The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
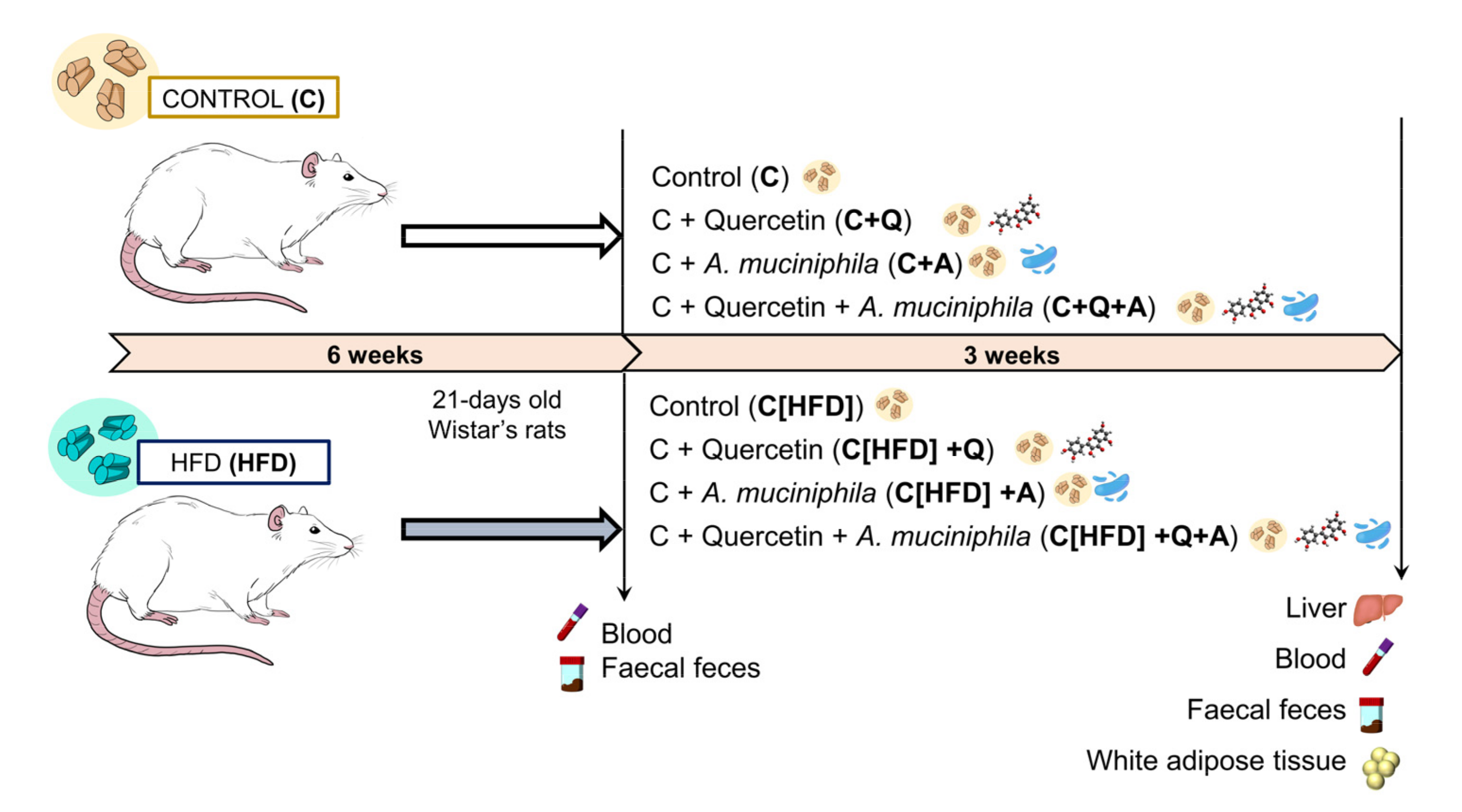
2.1. Animals and Experimental Diets
2.2. Dosage Information
2.3. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Fluorescent Microscopy
2.8. Hepatic Triglycerides Quantification
2.9. Gut Metagenomic Analysis
2.9.1. Fecal DNA Extraction
2.9.2. Amplification and Sequencing of 16S rRNA
2.9.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.10. Quantification of DNA and mRNA by Real-Time PCR
2.11. Plasma Bile Acid Quantification
2.12. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Identification and Quantification
2.13. Statistical Analysis
2.14. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. HFD Induces Juvenile Obesity and Metabolic Alterations in Rats
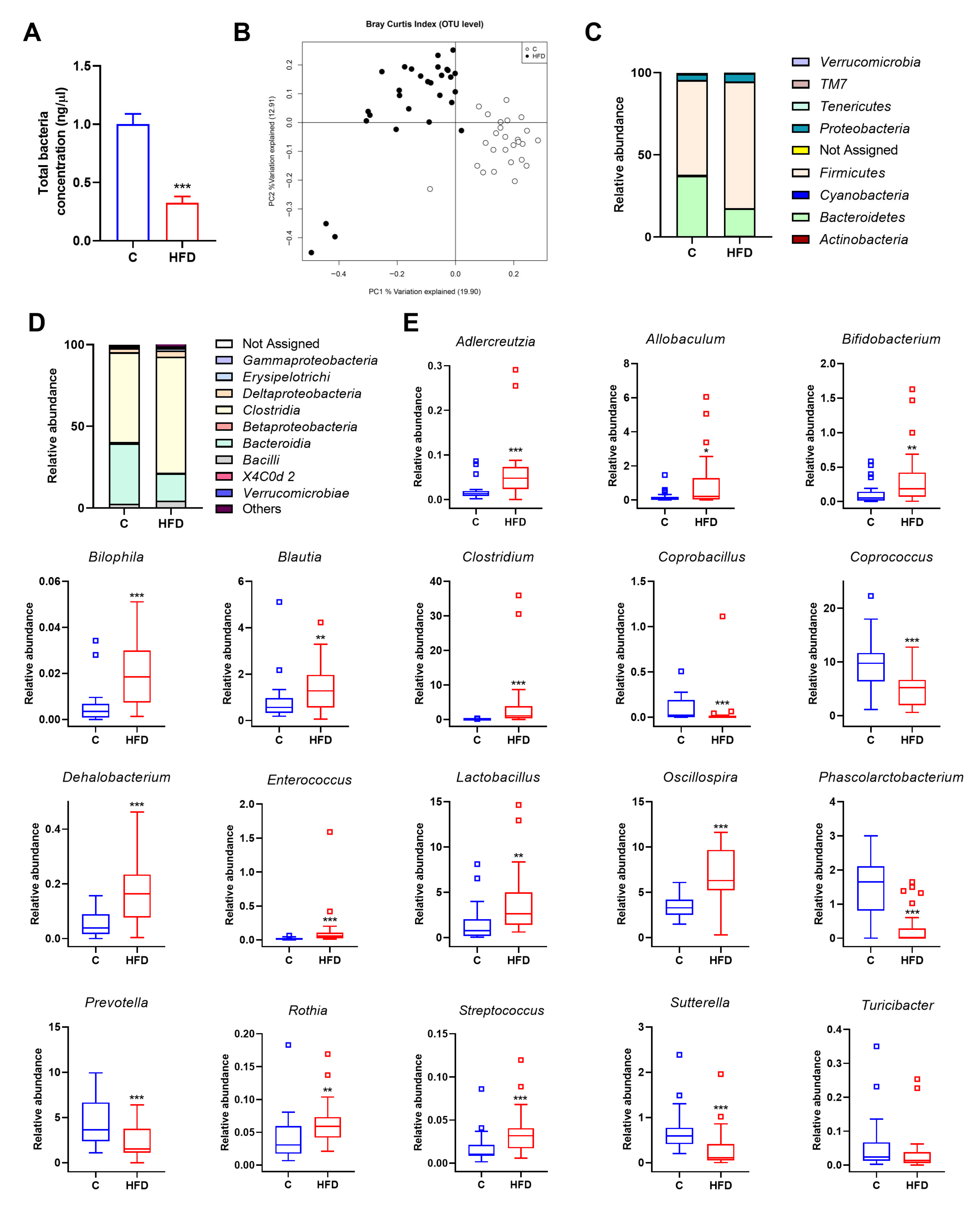
3.2. Gut Microbiota Is Altered by HFD in Juvenile Rats
3.3. Quercetin and A. muciniphila Counteract HFD-Induced Obesity-Associated Features in Juvenile Rats
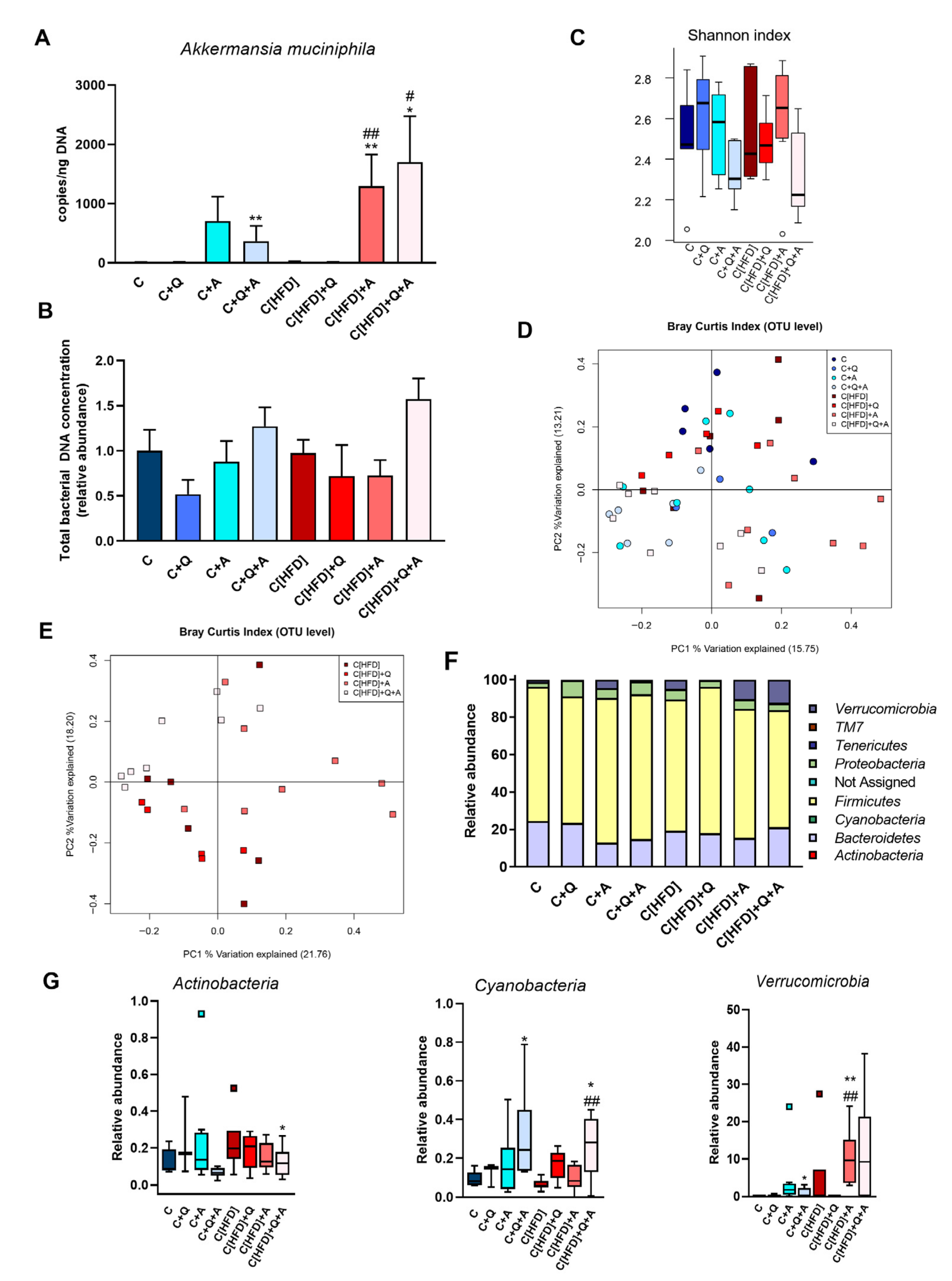
3.4. Effect of Diet, Quercetin and A. muciniphila Supplementation on Gut Microbiota Composition in the Early Obesity and NAFLD Model
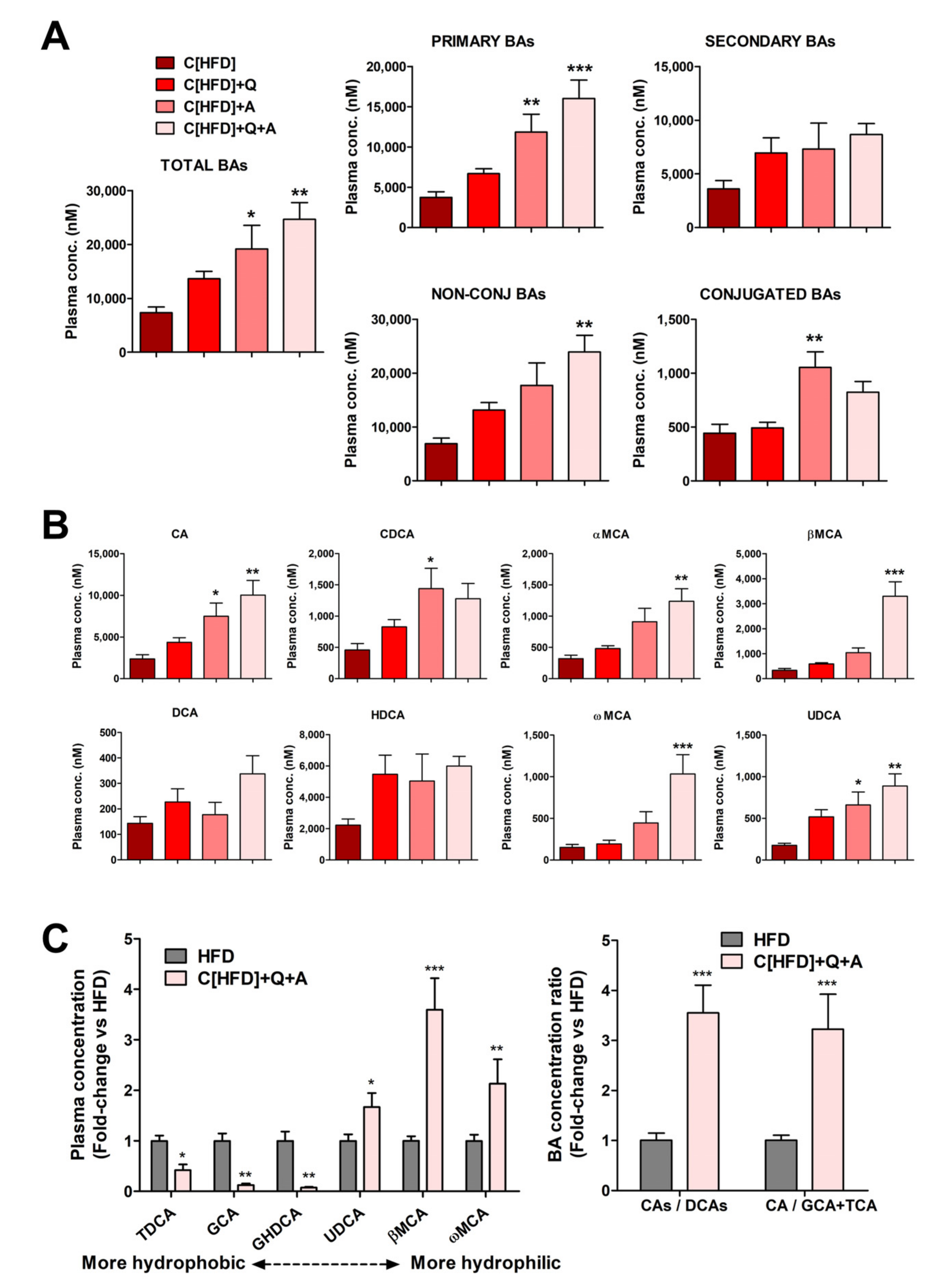
3.5. Effects of the Interventions on Plasma Bile Acid Levels
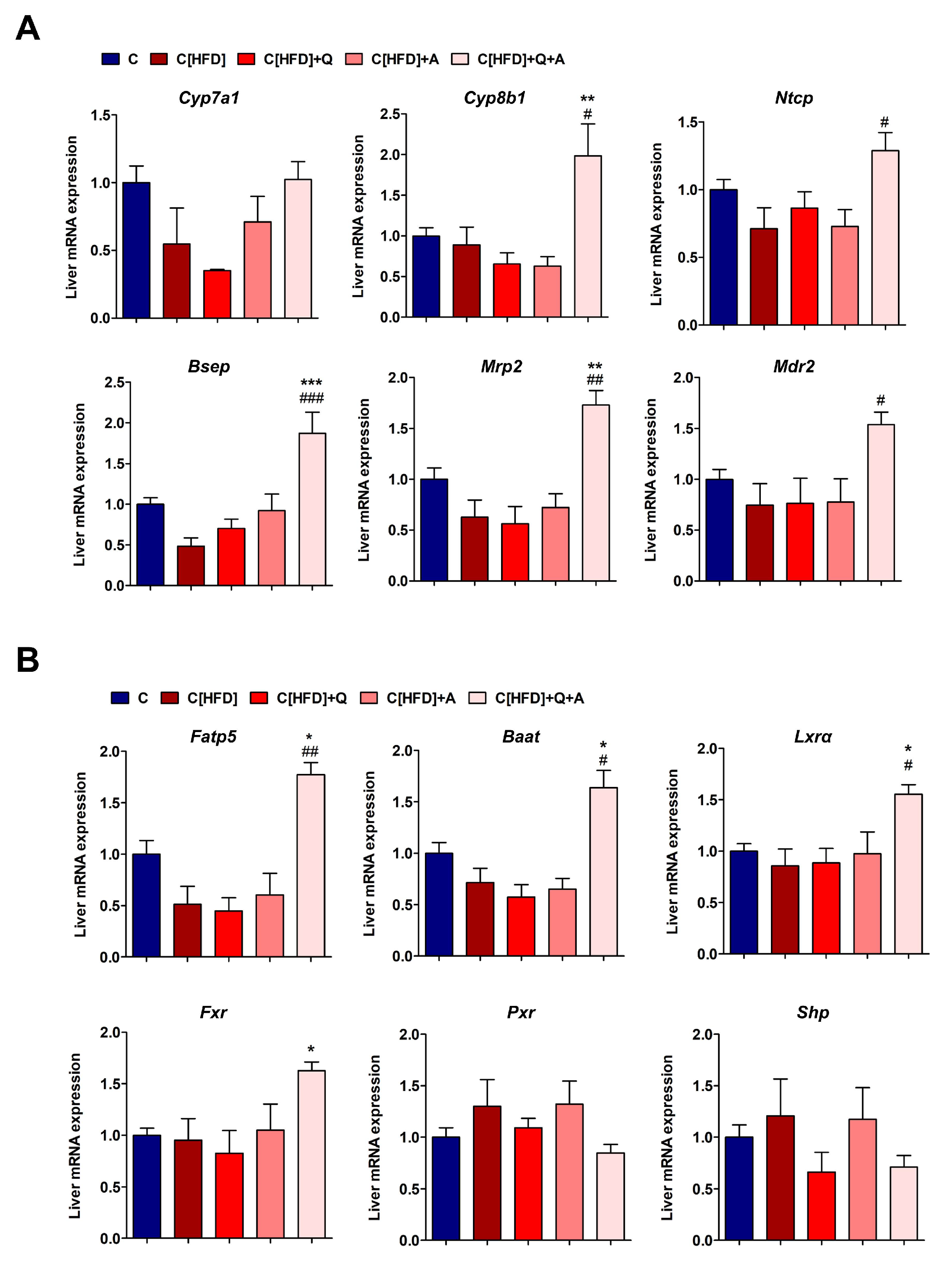
3.6. Effects of the Interventions on the Hepatic Expression of Bile Acid Synthesis, Metabolism and Transport Related Genes
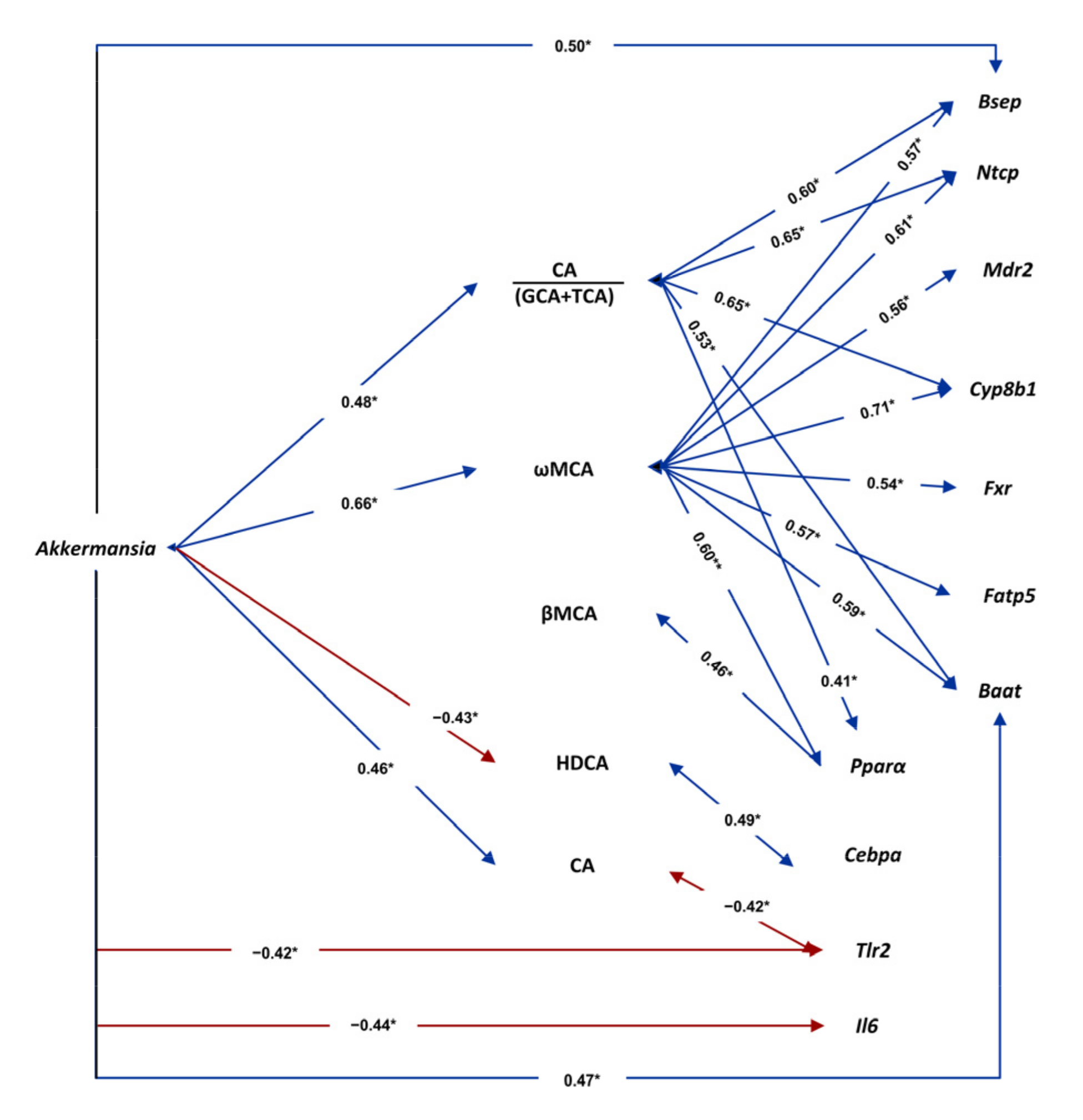
3.7. Associations among Gut Microbiota, Plasma Bile Acids and Liver Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Schwenger, K.J.P.; Bolzon, C.M.; Li, C.; Allard, J.P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity: The role of the gut bacteria. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Aging, gut microbiota and metabolic diseases: Management through physical exercise and nutritional interventions. Nutrients 2021, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagiakrishnan, K.; Halverson, T. Holistic perspective of the role of gut microbes in diabetes mellitus and its management. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monte, M.J.; Marin, J.J.; Antelo, A.; Vazquez-Tato, J. Bile acids: Chemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Baker, S.S.; Chapa-Rodriguez, A.; Liu, W.; Nugent, C.A.; Tsompana, M.; Mastrandrea, L.; Buck, M.J.; Baker, R.D.; Genco, R.J.; et al. Suppressed hepatic bile acid signalling despite elevated production of primary and secondary bile acids in NAFLD. Gut 2018, 67, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panera, N.; Barbaro, B.; Della Corte, C.; Mosca, A.; Nobili, V.; Alisi, A. A review of the pathogenic and therapeutic role of nutrition in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Res. 2018, 58, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittorio, J.; Lavine, J. E. Recent advances in understanding and managing pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. F1000Research 2020, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Almela, I.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Bullich-Vilarrubias, C.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Gómez Del Pulgar, E.M.; Francés, R.; Liebisch, G.; Sanz, Y. Bacteroides uniformis combined with fiber amplifies metabolic and immune benefits in obese mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1865706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; Jorquera, F.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Functional interactions between gut microbiota transplantation, quercetin, and high-fat diet determine non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development in germ-free mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Buch, H.; Zhang, F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Brient, A.; Phipps, K.R.; de Vos, W.M.; Cani, P.D. Toxicological safety evaluation of pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of pasteurised Akkermansia muciniphila as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia municiphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Guaita, D.; Moreno-Torres, M.; Jover, R.; Pareja, E.; Lendl, B.; Kuligowski, J.; Quintás, G.; Castell, J.V. Toward rapid screening of liver grafts at the operating room using mid-infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14542–14549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajo-Pescador, S.; Porras, D.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M.V.; Martinez-Florez, S.; Juarez-Fernandez, M.; Cuevas, M.J.; Mauriz, J.L.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sanchez-Campos, S. Beneficial effects of exercise on gut microbiota functionality and barrier integrity, and gut-liver crosstalk in an in vivo model of early obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pẽa, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Desantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benet, M.; Guzmán, C.