Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Collection and Analysis
- FeNO as a predictor of a good response to a specific biologic drug.
- FeNO modifications in severe asthmatic patients treated with biologic drug
- FeNO as a predictor of exacerbations and/or biomarker of asthma control in patients treated with biologic drugs.
3. Findings
3.1. FeNO as a Predictor of a Good Response
3.1.1. Omalizumab
3.1.2. Mepolizumab/Benralizumab/Reslizumab
3.1.3. Dupilumab
3.1.4. Tralokinumab/Lebrikizumab
3.1.5. Tezepelumab
3.2. FeNO Modifications in Severe Asthmatic Patients Treated with Biologic Drug
3.2.1. Omalizumab
3.2.2. Mepolizumab/Benralizumab
3.2.3. Dupilumab
3.2.4. Tralokinumab/Lebrikizumab
3.2.5. Tezepelumab
3.3. FeNO as a Predictor of Exacerbations and/or Biomarker of Asthma Control in Patients Treated with Biologic Drugs
3.3.1. Omalizumab
3.3.2. Mepolizumab/Benralizumab
3.3.3. Dupilumab
3.3.4. Tralokinumab/Lebrikizumab
3.3.5. Tezepelumab
| Author | Type | Study Population | Target | Drug | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hanania et al., 2013 [6] | RCT | 850 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Frix et al., 2020 [7] | Observational retrospective | 157 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Kavati et al., 2019 [8] | Observational retrospective | 473 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Brooks et al., 2019 [9] | Observational prospective | NR | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Solidoro et al., 2019 [10] | Observational retrospective | 34 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Mansur et al., 2017 [11] | Observational retrospective | 45 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Kurokawa et al., 2020 [12] | Observational prospective | 16 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Bhutani et al., 2017 [13] | Observational prospective | 99 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Y. Li et al., 2022 [14] | Meta-analysis | NR | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Casale et al., 2019 [15] | Observational prospective | 806 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of exacerbation during treatment |
| Hoch et al., 2017 [16] | RCT | 486 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Prediction of response |
| Pavord et al., 2012 [17] | RCT | 621 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Prediction of response |
| Castro et al., 2014 [18] | RCT | 324 | Eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Prediction of response |
| McDowell et al., 2021 [20] | Observational prospective | 145 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Prediction of response; Prediction of exacerbation during treatment |
| Yamada et al., 2021 [21] | Observational retrospective | 64 | Eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Hearn et al., 2021 [22] | Observational retrospective | 229 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab Benralizumab | Prediction of response; Prediction of exacerbation during treatment |
| Watanabe et al., 2022 [23] | Observational retrospective | 24 | Severe type 2 asthma | Benralizumab | Prediction of response |
| Castro et al., 2018 [24] | RCT | 1902 | Uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response |
| Shrimanker et al., 2019 [25] | Post hoc analysis | 606 + 1902 | Eosinophilic asthma | Dupilumab Mepolizumab | Prediction of response |
| Rabe et al., 2018 [26] | RCT | 210 | Glucocorticoid dependent severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Pavord et al., 2020 [27] | Post hoc analysis | 1037 | Uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Carpagnano et al., 2022 [28] | Observational retrospective | 12 | Uncontrolled severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Yang et al., 2020 [29] | Meta-analysis | 2992 | Uncontrolled asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response |
| Rabe et al., 2022 [30] | Post hoc analysis | 1902 | Moderate-to-severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response |
