Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Epilepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neuroanatomy and Physiology of the Vagus Nerve
3. Mechanisms of Action
3.1. Fiber-Specificity
3.2. Neural Pathways and Neurochemical Mechanisms
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Cytokine Modulation Mechanisms
4. Measuring and Describing Treatment Response
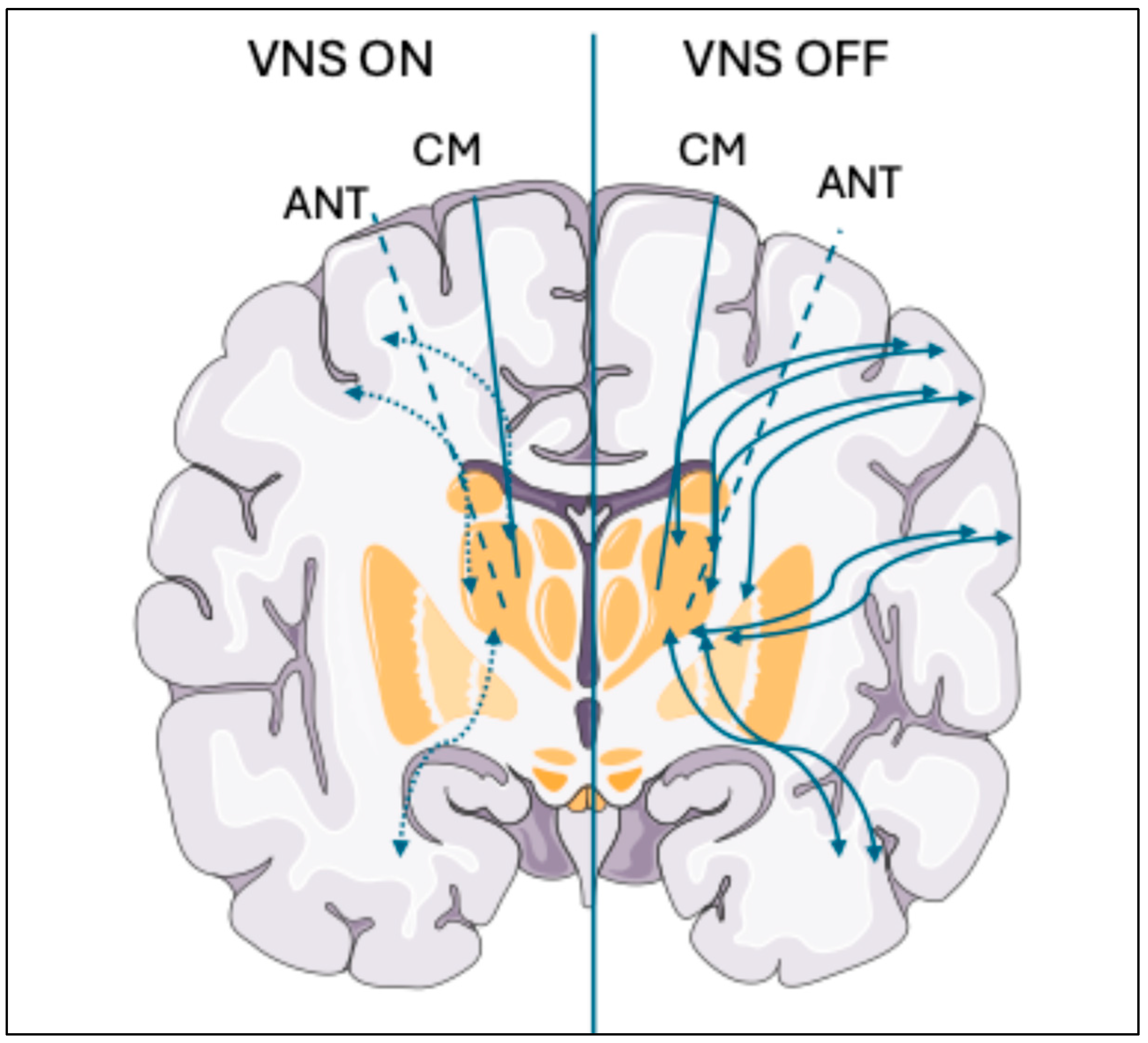
4.1. Functional Connectivity as a Descriptor of Treatment Response
4.2. Imaging-Based Descriptors of Treatment Response
5. Advances in VNS Methods
5.1. Current Clinical Outcomes
5.2. Technological Innovation and Parameter Optimization
5.3. Future Research Directions and Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanner, A.M. Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Generalized Epilepsy?…Show Me the Evidence! Epilepsy Curr. 2008, 8, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, N.; Akwayena, E.; Vodovotz, L.; Sharma, N.; Jeong, J.-H.; White, G.E.; Abel, T.J. Comparison of Traditional and Closed Loop Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Treatment of Pediatric Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Propensity-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study. Seizure 2022, 94, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reardon, J.P.; Cristancho, P.; Peshek, A.D. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) and Treatment of Depression: To the Brainstem and Beyond. Psychiatry 2006, 3, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Abdennadher, M.; Rohatgi, P.; Saxena, A. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy in Epilepsy: An Overview of Technical and Surgical Method, Patient Selection, and Treatment Outcomes. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, C.C.R.; Wrigley, B.; Greene, J.R.T. Re-examination of the Medullary Rootlets of the Accessory and Vagus Nerves. Clin. Anat. 2005, 20, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuys, R.; Jan Voogd, J.; Huijzen, C. Telencephalon: Neocortex. In The Human Central Nervous System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 491–679. [Google Scholar]
- Traylor, K.S.; Branstetter, B.F. Cranial Nerve Anatomy. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2022, 32, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, P.J.; Johnson, T.A.; Massari, V.J. Can Neurons in the Nucleus Ambiguus Selectively Regulate Cardiac Rate and Atrio-Ventricular Conduction? J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1996, 57, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patros, M.; Sivathamboo, S.; Simpson, H.D.; O’Brien, T.J.; Macefield, V.G. The physiology, anatomy and stimulation of the vagus nerve in epilepsy. J. Physiol. 2025, 603, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Zicca, A.; Barba, C.; Guerrini, R.; Genitori, L. Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Surgical Technique of Implantation and Revision and Related Morbidity. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffa, D.H.; Touma, L.; El Meskine, T.; Bouthillier, A.; Nguyen, D.K. Learnings from 30 Years of Reported Efficacy and Safety of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) for Epilepsy Treatment: A Critical Review. Seizure 2020, 83, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.; García Navarrete, E.; Pascual, J.M.; Carrasco, R.; Sánchez, A.; Shakur, S.F.; Pastor, J.; Sola, R.G. Treatment of refractory epilepsy in adult patients with right-sided vagus nerve stimulation. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevizol, A.; Barros, M.D.; Liquidato, B.; Cordeiro, Q.; Shiozawa, P. Vagus nerve stimulation in neuropsychiatry: Targeting anatomy-based stimulation sites. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 51, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.S.; Chang, P.H.; Jang, S.H. The ascending reticular activating system from pontine reticular formation to the thalamus in the human brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Neuhuber, W.L. Functional and chemical anatomy of the afferent vagal system. Auton. Neurosci. 