The Effect of the Human Peptide GHK on Gene Expression Relevant to Nervous System Function and Cognitive Decline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Nerve Outgrowth
- Copper Lack in Nerve Diseases
- Anti-Anxiety and Anti-Pain
- Anti-Oxidant Biological and Gene Expression Data
- DNA Repair Data and Gene Expression DNA Repair
- Restoring Regeneration after Cortisone Treatment
- Gene Expression—Clearing Damaged Protein with the Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS)
- Gene Expression—Neurons
- Gene Expression—Motor neurons
- Gene Expression—Glial cells
- Gene Expression—Astrocytes
- Gene Expression—Schwann
- Gene Expression—Myelin
- Gene Expression—Dendrite
- Gene Expression—Oligodendrocyte cells
- Gene Expression—Schwann cells
- Gene Expression—Spinal
- Possible methods of therapeutic use of GHK for nerve disease
3. Results
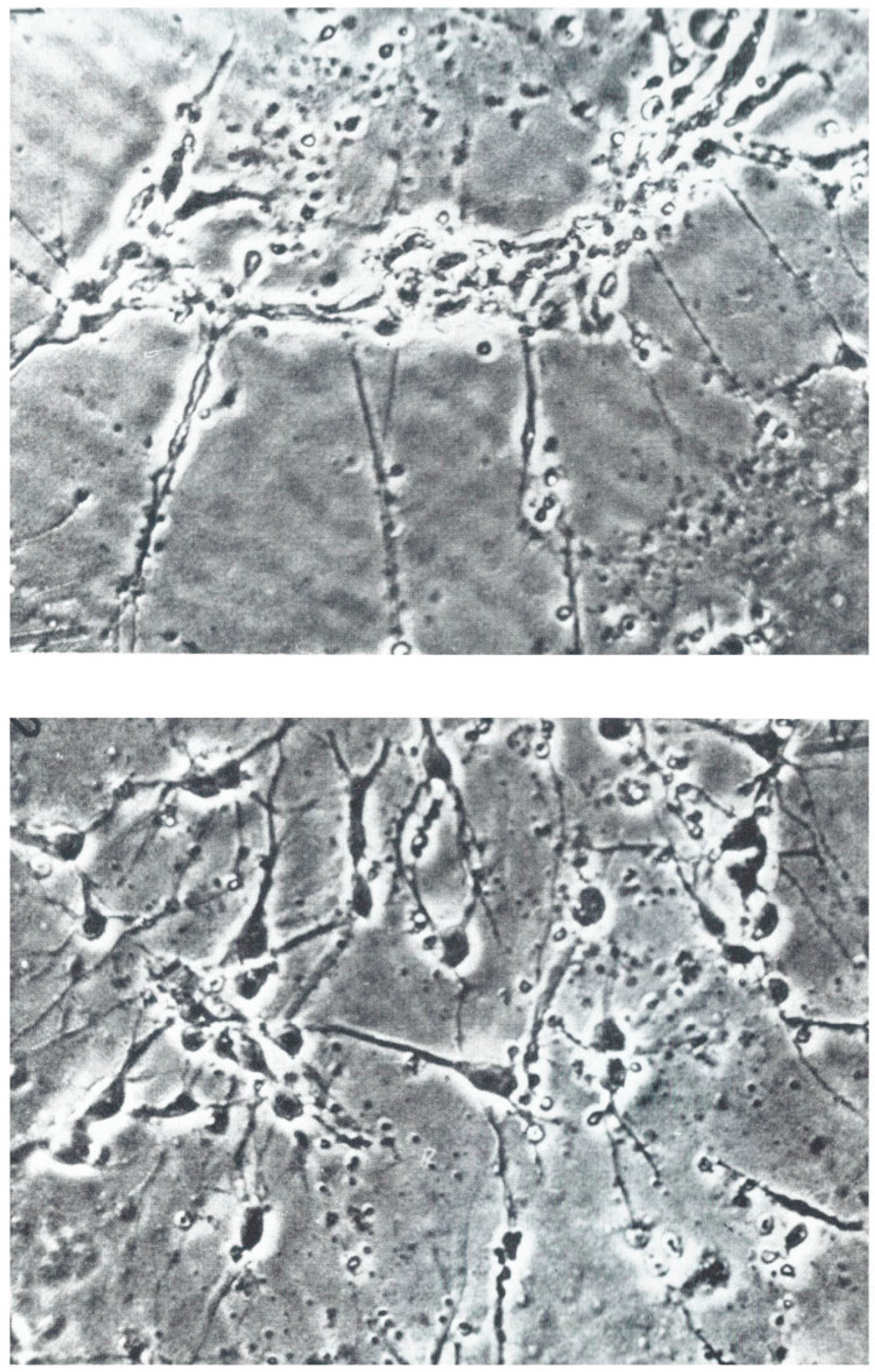
3.1. Nerve Outgrowth
3.2. Copper Deficiency, Dementia, and Nerve Dysfunction
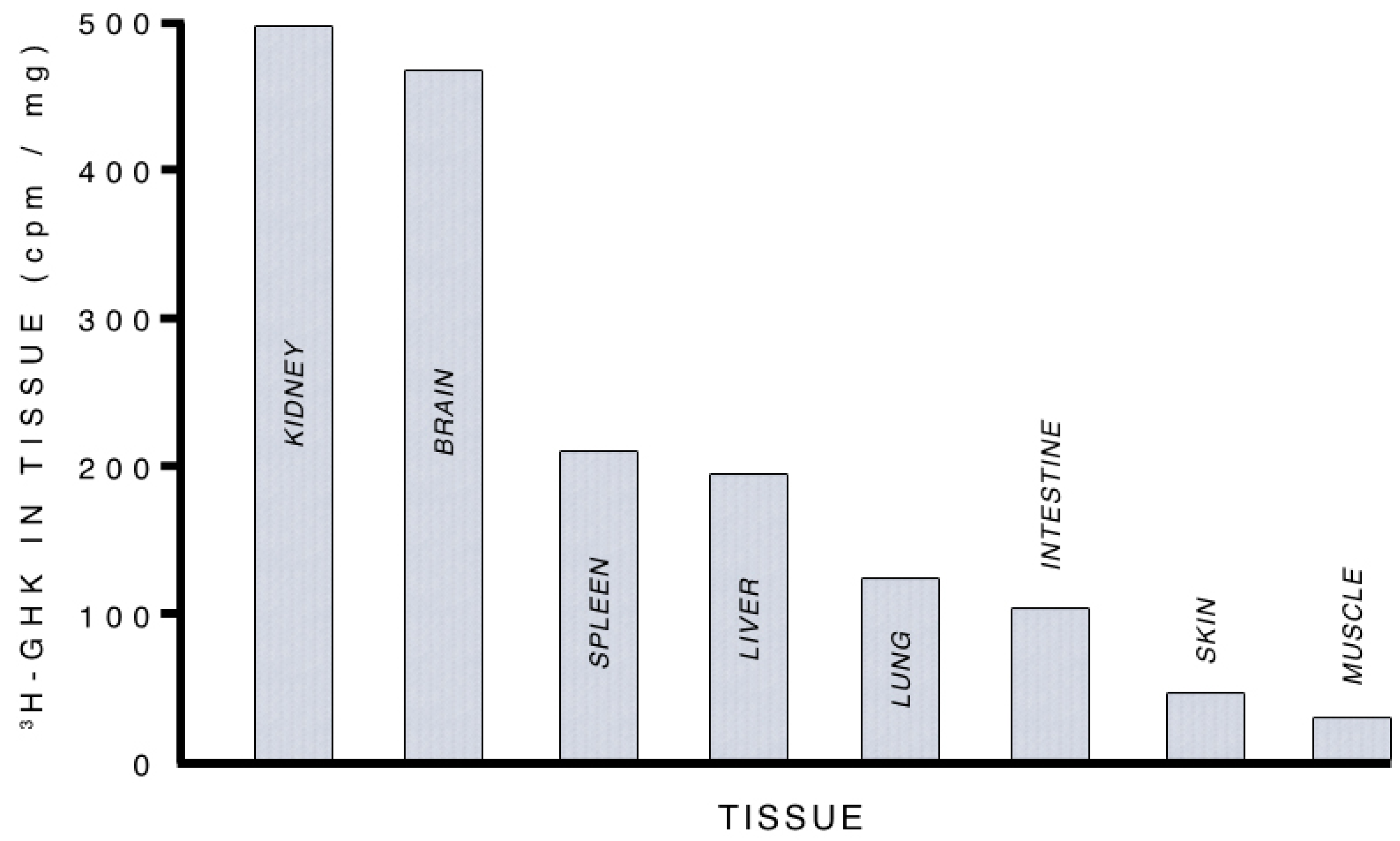
3.2.1. Supplying Copper to Nerve Cells
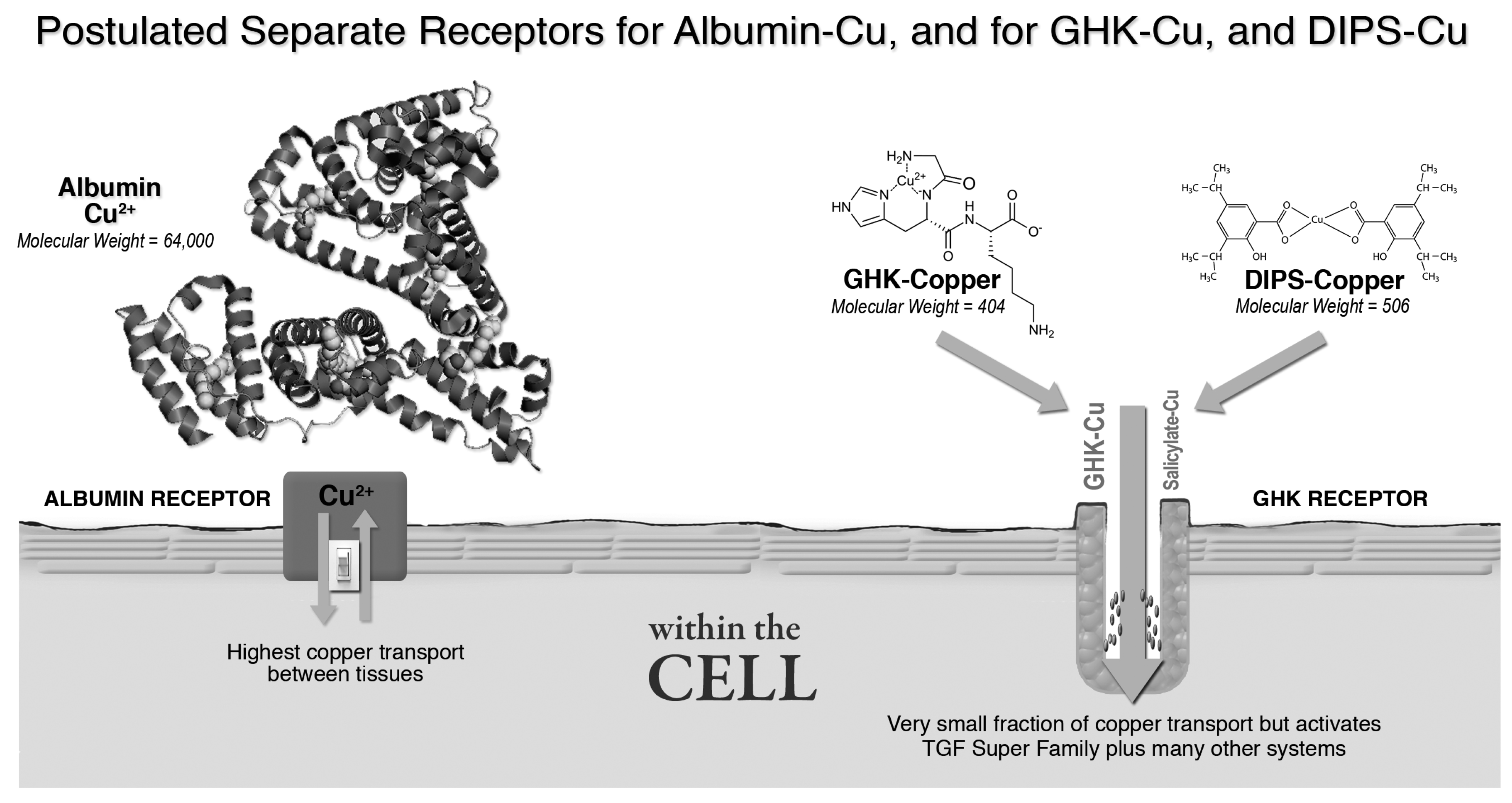
3.2.2. Albumin, GHK and Copper Transport
3.3. Anti-Anxiety (Anxiolytic) and Anti-Pain
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of the GHK Peptide
3.4.1. GHK’s Anti-Oxidant Effects in Mammals and Cell Culture
3.4.2. Synthesis of GHK-Cu Analogs with Higher Anti-ROS Activity
3.4.3. Antioxidant Gene Expression Analysis
3.5. DNA Repair, Cell Culture, and Gene Expression
3.6. Restoring Regeneration After Cortisone Treatment
3.7. Gene Expression—Clearing Damaged Protein—Ubiquitin Proteasome System
3.8. Gene Expression—Neurons
3.9. Motor Neurons
3.10. Gene Expression—Glial Cells
3.11. Astrocyte
3.12. Schwann Cells
3.13. Myelin
3.14. Gene Expression—Dendrites
3.15. Gene Expression—Oligodendrocytes
3.16. Gene Expression—Sensory Nerve cells
3.17. Spinal Nerve Cells
4. Possible Methods of Therapeutic Use of GHK for Nerve Diseases
4.1. Mode of Administering GHK-Cu to Patients
4.1.1. Skin Cream or Patch
4.1.2. Liposomal Encapsulated Oral Tablet
5. Conclusions
- The best data is in vivo mammalian data, including human clinical studies. As reviewed in this paper, these studies give overwhelming evidence of GHK’s effects on cells and tissue growth, as well as anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, wound-healing, anti-inflammation, anti-pain, anti-anxiety and skin regeneration actions.
- A second form of data is in vitro cell culture and organ culture results. Culture results give evidence about the effect of GHK on cellular production of collagen and other structural proteins, the effect on stem cell function, the recovery of cellular function after anticancer radiation or ultraviolet radiation, and sensitivity of cells to oxidative molecules.
- A third source of data is in Human Gene expression. Data analysis found that GHK induces a 50% or greater (plus or minus) change of expression in 31.2% of human genes, affecting genes linked to multiple biochemical pathways in many organs and tissue, including the nervous system.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummings, J.L.; Morstorf, T.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug-development pipeline: Few candidates, frequent failures. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L. A Tripeptide from Human Serum Which Enhances the Growth of Neoplastic Hepatocytes and the Survival of Normal Hepatocytes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Pickart, L.; Freedman, J.H.; Loker, W.J.; Peisach, J.; Perkins, C.M.; Stenkamp, R.E.; Weinstein, B. Growth-modulating plasma tripeptide may function by facilitating copper uptake into cells. Nature 1980, 288, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesakova, V.; Novotna, J.; Adam, M. Effect of the tripeptide glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine on the proliferation and synthetic activity of chick embryo chondrocytes. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.D.; Quan, S.; Kang, T.; Koch, R.J. Effects of copper tripeptide on the growth and expression of growth factors by normal and irradiated fibroblasts. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2005, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.A.; Choi, H.R.; Na, J.I.; Huh, C.H.; Kim, M.J.; Youn, S.W.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C. Copper-GHK increases integrin expression and p63 positivity by keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2009, 301, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L. The human tri-peptide GHK and tissue remodeling. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, N.Y.; Topal, A.; Cangul, I.T.; Yanik, K. The effects of topical tripeptide copper complex and helium-neon laser on wound healing in rabbits. Vet. Dermatol. 2008, 19, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arul, V.; Gopinath, D.; Gomathi, K.; Jayakumar, R. Biotinylated GHK peptide incorporated collagenous matrix: A novel biomaterial for dermal wound healing in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 73, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaim, S.F.; Vaughn, D.M.; Kincaid, S.A.; Morrison, N.E.; Murray, S.S.; Woodhead, M.A.; Hoffman, C.E.; Wright, J.C.; Kammerman, J.R. Effect of locally injected medications on healing of pad wounds in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Downey, T.; Eu, K.W.; Koh, P.K.; Cheah, P.Y. A “metastasis-prone” signature for early-stage mismatch-repair proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications for possible therapeutics. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2010, 27, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.D.; McDonough, J.E.; Zeskind, J.E.; Hackett, T.L.; Pechkovsky, D.V.; Brandsma, C.A.; Suzuki, M.; Gosselink, J.V.; Liu, G.; Alekseyev, Y.O.; et al. A gene expression signature of emphysema-related lung destruction and its reversal by the tripeptide GHK. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Margolina, A. GHK peptide as a natural modulator of multiple cellular pathways in skin regeneration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 648108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Margolina, A. The human tripeptide GHK-Cu in prevention of oxidative stress and degenerative conditions of aging: Implications for cognitive health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 324832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Margolina, A. Resetting Skin Genome Back to Health Naturally with GHK. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- National Center of Biotechnology Information. Gene. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene (accessed on 14 February 2017).
- Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Pickart, F.D.; Majnarich, J. GHK, the human skin remodeling peptide, induces anti-cancer expression of numerous caspase, growth regulatory, and DNA repair genes. J. Anal. Oncol. 2014, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuszynski, M.H.; Yang, J.H.; Barba, D.; U, H.S.; Bakay, R.A.; Pay, M.M.; Masliah, E.; Conner, J.M.; Kobalka, P.; Roy, S.; et al. Nerve growth factor gene therapy: activation of neuronal responses in Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Yang, W.; Qi, X.; Yao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Huang, L.; et al. Recombinant DNA vaccine against neurite outgrowth inhibitors attenuates behavioral deficits and decreases Abeta in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Cui, W.; Mak, S.; Xu, D.; Hu, Y.; Tang, J.; Choi, C.; Lee, M.; Pang, Y.; Han, Y. Substantial neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth-promoting activities by bis(propyl)-cognitin via the activation of alpha7-nAChR, a promising anti-Alzheimer’s dimer. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensenbrenner, M.; Jaros, G.G.; Moonen, G.; Mandel, P. Effects of synthetic tripeptide on the differentiation of dissociated cerebral hemisphere nerve cells in culture. Neurobiology 1975, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindner, G.; Grosse, G.; Halle, W.; Henklein, P. The effect of a synthetic tripeptide nervous tissue cultured in vitro. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 1979, 93, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Basha, S.H.; Gopinath, D.; Muthusamy, R.; Jayakumar, R. Initial upregulation of growth factors and inflammatory mediators during nerve regeneration in the presence of cell adhesive peptide-incorporated collagen tubes. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucconi, G.G.; Cipriani, S.; Scattoni, R.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Hawkins, D.P.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V. Copper deficiency elicits glial and neuronal response typical of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exley, C. Aluminium and iron, but neither copper nor zinc, are key to the precipitation of beta-sheets of Abeta_{42} in senile plaque cores in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2006, 10, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Exley, C.; House, E.; Polwart, A.; Esiri, M.M. Brain burdens of aluminum, iron, and copper and their relationships with amyloid-beta pathology in 60 human brains. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mold, M.; Ouro-Gnao, L.; Wieckowski, B.M.; Exley, C. Copper prevents amyloid-beta(1–42) from forming amyloid fibrils under near-physiological conditions in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Begley, P.; Church, S.J.; Patassini, S.; McHarg, S.; Kureishy, N.; Hollywood, K.A.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Elevation of brain glucose and polyol-pathway intermediates with accompanying brain-copper deficiency in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Metabolic basis for dementia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajonk, F.G.; Kessler, H.; Supprian, T.; Hamzei, P.; Bach, D.; Schweickhardt, J.; Herrmann, W.; Obeid, R.; Simons, A.; Falkai, P.; et al. Cognitive decline correlates with low plasma concentrations of copper in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005, 8, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Gross, J.B., Jr.; Ahlskog, J.E. Copper deficiency myelopathy produces a clinical picture like subacute combined degeneration. Neurology 2004, 63, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihl, C.C.; Lopate, G. Motor neuron disease associated with copper deficiency. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lazcano, J.C.; Montes, S.; Sanchez-Mendoza, M.A.; Rodriguez-Paez, L.; Perez-Neri, I.; Boll, M.C.; Campos-Arroyo, H.D.; Rios, C.; Perez-Severiano, F. Sub-chronic copper pretreatment reduces oxidative damage in an experimental Huntington’s disease model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deloncle, R.; Guillard, O. Is brain copper deficiency in Alzheimer’s, Lewy body, and Creutzfeldt Jakob diseases the common key for a free radical mechanism and oxidative stress-induced damage? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 43, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Kajita, K.; Sugimoto, N. Cu(2+) Inhibits the Aggregation of Amyloid beta-Peptide(1–42) in vitro. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2001, 40, 2274–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.M.; Bohic, S.; Carmona, A.; Ortega, R.; Cottam, V.; Hare, D.J.; Finberg, J.P.; Reyes, S.; Halliday, G.M.; Mercer, J.F.; Double, K.L. Copper pathology in vulnerable brain regions in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, S.; Rivera-Mancia, S.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Tristan-Lopez, L.; Rios, C. Copper and copper proteins in Parkinson’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 147251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, A.; Frazier, T.; Cave, M. Micronutrient-related neurologic complications following bariatric surgery. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naismith, R.T.; Shepherd, J.B.; Weihl, C.C.; Tutlam, N.T.; Cross, A.H. Acute and bilateral blindness due to optic neuropathy associated with copper deficiency. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, H.; Pajonk, F.G.; Bach, D.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Falkai, P.; Herrmann, W.; Multhaup, G.; Wiltfang, J.; Schäfer, S.; Wirths, O.; et al. Effect of copper intake on CSF parameters in patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot phase 2 clinical trial. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.R.; Trias, E.; Beilby, P.R.; Lopez, N.I.; Labut, E.M.; Bradford, C.S.; Roberts, B.R.; McAllum, E.J.; Crouch, P.J.; Rhoads, T.W.; et al. Copper delivery to the CNS by CuATSM effectively treats motor neuron disease in SOD(G93A) mice co-expressing the Copper-Chaperone-for-SOD. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.R.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.I.; Yang, S.R. The tri-peptide GHK-Cu complex ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58405–58417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L. The biological effects and mechanism of action of the plasma peptide glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine. Lymphokines 1983, 8, 425–446. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, J.R. Antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antiulcer activities of copper complexes suggest their use in a physiologic approach to treatment of arthritic diseases. Basic Life Sci. 1988, 49, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorenson, J.R.; Soderberg, L.S.; Chidambaram, M.V.; de la Rosa, D.T.; Salari, H.; Bond, K.; Kearns, G.L.; Gray, R.A.; Epperson, C.E.; Baker, M.L. Bioavailable copper complexes offer a physiologic approach to treatment of chronic diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1989, 258, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorenson, J.R. Copper complexes offer a physiological approach to treatment of chronic diseases. Prog. Med. Chem. 1989, 26, 437–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soderberg, L.S.; Barnett, J.B.; Baker, M.L.; Salari, H.; Sorenson, J.R. Postirradiation treatment with copper(II)2(3,5-diisopropylsalicylate)4 enhances radiation recovery and hemopoietic regeneration. Exp. Hematol. 1990, 18, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorenson, J.R.; Soderberg, L.S.; Chang, L.W. Radiation protection and radiation recovery with essential metalloelement chelates. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1995, 210, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderberg, L.S.; Barnett, J.B.; Baker, M.L.; Chang, L.W.; Salari, H.; Sorenson, J.R. Copper(II)2(3,5-diisopropylsalicylate)4 stimulates hemopoiesis in normal and irradiated mice. Exp. Hematol. 1988, 16, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Kuchler, S. Targeting inflammation and wound healing by opioids. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhathena, S.J.; Recant, L.; Voyles, N.R.; Timmers, K.I.; Reiser, S.; Smith, J.C.J.; Powell, A.S. Decreased plasma enkephalins in copper deficiency in man. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 43, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bobyntsev, I.I.; Chernysheva, O.I.; Dolgintsev, M.E.; Smakhtin, M.Y.; Belykh, A.E. Anxiolytic effects of Gly-His-Lys peptide and its analogs. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 158, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobyntsev, I.I.; Chernysheva, O.I.; Dolgintsev, M.E.; Smakhtin, M.Y.; Belykh, A.E. Effect of Gly-His-Lys peptide and its analogs on pain sensitivity in mice. Eksp Klin Farmakol 2014, 78, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hawk, S.N.; Lanoue, L.; Keen, C.L.; Kwik-Uribe, C.L.; Rucker, R.B.; Uriu-Adams, J.Y. Copper-deficient rat embryos are characterized by low superoxide dismutase activity and elevated superoxide anions. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Mishra, S.K.; Pant, H.C. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 2011, 572634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viader, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Kim, S.; Strickland, A.; Workman, C.S.; Yang, K.; Gross, R.W.; Milbrandt, J. Aberrant Schwann cell lipid metabolism linked to mitochondrial deficits leads to axon degeneration and neuropathy. Neuron 2013, 77, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, O. Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, M.C.; Rodriguez, E.E.; Valiente-Gabioud, A.A.; Torres-Monserrat, V.; Binolfi, A.; Quintanar, L.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernandez, C.O. Site-specific copper-catalyzed oxidation of alpha-synuclein: Tightening the link between metal binding and protein oxidative damage in Parkinson’s disease. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 4350–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Tamaoki, T.; Motohashi, N.; Nakamura, M.; McKeel, D.W., Jr.; Tabaton, M.; Lee, H.G.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. The earliest stage of cognitive impairment in transition from normal aging to Alzheimer disease is marked by prominent RNA oxidation in vulnerable neurons. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourassa, M.W.; Brown, H.H.; Borchelt, D.R.; Vogt, S.; Miller, L.M. Metal-deficient aggregates and diminished copper found in cells expressing SOD1 mutations that cause ALS. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Murata, N.; Noda, Y.; Tahara, S.; Kaneko, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Hatsuta, H.; Murayama, S.; Barnham, K.J.; Irie, K.; et al. SOD1 (copper/zinc superoxide dismutase) deficiency drives amyloid beta protein oligomerization and memory loss in mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44557–44568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, K.; Madhu, C.; Govindaraju, T. Natural Tripeptide-Based Inhibitor of Multifaceted Amyloid beta Toxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.E. The influence of medium components on Cu(2+)-dependent oxidation of low-density lipoproteins and its sensitivity to superoxide dismutase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1128, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G.; Arlandini, E.; Artali, R.; Anton, J.M.; Maffei Facino, R. Acrolein sequestering ability of the endogenous tripeptide glycyl-histidyl-lysine (GHK): Characterization of conjugation products by ESI-MSn and theoretical calculations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, G.; Artali, R.; Regazzoni, L.; Panigati, M.; Facino, R.M. Glycyl-histidyl-lysine (GHK) is a quencher of alpha,beta-4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal: A comparison with carnosine. insights into the mechanism of reaction by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, 1H NMR, and computational techniques. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrian, J.; Messeguer, A.; Facino, R.M.; Garcia Anton, J.M. New anti-RNS and -RCS products for cosmetic treatment. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smakhtin, M.; Konoplia, A.I.; Sever’ianova, L.A.; Shveinov, I.A. Pharmacological correction of immuno-metabolic disorders with the peptide Gly-His-Lys in hepatic damage induced by tetrachloromethane. Patol. Fiziol. Eksp. Ter. 2003, 2, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cherdakov, V.Y.; Smakhtin, M.Y.; Dubrovin, G.M.; Dudka, V.T.; Bobyntsev, I.I. Synergetic antioxidant and reparative action of thymogen, dalargin and peptide Gly-His-Lys in tubular bone fractures. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 4, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.M.; DeSilva, D.; Pickart, L.; Aust, S.D. Effects of glycyl-histidyl-lysyl chelated Cu(II) on ferritin dependent lipid peroxidation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 264, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Metal: Peptide Complexes and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 511,866,5, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mariappan, N.; Elks, C.M.; Sriramula, S.; Guggilam, A.; Liu, Z.; Borkhsenious, O.; Francis, J. NF-kappaB-induced oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial and cardiac dysfunction in type II diabetes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeij, W.P.; Florea, B.I.; Isenia, S.; Alia, A.; Brouwer, J.; Backendorf, C. Proteomic identification of in vivo interactors reveals novel function of skin cornification proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 3068–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeij, W.P.; Alia, A.; Backendorf, C. ROS quenching potential of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.J.; Xiang, Y.; Tan, Y.R.; Zhu, X.L.; Qin, X.Q. Wound repair and anti-oxidative capacity is regulated by ITGB4 in airway epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 341, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsoe, S.; Ahnstrom, J.; Christoffersen, C.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Plomgaard, P.; Heinecke, J.W.; Binder, C.J.; Bjorkbacka, H.; Dahlback, B.; Nielsen, L.B. Apolipoprotein M binds oxidized phospholipids and increases the antioxidant effect of HDL. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempster, S.L.; Belteki, G.; Licence, D.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Smith, G.C. Disruption of paraoxonase 3 impairs proliferation and antioxidant defenses in human A549 cells and causes embryonic lethality in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E103–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, D.; Kim, S.H.; Fantuzzi, G.; Reznikov, L.L.; Dinarello, C.A.; Rubinstein, M. Interleukin-18 binding protein: A novel modulator of the Th1 cytokine response. Immunity 1999, 10, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Ferroportin1 and hephaestin overexpression attenuate iron-induced oxidative stress in MES23.5 dopaminergic cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giguere, P.M.; Gall, B.J.; Ezekwe, E.A., Jr.; Laroche, G.; Buckley, B.K.; Kebaier, C.; Wilson, J.E.; Ting, J.P.; Siderovski, D.P.; Duncan, J.A. G Protein signaling modulator-3 inhibits the inflammasome activity of NLRP3. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33245–33257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, G.; Gong, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Burczynski, F.J. Hepatoprotective role of liver fatty acid binding protein in acetaminophen induced toxicity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Gong, Y.; Anderson, J.; Sun, D.; Minuk, G.; Roberts, M.S.; Burczynski, F.J. Antioxidative function of L-FABP in L-FABP stably transfected Chang liver cells. Hepatology 2005, 42, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhande, I.; Ma, W.; Hussain, T. Angiotensin AT2 receptor stimulation is anti-inflammatory in lipopolysaccharide-activated THP-1 macrophages via increased interleukin-10 production. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblat, M.; Karry, R.; Aviram, M. Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) is a more potent antioxidant and stimulant of macrophage cholesterol efflux, when present in HDL than in lipoprotein-deficient serum: Relevance to diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2006, 187, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Slikker, W., Jr.; Ali, S.F. Role of metallothionein and other antioxidants in scavenging superoxide radicals and their possible role in neuroprotection. Neurochem. Int. 1996, 29, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarengo, A.; Burlando, B.; Ceratto, N.; Panfoli, I. Antioxidant role of metallothioneins: A comparative overview. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2000, 46, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henry, G.E.; Momin, R.A.; Nair, M.G.; Dewitt, D.L. Antioxidant and cyclooxygenase activities of fatty acids found in food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2231–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itahana, Y.; Han, R.; Barbier, S.; Lei, Z.; Rozen, S.; Itahana, K. The uric acid transporter SLC2A9 is a direct target gene of the tumor suppressor p53 contributing to antioxidant defense. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center of Biotechnology Information. IL17A interleukin 17A. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/3605 (accessed on 14 February 2017).
