The Efficacy of Antioxidant Oral Supplements on the Progression of COVID-19 in Non-Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Nutritional Screening and Assessment
2.5. Anthropometric and Body-Composition Measures
2.6. Clinical Assessment
2.7. Biochemical Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Nutritional Characteristics of Study Groups
3.2. Anthropometric and Clinical Changes
3.3. Hematological Changes
3.4. Biochemical and Inflammatory Changes
3.5. Nutritional Status Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Systems Science and Engineering. COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6 (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Regulatory Affairs Professionals Society. COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker. Available online: https://www.raps.org/news-and-articles/news-articles/2020/3/covid-19-vaccine-tracker (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Schulert, G.S.; Volpi, S.; Lee, P.Y.; Kernan, K.F.; Caricchio, R.; Mahmud, S.; Hazen, M.M.; Halyabar, O. On the alert for cytokine storm: Immunopathology in COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftahi, G.; Bahari, Z.; Jangravi, Z.; Iman, M. A vicious circle between oxidative stress and cytokine storm in acute respiratory distress syndrome pathogenesis at COVID-19 infection. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2021, 93, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, E.M.; Grisham, M.B. Inflammation, free radicals, and antioxidants. Nutrition 1996, 12, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Arnoldi, A. Food-derived antioxidants and COVID-19. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Immunonutrition. BMJ 2003, 327, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, E.; Delange, J. COVID-19: Is there a role for immunonutrition, particularly in the over 65s? BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2020, 3, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovic, T.H.; Ali, S.R.; Ibrahim, N.; Jessop, Z.M.; Tarassoli, S.P.; Dobbs, T.D.; Holford, P.; Thornton, C.A.; Whitaker, I.S. Could vitamins help in the fight against COVID-19? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Leggeri, C.; Cinelli, G.