Multifaceted Role of Nef in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Histopathological Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
1. HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND): A Clinical Overview
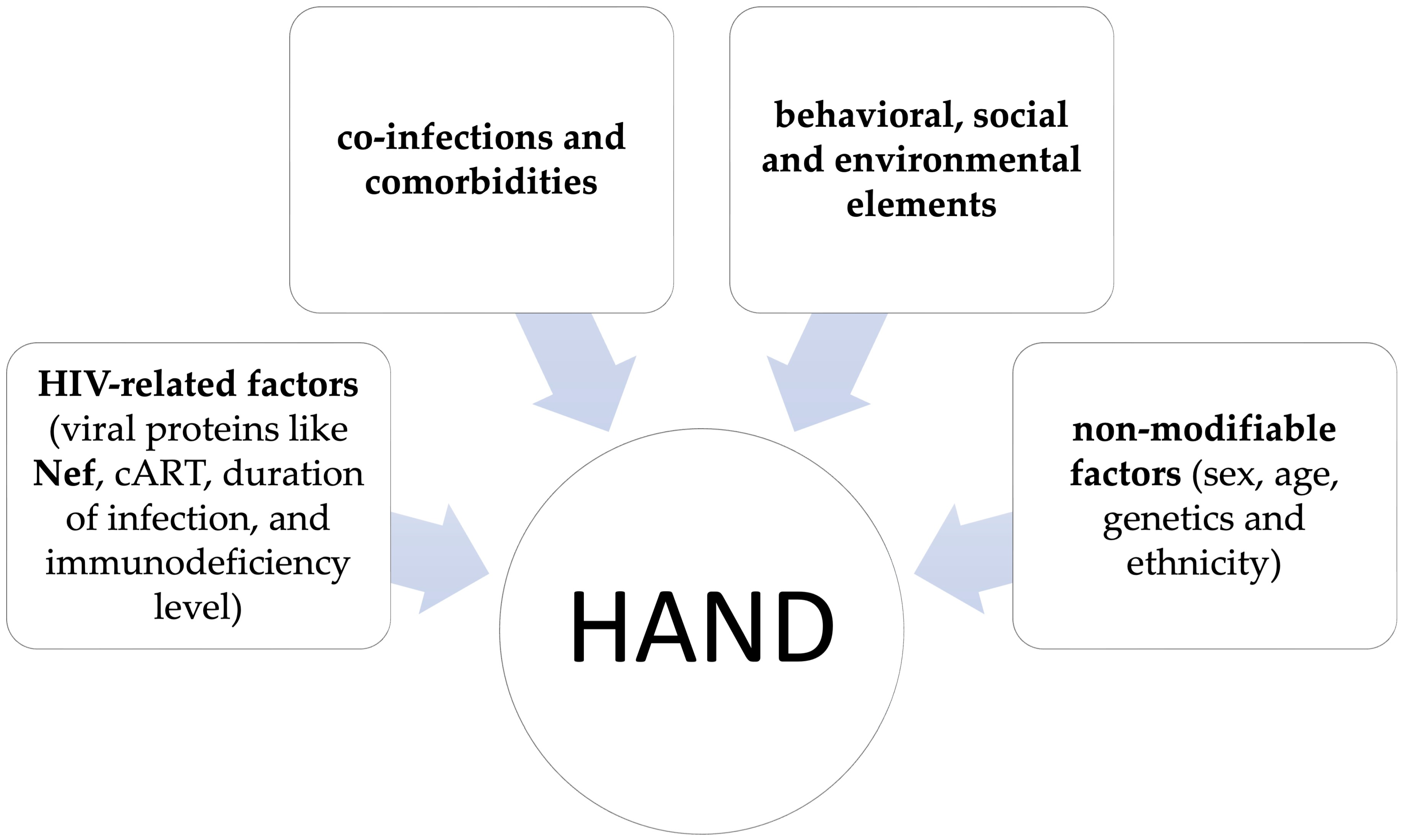
2. Pathogenetic Mechanisms Contributing to HAND
3. Brain Histopathological Changes Induced by Nef
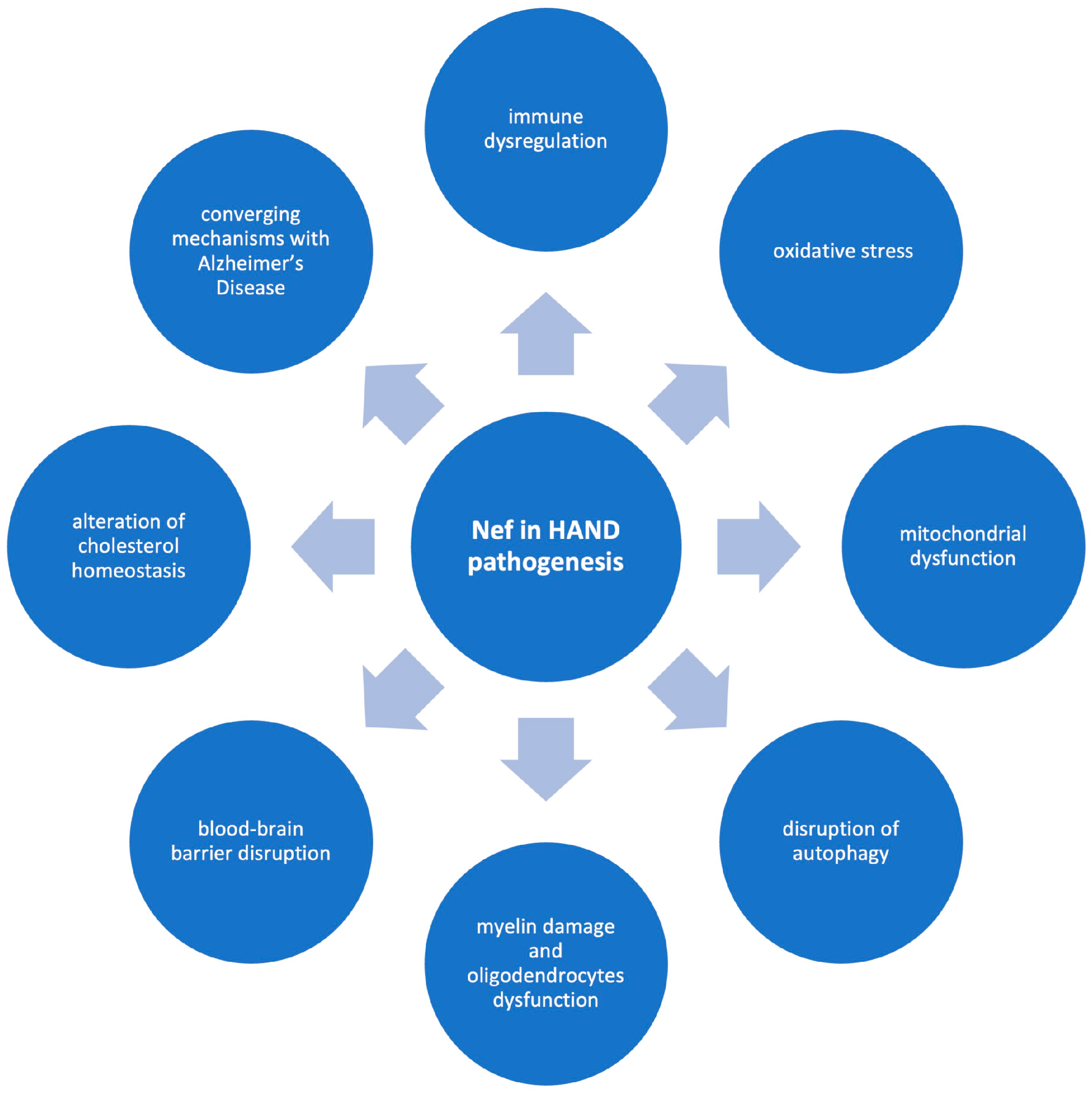
4. Potential Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Nef in HAND
4.1. Nef and Immune Dysregulation
4.2. Nef-Induced Oxidative Stress
4.3. Nef-Associated Mitochondrial Dysfunction
4.4. Disruption of Autophagy by Nef
4.5. Nef-Induced Myelin Damage and Oligodendrocytes Dysfunction
4.6. BBB Disruption Mediated by Nef
4.7. Nef-Mediated Disruption of Cholesterol Homeostasis
4.8. Converging Pathogenetic Mechanisms Between HAND and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Role for Nef
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yarandi, S.S.; Duggan, M.R.; Sariyer, I.K. Emerging Role of Nef in the Development of HIV Associated Neurological Disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağlık, İ.; Payaslıoğlu, M.; Ortaç, H.; Ayma Rüzgar, H. The Diagnostic Value of Signal-to-Cutoff Ratios in Architect and Alinity HIV Screening Assays: A 10-Year Experience in a Pandemic-Affected, Low-Prevalence Setting. Viruses 2025, 17, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andhavarapu, S.; Katuri, A.; Bryant, J.; Patel, V.; Gupta, U.; Asemu, G.; Makar, T.K. Intersecting roles of ER stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, autophagy, and calcium homeostasis in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder. J. Neurovirol. 2020, 26, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenebe, Y.; Necho, M.; Yimam, W.; Akele, B. Worldwide Occurrence of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders and Its Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 814362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylor, D.; Dickens, A.M.; Sacktor, N.; Haughey, N.; Slusher, B.; Pletnikov, M.; Mankowski, J.L.; Brown, A.; Volsky, D.J.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder--pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Lang, M.J.; Huang, M.B.; Raymond, A.; Bond, V.C.; Shiramizu, B.; Powell, M.D. Nef exosomes isolated from the plasma of individuals with HIV-associated dementia (HAD) can induce Abeta(1-42) secretion in SH-SY5Y neural cells. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, K.; Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, R.; Banerjee, R.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Ganguly, K.; Karak, P. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND): Optimal diagnosis, antiviral therapy, pharmacological treatment, management, and future scopes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 470, 123410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elendu, C.; Aguocha, C.M.; Okeke, C.V.; Okoro, C.B.; Peterson, J.C. HIV-related neurocognitive disorders: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Mental Health Implications: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e35652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I. Interrogating the impact of combination antiretroviral therapies on HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. HIV Med. 2021, 22, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caobi, A.; Werne, R.; Gomez, M.; Andre, M.; Thomas, C.; Yndart, A.; Lima-Hernandez, F.; Nair, M.; Raymond, A.D. Protein cargo of Nef-containing exosomal extracellular vesicles may predict HIV-associated Neurocognitive Impairment status. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Tancheva, L.; Kalfin, R.; Fagone, P.; Mangano, K. Gene Co-Expression Network Modular Analysis Reveals Altered Immune Mechanisms in HIV-HAND. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, L.; Guzik, H.; Macaluso, F.P.; Macian, F.; Cuervo, A.M.; Berman, J.W. HIV Nef and Antiretroviral Therapy Have an Inhibitory Effect on Autophagy in Human Astrocytes that May Contribute to HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. Cells 2020, 9, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridov, D.; Bukrinsky, M. Neuro-HIV-New insights into pathogenesis and emerging therapeutic targets. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ye, Q.; Chen, D.; Li, X. Neurocognitive function and its influencing factors in people living with HIV/AIDS. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2024, 49, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulop, T.; Witkowski, J.M.; Larbi, A.; Khalil, A.; Herbein, G.; Frost, E.H. Does HIV infection contribute to increased beta-amyloid synthesis and plaque formation leading to neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease? J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, I.S.; Cacabelos, R.; Naidoo, V. Risk Factors and Pathogenesis of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: The Role of Host Genetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saro, A.; Gao, Z.; Kambey, P.A.; Pielnaa, P.; Marcellin, D.F.H.; Luo, A.; Zheng, R.; Huang, Z.; Liao, L.; Zhao, M.; et al. HIV-Proteins-Associated CNS Neurotoxicity, Their Mediators, and Alternative Treatments. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 2553–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzar Dominkus, P.; Ferdin, J.; Plemenitas, A.; Peterlin, B.M.; Lenassi, M. Nef is secreted in exosomes from Nef.GFP-expressing and HIV-1-infected human astrocytes. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, W.; Tang, S.J. HIV-associated synaptic degeneration. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.F.; Brew, B.J. Neuropathogenesis of acute HIV: Mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic approaches. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2025, 20, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, J.K.; Clarkson-Paredes, C.; Pushkarsky, T.; Wang, Y.; Miller, R.H.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Nef mediates neuroimmune response, myelin impairment, and neuronal injury in EcoHIV-infected mice. Life Sci. Alliance 2025, 8, e202402879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navia, B.A.; Cho, E.S.; Petito, C.K.; Price, R.W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, S.D.; Alldred, M.J.; Gunnam, S.M.; Schiroli, C.; Lee, S.H.; Morgello, S.; Fischer, T. Expression profiling suggests microglial impairment in human immunodeficiency virus neuropathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Misra, V.; Yin, J.; Gabuzda, D. CSF Inflammation Markers Associated with Asymptomatic Viral Escape in Cerebrospinal Fluid of HIV-Positive Individuals on Antiretroviral Therapy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, A.; Lyons, J.L.; Misra, V.; Uno, H.; Morgello, S.; Singer, E.J.; Gabuzda, D. Monocyte activation markers in cerebrospinal fluid associated with impaired neurocognitive testing in advanced HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2012, 60, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, F.; Titanji, K.; De Milito, A.; Chiodi, F. Astrocyte activation and apoptosis: Their roles in the neuropathology of HIV infection. Brain Pathol. 