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; Donato, M.T.; Castell, J.V.; Joverr, R. Repression of the nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner by steatotic drugs and in advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 87, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrov, P.D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Guzmán, C.; Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Castell, J.V.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Jover, R. A network involving gut microbiota, circulating bile acids, and hepatic metabolism genes that protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1900487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, G.; Tabares, B.; Jover, R.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; Castell, J.V. Semi-automatic quantitative RT-PCR to measure CYP induction by drugs in human hepatocytes. Toxicol. Vitr. 2003, 17, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cañaveras, J.C.; Donato, M.T.; Castell, J.V.; Lahoz, A. Targeted profiling of circulating and hepatic bile acids in human, mouse, and rat using a UPLC-MRM-MS-validated method. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quiroga, R.; Nistal, E.; Estébanez, B.; Porras, D.; Juárez-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; de Paz, J.A.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Exercise training modulates the gut microbiota profile and impairs inflammatory signaling pathways in obese children. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, K.T.; Kim, D.J. Gut microbiota: Novel therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Intestinal microbiota modulation in obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badi, R.M.; Mostafa, D.G.; Khaleel, E.F.; Satti, H.H. Resveratrol protects against hepatic insulin resistance in a rat’s model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulation of GPAT-1 and DGAT2 expression and inhibition of PKC membranous translocation. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2019, 46, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indiani, C.M.D.S.P.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Castelo, P.M.