- Finkley, M.B.; Appa, Y.; Bhandarkar, S. Copper Peptide and Skin. In Cosmeceuticals and Active Cosmetics: Drugs vs. Cosmetics; Elsner, P., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 549–563. [Google Scholar]
- Canugovi, C.; Misiak, M.; Ferrarelli, L.K.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. The role of DNA repair in brain related disease pathology. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucholtz, N.; Demuth, I. DNA-repair in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonson, I.; Ougland, R.; Larsen, E. DNA repair mechanisms in Huntington’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, D.; Czarny, P.; Toma, M.; Jurkowska, N.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J.; Bachurska, A.; Szemraj, J.; Maes, M.; Berk, M.; et al. Associations between DNA Damage, DNA Base Excision Repair Gene Variability and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2016, 41, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bont, R.; van Larebeke, N. Endogenous DNA damage in humans: A review of quantitative data. Mutagenesis 2004, 19, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolkowitz, O.M.; Lupien, S.J.; Bigler, E.D. The “steroid dementia syndrome”: A possible model of human glucocorticoid neurotoxicity. Neurocase 2007, 13, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, L. Method of Using Copper(II) Containing Compounds to Accelerate Wound Healing. U.S. Patent 516,436,7, 17 November 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fecto, F.; Gorrie, G.; Zhai, H.; Liu, E.; Deng, H.; Sidd, T. Impaired activity of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in transgenic mice expressing ALS/dementia-linked mutant UBQLN2 (P02.170). Neurology 2013, 80, P02–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Hung, H.L.C.; Chang, R.C.C. Differential roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in experimental models of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2016 Neuroscience Symposium and Annual Scientific Conference of the Hong Kong Society of Neurosciences, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 18 May 2016.
- Opattova, A.; Cente, M.; Novak, M.; Filipcik, P. The ubiquitin proteasome system as a potential therapeutic target for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2015, 34, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, C.; Tabrizi, S.J. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in neurodegeneration. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 2302–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostynek, J.J.; Dreher, F.; Maibach, H.I. Human skin retention and penetration of a copper tripeptide in vitro as function of skin layer towards anti-inflammatory therapy. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, S.; Türkoglu, M. Glycyl-l-Histidyl-l-Liysine-Cu(2+) loaded liposome formulations. Marmara Pharm. J. 2010, 14, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, D.H.; Pickart, L.; Thaler, M.M. Growth-modulating serum tripeptide is glycyl-histidyl-lysine. Experientia 1977, 33, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, L.V.; Lake, C.R. Psychosis in an adolescent patient with Wilson’s disease: Effects of chelation therapy. Psychosom. Med. 1995, 57, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Action | GHK-Copper 2+ | Diisopropylsalicylate-Copper 2+ |
|---|---|---|
| Wound Healing | Yes | Yes |
| Inhibit Cancer Growth | Yes | Yes |
| Anti-Ulcer | Yes | Yes |
| Anti-Pain | Yes | Yes |
| Improve Recovery After Radiation | Yes | Yes |
| Increase Stem Cell Activity | Yes | Yes |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 0 | 0 |
| 100%–199% | 5 | 2 |
| 200%–299% | 1 | 0 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 0 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 7 | 2 |
| UP | Gene | Percent Change in Gene Expression | Comments |
| 1 | OPRMI | 1294 | Opioid mu 1-High Affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphins |
| 2 | OPRL1 | 246 | Receptor for neuropeptide nociceptin |
| 3 | CCKAR | 190 | Cholecystokinin A receptor, cholecystokinin affects satiety, release of beta-endorphin and dopamine |
| 4 | CNR1 | 172 | Cannabinoid receptor, pain-reducing |
| 5 | SIGMAR1 | 155 | Non-opioid receptor |
| 6 | PNOC | 150 | Prepronociceptin, complex interactions with pain and anxiety induction |
| 7 | OXT | 136 | Ocytocin, bonding protein—gene also increases human chorionic gonadotropin |
| DOWN | Gene | Percent Change in Gene Expression | Comments |
| 1 | AMPA 3/GRIA3 | −126.00% | Glutamate receptor, retrograde endocannaboid signaling, nervous system |
| 2 | OPRK1 | −119.00% | Reduced cocaine effects |
| Molecule | Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic Activity |
|---|---|
| Gly-His-Lys:Cu(2+) | 100 |
| Lys-His-Gly-Amide:Cu(2+) | 21 |
| Gly-His-Lys-Ala-Phe-Ala:Cu(2+) | 561 |
| Ala-His-Lys:Cu(2+) | 563 |
| Gly-His-Lys-Octyl Ester:Cu(2+) | 810 |
| Gly-His-Caprolactam:Cu(2+) | 4500 |
| His-Gly-Lys:Cu(2+) | 22,300 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 2 | 0 |
| 100%–199% | 7 | 1 |
| 200%–299% | 2 | 0 |
| 300%–399% | 1 | 0 |
| 400%–499% | 1 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 3 | 1 |
| Total | 16 | 2 |
| UP | Genes | Percent Change in Gene Expression | Comments |
| 1 | TLE1 | 762 | Inhibits the oxidative/inflammatory gene NF-κB [71]. |
| 2 | SPRR2C | 721 | This proline-rich, antioxidant protein protects outer skin cells from oxidative damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS). When the ROS level is low, the protein remains in the outer cell membrane, but when the ROS level is high, the protein clusters around the cell’s DNA to protect it [72,73]. |
| 3 | ITGB4 | 609 | Up-regulation of ITGB4 promotes wound repair ability and antioxidative ability [74]. |
| 4 | APOM | 403 | Binds oxidized phospholipids and increases the antioxidant effect of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) [75]. |
| 5 | PON3 | 319 | Absence of PON3 (paraoxonase 3) in mice resulted in increased rates of early fetal and neonatal death. Knockdown of PON3 in human cells reduced cell proliferation and total antioxidant capacity [76]. |
| 6 | IL18BP | 295 | The protein encoded by this gene is an inhibitor of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL18. IL18BP abolished IL18 induction of interferon-gamma (IFN gamma), IL8, and activation of NF-κB in vitro. Blocks neutrophil oxidase activity [77]. |
| 7 | HEPH | 217 | Inhibits the conversion of Fe(2+) to Fe(3+). HEPH increases iron efflux, lowers cellular iron levels, suppresses reactive oxygen species production, and restores mitochondrial transmembrane potential [78]. |
| 8 | GPSM3 | 193 | Acts as a direct negative regulator of NLRP3. NLRP3 triggers the maturation of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 [79]. |
| 9 | FABP1 | 186 | Reduces intracellular ROS level. Plays a significant role in reduction of oxidative stress [80,81]. |
| 10 | AGTR2 | 171 | AGTR2 exerts an anti-inflammatory response in macrophages via enhanced IL-10 production and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which may have protective roles in hypertension and associated tissue injury [82]. |
| 11 | PON1 | 149 | PON1 (paraoxonase 1) is a potent antioxidant and a major anti-atherosclerotic component of HDL [83]. |
| 12 | MT3 | 142 | Metallothioneins (MTs) display in vitro free radical scavenging capacity, suggesting that they may specifically neutralize hydroxyl radicals. Metallothioneins and metallothionein-like proteins isolated from mouse brain act as neuroprotective agents by scavenging superoxide radicals [84,85]. |
| 13 | PTGS2 | 120 | Produces cyclooxygenase-II (COX-II), which has antioxidant activities [86]. |
| 14 | SLC2A9 | 117 | The p53-SLC2A9 pathway is a novel antioxidant mechanism. During oxidative stress, SLC2A9 undergoes p53-dependent induction, and functions as an antioxidant by suppressing ROS, DNA damage, and cell death [87]. |
| DOWN | Genes | Percent Change in Gene Expression | Comments |
| 1 | IL17A | −1018 | This cytokine can stimulate the expression of IL6 and cyclooxygenase-2 (PTGS2/COX-2), as well as enhance the production of nitric oxide (NO). High levels of this cytokine are associated with several chronic inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis ([88]). |
| 2 | TNF | −115 | GHK suppresses this pro-oxidant TNF gene [89]. |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–100% | 41 | 4 |
| 100%–150% | 2 | 1 |
| 150%–200% | 1 | 0 |
| 200%–250% | 2 | 0 |
| 250%–300% | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 47 | 5 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change in Gene Expression |
| 1 | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 3, PARP3 | 253 |
| 2 | polymerase (DNA directed), mu, POLM | 225 |
| 3 | MRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A MRE11A | 212 |
| 4 | RAD50 homolog (S. cerevisiae), RAD50 | 175 |
| 5 | eyes absent homolog 3 (Drosophila), EYA3 | 128 |
| 6 | retinoic acid receptor, alpha, RARA | 123 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change in Gene Expression |
| 1 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 4, CHRNA4 | −105 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 31 | 1 |
| 100%–199% | 7 | 0 |
| 200%–299% | 0 | 0 |
| 300%–399% | 1 | 0 |
| 400%–499% | 1 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 41 | 1 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ubiquitin specific peptidase 29, USP29 | 1056 |
| 2 | ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2, UBR2 | 455 |
| 3 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 1 /// ubiquitin D, GABBR1 /// UBD | 310 |
| 4 | ubiquitin specific peptidase 34, USP34 | 195 |
| 5 | parkinson protein 2, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (parkin), PARK2 | 169 |
| 6 | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (UBC9 homolog, yeast), UBE2I | 150 |
| 7 | ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 4, UBR4 | 146 |
| 8 | ubiquitin protein ligase E3B, UBE3B | 116 |
| 9 | ubiquitin specific peptidase 2, USP2 | 104 |
| 10 | ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 6, UBA6 | 104 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 230 | 80 |
| 100%–199% | 99 | 80 |
| 200%–299% | 45 | 35 |
| 300%–399% | 19 | 14 |
| 400%–499% | 9 | 10 |
| 500%+ | 6 | 11 |
| Total | 408 | 230 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | opioid receptor, mu 1, OPRM1 | 1294 |
| 2 | tumor protein p73, TP73 | 938 |
| 3 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 1, KCND1 | 845 |
| 4 | solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 2, SLC8A2 | 737 |
| 5 | contactin associated protein-like 2, CNTNAP2 | 581 |
| 6 | stathmin-like 3, STMN3 | 500 |
| 7 | latrophilin 3, LPHN3 | 494 |
| 8 | angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 | 487 |
| 9 | synapsin III, SYN3 | 478 |
