Identifying Cardiovascular Risk by Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics Analysis: Translational Biomarker from Mice to Humans †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. ECG Surgery, ECG Recording and Data Processing
2.3. Drugs and Administration
2.4. Experimental Conditions
2.5. Statistical Analyses
| Condition */Drug (Abbreviation) | Function/Drug Action | Dose | Injection Site | n/Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Control (Co) | baseline (including saline and aCSF) | / | none, icv, ip, sc 1 | 23 |
| * Novelty (No) | behavioral stressor | / | / | 8 |
| * Restraint (Re) | behavioral stressor | / | / | 10 |
| * Sleep (Sl) | lowest resting-state condition | / | / | 11 |
| 6-OH-Dopamine (6) | noradrenergic and dopaminergic neurotoxin: peripheral sympathectomy | 200 mg/kg 2 | ip | 17 |
| Anesthesia by ketamine/xylazine (An) | NMDA receptor antagonist/α2 receptor agonist (on heating pad at 37 °C) | 130/13 mg/kg | ip | 11 |
| Atropine (A) | mACh receptor antagonist | 2 mg/kg | ip | 13 |
| Dobutamine (Do) | β1 receptor agonist | 15 mg/kg | ip | 10 |
| DSP-4 (D) | noradrenergic neurotoxin | 100 mg/kg 3 | sc | 6 |
| Hexamethonium (H) | nACh receptor antagonist | 15 mg/kg | ip | 10 |
| Isoproterenol (I) | β receptor agonist | 3 mg/kg | ip | 13 |
| Phenylephrine (P) | α1 receptor agonist (hypertensive) | 15 mg/kg | ip | 8 |
| Robinul (glycopyrrolate) (R) | peripheral mACh receptor antagonist | 0.8 mg/kg | ip | 12 |
| Sodium nitroprusside (Ni) | vasodilator (antihypertensive) | 0.18 mg/kg | ip | 12 |
| Sotalol (S) | peripheral β receptor antagonist | 2 mg/kg | ip | 12 |
| Sotalol + Atropine (SA) | β + mACh receptor antagonists | 2 mg/kg (both) | ip | 11 |
| Zatebradine (Z) | sinus node (HCN channel) inhibitor | 2 mg/kg | ip | 11 |
| Ovine CRF (oC) | preferential CRF1 receptor agonist | 210 ng/mouse | icv | 12 |
| Neuropeptide Y (N) | neuropeptide Y1–5 receptor agonist | 500 ng/mouse | icv | 10 |
| 8-OH-DPAT (8) | 5-HT1A/5-HT7 receptor agonist | 0.5 mg/kg | sc | 8 |
3. Results
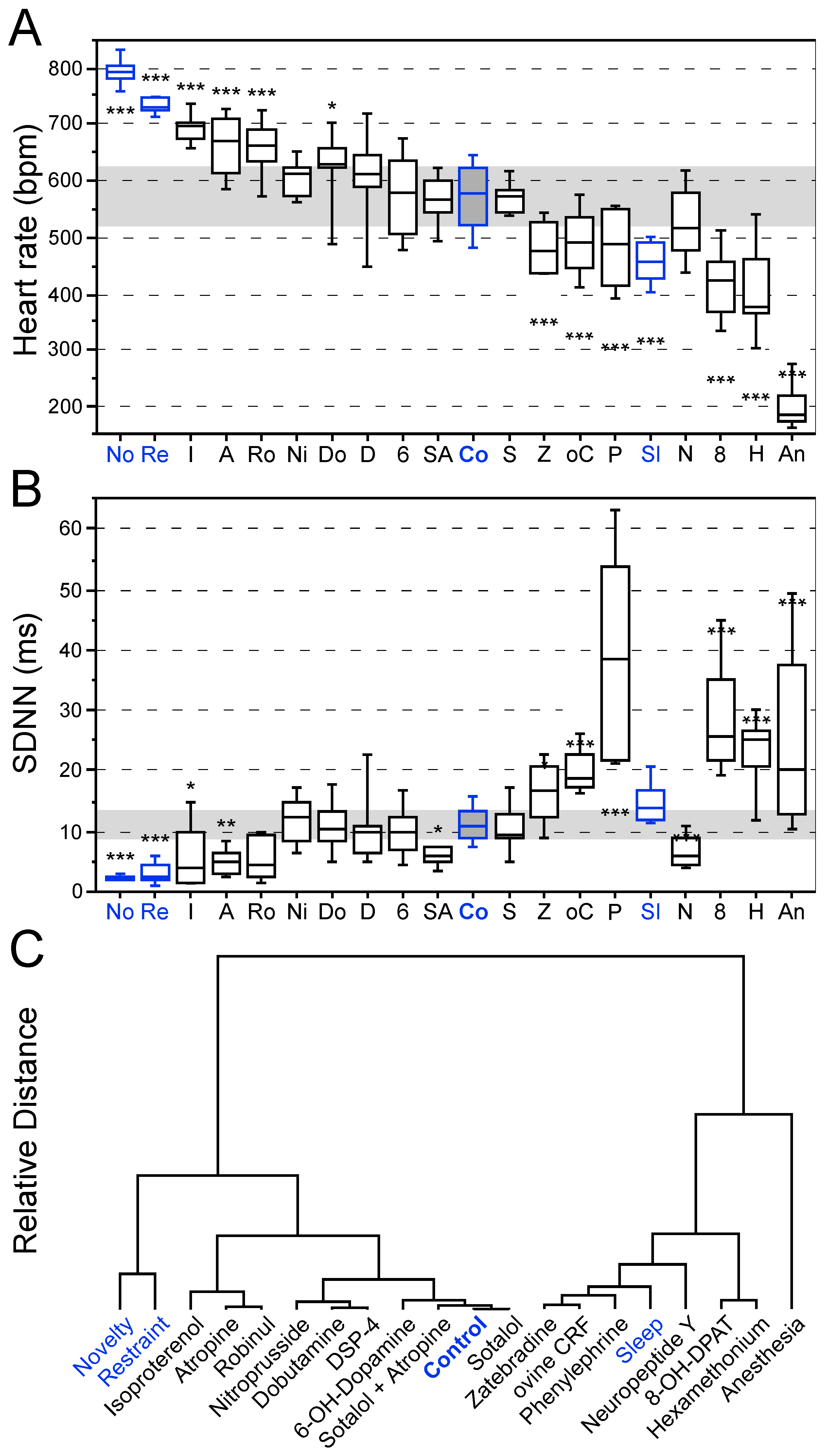
3.1. Effects of Behavioral States and Pharmacological Interventions on Linear Heart Rate Measures
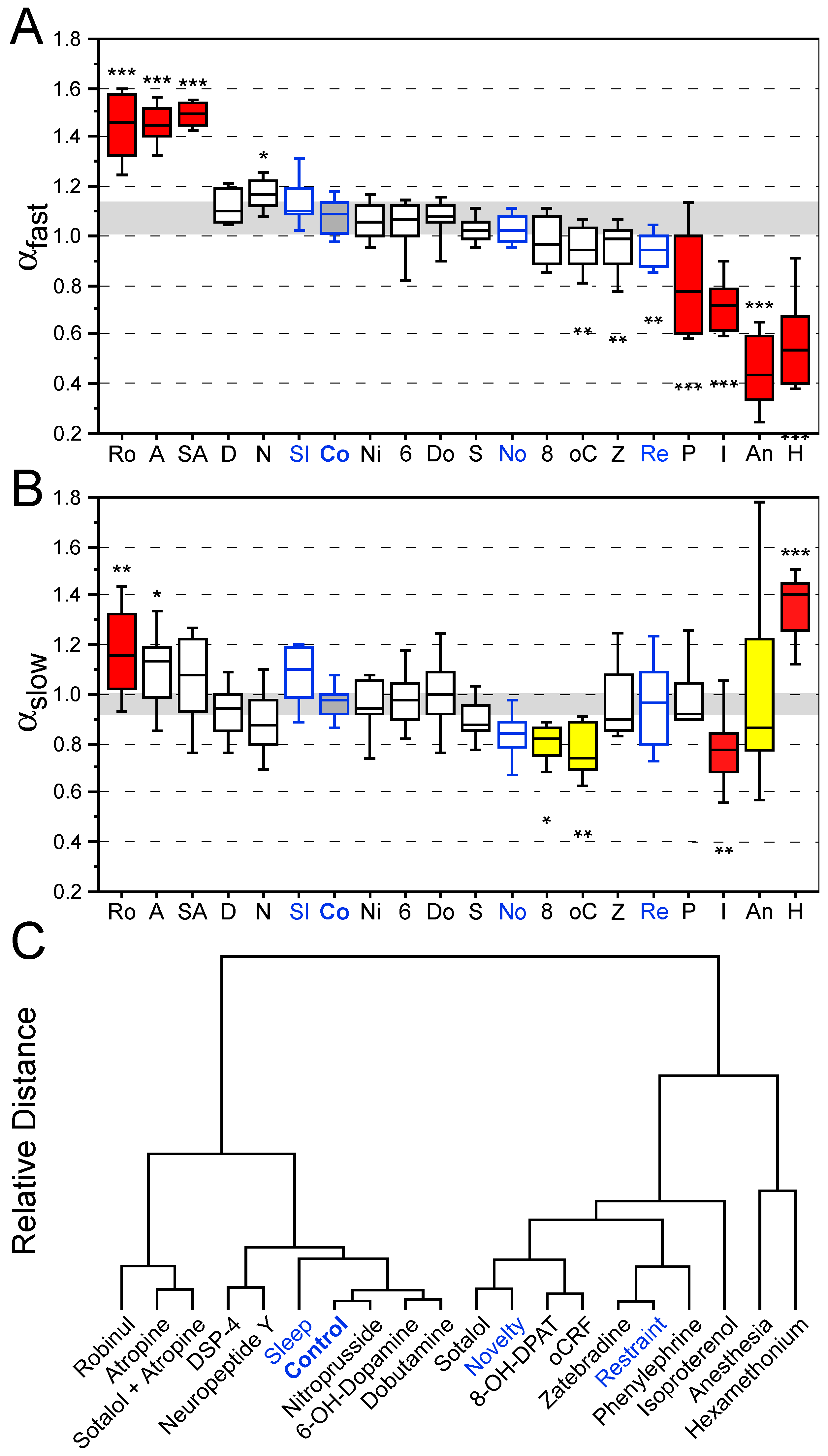
3.2. Effects of Behavioral States and Pharmacological Interventions on Nonlinear Heart Rate Measures
4. Discussion
4.1. Linear Heart Rate Measures in Mice and Autonomic Function
4.2. Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics in Mice to Assess Pathological States
4.3. Heart Rate Dynamics in Humans—Translational Validity
4.4. Brain–Heart Network Underlying Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics in Health and Disease