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Darrieux, M.; Parisotto, T.M. Childhood obesity and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yao, X.; Xia, F.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Q. Modulation of the gut microbiota in rats by hugan qingzhi tablets during the treatment of high-fat-diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7261619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nistal, E.; Sáenz de Miera, L.E.; Ballesteros Pomar, M.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Álvarez-Cuenllas, B.; Linares, P.; Olcoz, J.L.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; García-Lobo, J.M.; et al. An altered fecal microbiota profile in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) associated with obesity. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2019, 111, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.D.; Sun, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Bhoori, S.; Castelli, C.; Putignani, L.; Rivoltini, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Morelli, D.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Petito, V.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dao, M.C.; Everard, A.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Sokolovska, N.; Prifti, E.; Verger, E.O.; Kayser, B.D.; Levenez, F.; Chilloux, J.; Hoyles, L.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity: Relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology. Gut 2016, 65, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgermeister, E.; Schnoebelen, A.; Flament, A.; Benz, J.; Stihle, M.; Gsell, B.; Rufer, A.; Ruf, A.; Kuhn, B.; Märki, H.P.; et al. A novel partial agonist of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) recruits PPARγ-coactivator-1α, prevents triglyceride accumulation, and potentiates insulin signaling in vitro. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 809–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biondo, L.A.; Junior, E.A.L.; Souza, C.O.; Cruz, M.M.; Cunha, R.D.C.