| Campisi et al., 2021 [31] | Observational retrospective | 18 | Moderate-to-severe asthma | Dupilumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Panettieri et al., 2018 [32] | RCT | 1140 + 770 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma | Tralokinumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Corren et al., 2011 [33] | RCT | 219 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma | Lebrikizumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Corren et al., 2017 [34] | RCT | 550 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma with noneosinophilic inflammation | Tezepelumab | Variations during treatment |
| Menzies-Gow et al., 2021 [35] | RCT | 1061 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma | Tezepelumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Corren et al., 2022 [36] | RCT | 550 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma | Tezepelumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
| Cabrejos et al., 2020 [37] | Observational retrospective | 345 | Severe persistent allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Zietkowski et al., 2011 [38] | Clinical trial * | 19 | Severe persistent allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Silkoff et al., 2004 [39] | RCT | 29 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Zietkowski et al., 2011 [40] | Clinical trial * | 19 | Severe persistent allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Johansson et al., 2018 [41] | Observational prospective | 32 | Allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Ledford et al., 2017 [42] | RCT | 176 | Moderate-to-severe asthma receiving omalizumab | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment; Prediction of exacerbation during treatment |
| Pasha et al., 2014 [43] | RCT | 42 | Uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma | Omalizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Haldar et al., 2009 [48] | RCT | 61 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Li et al., 2021 [49] | Meta-analysis | 1457 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Kayser et al., 2021 [50] | Observational retrospective | 123 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Sposato et al., 2020 [51] | Observational retrospective | 134 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Caminati et al., 2019 [52] | Observational retrospective | 69 | Eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Carpagnano et al., 2021 [53] | Observational retrospective | 33 | Severe eosinophilic allergic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Cameli et al., 2020 [54] | Observational retrospective | 27 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Izumo et al., 2020 [55] | Observational prospective | 26 | Severe asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Farah et al., 2019 [56] | Observational prospective | 20 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Kobayashi et al., 2021 [57] | Observational prospective | 20 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Ramonell et al., 2021 [58] | Observational retrospective | 47 | Adult-onset severe asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Kalinauskaite Zukauske et al., 2019 [59] | Observational prospective | 9 | Severe non-allergic eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Crimi et al., 2021 [60] | Observational retrospective | 32 | Bronchiectasis + severe eosinophilic asthma | Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Pelletier et al., 2022 [61] | Observational retrospective | 13 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab Mepolizumab | Variations during treatment; Prediction of exacerbation during treatment |
| Padilla Galo et al., 2020 [62] | Observational prospective | 42 | Refractory eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Pelaia et al., 2021 [63] | Observational prospective | 111 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Matsuno et al., 2020 [64] | Observational retrospective | 17 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Numata et al., 2020 [65] | Observational retrospective | 24 | Severe eosinophilic asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Bagnasco et al., 2020 [66] | Observational retrospective | 59 | Severe uncontrolled asthma | Benralizumab | Variations during treatment |
| Russell et al., 2018 [69] | RCT | 224 | Moderate-to-severe asthma | Tralokinumab | Variations during treatment |
| Emson et al., 2021 [70] | Post hoc analysis | 550 | Severe, uncontrolled asthma | Tezepelumab | Prediction of response; Variations during treatment |