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Granger, H.J. Circulation: Overall regulation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1972, 34, 13–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leor, J.; Poole, W.K.; Kloner, R.A. Sudden cardiac death triggered by an earthquake. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steptoe, A.; Brydon, L. Emotional triggering of cardiac events. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 33, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvetnansky, R.; Sabban, E.L.; Palkovits, M. Catecholaminergic systems in stress: Structural and molecular genetic approaches. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 536–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, C.A.; Phelps, E.A. Changing fear: The neurocircuitry of emotion regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, S. Seeking a spotless mind: Extinction, deconsolidation, and erasure of fear memory. Neuron 2011, 70, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Horst, G.J.; Hautvast, R.W.; de Jongste, M.J.; Korf, J. Neuroanatomy of cardiac activity-regulating circuitry: A transneuronal retrograde viral labelling study in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B. The central autonomic nervous system: Conscious visceral perception and autonomic pattern generation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 433–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, S.M.; Wilson, J.X.; Guiraudon, C.; Cechetto, D.F. Insular cortex stimulation produces lethal cardiac arrhythmias: A mechanism of sudden cardiac death. Brain Res. 1991, 550, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.M.; Glasscock, E.; Yoo, J.; Chen, T.T.; Klassen, T.L.; Noebels, J.L. Arrhythmia in heart and brain: KCNQ1 mutations link epilepsy and sudden unexplained death. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 2ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Devinsky, O.; Rothermel, M.; Koch, H. Autonomic dysfunction in epilepsy mouse models with implications for SUDEP research. Front. Neurol. 2023, 13, 1040648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jänig, W. Neurocardiology: A neurobiologist’s perspective. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3955–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.J.; Malik, M.; Bigger, T.J.; Breithardt, G.; Cerutti, S.; Cohen, R.J.; Coumel, P.; Fallen, E.L.; Kennedy, H.L.; Kleiger, R.E.; et al. Heart rate variability—Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; McCraty, C.; Zerr, C.L. A healthy heart is not a metronome: An integrative review of the heart’s anatomy and heart rate variability. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Anna, V.; Messina, G.; Cibelli, G.; Monda, V.; Marsala, G.; Ruberto, M.; Biondi, A.; Cascio, O.; Bertozzi, G.; et al. Heart rate variability as predictive factor for sudden cardiac death. Aging 2018, 10, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geus, E.J.C.; Gianaros, P.J.; Brindle, R.C.; Jennings, J.R.; Berntson, G.G. Should heart rate variability be “corrected” for heart rate? Biological, quantitative, and interpretive considerations. Psychophysiology 2019, 56, e13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovote, P.; Meyer, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; von Hörsten, S.; Ögren, S.O.; Spiess, J.; Stiedl, O. Central NPY-mediated alteration of heart rate dynamics in mice during expression of fear conditioned to an auditory cue. Regul. Pept. 2004, 120, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.; Domitrovich, P.; Gottdiener, J. Sometimes higher heart rate variability is not better heart rate variability: Results of graphical and nonlinear analyses. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Mietus, J.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Long-range anticorrelations and non-Gaussian behavior of the heartbeat. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Stiedl, O. Self-affine fractal variability of human heartbeat interval dynamics in health and disease. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 90, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Hager, T.; Misane, I.; Pieneman, A.W.; Jansen, R.F.; Ögren, S.O.; Meyer, M.; Stiedl, O. Central 5-HT1A receptor-mediated modulation of heart rate dynamics and its adjustment by conditioned and unconditioned fear in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. Fractal dynamics in physiology: Alterations with disease and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agorastos, A.; Mansueto, A.C.; Hager, T.; Pappi, E.; Gardikioti, A.; Stiedl, O. Heart rate variability as a translational dynamic biomarker of altered autonomic function in health and psychiatric disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, A.E.; Vandeput, S.; Beckers, F.; Liu, J.; Verheyden, B.; van Huffel, S. Complexity of cardiovascular regulation in small animals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, F.; Verheyden, B.; Ramaekers, D.; Swynghedauw, B.; Aubert, A.E. Effects of autonomic blockade on non-linear cardiovascular variability indices in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos 1995, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. Fractal scaling of heartrate dynamics in health and disease. In Fractals in Biology and Medicine; Losa, G.A., Merlini, D., Nonnenmacher, T.F., Weibel, E.R., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovote, P.; Meyer, M.; Ronnenberg, A.; Ögren, S.O.; Spiess, J.; Stiedl, O. Heart rate dynamics and behavioral responses during acute emotional challenge in corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1-deficient and corticotropin-releasing factor-overexpressing mice. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiedl, O.; Meyer, M.; Jahn, O.; Ögren, S.O.; Spiess, J. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 and central heart rate regulation in mice during expression of conditioned fear. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Stiedl, O. Fractal rigidity by enhanced sympatho-vagal antagonism in heartbeat interval dynamics elicited by central application of corticotropin-releasing factor in mice. J. Math. Biol. 2006, 52, 830–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiedl, O.; Meyer, M. Fractal dynamics in circadian cardiac time series of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype-2 deficient mice. J. Math. Biol. 2003, 47, 169–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkiainen, T.H.; Kuusela, T.A.; Tahvanainen, K.U.O.; Hartikainen, J.E.K.; Tiittanen, P.; Timonen, K.L.; Vanninen, E.J. Comparison of methods for editing of ectopic beats in measurements of short-term non-linear heart rate dynamics. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2007, 27, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agorastos, A.; Boel, J.A.; Heppner, P.S.; Hager, T.; Moeller-Bertram, T.; Haji, U.; Motazedi, A.; Yanagi, M.A.; Baker, D.G.; Stiedl, O. Diminished vagal activity and blunted diurnal variation of heart rate dynamics in posttraumatic stress disorder. Stress 2013, 16, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiedl, O.; Jansen, R.F.; Pieneman, A.W.; Ögren, S.O.; Meyer, M. Assessing aversive emotional states through the heart in mice: Implications for cardiovascular dysregulation in affective disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, B.; Zethof, T.; Pattij, T.; van Boogaert, M.; van Oorschot, R.; Leahy, C.; Oosting, R.; Bouwknecht, A.; Veening, J.; van der Gugten, J.; et al. Stress-induced hyperthermia and anxiety: Pharmacological validation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, A.; Stiedl, O.; Steinlechner, S.; Meyer, M. Cardiac dynamics during daily torpor in the Djungarian hamster, Phodopus sungorus. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R639–R650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, T.; Jansen, R.F.; Pieneman, A.W.; Manivannan, S.N.; Golani, I.; van der Sluis, S.; Smit, A.B.; Verhage, M.; Stiedl, O. Display of individuality in avoidance behavior and risk assessment of inbred mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, K.J.F.; Simonsen, K.L.; McIntyre, L.M. Implementing false discovery rate control: Increasing your power. Oikos 2005, 108, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Baumgarten, P.; Hegemann, N.; Häseli, S.P.; Deubel, S.; Jelleschitz, J.; Höhn, A.; Berndt, N.; Kuebler, W.M.; Grune, J.; et al. Comparative phenotyping of C57BL/6J substrains reveals distinctive patterns of cardiac aging. GeroScience 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.S.; De Ruiter, S.; Westover, T.; Somarelli, J.A.; Blawas, A.M.; Dayanidhi, D.L.; Singh, A.; Steves, B.; Driesinga, S.; Halsey, L.G.; et al. Allometric scaling of metabolic rate and cardiorespiratory variables in aquatic and terrestrial mammals. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uechi, M.; Asai, K.; Osaka, M.; Smith, A.; Sato, N.; Wagner, T.E.; Ishikawa, Y.; Hayakawa, H.; Vatner, D.E.; Shannon, R.P.; et al. Depressed heart rate variability and arterial baroreflex in conscious transgenic mice with overexpression of cardiac Gsα. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, A.; Faulhaber, J.; Ehmke, H. Autonomic cardiovascular control in conscious mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R2214–R2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrmann, J.; Hammer, P.E.; Maguire, C.T.; Wakimoto, H.; Triedman, J.K.; Berul, C.I. Phenotypic screening for heart rate variability in the mouse. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H733–H740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiedl, O.; Tovote, P.; Ögren, S.O.; Meyer, M. Behavioral and autonomic dynamics during contextual fear conditioning in mice. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2004, 115, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.C.; Mantas, I.; Stroth, N.; Hager, T.; Pereira, M.; Jiang, H.; Jabre, S.; Paslawski, W.; Stiedl, O.; Svenningsson, P. P11 deficiency increases stress reactivity along with HPA axis and autonomic hyperresponsiveness. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, H.; Mitsubayashi, H.; Miao, T.; Shimizu, T. Short and long term analysis of heart rate variations in spontaneously hypertensive rats: Effects of DSP-4 administration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, S203–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, V.; Luft, F.C. Exercising restraint in measuring blood pressure in conscious mice. Hypertension 2003, 41, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bogaert, M.J.V.; Groenink, L.; Oosting, R.S.; Westphal, K.G.C.; Van Der Gugten, J.; Olivier, B. Mouse strain differences in autonomic responses to stress. Genes Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voikar, V.; Gaburro, S. Three pillars of automated home-cage phenotyping of mice: Novel findings, refinement, and reproducibility based on literature and experience. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 575434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorastos, A.; Kellner, M.; Stiedl, O.; Muhtz, C.; Becktepe, J.S.; Wiedemann, K.; Demiralay, C. The 5-HTTLPR genotype modulates heart rate variability and its adjustment by pharmacological panic challenge in healthy men. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 50, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorastos, A.; Kellner, M.; Stiedl, O.; Muhtz, C.; Wiedemann, K.; Demiralay, C. Blunted autonomic reactivity to pharmacological panic challenge under long-term escitalopram treatment in healthy men. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, pyu055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Buwalda, B.; de Boer, S.F.; Flügge, G.; Korte, M.; Meerlo, P.; Murison, R.; Olivier, B.; Palanza, P.; et al. Stress revisited: A critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, A.H.; Cloninger, C.R.; McCraty, R. Personality and heart rate variability: Exploring pathways from personality to cardiac coherence and health. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2013, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wei, L.; Kuang, J.; Tsien, J.Z.; Zhao, F. Heart rate and heart rate variability assessment identifies individual differences in fear response magnitudes to earthquake, free fall, and air puff in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntson, G.G.; Sarter, M.; Cacioppo, J.T. Anxiety and the cardiovascular reactivity: The basal forebrain cholinergic link. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 94, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penzel, T.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Grote, L.; Peter, J.