Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Promotes Estimation Strategy Execution in Individuals with Trait Anxiety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Design
2.3. Materials
2.3.1. Trait Anxiety Scale
2.3.2. Positive and Negative Affective Scale
2.3.3. Multiplication Estimation Problems
2.3.4. Cognitive Reappraisal Sentences
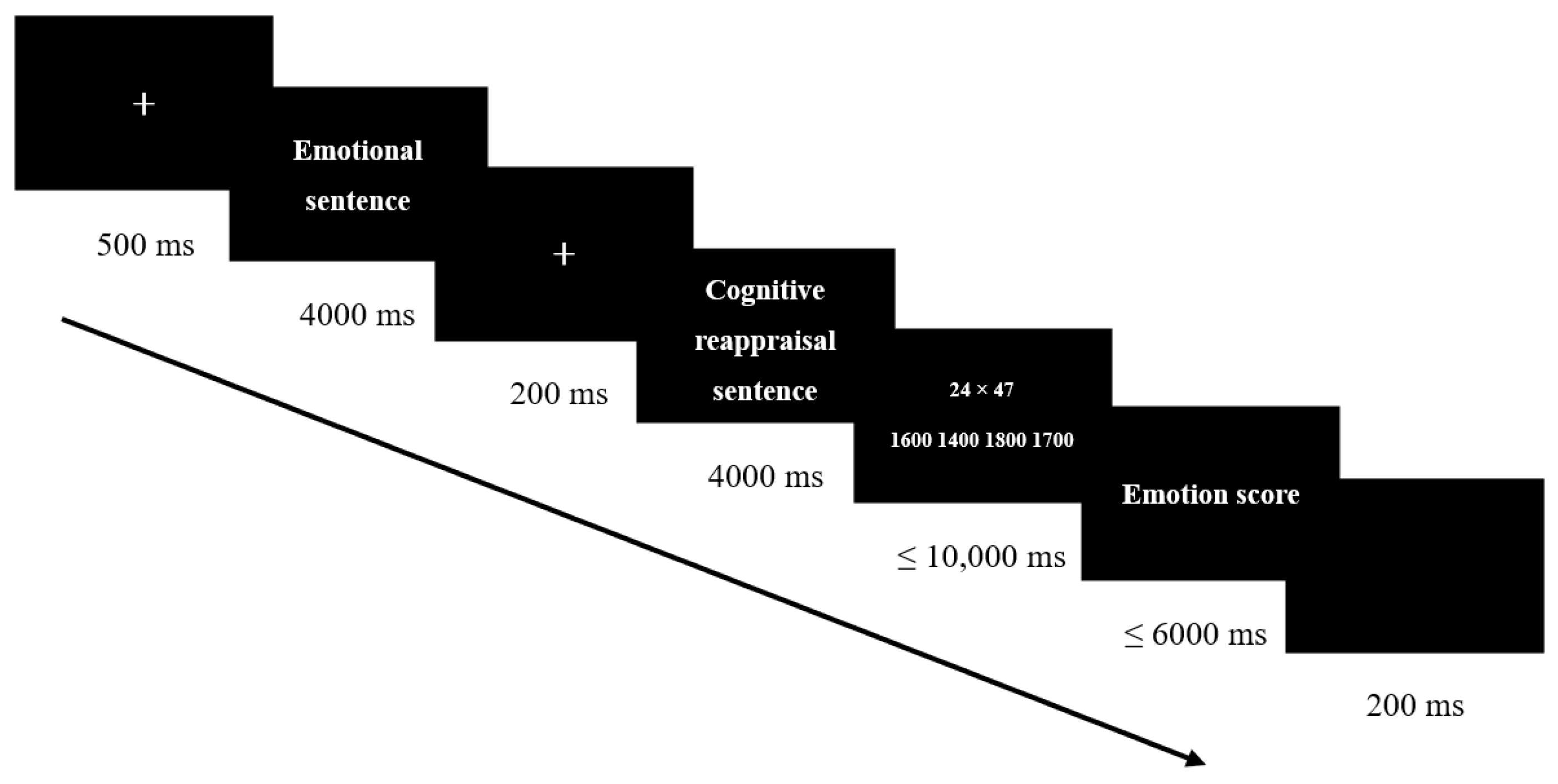
2.4. Procedure
3. Results
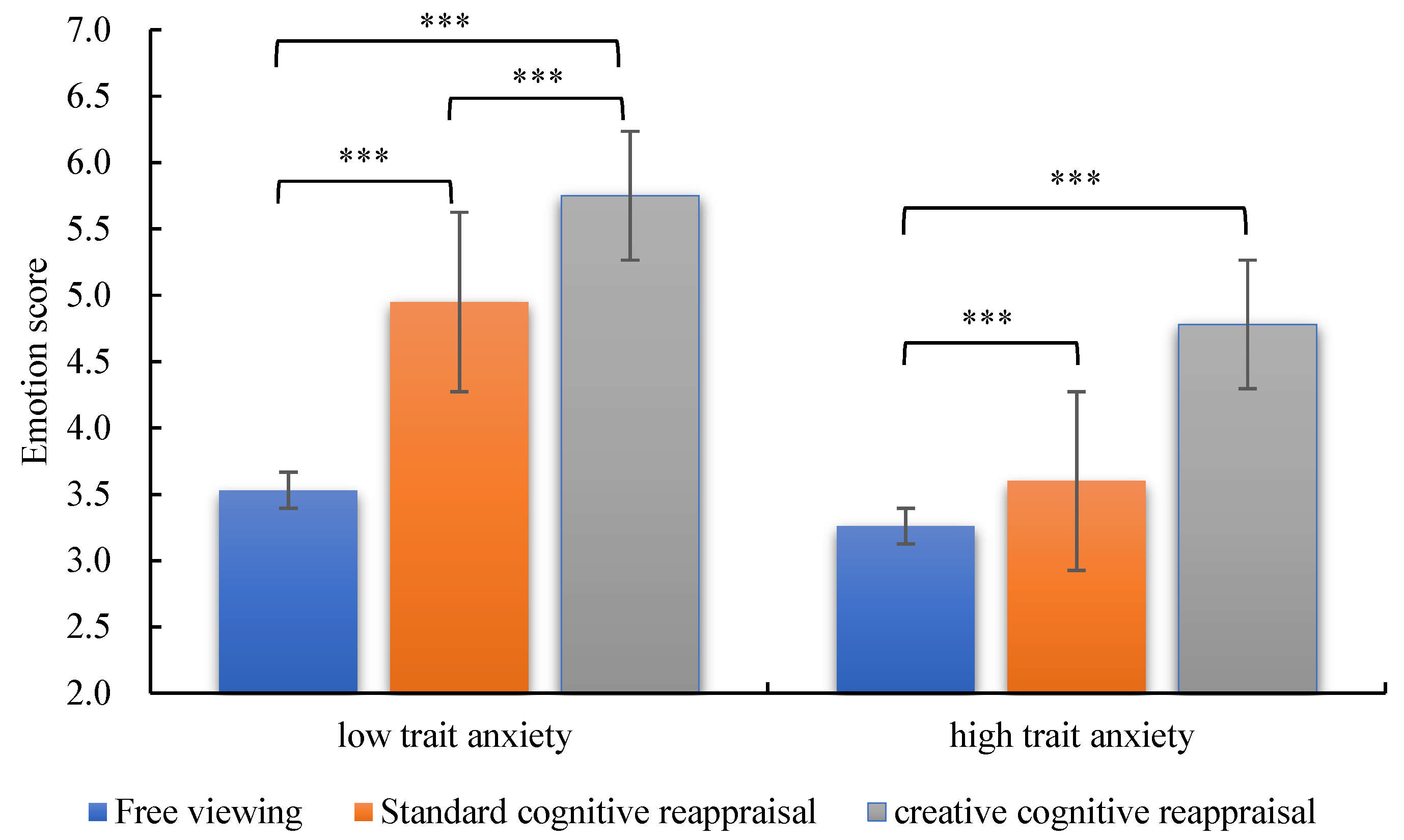
3.1. Subjective Emotional Ratings for College Students with HTA and LTA
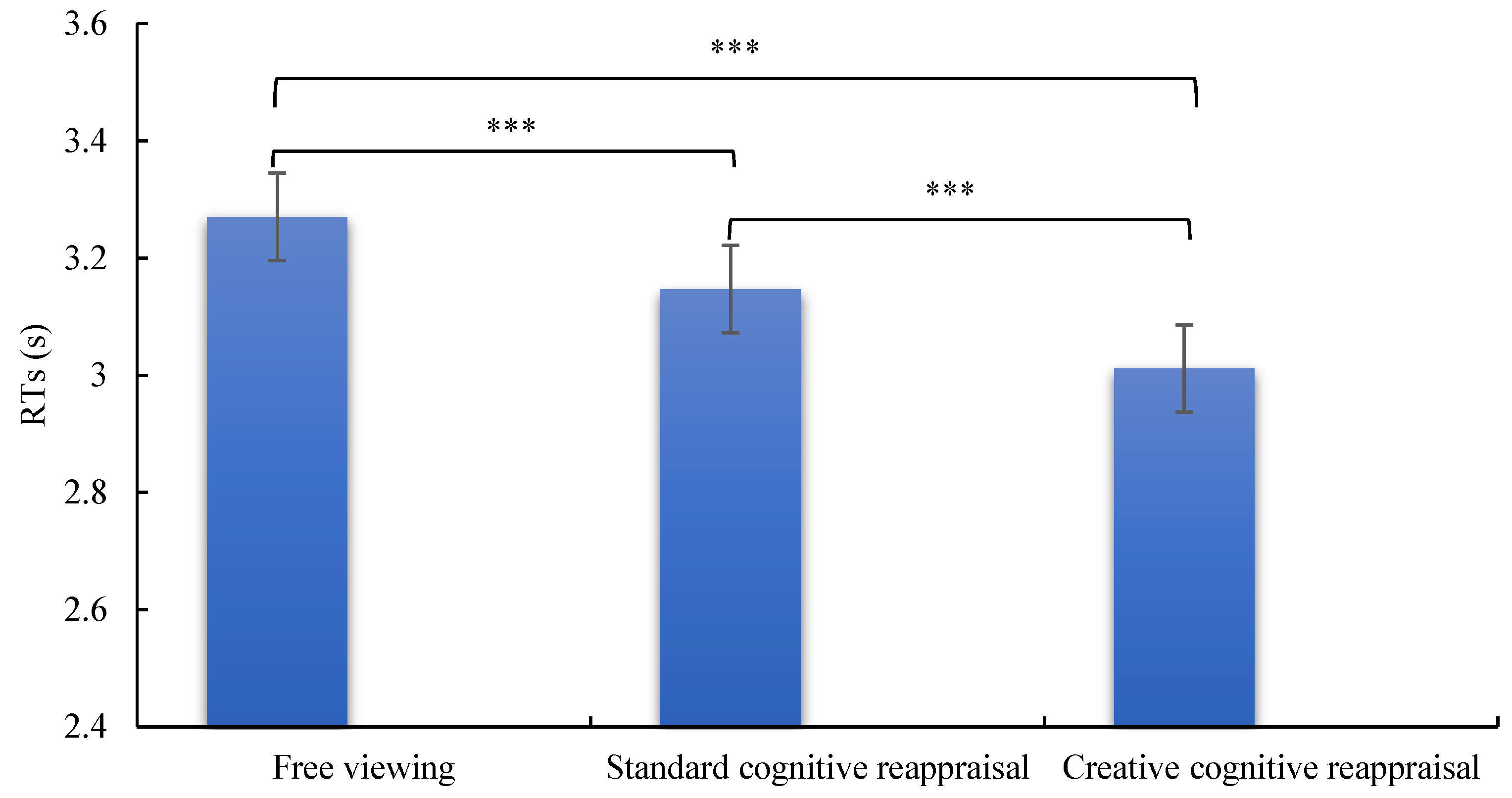
3.2. Accuracy and Reaction Times of Estimation Strategy Execution for HTA and LTA Individuals
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantage Effect of Creative Cognitive Reappraisal in Regulating Negative Emotions
4.2. Cognitive Reassessment of Creativity as a Facilitator of Estimation Strategy Execution in Students with Trait Anxiety
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elwood, L.S.; Wolitzky-Taylor, K.; Olatunji, B.O. Measurement of anxious traits: A contemporary review and synthesis. Anxiety Stress. Coping 2012, 25, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.; Jacobs, G. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (Form Y1–Y2); Consulting Psychogyists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Yue, C.; Cao, F.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y. Self-processing characteristics from first-person and third-person perspectives in individuals with social anxiety disorder: Insights into negative bias. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 1283624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; Yang, M.H.; He, S.; Mao, N.; Dong, X.; Cui, L. Trait anxiety is related to an impaired attention model for controllable threat cues: Evidence from ERPs. Biol. Psychol. 2023, 177, 108508. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Patrick, L. Aging and list-wide modulations of strategy execution: A study in arithmetic. Exp. Aging Res. 2017, 43, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire, P.; Callies, S. Children’s strategies in complex arithmetic. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2009, 103, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, P.; Lecacheur, M. Age-related changes in children’s executive functions and strategy selection: A study in computational estimation. Cognitive Dev. 2011, 26, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, M.; Josef, A.K.; Lemaire, P. Chapter 6—Adaptive Decision Making and Aging. In Aging and Decision Making; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Feng, H.; Si, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Dual-task coordination and task presentation mode influence arithmetic strategy execution in adults: Evidence from computational estimation. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2016, 48, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q. The Mediating Effect of Central Executive Function in Trait Anxiety in Different Difficulties. Master’s Thesis, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Tan, C.; Zhu, C.; Liu, D.; Peng, W. The influence of emotion regulation on estimation strategy execution in individuals with trait anxiety. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, M.W.; Moser, J.S.; Derakshan, N.; Hepsomali, P.; Allen, P. A neurocognitive account of attentional control theory: How does trait anxiety affect the brain’s attentional networks? Cogn. Emot. 2022, 37, 220–237. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, F.; Shu, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Luo, W. Emotional valence modulates arithmetic strategy execution in priming paradigm: An event-related potential study. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Luo, W. Arithmetic performance is modulated by cognitive reappraisal and expression suppression: Evidence from behavioral and ERP findings. Neuropsychologia 2021, 162, 108060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldin, P.R.; McRae, K.; Ramel, W.; Gross, J.J. The neural bases of emotion regulation: Reappraisal and suppression of negative emotion. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Strategy bias in the emotion regulation of high trait anxiety individuals: An investigation of underlying neural signatures using ERPs. Neuropsychology 2019, 33, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Basanovic, J.; Wang, L.; Xiang, S.; Hu, W.; Yi, X. Regulation of negative emotions through positive reappraisal and distancing in high-trait-anxious women. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 267, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolph, D.; Margraf, J. Differential effects of trait-like emotion regulation use and situational emotion regulation ability across the affective and anxiety disorders spectrum: A transdiagnostic examination. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26642. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, B.P. The more anxious, the less flexible? Association of trait anxiety with expressive flexibility and the mediating role of emotion regulation strategies. Curr. Psychol. 2024, 43, 26121–26133. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, K.E.; Moulder, R.G.; Boker, S.M.; Teachman, B.A. Trait social anxiety moderates the relationship between emotion-regulation strategy switching and state anxiety in daily life. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2025, 13, 160–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Wang, Q. The influence of creativity of cognitive reappraisal on negative emotion regulation. Explor. Psychol. 2023, 43, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Sills, L.; Barlow, D.H.; Brown, T.A.; Hofmann, S.G. Effects of suppression and acceptance on emotional responses of individuals with anxiety and mood disorders. Behav. Res. Ther. 2006, 44, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, J.S.; Moran, T.P.; Kneip, C.; Schroder, H.S.; Larson, M.J. Sex moderates the association between symptoms of anxiety, but not obsessive compulsive disorder, and error-monitoring brain activity: A meta-analytic review. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Carthy, T.; Horesh-Reinman, N.; Apter, A.; Edge, M.; Gross, J. Emotional reactivity and cognitive regulation in anxious children. Behav. Res. Ther. 2010, 48, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Guo, T.; Tan, T.; Zhang, W.; Qin, S.; Fan, J.; Luo, J. Superior emotional regulating effects of creative cognitive reappraisal. NeuroImage 2019, 200, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Sang, B. Effect of down regulation strategies in adolescents with trait anxiety: An ERP Study. J. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 43, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Yuan, Z.; Hommel, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gu, H. The impact of spontaneous and induced mood states on problem solving and memory. Think. Ski. Creat. 2019, 32, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Zeng, X.; Xu, B.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Fu, S. The application of artificial intelligence technology in education influences Chinese adolescent’s emotional perception. Curr. Psychol. 2024, 43, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Guo, Q.; Haihambo, N.; Wu, X.; Yu, S.; Luo, J. Revealing the distinct impacts of effectiveness recognition and memory retention on the transfer of creative cognitive reappraisal. Cogn. Emot. 2025, 39, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, T.; Tang, T.; Shi, B.; Luo, J. Role of creativity in the effectiveness of cognitive reappraisal. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1598. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z. Handbook of Commonly Used Psychological Assessment Scale; People’s Military Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Luo, W. Mathematical problem solving is modulated by word priming. PsyCh. J. 2024, 13, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X. Mental representations of arithmetic facts: Evidence from eye movement recordings supports the preferred operand-order-specific representation hypothesis. Exp. Psychol. 2012, 65, 661–674. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W. Establishment of the Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Sentence System of College Students. J. Leshan Norm. Univ. 2023, 38, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Mcrae, K.; Misra, S.; Prasad, A.; Pereira, S.; Gross, J. Bottom-up and top-down emotion generation: Implications for emotion regulation. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2011, 7, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinus, M.; Cao, Y.; Halperin, E.; Coman, A.; Gross, J.J.; Goldenberg, A. Emotion regulation contagion drives reduction in negative intergroup emotions. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, O.; Sher, H.; Aderka, I.M.; Weinbach, N. Does acceptance lead to change? Training in radical acceptance improves implementation of cognitive reappraisal. Behav. Res. Ther. 2023, 164, 104303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franconeri, S.; Alvarez, G.; Cavanagh, P. Flexible cognitive resources: Competitive content maps for attention and memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Creativity | Effectiveness | Appropriateness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Cognitive Reappraisal | 4.40 ± 0.36 | 5.97 ± 0.45 | 6.35 ± 0.43 |
| Creative Cognitive Reappraisal | 6.41 ± 0.33 | 6.20 ± 0.45 | 6.20 ± 0.001 |
| F | 1009.25 *** | 7.63 ** | 3.49 |
| Group | Creative Cognitive Reappraisal | Standard Cognitive Reappraisal | Free Viewing |
|---|---|---|---|
| LTA | 5.75 ± 1.18 | 4.95 ± 1.51 | 3.53 ± 1.45 |
| HTA | 4.78 ± 1.08 | 3.60 ± 1.08 | 3.26 ± 0.76 |
| Group | Emotion Regulation Strategy | Accuracy (%) | Reaction Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LTA | Free Viewing | 98.04 ± 2.00 | 3361.44 ± 760.39 |
| Standard Cognitive Reappraisal | 97.61 ± 2.32 | 3165.96 ± 766.55 | |
| Creative Cognitive Reappraisal | 97.83 ± 2.34 | 3115.34 ± 749.12 | |
| HTA | Free Viewing | 94.40 ± 1.92 | 3261.28 ± 831.31 |
| Standard Cognitive Reappraisal | 94.20 ± 2.22 | 3202.48 ± 766.06 | |
| Creative Cognitive Reappraisal | 94.40 ± 2.25 | 2984.55 ± 749.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Tan, C.; Zhu, C.; Liu, D.; Peng, W. Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Promotes Estimation Strategy Execution in Individuals with Trait Anxiety. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040378
Song H, Tan C, Zhu C, Liu D, Peng W. Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Promotes Estimation Strategy Execution in Individuals with Trait Anxiety. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040378
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Huan, Chenghui Tan, Chuanlin Zhu, Dianzhi Liu, and Wenbo Peng. 2025. "Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Promotes Estimation Strategy Execution in Individuals with Trait Anxiety" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040378
APA StyleSong, H., Tan, C., Zhu, C., Liu, D., & Peng, W. (2025). Creative Cognitive Reappraisal Promotes Estimation Strategy Execution in Individuals with Trait Anxiety. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040378