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.; Oyama, L.M.; Nascimento, C.M.O.; Pimentel, G.D.; dos Santos, R.V.T.; et al. Impact of doxorubicin treatment on the physiological functions of white adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Pan, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K. Regulation of SREBP-2 intracellular trafficking improves impaired autophagic flux and alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in NAFLD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Bian, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, X.; Yan, H.; Xia, M.; Chang, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Berberine attenuates nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the AMPK-SREBP-1c-SCD1 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serviddio, G.; Bellanti, F.; Vendemiale, G. Free radical biology for medicine: Learning from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 952–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizki, G.; Arnaboldi, L.; Gabrielli, B.; Yan, J.; Lee, G.S.; Ng, R.K.; Turner, S.M.; Badger, T.M.; Pitas, R.E.; Maher, J.J. Mice fed a lipogenic methionine-choline-deficient diet develop hypermetabolism coincident with hepatic suppression of SCD-1. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Tanaka, N. PPARs as metabolic regulators in the liver: Lessons from liver-specific PPAR-null mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, C.; Benet, M.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Moya, M.; García-Mediavilla, M.; Martínez-Chantar, M.; González-Gallego, J.; Castell, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Jover, R. The human liver fatty acid binding protein (FABP1) gene is activated by FOXA1 and PPARα; and repressed by C/EBPα: Implications in FABP1 down-regulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, C.; Luukkonen, P.; Sädevirta, S.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Salonen, A. Impact of short-term overfeeding of saturated or unsaturated fat or sugars on the gut microbiota in relation to liver fat in obese and overweight adults. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fei, Y.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Kang, J.; Wang, Z. Polygonatum odoratum polysaccharides modulate gut microbiota and mitigate experimentally induced obesity in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborti, C.K. New-found link between microbiota and obesity. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2015, 6, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, Z.