Abstract
Background/Objective: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) often represents the prodromal stage of neurodegenerative dementia. Identification of Alzheimer disease (AD) and other dementias in the MCI stage is essential for early intervention. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has gained interest as a non-invasive method to evaluate cortical excitability and neurotransmitter function. This systematic review aims to evaluate the diagnostic utility of TMS-derived indices, such as short-latency afferent inhibition (SAI), short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI), intracortical facilitation (ICF), and long-interval intracortical inhibition (LICI) in MCI populations. Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, 14 studies were selected, encompassing 476 MCI patients. Reported outcomes related to TMS measures (SAI, SICI, ICF, LICI) were reviewed across various MCI phenotypes. Results: Most studies report reduced SAI, a marker of cholinergic dysfunction, in amnestic MCI and MCI due to AD. Alterations in SICI and ICF, markers of GABAergic and glutamatergic dysfunction, were more variable, mainly observed in MCI of non-AD type. LICI showed no consistent changes. One study demonstrated increased clinicians’ diagnostic confidence when TMS data were incorporated. Conclusions: TMS measures hold promise as a non-invasive tool for early and differential diagnosis of MCI. Further standardized and longitudinal research is needed to confirm its clinical applicability.
Keywords:
mild cognitive impairment; MCI; short latency afferent inhibition; SAI; short-interval intracortical inhibition; SICI; long-interval intracortical inhibition; LICI; intracortical facilitation; ICF; transcranial magnetic stimulation; TMS; diagnostic markers; Alzheimer disease; frontotemporal dementia 1. Introduction
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition in which individuals demonstrate cognitive decline with minimal impact on instrumental activities of daily living [1].
MCI is considered a risk factor for developing dementia in the most common forms of neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) [2,3,4,5,6,7].
This condition can be classified as amnestic or non-amnestic, each affecting a single or multiple cognitive domains. Amnestic MCI (aMCI), which primarily impairs memory, is often a prodromal stage of AD. Non-amnestic MCI (na-MCI) involves other cognitive functions and may reflect different neuropathological processes [7,8].
Considering that people with MCI have an increased risk of developing dementia, early diagnosis is a crucial objective in clinical practice, as it allows differentiation between disorders and timely therapeutic intervention [9].
Biological markers such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis and amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) are used in clinical work-up to increase diagnostic accuracy and confirm or rule out AD [10]. One of the main challenges in this field is to identify alternative diagnostic markers that maintain the same level of reliability while being more cost-effective and non-invasive.
Recently, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has gained attention as a promising non-invasive tool to enhance diagnostic accuracy and simplify differential diagnosis [11,12,13,14]. TMS, when combined with electromyography (EMG) or electroencephalography (EEG), allows for assessment of corticospinal (via EMG) and cortico–cortical or thalamo–cortical excitability (via EEG) and even to indirectly evaluate neurotransmitters imbalance of acetylcholine, glutamate, or GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) pathways [13].
Several studies have investigated the therapeutic role of TMS, particularly in the context of repetitive TMS (rTMS) [15,16,17]. These studies have demonstrated the potential of rTMS as a non-pharmacological treatment for alleviating symptoms of various disorders, showing promising applications in both psychiatric and neurodegenerative fields.
Recent studies have also applied TMS to provide real-time information about neural function at the level of specific cortical circuits [14,18]. Among the most investigated TMS-derived measures are short-latency afferent inhibition (SAI), an indirect marker of cholinergic circuits, Short-interval Intracortical Inhibition (SICI) and intracortical facilitation (ICF), which partially depend on GABAergic and glutamatergic circuits, and long-interval intracortical inhibition (LICI), which relies on GABA-B circuits [12,13,14,19,20,21,22]. These paradigms are indirect proxies of system-wide neurotransmission, with implications for cortical network health.
These indices are obtained by stimulating primary motor cortex (M1), and recent TMS-EEG studies have shown that M1-based protocols can provide valuable insights into cortical function beyond motor control, particularly in the context of cognitive decline. In patients with MCI, and also with AD, stimulation of M1 reveals altered TMS-evoked potentials, reduced inter-trial coherence, and disrupted functional connectivity compared to those in cognitively healthy controls [23,24,25,26]. These abnormalities correlate with memory and executive deficits, suggesting that M1 physiology reflects broader cortical dysfunction associated with disease progression.
Ziemann and colleagues [27] reviewed the literature on the effects of drugs on TMS-EEG and TMS-EMG measures, identifying neurotransmitter receptor functions associated with the above-mentioned indices.
