Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine Treatment Immediately Following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury on Spatial Memory in Male Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Induction of Hypoxia Ischemia
2.3. Caffeine Administration
2.4. Behavioral Testing
2.4.1. Water Escape (P87)
2.4.2. Morris Water Maze (MWM; P90–P95)
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Escape (P87)
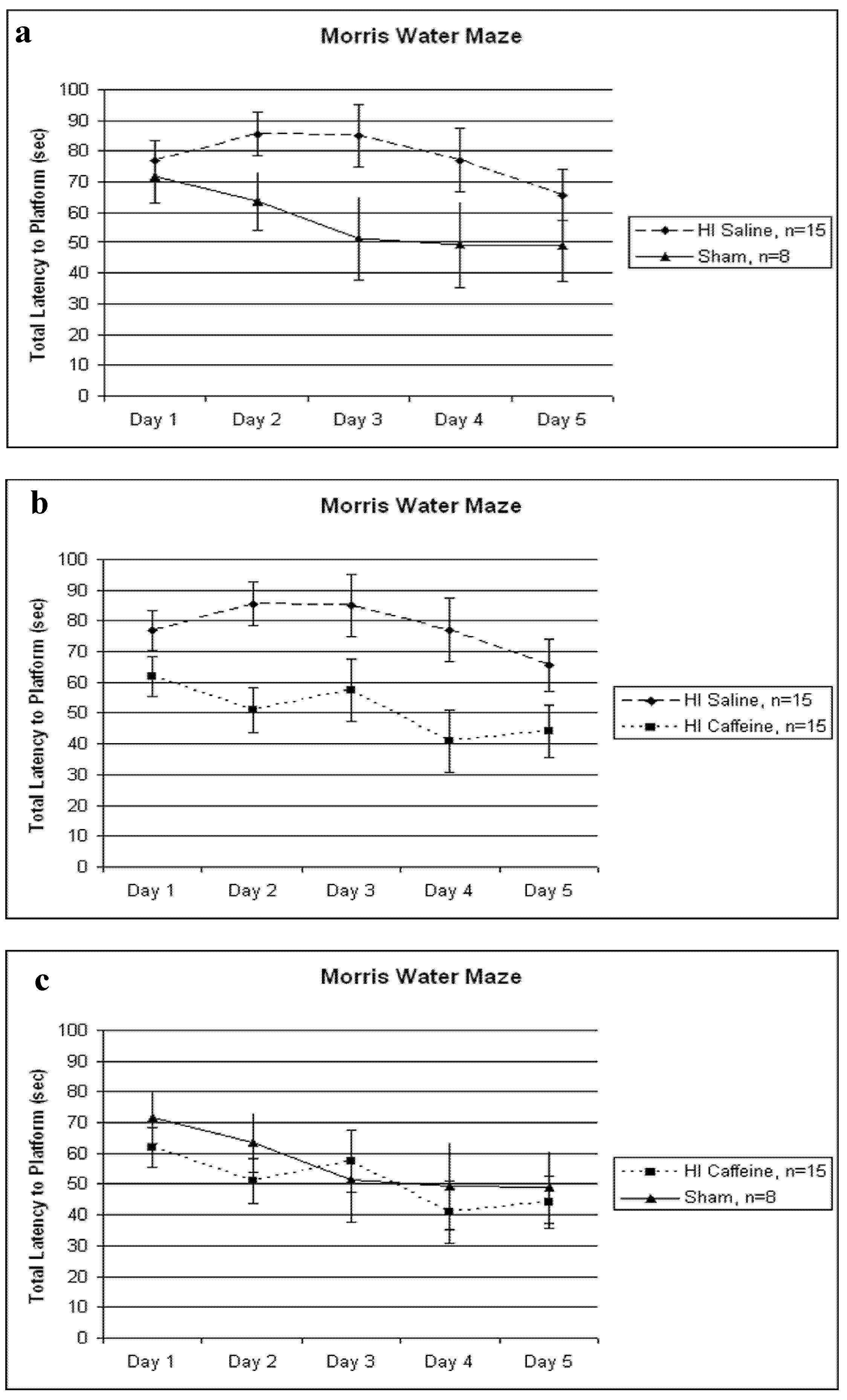
3.2. Morris Water Maze (P90–P95)
3.3. Histology
Volumetric Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Adenosine in Neonatal HI
4.2. Caffeine Treatment Following Neonatal HI
4.3. Central versus Peripheral Effects of Caffeine Treatment
5. Conclusions
References
- Volpe, J.J. Brain injury in premature infants: A complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, L.S.; Cowan, F.M. Evolving understanding of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term infant. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 16, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, R.C. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Neurology of the Newborn, 5th ed; Elsevier Health Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 347–400. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, J.; Gathercole, S.E.; Marlow, N. Short-term memory and language outcomes after extreme prematurity at birth. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1998, 41, 654–666. [Google Scholar]
- Vicari, S.; Caravale, B.; Carlesimo, G.A.; Casadei, A.M.; Allemand, F. Spatial working memory deficits in children at ages 3–4 who were low birth weight, preterm infants. Neuropsychology 2004, 18, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.M.; Ment, L.; Allan, W.; Schneider, K.; Vohr, B.R. Executive and memory function in adolescents born very preterm. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e639–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, M.H.; Thompson, D.K.; Howard, K.; Doyle, L.W.; Egan, G.F.; Inder, T.E.; Anderson, P.J. Preterm infant hippocampal volumes correlate with later working memory deficits. Brain 2008, 131, 2986–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, N.; Rose, A.S.; Rands, C.E.; Draper, E.S. Neuropsychological and educational problems at school age associated with neonatal encephalopathy. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005, 90, F380–F387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, R.C.; Vannucci, S.J. A model of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 19, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, R.C.; Vannucci, S.J. Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: Evolution of an animal model. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 27, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, M.; Olivier, P.; Chambon, C.; Pansiot, J.; Russier, M.; Liberge, M.; Xin, D.; Gestreau, C.; Alescio-Laurier, B.; Gressens, P.; et al. Neuroanatomical, sensorimotor and cognitive deficits in adult rats with white matter injury following prenatal ischemia. Brain Pathol. 2012, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.M.; Peiffer, A.M.; Rosen, G.D.; Fitch, R.H. Auditory processing deficits in rats with neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 23, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.M.; Threlkeld, S.W.; Fitch, R.H. Auditory processing and learning/memory following erythropoietin administration in neonatally hypoxic-ischemic injured rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1132, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteni, N.S.; Salgueiro, J.; Torres, I.; Achaval, M.; Netto, C.A. Neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia causes lateralized memory impairments in the adult rat. Brain Res. 2003, 973, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteni, N.S.; Pereira, L.O.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Lakinsky, D.; Achaval, M.E.; Netta, C.A. Lateralized and sex-dependant behavioral and morphological effects of unilateral neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 210, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Mishima, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Xia, X.Y.; Ikenoue, T. Selective and long-term learning impairment following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain insult in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 118, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.; Threlkeld, S.W.; Fitch, R.H. Early testosterone modulated sex differences in behavioral outcome following neonatal hypoxia ischemia in rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.M.; Threlkeld, S.W.; Rosen, G.D.; Fitch, R.H. Auditory processing deficits in unilaterally and bilaterally injured hypoxic-ischemic rats. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.M.; Threlkeld, S.W.; Rosen, G.D.; Fitch, R.H. Rapid auditory processing and learning deficits in rats with P1 versus P7 neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 172, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.; Threlkeld, S.; Fitch, R.H. The effects of erythropoietin on auditory processing following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2006, 1087, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Perinatal brain injury: From pathogenesis to neuroprotection. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2001, 7, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A. Neuroprotection by adenosine in the brain: From A(1) receptor activation to A (2A) receptor blockade. Purinergic Signal. 2005, 1, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkees, S.A.; Zhao, Z.; Porter, G.; Turner, C. Influences of adenosine on the fetus and newborn. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 74, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Chen, J.; Cunha, R.; Svenningsson, P.; Vaugeois, J. Adenosine and Brain Function. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2005, 63, 191–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Sebastiao, A.M. Caffeine and Adenosine. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.; Roberts, R.S.; Davis, P.; Doyle, L.W.; Barrington, K.J.; Ohlsson, A.; Solimano, A.; Tin, W. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity Trial Group. Caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2112–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Roberts, R.S.; Davis, P.; Doyle, L.W.; Barrington, K.J.; Ohlsson, A.; Solimano, A.; Tin, W. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity Trial Group. Long-term effects of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.K. On the caffeination of prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1967–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitz, W.E. Use of caffeine for apnea of prematurity also has long-term neurodevelopmental benefits. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.H.; Flenady, V.J.; Charles, B.G.; Steer, P.A. Caffeine Collaborative Study Group. Caffeine citrate for very preterm infants: Effects on development, temperament and behaviour. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2011, 47, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supcun, S.; Kutz, P.; Pielemeier, W.; Roll, C. Caffeine increases cerebral cortical activity in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, S.A.; Craig, A.; Luo, N.L.; Ren, J.; Akundi, R.S.; Ribeiro, I.; Rivkees, S.A. Protective effects of caffeine on chronic hypoxia-induced perinatal white matter injury. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkees, S.A.; Wendler, C.C. Adverse and protective influences of adenosine on the newborn and embryo: Implications for preterm white matter injury and embryo protection. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, V.C.; Belle, L.P.; Pinherio, F.V.; Bona, K.S.; Da Luz, S.C.A.; Moretto, M.B. Adenosine deaminase activity, lipid peroxidation and astrocyte responses in the cerebral cortex of rats alter neonatal hypoxia ischemia. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, V.C.; Pinherio, F.V.; de Bona, K.S.; Maldonado, P.A.; de Silva, C.R.; de Olivera, S.M.; Ferreria, J.; Bertoncheli, C.M.; Schetinger, M.R.; Da Luz, S.C.A.; Moretto, M.B. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury stimulates inflammatory responses and enzymatic activity in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Brain Res. 2011, 1388, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.P.; Yan, H.; Schwartz, M.; Othman, T.; Rivkees, S.A. A1 adenosine receptor activation induces ventriculomegaly and white matter loss. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhov, S.; McCaleb, J.L.; Goldstein, A.E.; Biaggioni, I.; Feoktistov, I. Role of adenosine receptors in the regulation of angiogenic factors and neovascularization in hypoxia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, N.; Pearson, T.; Frenguelli, B.G. Direct measurement of adenosine release during hypoxia in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampal slice. J. Physiol. 2000, 526, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenguelli, B.G.; Llaudet, E.; Dale, N. High-resolution real time recording with microelectrode biosensors reveals novel aspects of adenosine release during hypoxia in rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, A.; Ciocan, D.; Zagrean, A.M.; Nita, D.A.; Zagrean, L.; Moldovan, M. Endogenous activation of adenosine A1 receptor accelerates ischemic suppression of spontaneous electrocortical activity. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.P.; Seli, M.; Ment, L.; Stewart, W.; Yan, H.; Johansson, B.; Fredholm, B.B.; Blackburn, M.; Rivkees, S.A. A1 adenosine receptors mediate hypoxia-induced ventriculomegaly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003, 100, 11718–11722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, U.; Halldner, L.; Lagercrantz, H.; Dalmau, I.; Ledent, C.; Fredholm, B.B. Aggravated brain damage after hypoxic ischemia in immature adenosine A2A knockout mice. Stroke 2003, 34, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Battig, K.; Holmen, J.; Nehlig, A.; Zvartau, E.E. Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 83–133. [Google Scholar]