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice is associated with the indigenous opportunistic bacteria on the interior of Peyer’s patches. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 55, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Shen, X.; Wei, P. Alteration of the gut microbiota associated with childhood obesity by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monga Kravetz, A.; Testerman, T.; Galuppo, B.; Graf, J.; Pierpont, B.; Siebel, S.; Feinn, R.; Santoro, N. Effect of gut microbiota and PNPLA3 rs738409 variant on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in obese youth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3575–e3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Daita, K.; Joyce, A.; Mirshahi, F.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Cazanave, S.; Luketic, V.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Boyett, S.; Min, H.-K.; et al. The presence and severity of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with specific changes in circulating bile acids. Hepatology 2018, 67, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusler, R.A.; Camastra, S.; Nannipieri, M.; Astiarraga, B.; Castro-Perez, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Chakravarthy, M.; Ferrannini, E. Increased bile acid synthesis and impaired bile acid transport in human obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferslew, B.C.; Xie, G.; Johnston, C.K.; Su, M.; Stewart, P.W.; Jia, W.; Brouwer, K.L.R.; Sidney Barritt, A. Altered bile acid metabolome in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 3318–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahnel, J.; Zöhrer, E.; Alisi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Ceccarelli, S.; De Vito, R.; Scharnagl, H.; Stojakovic, T.; Fauler, G.; Trauner, M.; et al. Serum bile acid levels in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussy, C.; Hsu, C.; Singh, S.; Bassirian, S.; Kolar, J.; Faulkner, C.; Sinha, N.; Bettencourt, R.; Gara, N.; Valasek, M.A.; et al. Serum bile acid patterns are associated with the presence of NAFLD in twins, and dose-dependent changes with increase in fibrosis stage in patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD. Aliment. Pharm. 2019, 49, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.; Canbay, A. Why bile acids are so important in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progression. Cells 2019, 8, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippagunta, S.M.