SAI induces an inhibition of motor evoked potential (MEP) amplitude reflecting the sensorimotor integration mechanisms [18], due to median nerve stimulation prior to TMS stimulation over the contralateral primary motor cortex M1 around the time point of the N20 component [28]. This index involves thalamo–cortical and cortico–cortical inhibitory circuits [13], and, although the cholinergic system has the most important role in this dynamic, various pharmacological studies show a mediation through GABAA-receptors [27,29].
GABAA receptors are also involved in SICI, especially at 2.5 ms [28], which represents short-lasting inhibitory postsynaptic potential in corticospinal neurons [13,21], resulting in reduced MEP amplitude [27,28,30].
Although the procedure used for ICF is very similar to the one used for SICI, ICF does not involve GABAA-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission. Instead, it reflects glutamatergic neurotransmission via N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, representing intracortical excitatory neurotransmission [31] and leading to increased MEP amplitude [27,28,30].
Finally, the GABAergic system is also involved in LICI. However, unlike SICI, LICI predominantly involves metabotropic GABAB-receptors, which mediate inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and lead to a subsequent reduction in MEP amplitude [13,27,32,33].
Several studies have highlighted the potential clinical utility of these TMS parameters in the evaluation of various neurodegenerative disorders [12,14,15,17]. Reduced SAI has been observed in AD since the earliest disease stages [14,34]. Moreover, Shafiee and colleagues [35] demonstrated that Nucleus basalis of Meynert degeneration begins even before clinical MCI becomes apparent, with atrophy detectable in the initial phases of cognitive decline, suggesting a possible link between cholinergic neuronal loss and the reduction of cortical inhibition present from the onset of the disease.
Both SICI and ICF have been found to be significantly reduced in FTD [12,34,36,37]. In this form of dementia, both GABAergic and glutamatergic systems are disrupted. Loss of GABAergic neurons and reduced GABA levels contribute to behavioral disinhibition and executive dysfunction, while NMDA receptor dysfunction impairs synaptic plasticity and cognitive processing [38]. Together, these deficits likely underlie key cognitive and behavioral symptoms observed in FTD, which can thus be assessed using TMS, specifically through measures of SICI and ICF.
In DLB, Benussi and colleagues [39] found impaired SICI, ICF and SAI, meanwhile Marra [40] and Di Lazzaro [41] and colleagues reported reduced SAI, likely reflecting impaired cholinergic function [39,40,41].
Building on this evidence from established neurodegenerative conditions, it becomes relevant to explore whether these neurophysiological alterations can be identified in the earliest stages of neurodegenerative dementia, i.e., in the MCI phase. This review is timely because a substantial body of data has begun to accumulate, and MCI represents the prodromal stage that should be detected as early as possible, including through neurophysiological markers. The specific gap addressed by this manuscript is the utility of TMS parameters in this population, and the key question it seeks to explore is whether TMS can serve as a practical screening tool for early and differential diagnosis. Accordingly, the aim of this systematic review is to evaluate existing literature regarding the use of TMS in MCI populations, with a specific focus on the diagnostic value of SAI, SICI, ICF, and LICI as auxiliary tools for screening and early differential diagnosis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategies and Selection of the Studies
This systematic review was conducted in compliance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) (Supplementary Materials Tables S1 and S2) [42]. The PRISMA flow diagram is shown in Figure 1.
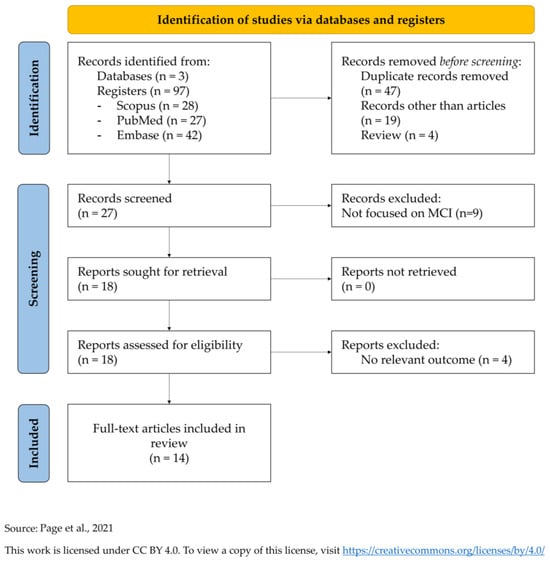
Figure 1.
PRISMA diagram for systematic literature reviews [42] (https://www.prisma-statement.org/prisma-2020-flow-diagram; accessed on date 31 July 2025).
The protocol for this review was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under registration number CRD420251112713 and is available in full on the program website (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/CRDWeb/HomePage.asp; accessed on 4 August 2025).
