More than Meets the Mind’s Eye? Preliminary Observations Hint at Heterogeneous Alpha Neuromarkers for Visual Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
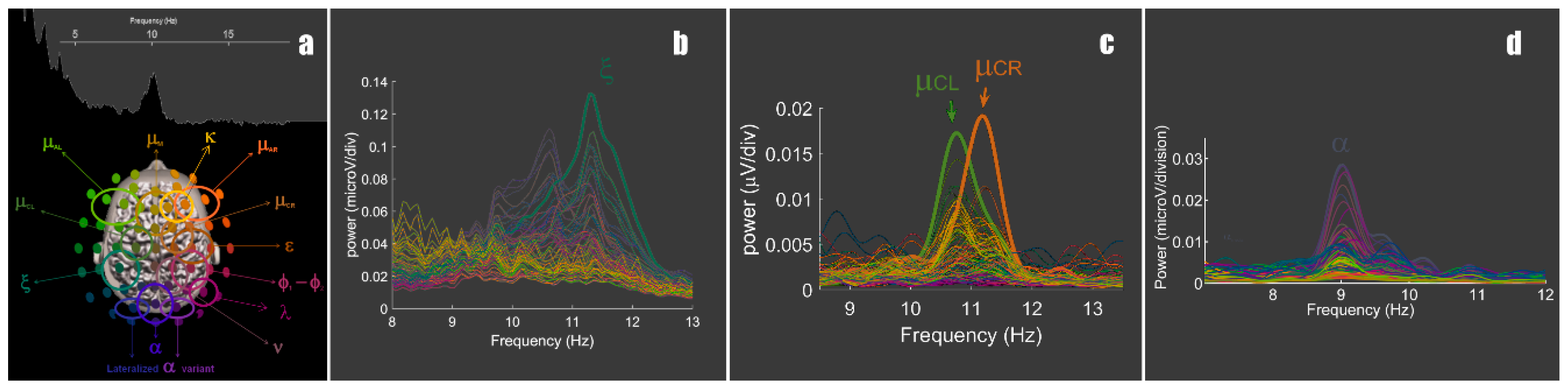
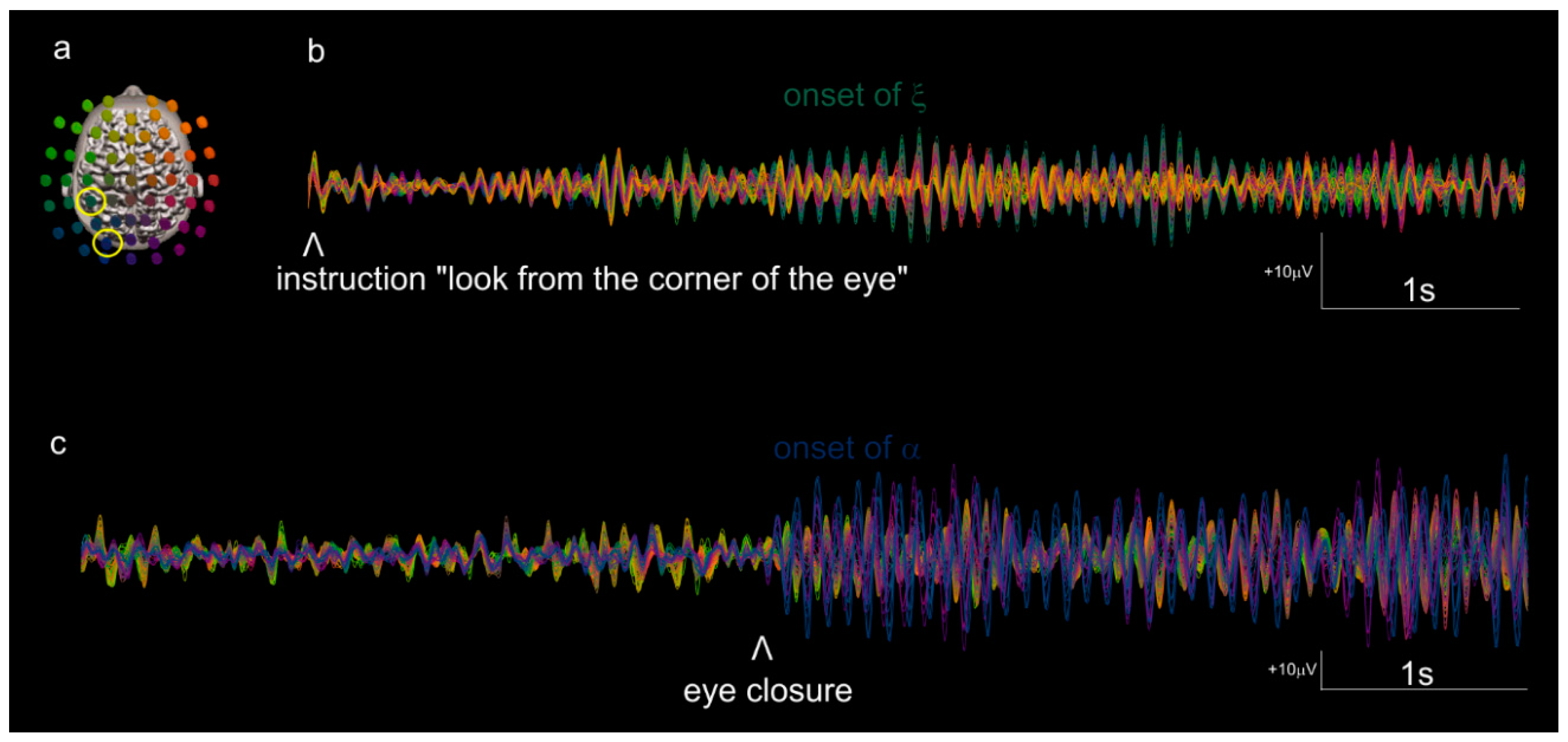
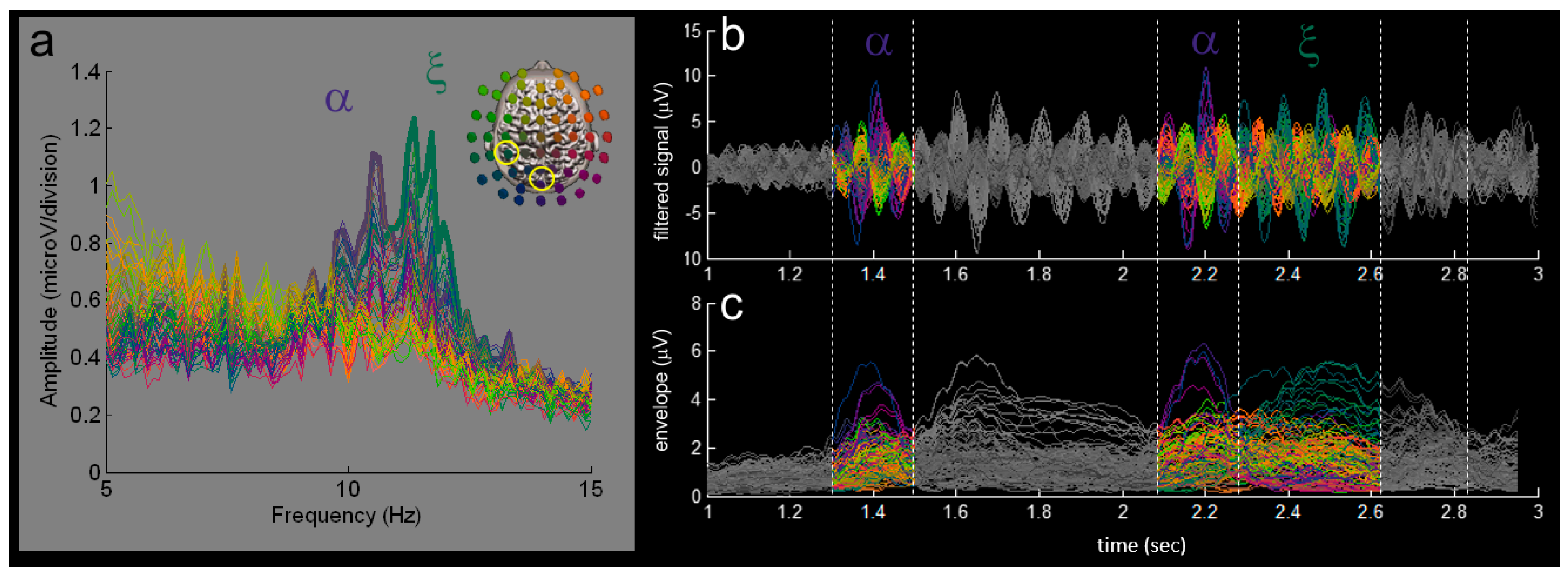
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Posner, M.I.; Snyder, C.R.; Davidson, B.J. Attention and the detection of signals. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1980, 109, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W. The Principles of Psychology; Henry Holt and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1890; pp. 402–458. [Google Scholar]
- Von Helmholtz, H. (1896/1989). Physiological Optics (1896-2nd German Edition, translated by M. Mackeben, from Nakayama and Mackeben. Vis. Res. 1989, 29, 1631–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert, A.; Poggio, T. Spotlight on attention. Trends Neurosci. 1985, 8, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.A.; Dark, V.J. Selective attention. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1986, 37, 43–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, J.; Baylis, G.C. Movement and visual attention: The spotlight metaphor breaks down. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1989, 15, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, K.R.; Bichot, N.P. Visuospatial attention: Beyond a spotlight model. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 1999, 6, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, F. Splitting the spotlight of visual attention. Neuron 2004, 42, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Posner, M.I.; Petersen, S.E. The attention system of the human brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, A.; Buhle, J. Typologies of attentional networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capotosto, P.; Babiloni, C.; Romani, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Frontoparietal cortex controls spatial attention through modulation of anticipatory alpha rhythms. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5863–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, H. Über das elektrenkephalogramm des menschen. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1929, 87, 527–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, P. Hans Berger on the electroencephalogram of man. The fourteen original reports on the human electroencephalogram. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1969, 28, 507. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, H. Ueber das Elektrenkephalogramm des Menschen. J. Psychol. Neurol. 1930, 40, 160–179. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, E.D.; Matthews, B.H. The Berger rhythm: Potential changes from the occipital lobes in man. Brain 1934, 57, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vaque, T.J. The history of EEG hans berger: Psychophysiologist. A historical vignette. J. Neurother. 