Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antiviral Metabolites Generated from Algae against SARS-CoV-2
2.1. Phycocyanobilins Antiviral Chromospheres against SARS-CoV-2
2.2. Antiviral Therapies Based on Algal Glycan against SARS-CoV-2
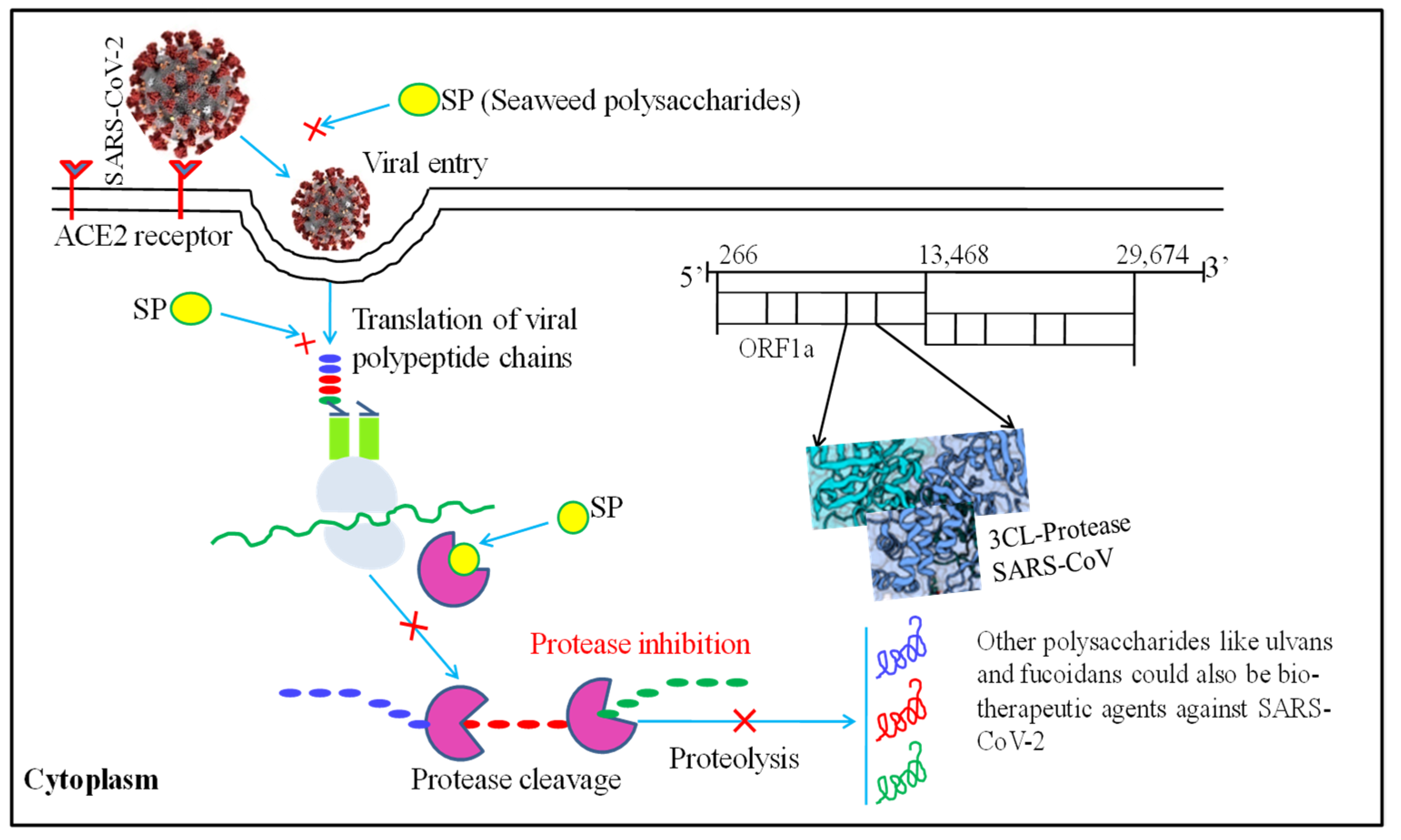
2.3. Antiviral Therapies Based on Algal Sulfated Polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2
2.4. Algal Polyphenols as Antiviral Therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2
2.5. Antioxidant Potential of Algal Metabolites and Therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, E.D.; Wright, G.D. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 2016, 529, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, P.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pandey, K.D.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, H. Biotechnological aspects of plants metabolites in the treatment of ulcer: A new perspective. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 18, e00256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Huang, J.W.; Chen, Y.C. Chinese herbal medicine network and core treatments for allergic skin diseases: Implications from a nationwide database. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, V.K.; Rai, A.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Shukla, L.; Kesawat, M.S.; Kumar Jaiswal, A.; Chung, S.-M.; et al. Potential Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis Activity of Plant Secondary Metabolites: Insight with Molecular Docking Interactions. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, H.P.; Irchhaiya, D.R.; Vermas, D.A. Review on some medicinal plants with antidiabetic activity. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2016, 6, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannes, W.A.; Marzouk, B. Research progress of Tunisian medicinal plants used for acute diabetes. J. Acute. Dis. 2016, 5, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucher, H.W.; Ambrose, P.G.; Chambers, H.F.; Ebright, R.H.; Jezek, A.; Murray, B.E.; Newland, J.G.; Ostrowsky, B.; Rex, J.H. White paper: Developing antimicrobial drugs for resistant pathogens, narrow-spectrum indications, and unmet needs. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, Y.W.; Balunas, M.J.; Chai, H.B.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug discovery from natural sources. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E239–E253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhowmick, S.; Mazumdar, A.; Mallick, A.; Adam, V. Algal metabolites: An inevitable substitute for antibiotics. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Silva, S.A.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Gullón, P.; Barroso, M.F.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Macroalgae as a Source of Valuable Antimicrobial Compounds: Extraction and Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N. A comprehensive review on medicinal plants as antimicrobial therapeutics: Potential avenues of biocompatible drug discovery. Metabolites 2019, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelrahman, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Comparative review of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and influenza a respiratory viruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leflaive, J.P.; Ten-Hage, L.O.Ï.C. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gamal, A.A. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suleria, H.A.R.; Globe, G.; Masci, P.; Osborne, S.A. Marine bioactive compounds and health-promoting perspectives; innovation pathways for drug discovery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Xu, J.L.; Wang, Z. Microalgae Biotechnology for Food, Health and High Value Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Belghit, I.; Ranger, J.D.; Heesch, S.; Biancarosa, I.; Liland, N.; Torstensen, B.; Waagbø, R.; Lock, E.J.; Bruckner, C.G. In-depth metabolic profiling of marine macroalgae confirms strong biochemical differences between brown, red and green algae. Algal Res. 2017, 26, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Rohit, M.V.; Chiranjeevi, P.; Chandra, R.; Navaneeth, B. Heterotrophic microalgae cultivation to synergize biodiesel production with waste remediation: Progress and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, G.E.; Acién, F.F.G.; García, C.F.; Chisti, Y. Photobioreactors: Light regime, mass transfer, and scaleup. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-García, O.; Escalante, F.; de Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Heterotrophic culture of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products. Water Res. 2011, 45, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez-Rocha, F.J.; Palma-Ramírez, D.; García-Alamilla, P.; López-Hernández, J.F.; Santiago-Morales, I.S.; Flores-Vela, A.I. Microalgae Cultivation for Secondary Metabolite Production. In Microalgae: From Physiology to Application; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, T.; Ramos, D.; García-Beltrán, T.; Brito-Bazan, M.; Galindo, E. Mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae: An alternative to produce high-value metabolites. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mondo, A.; Smerilli, A.; Sané, E.; Sansone, C.; Brunet, C. Challenging microalgal vitamins for human health. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Hayashi, K.; Maeda, M.; Kojima, I. Calcium spirulina, an inhibitor of enveloped virus replication, from a blue-green alga Spirulina platensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekiyo, K.; Lee, J.-B.; Hayashi, K.; Takenaka, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Endo, S.; Hayashi, T. Isolation of an antiviral polysaccharide, nostoflan, from a terrestrial cyanobacterium, Nostoc flagelliforme. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, M.R.; Gustafson, K.R.; McMahon, J.B.; Shoemaker, R.H.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mori, T.; Gulakowski, R.J.; Wu, L.; Rivera, M.I.; Laurent, C.M.; et al. Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: Potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, B.; Lerner, D.L.; Lusso, P.; Boyd, M.R.; Elder, J.H.; Berger, E.A. Multiple antiviral activities of cyanovirin-N: Blocking of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 interaction with CD4 and co-receptor and inhibition of diverse enveloped viruses. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4562–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Wheatley, A.K. Neutralizing Antibody Therapeutics for COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Bravo, C.; Torres-Carranza, D.; Sanchez-Trujillo, L.; Gómez-Lahoz, A.M.; Guijarro, L.G.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Asúnsolo, A.; Bujan, J.; et al. An Updated Review of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines and the Importance of Effective Vaccination Programs in Pandemic Times. Vaccines 2021, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Shabaan, M.T.; Hassan, L.; Morsi, H.H. Antiviral activity of algae biosynthesized silver and gold nanoparticles against Herpes Simplex (HSV-1) virus in vitro using cell-line culture technique. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 32, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.M.V.; Leite, J.P.G.; Ferreira, W.J.; Cavalcanti, D.N.; Villaça, R.C.; Giongo, V.; Teixeira, V.L.; Paixão, I.C.N.D.P. Marine natural seaweed products as potential antiviral drugs against bovine viral diarrhea virus. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, J.; Karthika, T.; Ajay, A.; Das, V.A.; Raj, V.S. Green tea and Spirulina extracts inhibit SARS, MERS, and SARS-2 spike pseudotyped virus entry in-vitro. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, N.; Malik, A.; Naik, S. Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae and its application in combating COVID-19: Mini review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 13, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Nagle, V.; Bhadra, B. COVID-19: Potential of microalgae derived natural astaxanthin as adjunctive supplement in alleviating cytokine storm. SSRN 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, F.E.; Sarath, G.P.; Neil, D.N.; Cross, S.S. Habitual, an unusual diterpene aldehyde from the marine alga Halimeda tuna. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, J.K.; Séron, K.; Labitt, R.N.; Danneels, A.; Palmer, K.E.; Whittaker, G.R.; Dubuisson, J.; Belouzard, S. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection is inhibited by Griffithsin. