Enhancing Grip Strength and Manual Dexterity in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial of Mirror Visual Feedback vs. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
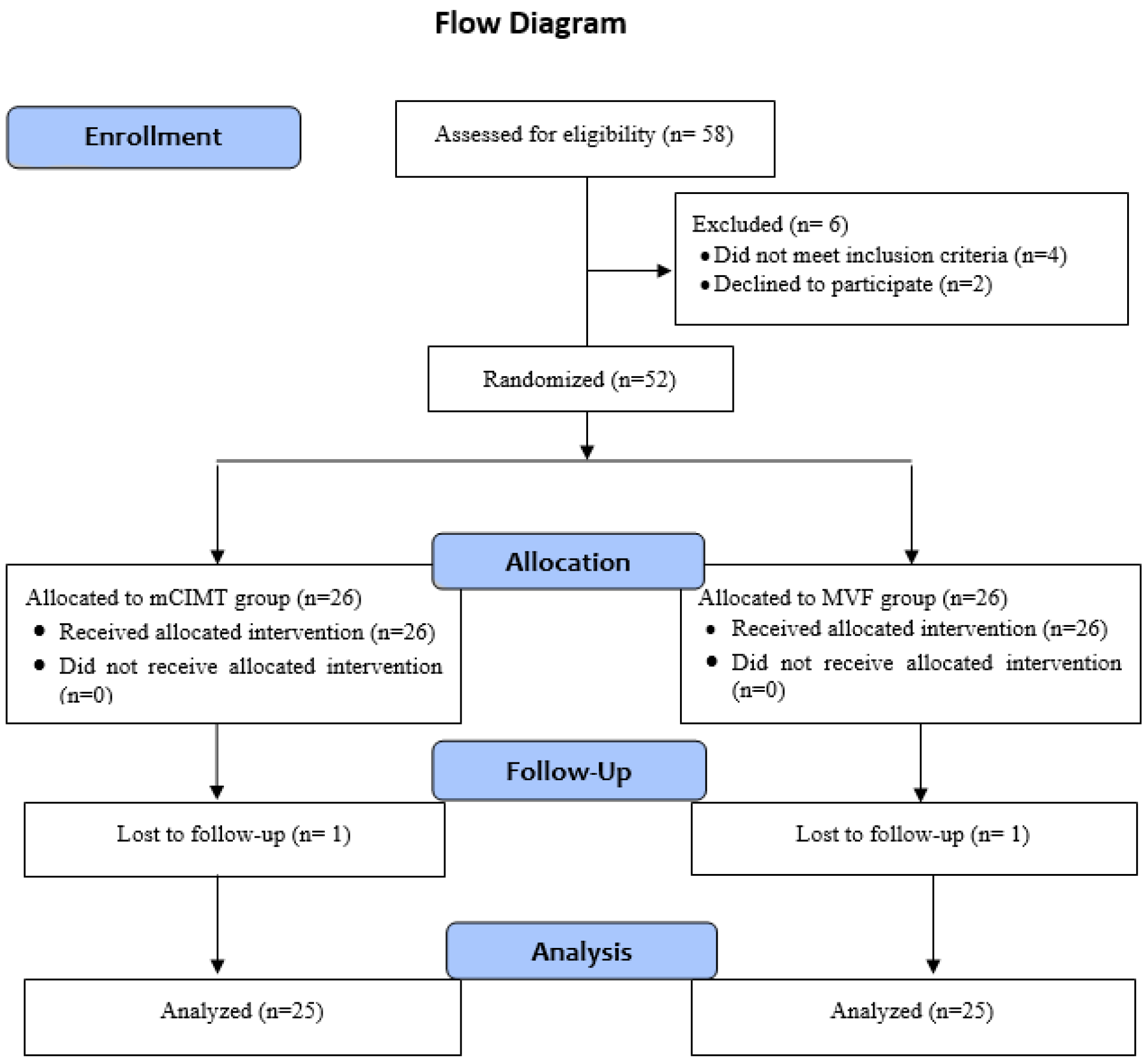
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Sample Size
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.3.1. Box and Block Test
2.3.2. Handheld Dynamometer
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Intervention Outcomes
3.2.1. Within-Group Comparisons
3.2.2. Between-Group Comparisons
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaniz, M.L.; Galit, E.; Necesito, C.I.; Rosario, E.R. Hand Strength, Handwriting, and Functional Skills in Children with Autism. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2015, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vaidya, S.M.; Nariya, D. Handgrip Strength as a Predictor of Muscular Strength and Endurance: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.M.; Hung, Y.; Ed, D.; Brandao, M.; Ferre, C.L.; Kuo, H.; Friel, K.; Petra, E.; Chinnan, A.; Charles, J.R. Bimanual Training and Constraint- Induced Movement Therapy in Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himpens, E.; Van den Broeck, C.; Oostra, A.; Calders, P.V.P. Review Prevalence, Type, Distribution, and Severity of Cerebral Palsy in Relation to Gestational Age: A Meta-Analytic Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, E. Epidemiology of the Cerebral Palsies. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 2010, 41, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.P.; Pearse, J.; Kelly, S.; Wisher, V.; Kisler, J. Early Intervention to Improve Hand Function in Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Front. Neurol. 2015, 5, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzamfar, P.; Heirani, A.; Sedighi, M. The Effect of Motor Training in Mirror Therapy on Gross Motor Skills of the Affected Hand in Children With Hemiplegia. Iran. Rehabil. J. 2017, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasschaert, V.F.P.; Vriezekolk, J.E.; Aarts, P.B.M.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Van den Ende, C.H.M. Interventions to Improve Upper Limb Function for Children with Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. CHILD Neurol. 2019, 61, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, H.; Mehrholz, J.; Pohl, M.; Behrens, J.D.C. Mirror Therapy for Improving Motor Function After Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Baek, S.; Park, S. Systematic Review of The Effects of Mirror Therapy in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Narimani, A.; Kalantari, M.; Dalvand, H.T.S. Effect of Mirror Therapy on Dexterity and Hand Grasp in Children Aged 9-14 Years with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 13, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palomo-carrión, R.; Zuil-escobar, J.C.; Cabrera-guerra, M.; Barreda-martínez, P.; Martínez-cepa, C.B. erapia En Espejo y de Observación de La Acción En Niños Con Parálisis Cerebral Espástica Unilateral: Estudio de Viabilidad [Mirror and Action Observation Therapy in Children with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Feasibility Study]. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 75, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, E.; Miller, N.E.; Novack, T.A.; Cook, E.W., 3rd; Fleming, W.C.; Nepomuceno, C.S.; Connell, J.S.C.J. Technique to Improve Chronic Motor Deficit after Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1993, 74, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Preetha, K.; Vimala, U.K.M. A Study to Compare Task-Based Mirror Therapy Versus Constraint Induced Movement Therapy for Hand Function In Hemiplegic Subjects. Biomedicine 2021, 41, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.; Ada, L. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Improves Upper Limb Activity and Participation in Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. J. Physiother. 2016, 62, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Shierk, A.; Alfonso, A.J.; Yeatts, P.; DeJong, T.L.; Clegg, N.J.; Baldwin, D.; Delgado, M.R. Improved Hand Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy with Repeat Doses of Group Based Hybrid Pediatric Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Disabilities 2022, 2, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.J.; Sisto, S.; Levine, P.; Mcgrath, R.E.; Sj, A.P.; Sa, S.; Levine, P.; Re, M. Efficacy of Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy in Chronic Stroke: A Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Madbouly; Khaled, A.; Olama, T.E.I.; Omar, M.S.E.F. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Versus Mirror Therapy on Affected Hand Functions in Hemiparetic Children. Ann. Clin. Anal. Med. 2021, 12, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, D.; Rajkumar, J.S. A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Mirror Therapy and Constrained Induced Movement Therapy in Cerebral Palsy. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pope, S.; Tyler, D. Effectiveness of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy on Upper- Extremity Function in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-kafy, E.M.A.B.D.; Elshemy, S.A.; Alghamdi, M.S. Effect of Constraint-Induced Therapy on Upper Limb Functions: A Randomized Control Trial. Scand. J. Occup. Ther. 2014, 21, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; He, L.; Mai, J.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y. Muscle Recruitment and Coordination following Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy with Electrical Stimulation on Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.J.; Chen, H.L.; Shieh, J.Y.W.T. Measurement Properties Of The Box and Block Test in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, R.; Ebner-Karestinos, D.; Paradis, J.; Saussez, G.; Friel, K.M.; Gordon, A.M.B.Y. Reliability and Responsiveness of the Jebsen-Taylor Test of Hand Function and the Box and Block Test for children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, K.; Janssen-Potten, Y.; Gordon, A.M.; Speth, L.; Smeets, R.R.E. Reliability of Maximum Isometric Arm, Grip and Pinch Strength Measurements in Children (7–12 years) with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Beld, W.A.; van der Sanden, G.A.; Sengers, R.C.; Verbeek, A.L.G.F. Validity and Reproducibility of Hand-Held Dynamometry in Children Aged 4 á 11 Years. J. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 38, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmaa, A.; Abo Nour Muhammad, G.; Saleh, E.H.E. Impact of Combining Mirror Therapy and Habit on Hand Grip Strength in Children with Hemiparesis. Int. J. Physiother 2016, 3, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Kang, L. Improvement of Upper Extremity Motor Control and Function After Home-Based Constraint Induced Therapy in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: Immediate and Long-Term Effects. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.K.; Yardimci, B.N.; Sahin, S.; Orhan, C.; Livanelioglu, A.S.A. Combined Effects of Mirror Therapy and Exercises on the Upper Extremities in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2020, 23, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, I.