| 10 | dipeptidyl-peptidase 6, DPP6 | 448 |
| 11 | somatostatin receptor 2, SSTR2 | 442 |
| 12 | G protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member B, GPRC5B | 431 |
| 13 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, alpha subunit, SCN3A | 423 |
| 14 | smoothened homolog (Drosophila), SMO | 415 |
| 15 | tryptophan hydroxylase 1, TPH1 | 409 |
| 16 | caspase 8, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, CASP8 | 399 |
| 17 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 /// gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-5-like, GABRA5 /// LOC100509612 | 392 |
| 18 | transcription factor 7 (T-cell specific, HMG-box), TCF7 | 372 |
| 19 | solute carrier family 17 (sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter), member 6, SLC17A6 | 369 |
| 20 | doublecortin-like kinase 1, DCLK1 | 365 |
| 21 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1, PAK1 | 363 |
| 22 | neurogenic differentiation 4, NEUROD4 | 362 |
| 23 | zinc finger protein 335, ZNF335 | 358 |
| 24 | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 3, WNT3 | 352 |
| 25 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 8, ADAM8 | 352 |
| 26 | neuropeptide Y, NPY | 346 |
| 27 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 3, KCNC3 | 332 |
| 28 | EPH receptor B1, EPHB1 | 330 |
| 29 | LIM domain kinase 1, LIMK1 | 322 |
| 30 | myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila), MLL | 318 |
| 31 | growth associated protein 43, GAP43 | 305 |
| 32 | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog, FOS | 305 |
| 33 | sal-like 1 (Drosophila), SALL1 | 302 |
| 34 | synovial sarcoma, X breakpoint 2 /// synovial sarcoma, X breakpoint 2B, SSX2 /// SSX2B | 301 |
| 35 | inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3, ITPR3 | 298 |
| 36 | bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IB, BMPR1B | 298 |
| 37 | synuclein, gamma (breast cancer-specific protein 1), SNCG | 292 |
| 38 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit, CACNA1A | 286 |
| 39 | capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, beta, CAPZB | 285 |
| 40 | plexin C1, PLXNC1 | 282 |
| 41 | nuclear factor I/B, NFIB | 279 |
| 42 | islet amyloid polypeptide, IAPP | 276 |
| 43 | nephroblastoma overexpressed gene, NOV | 275 |
| 44 | hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide-gated potassium channel 4, HCN4 | 269 |
| 45 | calsyntenin 2, CLSTN2 | 268 |
| 46 | potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1, KCNN1 | 266 |
| 47 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type II, alpha subunit, SCN2A | 264 |
| 48 | neuroligin 1, NLGN1 | 261 |
| 49 | ELKS/RAB6-interacting/CAST family member 2, ERC2 | 261 |
| 50 | scratch homolog 1, zinc finger protein (Drosophila), SCRT1 | 252 |
| 51 | low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1, LRP1 | 249 |
| 52 | hypothetical protein LOC728392 /// NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1, LOC728392 /// NLRP1 | 249 |
| 53 | opiate receptor-like 1, OPRL1 | 246 |
| 54 | myosin, heavy chain 14, non-muscle, MYH14 | 243 |
| 55 | nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal), NOS1 | 240 |
| 56 | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 2B, WNT2B | 238 |
| 57 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, GRM1 | 231 |
| 58 | glutamate receptor interacting protein 1, GRIP1 | 230 |
| 59 | myelin associated glycoprotein, MAG | 229 |
| 60 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 1 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 3, CCL3 /// CCL3L1 /// CCL3L3 | 228 |
| 61 | family with sequence similarity 162, member A, FAM162A | 228 |
| 62 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5, S1PR5 | 227 |
| 63 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R, PTPRR | 225 |
| 64 | IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros), IKZF1 | 225 |
| 65 | potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 3, KCNN3 | 221 |
| 66 | solute carrier family 18 (vesicular monoamine), member 2, SLC18A2 | 219 |
| 67 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 1, GRIN1 | 216 |
| 68 | v-src sarcoma (Schmidt-Ruppin A-2) viral oncogene homolog (avian), SRC | 216 |
| 69 | jagged 1, JAG1 | 215 |
| 70 | adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary), ADCYAP1 | 215 |
| 71 | ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 2, ATP2B2 | 214 |
| 72 | tripartite motif-containing 2, TRIM2 | 213 |
| 73 | netrin 1, NTN1 | 212 |
| 74 | paired related homeobox 1, PRRX1 | 209 |
| 75 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 3, P2RX3 | 207 |
| 76 | inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein, ID4 | 203 |
| 77 | solute carrier family 5 (choline transporter), member 7, SLC5A7 | 202 |
| 78 | empty spiracles homeobox 1, EMX1 | 202 |
| 79 | muscle, skeletal, receptor tyrosine kinase, MUSK | 200 |
| 80 | GATA binding protein 2, GATA2 | 193 |
| 81 | cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart), CDH13 | 192 |
| 82 | Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 2, ARHGEF2 | 191 |
| 83 | anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase, ALK | 191 |
| 84 | cholecystokinin A receptor, CCKAR | 190 |
| 85 | GLI family zinc finger 2, GLI2 | 183 |
| 86 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 1 (muscle), CHRNB1 | 182 |
| 87 | NK2 homeobox 2, NKX2-2 | 181 |
| 88 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4, P2RX4 | 180 |
| 89 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, rho 2, GABRR2 | 179 |
| 90 | PDZ and LIM domain 5, PDLIM5 | 177 |
| 91 | plasminogen activator, urokinase, PLAU | 172 |
| 92 | cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain), CNR1 | 172 |
| 93 | chondrolectin, CHODL | 172 |
| 94 | neurexin 2, NRXN2 | 171 |
| 95 | parkinson protein 2, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (parkin), PARK2 | 169 |
| 96 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1F subunit, CACNA1F | 168 |
| 97 | neuregulin 1, NRG1 | 164 |
| 98 | zinc finger protein 536, ZNF536 | 162 |
| 99 | endothelin 3, EDN3 | 161 |
| 100 | paired box 7, PAX7 | 161 |
| 101 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II beta, CAMK2B | 161 |
| 102 | solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 3, SLC30A3 | 160 |
| 103 | ciliary neurotrophic factor /// zinc finger protein 91 homolog (mouse) /// ZFP91-CNTF readthrough transcript, CNTF /// ZFP91 /// ZFP91-CNTF | 159 |
| 104 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1I subunit, CACNA1I | 156 |
| 105 | membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 2, MAGI2 | 155 |
| 106 | sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1, SIGMAR1 | 155 |
| 107 | leptin, LEP | 152 |
| 108 | microtubule-associated protein tau, MAPT | 150 |
| 109 | erythropoietin receptor, EPOR | 147 |
| 110 | frizzled homolog 8 (Drosophila), FZD8 | 147 |
| 111 | nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1, NUMA1 | 147 |
| 112 | ninjurin 2, NINJ2 | 144 |
| 113 | probable transcription factor PML-like /// promyelocytic leukemia, LOC652346 /// PML | 144 |
| 114 | fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1 (zygin I), FEZ1 | 143 |
| 115 | ribonucleotide reductase M1, RRM1 | 142 |
| 116 | retinoic acid receptor, beta, RARB | 142 |
| 117 | metallothionein 3, MT3 | 142 |
| 118 | vascular endothelial growth factor A, VEGFA | 141 |
| 119 | glycoprotein M6A, GPM6A | 140 |
| 120 | runt-related transcription factor 1, RUNX1 | 136 |
| 121 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, delta, CHRND | 135 |
| 122 | testis specific, 10, TSGA10 | 135 |
| 123 | growth hormone secretagogue receptor, GHSR | 135 |
| 124 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 3, GNB3 | 134 |
| 125 | glycine receptor, beta, GLRB | 132 |
| 126 | runt-related transcription factor 1; translocated to, 1 (cyclin D-related), RUNX1T1 | 131 |
| 127 | synaptotagmin V, SYT5 | 131 |
| 128 | bridging integrator 1, BIN1 | 130 |
| 129 | general transcription factor IIi, GTF2I | 128 |
| 130 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7, MAP2K7 | 127 |
| 131 | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha, PPARGC1A | 126 |
| 132 | v-erb-a erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4 (avian), ERBB4 | 125 |
| 133 | retinoic acid receptor, alpha, RARA | 123 |
| 134 | baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 1-like /// NLR family, apoptosis inhibitory protein, LOC100510692 /// NAIP | 123 |
| 135 | myosin VA (heavy chain 12, myoxin), MYO5A | 122 |
| 136 | heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic), class B member 1, HSP90AB1 | 121 |
| 137 | voltage-dependent anion channel 1, VDAC1 | 120 |
| 138 | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase), PTGS2 | 120 |
| 139 | spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 1, SPTBN1 | 120 |
| 140 | tubulin, beta 2A /// tubulin, beta 2B, TUBB2A /// TUBB2B | 119 |
| 141 | misshapen-like kinase 1, MINK1 | 119 |
| 142 | neural cell adhesion molecule 1, NCAM1 | 119 |
| 143 | kelch-like 1 (Drosophila), KLHL1 | 119 |
| 144 | sperm associated antigen 9, SPAG9 | 118 |
| 145 | gonadotropin-releasing hormone 1 (luteinizing-releasing hormone), GNRH1 | 116 |
| 146 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 3, CHRNB3 | 115 |
| 147 | neuralized homolog (Drosophila), NEURL | 115 |
| 148 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 14, SOX14 | 115 |
| 149 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 1, P2RX1 | 112 |
| 150 | transcription factor 4, TCF4 | 112 |
| 151 | lysozyme, LYZ | 111 |
| 152 | MYC associated factor X, MAX | 111 |
| 153 | synaptojanin 1, SYNJ1 | 108 |
| 154 | ret proto-oncogene, RET | 108 |
| 155 | cadherin 2, type 1, N-cadherin (neuronal), CDH2 | 108 |
| 156 | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase, AXL | 108 |
| 157 | ataxia telangiectasia mutated, ATM | 107 |
| 158 | parvalbumin, PVALB | 107 |
| 159 | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH | 107 |
| 160 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 1, RAPGEF1 | 106 |
| 161 | protein kinase C, gamma, PRKCG | 106 |
| 162 | neurofibromin 2 (merlin), NF2 | 105 |
| 163 | serrate RNA effector molecule homolog (Arabidopsis), SRRT | 105 |
| 164 | syntaxin 3, STX3 | 105 |
| 165 | X-box binding protein 1, XBP1 | 104 |
| 166 | potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, beta member 2, KCNMB2 | 104 |
| 167 | chemokine (C-X3-C motif) receptor 1, CX3CR1 | 104 |
| 168 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A2, ALDH1A2 | 103 |
| 169 | drebrin 1, DBN1 | 103 |
| 170 | UDP glycosyltransferase 8, UGT8 | 103 |
| 171 | achaete-scute complex homolog 1 (Drosophila), ASCL1 | 103 |
| 172 | POU class 4 homeobox 3, POU4F3 | 102 |
| 173 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| 174 | steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, STAR | 101 |