4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusive Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Initiative for Asthma, Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention 2022. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/GINA-Main-Report-2022-FINAL-22-07-01-WMS.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS Guidelines on Definition, Evaluation and Treatment of Severe Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselle, G.G.; Koppelman, G.H. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrasch, S.; Linde, K.; Rücker, G.; Sommer, H.; Karsch-Völk, M.; Kleijnen, J.; Jörres, R.A.; Schneider, A. Accuracy of FENO for Diagnosing Asthma: A Systematic Review. Thorax 2017, 72, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE 2017Asthma: Diagnosis, Monitoring and Chronic Asthma Management. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng80/resources/asthma-diagnosis-monitoring-and-chronic-asthma-management-pdf-1837687975621 (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Hanania, N.A.; Wenzel, S.; Rosén, K.; Hsieh, H.-J.; Mosesova, S.; Choy, D.F.; Lal, P.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Busse, W. Exploring the Effects of Omalizumab in Allergic Asthma: An Analysis of Biomarkers in the EXTRA Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frix, A.N.; Schleich, F.; Paulus, V.; Guissard, F.; Henket, M.; Louis, R. Effectiveness of Omalizumab on Patient Reported Outcomes, Lung Function, and Inflammatory Markers in Severe Allergic Asthma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 179, 113944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavati, A.; Zhdanava, M.; Ortiz, B.; Lecocq, J.; Schiffman, B.; Pilon, D.; Ho, H.; Lefebvre, P.; Stone, B. Retrospective Study on the Association of Biomarkers with Real-World Outcomes of Omalizumab-Treated Patients with Allergic Asthma. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 1956–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, E.A.; Massanari, M.; Hanania, N.A.; Weiner, D.J. Cost-Effectiveness of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) Measurement in Predicting Response to Omalizumab in Asthma. Clin. Outcomes Res. CEOR 2019, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solidoro, P.; Patrucco, F.; de Blasio, F.; Brussino, L.; Bellocchia, M.; Dassetto, D.; Pivetta, E.; Riccio, A.; Heffler, E.; Canonica, W.; et al. Predictors of Reversible Airway Obstruction with Omalizumab in Severe Asthma: A Real-Life Study. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13, 1753466619841274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.H.; Srivastava, S.; Mitchell, V.; Sullivan, J.; Kasujee, I. Longterm Clinical Outcomes of Omalizumab Therapy in Severe Allergic Asthma: Study of Efficacy and Safety. Respir. Med. 2017, 124, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Koya, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Hayashi, M.; Sakagami, T.; Ishioka, K.; Gon, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kikuchi, T. Association of Upper and Lower Airway Eosinophilic Inflammation with Response to Omalizumab in Patients with Severe Asthma. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2020, 57, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, M.; Yang, W.H.; Hébert, J.; de Takacsy, F.; Stril, J.-L. The Real World Effect of Omalizumab Add on Therapy for Patients with Moderate to Severe Allergic Asthma: The ASTERIX Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Q.; Lu, Y. Predictive Biomarkers for Response to Omalizumab in Patients with Severe Allergic Asthma: A Meta-Analysis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, T.B.; Luskin, A.T.; Busse, W.; Zeiger, R.S.; Trzaskoma, B.; Yang, M.; Griffin, N.M.; Chipps, B.E. Omalizumab Effectiveness by Biomarker Status in Patients with Asthma: Evidence from PROSPERO, a Prospective Real-World Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 156–164.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, H.E.; Calatroni, A.; West, J.B.; Liu, A.H.; Gergen, P.J.; Gruchalla, R.S.; Khurana Hershey, G.K.; Kercsmar, C.M.; Kim, H.; Lamm, C.I.; et al. Can We Predict Fall Asthma Exacerbations? Validation of the Seasonal Asthma Exacerbation Index. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1130–1137.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for Severe Eosinophilic Asthma (DREAM): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Wenzel, S.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Pizzichini, E.; Kuna, P.; Busse, W.W.; Gossage, D.L.; Ward, C.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Benralizumab, an Anti-Interleukin 5 Receptor α Monoclonal Antibody, versus Placebo for Uncontrolled Eosinophilic Asthma: A Phase 2b Randomised Dose-Ranging Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, H.G.; Liu, M.C.; Pavord, I.D.; Brusselle, G.G.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chetta, A.; Humbert, M.; Katz, L.E.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Mepolizumab Treatment in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, P.J.; Diver, S.; Yang, F.; Borg, C.; Busby, J.; Brown, V.; Shrimanker, R.; Cox, C.; Brightling, C.E.; Chaudhuri, R.; et al. The Inflammatory Profile of Exacerbations in Patients with Severe Refractory Eosinophilic Asthma Receiving Mepolizumab (the MEX Study): A Prospective Observational Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Nakajima, M.; Matsuyama, M.; Morishima, Y.; Arai, N.; Hida, N.; Nakaizumi, T.; Masuko, H.; Yatagai, Y.; Saito, T.; et al. Identification of Distinct Phenotypes Related to Benralizumab Responsiveness in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.P.; Kavanagh, J.; d’Ancona, G.; Roxas, C.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Fernandes, M.; Kent, B.D.; Dhariwal, J.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. The Relationship between Feno and Effectiveness of Mepolizumab and Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2093–2096.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Shirai, T.; Hirai, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Nakayasu, H.; Tamura, K.; Masuda, T.; Takahashi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kishimoto, Y.; et al. Blood Eosinophil Count and FeNO to Predict Benralizumab Effectiveness in Real-Life Severe Asthma Patients. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2022, 59, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Busse, W.W.; Ford, L.; Sher, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimanker, R.; Keene, O.; Hynes, G.; Wenzel, S.; Yancey, S.; Pavord, I.D. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Blood Eosinophil Count, Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide, and Their Combination in Severe Asthma: A Post Hoc Analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Nair, P.; Brusselle, G.; Maspero, J.F.; Castro, M.; Sher, L.; Zhu, H.; Hamilton, J.D.; Swanson, B.N.; Khan, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Glucocorticoid-Dependent Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Siddiqui, S.; Papi, A.; Corren, J.; Sher, L.D.; Bardin, P.; Langton, D.; Park, H.-S.; Rice, M.S.; Deniz, Y.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy in Patients Stratified by Baseline Treatment Intensity and Lung Function. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Scioscia, G.; Buonamico, E.; Lacedonia, D.; Diaferia, F.; Capozza, E.; Lepore, G.; Resta, O.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P. Early Effectiveness of Type-2 Severe Asthma Treatment with Dupilumab in a Real-Life Setting; a FeNO-Driven Choice That Leads to Winning Management. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2022, 17, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Huang, T.; Liu, B.; Du, Z.; Liu, C. Dupilumab in Patients with Uncontrolled Asthma: Type 2 Biomarkers Might Be Predictors of Therapeutic Efficacy. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2020, 57, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, K.F.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Castro, M.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.F.; Busse, W.W.; Izuhara, K.; Daizadeh, N.; Ortiz, B.; et al. Dupilumab Is Effective in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled GINA-Defined Type 2 Asthma Irrespective of an Allergic Asthma Phenotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, R.; Crimi, C.; Nolasco, S.; Beghè, B.; Antonicelli, L.; Guarnieri, G.; Scichilone, N.; Porto, M.; Macchia, L.; Scioscia, G.; et al. Real-World Experience with Dupilumab in Severe Asthma: One-Year Data from an Italian Named Patient Program. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, R.A.; Sjöbring, U.; Péterffy, A.; Wessman, P.; Bowen, K.; Piper, E.; Colice, G.; Brightling, C.E. Tralokinumab for Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma (STRATOS 1 and STRATOS 2): Two Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Lemanske, R.F.; Hanania, N.A.; Korenblat, P.E.; Parsey, M.V.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Scheerens, H.; Wu, L.C.; Su, Z.; et al. Lebrikizumab Treatment in Adults with Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Parnes, J.R.; Wang, L.; Mo, M.; Roseti, S.L.; Griffiths, J.M.; van der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab in Adults with Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Pham, T.-H.; Garcia Gil, E.; Sałapa, K.; Ren, P.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M. Baseline Type 2 Biomarker Levels and Response to Tezepelumab in Severe Asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrejos, S.; Moreira, A.; Ramirez, A.; Quirce, S.; Soto Campos, G.; Dávila, I.; Campo, P. FENOMA Study: Achieving Full Control in Patients with Severe Allergic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietkowski, Z.; Skiepko, R.; Tomasiak-Lozowska, M.M.; Lenczewska, D.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A. RANTES in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Patients with Severe Persistent Allergic Asthma during Omalizumab Therapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 154, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkoff, P.E.; Romero, F.A.; Gupta, N.; Townley, R.G.; Milgrom, H. Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma Receiving Xolair (Omalizumab), a Monoclonal Anti-Immunoglobulin E Antibody. Pediatrics 2004, 113, e308–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietkowski, Z.; Skiepko, R.; Tomasiak-Lozowska, M.M.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A. Airway Inflammation and Eotaxin in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Patients with Severe Persistent Allergic Asthma during Omalizumab Therapy. Adv. Med. Sci. 2011, 56, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.G.O.; Lilja, G.; Hallberg, J.; Nopp, A. A Clinical Follow-up of Omalizumab in Routine Treatment of Allergic Asthma Monitored by CD-Sens. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2018, 6, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, D.; Busse, W.; Trzaskoma, B.; Omachi, T.A.; Rosén, K.; Chipps, B.E.; Luskin, A.T.; Solari, P.G. A Randomized Multicenter Study Evaluating Xolair Persistence of Response after Long-Term Therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 162–169.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasha, M.A.; Jourd’heuil, D.; Jourd’heuil, F.; Mahon, L.; Romero, F.; Feustel, P.J.; Evans, M.; Smith, T.; Mitchell, J.; Gendapodi, P.; et al. The Effect of Omalizumab on Small Airway Inflammation as Measured by Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Moderate-to-Severe Asthmatic Patients. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014, 35, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Leyko, B.; Frieri, M. Effects of Omalizumab and Budesonide on Markers of Inflammation in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 95, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.; Smith, N.; Massanari, M.; Jimenez, P. Effects of Omalizumab on Markers of Inflammation in Patients with Allergic Asthma. Allergy 2009, 64, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noga, O.; Hanf, G.; Kunkel, G. Immunological and Clinical Changes in Allergic Asthmatics Following Treatment with Omalizumab. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 131, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellitto, A.; De Fanis, U.; Balestrieri, A.; Savoia, A.; Astarita, C.; Romano, C. Effects of Omalizumab Treatment on Serum Cytokine Concentrations of Atopic Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: A Preliminary Report. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, P.; Brightling, C.E.; Hargadon, B.; Gupta, S.; Monteiro, W.; Sousa, A.; Marshall, R.P.; Bradding, P.; Green, R.H.; Wardlaw, A.J.; et al. Mepolizumab and Exacerbations of Refractory Eosinophilic Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J. Real-World Effectiveness of Mepolizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, e192–e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, M.Z.; Drick, N.; Milger, K.; Fuge, J.; Kneidinger, N.; Korn, S.; Buhl, R.; Behr, J.; Welte, T.; Suhling, H. Real-World Multicenter Experience with Mepolizumab and Benralizumab in the Treatment of Uncontrolled Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Over 12 Months. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposato, B.; Camiciottoli, G.; Bacci, E.; Scalese, M.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Pelaia, C.; Santus, P.; Maniscalco, M.; Masieri, S.; Corsico, A.; et al. Mepolizumab Effectiveness on Small Airway Obstruction, Corticosteroid Sparing and Maintenance Therapy Step-down in Real Life. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 61, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminati, M.; Cegolon, L.; Vianello, A.; Chieco Bianchi, F.; Festi, G.; Marchi, M.R.; Micheletto, C.; Mazza, F.; Tognella, S.; Senna, G. Mepolizumab for Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Real-World Snapshot on Clinical Markers and Timing of Response. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Resta, E.; Povero, M.; Pelaia, C.; D’Amato, M.; Crimi, N.; Scichilone, N.; Scioscia, G.; Resta, O.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Clinical and Economic Consequences of Switching from Omalizumab to Mepolizumab in Uncontrolled Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, P.; Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Perruzza, M.; Cekorja, B.; Perillo, F.; Massa, E.; Ruzza, A.; Fossi, A.; Beltrami, V.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Mepolizumab Effectiveness in a Real-Life Setting. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, T.; Tone, M.; Kuse, N.; Awano, N.; Tanaka, A.; Jo, T.; Yoshimura, H.; Minami, J.; Takada, K.; Inomata, M. Effectiveness and Safety of Benralizumab for Severe Asthma in Clinical Practice (J-BEST): A Prospective Study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S.; Badal, T.; Reed, N.; Rogers, P.G.; King, G.G.; Thamrin, C.; Peters, M.J.; Seccombe, L.M. Mepolizumab Improves Small Airway Function in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Respir. Med. 2019, 148, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nagase, H.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanaka, A.; Fukunaga, K.; Atsuta, R.; Tagaya, E.; Hojo, M.; Gon, Y.; et al. Mepolizumab Decreased the Levels of Serum Galectin-10 and Eosinophil Cationic Protein in Asthma. Asia Pac. Allergy 2021, 11, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonell, R.P.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Levy, J.M.; Kuruvilla, M. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements Are Not Influenced by Anti-Eosinophil Therapy in Patients with Asthma: A Retrospective Analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinauskaite-Zukauske, V.; Januskevicius, A.; Janulaityte, I.; Miliauskas, S.; Malakauskas, K. Serum Levels of Epithelial-Derived Cytokines as Interleukin-25 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin after a Single Dose of Mepolizumab in Patients with Severe Non-Allergic Eosinophilic Asthma: A Short Report. Can. Respir. J. 2019, 2019, 8607657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimi, C.; Campisi, R.; Nolasco, S.; Cacopardo, G.; Intravaia, R.; Porto, M.; Impellizzeri, P.; Pelaia, C.; Crimi, N. Mepolizumab Effectiveness in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma and Co-Presence of Bronchiectasis: A Real-World Retrospective Pilot Study. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, G.; Godbout, K.; Boulay, M.-È.; Boulet, L.-P.; Morissette, M.C.; Côté, A. Increase in FeNO Levels Following IL5/IL5R-Targeting Therapies in Severe Asthma: A Case Series. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Galo, A.; Levy-Abitbol, R.; Olveira, C.; Valencia Azcona, B.; Pérez Morales, M.; Rivas-Ruiz, F.; Tortajada-Goitia, B.; Moya-Carmona, I.; Levy-Naon, A. Real-Life Experience with Benralizumab during 6 Months. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Benfante, A.