The electronic databases Medline (PubMed), Scopus, and Embase Web of Science Core Collection were searched for records without any time restrictions. The search strategy combined the following terms in the Title/Abstract fields: ((short-interval intracortical inhibition) OR (short-latency afferent inhibition) OR (intracortical facilitation) OR (long-interval intracortical inhibition) OR (paired pulse TMS)) AND (mild cognitive impairment).
Abstracts were reviewed and all relevant original research articles were examined in detail, including a review of the references in each publication to identify additional sources. Only English-language articles were selected (Figure 1).
2.2. Study Selection Criteria
Full-length articles were included if they met the following criteria: (i) original research; (ii) studies primarily focusing on at least one of the indices of interest (e.g., SAI, SICI, ICF, LICI); (iii) studies focusing on MCI or investigating MCI in the context of co-occurring neuro-degenerative disorders; and (iv) published before the 31 July 2025. Studies focusing on MCI but that did not investigate any of the TMS indices of interest were excluded.
Articles published in languages other than English, animal studies, reports of secondary data such as meta-analyses or reviews or letters were excluded.
2.3. Data Collection and Extraction
Two authors (E.D. and S.F.) independently removed duplicates, review articles, and conference abstracts. They then screened the remaining abstracts independently and selected articles that met the inclusion criteria. Disagreements regarding inclusion or exclusion were resolved by a third author (B.B.) through independent evaluation. Following this initial screening, the full texts of the selected articles were evenly distributed among two authors (E.D. and S.F.) for detailed review until the final corpus of literature included in this review was established. We extracted baseline information from the individual studies, including publication year, study design, participants’ characteristics and disease type. Moreover, outcome measures (SAI, SICI, ICF, LICI) were extracted.
2.4. Quality Assessment
All studies that met the inclusion criteria were assessed using the quality assessment ‘Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies’ (https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools; accessed on 1 August 2025) by two independent assessors (E.D. and S.F.) and disagreements were resolved through consensus or referral to a third reviewer (B.B.). Each record was classified according to the answers obtained in the quality assessment. All scores assigned to each study were agreed upon by consensus and are presented in Supplementary data (see Supplementary Materials Figure S1 for details).
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
Out of 97 initial records, 70 articles were rejected before the screening and other 13 articles after the screening. Finally, 14 full-text articles were included for this systematic review. All studies are summarized in Table 1 [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56].

Table 1.
Literature review on TMS measures in mild cognitive impairment.
Most of the studies compared the TMS indices between different groups. One study evaluated the effects of pharmacological treatment on the TMS measures [50], while one study [52] investigated the ability of TMS indices to increase diagnostic confidence (DC) and accuracy in discriminating different MCI subtypes. The fifteen included articles regarded 812 subjects, of whom 476 were MCI subjects, and were published between 2007 and 2024.
3.2. Short-Latency Afferent Inhibition (SAI)
Several studies have demonstrated that this type of inhibition is reduced in individuals with MCI, especially in MCI due to AD.
Mimura et al. [46] showed that SAI, using TMS-EEG, is characterized by lower amplitude of N100 evoked potential (TMS-evoked potential, TEP) in MCI group compared to healthy controls. The study just cited, in addition to reporting a significant reduction in SAI, also highlights that by employing a different methodology—namely TMS-EEG—it is possible to obtain the same parameter that is traditionally derived from TMS-EMG, thereby underscoring the complementary role of these two approaches.
Two studies [47,55] reported reduced inhibition in individuals with aMCI; in particular, Nardone and colleagues observed that the multiple domain subgroup showed the most pronounced reduction of SAI compared to healthy subjects and other MCI subtypes.
Padovani and colleagues [51] reported greater SAI reduction in MCI due to AD (MCI-AD) than MCI non-AD subtypes. Benussi et al. [43] also found impaired SAI in MCI due to DLB (MCI-DLB) subtype.
Other authors have focused on different populations, observing altered SAI in idiopathic REM behavioral Disorder (iRBD) [48], in Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients with REM behavioral disorder (PD-RBD) [49], and in PD with MCI (PD-MCI) [56].
Some of the aforementioned authors have also reported correlations between SAI alterations and performance on neuropsychological tests. Nardone et al. [47] described a correlation between SAI and scores on the Digit Span, Trail Making Test parts A and B, the Stroop Color–Word Test, and various measures of the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test in aMCI. Two other studies [48,56] reported a correlation between altered inhibition and cognitive test scores. Nardone et al. [48] found correlations with measures of episodic verbal memory and executive function in iRBD; while Yarnall et al. [56] reported a correlation with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores in PD patients.
Additionally, Padovani and colleagues [51] found a positive correlation between SAI and levels of CSF t-tau and p-tau in MCI-AD.
However, three studies have not found any significant differences or alterations of SAI measure between MCI and HC [44,53,54].