| 175 | histamine receptor H3, HRH3 | 101 |
| 176 | nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 6, NR2F6 | 100 |
| 177 | transforming growth factor, beta 1, TGFB1 | 100 |
| 178 | homeobox D3, HOXD3 | 100 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 81 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 3A, HTR3A | −100 |
| 82 | neuroligin 3, NLGN3 | −101 |
| 83 | aquaporin 1 (Colton blood group), AQP1 | −101 |
| 84 | SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 2, SHANK2 | −102 |
| 85 | neurochondrin, NCDN | −102 |
| 86 | astrotactin 1, ASTN1 | −102 |
| 87 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 2, MAPK8IP2 | −103 |
| 88 | limbic system-associated membrane protein, LSAMP | −103 |
| 89 | calcium binding protein 1, CABP1 | −106 |
| 90 | integrin, beta 1 (fibronectin receptor, beta polypeptide, antigen CD29 includes MDF2, MSK12), ITGB1 | −107 |
| 91 | discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 2, DLGAP2 | −108 |
| 92 | doublecortin, DCX | −108 |
| 93 | colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte), CSF3 | −108 |
| 94 | advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor, AGER | −108 |
| 95 | corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1, CRHR1 | −109 |
| 96 | neuropeptides B/W receptor 2, NPBWR2 | −109 |
| 97 | even-skipped homeobox 1, EVX1 | −110 |
| 98 | retinoid X receptor, gamma, RXRG | −110 |
| 99 | cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3, CPEB3 | −112 |
| 100 | alpha tubulin acetyltransferase 1, ATAT1 | −113 |
| 101 | paralemmin, PALM | −115 |
| 102 | tumor necrosis factor, TNF | −115 |
| 103 | fatty acid binding protein 7, brain, FABP7 | −118 |
| 104 | olfactory marker protein, OMP | −118 |
| 105 | Amphiregulin, AREG | −118 |
| 106 | opioid receptor, kappa 1, OPRK1 | −119 |
| 107 | calbindin 2, CALB2 | −119 |
| 108 | phosphodiesterase 10A, PDE10A | −121 |
| 109 | early growth response 1, EGR1 | −121 |
| 110 | cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation 1, CEND1 | −123 |
| 111 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 3B, HTR3B | −123 |
| 112 | synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa, SNAP23 | −123 |
| 113 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type XI, alpha subunit, SCN11A | −124 |
| 114 | growth arrest-specific 7, GAS7 | −124 |
| 115 | contactin 1, CNTN1 | −125 |
| 116 | neuroligin 4, X-linked, NLGN4X | −128 |
| 117 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 1, GABRA1 | −130 |
| 118 | leucine zipper, putative tumor suppressor 1, LZTS1 | −130 |
| 119 | mesenchyme homeobox 2, MEOX2 | −131 |
| 120 | TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase, TYRO3 | −131 |
| 121 | synaptophysin, SYP | −132 |
| 122 | coiled-coil domain containing 64, CCDC64 | −132 |
| 123 | leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1, LGI1 | −132 |
| 124 | nerve growth factor receptor, NGFR | −132 |
| 125 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, beta 4, CHRNB4 | −135 |
| 126 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A, HTR2A | −135 |
| 127 | myocyte enhancer factor 2C, MEF2C | −138 |
| 128 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 4, CHRNA4 | −139 |
| 129 | prodynorphin, PDYN | −142 |
| 130 | discs, large homolog 2 (Drosophila), DLG2 | −142 |
| 131 | neurexin 1, NRXN1 | −144 |
| 132 | secretin, SCT | −148 |
| 133 | serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 1, SERPINF1 | −148 |
| 134 | tachykinin receptor 3, TACR3 | −150 |
| 135 | Ras homolog enriched in brain, RHEB | −150 |
| 136 | PARK2 co-regulated, PACRG | −153 |
| 137 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 5, GRIK5 | −159 |
| 138 | bone morphogenetic protein 2, BMP2 | −159 |
| 139 | choline O-acetyltransferase, CHAT | −160 |
| 140 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type I, alpha subunit, SCN1A | −162 |
| 141 | TOX high mobility group box family member 3, TOX3 | −163 |
| 142 | gastric inhibitory polypeptide, GIP | −164 |
| 143 | corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 2, CRHR2 | −165 |
| 144 | kinesin family member 1A, KIF1A | −165 |
| 145 | RAB35, member RAS oncogene family, RAB35 | −166 |
| 146 | protein kinase C, theta, PRKCQ | −167 |
| 147 | cell adhesion molecule with homology to L1CAM (close homolog of L1), CHL1 | −171 |
| 148 | unc-51-like kinase 4 (C. elegans), ULK4 | −172 |
| 149 | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 4, WNT4 | −175 |
| 150 | thyroid stimulating hormone receptor, TSHR | −175 |
| 151 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3, KCND3 | −175 |
| 152 | contactin 2 (axonal), CNTN2 | −180 |
| 153 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A, GRIN2A | −180 |
| 154 | fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 1, FLRT1 | −183 |
| 155 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, gamma 3, GABRG3 | −186 |
| 156 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IG, CAMK1G | −187 |
| 157 | interleukin 6 receptor, IL6R | −190 |
| 158 | calsyntenin 3, CLSTN3 | −191 |
| 159 | vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (synaptobrevin 1), VAMP1 | −193 |
| 160 | promyelocytic leukemia, PML | −196 |
| 161 | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal accessory protein 2, ATP6AP2 | −209 |
| 162 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3, MAPK8IP3 | −209 |
| 163 | estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta), ESR2 | −216 |
| 164 | cytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide, CYBB | −217 |
| 165 | purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 11 /// PPAN-P2RY11 readthrough, P2RY11 /// PPAN-P2RY11 | −219 |
| 166 | sonic hedgehog, SHH | −220 |
| 167 | growth differentiation factor 11, GDF11 | −221 |
| 168 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D, PTPRD | −221 |
| 169 | ELK1, member of ETS oncogene family, ELK1 | −224 |
| 170 | regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 1, RIMS1 | −225 |
| 171 | hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif-like, HEYL | −228 |
| 172 | neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 3, NTRK3 | −230 |
| 173 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shab-related subfamily, member 2, KCNB2 | −233 |
| 174 | regulator of G-protein signaling 6, RGS6 | −235 |
| 175 | glycine receptor, alpha 3, GLRA3 | −235 |
| 176 | potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, beta member 1, KCNAB1 | −235 |
| 177 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha transducing activity polypeptide 1, GNAT1 | −242 |
| 178 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2, PCSK2 | −242 |
| 179 | nerve growth factor (beta polypeptide), NGF | −243 |
| 180 | corticotropin releasing hormone, CRH | −243 |
| 181 | laminin, alpha 1, LAMA1 | −245 |
| 182 | cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 3, CNGA3 | −249 |
| 183 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 1, GRIK1 | −254 |
| 184 | lin-28 homolog A (C. elegans), LIN28A | −259 |
| 185 | empty spiracles homeobox 2, EMX2 | −260 |
| 186 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35), CDK5R1 | −260 |
| 187 | agrin, AGRN | −264 |
| 188 | T-box, brain, 1, TBR1 | −272 |
| 189 | stathmin-like 2, STMN2 | −274 |
| 190 | microcephalin 1, MCPH1 | −275 |
| 191 | ELAV (embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila)-like 4 (Hu antigen D), ELAVL4 | −282 |
| 192 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 1, MAPK8IP1 | −289 |
| 193 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, N type, alpha 1B subunit, CACNA1B | −290 |
| 194 | FEZ family zinc finger 2, FEZF2 | −295 |
| 195 | dopamine receptor D4, DRD4 | −296 |
| 196 | zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1, ZEB1 | −300 |
| 197 | T-cell leukemia homeobox 1, TLX1 | −311 |
| 198 | sterile alpha motif domain containing 4A, SAMD4A | −315 |
| 199 | opioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like, OPCML | −333 |
| 200 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 2, FGFR2 | −337 |
| 201 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 1, SOX1 | −337 |
| 202 | neurogenin 1, NEUROG1 | −345 |
| 203 | PTK2B protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta, PTK2B | −348 |
| 204 | somatostatin receptor 5, SSTR5 | −353 |
| 205 | myelin basic protein, MBP | −361 |
| 206 | EPH receptor A7, EPHA7 | −365 |
| 207 | G protein-coupled receptor 173, GPR173 | −373 |
| 208 | S100 calcium binding protein A5, S100A5 | −374 |
| 209 | acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6, ACSL6 | −384 |
| 210 | family with sequence similarity 107, member A, FAM107A | −407 |
| 211 | Kv channel interacting protein 1, KCNIP1 | −413 |
| 212 | Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 2, FAIM2 | −416 |
| 213 | bradykinin receptor B1, BDKRB1 | −426 |
| 214 | discs, large homolog 4 (Drosophila), DLG4 | −452 |
| 215 | adenylate cyclase 10 (soluble), ADCY10 | −460 |
| 216 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39), CDK5R2 | −481 |
| 217 | EPH receptor A3, EPHA3 | −485 |
| 218 | phosphodiesterase 1A, calmodulin-dependent, PDE1A | −485 |
| 219 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4, CXCR4 | −496 |
| 220 | membrane metallo-endopeptidase, MME | −540 |
| 221 | paired-like homeodomain 3, PITX3 | −541 |
| 222 | notch 3, NOTCH3 | −547 |
| 223 | discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 1, DLGAP1 | −547 |
| 224 | slit homolog 1 (Drosophila), SLIT1 | −553 |
| 225 | bassoon (presynaptic cytomatrix protein), BSN | −563 |
| 226 | cadherin, EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 (flamingo homolog, Drosophila), CELSR1 | −647 |
| 227 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit, CACNB4 | −672 |
| 228 | necdin homolog (mouse), NDN | −729 |
| 229 | endothelin receptor type B, EDNRB | −768 |
| 230 | cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 2, CHRM2 | −1049 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 9 | 5 |
| 100%–199% | 2 | 0 |
| 200%–299% | 2 | 1 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 0 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 2 |
| 500%+ | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 13 | 9 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit, CACNA1A | 286 |
| 2 | plexin C1, PLXNC1 | 282 |
| 3 | GLI family zinc finger 2, GLI2 | 183 |
| 4 | NK2 homeobox 2, NKX2-2 | 181 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | slit homolog 1 (Drosophila), SLIT1 | −553 |
| 2 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4, CXCR4 | −496 |
| 3 | EPH receptor A3, EPHA3 | −485 |
| 4 | sonic hedgehog, SHH | −220 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 11 | 4 |
| 100%–199% | 7 | 3 |
| 200%–299% | 4 | 4 |
| 300%–399% | 2 | 1 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 1 |
| 500%+ | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 24 | 15 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | neurogenic differentiation 4, NEUROD4 | 362 |
