EEG Emotion Classification Using an Improved SincNet-Based Deep Learning Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Preliminary of Sincnet
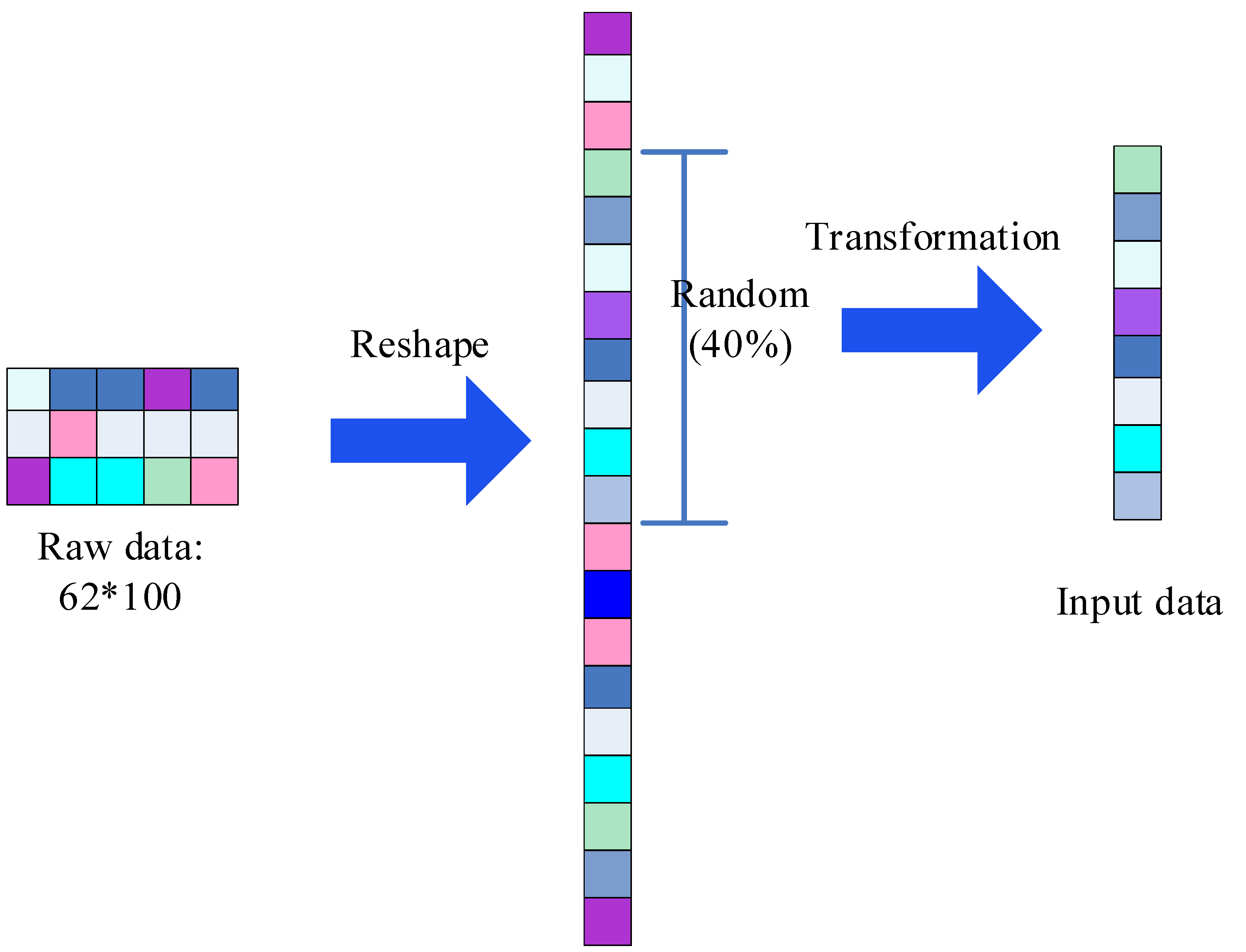
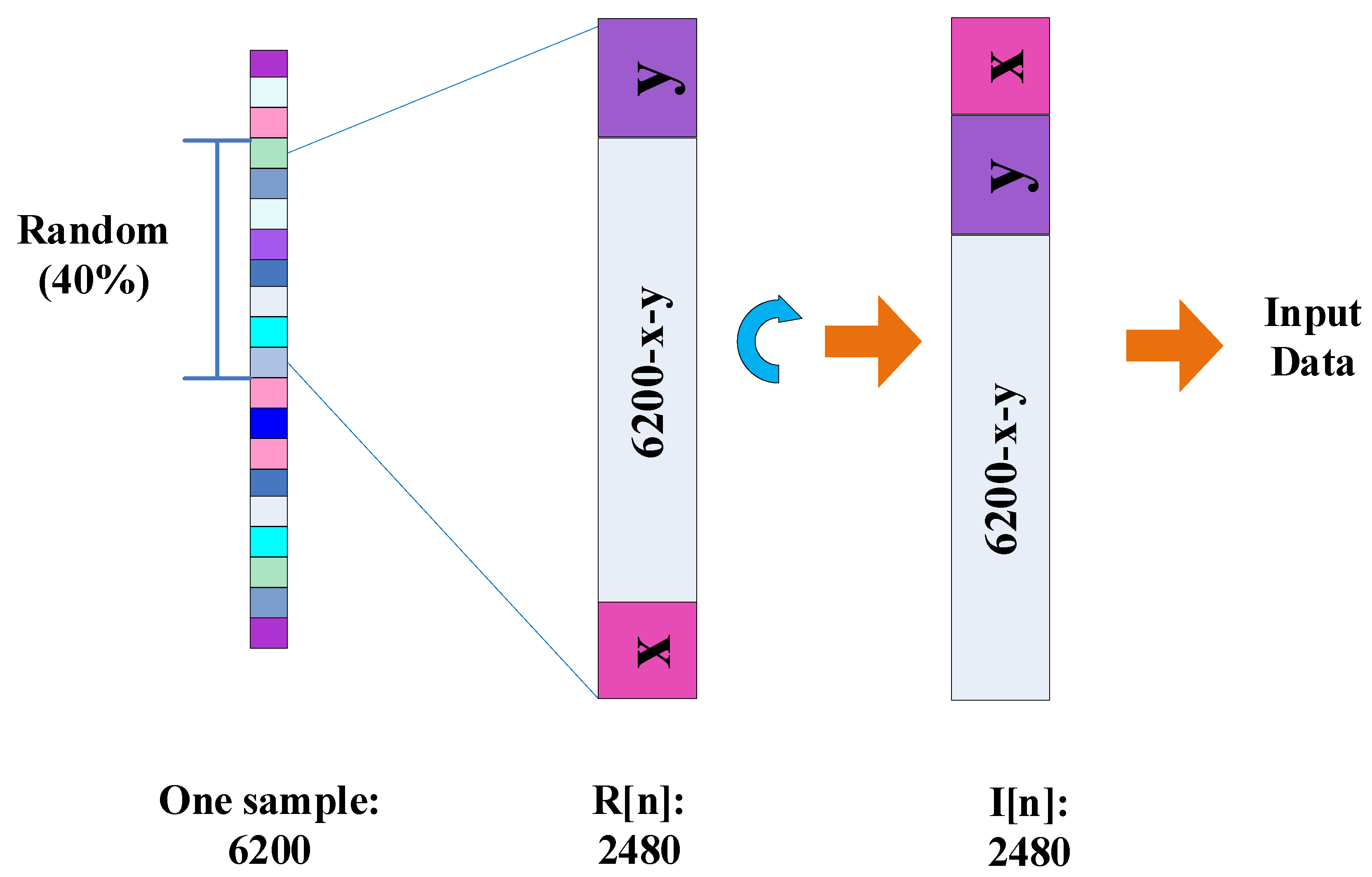
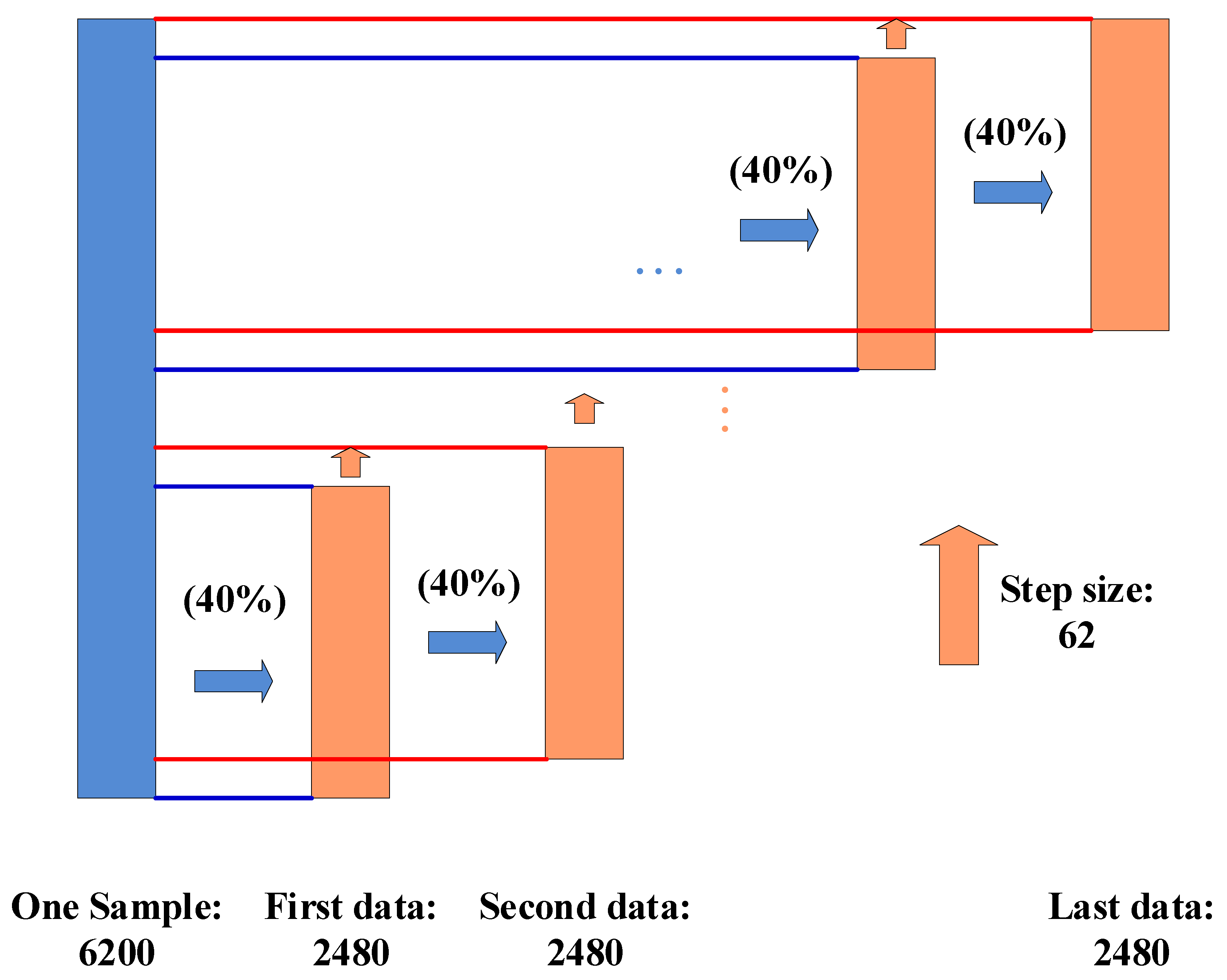
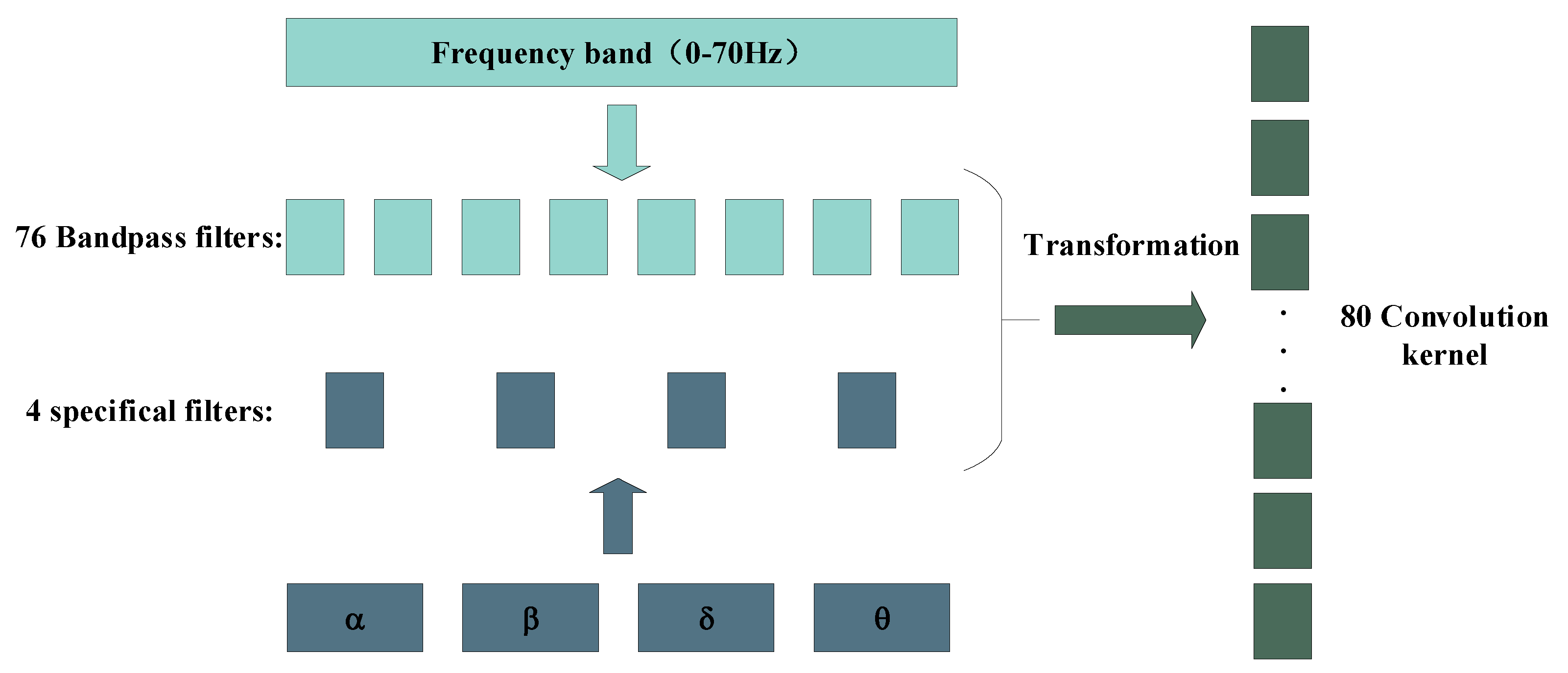
2.2. Design of Sincnet-R
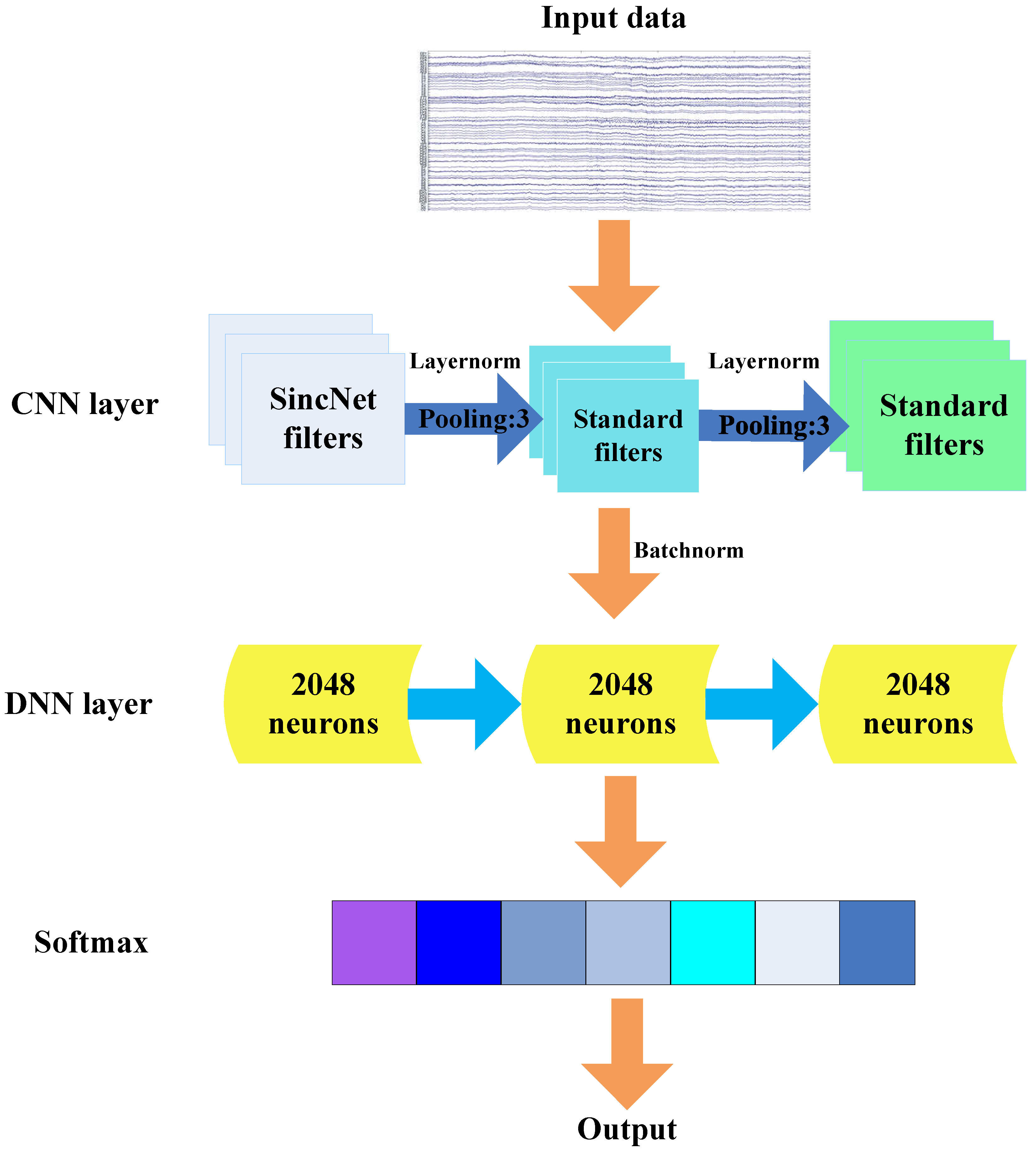
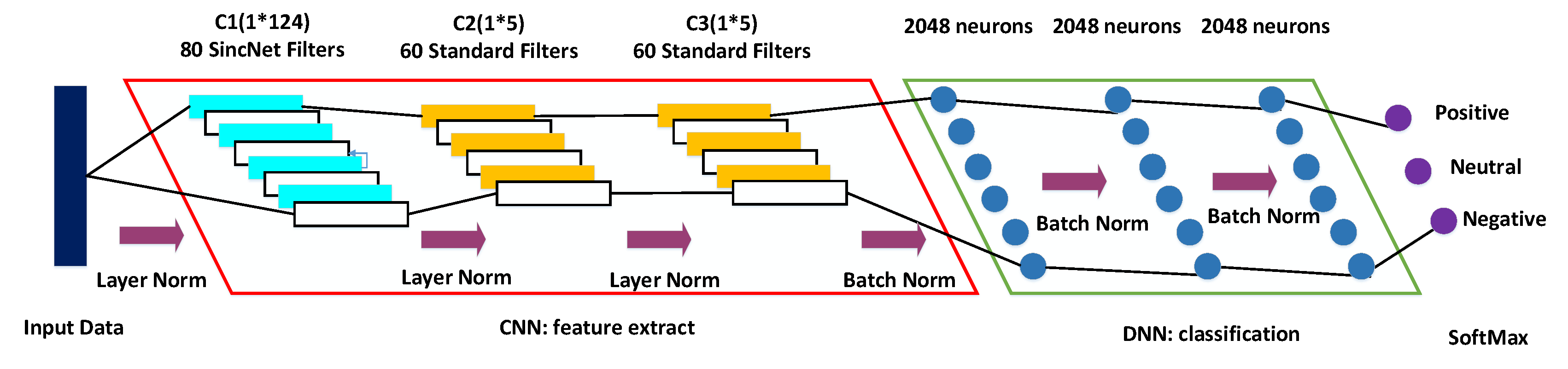
2.3. Architecture of Sincnet-R
3. Materials
3.1. Experimental Protocol
3.2. EEG Recording
3.3. The Establishment of EEG Data Sets
4. Results and Discussion
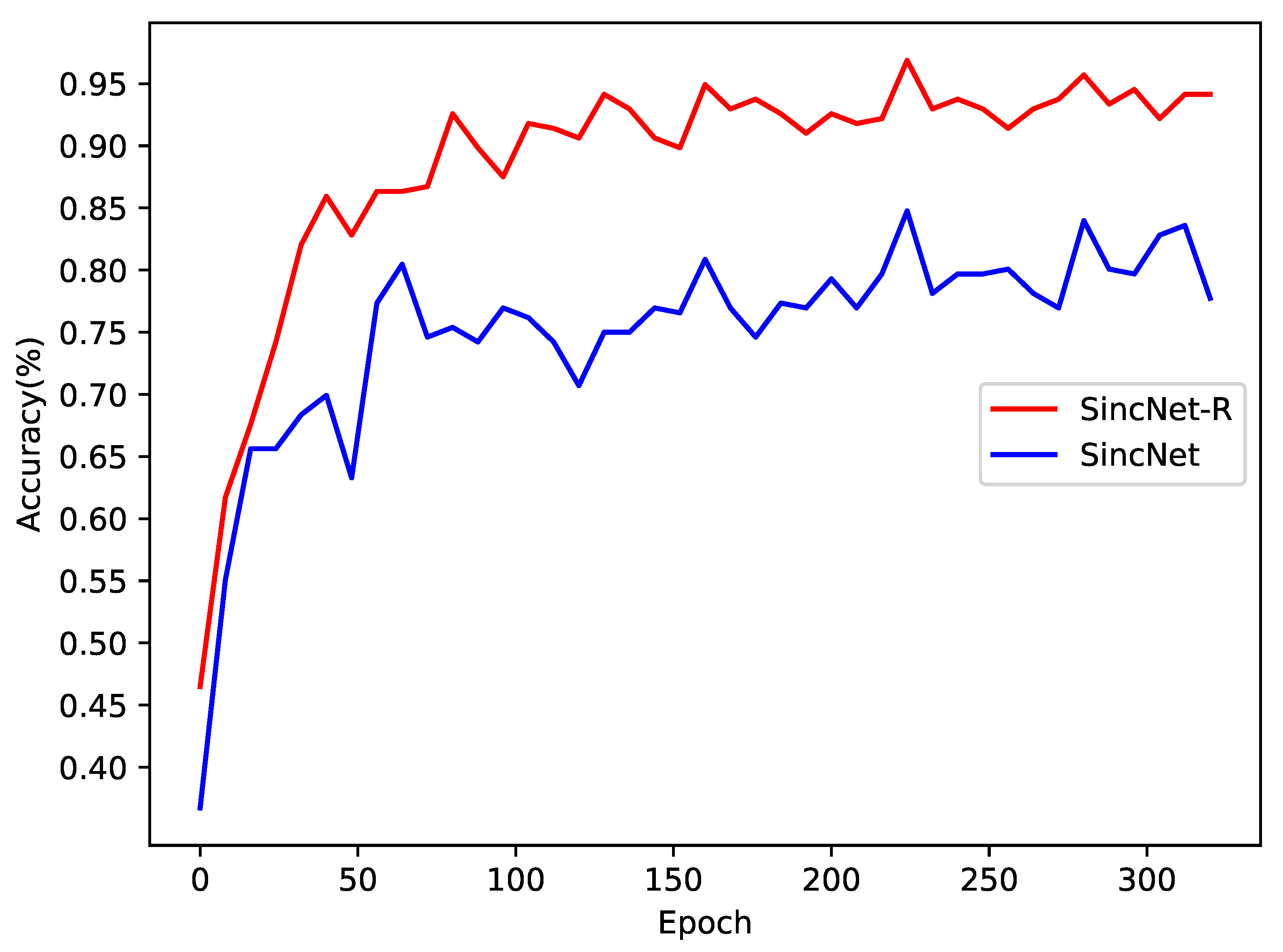
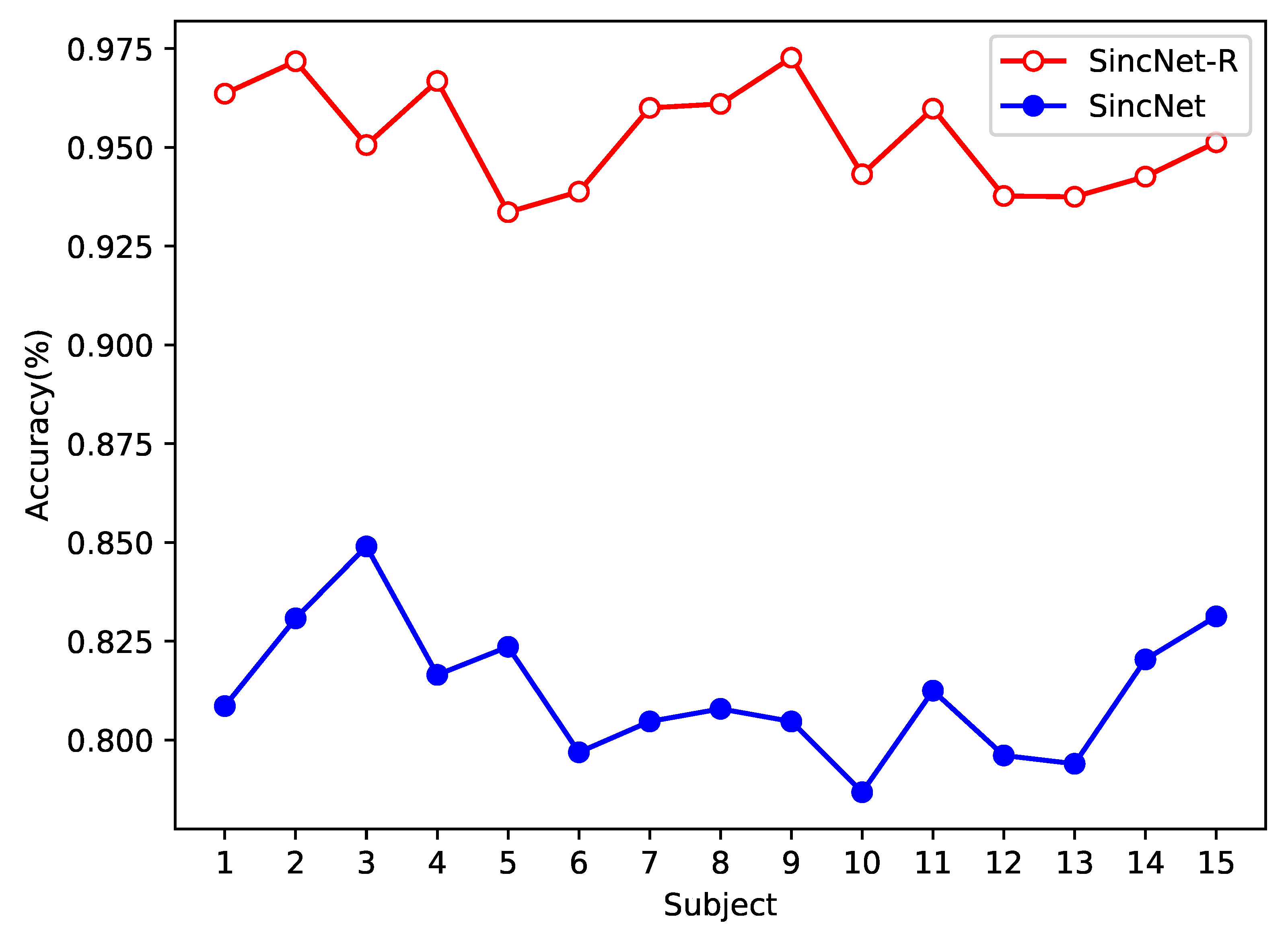
4.1. SincNet-R vs. SincNet
4.2. Compared to Other Classical Models
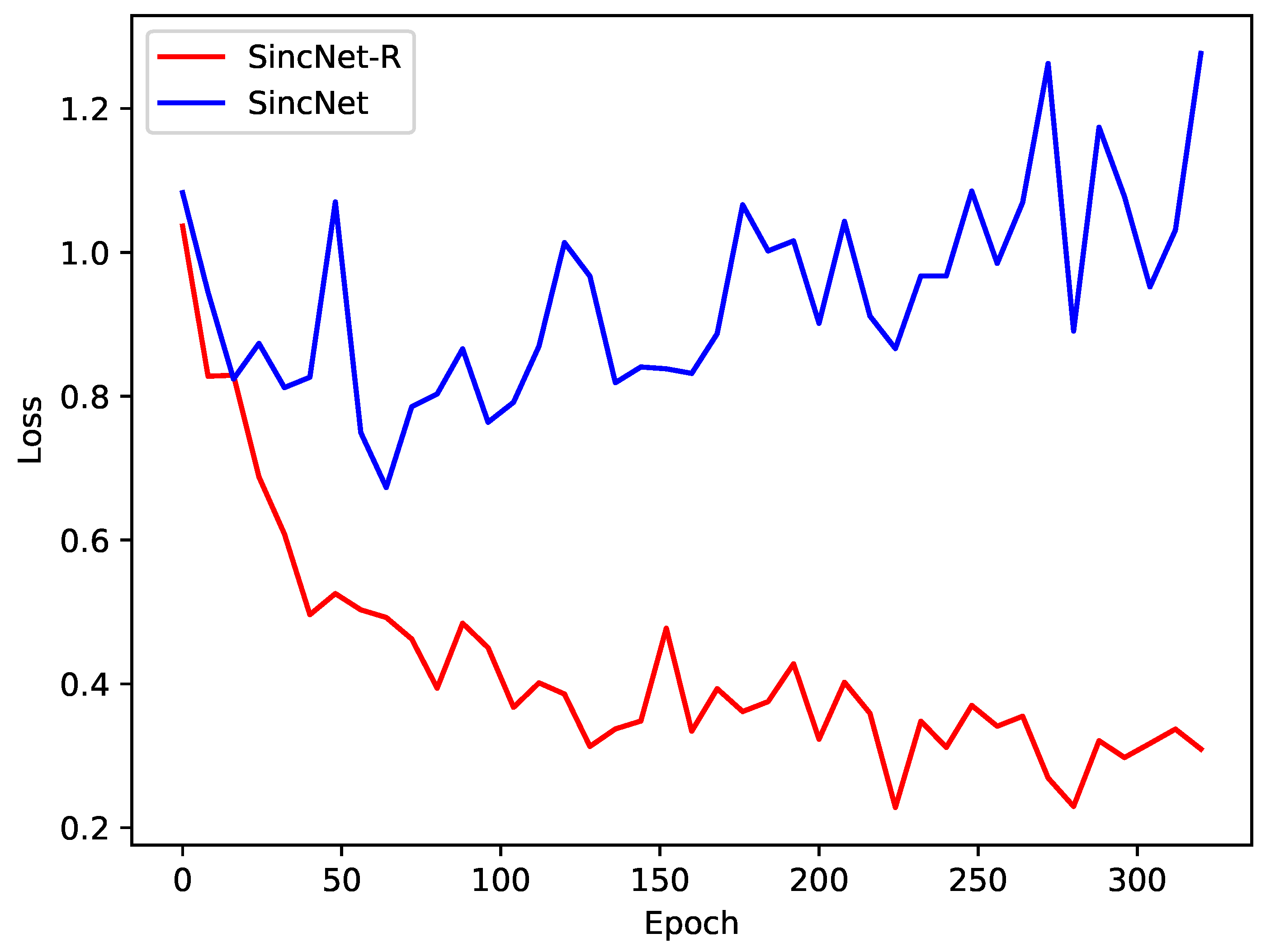
4.3. Variance and Convergency Analysis of Sincnet-R
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Soroush, M.Z.; Maghooli, K.; Setarehdan, S.K.; Nasrabadi, A.M. A Review on EEG Signals Based Emotion Recognition. Int. Clin. Neurosci. J. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, R.; Murugappan, M.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Sundaraj, K.; Omar, M.I.; Mohamad, K.; Palaniappan, R. Detection of emotions in Parkinson’s disease using higher order spectral features from brain’s electrical activity. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.K.; Han, Y.M.; Sze, S.L.; Chan, A.S. Altered right frontal cortical connectivity during facial emotion recognition in children with autism spectrum disorders. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2014, 8, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.M.; Harris, A.W.; Williams, L.M. Neural processing of facial expressions of emotion in first onset psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 219, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.A.; Kara, S.; Agambayev, S.; Bilgiç, V. Nonlinear analysis of EEGs of patients with major depression during different emotional states. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 67, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Cross-subject EEG feature selection for emotion recognition using transfer recursive feature elimination. Front. Neurorobotics 2017, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, L.A.M.; Mu noz-Delgado, J.; Sánchez-Ferrer, J.C.; Fresán, A.; Brüne, M.; Arango de Montis, I. Facial emotion recognition and empathy in employees at a juvenile detention center. Int. J. Offender Ther. Comp. Criminol. 2018, 62, 2430–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Phillips, P.; Dong, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.D. Intelligent facial emotion recognition based on stationary wavelet entropy and Jaya algorithm. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B. A brief review of facial emotion recognition based on visual information. Sensors 2018, 18, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morningstar, M.; Nelson, E.E.; Dirks, M.A. Maturation of vocal emotion recognition: Insights from the developmental and neuroimaging literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 18, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, B.L. Discriminative extreme learning machine with supervised sparsity preserving for image classification. Neurocomputing 2017, 261, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanouni, P.; Zwicker, J.G. Electrophysiological Responses to Emotional Facial Expressions in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 5, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lang, M.; Wang, W.; Xiao, F.; Li, J. Electrophysiological evidence for the effects of emotional content on false recognition memory. Cognition 2018, 179, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Hondt, F.; Lassonde, M.; Thebault-Dagher, F.; Bernier, A.; Gravel, J.; Vannasing, P.; Beauchamp, M.H. Electrophysiological correlates of emotional face processing after mild traumatic brain injury in preschool children. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroush, M.Z.; Maghooli, K.; Setarehdan, S.K.; Nasrabadi, A.M. Emotion classification through nonlinear EEG analysis using machine learning methods. Int. Clin. Neurosci. J. 2018, 5, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Zheng, W.; Song, P.; Cui, Z. Eeg emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Madrid, Spain, 3–6 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Yu, M.; Zhao, G.; Song, J.; Ge, Y.; Shi, Y. Real-time movie-induced discrete emotion recognition from EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, A.; Akan, A. Emotion recognition from EEG signals by using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2018, 21, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinando, H.; Seppänen, T.; Alasaarela, E. Enhancing Emotion Recognition from ECG Signals using Supervised Dimensionality Reduction. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2017), Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; pp. 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, H.; Iizuka, H.; Sugiyama, M. ECG-Based Concentration Recognition with Multi-Task Regression. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehri, V.; Ingle, R.; Patil, S.; Awale, R. Analysis of Facial EMG Signal for Emotion Recognition Using Wavelet Packet Transform and SVM. In Machine Intelligence and Signal Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E. EMG pattern recognition in the era of big data and deep learning. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.; Grage, T.; Kirschbaum, C.; Strobel, A. Processing emotions: Effects of menstrual cycle phase and premenstrual symptoms on the startle reflex, facial EMG and heart rate. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 351, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcao, S.M.; Fonseca, M.J. Emotions recognition using EEG signals: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Yazdani, A.; Soleymani, M.; Mühl, C.; Lee, J.S.; Nijholt, A.; Pun, T.; Ebrahimi, T.; Patras, I. Single trial classification of EEG and peripheral physiological signals for recognition of emotions induced by music videos. In International Conference on Brain Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Soleymani, M.; Lichtenauer, J.; Pun, T.; Pantic, M. A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Hsieh, S. Classifying different emotional states by means of EEG-based functional connectivity patterns. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanel, G.; Kierkels, J.J.; Soleymani, M.; Pun, T. Short-term emotion assessment in a recall paradigm. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2009, 67, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, T.L.; Jeng, S.K.; Chen, J.H. EEG-based emotion recognition in music listening: A comparison of schemes for multiclass support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.H.; Jung, T.P.; Wu, T.L.; Jeng, S.K.; Duann, J.R.; Chen, J.H. EEG-based emotion recognition in music listening. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, D.; Wang, X.W.; Shi, L.C.; Lu, B.L. EEG-based emotion recognition during watching movies. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Cancun, Mexico, 27 April–1 May 2011; pp. 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, R.N.; Wang, X.W.; Lu, B.L. EEG-based emotion recognition in listening music by using support vector machine and linear dynamic system. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 468–475. [Google Scholar]
- Murugappan, M.; Juhari, M.R.B.M.; Nagarajan, R.; Yaacob, S. An Investigation on visual and audiovisual stimulus based emotion recognition using EEG. Int. J. Med. Eng. Inform. 2009, 1, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatupaiboon, N.; Pan-Ngum, S.; Israsena, P. Subject-dependent and subject-independent emotion classification using unimodal and multimodal physiological signals. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2015, 5, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, B.L. Emotion classification based on gamma-band EEG. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in medicine and biology society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. An EEG-based brain-computer interface for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 2063–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Koelstra, S.; Patras, I. Fusion of facial expressions and EEG for implicit affective tagging. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.; Cao, R.; Li, L. Emotion recognition based on the sample entropy of EEG. Bio-Med Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Naghibi-Sistani, M.B. Emotion recognition method using entropy analysis of EEG signals. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2011, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, M. Emotion development system by interacting with human EEG and natural scene understanding. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2012, 14, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Gupta, A.; Jain, P.; Rani, A.; Yadav, J. Classification of human emotions from EEG signals using SVM and LDA Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 19–20 February 2015; pp. 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Frounchi, J.; Amiri, M. Wavelet-based emotion recognition system using EEG signal. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Gao, Z.K.; Wang, X.M.; Li, Y.L.; Han, J.W.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. A recurrence quantification analysis-based channel-frequency convolutional neural network for emotion recognition from EEG. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2018, 28, 085724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Mehmood, R.M. Deep learninig of EEG signals for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Turin, Italy, 29 June–3 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, H. Hierarchical convolutional neural networks for EEG-based emotion recognition. Cogn. Comput. 2018, 10, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Alam, M.G.R.; Uddin, M.Z.; Huda, S.; Almogren, A.; Fortino, G. Human emotion recognition using deep belief network architecture. Inf. Fusion 2019, 51, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, F.; Coyle, J.L.; Sejdić, E. Deep belief networks for electroencephalography: A review of recent contributions and future outlooks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Hamid, O.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jiang, H.; Deng, L.; Penn, G.; Yu, D. Convolutional Neural Networks for Speech Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 22, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, M.; Bengio, Y. Speaker Recognition from raw waveform with SincNet. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.00158. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R.; Schafer, R.W. Theory and Applications of Digital Speech Processing; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 64. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Yang, C.; Dai, G.; Qin, F.; Zhang, J.; Kong, W. EEG classification of driver mental states by deep learning. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2018, 12, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

