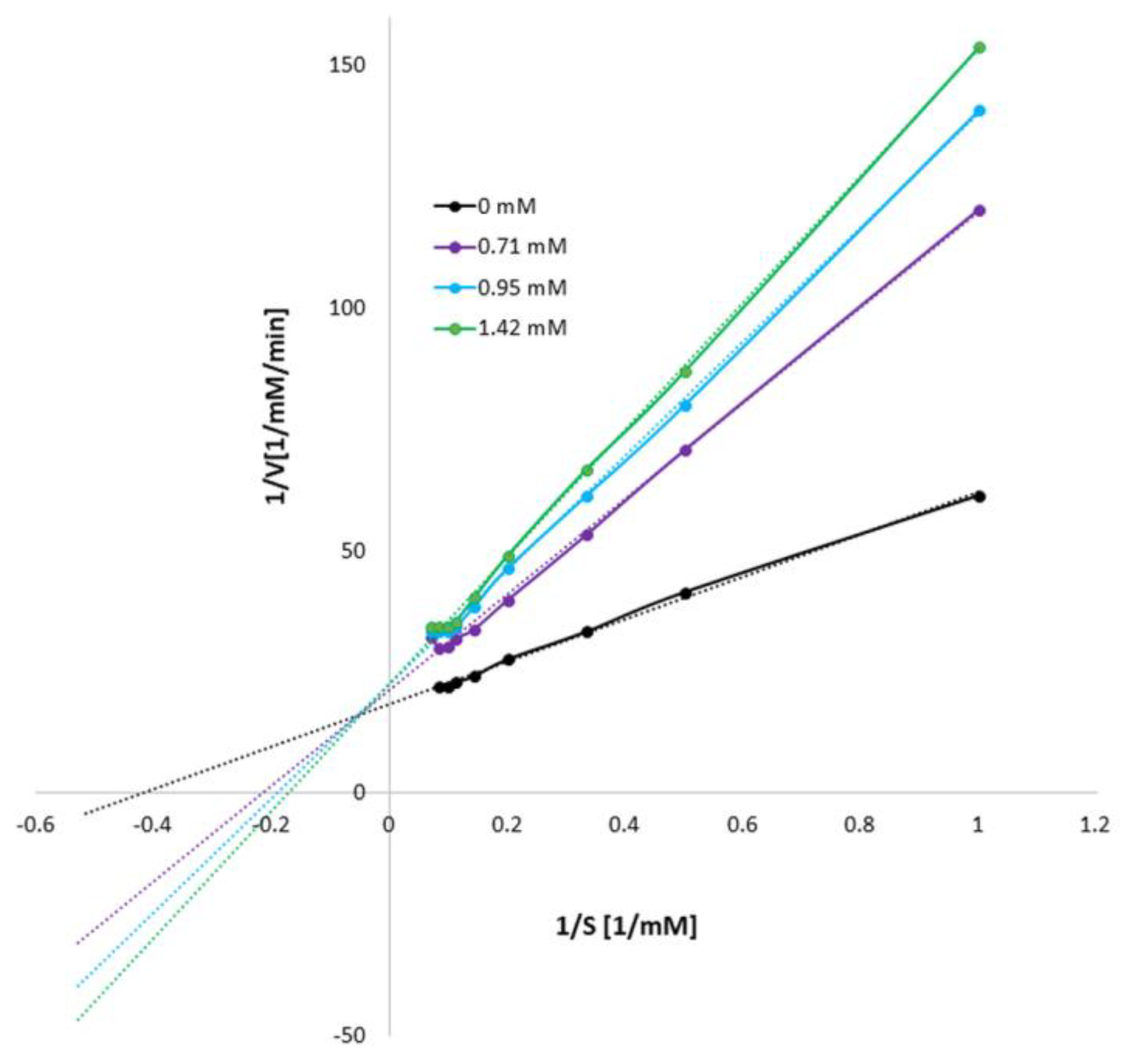
3.1. Influence of Mangiferin on Tyrosinase Activity
3.2. Results of Capillary Electrophoresis
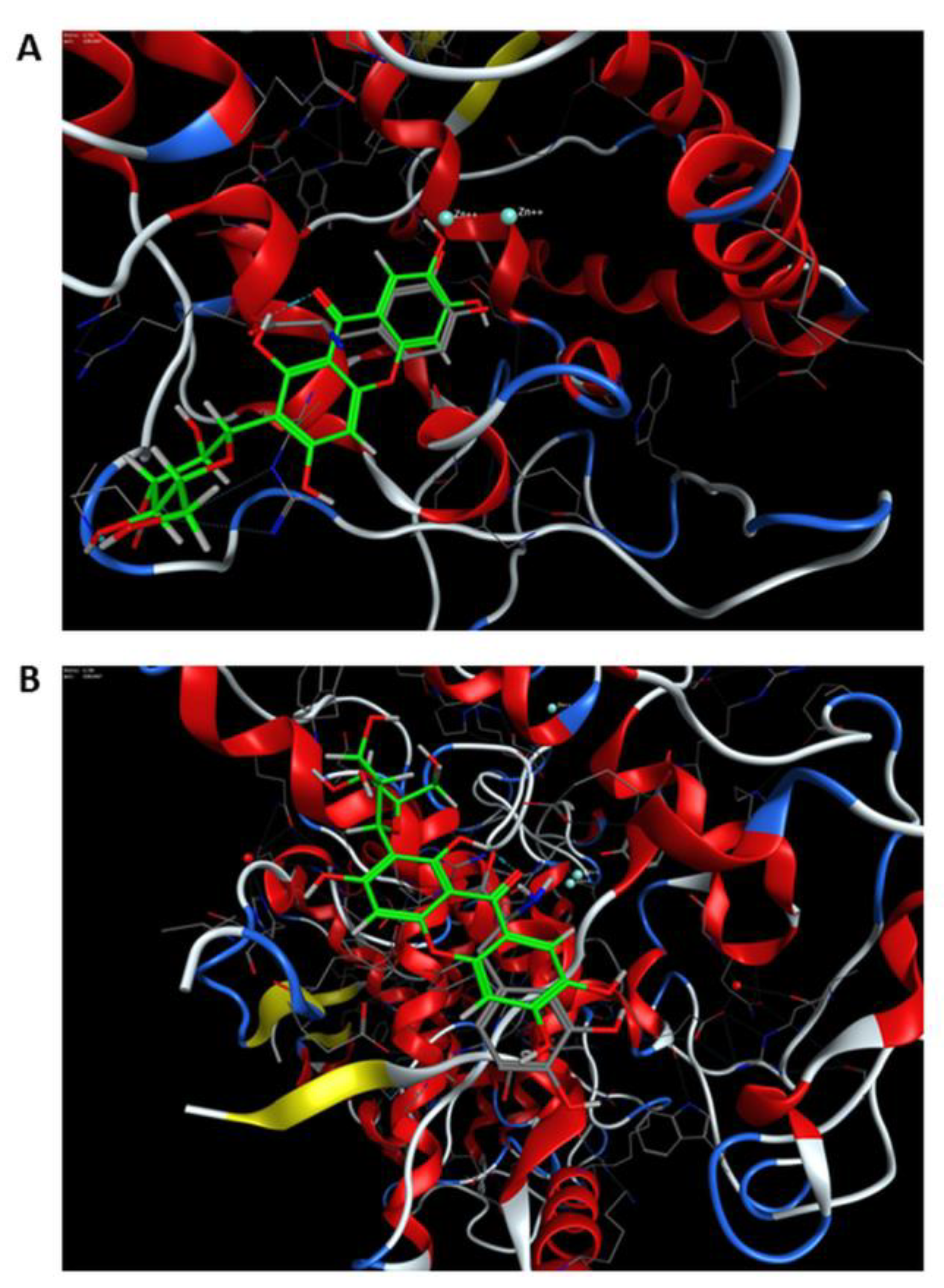
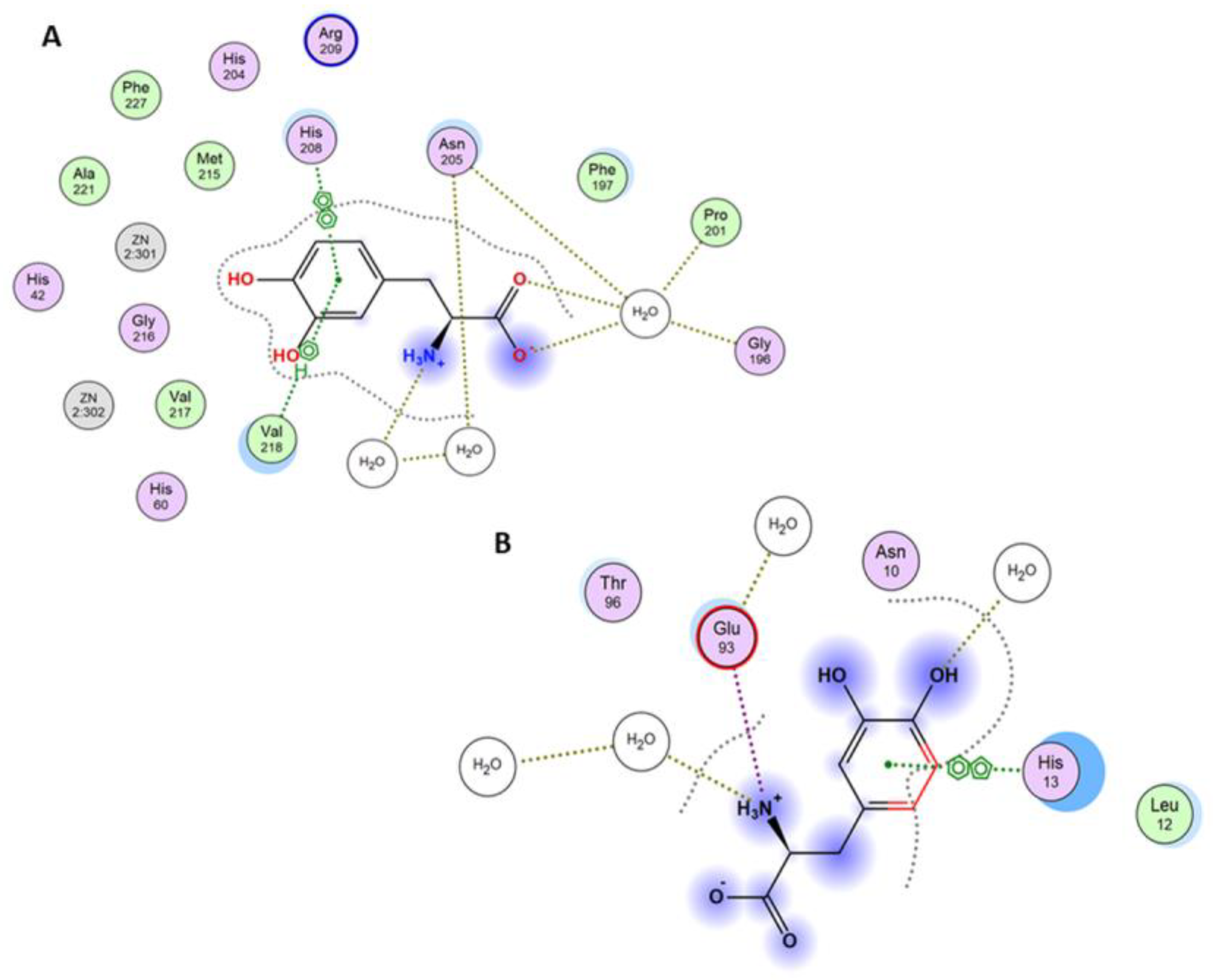
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopp, W. How western diet and lifestyle drive the pandemic of obesity and civilization diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, W.; Baj, J.; Maciejewski, R. Antioxidants: Classification, natural sources, activity/capacity measurements, and usefulness for the synthesis of nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meccariello, R.; D’Angelo, S. Impact of polyphenolic-food on longevity: An elixir of life. An overview. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masibo, M.; He, Q. Major mango polyphenols and their potential significance to human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lou, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Wu, Y. A rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic method for quantitative analysis of antidiabetic active components in Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizomes. Chromatographia 2005, 61, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nysschen, A.M.; Van Wyk, B.E.; Van Heerden, F.; Schutte, A.L. The major phenolic compounds in the leaves of Cyclopia species (Honeybush tea). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1996, 24, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisuthisakul, P.; Gordon, M.H. Antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of Mango seed kernel by product. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanov, G.M.; Nedialkov, P.T. Mangiferin and isomangiferin in some Hypericum species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1998, 26, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotshna, K.P.; Shanker, K. Mangiferin: A review of sources and interventions for biological activities. Biofactors 2016, 42, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Sadhukhan, P.