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Caparello, G.; Carrano, E. COVID-19: Is there a role for immunonutrition in obese patient? J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Soria-Castro, E.; Manzano Pech, L.; Pérez-Torres, I. Is antioxidant therapy a useful complementary measure for COVID-19 treatment? An algorithm for its application. Medicina 2020, 56, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.B.; Lahore, H.; McDonnell, S.L.; Baggerly, C.A.; French, C.B.; Aliano, J.L.; Bhattoa, H.P. Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients 2020, 12, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Y.; Kani, Y.A.; Iliya, S.; Muhammad, J.B.; Binji, A.; El-Fulaty Ahmad, A.; Kabir, M.B.; Umar Bindawa, K.; Ahmed, A.U. Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 2050312121991246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Yasui, H.; Suzuki, K.; Saitou, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ishizaka, T.; Nishida, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Gohma, I.; Ogawa, Y. Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment-relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiscano-Camón, L.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Roca, O.; Ferrer, R. Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, H.; Feehan, J.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Ali, H.I.; Platat, C.; Ismail, L.C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Stojanovska, L. Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: Could they help against COVID-19? Maturitas 2021, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiedra, R.; Lo, K.B.; Elbashabsheh, M.; Gul, F.; Wright, R.M.; Albano, J.; Azmaiprashvili, Z.; Aponte, G.P. The use of IV vitamin C for patients with COVID-19: A single center observational study. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 1259–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.W.; Parikh, N.; Megala, S.M.; Predeteanu, G.S. Unusual early recovery of a critical COVID-19 patient after administration of intravenous vitamin C. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e925521-1. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, E. Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, M.; Nahas, R.; Ali, S.; Elshafei, S.A.; Khaled, H. Impact of oral omega-3 fatty acids supplementation in early sepsis on clinical outcome and immunomodulation. Egypt. J. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 1, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B. How to calculate sample size in randomized controlled trial? J. Thorac. Dis. 2009, 1, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondrup, J.; Allison, S.P.; Elia, M.; Vellas, B.; Plauth, M. ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Fink, J.; Daniel de Mello, P.; Daniel de Mello, E. Subjective global assessment of nutritional status—A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulmeaty, M.M.; Almajwal, A.M.; Almadani, N.K.; Aldosari, M.S.; Alnajim, A.A.; Ali, S.B.; Hassan, H.M.; Elkatawy, H.A. Anthropometric and central obesity indices as predictors of long-term cardiometabolic risk among Saudi young and middle-aged men and women. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, B.W.; Toh, Q.C.; Chan, X.W.; Xu, H.; Li, J.L.; Lee, E.J. Assessment of muscle mass and its association with protein intake in a multi-ethnic Asian population: Relevance in chronic kidney disease. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 23, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iconaru, E.I.; Ciucurel, C. Hand grip strength variability during serial testing as an entropic biomarker of aging: A Poincaré plot analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, S.; Thomas, B.; Sutton, L.; Burnsall, M.; Lee, E.; Bradburn, M.; Loban, A.; Waterhouse, S.; Simmonds, R.; Biggs, K.; et al. Derivation and validation of a clinical severity score for acutely ill adults with suspected COVID-19: The PRIEST observational cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, C.; García, E.; Rodríguez, V.; Frías, L.; Garriga, R.; Álvarez, J.; Garcia-Peris, P.; León, M. Comparison of four nutritional screening tools to detect nutritional risk in hospitalized patients: A multicentre study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslan, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Torrinhas, R.S.M.; Ravacci, G.R.; Pereira, J.C.; Waitzberg, D.L. Complementarity of Subjective Global Assessment (SGA) and Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS 2002) for predicting poor clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, J.N. Bedside nutrition assessment past, present, and future: A review of the Subjective Global Assessment. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Velthuis, A.J.; van den Worm, S.H.; Sims, A.C.; Baric, R.S.; Snijder, E.J.; van Hemert, M.J. Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.P.; Lovegrove, J.A. Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: A UK perspective. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesalski, H.K.; Grune, T.; Tinz, J.; Zöllner, I.; Blumberg, J.B. Reexamination of a meta-analysis of the effect of antioxidant supplementation on mortality and health in randomized trials. Nutrients 2010, 2, 929–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, L.L.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases (Review). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Torgerson, D.J. Baseline imbalance in randomised controlled trials. BMJ 1999, 319, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanicolas, P.J.; Farrokhyar, F.; Bhandari, M. Blinding: Who, what, when, why, how? Can. J. Surg. 2010, 53, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
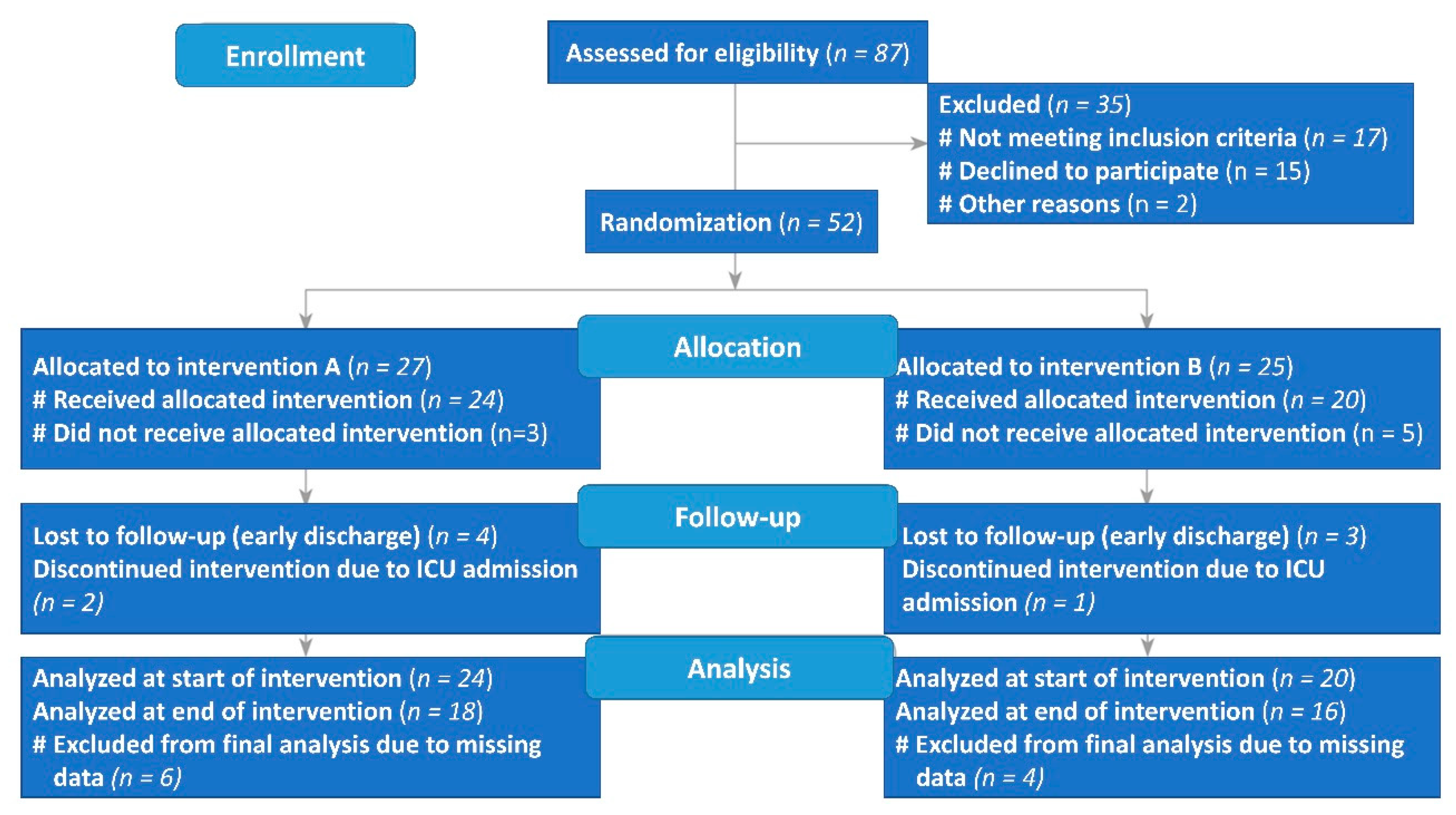

| Variables | Supplement (n = 24) | Placebo (n = 20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % within Variable (% within the Group) | % within Variable (% within the Group) | p-Value | |
| Gender | 0.675 | ||
| Female | 62.5 (41.7) | 37.5 (30.0) | |
| Male | 50.0 (58.3) | 50.0 (70.0) | |
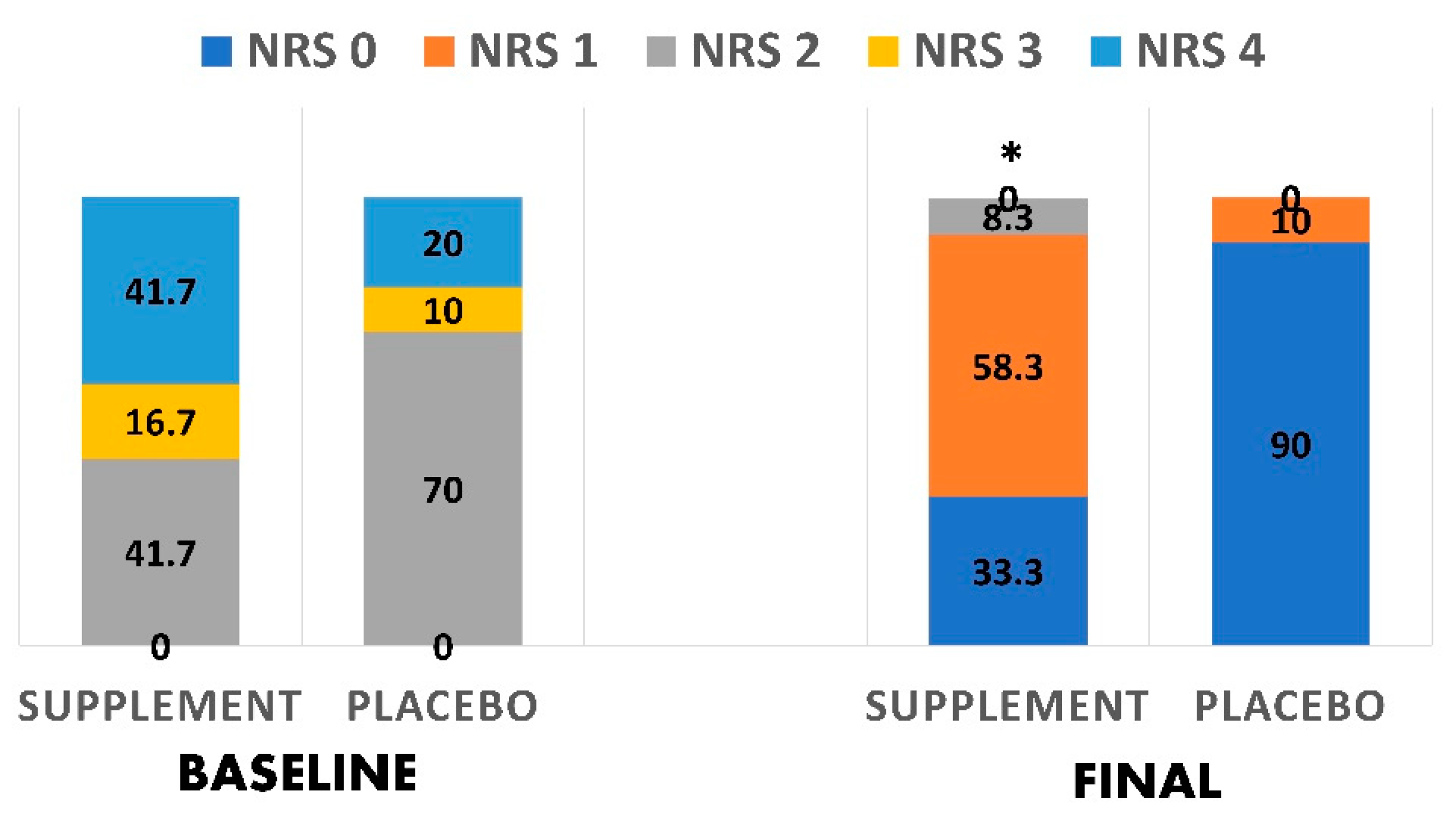
| Scores of nutritional risk screening 2002 * | 0.410 | ||
| Score 2 | 41.7 (41.7) | 58.3 (70.0) | |
| Score 3 | 66.7 (16.7) | 33.3 (10.0) | |
| Score 4 | 71.4 (41.7) | 28.6 (20.0) | |
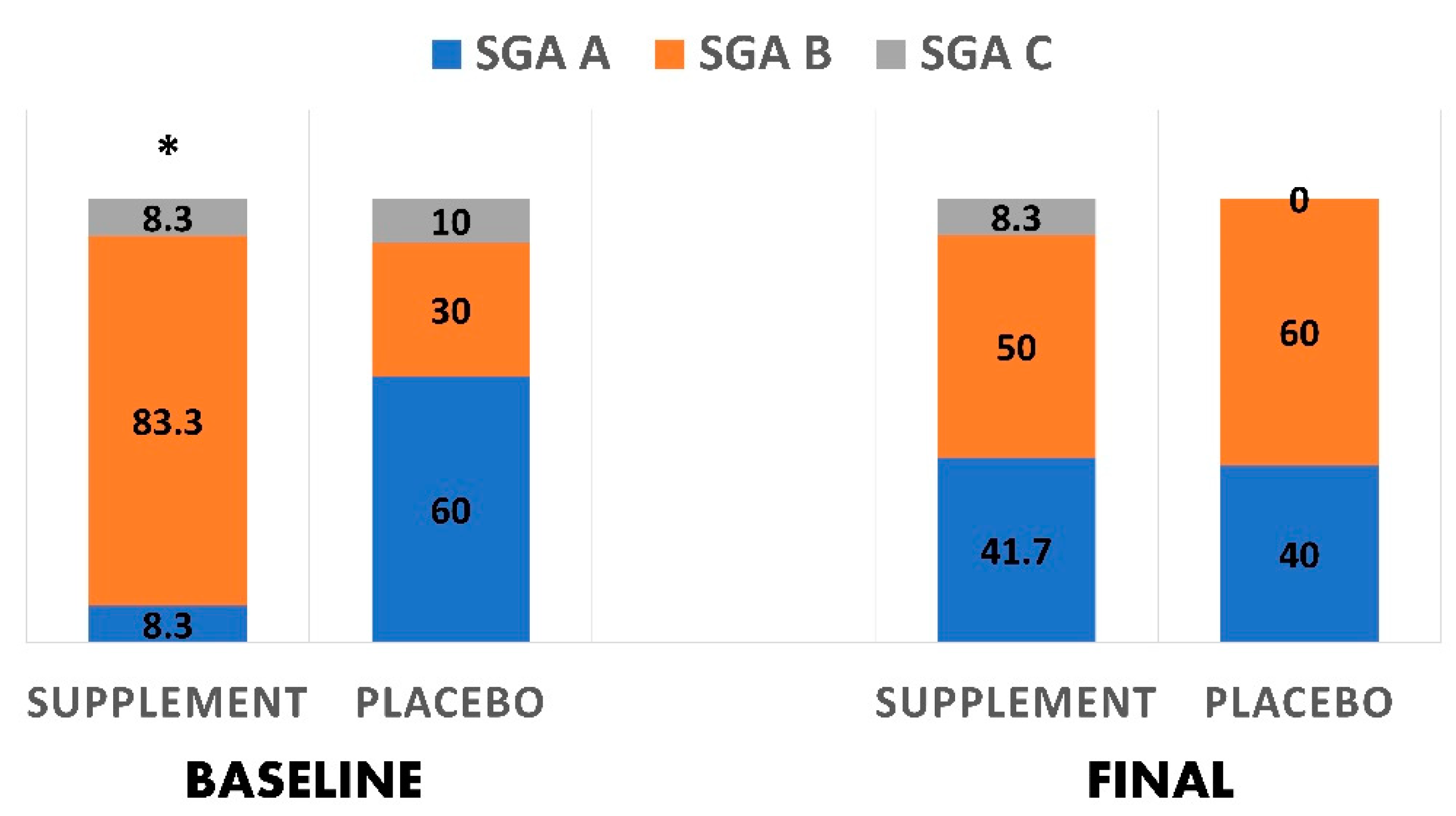
| Scores of subjective global assessment ** | 0.027 | ||
| A | 14.3 (8.3) | 85.7 (60.0) | |
| B | 76.9 (83.3) | 23.1 (30.0) | |
| C | 50.0 (8.3) | 50.0 (10.0) |
| Variables | Supplement (n = 18) | Placebo (n = 16) | p-Value ** | p-Value *** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | |||
| Weight (kg) | 80.97 ± 20.16 | 80.04 ± 17.34 | 0.775 | 85.60 ± 19.57 | 83.59 ± 19.01 | 0.172 | 0.577 | 0.644 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.22 ± 4.99 | 28.85 ± 3.53 | 0.753 | 30.93 ± 7.64 | 30.21 ± 7.54 | 0.166 | 0.462 | 0.509 |