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Adams, A.C.; Hillgartner, F.B. Cholic acid supplementation of a high-fat obesogenic diet suppresses hepatic triacylglycerol accumulation in mice via a fibroblast growth factor 21-dependent mechanism. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Mizushima, K.; Inoue, R.; Yasukawa, Z.; Abe, A.; Takagi, T. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating the interaction between gut microbiota and bile acids. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020, 67, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Kim, J.G.; Shin, Y.W.; Kim, S.H.; Whang, K.Y. Effect of dietary inclusion of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 43121 on cholesterol metabolism in rats. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Krausz, K.W.; Shi, J.; Brocker, C.N.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.G.; Bisson, W.H.; et al. Intestine-selective farnesoid X receptor inhibition improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, F.J.; Jiang, C.; Patterson, A.D. An intestinal microbiota–farnesoid X receptor axis modulates metabolic disease. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudling, M. Understanding mouse bile acid formation: Is it time to unwind why mice and rats make unique bile acids. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Bonde, Y.; Eggertsen, G.; Rudling, M. Muricholic bile acids are potent regulators of bile acid synthesis via a positive feedback mechanism. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 275, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sydor, S.; Best, J.; Messerschmidt, I.; Manka, P.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Brodesser, S.; Lucas, C.; Wegehaupt, A.; Wenning, C.; Aßmuth, S.; et al. Altered microbiota diversity and bile acid signaling in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic NASH-HCC. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, S.V.; Macovei, I.; Bujor, A.; Miron, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Trifan, A. Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: The role of metabolites. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 626–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murota, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Uehara, M. Flavonoid metabolism: The interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| C | HFD | |