- Costenla, A.R.; Cunha, R.A.; de Mendonca, A. Caffeine, adenosine receptors and synaptic plasticity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Aden, U. Methylxanthines during pregnancy and early postnatal life. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 200, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.S.; Richetti, S.K.; da Silveira, V.G.; Battastini, A.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Lara, D.R.; Bonan, C.D. Maternal caffeine intake affects acetylcholinesterase in hippocampus of neonate rat. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Hartman, A.D.; Hiller, H.I.; Temples, T.E.; Nakamoto, T. Chronic caffeine intake alters the composition of various parts of the brain in young growing rats. Dev. Pharnacol. Ther. 1988, 11, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Guillet, R.; Kellogg, C. Neonatal exposure to therapeutic caffeine alters the ontogeny of adenosine A1 receptors in the brain of rats. Neuropharmacology 1991, 30, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.G.; Metin, C.; Machado, N.J.; Darmopil, S.; Launay, P.; Ghestem, A.; Nesa, M.P.; Baqi, Y.; Muller, C.E.; Ivanov, A.; et al. Caffeine Exposure during Pregnancy Disrupts Gabaergic Circuits in Offspring. In Presented at the Society for Neuroscience Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, October 2012.
- Chavez-Valdez, R.; Ahlawat, R.; Wills-Karp, M.; Nathan, A.; Ezell, T.; Gauda, E.B. Correlation between serum caffeine levels and changes in cytokine profile in a cohort of preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Valdez, R.; Wills-Karp, M.; Ahlawat, R.; Cristofalo, E.A.; Nathan, A.; Gauda, E.B. Caffeine modulates TNF-alpha production by cord blood monocytes: The role of adenosine receptors. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.; Kingsbury, T.J. Caffeine modulates CREB-dependant gene expression in developing cortical neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 25, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognato, G.P.; Agostinho, P.M.; Hockemeyer, J.; Muller, C.E.; Souza, D.O.; Cunha, R.A. Caffeine and adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonist prevent memory impairment and synaptotoxicity in adult rats triggered by a convulsive episode in early life. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, B.G.; Townsend, S.R.; Steer, P.A.; Flenady, V.J.; Gray, P.H.; Shearman, A. Caffeine citrate treatment for extremely premature infants with apnea: Population pharmacokinetics, absolute bioavailability, and implications for therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.I.A.; Jafri, A.; Martin, R.J.; Haxhiu, M.A. Adenosine A2A receptors are expressed by GABAergic neurons of medulla oblongata in developing rat. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexander, M.; Smith, A.L.; Rosenkrantz, T.S.; Fitch, R.H. Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine Treatment Immediately Following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury on Spatial Memory in Male Rats. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 177-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010177
Alexander M, Smith AL, Rosenkrantz TS, Fitch RH. Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine Treatment Immediately Following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury on Spatial Memory in Male Rats. Brain Sciences. 2013; 3(1):177-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010177
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexander, Michelle, Amanda L. Smith, Ted S. Rosenkrantz, and R. Holly Fitch. 2013. "Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine Treatment Immediately Following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury on Spatial Memory in Male Rats" Brain Sciences 3, no. 1: 177-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010177
APA StyleAlexander, M., Smith, A. L., Rosenkrantz, T. S., & Fitch, R. H. (2013). Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine Treatment Immediately Following Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury on Spatial Memory in Male Rats. Brain Sciences, 3(1), 177-190. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010177