3.3. Short-Intracortical Inhibition (SICI)
Only three works have reported significant findings indicating alterations in SICI in subjects with MCI. Padovani et al. [51] found impaired SICI in MCI non-AD compared to MCI-AD, and a correlation between SICI and CSF t-tau levels in both groups. Benussi and colleagues [43] observed impaired SICI in both MCI-FTD and MCI-DLB subtypes. Kamble et al. [45] reported significant impairment in patients with extrapyramidal symptoms, that increased progressively in PD patients to PD-MCI and PD with dementia (PDD) patients.
Five studies did not find any significant alterations in the SICI index [44,47,48,49,55] in MCI groups. Another study [50] showed a trend toward significance at a 2 ms interstimulus interval (ISI) between MCI-AD and HC.
3.4. Intracortical Facilitation (ICF)
Most of the studies [47,48,49,55] did not find any significant results concerning ICF.
However, Olazaran et al. [50] observed a trend of less facilitation in MCI-AD compared to HC.
Benussi and colleagues [43] found impaired ICF in both MCI-FTD and MCI-DLB subtypes, and Kamble [45] reported reduced facilitation as the disease progressed from PD through PD-MCI to PDD.
3.5. Long-Intracortical Inhibition (LICI)
Only two studies addressing LICI was identified in the literature search [43,50]; this index was not found to be impaired in any of the patient groups considered in Benussi or in Olazaran.
4. Discussion
Although MCI is a condition with a high incidence rate [7] and a risk factor for the development of dementia over the long term, there is a need of investigating early neurophysiological diagnostic markers.
TMS has emerged as a practical, safe, and efficient tool, not only in the research/scientific field, but also in the diagnostic domain, contributing to a better understanding of pathophysiology and providing real-time information [14].
While CSF and amyloid PET demonstrate high accuracy (85–95%) in distinguishing MCI-AD from MCI non-AD, TMS achieves comparable accuracy (91.3%) while offering a more non-invasive and cost-effective alternative [51].
While many studies have investigated the use of TMS in neurodegenerative diseases [14,19,20,34], studies in individuals with MCI remain limited and show heterogeneous results. Some studies have not found significant differences between MCI subjects and healthy controls, whereas others have reported neurophysiological alterations. However, comparing findings across studies is challenging due to the consideration of a considerable methodological variability which may have led to different results within the same population: different clinical populations have been included with variable etiological characterization, acquisition procedures vary, some studies distinguish between amnestic and non-amnestic MCI, while others treat MCI as a single entity. Additionally, in some cases, cognitive impairment has been investigated in the context of other neurodegenerative conditions, such as PD, further complicating the interpretation of the results.
Since MCI often progress to AD, most of the studies identified through the literature review on TMS indices have focused on SAI, with the specific purpose of investigating cholinergic impairment [27], not only through the use of TMS-EMG, but also by demonstrating that it is possible to employ a high–temporal resolution technique such as TMS-EEG to investigate the same phenomenon [46], thereby opening the possibility for future applications of this methodology in the study of other neurophysiological markers and cortical plasticity, especially in MCI.
Sakuma et al. [54] found impaired SAI in AD population, but not in individuals with aMCI or HC. However, a limit of this study, acknowledged by the authors themselves, was the absence of follow-up measures necessary to capture the critical point at which SAI becomes abnormal. On the contrary different authors found that patients with aMCI have greater SAI reduction compared to the other MCI subtypes [47,55]. This supports the hypothesis that SAI is an early marker in individuals at higher risk of developing AD. However, cholinergic dysfunction is a hallmark of Lewy bodies pathology. In this view, other studies reviewed here suggest that reduced SAI may also be associated Lewy bodies-related disorders, such as MCI with iRBD, MCI-DLB, or PDD [48,49,56]. Altogether, these findings suggest that this index could be helpful not only in the early diagnosis of AD, but also in patients with different pathologies characterized by cholinergic dysfunction. Accordingly, it has been demonstrated that treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, specifically donepezil, was able to restore this index [47].
Additionally, SICI and ICF were investigated by the majority of the articles considered. However, the results were less consistent compared to those observed for SAI. However, alterations in SICI and ICF were primarily observed in MCI non-AD [51] while individuals with MCI-AD showed more impaired SAI. It would have been interesting to know the etiological diagnoses within the MCI non-AD group, as this would allowed for a more precise characterization of the typical changes in these indices.
Other studies did not find any alterations in SICI and ICF in the MCI group [55], suggesting that these two indices may not be optimal markers for the diagnosis of early-stage AD, but could instead potentially be more relevant for other MCI phenotypes. Supporting this hypothesis, Benussi and colleagues [43] took into account a cohort of 106 MCI subjects, discriminated by their subtype, and found that impairments in both SICI and ICF allowed to distinguish MCI-FTD and MCI-DLB from other phenotypes.