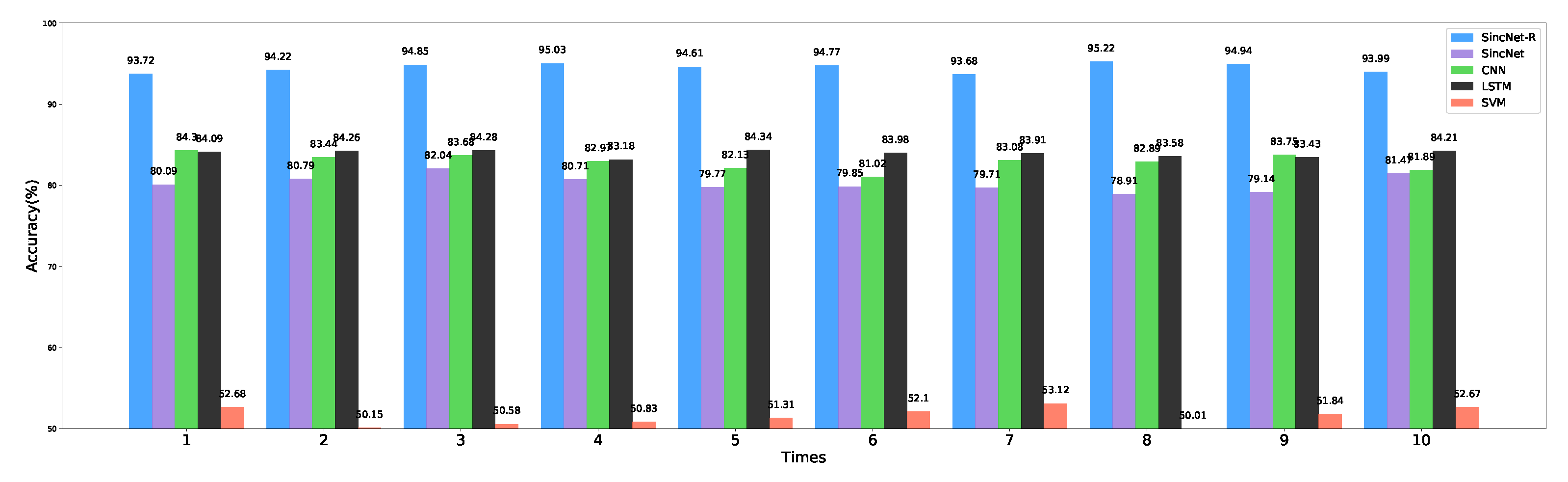
| Model | SincNet-R | SincNet | CNN | LSTM | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average accuracy (%) | 94.503 | 80.248 | 82.915 | 83.926 | 51.529 |
| Model | SincNet-R | SincNet | CNN | LSTM | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance | 0.282 | 0.893 | 0.877 | 0.144 | 1.123 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, G.; Kong, W. EEG Emotion Classification Using an Improved SincNet-Based Deep Learning Model. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110326
Zeng H, Wu Z, Zhang J, Yang C, Zhang H, Dai G, Kong W. EEG Emotion Classification Using an Improved SincNet-Based Deep Learning Model. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(11):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110326
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Hong, Zhenhua Wu, Jiaming Zhang, Chen Yang, Hua Zhang, Guojun Dai, and Wanzeng Kong. 2019. "EEG Emotion Classification Using an Improved SincNet-Based Deep Learning Model" Brain Sciences 9, no. 11: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110326
APA StyleZeng, H., Wu, Z., Zhang, J., Yang, C., Zhang, H., Dai, G., & Kong, W. (2019). EEG Emotion Classification Using an Improved SincNet-Based Deep Learning Model. Brain Sciences, 9(11), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110326