| 2 | growth associated protein 43, GAP43 | 305 |
| 3 | nuclear factor I/B, NFIB | 279 |
| 4 | caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase), CASP1 | 257 |
| 5 | Kruppel-like factor 15, KLF15 | 238 |
| 6 | adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary), ADCYAP1 | 215 |
| 7 | neuregulin 1, NRG1 | 164 |
| 8 | versican, VCAN | 134 |
| 9 | protein kinase C, eta, PRKCH | 124 |
| 10 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4, SMARCA4 | 107 |
| 11 | chemokine (C-X3-C motif) receptor 1, CX3CR1 | 104 |
| 12 | achaete-scute complex homolog 1 (Drosophila), ASCL1 | 103 |
| 13 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | necdin homolog (mouse), NDN | −729 |
| 2 | insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C), IGF1 | −522 |
| 3 | forkhead box D4 /// forkhead box D4-like 1, FOXD4 /// FOXD4L1 | −498 |
| 4 | PTK2B protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta, PTK2B | −348 |
| 5 | pleiomorphic adenoma gene 1, PLAG1 | −276 |
| 6 | lin-28 homolog A (C. elegans), LIN28A | −259 |
| 7 | sonic hedgehog, SHH | −220 |
| 8 | forkhead box E1 (thyroid transcription factor 2), FOXE1 | −204 |
| 9 | allograft inflammatory factor 1, AIF1 | −144 |
| 10 | GDNF family receptor alpha 2, GFRA2 | −141 |
| 11 | chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4, CSPG4 | −113 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 8 | 3 |
| 100%–199% | 5 | 2 |
| 200%–299% | 2 | 1 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 0 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 15 | 6 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 1 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 3, CCL3 /// CCL3L1 /// CCL3L3 | 228 |
| 2 | inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein, ID4 | 203 |
| 3 | NK2 homeobox 2, NKX2-2 | 181 |
| 4 | metallothionein 3, MT3 | 142 |
| 5 | bridging integrator 1, BIN1 | 130 |
| 6 | matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted), MMP14 | 114 |
| 7 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 3, NTRK3 | −230 |
| 2 | contactin 2 (axonal), CNTN2 | −180 |
| 3 | bone morphogenetic protein 2, BMP2 | −159 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 5 | 1 |
| 100%–199% | 2 | 0 |
| 200%–299% | 0 | 0 |
| 300%–399% | 1 | 1 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 8 | 2 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | Mediator complex subunit 12, MED12 | 393 |
| 2 | neurofibromin 2 (merlin), NF2 | 105 |
| 3 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1, CYP11A1 | −393 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 24 | 5 |
| 100%–199% | 8 | 8 |
| 200%–299% | 4 | 0 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 3 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 2 |
| 500%+ | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 36 | 18 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3, ITPR3 | 298 |
| 2 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type II, alpha subunit, SCN2A | 264 |
| 3 | myelin associated glycoprotein, MAG | 229 |
| 4 | inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein, ID4 | 203 |
| 5 | aspartoacylase, ASPA | 195 |
| 6 | probable transcription factor PML-like /// promyelocytic leukemia, LOC652346 /// PML | 144 |
| 7 | retinoic acid receptor, beta, RARB | 142 |
| 8 | retinoic acid receptor, alpha, RARA | 123 |
| 9 | myosin VA (heavy chain 12, myoxin), MYO5A | 122 |
| 10 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| 11 | histamine receptor H3, HRH3 | 101 |
| 12 | transforming growth factor, beta 1, TGFB1 | 100 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4, CXCR4 | −496 |
| 2 | gap junction protein, gamma 2, 47kDa, GJC2 | −428 |
| 3 | lethal giant larvae homolog 1 (Drosophila), LLGL1 | −393 |
| 4 | myelin basic protein, MBP | −361 |
| 5 | chromosome 11 open reading frame 9, C11orf9 | −342 |
| 6 | promyelocytic leukemia, PML | −196 |
| 7 | myelin protein zero, MPZ | −180 |
| 8 | contactin 2 (axonal), CNTN2 | −180 |
| 9 | toll-like receptor 2, TLR2 | −169 |
| 10 | laminin, alpha 2, LAMA2 | −150 |
| 11 | retinoid X receptor, gamma, RXRG | −110 |
| 12 | integrin, beta 1 (fibronectin receptor, beta polypeptide, antigen CD29 includes MDF2, MSK12), ITGB1 | −107 |
| 13 | thyroglobulin, TG | −100 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 47 | 14 |
| 100%–199% | 19 | 31 |
| 200%–299% | 11 | 15 |
| 300%–399% | 8 | 3 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 3 |
| 500%+ | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 87 | 68 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 1, KCND1 | 845 |
| 2 | contactin associated protein-like 2, CNTNAP2 | 581 |
| 3 | leukocyte specific transcript 1, LST1 | 395 |
| 4 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 /// gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-5-like, GABRA5 /// LOC100509612 | 392 |
| 5 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19, CCL19 | 378 |
| 6 | doublecortin-like kinase 1, DCLK1 | 365 |
| 7 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1, PAK1 | 363 |
| 8 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 3, KCNC3 | 332 |
| 9 | EPH receptor B1, EPHB1 | 330 |
| 10 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 1 /// ubiquitin D, GABBR1 /// UBD | 310 |
| 11 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit, CACNA1A | 286 |
| 12 | nephroblastoma overexpressed gene, NOV | 275 |
| 13 | obscurin-like 1, OBSL1 | 263 |
| 14 | neuroligin 1, NLGN1 | 261 |
| 15 | low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1, LRP1 | 249 |
| 16 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 3, GRIK3 | 246 |
| 17 | RNA binding protein, fox-1 homolog (C. elegans) 2, RBFOX2 | 245 |
| 18 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, GRM1 | 231 |
| 19 | glutamate receptor interacting protein 1, GRIP1 | 230 |
| 20 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 1, GRIN1 | 216 |
| 21 | MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence, MCF2 | 202 |
| 22 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4, P2RX4 | 180 |
| 23 | synapsin I, SYN1 | 170 |
| 24 | Abl-interactor 2, ABI2 | 168 |
| 25 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1F subunit, CACNA1F | 168 |
| 26 | membrane associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain containing 2, MAGI2 | 155 |
| 27 | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (UBC9 homolog, yeast), UBE2I | 150 |
| 28 | nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1, NUMA1 | 147 |
| 29 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 2C, GRIN2C | 146 |
| 30 | probable transcription factor PML-like /// promyelocytic leukemia, LOC652346 /// PML | 144 |
| 31 | fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1 (zygin I), FEZ1 | 143 |
| 32 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 7, GRM7 | 140 |
| 33 | acetylcholinesterase, ACHE | 131 |
| 34 | retinoic acid receptor, alpha, RARA | 123 |
| 35 | misshapen-like kinase 1, MINK1 | 119 |
| 36 | kelch-like 1 (Drosophila), KLHL1 | 119 |
| 37 | neuralized homolog (Drosophila), NEURL | 115 |
| 38 | protein kinase C, gamma, PRKCG | 106 |
| 39 | drebrin 1, DBN1 | 103 |
| 40 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | bassoon (presynaptic cytomatrix protein), BSN | −563 |
| 2 | membrane metallo-endopeptidase, MME | −540 |
| 3 | adenylate cyclase 10 (soluble), ADCY10 | −460 |
| 4 | discs, large homolog 4 (Drosophila), DLG4 | −452 |
| 5 | Kv channel interacting protein 1, KCNIP1 | −413 |
| 6 | EPH receptor A7, EPHA7 | −365 |
| 7 | PTK2B protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta, PTK2B | −348 |
| 8 | sterile alpha motif domain containing 4A, SAMD4A | −315 |
| 9 | dopamine receptor D4, DRD4 | −296 |
| 10 | FEZ family zinc finger 2, FEZF2 | −295 |
| 11 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, N type, alpha 1B subunit, CACNA1B | −290 |
| 12 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 1, MAPK8IP1 | −289 |
| 13 | regulator of G-protein signaling 11, RGS11 | −266 |
| 14 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35), CDK5R1 | −260 |
| 15 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 1, GRIK1 | −254 |
| 16 | thyroid hormone receptor, alpha (erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-a) oncogene homolog, avian), THRA | −253 |
| 17 | cyclic nucleotide gated channel alpha 3, CNGA3 | −249 |
| 18 | adenylate cyclase 2 (brain), ADCY2 | −247 |
| 19 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2, PCSK2 | −242 |
| 20 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 15, ARHGEF15 | −230 |
| 21 | potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 3, KCND3 | −224 |
| 22 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D, PTPRD | −221 |
| 23 | cytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide, CYBB | −217 |
| 24 | GABA(A) receptors associated protein like 3, pseudogene, GABARAPL3 | −197 |
| 25 | neutrophil cytosolic factor 1C pseudogene, NCF1C | −196 |
| 26 | promyelocytic leukemia, PML | −196 |
| 27 | C-reactive protein, pentraxin-related, CRP | −182 |
| 28 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 2A, GRIN2A | −180 |
| 29 | tubby like protein 1, TULP1 | −176 |
| 30 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3, MAPK8IP3 | −174 |
| 31 | cell adhesion molecule with homology to L1CAM (close homolog of L1), CHL1 | −171 |
| 32 | choline O-acetyltransferase, CHAT | −160 |
| 33 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 5, GRIK5 | −159 |
| 34 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 4, GRIK4 | −155 |
| 35 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 6, HTR6 | −150 |
| 36 | tachykinin receptor 3, TACR3 | −150 |
| 37 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, HTR5A | −149 |
| 38 | protease, serine, 12 (neurotrypsin, motopsin), PRSS12 | −141 |
| 39 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 4, CHRNA4 | −139 |
| 40 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A, HTR2A | −135 |
| 41 | leucine zipper, putative tumor suppressor 1, LZTS1 | −130 |
| 42 | neuroligin 4, X-linked, NLGN4X | −128 |
| 43 | glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 3, GRIA3 | −126 |
| 44 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 6, GRM6 | −120 |
| 45 | paralemmin, PALM | −115 |
| 46 | copine VI (neuronal), CPNE6 | −114 |
| 47 | cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 3, CPEB3 | −112 |
| 48 | corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1, CRHR1 | −109 |
| 49 | doublecortin, DCX | −108 |
| 50 | regulator of G-protein signaling 14, RGS14 | −108 |
| 51 | apolipoprotein E, APOE | −107 |
| 52 | calcium binding protein 1, CABP1 | −106 |
| 53 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 2, MAPK8IP2 | −103 |
| 54 | neurochondrin, NCDN | −102 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 6 | 4 |
