Use of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Distribution of Animals by Severity of Brain Tissue Damage in a Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Model in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design and Group Allocation
- -
- TTC staining at 24 h: mild group (n = 6), moderate group (n = 6), severe group (n = 4), intact controls (n = 3). NVD (n = 6)
- -
- Survival monitoring over 7 days: mild (n = 10), moderate (n = 9), severe (n = 7), intact (n = 3).
- -
- LSCI at 7 days: mild (n = 7), moderate (n = 7), severe (n = 2), intact (n = 3). Not all survivors from the mild and moderate groups could be re-imaged due to scalp wound healing.
- -
- TTC staining at 7 days: mild (n = 10), moderate (n = 9), severe (n = 2), intact (n = 3). This analysis included all available brains at the endpoint.
2.3. Modeling of Neonatal Hypoxia–Ischemia
2.4. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging
2.5. Post-Traumatic Assessment
2.6. Euthanasia of Animals
2.7. Macroscopic Evaluation of Brain Damage
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
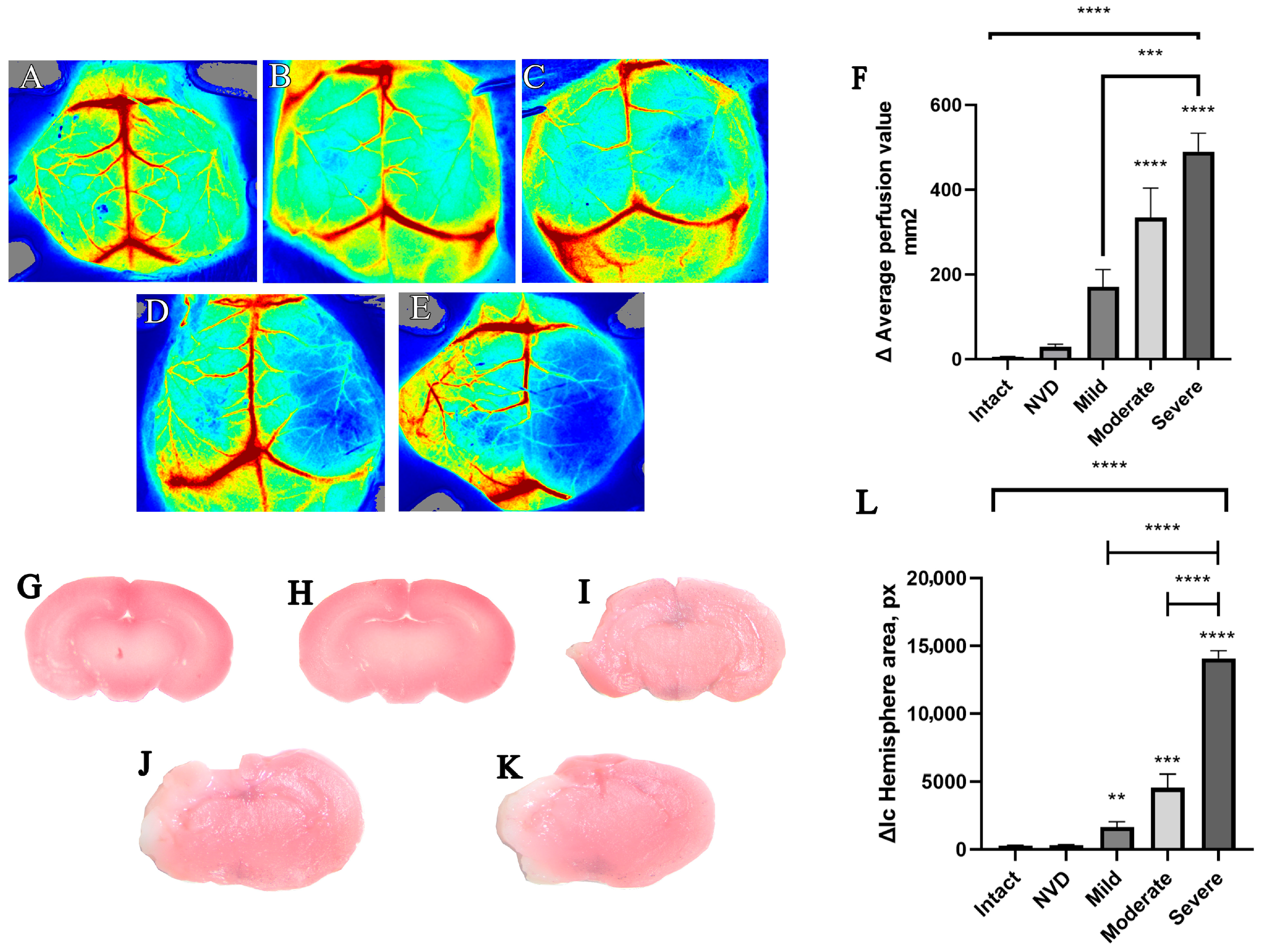
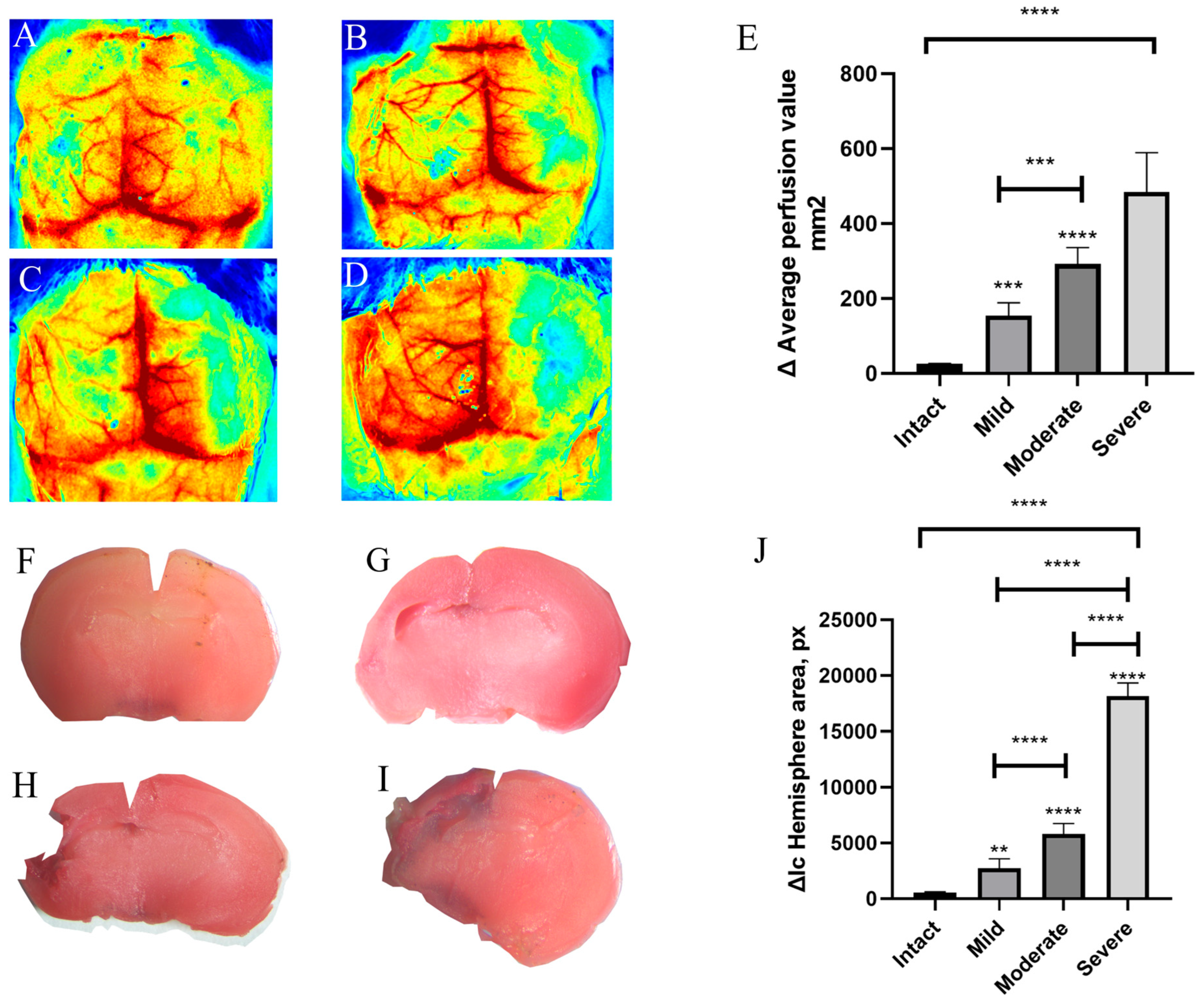
3.1. Randomization of Animals by Severity in the Acute Period
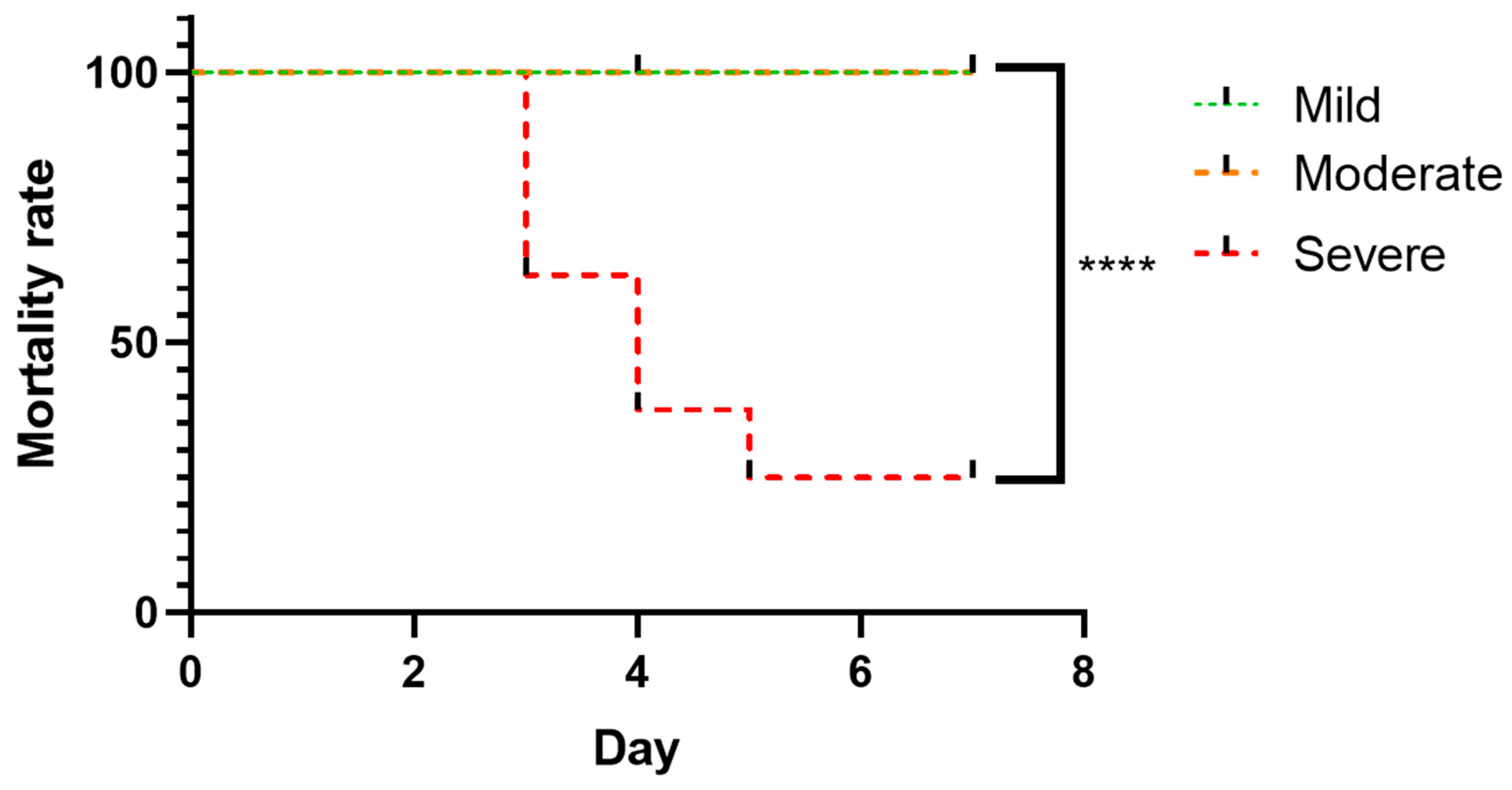
3.2. Survival Analysis Following Severity-Based Stratification
3.3. Delayed Assessment at Day 7 of Cerebral Perfusion and Brain Damage
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSCI | Laser speckle contrast imaging |
| HI | Neonatal hypoxia–ischemia |
| NVD | No-visible-damage |
| TTC | 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
References
- Kromm, G.H.; Patankar, H.; Nagalotimath, S.; Wong, H.; Austin, T. Socioemotional and Psychological Outcomes of Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023063399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmen, S.; Maes, E.; Zweyer, M.; Schleehuber, Y.; Imam, F.B.; Silverman, J.; White, Y.; Pang, R.; Pasca, A.M.; Robertson, N.J.; et al. Comparing the efficacy in reducing brain injury of different neuroprotective agents following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in newborn rats: A multi-drug randomized controlled screening trial. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenpour, H.; Pesce, M.; Patruno, A.; Bahrami, A.; Pour, P.M.; Farzaei, M.H. A Review of Plant Extracts and Plant-Derived Natural Compounds in the Prevention/Treatment of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnsed, J.C.; Chavez-Valdez, R.; Hossain, M.S.; Kesavan, K.; Martin, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Northington, F.J. Hypoxia-ischemia and therapeutic hypothermia in the neonatal mouse brain-a longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, P.V.; Zhang, J.; Sosunov, S.; Galkin, A.; Niatsetskaya, Z.; Starkov, A.; Brookes, P.S.; Ten, V.S. Krebs cycle metabolites and preferential succinate oxidation following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in mice. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Windsor, C.; Ferriero, D.M. Strain-Related Differences in Mouse Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 40, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Sanchez, K.; Hu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q. 3D doppler ultrasound imaging of cerebral blood flow for assessment of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in mice. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodygensky, G.A.; Inder, T.E.; Neil, J.J. Application of magnetic resonance imaging in animal models of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaydin, B.; Bicki, E.; Taparli, O.E.; Sheikh, T.Z.; Schmidt, D.K.; Yapici, S.; Hackett, M.B.; Karahan-Keles, N.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Corcoran, K.; et al. Novel Injury Scoring Tool for Assessing Brain Injury following Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia in Mice. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 44, 394–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, M.; Burnsed, J.; Martin, L.J.; Northington, F.J.; Zhang, J. Imaging neurodegeneration in the mouse hippocampus after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia using oscillating gradient diffusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adén, U.; Dahlberg, V.; Fredholm, B.B.; Lai, L.-J.; Chen, Z.; Bjelke, B. MRI evaluation and functional assessment of brain injury after hypoxic ischemia in neonatal mice. Stroke 2002, 33, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, A.K. Laser speckle contrast imaging of cerebral blood flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.; Wu, G.; Zhao, H. Targeting PD-L1 for Ischemic Stroke Recovery: Age-Dependent Modulation of Immune and BBB Pathways. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limam, S.; Patel, A.; Satav, D.; Miryala, S.; Dharap, A. Widespread induction of SINE-RNA expression in the mouse brain following transient focal ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 394, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-J.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Fu, L.-L.; Ge, G.; Zhu, J.-D. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates neuroinflammation via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to exert neuroprotective effect on cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1555067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, D.A.; Dunn, A.K. Laser speckle contrast imaging in biomedical optics. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 011109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.B.; Shin, H.K.; Boas, D.A.; Hyman, B.T.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C.; Dunn, A.K. Simultaneous multispectral reflectance imaging and laser speckle flowmetry of cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.E., 3rd; Vannucci, R.C.; Brierley, J.B. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open-source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Yu, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Wi, S.; Baek, A.; Song, S.Y.; Cho, S.R. Neurobehavioral Assessments in a Mouse Model of Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Injury. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 129, 55838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Pokrovskii, V.; Lapin, K.; Antonova, V.; Korokin, M.; Gudyrev, O.; Gureev, V.; Korokina, L.; Scheblykina, O.; Nesterov, A.; Maslinikova, M.; et al. Use of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Distribution of Animals by Severity of Brain Tissue Damage in a Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Model in Mice. Brain Sci. 2026, 16, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci16010102
Pokrovskii V, Lapin K, Antonova V, Korokin M, Gudyrev O, Gureev V, Korokina L, Scheblykina O, Nesterov A, Maslinikova M, et al. Use of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Distribution of Animals by Severity of Brain Tissue Damage in a Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Model in Mice. Brain Sciences. 2026; 16(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci16010102
Chicago/Turabian StylePokrovskii, Vladimir, Konstantin Lapin, Viktoria Antonova, Mikhail Korokin, Oleg Gudyrev, Vladimir Gureev, Liliya Korokina, Olesya Scheblykina, Arkadii Nesterov, Maria Maslinikova, and et al. 2026. "Use of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Distribution of Animals by Severity of Brain Tissue Damage in a Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Model in Mice" Brain Sciences 16, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci16010102
APA StylePokrovskii, V., Lapin, K., Antonova, V., Korokin, M., Gudyrev, O., Gureev, V., Korokina, L., Scheblykina, O., Nesterov, A., Maslinikova, M., Chatsky, I., Mukhamedov, D., & Pokrovskii, M. (2026). Use of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Distribution of Animals by Severity of Brain Tissue Damage in a Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Model in Mice. Brain Sciences, 16(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci16010102