-H.; Bunde, A. Comparison of detrended fluctuation analysis and spectral analysis for heart rate variability in sleep and sleep apnea. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Seymour, R.S. Allometric scaling of mammalian metabolism. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Späni, D.; Arras, M.; König, B.; Rülicke, T. Higher heart rate of laboratory mice housed individually vs in pairs. Lab Anim. 2003, 37, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschneider, D.P.; Scremin, O.U.; Chialvo, D.R.; Chen, K.; Shih, J.C. Heart rate dynamics in monoamine oxidase-A- and -B-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H1751–H1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieber, J.; Wieland, K.; Stöckl, G.; Ludwig, A.; Hofmann, F. Bradycardic and proarrhythmic properties of sinus node inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, P.K.; Kleiger, R.E. Insights from the study of heart rate variability. Annu. Rev. Med. 1999, 50, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huikuri, H.V.; Stein, P.K. Heart rate variability in risk stratification of cardiac patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 56, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, T.E.; Holst, S.; Stan, T.L.; Hager, T.; Sjögren, B.; Ögren, S.O.; Svenningsson, P.; Stiedl, O. 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptor crosstalk in the regulation of emotional memory: Implications for effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareba, W. Drug induced QT prolongation. Cardiol. J. 2007, 14, 523–533. [Google Scholar]
- Unterecker, S.; Warrings, B.; Deckert, J.; Pfuhlmann, B. Correlation of QTc interval prolongation and serum level of citalopram after intoxication—A case report. Pharmacopsychiatry 2012, 45, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harteveld, L.M.; Nederend, I.; ten Harkel, A.D.J.; Schutte, N.M.; de Rooij, S.R.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Oldenhof, H.; Popma, A.; Jansen, L.M.C.; Suurland, J.; et al. Maturation of the cardiac autonomic nervous system activity in children and adolescents. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e017405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Marconi, C.; Ferretti, G.; Fiocchi, R.; Cerretelli, P.; Skinner, J.E. Heart rate variability in the human transplanted heart: Nonlinear dynamics and QT vs RR alterations during exercise suggest a return of neurocardiac regulation in long-term recovery. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 1996, 31, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Vanhaecke, J.; Aubert, A.E.; Fagard, R.H. Heart rate variability after heart transplantation: A 10-year longitudinal follow-up study. J. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Kato, K.; Hughson, R.L. On the fractal nature of heart rate variability in humans: Effects of vagal blockade. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1995, 269, R830–R837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumati, S.; Paulus, M.P.; Northoff, G. Out-of-Step: Brain-Heart Desynchronization in Anxiety Disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balocchi, R.; Michelassi, C.; Varanini, M.; Barbi, M.; Chillemi, S.; Di Garbo, A.; Raimondi, G.; Legramante, J.M. Heartbeat scaling properties in intact and denervated rabbits. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 2002, 1, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, P.C.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Goldberger, A.L.; Havlin, S.; Rosenblum, M.G.; Struzik, Z.R.; Stanley, H.E. Multifractality in human heartbeat dynamics. Nature 1999, 399, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasch, M.G.; Herry, C.L.; Niu, Y.; Giussani, D.A. First Evidence That Intrinsic Fetal Heart Rate Variability Exists and Is Affected by Hypoxic Pregnancy. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Wahbi, K. CNS-disease affecting the heart: Brain–heart disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 345, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.; Benton, D. We should be using nonlinear indices when relating heart-rate dynamics to cognition and mood. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Lane, R.D. The role of vagal function in the risk for cardiovascular disease and mortality. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Yamamoto, S.S.; Brosschot, J.F. The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 141, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.E.; Edmondson, D.; Kronish, I.M. State of the art review: Depression, stress, anxiety, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Honig, A.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Schoevers, R.A.; van Eijk, J.T.M.; van Tilburg, W. Depression and cardiac mortality. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2001, 58, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Schwerdtfeger, A. Autonomic dysfunction in posttraumatic stress disorder indexed by heart rate variability: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Winters, B.R.; Koshman, Y.E.; Authier, S.; Foley, C.M.; Hayes, E.S.; Curtis, M.J. Innovative approaches to cardiovascular safety pharmacology assessment. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2024, 128, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wujtewicz, M.; Owczuk, R. Heart rate variability in anaesthesiology—Narrative review. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2023, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.-Y.; Shieh, J.-S.; Yeh, J.-R.; Fan, S.-Z. Fractal Properties of Heart Rate Dynamics: A new biomarker for anesthesia—Biphasic changes in general anesthesia and decrease in spinal anesthesia. Sensors 2022, 22, 9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, A.; de Toffol, B.; Pallix, M.; Breard, G.; Babuty, D. Cardiac arrest: It’s all in the head. Lancet 2008, 371, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryvlin, P.; Nashef, L.; Lhatoo, S.D.; Bateman, L.M.; Bird, J.; Bleasel, A.; Boon, P.; Crespel, A.; Dworetzky, B.A.; Høgenhaven, H.; et al. Incidence and mechanisms of cardiorespiratory arrests in epilepsy monitoring units (MORTEMUS): A retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deisseroth, K. Optogenetics: 10 years of microbial opsins in neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Brosschot, J.F. Psychosomatics and psychopathology: Looking up and down from the brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsel, A.; von Känel, R. The ventro-medial prefrontal cortex: A major link between the autonomic nervous system, regulation of emotion, and stress reactivity? BioPsychoSocial Med. 2008, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, B. Corticolimbic regulation of cardiovascular responses to stress. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 172, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. The central autonomic network: Functional organization, dysfunction, and perspective. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1993, 68, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstenpointner, J.; Elman, I.; Freeman, R.; Borsook, D. The omnipresence of autonomic modulation in health and disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 210, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

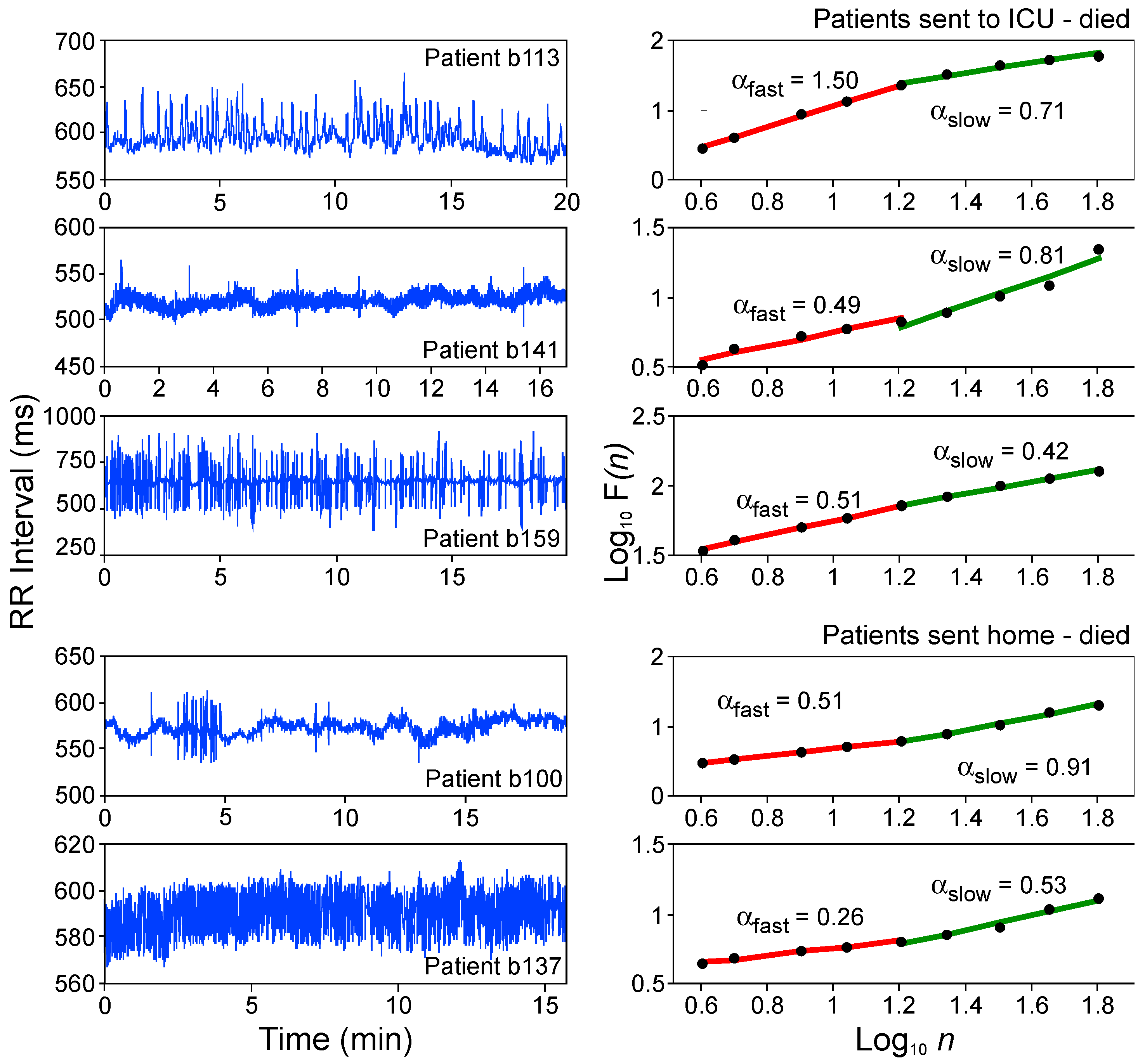
| Condition/Treatment (Remarks) | n/Group | DFA α 2 ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy adults (unsteady state, daytime) | 17 | 1.01 ± 0.11 | |
| Healthy adults (steady state, 24 h) | 14 | 0.99 ± 0.07 | |
| Healthy adults (unsteady state, 24 h) | 9 | 0.99 ± 0.04 | |
| Healthy adults (4 h daytime) | 9 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | |
| Healthy adults (4 h nighttime) | 9 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | |
| Healthy children (before maturation) | 9 | 0.75 ± 0.08 | |
| Congestive heart failure (unsteady state) | 20 | 1.24 ± 0.16 | |
| Heart transplantation (steady state, supine) | <2 years after transplantation | 13 | 1.48 ± 0.11 |
| >2 years after transplantation | 17 | 1.02 ± 0.16 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hager, T.; Agorastos, A.; Ögren, S.O.; Stiedl, O. Identifying Cardiovascular Risk by Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics Analysis: Translational Biomarker from Mice to Humans. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030306
Hager T, Agorastos A, Ögren SO, Stiedl O. Identifying Cardiovascular Risk by Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics Analysis: Translational Biomarker from Mice to Humans. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(3):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030306
Chicago/Turabian StyleHager, Torben, Agorastos Agorastos, Sven Ove Ögren, and Oliver Stiedl. 2025. "Identifying Cardiovascular Risk by Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics Analysis: Translational Biomarker from Mice to Humans" Brain Sciences 15, no. 3: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030306
APA StyleHager, T., Agorastos, A., Ögren, S. O., & Stiedl, O. (2025). Identifying Cardiovascular Risk by Nonlinear Heart Rate Dynamics Analysis: Translational Biomarker from Mice to Humans. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030306









