Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Hellenic Longitudinal Investigation of Aging and Diet (HELIAD): A population-based study that provided prevalence rates for MCI and dementia, stratified by sex and age categories (65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85+) [4];
- Hellenic Statistical Authority (ELSTAT): Census data from 1991, 2001, 2011, and 2023 (delayed from 2012 due to COVID-19 delays), detailing the population distribution by age, sex, and region [1].
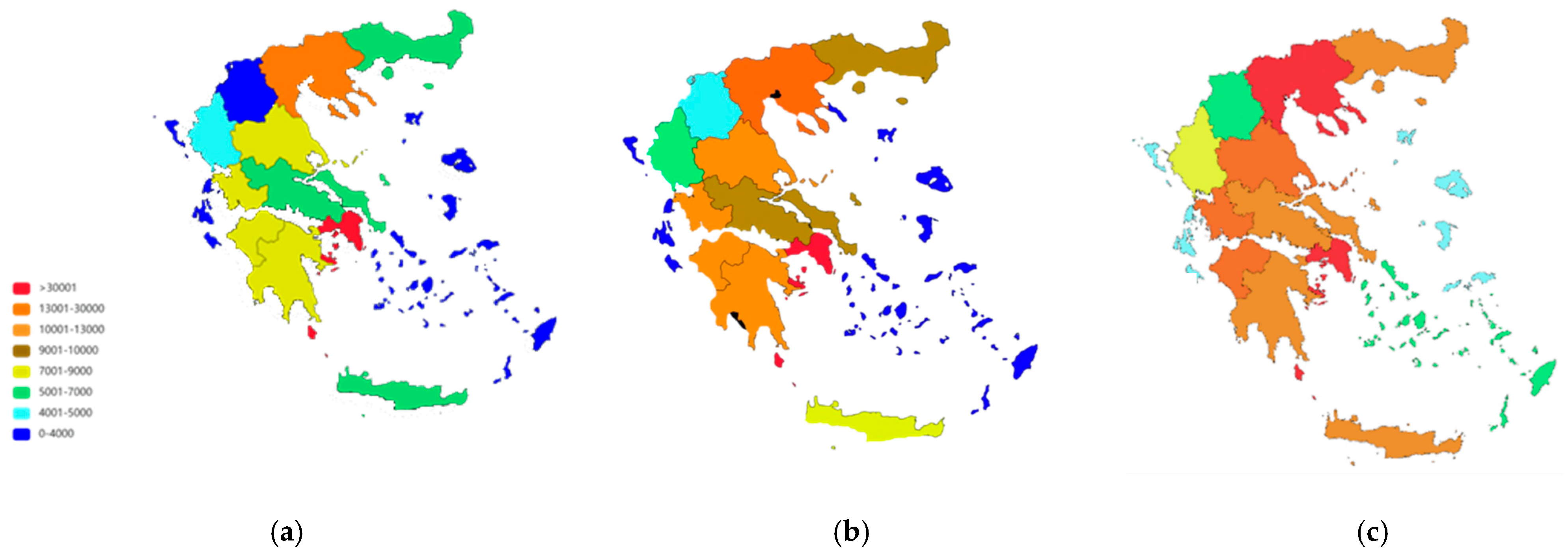
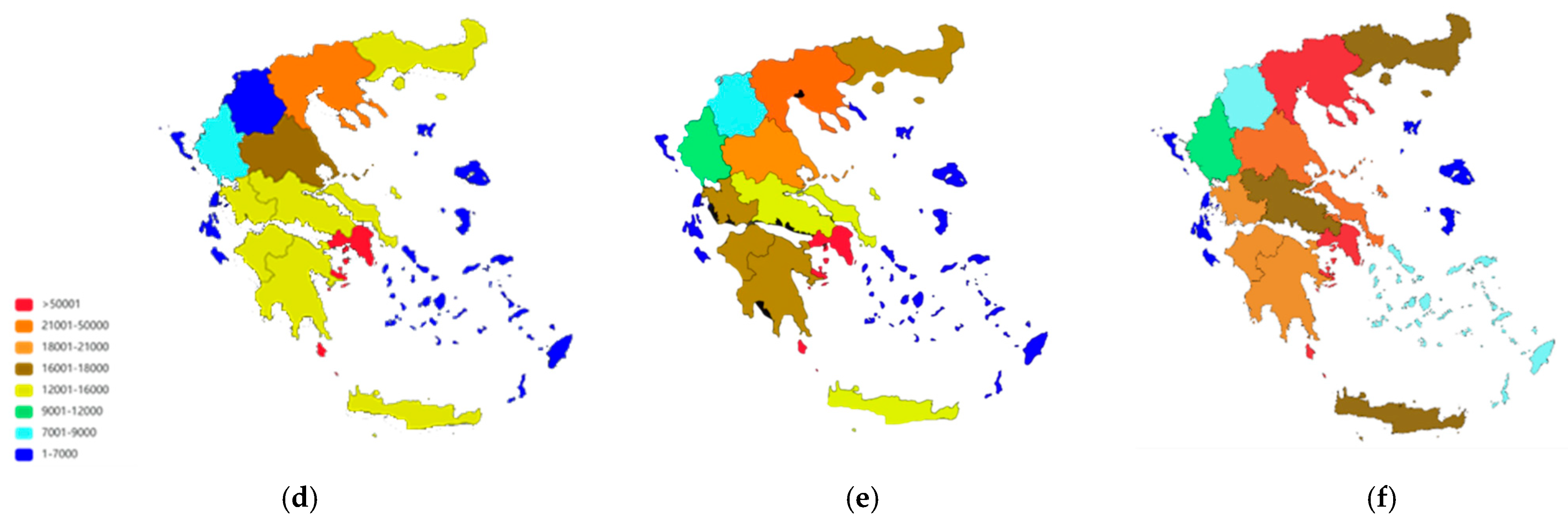
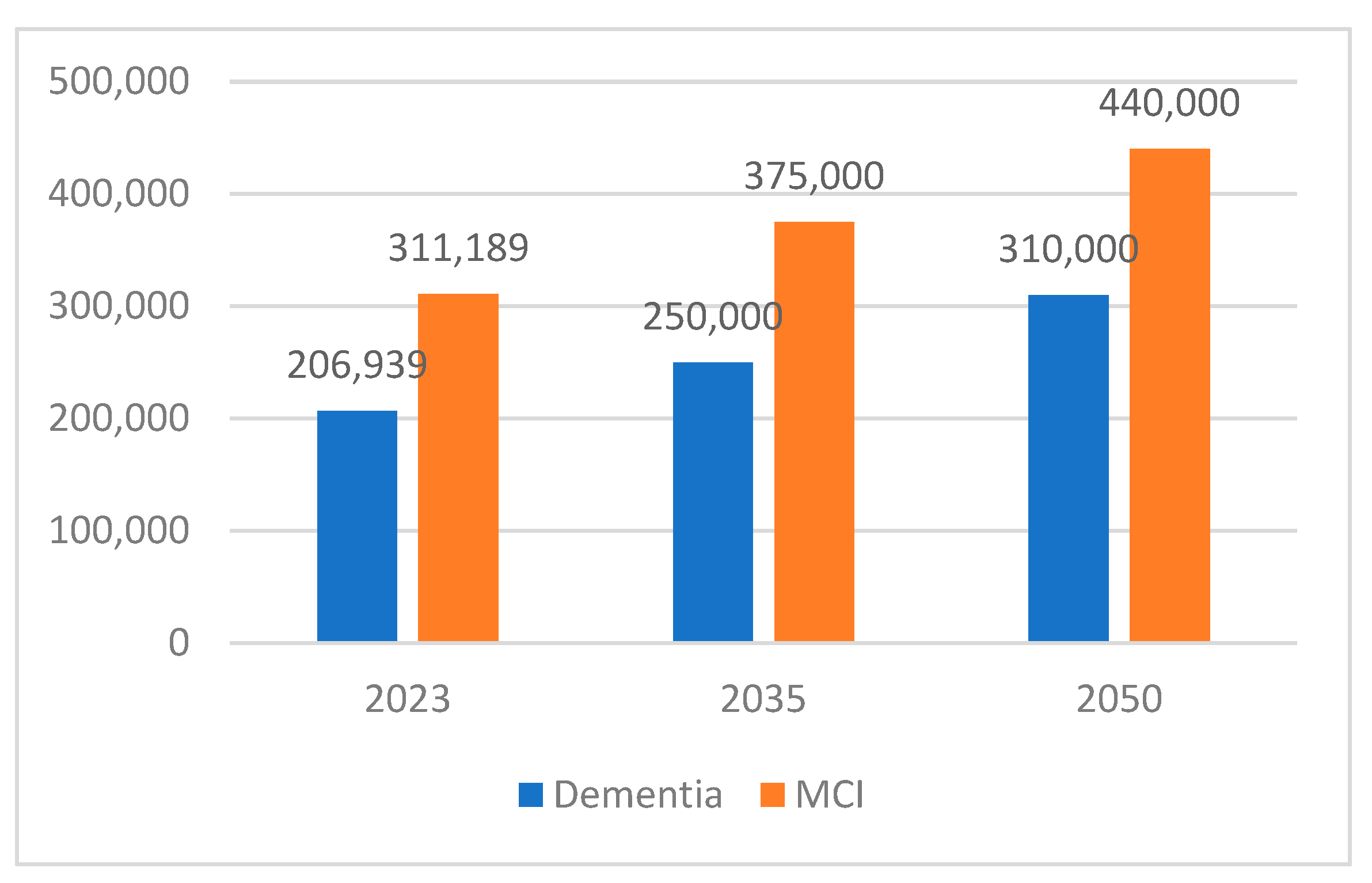
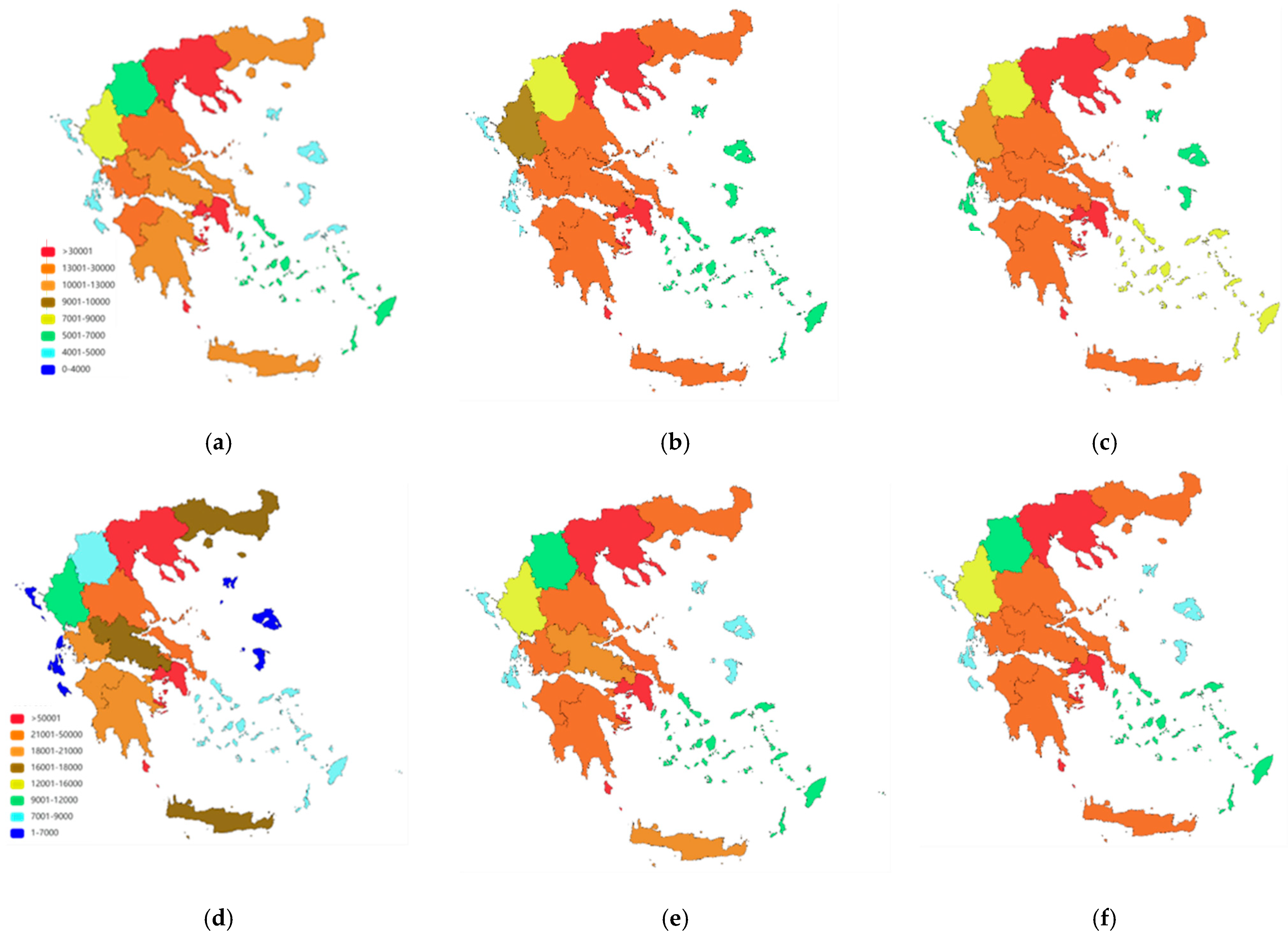
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ELSTAT. Population and Housing Census’; Hellenic Statistical Authority; ELSTAT: Piraeus, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Dementia Statistics; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer Europe. Dementia in Europe Yearbook; Alzheimer Europe: Senningerberg, Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, G.S.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Yannakoulia, M.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Sakka, P.; Ntanasi, E.; Stefanis, L.; Scarmeas, N. Prevalence of Mild Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly Population in Greece: Results from the HELIAD Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2020, 34, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raybould, R.; Sims, R. Searching the Dark Genome for Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Variants. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small and Medium Enterprises Institute. Demographic Developments and Challenges; Researches & Studies; Small and Medium Enterprises Institute: Athens, Greece, 2021; ISBN 978-618-5025-78-6. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Ott, A.; Breteler, M.M.B.; van Harskamp, F.; Claus, J.J.; van der Cammen, T.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hofman, A. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia: Association with education. The Rotterdam study. BMJ 1995, 310, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Lotfi, F.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Heidarian, P.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Fazeli, J.; Najafi, H.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in geriatric population with emphasis on influential factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, B.S.; Johnston, D.; Leoutsakos, J.; Reuland, M.; Kelly, J.; Amjad, H.; Davis, K.; Willink, A.; Sloan, D.; Lyketsos, C.; et al. Unmet needs in community-living persons with dementia are common, often non-medical and related to patient and caregiver characteristics. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2019, 31, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.; Rosenheck, R.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Schneider, L.S. Caregiver burden in Alzheimer disease: Cross-sectional and longitudinal patient correlates. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2010, 18, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huque, H.; Eramudugolla, R.; Chidiac, B.; Ee, N.; Ehrenfeld, L.; Matthews, F.E.; Peters, R.; Anstey, K.J. Could Country-Level Factors Explain Sex Differences in Dementia Incidence and Prevalence? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2023, 91, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, A.; Norton, N.; Fast, T.; Frölich, L.; Georges, J.; Holzapfel, D.; Kirabali, T.; Krolak-Salmon, P.; Rossini, P.M.; Ferretti, M.T.; et al. Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD Dementia Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukadam, N.; Wolters, F.J.; Walsh, S.; Wallace, L.; Brayne, C.; Matthews, F.E.; Sacuiu, S.; Skoog, I.; Seshadri, S.; Beiser, A.; et al. Changes in prevalence and incidence of dementia and risk factors for dementia: An analysis from cohort studies. Lancet Public Health 2024, 9, e443–e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Ye, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Chen, G.; Hu, H. Predictive models of Alzheimer’s disease dementia risk in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and critical appraisal. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Manolopoulos, A.; Ferrucci, L.; Fakhoury, M.; Picone, P.; Baglio, F.; Gareri, P.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Tzavellas, E. Critical assessment of anti-amyloid-β monoclonal antibodies effects in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis highlighting target engagement and clinical meaningfulness. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cao, M.; Chen, N.; Zeng, Q.; Lai, M.K.P.; Fan, D.; Sethi, G.; Cao, Y. Fluid-based biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 108, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.B.; Li, Y.Z.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.T.; Wu, B.S.; Tan, L.; Dong, Q.; Pan, A.; et al. Socioeconomic status, lifestyle and risk of incident dementia: A prospective cohort study of 276730 participants. Geroscience 2024, 46, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Vergallo, A.; Iwatsubo, T.; Cho, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Wang, H.; Kurzman, H.R.; Chen, C. Evaluation of major national dementia policies and health-care system preparedness for early medical action and implementation. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age | Prevalence of MCI | Prevalence of Dementia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | ♂ | ♀ | Total | ♂ | ♀ | Total |
| 65–69 | 12.00% | 8.40% | 10.10% | 3.00% | 0.80% | 1.90% |
| 70–74 | 10.20% | 10.20% | 10.20% | 3.50% | 1.80% | 2.40% |
| 75–79 | 16.70% | 16.70% | 16.70% | 6.80% | 6.80% | 6.90% |
| 80–84 | 12.10% | 18.30% | 15.70% | 11.20% | 16.30% | 15.40% |
| 85+ | 25.70% | 7.90% | 14.50% | 11.40% | 31.60% | 21.40% |
| ≥65 | 13.90% | 12.40% | 13.00% | 6.10% | 8.90% | 7.60% |
| 1991 | 2001 | 2011 | 2023 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | T | M | F | T | M | F | T | M | F | T | |
| 55–59 | 322,468 | 332,641 | 655,109 | 271,095 | 289,120 | 560,215 | 321,466 | 338,902 | 660,368 | 461,932 | 310,043 | 771,975 |
| 60–64 | 308,403 | 336,362 | 644,765 | 298,181 | 341,893 | 640,074 | 301,589 | 324,180 | 625,769 | 441,046 | 303,671 | 744,717 |
| 65–69 | 210,101 | 243,705 | 453,806 | 291,600 | 331,645 | 623,245 | 241,832 | 266,444 | 508,276 | 395,478 | 270,848 | 666,326 |
| 70–74 | 150,599 | 193,396 | 343,995 | 247,136 | 297,882 | 545,018 | 246,264 | 295,901 | 542,165 | 349,537 | 248,378 | 597,915 |