1999, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millett, D. Hans Berger: From psychic energy to the EEG. Perspect. Biol. Med. 2001, 44, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, J.L.; Atienza, M.; Gómez, C.M.; Salas, R.M. Spectral structure and brain mapping of human alpha activities in different arousal states. Neuropsychobiology 1999, 39, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.C. The Brain’s Alpha Rhythms and the Mind; BV Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.; Mazaheri, A. Shaping functional architecture by oscillatory alpha activity: Gating by inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxe, J.J.; Snyder, A.C. The role of alpha-band brain oscillations as a sensory suppression mechanism during selective attention. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, C.; Keitel, A.; Benwell, C.S.; Daube, C.; Thut, G.; Gross, J. Stimulus-driven brain rhythms within the alpha band: The attentional-modulation conundrum. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 3119–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, W.J.; Cole, H.W. EEG alpha activity reflects attentional demands, and beta activity reflects emotional and cognitive processes. Science 1985, 228, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesch, W.; Doppelmayr, M.; Russegger, H.; Pachinger, T.; Schwaiger, J. Induced alpha band power changes in the human EEG and attention. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 244, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxe, J.J.; Simpson, G.V.; Ahlfors, S.P. Parieto-occipital ∼ 10 Hz activity reflects anticipatory state of visual attention mechanisms. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 3929–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worden, M.S.; Foxe, J.J.; Wang, N.; Simpson, G.V. Anticipatory biasing of visuospatial attention indexed by retinotopically specific-band electroencephalography increases over occipital cortex. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, RC63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Stadler, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M.; Hanslmayr, S.; Gruber, W.R.; Birbaumer, N. A shift of visual spatial attention is selectively associated with human EEG alpha activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thut, G.; Nietzel, A.; Brandt, S.A.; Pascual-Leone, A. α-Band electroencephalographic activity over occipital cortex indexes visuospatial attention bias and predicts visual target detection. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 9494–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doesburg, S.M.; Roggeveen, A.B.; Kitajo, K.; Ward, L.M. Large-scale gamma-band phase synchronization and selective attention. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyart, V.; Tallon-Baudry, C. Neural dissociation between visual awareness and spatial attention. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, D.; Simpson, G.V.; Weber, D.L.; Dale, C.L.; Nichols, T.E.; Leahy, R.M. A novel ANCOVA design for analysis of MEG data with application to a visual attention study. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Snyder, A.C.; Molholm, S.; Foxe, J.J. Oscillatory alpha-band mechanisms and the deployment of spatial attention to anticipated auditory and visual target locations: Supramodal or sensory-specific control mechanisms? J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9923–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohenkohl, G.; Nobre, A.C. Alpha oscillations related to anticipatory attention follow temporal expectations. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14076–14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, S.; D’Zmura, M.; Srinivasan, R. Lateralization of frequency-specific networks for covert spatial attention to auditory stimuli. Brain Topogr. 2012, 25, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, K.D.; Vaina, L.M. Functional roles of 10 Hz alpha-band power modulating engagement and disengagement of cortical networks in a complex visual motion task. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikkai, A.; Dandekar, S.; Curtis, C.E. Lateralization in alpha-band oscillations predicts the locus and spatial distribution of attention. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaha, J.; Gosseries, O.; Postle, B.R. Distinct oscillatory frequencies underlie excitability of human occipital and parietal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2824–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizuk, S.A.; Mathewson, K.E. Power and phase of alpha oscillations reveal an interaction between spatial and temporal visual attention. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 29, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosmelli, D.; López, V.; Lachaux, J.P.; López-Calderón, J.; Renault, B.; Martinerie, J.; Aboitiz, F. Shifting visual attention away from fixation is specifically associated with alpha band activity over ipsilateral parietal regions. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treder, M.S.; Bahramisharif, A.; Schmidt, N.M.; Van Gerven, M.A.; Blankertz, B. Brain-computer interfacing using modulations of alpha activity induced by covert shifts of attention. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.; Dähne, S.; Blankertz, B. EEG predictors of covert vigilant attention. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüers, S.; VanRullen, R. Alpha power modulates perception independently of endogenous factors. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D. Multichannel topography of human alpha EEG fields. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1971, 31, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W.; Doppelmayr, M.; Schimke, H.; Pachinger, T. Alpha frequency, reaction time, and the speed of processing information. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 13, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, T.; Runnals, S. Evaluation of attention and alertness with a stimulus-brain feedback loop. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1962, 14, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, N.R.; Croft, R.J.; Dominey, S.J.; Burgess, A.P.; Gruzelier, J.H. Paradox lost? Exploring the role of alpha oscillations during externally vs. internally directed attention and the implications for idling and inhibition hypotheses. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2003, 47, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihs, T.A.; Michel, C.M.; Thut, G. A bias for posterior α-band power suppression versus enhancement during shifting versus maintenance of spatial attention. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedek, M.; Schickel, R.J.; Jauk, E.; Fink, A.; Neubauer, A.C. Alpha power increases in right parietal cortex reflects focused internal attention. Neuropsychologia 2014, 56, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiloni, C.; Miniussi, C.; Babiloni, F.; Carducci, F.; Cincotti, F.; Del Percio, C.; Sirello, G.; Fracassi, C.; Nobre, A.C.; Rossini, P.M. Sub-second “temporal attention” modulates alpha rhythms. A high-resolution EEG study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2004, 19, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncompte, G.; Villena-González, M.; Cosmelli, D.; López, V. Spontaneous alpha power lateralization predicts detection performance in an un-cued signal detection task. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.J.; Sutterer, D.W.; Serences, J.T.; Vogel, E.K.; Awh, E. Alpha-band oscillations enable spatially and temporally resolved tracking of covert spatial attention. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 28, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doesburg, S.M.; Bedo, N.; Ward, L.M. Top-down alpha oscillatory network interactions during visuospatial attention orienting. Neuroimage 2016, 132, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schouwenburg, M.R.; Zanto, T.P.; Gazzaley, A. Spatial attention and the effects of frontoparietal alpha band stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proskovec, A.L.; Heinrichs-Graham, E.; Wiesman, A.I.; McDermott, T.J.; Wilson, T.W. Oscillatory dynamics in the dorsal and ventral attention networks during the reorienting of attention. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 2177–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognoli, E.; Lagarde, J.; DeGuzman, G.C.; Kelso, J.A.S. The phi complex as a neuromarker of human social coordination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8190–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognoli, E.; Kelso, J.A.S. The coordination dynamics of social neuromarkers. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognoli, E.; Kelso, J.A.S. The metastable brain. Neuron 2014, 81, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazanova, O.M.; Vernon, D. Interpreting EEG alpha activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, R. Brain computer interface and neuroprosthetics. ProQuest 2007. Available online: http://purl.flvc.org/fau/fd/FA00012509 (accessed on 2 November 2019).
- Chatrian, G.E.; Lettich, E.; Nelson, P.L. Ten percent electrode system for topographic studies of spontaneous and evoked EEG activities. Am. J. EEG Technol. 1985, 25, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picton, T.W.; Bentin, S.; Berg, P.; Donchin, E.; Hillyard, S.A.; Johnson, R.; Miller, G.A.; Ritter, W.; Ruchkin, D.S.; Rugg, M.D.; et al. Guidelines for using human event-related potentials to study cognition: Recording standards and publication criteria. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognoli, E.; Kelso, J.A.S. Brain coordination dynamics: True and false faces of phase synchrony and metastability. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognoli, E.; Kelso, J.A.S. Spectral dissociation of lateralized pairs of brain rhythms. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.7662. [Google Scholar]
- Zani, A.; Proverbio, A.M. How voluntary orienting of attention and alerting modulate costs of conflict processing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulke, L.V.; Atkinson, J.; Braddick, O. Neural differences between covert and overt attention studied using EEG with simultaneous remote eye tracking. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tognoli, E. More than Meets the Mind’s Eye? Preliminary Observations Hint at Heterogeneous Alpha Neuromarkers for Visual Attention. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110307
Tognoli E. More than Meets the Mind’s Eye? Preliminary Observations Hint at Heterogeneous Alpha Neuromarkers for Visual Attention. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(11):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110307
Chicago/Turabian StyleTognoli, Emmanuelle. 2019. "More than Meets the Mind’s Eye? Preliminary Observations Hint at Heterogeneous Alpha Neuromarkers for Visual Attention" Brain Sciences 9, no. 11: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110307
APA StyleTognoli, E. (2019). More than Meets the Mind’s Eye? Preliminary Observations Hint at Heterogeneous Alpha Neuromarkers for Visual Attention. Brain Sciences, 9(11), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9110307