Kamble et al. [45] analyzed cognitive impairment in PD patients and, contrary to previous studies [57,58], found significant impairments in SICI and ICF both in PD-MCI and in PDD. These results suggest that, in addition to cholinergic deficiency, progression from PD without cognitive decline through PD-MCI to PDD may involve enhanced GABAergic and reduced glutamatergic neurotransmission. Importantly, this highlights that TMS measures can differentiate Parkinsonian syndromes with cognitive impairment (PD-MCI, PDD) from those without dementia, reflecting distinct neurophysiological profiles across the spectrum of the disease.
The results reported above prompted a study where the authors analyzed TMS parameters recorded from 107 individuals with different MCI subtypes to evaluate whether these indices could enhance the clinicians’ diagnostic confidence of the clinical work-up alone. Indeed, clinicians’ diagnostic confidence significantly increased with the disclosure of TMS measures, highlighting the added value of TMS in differentiating MCI subtypes and in complementing current biomarker workflow. In this sense, TMS could serve not only as a supportive tool alongside established biomarkers, but also as a cost-effective and accessible screening method, potentially enabling earlier stratification and intervention in at-risk individuals.
Based on the considerations regarding the parameters examined and the related studies, it is also important to highlight the potential use of TMS through additional stimulation protocols, such as theta-burst stimulation (TBS) and paired associative stimulation (PAS). These protocols allow the investigation of other aspects of cortical activity with potential future clinical relevance in the field of dementia, including long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). Some studies [59,60] have demonstrated that the application of TMS can be extended beyond paired-pulse protocols, providing insights into cortical plasticity processes, which are often impaired in individuals with dementia. Expanding knowledge on these two protocols, particularly in the context of MCI would be a valuable objective, as they may contribute to a deeper understanding of the disorder and offer potential diagnostic applications.
5. Conclusions
This systematic review has several limitations. Due to the scarcity of studies in the existing literature, it would have been preferable not to restrict the search to only Title/Abstract fields, but to adopt a broader strategy. Nevertheless, this more focused approach enabled a highly specific selection and facilitated the identification of the most relevant studies. To mitigate the risk of missing relevant studies, we conducted the search across three databases.
A key finding of this review is the need for longitudinal studies and extended follow-up in the context of MCI, which, by definition, may progress into various neurodegenerative disorders.
A crucial step forward for TMS research and its potential clinical application is the standardization of experimental procedures to improve comparability across studies and ensure methodological rigor. In cases where full standardization is not feasible, reliable methods to normalize neurophysiological data should be implemented. Additionally, to enable TMS to serve effectively as a screening tool, it is necessary to establish standardized protocols, build normative datasets, and ensure that specialized personnel receive proper training. This highlights the practical steps needed to move from experimental use to clinical implementation. In conclusions, substantial work is still needed to integrate SAI, SICI and ICF indexes, and TMS in general, into routine clinical practice. Given the high conversion rate from MCI to AD and other neurodegenerative dementias, TMS could offer a practical and accessible screening tool to support timely decision-making and diagnostic algorithms. This is particularly important given the short time window often observed between MCI and dementia conversion [2,7]. EEG-informed TMS could also represent a valuable method to enhance the assessment of cortical function in these populations, as it allows real-time monitoring of neural activity, improves the signal-to-noise ratio of TMS-evoked potentials, and enables closed-loop stimulation tailored to individual cortical dynamics [61].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/brainsci15090969/s1, Figure S1: Risk-of-bias plot of included studies (adapted from [62]); Table S1: PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts Checklist [42]; Table S2: PRISMA 2020 Checklist [42].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M., M.C., and B.B.; methodology, E.D., S.F., E.C., R.M., M.C. and B.B.; validation, R.M., M.C. and B.B.; formal analysis, E.D. and S.F.; investigation, E.D., S.F., E.C. and B.B.; data curation, E.D. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, E.D. and S.F.; writing—review and editing, R.M., M.C. and B.B., supervision, R.M., M.C. and B.B., and project administration, B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union—Next Generation EU—PNRR M6C2—Investimento 2.1 Valorizzazione e potenziamento della ricerca biomedica del SSN (PNRR-MCNT2-2023-12377069; CUP=C83C24000200007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| aMCI | amnestic mild cognitive impairment |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DC | diagnostic confidence |
| DLB | dementia with Lewy bodies |