| MAC (cm) | 33.27 ± 3.28 | 33.09 ± 3.56 | 0.785 | 32.95 ± 5.60 | 31.65 ± 4.85 | 0.165 | 0.927 | 0.483 |
| TST (mm) | 27.27 ± 4.03 | 26.55 ± 6.33 | 0.650 | 24.40 ± 8.88 | 23.90 ± 11.86 | 0.858 | 0.372 | 0.541 |
| MAMC (cm) | 24.70 ± 2.76 | 24.75 ± 3.57 | 0.954 | 25.28 ± 3.79 | 24.14 ± 2.49 | 0.255 | 0.646 | 0.704 |
| MAMA (cm2) | 49.11 ± 10.68 | 49.66 ± 14.17 | 0.860 | 51.89 ± 16.50 | 46.82 ± 9.83 | 0.268 | 0.599 | 0.653 |
| Temperature (°C) | 37.28 ± 0.61 | 36.69 ± 0.41 | 0.004 | 36.88 ± 0.45 | 36.58 ± 0.23 | 0.165 | 0.156 | 0.473 |
| Pulse (b/min) | 87.91 ± 10.85 | 82.64 ± 7.89 | 0.147 | 77.80 ± 9.80 | 90.40 ± 15.92 | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.148 |
| SpO2 (%) | 95.18 ± 1.99 | 95.18 ± 1.89 | 1.000 | 95.00 ± 2.00 | 95.20 ± 2.04 | 0.764 | 0.699 | 0.968 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 123.82 ± 18.05 | 121.18 ± 15.25 | 0.640 | 124.60 ± 8.49 | 125.40 ± 8.49 | 0.882 | 0.912 | 0.697 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 69.82 ± 8.24 | 73.73 ± 9.73 | 0.313 | 70.90 ± 8.05 | 79.90 ± 12.70 | 0.131 | 0.833 | 0.178 |
| RR (b/min) | 21.45 ± 1.97 | 20.00 ± 1.26 | 0.020 | 21.00 ± 1.25 | 19.20 ± 1.32 | 0.027 | 0.421 | 0.153 |
| Hand grip (kg) | 18.15 ± 7.66 | 20.50 ± 9.21 | 0.393 | 17.60 ± 7.92 | 22.55 ± 10.23 | 0.051 | 0.659 | 0.767 |
| Variables | Supplement (n = 18) | Placebo (n = 16) | p-Value ** | p-Value *** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | |||
| WBC (103/uL) | 6.31 ± 2.10 | 8.06 ± 2.61 | 0.035 | 7.98 ± 2.86 | 8.86 ± 2.18 | 0.433 | 0.119 | 0.422 |
| RBC (103/uL) | 4.76 ± 0.47 | 4.70 ± 0.35 | 0.534 | 4.73 ± 0.62 | 4.77 ± 0.85 | 0.803 | 0.996 | 0.828 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 14.18 ± 1.37 | 14.06 ± 1.35 | 0.585 | 13.19 ± 1.67 | 13.55 ± 1.49 | 0.158 | 0.181 | 0.643 |
| MCV (fL) | 90.08 ± 5.87 | 88.64 ± 4.79 | 0.041 | 85.83 ± 8.36 | 85.89 ± 10.19 | 0.962 | 0.172 | 0.432 |
| MCH (pg) | 29.87 ± 2.02 | 29.72 ± 2.10 | 0.521 | 28.04 ± 2.94 | 28.95 ± 4.12 | 0.268 | 0.104 | 0.591 |
| HCT (%) | 42.81 ± 4.38 | 42.00 ± 3.44 | 0.251 | 40.42 ± 5.01 | 40.35 ± 5.13 | 0.942 | 0.288 | 0.580 |
| Platelets (103/uL) | 207.91 ± 68.26 | 360.27 ± 156.99 | 0.005 | 318.40 ± 144.24 | 389.50 ± 120.23 | 0.147 | 0.034 | 0.868 |
| Neutrophils (103/uL) | 4.85 ± 2.21 | 5.82 ± 2.44 | 0.167 | 6.07 ± 2.61 | 5.86± 1.71 | 0.822 | 0.227 | 0.973 |