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Patra, S.; Bhuyan, P.P.; Dash, S.R.; Ki, J.S.; Adhikary, S.P.; Ragusa, A.; Jena, M. Cyanobacteria and Algae-Derived Bioactive Metabolites as Antiviral Agents: Evidence, Mode of Action, and Scope for Further Expansion; A Comprehensive Review in Light of the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 66–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Griffithsin, a highly potent broad-spectrum antiviral lectin from red algae: From discovery to clinical application. Marine Drugs 2019, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, L.; Critchley, A.T. The COVID 19 novel coronavirus pandemic 2020: Seaweeds to the rescue? Why does substantial, supporting research about the antiviral properties of seaweed polysaccharides seem to go unrecognized by the pharmaceutical community in these desperate times? J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 1875–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geahchan, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Rahman, M.A. The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Bilal, M.; Afroze, C.A.; Ahmed, M.; Iqbal, H.; Xu, J. Algae-derived bioactive molecules for the potential treatment of sars-cov-2. Molecules 2021, 26, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nova, P.; Pimenta-Martins, A.; Laranjeira Silva, J.; Silva, A.M.; Gomes, A.M.; Freitas, A.C. Health benefits and bioavailability of marine resources components that contribute to health—What’s new? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3680–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Gong, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Brennan, C.; Kulikouskaya, V. Beneficial effects of three brown seaweed polysaccharides on gut microbiota and their structural characteristics: An overview. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovic, T.H.; Ali, S.R.; Ibrahim, N.; Jessop, Z.M.; Tarassoli, S.P.; Dobbs, T.D.; Holford, P.; Thornton, C.A.; Whitaker, I.S. Could vitamins help in the fight against COVID-19? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroprese, M.; Ciliberti, M.G.; Albenzio, M. Immunological Activity of Marine Microalgae Extracts. Mar. Algae Extr. Process. Prod. Appl. 2015, 18, 395–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, F.J.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Schroeder, D.; Ngoi, S.M.; Tran, M.; McDonald, D.; Jiang, L.; Chang, J.T.; Knight, R.; Mayfield, S. Effects of the microalgae Chlamydomonas on gastrointestinal health. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Taminiau, B.; Walgrave, H.; Daube, G.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Spirulina protects against hepatic inflammation in aging: An effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota? Nutrients 2017, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U.; Liyanage, T.D.; Edirisinghe, S.L.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Thulshan, E.H.T.; Nikapitiya, C.; Oh, C.; Kang, D.H.; De Zoysa, M. Marine microalgae, Spirulina maxima-derived modified pectin and modified pectin nanoparticles modulate the gut microbiota and trigger immune responses in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Han, W.; Wang, G.; Zhao, X. Application prospect of polysaccharides in the development of anti-novel coronavirus drugs and vaccines. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2020, 164, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shang, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Yu, G. Degradation of marine algae-derived carbohydrates by Bacteroidetes isolated from human gut microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Walton, G.; Sousa, S.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Freitas, A.C.; Gomes, A.M. In-vitro fermentation and prebiotic potential of selected extracts from seaweeds and mushrooms. LWT 2016, 73, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.H.; Ren, L.F.; Li, J.F.; Wu, Y.N.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Intestinal flora as a potential strategy to fight SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.M.; Dufresne, M.; Helle, F.; Hoffmann, T.W.; François, C.; Brochot, E.; Paullier, P.; Legallais, C.; Duverlie, G.; Castelain, S. Alginate hydrogel protects encapsulated hepatic HuH-7 cells against hepatitis C virus and other viral infections. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagle, V.; Gaikwad, M.; Pawar, Y.; Dasgupta, S. Marine red alga Porphyridium sp. as a source of sulfated polysaccharides (SPs) for combating against COVID-19. Preprints 2020, 2020040168. [Google Scholar]
- Grassauer, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E. Antiviral Composition Comprising a Sulfated Polysaccharide. U.S.Patent Application US 12/673,145, 10 March 2011.