2003, 13, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Kelschenbach, J.; Borjabad, A.; Hadas, E.; He, H.; Potash, M.J.; Nedelcovych, M.T.; Rais, R.; Haughey, N.J.; McArthur, J.C.; et al. Intranasal insulin therapy reverses hippocampal dendritic injury and cognitive impairment in a model of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders in EcoHIV-infected mice. AIDS 2019, 33, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelschenbach, J.; He, H.; Kim, B.H.; Borjabad, A.; Gu, C.J.; Chao, W.; Do, M.; Sharer, L.R.; Zhang, H.; Arancio, O.; et al. Efficient Expression of HIV in Immunocompetent Mouse Brain Reveals a Novel Nonneurotoxic Viral Function in Hippocampal Synaptodendritic Injury and Memory Impairment. mBio 2019, 10, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, M.J.; Figueiredo, A.; Cowley, D.; Gray, L.; Purcell, D.F.; Sullivan, J.S.; McPhee, D.A.; Wesselingh, S.L.; Brew, B.J.; Gorry, P.R. Transcriptional activity of blood-and cerebrospinal fluid-derived nef/long-terminal repeat sequences isolated from a slow progressor infected with nef-deleted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) who developed HIV-associated dementia. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, S.L.; Poon, A.F.; McGrath, M.S. HIV-1 nef protein structures associated with brain infection and dementia pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agopian, K.; Wei, B.L.; Garcia, J.V.; Gabuzda, D. CD4 and MHC-I downregulation are conserved in primary HIV-1 Nef alleles from brain and lymphoid tissues, but Pak2 activation is highly variable. Virology 2007, 358, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamers, S.L.; Fogel, G.B.; Liu, E.S.; Barbier, A.E.; Rodriguez, C.W.; Singer, E.J.; Nolan, D.J.; Rose, R.; McGrath, M.S. Brain-specific HIV Nef identified in multiple patients with neurological disease. J. Neurovirol. 2018, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.; Aluvihare, V.; McMichael, A. Nef triggers a transcriptional program in T cells imitating single-signal T cell activation and inducing HIV virulence mediators. Immunity 2001, 14, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, S.R.; Luo, X.; He, J.J. Nef inhibits HIV transcription and gene expression in astrocytes and HIV transmission from astrocytes to CD4(+) T cells. J. Neurovirol. 2022, 28, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, N.J.; Tsykin, A.; Solomon, A.; Smith, K.; Ludford-Menting, M.; Hooker, D.J.; McPhee, D.A.; Greenway, A.L.; Ellett, A.; Chatfield, C.; et al. Genomic structure of an attenuated quasi species of HIV-1 from a blood transfusion donor and recipients. Science 1995, 270, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulizia, R.J.; Collman, R.G.; Levy, J.A.; Trono, D.; Mosier, D.E. Deletion of nef slows but does not prevent CD4-positive T-cell depletion in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected human-PBL-SCID mice. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4161–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestler, H.W., 3rd; Ringler, D.J.; Mori, K.; Panicali, D.L.; Sehgal, P.K.; Daniel, M.D.; Desrosiers, R.C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell 1991, 65, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmaciogullari, S.; Pizzato, M. The activity of Nef on HIV-1 infectivity. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Kaake, R.M.; Echeverria, I.; Suarez, M.; Karimian Shamsabadi, M.; Stoneham, C.; Ramirez, P.W.; Kress, J.; Singh, R.; Sali, A.; et al. Structural basis of CD4 downregulation by HIV-1 Nef. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami Saribas, A.; Cicalese, S.; Ahooyi, T.M.; Khalili, K.; Amini, S.; Sariyer, I.K. HIV-1 Nef is released in extracellular vesicles derived from astrocytes: Evidence for Nef-mediated neurotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditiatkovski, M.; Mukhamedova, N.; Dragoljevic, D.; Hoang, A.; Low, H.; Pushkarsky, T.; Fu, Y.; Carmichael, I.; Hill, A.F.; Murphy, A.J.; et al. Modification of lipid rafts by extracellular vesicles carrying HIV-1 protein Nef induces redistribution of amyloid precursor protein and Tau, causing neuronal dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13377–13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Ortiz, J.; Pla-Tenorio, J.; Cruz, M.L.; Colon, K.; Perez-Morales, J.; Rodriguez, J.A., Jr.; Martinez-Sicari, J.; Noel, R.J., Jr. Blockade of beta adrenergic receptors protects the blood brain barrier and reduces systemic pathology caused by HIV-1 Nef protein. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shah, A.; Gangwani, M.R.; Silverstein, P.S.; Fu, M.; Kumar, A. HIV-1 Nef induces CCL5 production in astrocytes through p38-MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathway and utilizes NF-kB, CEBP and AP-1 transcription factors. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancheva, L.; Petralia, M.C.; Miteva, S.; Dragomanova, S.; Solak, A.; Kalfin, R.; Lazarova, M.; Yarkov, D.; Ciurleo, R.; Cavalli, E.; et al. Emerging Neurological and Psychobiological Aspects of COVID-19 Infection. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompre, G.; Cruz, E.; Maldonado, L.; Rivera-Amill, V.; Porter, J.T.; Noel, R.J., Jr. Astrocytic expression of HIV-1 Nef impairs spatial and recognition memory. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 49, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Makar, P.; Nema, V. The NeuroinflammatoryPotential of HIV-1 NefVariants in Modulating the Gene Expression Profile of Astrocytes. Cells 2022, 11, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordelet, E.; Kissa, K.; Cressant, A.; Gray, F.; Ozden, S.; Vidal, C.; Charneau, P.; Granon, S. Histopathological and cognitive defects induced by Nef in the brain. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- van Marle, G.; Henry, S.; Todoruk, T.; Sullivan, A.; Silva, C.; Rourke, S.B.; Holden, J.; McArthur, J.C.; Gill, M.J.; Power, C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein mediates neural cell death: A neurotoxic role for IP-10. Virology 2004, 329, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, X.; Zuo, D.; Xue, M.; Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, L.; Cao, Q.; Li, X.; et al. HIV-1 Nef-induced lncRNA AK006025 regulates CXCL9/10/11 cluster gene expression in astrocytes through interaction with CBP/P300. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompre, G.; Martinez-Orengo, N.; Cruz, M.; Porter, J.T.; Noel, R.J., Jr. TGFbetaRI antagonist inhibits HIV-1 Nef-induced CC chemokine family ligand 2 (CCL2) in the brain and prevents spatial learning impairment. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, K.C.; Agopian, K.A.; Mukerji, J.; Gabuzda, D. Evidence for adaptive evolution at the divergence between lymphoid and brain HIV-1 nef genes. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2010, 26, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, L.R.; Gabuzda, D.; Cowley, D.; Ellett, A.; Chiavaroli, L.; Wesselingh, S.L.; Churchill, M.J.; Gorry, P.R. CD4 and MHC class 1 down-modulation activities of nef alleles from brain- and lymphoid tissue-derived primary HIV-1 isolates. J. Neurovirol. 2011, 17, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedel, U.; Kohleisen, B.; Sporer, B.; Lahrtz, F.; Ovod, V.; Fontana, A.; Erfle, V.; Pfister, H.W. HIV type 1 Nef protein is a viral factor for leukocyte recruitment into the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, S.; Byrnes, S.; Cochrane, C.; Roche, M.; Estes, J.D.; Selemidis, S.; Angelovich, T.A.; Churchill, M.J. The role of oxidative stress in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 13, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Nema, V. HIV-Associated Neurotoxicity: The Interplay of Host and Viral Proteins. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 1267041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, J.A.; Ellis, R.J. HIV in the cART era and the mitochondrial: Immune interface in the CNS. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 145, pp. 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, L.M.; Purnell, P.R.; Stauch, K.L.; Callen, S.E.; Buch, S.J.; Fox, H.S. HIV-1 transgenic rats display mitochondrial abnormalities consistent with abnormal energy generation and distribution. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saribas, A.S.; Khalili, K.; Sariyer, I.K. Dysregulation of autophagy by HIV-1 Nef in human astrocytes. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2899–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, J.K.; Karl, M.T.; Clarkson-Paredes, C.; Bastin, A.; Pushkarsky, T.; Brichacek, B.; Miller, R.H.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Extracellular vesicles produced by HIV-1 Nef-expressing cells induce myelin impairment and oligodendrocyte damage in the mouse central nervous system. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, N.; Kanmogne, G.D. Structural and Functional Dysregulation of the Brain Endothelium in HIV Infection and Substance Abuse. Cells 2024, 13, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atluri, V.S.; Hidalgo, M.; Samikkannu, T.; Kurapati, K.R.; Jayant, R.D.; Sagar, V.; Nair, M.P. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus on blood-brain barrier integrity and function: An update. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzini, V.; Calistri, A.; Salata, C.; Del Vecchio, C.; Sartori, E.; Parolin, C.; Palu, G. Nef and cell signaling transduction: A possible involvement in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. J. Neurovirol. 2009, 15, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodidela, S.; Gerth, K.; Haque, S.; Gong, Y.; Ismael, S.; Singh, A.; Tauheed, I.; Kumar, S. Extracellular Vesicles: A Possible Link between HIV and Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology in HIV Subjects? Cells 2019, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridov, D.; Mukhamedova, N.; Makarov, A.A.; Adzhubei, A.; Bukrinsky, M. Comorbidities of HIV infection: Role of Nef-induced impairment of cholesterol metabolism and lipid raft functionality. AIDS 2020, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarsky, T.; Ward, A.; Ivanov, A.; Lin, X.; Sviridov, D.; Nekhai, S.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Abundance of Nef and p-Tau217 in Brains of Individuals Diagnosed with HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders Correlate with Disease Severance. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Schierer, S.; Blume, K.; Dindorf, J.; Wittki, S.; Xiang, W.; Ostalecki, C.; Koliha, N.; Wild, S.; Schuler, G.; et al. HIV-Nef and ADAM17-Containing Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Induce and Correlate with Immune Pathogenesis in Chronic HIV Infection. eBioMedicine 2016, 6, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanpouille, C.; Brichacek, B.; Pushkarsky, T.; Dubrovsky, L.; Fitzgerald, W.; Mukhamedova, N.; Garcia-Hernandez, S.; Matthies, D.; Popratiloff, A.; Sviridov, D.; et al. HIV-1 Nef is carried on the surface of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R.P.; Costantini, L.M.; Myers, T.A.; Schouest, B.; Maness, N.J.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.A.; MacLean, A.G.; Dittmer, D.P. Nef Secretion into Extracellular Vesicles or Exosomes Is Conserved across Human and Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses. mBio 2018, 9, e02344-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emert-Sedlak, L.A.; Shi, H.; Tice, C.M.; Chen, L.; Alvarado, J.J.; Shu, S.T.; Du, S.; Thomas, C.E.; Wrobel, J.E.; Reitz, A.B.; et al. Antiretroviral Drug Discovery Targeting the HIV-1 Nef Virulence Factor. Viruses 2022, 14, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, J.; Herate, C.; Guenzel, C.A.; Verollet, C.; Jarviluoma, A.; Mazzolini, J.; Rafie, S.; Chames, P.; Baty, D.; Saksela, K.; et al. Single-domain antibody-SH3 fusions for efficient neutralization of HIV-1 Nef functions. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4856–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emert-Sedlak, L.A.; Moukha-Chafiq, O.; Shi, H.; Du, S.; Alvarado, J.J.; Pathak, V.; Tanner, S.G.; Hunter, R.N.; Nebane, M.; Chen, L.; et al. Inhibitors of HIV-1 Nef-Mediated Activation of the Myeloid Src-Family Kinase Hck Block HIV-1 Replication in Macrophages and Disrupt MHC-I Downregulation. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tice, C.M.; Emert-Sedlak, L.; Chen, L.; Li, W.F.; Carlsen, M.; Wrobel, J.E.; Reitz, A.B.; Smithgall, T.E. Tight-Binding Hydroxypyrazole HIV-1 Nef Inhibitors Suppress Viral Replication in Donor Mononuclear Cells and Reverse Nef-Mediated MHC-I Downregulation. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scuderi, G.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Basile, M.S. Multifaceted Role of Nef in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Histopathological Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090987
Scuderi G, Fagone P, Petralia MC, Nicoletti F, Basile MS. Multifaceted Role of Nef in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Histopathological Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(9):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090987
Chicago/Turabian StyleScuderi, Grazia, Paolo Fagone, Maria Cristina Petralia, Ferdinando Nicoletti, and Maria Sofia Basile. 2025. "Multifaceted Role of Nef in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Histopathological Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms" Brain Sciences 15, no. 9: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090987
APA StyleScuderi, G., Fagone, P., Petralia, M. C., Nicoletti, F., & Basile, M. S. (2025). Multifaceted Role of Nef in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Histopathological Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms. Brain Sciences, 15(9), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090987