|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 418.36 ± 5.37 | 440.58 ± 6.85 * |
| Food intake (g/day) | 20.42 ± 0.68 | 17.94 ± 0.81 *** |
| Food intake (kcal/day) | 77.92 ± 1.30 | 93.08 ± 1.85 *** |
| ALT (U/L) | 27.26 ± 1.78 | 48.28 ± 2.60 *** |
| AST (U/L) | 114.19 ± 7.05 | 115.17 ± 4.46 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.09 ± 0.06 | 1.10 ± 0.09 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 56.76 ± 1.92 | 62.97 ± 2.28 * |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 2.58 ± 0.26 | 3.55 ± 0.27 * |
| Plasma albumin (g/L) | 34.68 ± 0.49 | 34.76 ± 0.45 |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 122.48 ± 3.61 | 112.97 ± 2.49 * |
| Plasma insulin (ng/mL) | 4.39 ± 0.33 | 6.86 ± 0.83 * |
| HOMA-IR | 1.17 ± 0.12 | 2.02 ± 0.35 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; Petrov, P.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Soluyanova, P.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Jover, R.; et al. The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10122001
Juárez-Fernández M, Porras D, Petrov P, Román-Sagüillo S, García-Mediavilla MV, Soluyanova P, Martínez-Flórez S, González-Gallego J, Nistal E, Jover R, et al. The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(12):2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10122001
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuárez-Fernández, María, David Porras, Petar Petrov, Sara Román-Sagüillo, María Victoria García-Mediavilla, Polina Soluyanova, Susana Martínez-Flórez, Javier González-Gallego, Esther Nistal, Ramiro Jover, and et al. 2021. "The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation" Antioxidants 10, no. 12: 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10122001
APA StyleJuárez-Fernández, M., Porras, D., Petrov, P., Román-Sagüillo, S., García-Mediavilla, M. V., Soluyanova, P., Martínez-Flórez, S., González-Gallego, J., Nistal, E., Jover, R., & Sánchez-Campos, S. (2021). The Synbiotic Combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and Quercetin Ameliorates Early Obesity and NAFLD through Gut Microbiota Reshaping and Bile Acid Metabolism Modulation. Antioxidants, 10(12), 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10122001