- da Silva, J.K.R.; Figueiredo, P.L.B.; Byler, K.G.; Setzer, W.N. Essential Oils as Antiviral Agents, Potential of Essential Oils to Treat SARS-CoV-2 Infection: An In-Silico Investigation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Smolina, T.P.; Makarenkova, I.D.; Ivanushko, L.A.; Persiyanova, E.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Silchenko, A.S.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Besednova, N.N.; Fedyanina, L.N.; et al. Immunoadjuvant activity of fucoidans from the brown alga Fucus evanescens. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; et al. The comparative analysis of antiviral activity of native and modified fucoidans from brown algae Fucus evanescens in-vitro and in-vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Keefe, B.R.; Smee, D.F.; Turpin, J.A.; Saucedo, C.J.; Gustafson, K.R.; Mori, T.; Blakeslee, D.; Buckheit, R.; Boyd, M.R. Potent anti-influenza activity of cyanovirin-N and interactions with viral hemagglutinin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, Y.; Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Isolation of sulfated galactan from Codium fragile and its antiviral effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Malcata, F.X. Algal spent biomass—A pool of applications. In Biofuels from Algae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 397–433. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ooike, M.; Tsunomura, T.; Sakaguchi, M. Antioxidant activities of phycocyanobilin prepared from Spirulina platensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, M.F. Clinical potential of spirulina as a source of phycocyanobilin. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, R. Antiviral properties of Cyanobacterium, Spirulina platensis—A review. Int. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pendyala, B.; Patras, A. In-Silico Screening of Food Bioactive Compounds to Predict Potential Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mopar) and RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Kaur, R.; Bansal, A.; Kapur, S.; Sundaram, S. Biotechnological exploitation of cyanobacteria and microalgae for bioactive compounds. In Biotechnological Production of Bioactive Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 221–259. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, L.; Vernès, L.; Cadoret, J.P. Docking and in-silico toxicity assessment of Arthrospira compounds as potential antiviral agents against SARS-CoV-2. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 1579–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikhra, V. The Trans-zoonotic Virome interface: Measures to balance, control and treat epidemics. Ann. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2020, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, G.K.; Kuo, S.M.; Huang, S.Y.; Hu, I.C.; Lo, Y.L.; Shih, S.R. Well-tolerated Spirulina extract inhibits influenza virus replication and reduces virus-induced mortality. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 296, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Parihar, P.; Singh, M.; Bajguz, A.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Uncovering potential applications of cyanobacteria and algal metabolites in biology, agriculture and medicine: Current status and future prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 459–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elaya Perumal, U.; Sundararaj, R. Algae: A potential source to prevent and cure the novel coronavirus—A review. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 11, 479–483. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Frances, E.; Escudero-Onate, C. Cyanobacteria and microalgae in the production of valuable bioactive compounds. Microalgal. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 104–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bedoux, G.; Caamal-Fuentes, E.; Boulho, R.; Marty, C.; Bourgougnon, N.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Robledo, D. Antiviral and cytotoxic activities of polysaccharides extracted from four tropical seaweed species. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lodermeyer, V.; Ssebyatika, G.; Passos, V.; Ponnurangam, A.; Malassa, A.; Ewald, E.; Stürzel, C.M.; Kirchhoff, F.; Rotger, M.; Falk, C.S.; et al. The antiviral activity of the cellular glycoprotein LGALS3BP/90K is species specific. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00226-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagdonaite, I.; Wandall, H.H. Global aspects of viral glycosylation. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, G.; Harvey, D.J.; Feldmann, F.; Stroeher, U.; Feldmann, H.; Royle, L.; Dwek, R.A.; Rudd, P.M. Identification of N-linked carbohydrates from severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spike glycoprotein. Virology 2010, 399, 57–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Allen, J.D.; Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S.; Crispin, M. Site-specific glycan analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike. Science 2020, 369, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrap, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivrale, A.U.; Ingale, A.G. Plant as a plenteous reserve of lectin. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e26595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, B.A.; Waaland, S.D. Partial purification and characterization of a glycoprotein cell fusion hormone from Griffithsia Pacifica, a red alga. Plant Physiol. 1983, 71, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, T.