-Y.; Ryu, J.-S.; Pyun, S.-B.; Yoo, S.-D.; Song, W.-H.; Park, M.-J. Efficacy of Forced-Use Therapy in Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.C.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Gordon, A.M.; Feys, H.; Klingels, K.; Aarts, P.B.; Rameckers, E.; Autti-Rämö, I.; Hoare, B. Guidelines for Future Research in Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: An Expert Consensus. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, S.J.; Boe, S.; Levine, P. What Are the “ingredients” of Modified Constraint-Induced Therapy ? An Evidence-Based Review, Recipe, and Recommendations. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, A.R.; Amini, M. The effects of Constraint Induced Movement Therapy on Functions of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 12, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thieme, H.; Morkisch, N.; Mehrholz, J.; Pohl, M.; Behrens, J.; Borgetto, B.; Dohle, C. Mirror Therapy for Improving Motor Function After Stroke (Review). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, CD008449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuzer, G.; Selles, R.; Sezer, N.; Sütbeyaz, S.; Bussmann, J.B.; Köseoğlu, F.; Atay, M.B.; Stam, H.J. Mirror Therapy Improves Hand Function in Subacute Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gygax, M.J.; Schneider, P.N.C. Mirror Therapy in Children with Hemiplegia: A Pilot Study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsepaee, M.I.; Elhadidy, E.I.; Emara, H.A.; Nawar, E.A. Effect of Mirror Visual Feedback on Hand Functions in Children with Hemiparesis. Int. J. Physiother. 2016, 3, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchez, R.; Jequier Gygax, M.; Roches, S.; Fluss, J.; Jacquier, D.; Ballabeni, P.; Grunt, S.; Newman, C.J. Mirror Therapy in Children with Hemiparesis: A Randomized Observer-Blinded Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Gulati, S.; Kabra, M.; Pal, U. Efficacy Of Modified Constraint Induced Movement Therapy in Improving Upper Limb Function in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BRAIN Dev. 2013, 35, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhat, W.; Ahmed, U.; Asghar, M.; Hanif, K.; Bibi, S. Effects of Expanded Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy on Hand Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Heal. J. Physiother. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, S.L.; DeLuca, S.C.; Stevenson, R.D.; Conaway, M.; Darragh, A.R.L.W.C. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2020033878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.; Connelly, A.; Neville, B.; Vargha-Khadem, F.; Jessop, N.; Murphy, T.; Ganesan, V. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy after Childhood Stroke. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, C.; Taub, E.; Davis, D.; Rickards, T.; Gauthier, L.V.; Griffin, A.U.G. Structural Neuroplastic Change After Constraint- Induced Movement Therapy in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1664–e1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusz, P.J.; Key, A.P.; Gogliotti, S.; Pearson, J.; Auld, M.L.; Murray, M.M.M.N. Somatosensory Plasticity in Pediatric Cerebral Palsy following Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Neural Plast. 2018, 1891978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilderley, A.J.; Wright, F.V.; Taylor, M.J.; Chen, J.L.F.D. Functional Neuroplasticity and Motor Skill Change Following Gross Motor Interventions for Children With Diplegic Cerebral Palsy. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2023, 37, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.E.; Macdonald, J.R.; Gnip, C. Counting Repetitions: An Observational Study of Outpatient Therapy for People with Hemiparesis. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2007, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.J.; Levine, P.; Leonard, A.C. Modified Constraint-Induced Therapy in Acute Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2005, 19, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| mCIMT Group, n = 25 | MVF Group, n = 25 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean ± SD a | 6.82 ± 1.71 | 7.46 ± 1.52 |
| Height, cm, mean ± SD a | 132.5 ± 25.82 | 133.23 ± 26.64 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD a | 33.53 ± 6.37 | 35.17 ± 7.54 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean ± SD a | 17.82 ± 4.42 | 19.15 ± 3.31 |
| Boys/girls b | 14/11 | 13/12 |
| Hypertonia, 1/1+ b | 13/12 | 12/13 |
| MACS level, II/III b | 12/13 | 14/11 |
| Age group, years 5–7/7–9 b | 15/10 | 17/8 |
| Variables | mCIMT Group (n = 25) (M ± SD) | MVF Group (n = 25) (M ± SD) | p Value (Between Groups) | Cohen’s d (Effect Size) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Dexterity (N. of Blocks) | ||||
| Baseline | 12.64 ± 3.44 | 12.19 ± 3.69 | 0.672 | |
| Post-treatment | 18.97 ± 4.11 | 16.24 ± 3.1 | 0.014 * | 0.75 |
| p value within group | 0.001 * | 0.002 * | ||
| MD (95% CI) | 6.330 (3.593–9.066) | 4.05 (1.589–6.510) | ||
| Effect size | 1.26 | 0.98 | ||
| Maximum Isometric Strength of Hand Muscles (kg) | ||||
| Baseline | 6.53 ± 1.40 | 6.9 ± 1.40 | 0.375 | |
| Post-treatment | 9.13 ± 1.68 | 7.93 ± 1.53 | 0.017 * | 0.79 |
| p value within group | 0.001 * | 0.012 * | ||
| MD (95% CI) | 2.6 (1.483–3.716) | 1.83 (0.771–2.888) | ||
| Effect size | 1.31 | 0.85 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel Ghafar, M.A.; Abdelraouf, O.R.; Alkhamees, N.H.; Mohamed, M.E.; Harraz, E.M.; Seyam, M.K.; Ibrahim, Z.M.; Alnamnakani, A.; Elborady, A.A.; Radwan, R.E. Enhancing Grip Strength and Manual Dexterity in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial of Mirror Visual Feedback vs. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030305
Abdel Ghafar MA, Abdelraouf OR, Alkhamees NH, Mohamed ME, Harraz EM, Seyam MK, Ibrahim ZM, Alnamnakani A, Elborady AA, Radwan RE. Enhancing Grip Strength and Manual Dexterity in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial of Mirror Visual Feedback vs. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(3):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030305
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel Ghafar, Mohamed A., Osama R. Abdelraouf, Nouf H. Alkhamees, Mariam E. Mohamed, Eman M. Harraz, Mohamed K. Seyam, Zizi M. Ibrahim, Amani Alnamnakani, Amal A. Elborady, and Rafik E. Radwan. 2025. "Enhancing Grip Strength and Manual Dexterity in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial of Mirror Visual Feedback vs. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy" Brain Sciences 15, no. 3: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030305
APA StyleAbdel Ghafar, M. A., Abdelraouf, O. R., Alkhamees, N. H., Mohamed, M. E., Harraz, E. M., Seyam, M. K., Ibrahim, Z. M., Alnamnakani, A., Elborady, A. A., & Radwan, R. E. (2025). Enhancing Grip Strength and Manual Dexterity in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial of Mirror Visual Feedback vs. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030305