| 75+ | 257,197 | 349,245 | 606,442 | 278,765 | 380,205 | 658,970 | 441,729 | 616,682 | 1,058,411 | 722,215 | 580,110 | 1,302,325 |
| Total Population | 65+ | 85+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Census 1951 | 7629.7 | 522.4 | 30.8 | |
| 1/2015 (ELSTAT) | 10,858.0 | 2269.0 | 303.2 | |
| 1/1/2020 | 10,718.6 | 2386.2 | 377.0 | |
| Baseline projections | 1/1/2035 | 10,104.6 | 2853.0 | 483.5 |
| 1/1/2050 | 9503.1 | 3208.8 | 667.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Exarchos, T.P.; Skolariki, K.; Mahairaki, V.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Vlamos, P.; Scarmeas, N.; Dardiotis, E.; on behalf of the Hellenic Initiative Against Alzheimer’s Disease (HIAAD). Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060661
Exarchos TP, Skolariki K, Mahairaki V, Lyketsos CG, Vlamos P, Scarmeas N, Dardiotis E, on behalf of the Hellenic Initiative Against Alzheimer’s Disease (HIAAD). Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060661
Chicago/Turabian StyleExarchos, Themis P., Konstantina Skolariki, Vasiliki Mahairaki, Constantine G. Lyketsos, Panagiotis Vlamos, Nikolaos Scarmeas, Efthimios Dardiotis, and on behalf of the Hellenic Initiative Against Alzheimer’s Disease (HIAAD). 2025. "Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060661
APA StyleExarchos, T. P., Skolariki, K., Mahairaki, V., Lyketsos, C. G., Vlamos, P., Scarmeas, N., Dardiotis, E., & on behalf of the Hellenic Initiative Against Alzheimer’s Disease (HIAAD). (2025). Geographic Distribution and Future Projections of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Greece: Analysis from 1991 to 2050. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060661