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin: A xanthonoid with multipotent anti-inflammatory potential. Biofactors 2016, 42, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.T.; Wang, Z.Z.; Yuan, Y.H.; Sun, H.M.; Chen, N.H.; Zhang, Y. Mangiferin: A multipotent natural product preventing neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease models. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochocka, R.; Hering, A.; Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Cal, K.; Barańska, H. The effect of mangiferin on skin: Penetration, permeation and inhibition of ECM enzymes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Rajendran, P.; Jayakumar, T.; Nishigaki, I.; Ekambaram, G.; Nishigaki, Y.; Vetriselvi, J. Immunomodulatory Effect of Mangiferin in Experimental Animals with Benzo(a)Pyrene-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, R.; Ye, M.; Yin, X.; Wan, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of mangiferin on sepsis-induced lung injury in mice via up-regulation of heme oxygenase- 1. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Kamalraj, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Kandasamy, M. Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 12, 750109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeedi, F.J. Mangiferin protect oxidative stress against deoxynivalenol induced damages through Nrf2 signalling pathways in endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmaco.l Physiol. 2021, 48, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.R.; Gao, Y.D.; Ma, C.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Huang, C.G.; Huang, J.F.; Zheng, Y.T. Mangiferin, an anti-HIV-1 agent targeting protease and effective against resistant strains. Molecules 2011, 16, 4264–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, L.; García-Bueno, B.; Madrigal, J.L.; Leza, J.C. Mangiferin decreases inflammation and oxidative damage in rat brain after stress. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M. Growth Inhibitory Effect of Mangiferin on Thyroid Cancer Cell Line TPC1. Biotechnol. Bioproc. E 2018, 23, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, H.; Yang, L.; Li, P. Mangiferin inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is correlated with downregulation of B-cell lymphoma-2 and upregulation of microRNA-182. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Luo, Q.L. Optimizing mangiferin extraction from Mangifera indica L. peel and analyzing its antibacterial activity. J. South. Agric. 2014, 45, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Lu, R.; Cai, Q.; Fan, L.; Yan, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, L.; Cao, Y. Mangiferin enhances the antifungal activities of caspofungin by destroying polyamine accumulation. Virulence 2021, 12, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yi, L.; Tong, X.; Kang, L.; Pei, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ding, Y.; et al. Roles of inflammation factors in melanogenesis (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Cicoira, F.; Di Mauro, E.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Commo, S.; Galván, I.; Ghanem, G.; Kenzo, K.; Meredith, P.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: From pigment cells to human health and technological applications. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 520–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin Pigmentation in Mammalian Skin and Its Hormonal Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.C. Cosmetology and Skin Pharmacology; PZWL: Warsaw, Poland, 2007; pp. 156–163. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The Protective Role of Melanin Against UV Damage in Human Skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.A. Melanin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, G.; Bercovich, D. Melanin directly converts light for vertebrate metabolic use: Heuristic thoughts on birds, Icarus and dark human skin. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, H.; Tuczek, F. Tyrosinase/catecholoxidase activity of hemocyanins: Structural basis and molecular mechanism. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Uyama, H. Tyrosinase inhibitors from natural and synthetic sources: Structure, inhibition mechanism and perspective for the future. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M. Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: Going places? A review. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerya, O.; Ben-Arie, R.; Luzzatto, T.; Musa, R.; Khatib, S.; Vaya, J. Prevention of Agaricus bisporus postharvest browning with tyrosinase inhibitors. Postharv. Biol. Technol. 2006, 39, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.M.; Kwon, E.B.; Lee, B.; Kim, C.Y. Recent Trends in Controlling the Enzymatic Browning of Fruit and Vegetable Products. Molecules 2020, 25, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aguiar Cipriano, P.; Ekici, L.; Barnes, R.C.; Gomes, C.; Talcott, S.T. Pre-heating and polyphenol oxidase inhibition impact on extraction of purple sweet potato anthocyanins. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, E.; Gonzalez, J.; Peiró, J.; Oria, R.; Lopez-Buesa, P. Browning prevention by ascorbic acid and 4-hexylresorcinol: Different mechanisms of action on polyphenol oxidase in the presence and in the absence of substrates. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C464–C470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, A.; Kanbara, T.; Morinobu, N. Inhibition of mushroom-tyrosinase by aloe extract. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.; Kubo, I. Kinetics of mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4108–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfeder, M.; Kanteev, M.; Isaschar-Ovdat, S.; Adir, N.; Fishman, A. Determination of tyrosinase substrate-binding modes reveals mechanistic differences between type-3 copper proteins. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Dziubakiewicz, E. Electromigration Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.H.; Avila, L.Z.; Biebuyck, H.A. Whitesides GM. Use of Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis To Measure Binding Constants of Ligands to Proteins. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 2915–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszewski, R.; Hering, A.; Marszałł, M.; Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Bartoszewska, S.; Kapoor, N.; Kochan, K.; Ochocka, J.R. Mangiferin has an additive effect on the apoptotic properties of hesperidin in Cyclopia sp. tea extracts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Tong, L.; Zhang, T. Improving permeability and oral absorption of mangiferin by phospholipid complexation. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, A.; Ochocka, J.R.; Baranska, H.; Cal, K.; Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J. Mangiferin and Hesperidin Transdermal Distribution and Permeability through the Skin from Solutions and Honeybush Extracts (Cyclopia sp.)-A Comparison Ex Vivo Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hering, A.; Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Dziomba, S.; Halasa, R.; Krzemieniecki, R.; Sappati, S.; Baginski, M.; Ochocka, J.R. Mangiferin Affects Melanin Synthesis by an Influence on Tyrosinase: Inhibition, Mechanism of Action and Molecular Docking Studies. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12051016
Hering A, Stefanowicz-Hajduk J, Dziomba S, Halasa R, Krzemieniecki R, Sappati S, Baginski M, Ochocka JR. Mangiferin Affects Melanin Synthesis by an Influence on Tyrosinase: Inhibition, Mechanism of Action and Molecular Docking Studies. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(5):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12051016
Chicago/Turabian StyleHering, Anna, Justyna Stefanowicz-Hajduk, Szymon Dziomba, Rafal Halasa, Radoslaw Krzemieniecki, Subrahmanyam Sappati, Maciej Baginski, and Jadwiga Renata Ochocka. 2023. "Mangiferin Affects Melanin Synthesis by an Influence on Tyrosinase: Inhibition, Mechanism of Action and Molecular Docking Studies" Antioxidants 12, no. 5: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12051016
APA StyleHering, A., Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J., Dziomba, S., Halasa, R., Krzemieniecki, R., Sappati, S., Baginski, M., & Ochocka, J. R. (2023). Mangiferin Affects Melanin Synthesis by an Influence on Tyrosinase: Inhibition, Mechanism of Action and Molecular Docking Studies. Antioxidants, 12(5), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12051016