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Sowder, R.C.; Bringans, S.; Gardella, R.; Berg, S.; Cochran, P.; Turpin, J.A.; Buckheit, R.W.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Griffithsin, a novel HIV-inactivating protein, from the red alga Griffithsia sp. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9345–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lusvarghi, S.; Bewley, C.A. Griffithsin: An antiviral lectin with outstanding therapeutic potential. Viruses 2016, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Choudhir, G.; Shukla, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Tyagi, P.; Bhushan, A.; Rathore, M. Identification of phytochemical inhibitors against main protease of COVID-19 using molecular modeling approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 3760–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumla, A.; Chan, J.F.; Azhar, E.I.; Hui, D.S.; Yuen, K.Y. Coronaviruses—drug discovery and therapeutic options. Nat. Rev. Drug Dis. 2016, 15, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishag, H.Z.; Li, C.; Huang, L.; Sun, M.X.; Wang, F.; Ni, B.; Malik, T.; Chen, P.Y.; Mao, X. Griffithsin inhibits Japanese encephalitis virus infection in-vitro and in-vivo. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levendosky, K.; Mizenina, O.; Martinelli, E.; Jean-Pierre, N.; Kizima, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Kleinbeck, K.; Bonnaire, T.; Robbiani, M.; Zydowsky, T.M.; et al. Griffithsin and carrageenan combination to target herpes simplex virus 2 and human papillomavirus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7290–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, B.; Stefanidou, M.; Mesquita, P.M.; Fakioglu, E.; Segarra, T.; Rohan, L.; Halford, W.; Palmer, K.E.; Herold, B.C. Griffithsin protects mice from genital herpes by preventing cell-to-cell spread. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6257–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Keefe, B.R.; Giomarelli, B.; Barnard, D.L.; Shenoy, S.R.; Chan, P.K.; McMahon, J.B.; Palmer, K.E.; Barnett, B.W.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.L.; et al. Broad-spectrum in-vitro activity and in-vivo efficacy of the antiviral protein griffithsin against emerging viruses of the family Coronaviridae. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.J.; Han, J.W.; Jeon, H.; Cho, K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.S.; Han, J.W. Characterization of a novel mannose-binding lectin with antiviral activities from red alga, Grateloupia chiangii. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, T. Native morphology of influenza virions. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, C.; Kaushal, S.; Yeo, D. Enteric involvement of coronaviruses: Is faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2 possible? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.X.; Guan, H.S. The antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuleman, P.; Albecka, A.; Belouzard, S.; Vercauteren, K.; Verhoye, L.; Wychowski, C.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Palmer, K.E.; Dubuisson, J. Griffithsin has antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5159–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micewicz, E.D.; Cole, A.L.; Jung, C.L.; Luong, H.; Phillips, M.L.; Pratikhya, P.; Sharma, S.; Waring, A.J.; Cole, A.M.; Ruchala, P. Grifonin-1: A small HIV-1 entry inhibitor derived from the algal lectin, Griffithsin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gondim, A.C.; da Silva, S.R.; Mathys, L.; Noppen, S.; Liekens, S.; Sampaio, A.H.; Nagano, C.S.; Rocha, C.R.C.; Nascimento, K.S.; Cavada, B.S.; et al. Potent antiviral activity of carbohydrate-specific algal and leguminous lectins from the Brazilian biodiversity. Med. Chem. Comm. 2019, 10, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keeffe, J.R.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.; Gillespie, S.K.; Yong, J.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Mayo, S.L. Designed oligomers of cyanovirin-N show enhanced HIV neutralization. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14079–14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huskens, D.; Férir, G.; Vermeire, K.; Kehr, J.C.; Balzarini, J.; Dittmann, E.; Schols, D. Microvirin, a novel α (1, 2)-mannose-specific lectin isolated from Microcystis aeruginosa, has anti-HIV-1 activity comparable with that of cyanovirin-N but a much higher safety profile. J. Biolog. Chem. 2010, 285, 24845–24854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bewley, C.A.; Cai, M.; Ray, S.; Ghirlando, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Muramoto, K. New carbohydrate specificity and HIV-1 fusion blocking activity of the cyanobacterial protein MVL: NMR, ITC and sedimentation equilibrium studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 339, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Kubo, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nishizono, A.; Hirayama, M.; Hori, K. Entry inhibition of influenza viruses with high mannose-binding lectin ESA-2 from the red alga Eucheuma Serra through the recognition of viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3454–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, J.; Hirayama, M.; Sato, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Hori, K. A novel high-mannose specific lectin from the green alga Halimeda renschii exhibits a potent anti-influenza virus activity through high-affinity binding to the viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takebe, Y.; Saucedo, C.J.; Lund, G.; Uenishi, R.; Hase, S.; Tsuchiura, T.; Kneteman, N.; Ramessar, K.; Tyrrell, D.L.J.; Shirakura, M.; et al. Antiviral lectins from red and blue-green algae show potent in-vitro and in-vivo activity against hepatitis C virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrison, A.R.; Giomarelli, B.G.; Lear-Rooney, C.M.; Saucedo, C.J.; Yellayi, S.; Krumpe, L.R.; Rose, M.; Paragas, J.; Bray, M.; Olinger, G.G., Jr.; et al. The cyanobacterial lectin scytovirin displays potent in-vitro and in-vivo activity against Zaire Ebola virus. Antivir. Res. 2014, 112, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassauer, A.; Weinmuellner, R.; Meier, C.; Pretsch, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E.; Unger, H. Iota-Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of rhinovirus infection. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilliou, L.; Larotonda, F.D.S.; Abreu, P.; Ramos, A.M.; Sereno, A.M.; Gonçalves, M.P. Effect of extraction parameters on the chemical structure and gel properties of κ/ι-hybrid carrageenans obtained from Mastocarpus stellatus. Biomol. Eng. 2006, 23, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, M. Developments on gelling algal galactans, their structure and physical-chemistry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Li, Y.; Ni, L.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Cui, Y.S.; Jiang, S.L.; Xie, E.Y.; Du, J.; Deng, F.; Dong, C.X. Structural characterization and antiviral activity of two fucoidans from the brown algae Sargassum henslowianum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Briseno, J.A.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Sassi, J.F.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Zapata-Benavides, P.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. Sulphated polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus seaweeds both inhibit viral attachment/entry and cell-cell fusion, in NDV infection. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L.; Yue, Y.; Li, K.; Li, P. Characterization and comparison of the structural features, immune-modulatory and anti-avian influenza virus activities conferred by three algal sulfated polysaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Hou, L.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Li, W.; Mao, W. A sulfated glucuronorhamnan from the green seaweed Monostroma nitidum: Characteristics of its structure and antiviral activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitlin, L.; Whaley, K.J.; Hegarty, T.A.; Moench, T.R.; Cone, R.A. Tests of vaginal microbicides in the mouse genital herpes model. Contraception 1997, 56, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.; Meier, C.; Jawad, M.; Weinmüllner, R.; Grassauer, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E. Efficacy and safety of an antiviral Iota-Carrageenan nasal spray: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled exploratory study in volunteers with early symptoms of the common cold. Respir Res. 2010, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koenighofer, M.; Lion, T.; Bodenteich, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E.; Grassauer, A.; Unger, H.; Mueller, C.A.; Fazekas, T. Carrageenan nasal spray in virus confirmed common cold: Individual patient data analysis of two randomized controlled trials. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2014, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, P.S.; Oh, H.; Kwon, S.J.; Jin, W.; Zhang, F.; Fraser, K.; Hong, J.J.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Sulfated polysaccharides effectively inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in-vitro. Cell Dis. 2020, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramus, J. Cell-surface polysaccharides of the red alga Porphyridium. Biog. Plant Cell Wall Polysacch. 1973, 333–359. [Google Scholar]
- Pitsillou, E.; Liang, J.; Ververis, K.; Lim, K.W.; Hung, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of the deubiquitinating activity of the SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease: In silico molecular docking studies and in vitro enzymatic activity assay. Front. Chem. 2020, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huheihel, M.; Ishanu, V.; Tal, J.; Arad, S.M. Activity of Porphyridium sp. polysaccharide against herpes simplex viruses in-vitro and in-vivo. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 2002, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radonic, A.; Thulke, S.; Achenbach, J.; Kurth, A.; Vreemann, A.; König, T.; Walter, C.; Possinger, K.; Nitsche, A. Anionic polysaccharides from phototrophic microorganisms exhibit antiviral activities to Vaccinia virus. J. Antivir. Antiretrovir. 2011, 2, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raposo, M.F.D.J.; De Morais, R.M.S.C.; Bernardo de Morais, A.M.M. Bioactivity and applications of sulphated polysaccharides from marine microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, R.; Zheng, Y. Overview of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and their applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Yoon, K.D.; Min, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, N.G.; Huh, H.; Kim, J. Inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and protease by phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia cava. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karadeniz, F.; Kang, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.K. Anti-HIV-1 activity of phlorotannin derivative 8, 4‴-dieckol from Korean brown alga Ecklonia cava. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-Santibañez, K.; Peña-Hernández, M.A.; Cruz-Suárez, L.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Skouta, R.; Vasquez, A.H.