New Neurons in the Postnatal Olfactory System: Functions in the Healthy and Regenerating Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
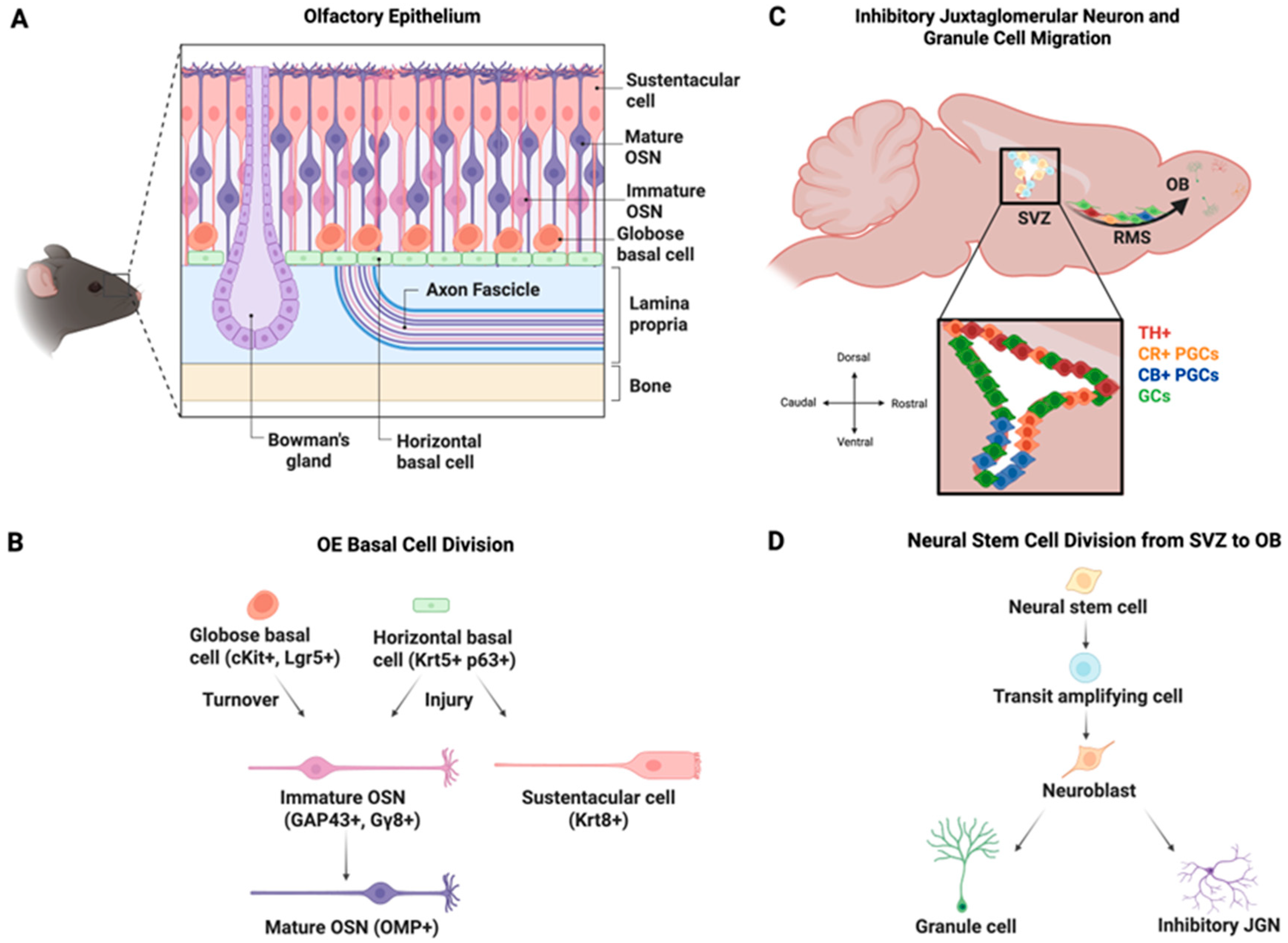
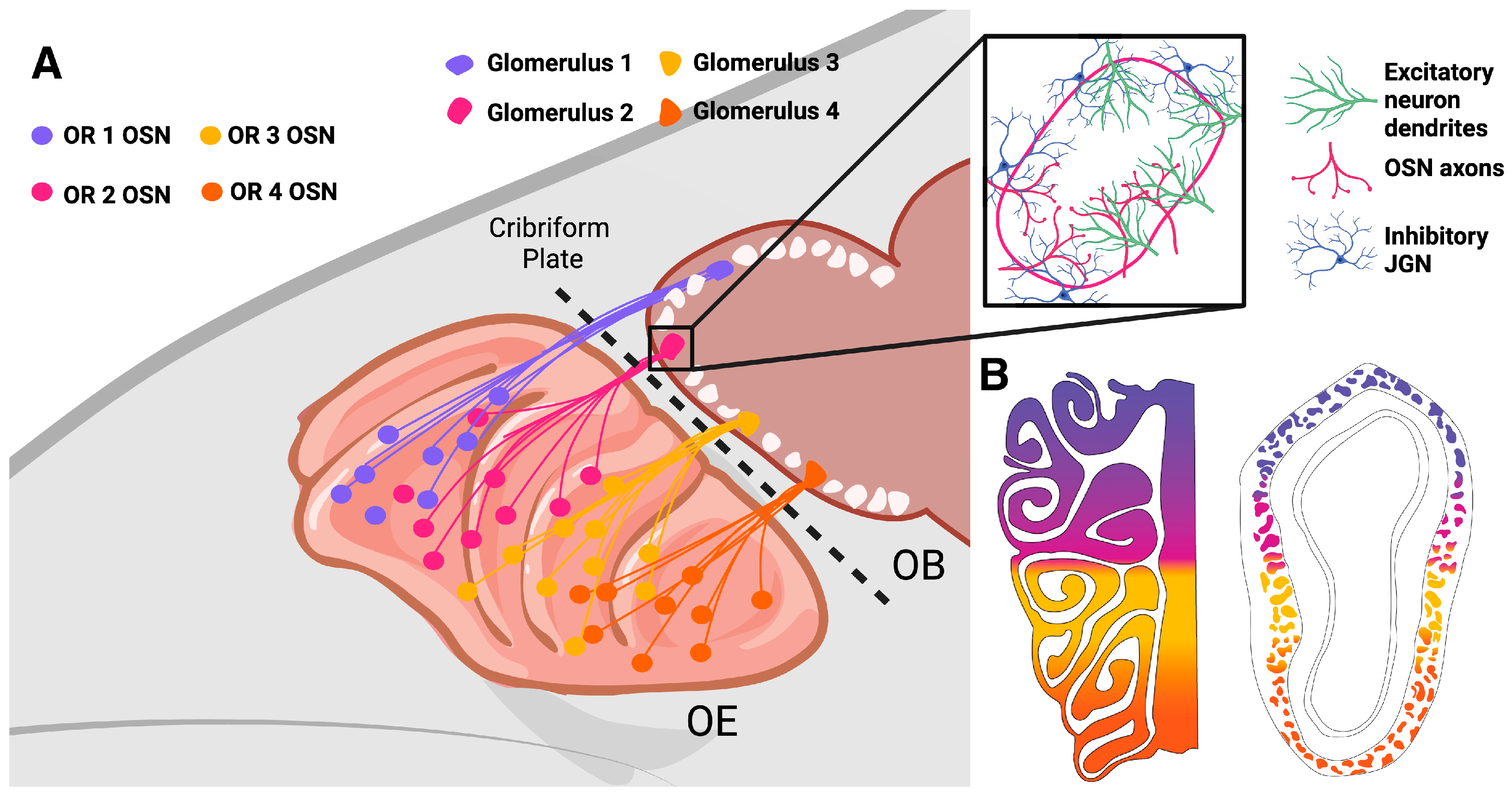
2. Postnatal Neurogenesis of OSNs
2.1. Dynamics of OSN Neurogenesis
2.2. Activity Dependence of OSN Neurogenesis
2.3. Roles for Immature OSNs
2.4. OSN Neurogenesis Following OE Damage
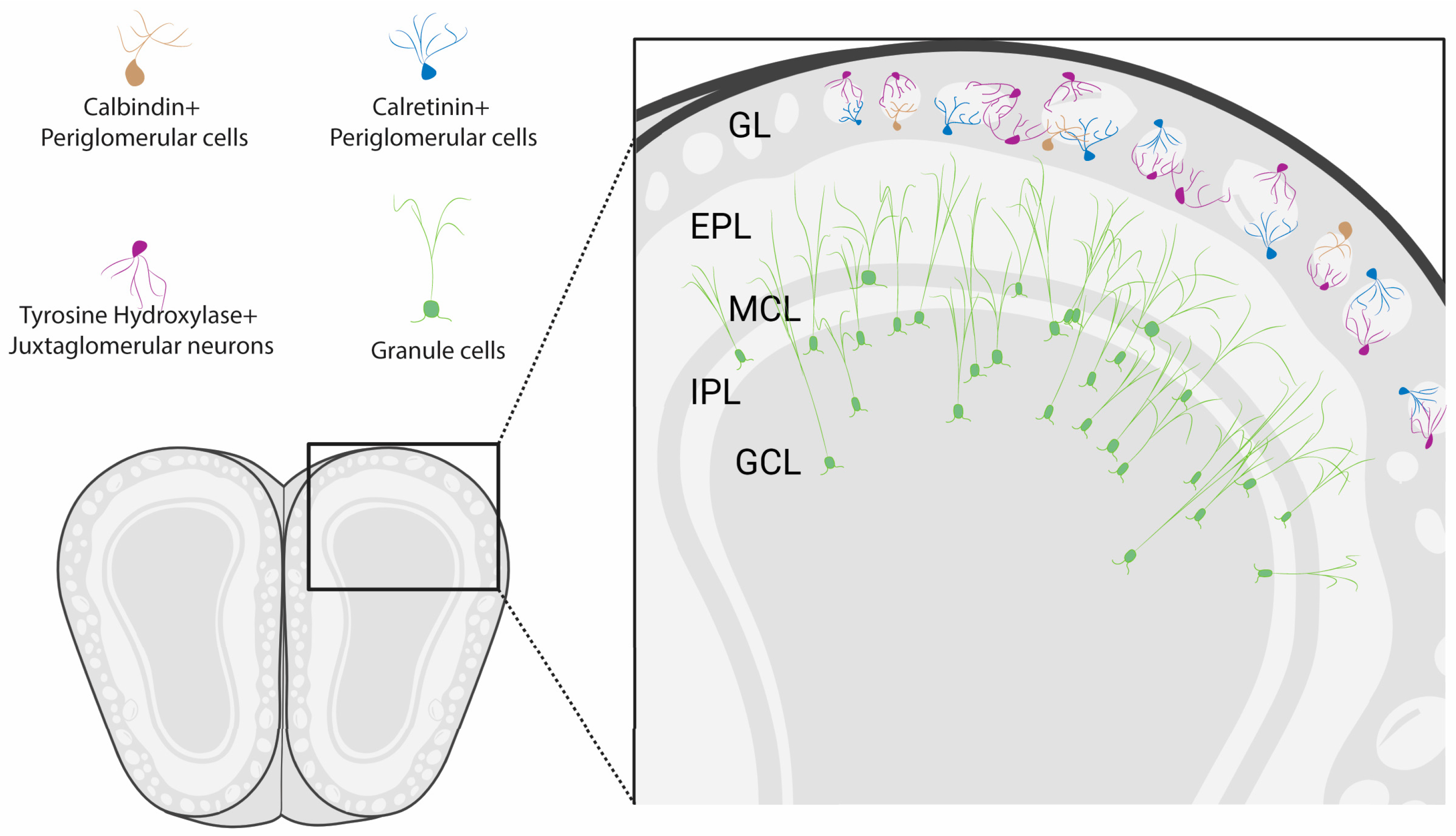
3. Postnatal Neurogenesis of OB GL Neurons
3.1. Integration of Adult-Born OB GL Neurons
3.2. Calretinin- and Calbindin-Expressing Periglomerular Cells
3.2.1. Properties of Calretinin-Expressing PGCs
3.2.2. Properties of Calbindin-Expressing PGCs
3.2.3. Role of Postnatal Neurogenesis of Calretinin- and Calbindin-Expressing PGCs
3.3. Postnatal Neurogenesis of Dopaminergic Neurons
3.3.1. Structure and Function of DA Neurons
3.3.2. Activity Dependence of DA Neuron Survival and Function
3.3.3. Activity Dependence of DA Neurogenesis
3.3.4. Role of Postnatal Neurogenesis of OB DA Neurons
4. Granule Cells
4.1. Postnatal Generation and Maturation of GCs
4.2. Survival of Postnatally Generated GCs
4.3. Functional Role of Postnatally Generated GCs
4.3.1. The Role of Postnatally Generated GCs in Olfactory Perceptual Learning
4.3.2. The Role of Postnatally Generated GCs in Olfactory Associative Learning
4.3.3. Cellular and Circuit Mechanisms Underlying Enhanced Olfactory Associative Learning
4.3.4. Other Functions of Postnatal GC Neurogenesis
4.4. Postnatal Neurogenesis of Neurochemically Defined GC Subtypes
4.4.1. CaMKII-Expressing GCs
4.4.2. Calretinin-Expressing GCs
4.4.3. 5T4-Expressing GCs
4.4.4. mGluR2-Expressing GCs
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagahara, Y. Experimentelle Studien Tiber Die Histologischen Veranderungen Des Geruchsorgans Nach Der Olfactoriusdurchschneidung. Beitrage Zur Kenntnis Des Feineren Baus Des Geruchsorgans. Med. Sci. Pathol. 1940, 5, 165–199. [Google Scholar]
- Graziadei, P.; Graziadei, G.M. Continuous Nerve Cell Renewal in the Olfactory System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, J.; Graziadei, P.P.C.; Graziadei, G.A.M.; Margolis, F.L. Denervation in the Primary Olfactory Pathway of Mice. IV. Biochemical and Morphological Evidence for Neuronal Replacement Following Nerve Section. Brain Res. 1977, 132, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huard, J.M.T.; Schwob, J.E. Cell Cycle of Globose Basal Cells in Rat Olfactory Epithelium. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryba, N.; Tirindelli, R. A Novel GTP-Binding Protein Gamma-Subunit, G Gamma 8, Is Expressed during Neurogenesis in the Olfactory and Vomeronasal Neuroepithelia. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6757–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaagen, J.; Oestreicher, A.; Gispen, W.; Margolis, F. The Expression of the Growth Associated Protein B50/GAP43 in the Olfactory System of Neonatal and Adult Rats. J. Neurosci. 1989, 9, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, J.C.; Titlow, W.B.; McClintock, T.S. Axon Growth and Guidance Genes Identify Nascent, Immature, and Mature Olfactory Sensory Neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3243–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, J.E.; Jang, W.; Holbrook, E.H.; Lin, B.; Herrick, D.B.; Peterson, J.N.; Coleman, J. Stem and Progenitor Cells of the Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium: Taking Poietic License. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 1034–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, M.D.; Breheny, P.; Stromberg, A.J.; McClintock, T.S. Genomics of Mature and Immature Olfactory Sensory Neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 2608–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miragall, F.; Graziadei, G.M. Experimental Studies on the Olfactory Marker Protein. II. Appearance of the Olfactory Marker Protein during Differentiation of the Olfactory Sensory Neurons of Mouse: An Immunohistochemical and Autoradiographic Study. Brain Res. 1982, 239, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Suzukawa, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kanaya, K.; Ushio, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nibu, K.; Kaga, K.; Yamasoba, T. Age-related Changes in Cell Dynamics of the Postnatal Mouse Olfactory Neuroepithelium: Cell Proliferation, Neuronal Differentiation, and Cell Death. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, J.E. Neural Regeneration and the Peripheral Olfactory System. Anat. Rec. 2002, 269, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savya, S.P.; Kunkhyen, T.; Cheetham, C. Low Survival Rate of Young Adult-Born Olfactory Sensory Neurons in the Undamaged Mouse Olfactory Epithelium. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2019, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberia, T.; Martin-Lopez, E.; Meller, S.J.; Greer, C.A. Sequential Maturation of Olfactory Sensory Neurons in the Mature Olfactory Epithelium. Eneuro 2019, 6, ENEURO.0266-19.2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gil, D.J.; Bartel, D.L.; Jaspers, A.W.; Mobley, A.S.; Imamura, F.; Greer, C.A. Odorant Receptors Regulate the Final Glomerular Coalescence of Olfactory Sensory Neuron Axons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, M.; Kauer, J.S.; Hunter, D.D. Globose Basal Cells Are Neuronal Progenitors in the Olfactory Epithelium: A Lineage Analysis Using a Replication-Incompetent Retrovirus. Neuron 1994, 13, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, E.H.; Szumowski, K.E.M.; Schwob, J.E. An Immunochemical, Ultrastructural, and Developmental Characterization of the Horizontal Basal Cells of Rat Olfactory Epithelium. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 363, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.T.; Coulombe, P.A.; Reed, R.R. Contribution of Olfactory Neural Stem Cells to Tissue Maintenance and Regeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, N.; Zhou, Z.; Roop, D.R.; Behringer, R.R. Horizontal Basal Cells Are Multipotent Progenitors in Normal and Injured Adult Olfactory Epithelium. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.K.; Henriques, T.; Marini, M.; Pedemonte, N.; Galietta, L.J.V.; Rock, J.R.; Harfe, B.D.; Menini, A. Development of the Olfactory Epithelium and Nasal Glands in TMEM16A-/- and TMEM16A+/+ Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti-Graziadei, G.A.; Margolis, F.L.; Harding, J.W.; Graziadei, P.P. Immunocytochemistry of the Olfactory Marker Protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 1977, 25, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, A.; Schnittke, N.; Romano, R.-A.; Sinha, S.; Schwob, J.E. ΔNp63 Regulates Stem Cell Dynamics in the Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8748–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calof, A.L.; Chikaraishi, D.M. Analysis of Neurogenesis in a Mammalian Neuroepithelium: Proliferation and Differentiation of an Olfactory Neuron Precursor in Vitro. Neuron 1989, 3, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.J.; Goss, G.M.; Hatzistergos, K.E.; Rangel, E.B.; Seidler, B.; Saur, D.; Hare, J.M. Adult C-Kit(+) Progenitor Cells Are Necessary for Maintenance and Regeneration of Olfactory Neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Tian, S.; Yang, X.; Lane, A.P.; Reed, R.R.; Liu, H. Wnt-Responsive Lgr5+ Globose Basal Cells Function as Multipotent Olfactory Epithelium Progenitor Cells. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8268–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, F.T.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Mosaic Organization of Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain. Science 2007, 317, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweat, S.C.; Cheetham, C.E.J. Deficits in Olfactory System Neurogenesis in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Genesis 2024, 62, e23590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasowski, H.J.; Kim, H.; Greer, C.A. Compartmental Organization of the Olfactory Bulb Glomerulus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 407, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R.; Ngai, J.; Axel, R. Spatial Segregation of Odorant Receptor Expression in the Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium. Cell 1993, 74, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, K.; Sullivan, S.; Buck, L. A Zonal Organization of Odorant Receptor Gene Expression in the Olfactory Epithelium. Cell 1993, 73, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, J.; Wanner, I.; Helfrich, T.; Beck, A.; Meinken, C.; Kubick, S.; Breer, H. Olfactory Neurones Expressing Distinct Odorant Receptor Subtypes Are Spatially Segregated in the Nasal Neuroepithelium. Cell Tissue Res. 1994, 276, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwema, C.L.; Fang, H.; Kurtz, D.B.; Youngentob, S.L.; Schwob, J.E. Odorant Receptor Expression Patterns Are Restored in Lesion-Recovered Rat Olfactory Epithelium. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamichi, K.; Serizawa, S.; Kimura, H.M.; Sakano, H. Continuous and Overlapping Expression Domains of Odorant Receptor Genes in the Olfactory Epithelium Determine the Dorsal/Ventral Positioning of Glomeruli in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapiec, B.; Mombaerts, P. The Zonal Organization of Odorant Receptor Gene Choice in the Main Olfactory Epithelium of the Mouse. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4220–4234.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, T.A.; Clancy, A.N.; Forbes, W.B.; Macrides, F. The Spatial Organization of the Peripheral Olfactory System of the Hamster. Part I: Receptor Neuron Projections to the Main Olfactory Bulb. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 34, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajal, S.R.Y. Degeneration & Regeneration of the Nervous System; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and Histological Evidence of Postnatal Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and Histological Studies of Postnatal Neurogenesis. I. A Longitudinal Investigation of the Kinetics, Migration and Transformation of Cells Incoorporating Tritiated Thymidine in Neonate Rats, with Special Reference to Postnatal Neurogenesis in Some Brain Regions. J. Comp. Neurol. 1966, 126, 337–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetsch, F.; Caillé, I.; Lim, D.A.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Subventricular Zone Astrocytes Are Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Cell 1999, 97, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The Adult Ventricular–Subventricular Zone (V-SVZ) and Olfactory Bulb (OB) Neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynac, M.; Morizur, L.; Chicheportiche, A.; Mouthon, M.-A.; Boussin, F.D. Age-Related Neurogenesis Decline in the Subventricular Zone Is Associated with Specific Cell Cycle Regulation Changes in Activated Neural Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwere, E.; Shingo, T.; Gregg, C.; Fujikawa, H.; Ohta, S.; Weiss, S. Aging Results in Reduced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling, Diminished Olfactory Neurogenesis, and Deficits in Fine Olfactory Discrimination. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8354–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.S.; Hinds, J.W. Neurogenesis in the Adult Rat: Electron Microscopic Analysis of Light Radioautographs. Science 1977, 197, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirich, J.M.; Williams, N.C.; Berlau, D.J.; Brunjes, P.C. Comparative Study of Aging in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 454, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, G.; Song, H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Mammalian Brain: Significant Answers and Significant Questions. Neuron 2011, 70, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lledo, P.-M.M.; Alonso, M.; Grubb, M.S. Adult Neurogenesis and Functional Plasticity in Neuronal Circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, F.r.e.d.H. Mammalian Neural Stem Cells. Science 2000, 287, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, J. Autoradiographic and Histological Studies of Postnatal Neurogenesis. IV. Cell Proliferation and Migration in the Anterior Forebrain, with Special Reference to Persisting Neurogenesis in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 1969, 137, 433–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.W. Autoradiographic Study of Histogenesis in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. II. Cell Proliferation and Migration. J. Comp. Neurol. 1968, 134, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, K.; Peng, J.Y.; Kakuta, S.; Murakami, K.; Kuroda, M.; Yokota, S.; Hayakawa, S.; Kuge, T.; Asayama, T. Migration of Bipolar Subependymal Cells, Precursors of the Granule Cells of the Rat Olfactory Bulb, with Reference to the Arrangement of the Radial Glial Fibers. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2011, 53, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, M.B. Restricted Proliferation and Migration of Postnatally Generated Neurons Derived from the Forebrain Subventricular Zone. Neuron 1993, 11, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Long-Distance Neuronal Migration in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Science 1994, 264, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.M.; Aigner, R.; Winkler, J.; Kuhn, H.G. Long-term Survival and Cell Death of Newly Generated Neurons in the Adult Rat Olfactory Bulb. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.S.; McNelly, N.A.; Hinds, J.W. Population Dynamics of Adult-formed Granule Neurons of the Rat Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 239, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Buylla, A.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Tramontin, A.D. A Unified Hypothesis on the Lineage of Neural Stem Cells. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluzzi, O.; Benedusi, M.; Ackman, J.; LoTurco, J.J. Electrophysiological Differentiation of New Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10411–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lledo, P.-M.; Saghatelyan, A. Integrating New Neurons into the Adult Olfactory Bulb: Joining the Network, Life–Death Decisions, and the Effects of Sensory Experience. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, F.J.F.; Luque-Molina, I.; Vecino, R.; Díaz-Guerra, E.; Defterali, Ç.; Pignatelli, J.; Vicario, C. Morphological Diversity of Calretinin Interneurons Generated from Adult Mouse Olfactory Bulb Core Neural Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 932297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defteralı, Ç.; Moreno-Estellés, M.; Crespo, C.; Díaz-Guerra, E.; Díaz-Moreno, M.; Vergaño-Vera, E.; Nieto-Estévez, V.; Hurtado-Chong, A.; Consiglio, A.; Mira, H.; et al. Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Olfactory Bulb Core Generate Mature Neurons in Vivo. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1253–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, M.A.; Saghatelyan, A.; de Chevigny, A.; Pfeifer, A.; Ashery-Padan, R.; Lledo, P.-M.; Götz, M. Neuronal Fate Determinants of Adult Olfactory Bulb Neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, A.; Bonfanti, L.; Doetsch, F.; Caille, I.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Lim, D.A.; Galli, R.; Verdugo, J.M.G.; Herrera, D.G.; Vescovi, A.L. Multipotent Neural Stem Cells Reside into the Rostral Extension and Olfactory Bulb of Adult Rodents. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.; Yokouchi, K.; Kawagishi, K.; Moriizumi, T. Differential Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis by Local and Migrating Neural Stem Cells in the Olfactory Bulb. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 44, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Martin, L.J. Olfactory Bulb Core Is a Rich Source of Neural Progenitor and Stem Cells in Adult Rodent and Human. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 459, 368–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, M.; Saghatelyan, A.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Lledo, P.-M. Neonatal and Adult Neurogenesis Provide Two Distinct Populations of Newborn Neurons to the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6816–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Ortega-Pérez, I.; Grubb, M.S.; Bourgeois, J.-P.; Charneau, P.; Lledo, P.-M. Turning Astrocytes from the Rostral Migratory Stream into Neurons: A Role for the Olfactory Sensory Organ. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11089–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandairon, N.; Jourdan, F.; Didier, A. Deprivation of Sensory Inputs to the Olfactory Bulb Up-Regulates Cell Death and Proliferation in the Subventricular Zone of Adult Mice. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, S.B.; Steveninck, R.R. de R. van; Anderson, J.C. The Metabolic Cost of Neural Information. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G. Adult Neurogenesis: An Evolutionary Perspective. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, A.-M. Survival of Mature Mouse Olfactory Sensory Neurons Labeled Genetically Perinatally. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay-Sim, A.; Kittel, P. On the Life Span of Olfactory Receptor Neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1991, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.W.; Hinds, P.L.; McNelly, N.A. An Autoradiographic Study of the Mouse Olfactory Epithelium: Evidence for Long-lived Receptors. Anat. Rec. 1984, 210, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirindelli, R.; Ryba, N. The G-Protein Gamma-Subunit G Gamma 8 Is Expressed in the Developing Axons of Olfactory and Vomeronasal Neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, J.H.; Ellis, D.P.; Ku, B.S.; Spinazzi, E.F.; Firestein, S. Injury in Aged Animals Robustly Activates Quiescent Olfactory Neural Stem Cells. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, A.T.; Youngentob, S.L.; Kent, P.F.; Schwob, J.E. The Aging Olfactory Epithelium: Neurogenesis, Response to Damage, and Odorant-Induced Activity. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1996, 14, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwob, J.E.; Szumowski, K.E.; Stasky, A.A. Olfactory Sensory Neurons Are Trophically Dependent on the Olfactory Bulb for Their Prolonged Survival. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 3896–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalik, T.J. Apparent Apoptotic Cell Death in the Olfactory Epithelium of Adult Rodents: Death Occurs at Different Developmental Stages. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 372, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, V.; Farbman, A.I. The Dynamics of Cell Death in the Olfactory Epithelium. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 124, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.W.; Dulac, C. The Activity-Dependent Histone Variant H2BE Modulates the Life Span of Olfactory Neurons. eLife 2012, 1, e00070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Reed, R.R. X Inactivation of the OCNC1 Channel Gene Reveals a Role for Activity-Dependent Competition in the Olfactory System. Cell 2001, 104, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, W.C.; Sakano, H.; Lee, Z.-Y.; Reusch, J.E.; Trinh, K.; Storm, D.R. Odorant Stimulation Enhances Survival of Olfactory Sensory Neurons via MAPK and CREB. Neuron 2004, 41, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Soria, X.; Nakahara, T.S.; Lilue, J.; Jiang, Y.; Trimmer, C.; Souza, M.A.; Netto, P.H.; Ikegami, K.; Murphy, N.R.; Kusma, M.; et al. Variation in Olfactory Neuron Repertoires Is Genetically Controlled and Environmentally Modulated. eLife 2017, 6, e21476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Laziz, I.; Rimbaud, S.; Grebert, D.; Durieux, D.; Pajot-Augy, E.; Meunier, N. Early Survival Factor Deprivation in the Olfactory Epithelium Enhances Activity-Driven Survival. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van der Linden, C.J.; Gupta, P.; Bhuiya, A.I.; Riddick, K.R.; Hossain, K.; Santoro, S.W. Olfactory Stimulation Regulates the Birth of Neurons That Express Specific Odorant Receptors. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, K.; Smith, M.; Rufenacht, K.E.; O’Rourke, R.; Santoro, S.W. In Mice, Discrete Odors Can Selectively Promote the Neurogenesis of Sensory Neuron Subtypes That They Stimulate. eLife 2025, 13, RP96152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, R.P.; Lomvardas, S. Chemosensory Receptor Specificity and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 38, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadiou, H.; Aoudé, I.; Tazir, B.; Molinas, A.; Fenech, C.; Meunier, N.; Grosmaitre, X. Postnatal Odorant Exposure Induces Peripheral Olfactory Plasticity at the Cellular Level. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallin, M.A.; Powell, K.; Biju, K.C.; Fadool, D.A. State-Dependent Sculpting of Olfactory Sensory Neurons Is Attributed to Sensory Enrichment, Odor Deprivation, and Aging. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 483, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Tian, H.; Ma, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, C.R.; Ma, M. Activity-Dependent Modulation of Odorant Receptor Gene Expression in the Mouse Olfactory Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, C.E.; Park, U.; Belluscio, L. Rapid and Continuous Activity-Dependent Plasticity of Olfactory Sensory Input. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziadei, M.G. Experimental Studies on the Olfactory Marker Protein. III. The Olfactory Marker Protein in the Olfactory Neuroepithelium Lacking Connections with the Forebrain. Brain Res. 1983, 262, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwema, C.L.; Schwob, J.E. Odorant Receptor Expression as a Function of Neuronal Maturity in the Adult Rodent Olfactory System. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 459, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchate, N.K.; Kondoh, K.; Lu, Z.; Kuang, D.; Ye, X.; Qiu, X.; Pachter, L.; Trapnell, C.; Buck, L.B. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Receptor Transformations during Olfactory Neurogenesis. Science 2015, 350, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, P.M.; Stromberg, A.J.; Breheny, P.; McClintock, T.S. Molecular Events in the Cell Types of the Olfactory Epithelium during Adult Neurogenesis. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F. Sustentacular Cell Enwrapment of Olfactory Receptor Neuronal Dendrites: An Update. Genes 2020, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón, M.R.; Fazzari, P. FAK: Dynamic Integration of Guidance Signals at the Growth Cone. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón, M.R.; Navarro, A.I.; Cuesto, G.; del Pino, I.; Scott, R.; Morales, M.; Rico, B. Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Actin Nucleation and Neuronal Filopodia Formation during Axonal Growth. Development 2012, 139, 3200–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menco, B.P.h.M.; Farbman, A.I. Genesis of Cilia and Microvilli of Rat Nasal Epithelia during Pre-Natal Development: II. Olfactory Epithelium, a Morphometric Analysis. J. Cell Sci. 1985, 78, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Kunkhyen, T.; Rangel, A.N.; Brechbill, T.R.; Gregory, J.D.; Winson-Bushby, E.D.; Liu, B.; Avon, J.T.; Muggleton, R.J.; Cheetham, C.E.J. Immature Olfactory Sensory Neurons Provide Behaviourally Relevant Sensory Input to the Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, Q.; Xie, S.X. Olfactory Sensory Neurons Transiently Express Multiple Olfactory Receptors during Development. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, F.; Maier-Balough, E.; Zou, D.; Firestein, S. Exuberant Growth and Synapse Formation of Olfactory Sensory Neuron Axonal Arborizations. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 3713–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, G.D. Morphological Study of the Effects of Intranasal Zinc Sulfate Irrigation on the Mouse Olfactory Epithelium and Olfactory Bulb. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1993, 24, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, I.; Brittebo, E.B.; Feil, V.J.; Bakke, J.E. Irreversible Binding and Toxicity of the Herbicide Dichlobenil (2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile) in the Olfactory Mucosa of Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1990, 103, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.A.S.; Key, B. Axon Mis-Targeting in the Olfactory Bulb During Regeneration of Olfactory Neuroepithelium. Chem. Senses 2003, 28, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Fang, C.; Schnittke, N.; Schwob, J.E.; Ding, X. Mechanisms of Permanent Loss of Olfactory Receptor Neurons Induced by the Herbicide 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile: Effects on Stem Cells and Noninvolvement of Acute Induction of the Inflammatory Cytokine IL-6. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedin, V.; Slotnick, B.; Berghard, A. Zonal Ablation of the Olfactory Sensory Neuroepithelium of the Mouse: Effects on Odorant Detection. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expression of hM4Di in the Forebrain Excitatory Neuron Improves Stroke Outcome. 2022. Available online: https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates/details/t-63a4bb294320eed9320ebcdb-expression-of-hm4di-in-the-forebrain-excitatory-neuron-impro (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Cummings, D.M.; Emge, D.K.; Small, S.L.; Margolis, F.L. Pattern of Olfactory Bulb Innervation Returns after Recovery from Reversible Peripheral Deafferentation. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 421, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Nagayama, S.; Kanaya, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Kondo, K.; Tsunoda, K.; Mori, K.; Yamasoba, T. Sensory Deprivation Disrupts Homeostatic Regeneration of Newly Generated Olfactory Sensory Neurons after Injury in Adult Mice. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 2657–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, J.E.; Youngentob, S.L.; Mezza, R.C. Reconstitution of the Rat Olfactory Epithelium after Methyl Bromide-induced Lesion. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 359, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittke, N.; Herrick, D.B.; Lin, B.; Peterson, J.; Coleman, J.H.; Packard, A.I.; Jang, W.; Schwob, J.E. Transcription Factor P63 Controls the Reserve Status but Not the Stemness of Horizontal Basal Cells in the Olfactory Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5068–E5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Youngentob, S.L.; Schwob, J.E. Globose Basal Cells Are Required for Reconstitution of Olfactory Epithelium after Methyl Bromide Lesion. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 460, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R.B.; Prasol, M.S.; Estrada, J.; Baudhuin, A.; Vranizan, K.; Choi, Y.G.; Ngai, J. P63 Regulates Olfactory Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation. Neuron 2011, 72, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadye, L.; Das, D.; Sanchez, M.A.; Street, K.; Baudhuin, A.; Wagner, A.; Cole, M.B.; Choi, Y.; Yosef, N.; Purdom, E.; et al. Injury Activates Transient Olfactory Stem Cell States with Diverse Lineage Capacities. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 775–790.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, D.B.; Guo, Z.; Jang, W.; Schnittke, N.; Schwob, J.E. Canonical Notch Signaling Directs the Fate of Differentiating Neurocompetent Progenitors in the Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 5022–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtt, M.E.; Morgan, K.T.; Working, P.K. Histopathology of Acute Toxic Responses in Selected Tissues from Rats Exposed by Inhalation to Methyl Bromide. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1987, 9, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtt, M.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Working, P.K.; Monticello, T.M.; Morgan, K.T. Degeneration and Regeneration of the Olfactory Epithelium Following Inhalation Exposure to Methyl Bromide: Pathology, Cell Kinetics, and Olfactory Function. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1988, 94, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, L.; Miller, M.L.; Minnema, D.J.; Evans, J.; Radike, M. Effects of Methyl Bromide on the Rat Olfactory System. Chem. Senses 1991, 16, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, J.E.; Youngentob, S.L.; Ring, G.; Iwema, C.L.; Mezza, R.C. Reinnervation of the Rat Olfactory Bulb after Methyl Bromide-induced Lesion: Timing and Extent of Reinnervation. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 412, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, U.; Östergren, A.; Gustafson, A.-L.; Brittebo, E. Differential Effects of Olfactory Toxicants on Olfactory Regeneration. Arch. Toxicol. 2002, 76, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Kondo, K.; Kashio, A.; Suzukawa, K.; Yamasoba, T. Methimazole-Induced Cell Death in Rat Olfactory Receptor Neurons Occurs via Apoptosis Triggered through Mitochondrial Cytochrome c-Mediated Caspase-3 Activation Pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, U.; Giovanetti, A.; Piras, E.; Brittebo, E.B. Methimazole-Induced Damage in the Olfactory Mucosa: Effects on Ultrastructure and Glutathione Levels. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Hernández, E.; Valle-Leija, P.; Zomosa-Signoret, V.; Drucker-Colín, R.; Vidaltamayo, R. Odor Memory Stability after Reinnervation of the Olfactory Bulb. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miwa, T.; Shiga, H.; Sakata, H.; Shigeta, D.; Hatta, T. Histological Changes in the Olfactory Bulb and Rostral Migratory Stream Due to Interruption of Olfactory Input. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, L.P.; Crespo, A.; Grubb, M.S. Rapid Presynaptic Maturation in Naturally Regenerating Axons of the Adult Mouse Olfactory Nerve. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkhyen, T.; Brechbill, T.R.; Berg, S.P.R.; Pothuri, P.; Rangel, A.N.; Gupta, A.; Cheetham, C.E.J. Cell Type- and Layer-Specific Plasticity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons Following Olfactory Sensory Neuron Ablation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, V.M.; Ring, G.; Youngentob, S.L.; Schwob, J.E.; Farbman, A.I. Altered Epithelial Density and Expansion of Bulbar Projections of a Discrete HSP70 Immunoreactive Subpopulation of Rat Olfactory Receptor Neurons in Reconstituting Olfactory Epithelium Following Exposure to Methyl Bromide. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 469, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.C.; Jang, W.; Schwob, J.E.; Wachowiak, M. Functional Recovery of Odor Representations in Regenerated Sensory Inputs to the Olfactory Bulb. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, E.H.; Iwema, C.L.; Peluso, C.E.; Schwob, J.E. The Regeneration of P2 Olfactory Sensory Neurons Is Selectively Impaired Following Methyl Bromide Lesion. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkhyen, T.; Curtis, K.A.; Deakin, T.P.; Huang, J.S.; Gregory, J.D.; Cheetham, C.E.J. Regional Deficits in Endogenous Regeneration of Mouse Olfactory Sensory Neuron Axons. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Duyck, K.; Long, C.C.; Moran, A.; Scheerer, H.; Blanck, J.; Peak, A.; Box, A.; Perera, A.; et al. A Population of Navigator Neurons Is Essential for Olfactory Map Formation during the Critical Period. Neuron 2018, 100, 1066–1082.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, A.; Petreanu, L.T.; Lansford, R.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Lledo, P.-M. Becoming a New Neuron in the Adult Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslyukov, A.; Li, K.; Su, X.; Kovalchuk, Y.; Garaschuk, O. Spontaneous Calcium Transients in the Immature Adult-Born Neurons of the Olfactory Bulb. Cell Calcium 2018, 74, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, Y.; Homma, R.; Liang, Y.; Maslyukov, A.; Hermes, M.; Thestrup, T.; Griesbeck, O.; Ninkovic, J.; Cohen, L.B.; Garaschuk, O. In Vivo Odourant Response Properties of Migrating Adult-Born Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomin-Thunemann, N.; Kovalchuk, Y.; Fink, S.; Alsema, A.; Mojtahedi, N.; Zirdum, E.; Garaschuk, O. Unique Functional Properties of Mature Adult-Born Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, A. Dendritic Development and Plasticity of Adult-Born Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livneh, Y.; Feinstein, N.; Klein, M.; Mizrahi, A. Sensory Input Enhances Synaptogenesis of Adult-Born Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Kovalchuk, Y.; Mojtahedi, N.; Kamari, F.; Claassen, M.; Garaschuk, O. Neuronal Silence as a Prosurvival Factor for Adult-Born Olfactory Bulb Interneurons. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 18, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, Y.; Mizrahi, A. Long-term Changes in the Morphology and Synaptic Distributions of Adult-born Neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, M.S.; Nissant, A.; Murray, K.; Lledo, P.-M.M. Functional Maturation of the First Synapse in Olfaction: Development and Adult Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2919–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, Y.; Adam, Y.; Mizrahi, A. Odor Processing by Adult-Born Neurons. Neuron 2014, 81, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, A.; Lu, J.; Irving, R.; Feng, G.; Katz, L.C. In Vivo Imaging of Juxtaglomerular Neuron Turnover in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkovic, J.; Mori, T.; Götz, M. Distinct Modes of Neuron Addition in Adult Mouse Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10906–10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, M.C.; Greer, C.A. Adult-generated Neurons Exhibit Diverse Developmental Fates. Dev. Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovetti, S.; Veyrac, A.; Peretto, P.; Fasolo, A.; Marchis, S. Olfactory Enrichment Influences Adult Neurogenesis Modulating GAD67 and Plasticity-Related Molecules Expression in Newborn Cells of the Olfactory Bulb. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastien-Dionne, P.; David, L.S.; Parent, A.; Saghatelyan, A. Role of Sensory Activity on Chemospecific Populations of Interneurons in the Adult Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 1847–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, N.; Gaborieau, E.; Diez, A.S.; Kosar, S.; Foucault, L.; Raineteau, O.; Jan, D.D.S. A Pool of Postnatally Generated Interneurons Persists in an Immature Stage in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9870–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista-Brito, R.; Close, J.; Machold, R.; Fishell, G. The Distinct Temporal Origins of Olfactory Bulb Interneuron Subtypes. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3966–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchis, S.D.; Bovetti, S.; Carletti, B.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Garzotto, D.; Peretto, P.; Fasolo, A.; Puche, A.C.; Rossi, F. Generation of Distinct Types of Periglomerular Olfactory Bulb Interneurons during Development and in Adult Mice: Implication for Intrinsic Properties of the Subventricular Zone Progenitor Population. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinandy, F.; Ninkovic, J.; Götz, M. Restrictions in Time and Space—New Insights into Generation of Specific Neuronal Subtypes in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, C.; Lin, C.; Ma, T.; Madhavan, M.C.; Campbell, K.; Yang, Z. The Transcription Factor Sp8 Is Required for the Production of Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8450–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohwi, M.; Petryniak, M.A.; Long, J.E.; Ekker, M.; Obata, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. A Subpopulation of Olfactory Bulb GABAergic Interneurons Is Derived from Emx1- and Dlx5/6-Expressing Progenitors. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6878–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K.; Toida, K.; Margolis, F.L.; Kosaka, T. Chemically Defined Neuron Groups and Their Subpopulations in the Glomerular Layer of the Rat Main Olfactory Bulb--II. Prominent Differences in the Intraglomerular Dendritic Arborization and Their Relationship to Olfactory Nerve Terminals. Neuroscience 1997, 76, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K.; Kosaka, T. Synaptic Organization of the Glomerulus in the Main Olfactory Bulb: Compartments of the Glomerulus and Heterogeneity of the Periglomerular Cells. Anat. Sci. Int. 2005, 80, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najac, M.; Diez, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Benito, N.; Charpak, S.; Jan, D.D.S. Intraglomerular Lateral Inhibition Promotes Spike Timing Variability in Principal Neurons of the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4319–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, K.; Kosaka, T. Chemical Properties of Type 1 and Type 2 Periglomerular Cells in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb Are Different from Those in the Rat Olfactory Bulb. Brain Res. 2007, 1167, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, C.; Alonso, J.R.; Briñón, J.G.; Weruaga, E.; Porteros, A.; Arévalo, R.; Aijón, J. Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Periglomerular Region of Typical and Typical Olfactory Glomeruli. Brain Res. 1997, 745, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, A.S.; Najac, M.; Jan, D.D.S. Basal Forebrain GABAergic Innervation of Olfactory Bulb Periglomerular Interneurons. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2547–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzanelli, P.; Fritschy, J.M.; Yanagawa, Y.; Obata, K.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M. GABAergic Phenotype of Periglomerular Cells in the Rodent Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 502, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseppe, A.F.; Pignatelli, A.; Belluzzi, O. Calretinin-Periglomerular Interneurons in Mice Olfactory Bulb: Cells of Few Words. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Kosaka, K. Heterogeneity of Calbindin-Containing Neurons in the Mouse Main Olfactory Bulb: I. General Description. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 67, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toida, K.; Kosaka, K.; Heizmann, C.W.; Kosaka, T. Chemically Defined Neuron Groups and Their Subpopulations in the Glomerular Layer of the Rat Main Olfactory Bulb: III. Structural Features of Calbindin D28K-immunoreactive Neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 392, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röckle, I.; Hildebrandt, H. Deficits of Olfactory Interneurons in Polysialyltransferase- and NCAM-deficient Mice. Dev. Neurobiol. 2016, 76, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finne, J. Occurrence of Unique Polysialosyl Carbohydrate Units in Glycoproteins of Developing Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 11966–11970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Brackenbury, R.; Cunningham, B.A.; Edelman, G.M. Differences in the Carbohydrate Structures of Neural Cell-Adhesion Molecules from Adult and Embryonic Chicken Brains. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 11064–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuerbitz, J.; Madhavan, M.; Ehrman, L.A.; Kohli, V.; Waclaw, R.R.; Campbell, K. Temporally Distinct Roles for the Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 in the Generation and Migration of Dorsal Lateral Ganglionic Eminence (DLGE)-Derived Neuronal Subtypes in the Mouse. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 31, 1744–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanić, D.; Paratcha, G.; Ledda, F.; Herzog, H.; Kopin, A.S.; Hökfelt, T. Peptidergic Influences on Proliferation, Migration, and Placement of Neural Progenitors in the Adult Mouse Forebrain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3610–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester-Lurbe, B.; González-Granero, S.; Mocholí, E.; Poch, E.; García-Manzanares, M.; Dierssen, M.; Pérez-Roger, I.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Guasch, R.M.; Terrado, J. RhoE Deficiency Alters Postnatal Subventricular Zone Development and the Number of Calbindin-Expressing Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb of Mouse. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 3113–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-M.; Kim, S.-S.; Choi, C.-I.; Cha, H.L.; Oh, H.-H.; Ghil, S.; Lee, Y.-D.; Birnbaumer, L.; Suh-Kim, H. Development of the Main Olfactory System and Main Olfactory Epithelium-Dependent Male Mating Behavior Are Altered in Go-Deficient Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10974–10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, K.S.; Anholt, R.R.H. Differential Expression of G Proteins in the Mouse Olfactory System. Brain Res. 1999, 837, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpot, B.D.; Lim, J.H.; Brunjes, P.C. Activity-dependent Regulation of Calcium-binding Proteins in the Developing Rat Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 387, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzano, S.; Bovetti, S.; Fasolo, A.; Peretto, P.; Marchis, S. Odour Enrichment Increases Adult-born Dopaminergic Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 3450–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasz, N.; Ljungdahl, A.; Ho¨kfelt, T.; Johansson, O.; Goldstein, M.; Park, D.; Biberfeld, P. Transmitter Histochemistry of the Rat Olfactory Bulb. I. Immunohistochemical Localization of Monoamine Synthesizing Enzymes. Support for Intrabulbar, Periglomerular Dopamine Neurons. Brain Res. 1977, 126, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokage, E.; Pan, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z.; Kobayashi, K.; Szabo, G.; Yanagawa, Y.; Obata, K.; Okano, H.; Toida, K.; Puche, A.C.; et al. Molecular Identity of Periglomerular and Short Axon Cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, Y.; Mizrahi, A. Long-Term Imaging Reveals Dynamic Changes in the Neuronal Composition of the Glomerular Layer. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7967–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, T.; Kosaka, K. Neuronal Organization of the Main Olfactory Bulb Revisited. Anat. Sci. Int. 2016, 91, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galliano, E.; Franzoni, E.; Breton, M.; Chand, A.N.; Byrne, D.J.; Murthy, V.N.; Grubb, M. Embryonic and Postnatal Neurogenesis Produce Functionally Distinct Subclasses of Dopaminergic Neuron. eLife 2018, 7, e32373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capsoni, S.; Iseppe, A.F.; Casciano, F.; Pignatelli, A. Unraveling the Role of Dopaminergic and Calretinin Interneurons in the Olfactory Bulb. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 718221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, K.S.; Blakemore, L.J.; Trombley, P.Q. Illuminating and Sniffing Out the Neuromodulatory Roles of Dopamine in the Retina and Olfactory Bulb. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.; Shipley, M. Postmitotic, Postmigrational Expression of Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Olfactory Bulb Dopaminergic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 3658–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Pignatelli, A.; Kosaka, K. Heterogeneity of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expressing Neurons in the Main Olfactory Bulb of the Mouse. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 157, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Okano, H.; Belluzzi, O. Functional Properties of Dopaminergic Neurones in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Physiol. 2005, 564, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, N.; Johansson, O.; Hökfelt, T.; Ljungdahl, Å.; Goldstein, M. Immunohistochemical Identification of Two Types of Dopamine Neuron in the Rat Olfactory Bulb as Seen by Serial Sectioning. J. Neurocytol. 1981, 10, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Kosaka, K. Two Types of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Positive GABAergic Juxtaglomerular Neurons in the Mouse Main Olfactory Bulb Are Different in Their Time of Origin. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 64, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Kosaka, K. Tyrosine Hydroxylase-Positive GABAergic Juxtaglomerular Neurons Are the Main Source of the Interglomerular Connections in the Mouse Main Olfactory Bulb. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 60, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, A.N.; Galliano, E.; Chesters, R.A.; Grubb, M.S. A Distinct Subtype of Dopaminergic Interneuron Displays Inverted Structural Plasticity at the Axon Initial Segment. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 1573–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puopolo, M.; Bean, B.P.; Raviola, E. Spontaneous Activity of Isolated Dopaminergic Periglomerular Cells of the Main Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, B.J.; Westbrook, G.L. Co-Transmission of Dopamine and GABA in Periglomerular Cells. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisovska, M.; Bensen, A.L.; Chong, G.; Westbrook, G.L. Distinct Modes of Dopamine and GABA Release in a Dual Transmitter Neuron. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Plachez, C.; Shao, Z.; Puche, A.; Shipley, M.T. Olfactory Bulb Short Axon Cell Release of GABA and Dopamine Produces a Temporally Biphasic Inhibition–Excitation Response in External Tufted Cells. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 2916–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, A.; Belluzzi, O. Dopaminergic Neurones in the Main Olfactory Bulb: An Overview from an Electrophysiological Perspective. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaaga, C.E.; Yorgason, J.T.; Williams, J.T.; Westbrook, G.L. Presynaptic Gain Control by Endogenous Cotransmission of Dopamine and GABA in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, M.; Zhou, F.-M.; Ciombor, K.J.; Aroniadou-Anderjaska, V.; Hayar, A.; Borrelli, E.; Zimmer, L.A.; Margolis, F.; Shipley, M.T. Dopamine D2 Receptor–Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition of Olfactory Nerve Terminals. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, A.Y.; Vincent, J.-D.; Lledo, P.-M. Dopamine Depresses Synaptic Inputs into the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGann, J.P. Presynaptic Inhibition of Olfactory Sensory Neurons: New Mechanisms and Potential Functions. Chem. Senses 2013, 38, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pírez, N.; Wachowiak, M. In Vivo Modulation of Sensory Input to the Olfactory Bulb by Tonic and Activity-Dependent Presynaptic Inhibition of Receptor Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6360–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Puche, A.C.; Shipley, M.T. The Interglomerular Circuit Potently Inhibits Olfactory Bulb Output Neurons by Both Direct and Indirect Pathways. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 9604–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Marbach, F.; Anselmi, F.; Koh, M.S.; Davis, M.B.; Garcia da Silva, P.; Delevich, K.; Oyibo, H.K.; Gupta, P.; Li, B.; et al. An Interglomerular Circuit Gates Glomerular Output and Implements Gain Control in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Neuron 2015, 87, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, F.; Puche, A.C.; Shipley, M.T. Reciprocal Inhibitory Glomerular Circuits Contribute to Excitation–Inhibition Balance in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. eNeuro 2019, 6, ENEURO.0048-19.2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.; Kawano, T.; Margolis, F.; Joh, T. Transneuronal Regulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expression in Olfactory Bulb of Mouse and Rat. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.; Morel, K.; Stone, D.; Maruniak, J. Adult Naris Closure Profoundly Reduces Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expression in Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Brain Res. 1993, 614, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.; Kawano, T.; Albert, V.; Joh, T.H.; Reis, D.J.; Margolis, F.L. Olfactory Bulb Dopamine Neurons Survive Deafferentation-Induced Loss of Tyrosine Hydroxylase. Neuroscience 1984, 11, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadi, N.S.; Head, R.; Grillo, M.; Hempstead, J.; Grannot-Reisfeld, N.; Margolis, F.L. Chemical Deafferentation of the Olfactory Bulb: Plasticity of the Levels of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, Dopamine and Norepinephrine. Brain Res. 1981, 213, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Margolis, F.L. Transsynaptic Regulation of Olfactory Bulb Catecholamines in Mice and Rats. J. Neurochem. 1982, 39, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.J.; Lipovsek, M.; Crespo, A.; Grubb, M.S. Brief Sensory Deprivation Triggers Plasticity of Dopamine-synthesising Enzyme Expression in Genetically Labelled Olfactory Bulb Dopaminergic Neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 3591–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, B.D.; Belluscio, L.; Cheetham, C.E. Olfactory Sensory Activity Modulates Microglial-Neuronal Interactions during Dopaminergic Cell Loss in the Olfactory Bulb. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, M.; Kaneko, N.; Inada, H.; Wake, H.; Kato, Y.; Yanagawa, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Nemoto, T.; Nabekura, J.; Sawamoto, K. Sensory Input Regulates Spatial and Subtype-Specific Patterns of Neuronal Turnover in the Adult Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 11587–11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelova, A.; Tiveron, M.-C.; Loizeau, M.D.; Cremer, H.; Platel, J.-C. Effects of Sensory Deprivation on Glomerular Interneurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb: Differences in Mortality and Phenotypic Adjustment of Dopaminergic Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1170170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissant, A.; Bardy, C.; Katagiri, H.; Murray, K.; Lledo, P.-M. Adult Neurogenesis Promotes Synaptic Plasticity in the Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish-Aungst, S.; Shipley, M.T.; Erdelyi, F.; Szabo, G.; Puche, A.C. Quantitative Analysis of Neuronal Diversity in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 501, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.B.; Taylor, S.R.; Greer, C.A. Age-Induced Disruption of Selective Olfactory Bulb Synaptic Circuits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15613–15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.D. Inhibitory Circuits of the Mammalian Main Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 118, 2034–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rall, W.; Shepherd, G.M.; Reese, T.S.; Brightman, M.W. Dendrodendritic Synaptic Pathway for Inhibition in the Olfactory Bulb. Exp. Neurol. 1966, 14, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, A.Y.; Barone, T.A.; Plunkett, R.J.; Pruitt, S.C. Neural Stem Cell Detection, Characterization, and Age-Related Changes in the Subventricular Zone of Mice. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropepe, V.; Craig, C.G.; Morshead, C.M.; Kooy, D. van der Transforming Growth Factor-α Null and Senescent Mice Show Decreased Neural Progenitor Cell Proliferation in the Forebrain Subependyma. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 7850–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackmore, D.G.; Golmohammadi, M.G.; Large, B.; Waters, M.J.; Rietze, R.L. Exercise Increases Neural Stem Cell Number in a Growth Hormone-Dependent Manner, Augmenting the Regenerative Response in Aged Mice. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, N.L.; Sacquet, J.; Veyrac, A.; Jourdan, F.; Didier, A. Behavioral and Cellular Markers of Olfactory Aging and Their Response to Enrichment. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 626.e9–626.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shook, B.A.; Manz, D.H.; Peters, J.J.; Kang, S.; Conover, J.C. Spatiotemporal Changes to the Subventricular Zone Stem Cell Pool through Aging. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6947–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardy, C.; Alonso, M.; Bouthour, W.; Lledo, P.-M. How, When, and Where New Inhibitory Neurons Release Neurotransmitters in the Adult Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 17023–17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreanu, L.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Maturation and Death of Adult-Born Olfactory Bulb Granule Neurons: Role of Olfaction. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6106–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotto, M.; Nissant, A.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Rudolph, U.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Lledo, P.-M. Early Formation of GABAergic Synapses Governs the Development of Adult-Born Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9103–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magavi, S.S.P.; Mitchell, B.D.; Szentirmai, O.; Carter, B.S.; Macklis, J.D. Adult-Born and Preexisting Olfactory Granule Neurons Undergo Distinct Experience-Dependent Modifications of Their Olfactory Responses In Vivo. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10729–10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Wienisch, M.; Murthy, V.N. Development and Refinement of Functional Properties of Adult-Born Neurons. Neuron 2017, 96, 883–896.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M.; Ieki, N.; Miyoshi, G.; Mochimaru, D.; Miyachi, H.; Imura, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Fishell, G.; Mori, K.; Kageyama, R.; et al. Continuous Postnatal Neurogenesis Contributes to Formation of the Olfactory Bulb Neural Circuits and Flexible Olfactory Associative Learning. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5788–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramita, M.A.; Burton, S.D.; Urban, N.N. Distinct Lateral Inhibitory Circuits Drive Parallel Processing of Sensory Information in the Mammalian Olfactory Bulb. eLife 2016, 5, e16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orona, E.; Rainer, E.C.; Scott, J.W. Dendritic and Axonal Organization of Mitral and Tufted Cells in the Rat Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 226, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Kishi, K.; Ojima, H. Distribution of Dendrites of Mitral, Displaced Mitral, Tufted, and Granule Cells in the Rabbit Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 219, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellis, D.P.; Scott, J.W. Intracellular Responses of Identified Rat Olfactory Bulb Interneurons to Electrical and Odor Stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 1990, 64, 932–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, K. Critical Period for Sensory Experience-Dependent Survival of Newly Generated Granule Cells in the Adult Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9697–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Viollet, C.; Gabellec, M.-M.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Lledo, P.-M. Olfactory Discrimination Learning Increases the Survival of Adult-Born Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10508–10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachino, C.; Marchis, S.D.; Giampietro, C.; Parlato, R.; Perroteau, I.; Schütz, G.; Fasolo, A.; Peretto, P. CAMP Response Element-Binding Protein Regulates Differentiation and Survival of Newborn Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10105–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imayoshi, I.; Sakamoto, M.; Ohtsuka, T.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, K.; Ikeda, T.; Itohara, S.; Kageyama, R. Roles of Continuous Neurogenesis in the Structural and Functional Integrity of the Adult Forebrain. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Sim, S.; Ainsworth, A.; Okada, M.; Kelsch, W.; Lois, C. Genetically Increased Cell-Intrinsic Excitability Enhances Neuronal Integration into Adult Brain Circuits. Neuron 2010, 65, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platel, J.-C.; Angelova, A.; Bugeon, S.; Wallace, J.; Ganay, T.; Chudotvorova, I.; Deloulme, J.-C.; Beclin, C.; Tiveron, M.-C.; Coré, N.; et al. Neuronal Integration in the Adult Mouse Olfactory Bulb Is a Non-Selective Addition Process. eLife 2019, 8, e44830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandairon, N.; Sacquet, J.; Jourdan, F.; Didier, A. Long-Term Fate and Distribution of Newborn Cells in the Adult Mouse Olfactory Bulb: Influences of Olfactory Deprivation. Neuroscience 2006, 141, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghatelyan, A.; Roux, P.; Migliore, M.; Rochefort, C.; Desmaisons, D.; Charneau, P.; Shepherd, G.M.; Lledo, P.-M. Activity-Dependent Adjustments of the Inhibitory Network in the Olfactory Bulb Following Early Postnatal Deprivation. Neuron 2005, 46, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsch, W.; Lin, C.-W.; Mosley, C.P.; Lois, C. A Critical Period for Activity-Dependent Synaptic Development during Olfactory Bulb Adult Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11852–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochefort, C.; Gheusi, G.; Vincent, J.-D.D.; Lledo, P.-M.M. Enriched Odor Exposure Increases the Number of Newborn Neurons in the Adult Olfactory Bulb and Improves Odor Memory. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.M.; Linster, C.; Escanilla, O.; Sacquet, J.; Didier, A.; Mandairon, N. Olfactory Perceptual Learning Requires Adult Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17980–17985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, J.; Chalençon, L.; Midroit, M.; Terrier, C.; Caillé, I.; Sacquet, J.; Benetollo, C.; Martin, K.; Richard, M.; Didier, A.; et al. Role of Adult-Born Versus Preexisting Neurons Born at P0 in Olfactory Perception in a Complex Olfactory Environment in Mice. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 30, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, J.; Moreno, M.; Cavelius, M.; Chalençon, L.; Ziessel, A.; Sacquet, J.; Richard, M.; Didier, A.; Mandairon, N. Short-Term Availability of Adult-Born Neurons for Memory Encoding. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandairon, N.; Kuczewski, N.; Kermen, F.; Forest, J.; Midroit, M.; Richard, M.; Thevenet, M.; Sacquet, J.; Linster, C.; Didier, A. Opposite Regulation of Inhibition by Adult-Born Granule Cells during Implicit versus Explicit Olfactory Learning. eLife 2018, 7, e34976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco-Vuilloud, J.; Midroit, M.; Terrier, C.; Forest, J.; Sacquet, J.; Mandairon, N.; Didier, A.; Richard, M. 12 Months Is a Pivotal Age for Olfactory Perceptual Learning and Its Underlying Neuronal Plasticity in Aging Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2022, 114, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandairon, N.; Sacquet, J.; Garcia, S.; Ravel, N.; Jourdan, F.; Didier, A. Neurogenic Correlates of an Olfactory Discrimination Task in the Adult Olfactory Bulb. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 3578–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Lefort, J.M.; Sacquet, J.; Mandairon, N.; Didier, A. Acquisition of an Olfactory Associative Task Triggers a Regionalized Down-Regulation of Adult Born Neuron Cell Death. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belnoue, L.; Grosjean, N.; Abrous, D.N.; Koehl, M. A Critical Time Window for the Recruitment of Bulbar Newborn Neurons by Olfactory Discrimination Learning. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouret, A.; Gheusi, G.; Gabellec, M.-M.; de Chaumont, F.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Lledo, P.-M. Learning and Survival of Newly Generated Neurons: When Time Matters. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11511–11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton-Provencher, V.; Lemasson, M.; Peralta, M.R.; Saghatelyan, A. Interneurons Produced in Adulthood Are Required for the Normal Functioning of the Olfactory Bulb Network and for the Execution of Selected Olfactory Behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15245–15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini, F.; Mouthon, M.