| Lymphocytes (103/uL) | 1.05 ± 0.55 | 1.58 ± 0.86 | 0.008 | 1.22 ± 0.38 | 2.09 ± 0.67 | <0.001 | 0.498 | 0.135 |
| NLR | 6.29 ± 4.43 | 5.70 ± 5.46 | 0.664 | 5.59 ± 3.13 | 3.17 ± 1.81 | 0.011 | 0.796 | 0.190 |
| Monocytes (103/uL) | 0.38 ± 0.17 | 0.47 ± 0.26 | 0.228 | 0.57 ± 0.31 | 0.79 ± 0.31 | 0.159 | 0.065 | 0.020 |
| Basophils (103/uL) | 0.005 ± 0.005 | 0.006 ± 0.013 | 0.659 | 0.005 ± 0.007 | 0.002 ± 0.006 | 0.394 | 1.000 | 0.344 |
| Eosinophils (103/uL) | 0.006 ± 0.015 | 0.026 ± 0.069 | 0.252 | 0.084 ± 0.131 | 0.055 ± 0.096 | 0.516 | 0.052 | 0.438 |
| Variables | Supplement (n = 18) | Placebo (n = 16) | p-Value ** | p-Value *** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | Baseline Mean ± SD | Final Mean ± SD | p-Value * | |||
| ALT (U/L) | 63.36 ± 40.19 | 65.00 ± 48.45 | 0.922 | 50.44 ± 20.21 | 58.44 ± 51.07 | 0.668 | 0.586 | 0.772 |
| AST(U/L) | 69.73 ± 39.73 | 38.82 ± 23.66 | 0.017 | 46.67 ± 17.03 | 30.44 ± 24.49 | 0.175 | 0.151 | 0.448 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 39.64 ± 4.86 | 41.64 ± 3.26 | 0.249 | 34.22 ± 2.49 | 40.31 ± 5.43 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.506 |
| AlkP (U/L) | 58.63 ± 15.45 | 56.25 ± 8.07 | 0.741 | 83.75 ± 15.20 | 110.50 ± 57.29 | 0.373 | 0.276 | 0.020 |
| Total Bilirubin (umol/L) | 7.59 ± 6.29 | 6.68 ± 2.26 | 0.713 | 5.35 ± 2.65 | 6.78 ± 2.19 | 0.377 | 0.834 | 0.943 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 103.00 ± 2.93 | 101.13 ± 2.53 | 0.294 | 103.00 ± 3.74 | 98.75 ± 4.11 | 0.178 | 0.373 | 0.238 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 72.55 ± 7.67 | 70.04 ± 11.69 | 0.299 | 78.66 ± 13.24 | 71.97 ± 17.98 | 0.222 | 0.201 | 0.896 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.19 ± 0.34 | 4.50 ± 0.56 | 0.138 | 4.98 ± 1.19 | 5.45 ± 2.02 | 0.650 | 0.040 | 0.225 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138.88 ± 3.18 | 136.88 ± 3.36 | 0.159 | 134.75 ± 3.30 | 134.00 ± 2.94 | 0.718 | 0.271 | 0.178 |