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Calabrese, C.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Ciotta, D.; D’Amato, M.; Macchia, L.; Nolasco, S.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Benralizumab Assessed in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: Real-Life Evaluation Correlated with Allergic and Non-Allergic Phenotype Expression. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, O.; Minamoto, S. Rapid Effect of Benralizumab for Severe Asthma with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 64, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Miyagawa, H.; Nishioka, S.; Okuda, K.; Utsumi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Minagawa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Hara, H.; Araya, J.; et al. Efficacy of Benralizumab for Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Retrospective, Real-Life Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Brussino, L.; Bonavia, M.; Calzolari, E.; Caminati, M.; Caruso, C.; D’Amato, M.; De Ferrari, L.; Di Marco, F.; Imeri, G.; et al. Efficacy of Benralizumab in Severe Asthma in Real Life and Focus on Nasal Polyposis. Respir. Med. 2020, 171, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brøgger, P.; Blom, L.H.; Simonsen, S.; Thyssen, J.P.; Skov, L. Antagonism of the Interleukin 4 Receptor α Promotes TH 1-Signalling among T Cells from Patients with Atopic Dermatitis after Stimulation. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 91, e12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, D.S.; van der Wal, M.M.; Heeb, L.E.M.; Giovannone, B.; Asamoah, M.; Delemarre, E.M.; Drylewicz, J.; Nierkens, S.; Boyman, O.; de Bruin-Weller, M.S.; et al. Early and Long-Term Effects of Dupilumab Treatment on Circulating T-Cell Functions in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1943–1953.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.J.; Chachi, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Backer, V.; Olivenstein, R.; Titlestad, I.L.; Ulrik, C.S.; Harrison, T.; Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, R.; et al. Effect of Tralokinumab, an Interleukin-13 Neutralising Monoclonal Antibody, on Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in Uncontrolled Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (MESOS): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emson, C.; Corren, J.; Sałapa, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G. Efficacy of Tezepelumab in Patients with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma with and without Nasal Polyposis: A Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase 2b PATHWAY Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
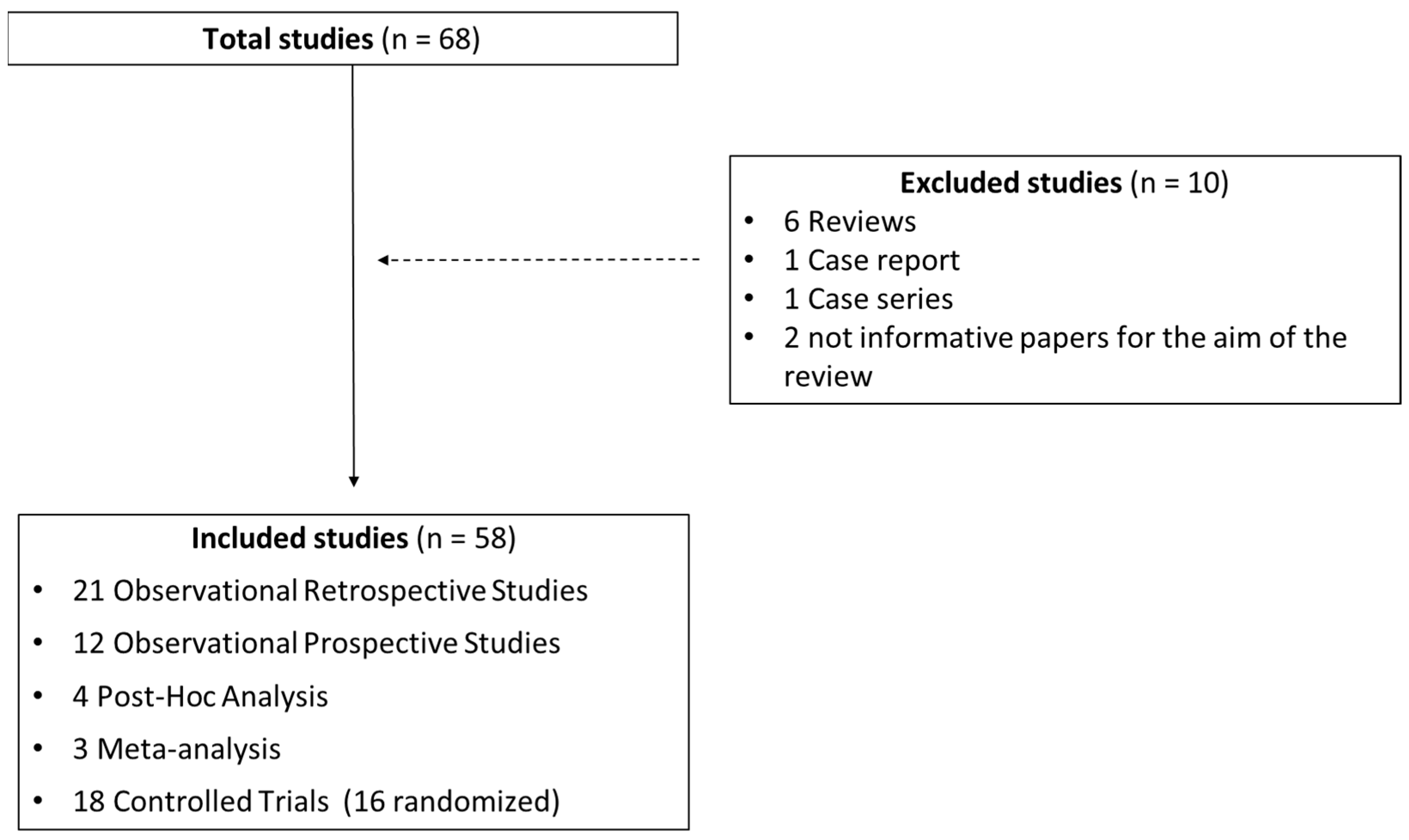

| Total Studies 68 | Excluded Studies | 10 | Included Studies | 58 |
| Case report | 1 | Observational retrospective studies | 21 | |
| Reviews | 6 | Observational prospective studies | 12 | |
| Case series | 1 | Post hoc analysis | 4 | |
| Not informative papers for the aim of the review | 2 | Meta-analysis | 3 | |
| Controlled trials (16 randomized) | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pianigiani, T.; Alderighi, L.; Meocci, M.; Messina, M.; Perea, B.; Luzzi, S.; Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Refini, R.M.; Bargagli, E.; et al. Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020400
Pianigiani T, Alderighi L, Meocci M, Messina M, Perea B, Luzzi S, Bergantini L, D’Alessandro M, Refini RM, Bargagli E, et al. Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(2):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020400
Chicago/Turabian StylePianigiani, Tommaso, Lorenzo Alderighi, Martina Meocci, Maddalena Messina, Beatrice Perea, Simona Luzzi, Laura Bergantini, Miriana D’Alessandro, Rosa Metella Refini, Elena Bargagli, and et al. 2023. "Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review" Antioxidants 12, no. 2: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020400
APA StylePianigiani, T., Alderighi, L., Meocci, M., Messina, M., Perea, B., Luzzi, S., Bergantini, L., D’Alessandro, M., Refini, R. M., Bargagli, E., & Cameli, P. (2023). Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants, 12(2), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020400