| EEG | electromyography |
| EMG | electroencephalography |
| FTD | frontotemporal dementia |
| GABA | gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| HC | healthy control |
| ICF | intracortical facilitation |
| iRBD | idiopathic REM behavioral disorder |
| ISI | interstimulus interval |
| LICI | long interval intracortical inhibition |
| LTD | long-term depression |
| LTP | long-term potentiation |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| MCI-AD | mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease |
| MCI-DLB | mild cognitive impairment due to dementia with Lewy bodies |
| MCI-FTD | mild cognitive impairment due to frontotemporal dementia |
| MCI non-AD | mild cognitive impairment not due to Alzheimer’s disease |
| MCI-other | mild cognitive impairment due to other than AD/FTD/DLB |
| MD | multiple domain |
| na-MCI | non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment |
| PAS | paired associative stimulation |
| PD | Parkinson‘s disease |
| PD-MCI | Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment |
| PD-RBD | Parkinson’s disease with REM behavioral disorder |
| PDD | Parkinson‘s disease dementia |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RBD | REM behavioral disorder |
| rTMS | repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| SAI | short-latency afferent inhibition |
| SD | single domain |
| SICI | short-interval intracortical inhibition |
| TBS | theta-burst stimulation |
| TEP | transcranial magnetic stimulation-evoked potential |
| TMS | transcranial magnetic stimulation |
References
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA; London, UK, 2013; 947p, ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mendonça, A.; Ribeiro, F.; Guerreiro, M.; Garcia, C. Frontotemporal Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2004, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Current View. J. Neural Transm. 2025, 132, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Goldman, J.G.; Tröster, A.I.; Schmand, B.A.; Weintraub, D.; Petersen, R.C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Adler, C.H.; Marder, K.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force Guidelines. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Fourth Consensus Report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Caracciolo, B.; Brayne, C.; Gauthier, S.; Jelic, V.; Fratiglioni, L. Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Concept in Evolution. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 275, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Negash, S. Mild Cognitive Impairment: An Overview. CNS Spectr. 2008, 13, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Miraglia, F.; Vecchio, F. Early Dementia Diagnosis, MCI-to-dementia Risk Prediction, and the Role of Machine Learning Methods for Feature Extraction from Integrated Biomarkers, in Particular for EEG Signal Analysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Festari, C.; Massa, F.; Cotta Ramusino, M.; Orini, S.; Aarsland, D.; Agosta, F.; Babiloni, C.; Borroni, B.; Cappa, S.F.; et al. European Intersocietal Recommendations for the Biomarker-Based Diagnosis of Neurocognitive Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antczak, J.; Rusin, G.; Słowik, A. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool in Various Types of Dementia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benussi, A.; Grassi, M.; Palluzzi, F.; Koch, G.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Nardone, R.; Cantoni, V.; Dell’Era, V.; Premi, E.; Martorana, A.; et al. Classification Accuracy of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Dementias. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, Y.; Nishida, H.; Nakajima, S.; Tsugawa, S.; Morita, S.; Yoshida, K.; Tarumi, R.; Ogyu, K.; Wada, M.; Kurose, S.; et al. Neurophysiological Biomarkers Using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 121, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucic, S.; Chen, K.-H.S.; Kiernan, M.C.; Hallett, M.; Benninger, D.H.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Rossini, P.M.; Benussi, A.; Berardelli, A.; Currà, A.; et al. Clinical Diagnostic Utility of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neurological Disorders. Updated Report of an IFCN Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 150, 131–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoglu, L.; Toplutas, E.; Saricaoglu, M.; Velioglu, H.A.; Yildiz, S.; Yulug, B. Therapeutic Role of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease: Electroencephalography Microstate Correlates. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 798558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuteboom, D.; Zantvoord, J.B.; Goya-Maldonado, R.; Wilkening, J.; Dols, A.; Van Exel, E.; Lok, A.; De Haan, L.; Scheepstra, K.W.F. Accelerated Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 327, 115429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.; Evangelisti, S.; Siniscalco, A.; Lodi, R.; Tonon, C.; Mitolo, M. Non-Pharmacological Treatments in Lewy Body Disease: A Systematic Review. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2023, 52, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Cutrona, C.; Leodori, G.; Malimpensa, L.; D’antonio, F.; Conte, A.; Belvisi, D. Exploring Easily Accessible Neurophysiological Biomarkers for Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease Progression: A Systematic Review. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Bella, R.; Benussi, A.; Bologna, M.; Borroni, B.; Capone, F.; Chen, K.-H.S.; Chen, R.; Chistyakov, A.V.; Classen, J.; et al. Diagnostic Contribution and Therapeutic Perspectives of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Dementia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2568–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benussi, A.; Alberici, A.; Ferrari, C.; Cantoni, V.; Dell’Era, V.; Turrone, R.; Cotelli, M.S.; Binetti, G.; Paghera, B.; Koch, G.; et al. The Impact of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Diagnostic Confidence in Patients with Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.; Sundman, M.; Ton That, V.; Green, J.; Trapani, C. Cortical Excitability and Plasticity in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Tezzon, F.; Höller, Y.; Golaszewski, S.; Trinka, E.; Brigo, F. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)/Repetitive TMS in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarotto, S.; Määttä, S.; Herukka, S.-K.; Pigorini, A.; Napolitani, M.; Gosseries, O.; Niskanen, E.; Könönen, M.; Mervaala, E.; Rosanova, M.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation-Evoked EEG/Cortical Potentials in Physiological and Pathological Aging. NeuroReport 2011, 22, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, F.; Vecchio, F.; Vollero, L.; Guerra, A.; Petrichella, S.; Ponzo, D.; Määtta, S.; Mervaala, E.; Könönen, M.; Ursini, F.; et al. Sensorimotor Cortex Excitability and Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease: A TMS-EEG Co-Registration Study: Sensorimotor Cortex Excitability and Connectivity in AD. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 2083–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagattini, C.; Mutanen, T.P.; Fracassi, C.; Manenti, R.; Cotelli, M.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Miniussi, C.; Bortoletto, M. Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease Severity by Means of TMS–EEG Coregistration. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 80, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, E.P.; Pellicciari, M.C.; Bonnì, S.; Borghi, I.; Maiella, M.; Assogna, M.; Minei, M.; Motta, C.; D’Acunto, A.; Porrazzini, F.; et al. Decreased Frontal Gamma Activity in Alzheimer Disease Patients. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemann, U.; Reis, J.; Schwenkreis, P.; Rosanova, M.; Strafella, A.; Badawy, R.; Müller-Dahlhaus, F. TMS and Drugs Revisited 2014. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Ferreri, F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; George, M.S.; et al. Non-Invasive Electrical and Magnetic Stimulation of the Brain, Spinal Cord, Roots and Peripheral Nerves: Basic Principles and Procedures for Routine Clinical and Research Application. An Updated Report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, V.T.; Cserép, C.; Schlingloff, D.; Pósfai, B.; Szőnyi, A.; Sos, K.E.; Környei, Z.; Dénes, Á.; Gulyás, A.I.; Freund, T.F.; et al. Co-Transmission of Acetylcholine and GABA Regulates Hippocampal States. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Rothwell, J.C.; Ridding, M.C. Interaction between Intracortical Inhibition and Facilitation in Human Motor Cortex. J. Physiol. 1996, 496, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Byblow, W.D.; Berardelli, A.; Siebner, H.R.; Classen, J.; Cohen, L.G.; Rothwell, J.C. Consensus: Motor Cortex Plasticity Protocols. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.N.; Orekhov, Y.; Ziemann, U. The Role of GABAB Receptors in Intracortical Inhibition in the Human Motor Cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucic, S.; Howells, J.; Trevillion, L.; Kiernan, M.C. Assessment of Cortical Excitability Using Threshold Tracking Techniques. Muscle Nerve 2006, 33, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benussi, A.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Dell’Era, V.; Cosseddu, M.; Alberici, A.; Caratozzolo, S.; Cotelli, M.S.; Micheli, A.; Rozzini, L.; Depari, A.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Distinguishes Alzheimer Disease from Frontotemporal Dementia. Neurology 2017, 89, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, N.; Fonov, V.; Dadar, M.; Spreng, R.N.; Collins, D.L. Degeneration in Nucleus Basalis of Meynert Signals Earliest Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Neurobiol. Aging 2024, 139, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benussi, A.; Dell’Era, V.; Cantoni, V.; Cotelli, M.S.; Cosseddu, M.; Spallazzi, M.; Micheli, A.; Turrone, R.; Alberici, A.; Borroni, B. TMS for Staging and Predicting Functional Decline in Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benussi, A.; Dell’Era, V.; Cosseddu, M.; Cantoni, V.; Cotelli, M.S.; Cotelli, M.; Manenti, R.; Benussi, L.; Brattini, C.; Alberici, A.; et al. Transcranial Stimulation in Frontotemporal Dementia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Sham-controlled Trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murley, A.G.; Rowe, J.B. Neurotransmitter Deficits from Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Brain 2018, 141, 1263–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benussi, A.; Pilotto, A.; Cantoni, V.; Ferrari, E.; Borroni, B.; Padovani, A. Neurophysiological Correlates of Motor and Cognitive Dysfunction in Prodromal and Overt Dementia with Lewy Bodies. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, C.; Quaranta, D.; Profice, P.; Pilato, F.; Capone, F.; Iodice, F.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Gainotti, G. Central Cholinergic Dysfunction Measured “in Vivo” Correlates with Different Behavioral Disorders in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Body. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Pilato, F.; Dileone, M.; Saturno, E.; Profice, P.; Marra, C.; Daniele, A.; Ranieri, F.; Quaranta, D.; Gainotti, G.; et al. Functional Evaluation of Cerebral Cortex in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benussi, A.; Grassi, M.; Palluzzi, F.; Cantoni, V.; Cotelli, M.S.; Premi, E.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Pellicciari, M.C.; Ranieri, F.; Musumeci, G.; et al. Classification Accuracy of TMS for the Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, D.; Guerra, A.; Paparella, G.; Cioffi, E.; Di Vita, A.; Trebbastoni, A.; Berardelli, A.; Bologna, M. Motor Dysfunction in Mild Cognitive Impairment as Tested by Kinematic Analysis and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, N.; Bhattacharya, A.; Hegde, S.; Vidya, N.; Gothwal, M.; Yadav, R.; Pal, P.K. Cortical Excitability Changes as a Marker of Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 422, 113733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, Y.; Tobari, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Takano, M.; Wada, M.; Honda, S.; Bun, S.; Tabuchi, H.; Ito, D.; Matsui, M.; et al. Decreased Short-Latency Afferent Inhibition in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A TMS-EEG Study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 132, 110967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Bergmann, J.; Christova, M.; Caleri, F.; Tezzon, F.; Ladurner, G.; Trinka, E.; Golaszewski, S. Short Latency Afferent Inhibition Differs among the Subtypes of Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Bergmann, J.; Kunz, A.; Christova, M.; Brigo, F.; Tezzon, F.; Trinka, E.; Golaszewski, S. Cortical Afferent Inhibition Is Reduced in Patients with Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Cognitive Impairment: A TMS Study. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Bergmann, J.; Brigo, F.; Christova, M.; Kunz, A.; Seidl, M.; Tezzon, F.; Trinka, E.; Golaszewski, S. Functional Evaluation of Central Cholinergic Circuits in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: A TMS Study. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazarán, J.; Prieto, J.; Cruz, I.; Esteban, A. Cortical Excitability in Very Mild Alzheimer’s Disease: A Long-Term Follow-up Study. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, A.; Benussi, A.; Cantoni, V.; Dell’Era, V.; Cotelli, M.S.; Caratozzolo, S.; Turrone, R.; Rozzini, L.; Alberici, A.; Altomare, D.; et al. Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer’s Disease with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 65, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, A.; Benussi, A.; Cotelli, M.S.; Ferrari, C.; Cantoni, V.; Dell’Era, V.; Turrone, R.; Paghera, B.; Borroni, B. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Amyloid Markers in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Impact on Diagnostic Confidence and Diagnostic Accuracy. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.; Mayer, I.; Kammer, T.; Minkova, L.; Lahr, J.; Klöppel, S.; Grothe, M.J.; Orth, M. The Relationship between Cholinergic System Brain Structure and Function in Healthy Adults and Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, K.; Murakami, T.; Nakashima, K. Short Latency Afferent Inhibition Is Not Impaired in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Hanajima, R.; Hamada, M.; Shirota, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Terao, Y.; Ohminami, S.; Yamakawa, Y.; Shimada, H.; Tsuji, S.; et al. Reduced Interhemispheric Inhibition in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Exp. Brain Res. 2012, 218, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnall, A.J.; Rochester, L.; Baker, M.R.; David, R.; Khoo, T.K.; Duncan, G.W.; Galna, B.; Burn, D.J. Short Latency Afferent Inhibition: A Biomarker for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease? Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, C.; Dileone, M.; Pagge, C.; Catanzaro, V.; Mata-Marín, D.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; Monje, M.H.G.; Sánchez-Ferro, Á.; Fernández-Rodríguez, B.; Gasca-Salas, C.; et al. Cortical Disinhibition in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2020, 143, 3408–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Bahl, N.; Gunraj, C.A.; Mazzella, F.; Chen, R. Increased Motor Cortical Facilitation and Decreased Inhibition in Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Ponzo, V.; Motta, C.; Bonnì, S.; Picazio, S.; Caltagirone, C.; Bozzali, M.; Martorana, A.; Koch, G. Impaired Spike Timing Dependent Cortico-Cortical Plasticity in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Motta, C.; Bonnì, S.; Mercuri, N.B.; Caltagirone, C.; Martorana, A.; Koch, G. LTP-like Cortical Plasticity Is Associated with Verbal Memory Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varone, G.; Biabani, M.; Tremblay, S.; Brown, J.C.; Kallioniemi, E.; Rogasch, N.C. The Golden Age of Online Readout: EEG-Informed TMS from Manual Probing to Closed-Loop Neuromodulation. PsyArXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Syn. Meth. 2020, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).