| Total Protein (g/L) | 71.13 ± 6.62 | 70.50 ± 3.59 | 0.749 | 65.00 ± 5.94 | 68.75 ± 8.02 | 0.122 | 0.063 | 0.603 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 4.95 ± 2.16 | 4.76 ± 1.56 | 0.819 | 7.08 ± 3.41 | 6.68 ± 2.32 | 0.789 | 0.108 | 0.118 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.70 ± 3.85 | 1.28 ± 1.19 | 0.049 | 7.35 ± 6.47 | 1.44 ± 1.05 | 0.033 | 0.915 | 0.603 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 619.2 ± 588.1 | 354.1 ± 318.9 | 0.160 | 386.2 ± 256.3 | 359.6 ± 233.4 | 0.190 | 0.513 | 0.979 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 565.73 ± 39.70 | 243.09 ± 37.80 | <0.001 | 659.33 ± 64.29 | 375.33 ± 62.75 | <0.001 | 0.005 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 22.09 ± 6.58 | 8.91 ± 4.23 | <0.001 | 23.56 ± 7.06 | 11.89 ± 1.62 | <0.001 | 0.692 | 0.035 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 46.36 ± 3.20 | 14.91 ± 5.32 | <0.001 | 47.11 ± 3.62 | 21.11 ± 3.89 | <0.001 | 0.252 | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abulmeaty, M.M.A.; Aljuraiban, G.S.; Shaikh, S.M.; ALEid, N.E.; Mazrou, L.R.A.; Turjoman, A.A.; Aldosari, M.S.; Razak, S.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Areabi, T.M.; et al. The Efficacy of Antioxidant Oral Supplements on the Progression of COVID-19 in Non-Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050804
Abulmeaty MMA, Aljuraiban GS, Shaikh SM, ALEid NE, Mazrou LRA, Turjoman AA, Aldosari MS, Razak S, El-Sayed MM, Areabi TM, et al. The Efficacy of Antioxidant Oral Supplements on the Progression of COVID-19 in Non-Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(5):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050804
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbulmeaty, Mahmoud M. A., Ghadeer S. Aljuraiban, Sumaya M. Shaikh, Naif E. ALEid, Lulwa R. Al Mazrou, Abdullah A. Turjoman, Mona S. Aldosari, Suhail Razak, Mervat M. El-Sayed, Tahani M. Areabi, and et al. 2021. "The Efficacy of Antioxidant Oral Supplements on the Progression of COVID-19 in Non-Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Antioxidants 10, no. 5: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050804
APA StyleAbulmeaty, M. M. A., Aljuraiban, G. S., Shaikh, S. M., ALEid, N. E., Mazrou, L. R. A., Turjoman, A. A., Aldosari, M. S., Razak, S., El-Sayed, M. M., Areabi, T. M., Alsalafi, R. M., Al-Helio, Y. S., Almutairy, A. B., & Molla, H. N. (2021). The Efficacy of Antioxidant Oral Supplements on the Progression of COVID-19 in Non-Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Antioxidants, 10(5), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050804