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. Virucidal and synergistic activity of polyphenol-rich extracts of seaweeds against measles virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangtani, R.; Ghosh, A.; Jha, H.C.; Parmar, H.S.; Bala, K. Potential of algal metabolites for the development of broad-spectrum antiviral therapeutics: Possible implications in COVID-19 therapy. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2296–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, J.M.; Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.S.; Ryu, Y.B. Dieckol, a SARS-CoV 3CLpro inhibitor, isolated from the edible brown algae Ecklonia cava. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.; Patamia, V.; Scala, A.; Sciortino, M.T.; Piperno, A.; Rescifina, A. Putative inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease from a library of marine natural products: A virtual screening and molecular modeling study. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Kumari, N.; Thakur, N.; Bhatia, S.K.; Saratale, G.D.; Ghodake, G.; Mistry, B.M.; Alavilli, H.; Kishor, D.S.; Du, X.; et al. A Comprehensive Overview on the Production of Vaccines in Plant-Based Expression Systems and the Scope of Plant Biotechnology to Combat against SARS-CoV-2 Virus Pandemics. Plants 2021, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Highly brominated mono- and bis-phenols from the marine red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula with radical-scavenging activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Jung, H.A.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, W.C. A cyclohexanonyl bromophenol from the red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, X.M.; Ji, N.Y.; Wang, B.G. Bromophenols from the marine red alga Polysiphonia urceolata with DPPH radical scavenging activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, X.M.; Wang, W.J.; Ai, X.Z.; Li, X.; Yang, S.Q.; Gloer, J.B.; Wang, B.G.; Xu, T. Isolation, synthesis, and radical-scavenging activity of rhodomelin A, a ureidobromophenol from the marine red alga Rhodomela confervoides. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Dhara, S. First report of substituted 2H-pyranoids from brown seaweed Turbinaria conoides with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.R.; Kim, S.J. Fucoidan as bio-functional molecule: Insights into the anti-inflammatory potential and associated molecular mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Yin, L.Y.; Gao, J.H.; Chen, J.H.; Li, J.X.; Song, F.H. Two new bromophenols with radical scavenging activity from marine red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.H.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, B.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, J. Chromenes from the brown alga Sargassum siliquastrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Mikami, D.; Kurihara, H. Two new algal bromophenols from Odonthalia corymbifera. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 4119–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.L.; Lee, H.-S.; Kang, I.-J.; Won, M.-H.; You, S.G. Antioxidant properties of extract and fractions from Enteromorpha prolifera, a type of green seaweed. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Panchagnula, G.K.; Gottumukkala, A.L.; Subbaraju, G.V. Synthesis, structural revision, and biological activities of 4−-chloroaurone, a metabolite of marine brown alga Spatoglossum variabile. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 6909–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressler, V.; Stein, É.M.; Dörr, F.; Fujii, M.T.; Colepicolo, P.; Pinto, E. Sesquiterpenes from the essential oil of Laurencia dendroidea (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta): Isolation, biological activities and distribution among seaweeds. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 21, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, V.L.M.; Seca, A.M.L.; Barreto, M.C.; Neto, A.I.; Kijjoa, A.; Silva, A.M.S. Cytotoxic meroterpenoids from the macro alga Cystoseira abies-marina. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, X.M.; Gloer, J.B.; Wang, B.G. New nitrogen-containing bromophenols from the marine red alga Rhodomela confervoides and their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M. Biologically active macromolecules: Extraction strategies, therapeutic potential and biomedical perspective. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterhans, E. Oxidants and antioxidants in viral diseases: Disease mechanisms and metabolic regulation. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 962S–965S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kesarwani, P.; Murali, A.K.; Al-Khami, A.A.; Mehrotra, S. Redox regulation of T-cell function: From molecular mechanisms to significance in human health and disease. Antiox. Redox Sign. 2013, 18, 1497–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, T.; Salomon, P.S.; Hamerski, L.; Walter, J.; Menezes, R.B.; Siqueira, J.E.; Santos, A.; Santos, J.A.M.; Ferme, N.; Guimarães, T.; et al. Inhibitory effect of microalgae and cyanobacteria extracts on influenza virus replication and neuraminidase activity. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khomich, O.A.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Bartosch, B.; Ivanov, A.V. Redox biology of respiratory viral infections. Viruses 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Roche, L.; Mesta, F. Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, R.; Cecchini, A.L. SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression. Med. Hypotheses. 2020, 143, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, S. Oxidative stress associated with SARS-Cov-2 (COVID-19) increases the severity of the lung disease—A systematic review. J. Infect. Dis. Epidemiol. 2020, 6, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Sansone, C.; Brunet, C.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A. Marine algal antioxidants as potential vectors for controlling viral diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Algal Species | Antiviral Metabolites | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laminaria japonica, Laminaria digitata | Alginate | Inhibition of inverse transcriptase in the RNA virus | [57] |