| 100%–199% | 6 | 3 |
| 200%–299% | 3 | 1 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 1 |
| 400%–499% | 0 | 1 |
| 500%+ | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 16 | 10 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | tumor protein p73, TP73 | 938 |
| 2 | adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary), ADCYAP1 | 215 |
| 3 | gelsolin, GSN | 214 |
| 4 | inhibitor of DNA binding 4, dominant negative helix-loop-helix protein, ID4 | 203 |
| 5 | aspartoacylase, ASPA | 195 |
| 6 | NK2 homeobox 2, NKX2-2 | 181 |
| 7 | dopamine receptor D3, DRD3 | 164 |
| 8 | histone deacetylase 11, HDAC11 | 105 |
| 9 | achaete-scute complex homolog 1 (Drosophila), ASCL1 | 103 |
| 10 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4, CXCR4 | −496 |
| 2 | chromosome 11 open reading frame 9, C11orf9 | −342 |
| 3 | sonic hedgehog, SHH | −220 |
| 4 | zinc finger protein 287, ZNF287 | −143 |
| 5 | early growth response 1, EGR1 | −121 |
| 6 | apolipoprotein E, APOE | −107 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 45 | 25 |
| 100%–199% | 24 | 36 |
| 200%–299% | 18 | 6 |
| 300%–399% | 7 | 1 |
| 400%–499% | 1 | 3 |
| 500%+ | 2 | 4 |
| Total | 97 | 75 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | opioid receptor, mu 1, OPRM1 | 1294 |
| 2 | T-box 1, TBX1 | 553 |
| 3 | adrenergic, beta-1-, receptor, ADRB1 | 477 |
| 4 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, alpha 5 /// gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-5-like, GABRA5 /// LOC100509612 | 392 |
| 5 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1D subunit, CACNA1D | 372 |
| 6 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily W, member 1, OR2W1 | 370 |
| 7 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha activating activity polypeptide, olfactory type, GNAL | 366 |
| 8 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily B, member 6, OR2B6 | 345 |
| 9 | cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1, CNGB1 | 330 |
| 10 | EPH receptor B1, EPHB1 | 330 |
| 11 | inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 3, ITPR3 | 298 |
| 12 | olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily A, member 17, OR7A17 | 285 |
| 13 | nuclear factor I/B, NFIB | 279 |
| 14 | islet amyloid polypeptide, IAPP | 276 |
| 15 | opiate receptor-like 1, OPRL1 | 246 |
| 16 | potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 4, KCNQ4 | 245 |
| 17 | myosin, heavy chain 14, non-muscle, MYH14 | 243 |
| 18 | taste receptor, type 2, member 13, TAS2R13 | 237 |
| 19 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily F, member 2, OR2F2 | 232 |
| 20 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, GRM1 | 231 |
| 21 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 1 /// chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3-like 3, CCL3 /// CCL3L1 /// CCL3L3 | 228 |
| 22 | polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1, PKD2L1 | 225 |
| 23 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 1, GRIN1 | 216 |
| 24 | adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (pituitary), ADCYAP1 | 215 |
| 25 | ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 2, ATP2B2 | 214 |
| 26 | olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily C, member 1, OR7C1 | 207 |
| 27 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 3, P2RX3 | 207 |
| 28 | neuropeptide Y receptor Y1, NPY1R | 201 |
| 29 | family with sequence similarity 38, member B, FAM38B | 193 |
| 30 | olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily A, member 1, OR1A1 | 189 |
| 31 | taste receptor, type 2, member 14, TAS2R14 | 181 |
| 32 | purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4, P2RX4 | 180 |
| 33 | receptor accessory protein 2, REEP2 | 174 |
| 34 | endothelin receptor type A, EDNRA | 173 |
| 35 | cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain), CNR1 | 172 |
| 36 | melanocortin 1 receptor (alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone receptor), MC1R | 164 |
| 37 | olfactory receptor, family 12, subfamily D, member 3 /// olfactory receptor, family 5, subfamily V, member 1, OR12D3 /// OR5V1 | 163 |
| 38 | odorant binding protein 2A /// odorant binding protein 2B, OBP2A /// OBP2B | 162 |
| 39 | prepronociceptin, PNOC | 150 |
| 40 | phospholipase C, beta 2, PLCB2 | 148 |
| 41 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 7, GRM7 | 140 |
| 42 | oxytocin, prepropeptide, OXT | 136 |
| 43 | WD repeat domain 1, WDR1 | 127 |
| 44 | olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily D, member 4 (gene/pseudogene) /// olfactory receptor, family 1, subfamily D, member 5, OR1D4 /// OR1D5 | 125 |
| 45 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase 2 family, polypeptide A1 /// UDP glucuronosyltransferase 2 family, polypeptide A2, UGT2A1 /// UGT2A2 | 121 |
| 46 | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase), PTGS2 | 120 |
| 47 | taste receptor, type 2, member 4, TAS2R4 | 118 |
| 48 | lysozyme, LYZ | 111 |
| 49 | protein kinase C, gamma, PRKCG | 106 |
| 50 | collagen, type XI, alpha 1, COL11A1 | 103 |
| 51 | POU class 4 homeobox 3, POU4F3 | 102 |
| 52 | nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 6, NR2F6 | 100 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | taste receptor, type 2, member 9, TAS2R9 | −1494 |
| 2 | endothelin receptor type B, EDNRB | −768 |
| 3 | necdin homolog (mouse), NDN | −729 |
| 4 | membrane metallo-endopeptidase, MME | −540 |
| 5 | EPH receptor A3, EPHA3 | −485 |
| 6 | arachidonate lipoxygenase 3, ALOXE3 | −461 |
| 7 | bradykinin receptor B1, BDKRB1 | −426 |
| 8 | gap junction protein, beta 4, 30.3kDa, GJB4 | −317 |
| 9 | nerve growth factor (beta polypeptide), NGF | −243 |
| 10 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha transducing activity polypeptide 1, GNAT1 | −242 |
| 11 | olfactory receptor, family 3, subfamily A, member 1, OR3A1 | −234 |
| 12 | apelin receptor, APLNR | −230 |
| 13 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily F, member 1 /// olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily F, member 2, OR2F1 /// OR2F2 | −212 |
| 14 | olfactory receptor, family 12, subfamily D, member 3, OR12D3 | −201 |
| 15 | olfactory receptor, family 6, subfamily A, member 2, OR6A2 | −199 |
| 16 | cholecystokinin B receptor, CCKBR | −198 |
| 17 | carbonic anhydrase VI, CA6 | −192 |
| 18 | olfactory receptor, family 5, subfamily I, member 1, OR5I1 | −191 |
| 19 | collagen, type XI, alpha 2, COL11A2 | −186 |
| 20 | olfactory receptor, family 10, subfamily H, member 3, OR10H3 | −182 |
| 21 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A, GRIN2A | −180 |
| 22 | protein phosphatase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 2, PPEF2 | −178 |
| 23 | sodium channel, nonvoltage-gated 1 alpha, SCNN1A | −175 |
| 24 | trace amine associated receptor 5, TAAR5 | −168 |
| 25 | gastric inhibitory polypeptide, GIP | −164 |
| 26 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily H, member 1, OR2H1 | −156 |
| 27 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily J, member 2, OR2J2 | −155 |
| 28 | otoferlin, OTOF | −155 |
| 29 | discs, large homolog 2 (Drosophila), DLG2 | −142 |
| 30 | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 4, CHRNA4 | −139 |
| 31 | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A, HTR2A | −135 |
| 32 | tectorin alpha, TECTA | −126 |
| 33 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type XI, alpha subunit, SCN11A | −124 |
| 34 | olfactory receptor, family 7, subfamily C, member 2, OR7C2 | −120 |
| 35 | taste receptor, type 2, member 16, TAS2R16 | −120 |
| 36 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 6, GRM6 | −120 |
| 37 | opioid receptor, kappa 1, OPRK1 | −119 |
| 38 | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 56/58kDa, V1 subunit B1, ATP6V1B1 | −118 |
| 39 | olfactory marker protein, OMP | −118 |
| 40 | contactin 5, CNTN5 | −116 |
| 41 | cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2, CYSLTR2 | −113 |
| 42 | olfactory receptor, family 2, subfamily H, member 2, OR2H2 | −110 |
| 43 | rhodopsin, RHO | −108 |
| 44 | interleukin 10, IL10 | −107 |
| 45 | olfactory receptor, family 11, subfamily A, member 1, OR11A1 | −107 |
| 46 | polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, PIGR | −107 |
| 47 | guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 13, GNG13 | −106 |
| 48 | tubby homolog (mouse), TUB | −101 |
| 49 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 8, GRM8 | −101 |
| 50 | cystatin S, CST4 | −101 |
| Percent Change in Gene Expression | Genes UP | Genes DOWN |
|---|---|---|
| 50%–99% | 8 | 6 |
| 100%–199% | 9 | 3 |
| 200%–299% | 1 | 2 |
| 300%–399% | 0 | 1 |
| 400%–499% | 1 | 0 |
| 500%+ | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 20 | 13 |
| UP | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | tumor protein p73, TP73 | 938 |
| 2 | smoothened homolog (Drosophila), SMO | 415 |
| 3 | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit, CACNA1A | 286 |
| 4 | GATA binding protein 2, GATA2 | 193 |
| 5 | GLI family zinc finger 2, GLI2 | 183 |
| 6 | NK2 homeobox 2, NKX2-2 | 181 |
| 7 | dopamine receptor D3, DRD3 | 164 |
| 8 | paired box 7, PAX7 | 161 |
| 9 | slit homolog 3 (Drosophila), SLIT3 | 154 |
| 10 | polycystic kidney disease 1 (autosomal dominant), PKD1 | 137 |
| 11 | achaete-scute complex homolog 1 (Drosophila), ASCL1 | 103 |
| 12 | neurofibromin 1, NF1 | 102 |
| DOWN | Gene Title | Percent Change |
| 1 | slit homolog 1 (Drosophila), SLIT1 | −553 |
| 2 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 1, SOX1 | −337 |
| 3 | growth differentiation factor 11, GDF11 | −221 |
| 4 | sonic hedgehog, SHH | −220 |
| 5 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl d-aspartate 2A, GRIN2A | −180 |
| 6 | even-skipped homeobox 1, EVX1 | −110 |
| 7 | aquaporin 1 (Colton blood group), AQP1 | −101 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Margolina, A. The Effect of the Human Peptide GHK on Gene Expression Relevant to Nervous System Function and Cognitive Decline. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7020020
Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. The Effect of the Human Peptide GHK on Gene Expression Relevant to Nervous System Function and Cognitive Decline. Brain Sciences. 2017; 7(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7020020
Chicago/Turabian StylePickart, Loren, Jessica Michelle Vasquez-Soltero, and Anna Margolina. 2017. "The Effect of the Human Peptide GHK on Gene Expression Relevant to Nervous System Function and Cognitive Decline" Brain Sciences 7, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7020020
APA StylePickart, L., Vasquez-Soltero, J. M., & Margolina, A. (2017). The Effect of the Human Peptide GHK on Gene Expression Relevant to Nervous System Function and Cognitive Decline. Brain Sciences, 7(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7020020