-A.; Gheusi, G.; de Chaumont, F.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Lamarque, S.; Abrous, D.N.; Boussin, F.D.; Lledo, P.-M. Cellular and Behavioral Effects of Cranial Irradiation of the Subventricular Zone in Adult Mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Mandairon, N.; Kermen, F.; Garcia, S.; Sacquet, J.; Didier, A. Learning-dependent Neurogenesis in the Olfactory Bulb Determines Long-term Olfactory Memory. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Chu, M.W.; Wu, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Imayoshi, I.; Komiyama, T. Adult-Born Neurons Facilitate Olfactory Bulb Pattern Separation during Task Engagement. eLife 2018, 7, e33006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandairon, N.; Sultan, S.; Nouvian, M.; Sacquet, J.; Didier, A. Involvement of Newborn Neurons in Olfactory Associative Learning? The Operant or Non-Operant Component of the Task Makes All the Difference. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12455–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermen, F.; Sultan, S.; Sacquet, J.; Mandairon, N.; Didier, A. Consolidation of an Olfactory Memory Trace in the Olfactory Bulb Is Required for Learning-Induced Survival of Adult-Born Neurons and Long-Term Memory. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda-Carvalho, M.; Akers, K.G.; Guskjolen, A.; Sakaguchi, M.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Posttraining Ablation of Adult-Generated Olfactory Granule Cells Degrades Odor–Reward Memories. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15793–15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Rey, N.; Sacquet, J.; Mandairon, N.; Didier, A. Newborn Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb Selected for Long-Term Survival through Olfactory Learning Are Prematurely Suppressed When the Olfactory Memory Is Erased. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14893–14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alonso, M.; Lepousez, G.; Wagner, S.; Bardy, C.; Gabellec, M.-M.; Torquet, N.; Lledo, P.-M. Activation of Adult-Born Neurons Facilitates Learning and Memory. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grelat, A.; Benoit, L.; Wagner, S.; Moigneu, C.; Lledo, P.-M.; Alonso, M. Adult-Born Neurons Boost Odor–Reward Association. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragado-Alonso, S.; Reinert, J.K.; Marichal, N.; Massalini, S.; Berninger, B.; Kuner, T.; Calegari, F. An Increase in Neural Stem Cells and Olfactory Bulb Adult Neurogenesis Improves Discrimination of Highly Similar Odorants. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e98791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepousez, G.; Nissant, A.; Bryant, A.K.; Gheusi, G.; Greer, C.A.; Lledo, P.-M. Olfactory Learning Promotes Input-Specific Synaptic Plasticity in Adult-Born Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13984–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton-Provencher, V.; Bakhshetyan, K.; Hardy, D.; Bammann, R.R.; Cavarretta, F.; Snapyan, M.; Côté, D.; Migliore, M.; Saghatelyan, A. Principal Cell Activity Induces Spine Relocation of Adult-Born Interneurons in the Olfactory Bulb. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, E.; Swanson, J.; Arenkiel, B.R. GABAergic Input from the Basal Forebrain Promotes the Survival of Adult-Born Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Front. Neural Circuits 2020, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani-Narkiss, H.; Vinograd, A.; Landau, I.D.; Tasaka, G.; Yayon, N.; Terletsky, S.; Groysman, M.; Maor, I.; Sompolinsky, H.; Mizrahi, A. Young Adult-Born Neurons Improve Odor Coding by Mitral Cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassi, A.; Breton, M.; Chalençon, L.; Brunelin, J.; Didier, A.; Bath, K.; Mandairon, N. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Alters Odor Hedonics and Adult Olfactory Neurogenesis in Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1224941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopel, H.; Schechtman, E.; Groysman, M.; Mizrahi, A. Enhanced Synaptic Integration of Adult-Born Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb of Lactating Mothers. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 7519–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaker, Z.; Segalada, C.; Kretz, J.A.; Acar, I.E.; Delgado, A.C.; Crotet, V.; Moor, A.E.; Doetsch, F. Pregnancy-Responsive Pools of Adult Neural Stem Cells for Transient Neurogenesis in Mothers. Science 2023, 382, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.; Greer, C.A.; Firestein, S. Expression Pattern of ACaMKII in the Mouse Main Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 443, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvaut, S.; Gribaudo, S.; Hardy, D.; David, L.; Daroles, L.; Labrecque, S.; Lebel-Cormier, M.-A.; Chaker, Z.; Coté, D.; Koninck, P.; et al. CaMKIIα Expression Defines Two Functionally Distinct Populations of Granule Cells Involved in Different Types of Odor Behavior. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3315–3329.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Néant-Fery, M.; Pérès, E.; Nasrallah, C.; Kessner, M.; Gribaudo, S.; Greer, C.; Didier, A.; Trembleau, A.; Caillé, I. A Role for Dendritic Translation of CaMKIIα MRNA in Olfactory Plasticity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, D.; Malvaut, S.; Breton-Provencher, V.; Saghatelyan, A. The Role of Calretinin-Expressing Granule Cells in Olfactory Bulb Functions and Odor Behavior. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nishimura, N.; Naritsuka, H.; Shirao, T.; Hirai, H.; Yoshihara, Y.; Mori, K.; Stern, P.L.; Tsuboi, A. 5T4 Glycoprotein Regulates the Sensory Input-Dependent Development of a Specific Subtype of Newborn Interneurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshihara, S.; Asahina, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Kitano, T.; Kitsuki, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Okuda, M.; Tatsumi, K.; et al. A Subtype of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons Is Required for Odor Detection and Discrimination Behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8210–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, F.; Nagao, H.; Naritsuka, H.; Murata, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Mori, K. A Leucine-rich Repeat Membrane Protein, 5T4, Is Expressed by a Subtype of Granule Cells with Dendritic Arbors in Specific Strata of the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 495, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, H.; Shigemoto, R.; Nakanishi, S.; Mizuno, N. Distribution of the Messenger RNA for a Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGluR2, in the Central Nervous System of the Rat. Neuroscience 1993, 53, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Imai, M.; Nakanishi, S.; Watanabe, D.; Pastan, I.; Kobayashi, K.; Nihira, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Yamada, S.; Mori, K.; et al. Compensation of Depleted Neuronal Subsets by New Neurons in a Local Area of the Adult Olfactory Bulb. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10540–10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, J.P.; Schreck, M.; Moberly, A.H.; Luo, W.; Ma, M. Aversive Learning Increases Release Probability of Olfactory Sensory Neurons. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 31–41.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, M.D.; Rosenthal, M.C.; Pottackal, J.; McGann, J.P. Fear Learning Enhances Neural Responses to Threat-Predictive Sensory Stimuli. Science 2013, 342, 1244916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gregory, J.D.; Kunkhyen, T.; Sweat, S.C.; Huang, J.S.; Brechbill, T.R.; Cheetham, C.E.J. New Neurons in the Postnatal Olfactory System: Functions in the Healthy and Regenerating Brain. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060597
Gregory JD, Kunkhyen T, Sweat SC, Huang JS, Brechbill TR, Cheetham CEJ. New Neurons in the Postnatal Olfactory System: Functions in the Healthy and Regenerating Brain. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060597
Chicago/Turabian StyleGregory, Jordan D., Tenzin Kunkhyen, Sean C. Sweat, Jane S. Huang, Taryn R. Brechbill, and Claire E. J. Cheetham. 2025. "New Neurons in the Postnatal Olfactory System: Functions in the Healthy and Regenerating Brain" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060597
APA StyleGregory, J. D., Kunkhyen, T., Sweat, S. C., Huang, J. S., Brechbill, T. R., & Cheetham, C. E. J. (2025). New Neurons in the Postnatal Olfactory System: Functions in the Healthy and Regenerating Brain. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060597