| Gigartina skottsbergii | Carrageenan | Inhibition of binding or internalization of viruses into host cells | [58,59] |
| Ecklonia cava | Dieckol; 8,8-bieckol | Protease inhibitor | [60] |
| Porphyridium sp. | Exopolysaccharides | Internalization or virus binding on host cells is inhibited. | [58] |
| Adenocytis utricularis, Cystoseira indica, Fucus vesiculosus, Undaria pinnatifid | Fucoidan | Inhibition of adhesion and blocking of reverse transcriptase | [61,62] |
| Griffiths sp. | Griffithsin | Griffithsin interacts with oligosaccharides components of spike glycoproteins of the various viruses. | [39,63] |
| Agardhiella tenera, Schizymenia binderi, Callophyllis variegata | Galactan | Blocking of virus adhesion and replication into host cells | [64] |
| Marine Algal Source | Lectin Designated | Active against Viruses | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Griffiths Sp. | GRFT | SARS-CoV, HCV, HIV | [99,100,101] |
| Amansia multifida, Hypnea musciformis, Bryothamnion seaforthii, Solieria filiformis, Meristiella echinocarpa | AML, HML, BSL, Sfl, MEL | HIV and influenza | [102] |
| Nostoc ellipsosporum | Cyanovirin | HIV | [103] |
| Microcystis aeruginosa | Microvirin | HIV-1 | [104] |
| Microcystis Viridis | MVL | HIV-1 | [105] |
| Eucheuma serrai | ESA-2 | Influenza | [106] |
| Halimeda renschii | HRL40 | Influenza | [107] |
| Kappaphycus alvarezii | KAA-2 | Influenza | [106] |
| Scytonema varium | Scytovirin | HCV, HIV, Ebola | [108,109] |
| Compound | Isolation Source | Assay/Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| methyl-21-yl-[5′,6′-dihydro-5′-yl-{54-(4-hydroxybenzoyl)-oxy-(52-methylbutyl)}-3′-methyl-2H-pyran]-21-methyl butanoate (1), 11-[(3′,6′-dihydro-4′-methyl-2′-oxo-2H-pyran-3′-yl)methyl]-10-methylhexyl benzoate (2) and [6-ethyl-3,4-dimethyl-(tetrahydro-2′, 2′, 6′-trimethyl-2H-pyran-3′-yl)-2,5-cycloheptadiene]-1-propanoate (3) | Turbinaria conoides | DPPH radical scavenging activity with IC50 range from 0.54 to 1.1 mg mL−1 | [138] |
| Fucoidan | Undaria pinnatifida | DPPH radical scavenging activity | [139] |
| methyl N′-(2,3,6-tibromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzyl)-γ-ureidobutyrate | Symphyocladia latiuscula | DPPH radical scavenging activity: IC50 = 27.9 µM | [140] |
| Sargachromanols | Sargassum siliquastrum | DPPH scavenging activity IC50 = 0.23 mM | [141] |
| Odonthalol and Odonthadione | Odonthalia corymbifera | DPPH radical scavenging activity: IC50 = 24.7 ± 0.0 µM | [142] |
| Pheophorbide A | Enteromorpha prolifera | The DPPH and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacities of the chloroform fraction were compared, butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and α-tocopherol, at concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 1.0 mg/mL. | [143] |
| 4′-chloro-2-hydroxyaurone and 4−chloroaurone | Spatoglossum variabile | O2− scavenging activity: IC50 = 22.2 µM | [144] |
| Fucoidan | Undaria pinnatifida | Scavenging of DPPH radicals: 9.01 ± 1.93 µg/mL | [145] |
| 7-epi-silphiperfolan-6β-ol and silphiperfolan-7β-ol | Laurencia dendroidea | Scavenging of DPPH radicals; 27.5 and 30.3% at 500 µg mL−1, respectively | [146] |
| Cystoazorones A and B and cystoazorol A | Cystoseira abies-marina | Scavenging of DPPH radicals: 29% at 1.06 mM | [147] |
| 3-(2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione; methyl 4-(2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzylamino)-4-oxobutanoat;4-(2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzylamino)-4-oxobutanoic acid; 3-bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide; and 2-(3-bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)acetamide | Rhodomela confervoides | These compounds showed potent scavenging activity against DPPH radicals, with IC50 values ranging from 5.22 to 23.60 μM. | [148] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Singh, R.P.; Kumar, I.; Yadav, P.; Singh, S.K.; Kaushalendra; Singh, P.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, S.M.; Kesawat, M.S.; et al. Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030452
Kumar A, Singh RP, Kumar I, Yadav P, Singh SK, Kaushalendra, Singh PK, Gupta RK, Singh SM, Kesawat MS, et al. Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(3):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030452
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Ajay, Rahul Prasad Singh, Indrajeet Kumar, Priya Yadav, Sandeep Kumar Singh, Kaushalendra, Prashant Kumar Singh, Rajan Kumar Gupta, Shiv Mohan Singh, Mahipal Singh Kesawat, and et al. 2022. "Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic" Antioxidants 11, no. 3: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030452
APA StyleKumar, A., Singh, R. P., Kumar, I., Yadav, P., Singh, S. K., Kaushalendra, Singh, P. K., Gupta, R. K., Singh, S. M., Kesawat, M. S., Saratale, G. D., Chung, S.-M., & Kumar, M. (2022). Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic. Antioxidants, 11(3), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030452