2000, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, P.W.; Fisch, B.J.; Carey, M.; Butterbaugh, G.; Happel, L.; Tardo, C. The Effect of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Epileptiform Activity Recorded from Hippocampal Depth Electrodes. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeroff, C.B.; Mayberg, H.S.; Krahl, S.E.; McNamara, J.; Frazer, A.; Henry, T.R.; George, M.S.; Charney, D.S.; Brannan, S.K. VNS Therapy in Treatment-Resistant Depression: Clinical Evidence and Putative Neurobiological Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, N.; Song, W.; Toth, V.; Vardhan, A.; Levy, T.; Tomaio, J.; Qanud, K.; Mughrabi, I.; Chang, Y.-C.; Rob, M.; et al. Organ- and Function-Specific Anatomical Organization of Vagal Fibers Supports Fascicular Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 484–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakenborg, N.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Verlinden, T.J.M.; Wolthuis, A.M.; D’Hoore, A.; Farré, R.; Herijgers, P.; Matteoli, G.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Comparison between the Cervical and Abdominal Vagus Nerves in Mice, Pigs, and Humans. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, D.M.; Woodbury, J.W. Effects of Vagal Stimulation on Experimentally Induced Seizures in Rats. Epilepsia 1990, 31, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmers, S.L.; Begnaud, J.; Cowley, A.; Corwin, H.M.; Edwards, J.C.; Holder, D.L.; Kostov, H.; Larsson, P.G.; Levisohn, P.M.; De Menezes, M.S.; et al. Application of a Computational Model of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VNS Therapy® System Epilepsy Physician’s Manual PulseTM Generator-Model 102 Pulse DuoTM Generator-Model 102R Demipulse® Generator-Model 103 Demipulse Duo® Generator-Model 104 AspireHC® Generator-Model 105 AspireSR® Generator-Model 106 SenTiva® Generator-Model 1000 Lead-Model 302 PerenniaFLEX® Lead-Model 304 PerenniaDURA® Lead-Model 303. 2019. Available online: https://epilepsy.livanova.com/manuals (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Fahoum, F.; Boffini, M.; Kann, L.; Faini, S.; Gordon, C.; Tzadok, M.; Tahry, R.E. VNS Parameters for Clinical Response in Epilepsy. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, P.B.; Lubock, N.B.; Hincapie, J.G.; Ruble, S.B.; Hamann, J.J.; Grill, W.M. High-Resolution Measurement of Electrically-Evoked Vagus Nerve Activity in the Anesthetized Dog. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoro, M.A.; Yoo, P.B.; Hincapie, J.G.; Hamann, J.J.; Ruble, S.B.; Wolf, P.D.; Grill, W.M. Excitation Properties of the Right Cervical Vagus Nerve in Adult Dogs. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, E.D.; Pelot, N.A.; Grill, W.M. Validated Computational Models Predict Vagus Nerve Stimulation Thresholds in Preclinical Animals and Humans. J. Neural Eng. 2023, 20, 036032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, C.; Helmers, S.L.; DeGiorgio, C.M. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy, Epilepsy, and Device Parameters. Neurology 2002, 59, S31–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Cracchiolo, M.; Ahmed, U.; Mughrabi, I.; Gabalski, A.; Daytz, A.; Rieth, L.; Becker, L.; Datta-Chaudhuri, T.; Al-Abed, Y.; et al. Quantitative Estimation of Nerve Fiber Engagement by Vagus Nerve Stimulation Using Physiological Markers. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahl, S.E.; Senanayake, S.S.; Handforth, A. Destruction of Peripheral C-Fibers Does Not Alter Subsequent Vagus Nerve Stimulation-Induced Seizure Suppression in Rats. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabara, J. Inhibition of Experimental Seizures in Canines by Repetitive Vagal Stimulation. Epilepsia 1992, 33, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carron, R.; Roncon, P.; Lagarde, S.; Dibué, M.; Zanello, M.; Bartolomei, F. Latest Views on the Mechanisms of Action of Surgically Implanted Cervical Vagal Nerve Stimulation in Epilepsy. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.S.; Verma-Ahuja, S.; Naritoku, D.K.; Espinosa, J.A. Intraoperative Human Vagus Nerve Compound Action Potentials. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2004, 110, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laere, K.; Vonck, K.; Boon, P.; Brans, B.; Vandekerckhove, T.; Dierckx, R. Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Refractory Epilepsy: SPECT Activation Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Menachem, E. Vagus-Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaseja, H. EEG-desynchronization as the major mechanism of anti-epileptic action of vagal nerve stimulation in patients with intractable seizures: Clinical neurophysiological evidence. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, H.J.; Paranathala, M.P.; Wang, Y.; Thomas, R.H.; Da Silva Costa, T.; Duncan, J.S.; Taylor, P.N. Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Epilepsy: A Narrative Review of Factors Predictive of Response. Epilepsia 2024, 65, 3441–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, H.; Moga, M.M.; Saper, C.B. Connections of the Parabrachial Nucleus with the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract and the Medullary Reticular Formation in the Rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 293, 540–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Ni, D.; Yu, T.; Zhang, G.; et al. A resting-state functional MRI study on the effect of vagal nerve stimulation on spontaneous regional brain activity in drug-resistant epilepsy patients. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 392, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.R. Therapeutic mechanisms of vagus nerve stimulation. Neurology 2002, 59 (Suppl. S4), S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.R.; Bakay, R.A.E.; Votaw, J.R.; Pennell, P.B.; Epstein, C.M.; Faber, T.L.; Grafton, S.T.; Hoffman, J.M. Brain blood flow alterations induced by therapeutic vagus nerve stimulation in partial epilepsy: I. Acute effects at high and low levels of stimulation. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosevelt, R.W.; Smith, D.C.; Clough, R.W.; Jensen, R.A.; Browning, R.A. Increased Extracellular Concentrations of Norepinephrine in Cortex and Hippocampus Following Vagus Nerve Stimulation in the Rat. Brain Res. 2006, 1119, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, S.; Dong, J.; Debonnel, G.; Blier, P. Enhancement of the Function of Rat Serotonin and Norepinephrine Neurons by Sustained Vagus Nerve Stimulation. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009, 34, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raedt, R.; Clinckers, R.; Mollet, L.; Vonck, K.; El Tahry, R.; Wyckhuys, T.; De Herdt, V.; Carrette, E.; Wadman, W.; Michotte, Y.; et al. Increased Hippocampal Noradrenaline Is a Biomarker for Efficacy of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in a Limbic Seizure Model. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Menachem, E.; Hamberger, A.; Hedner, T.; Hammond, E.J.; Uthman, B.M.; Slater, J.; Treig, T.; Stefan, H.; Ramsay, R.E.; Wernicke, J.F. Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Amino Acids and Other Metabolites in the CSF of Patients with Partial Seizures. Epilepsy Res. 1995, 20, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrosu, F.; Serra, A.; Maleci, A.; Puligheddu, M.; Biggio, G.; Piga, M. Correlation between GABAA receptor density and vagus nerve stimulation in individuals with drug-resistant partial epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2003, 55, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, C.; Coa, R.; Murru, E.; Carta, G.; Pinna, G.; Sanfilippo, R.; Polizzi, L.; Pistis, M.; Follesa, P.; Puligheddu, M.; et al. Identification of Metabolic Biomarkers of Chronic Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) in Subjects with Drug-resistant Epilepsy (DRE). Epilepsia Open 2023, 9, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoie, H.J.M.; Rijkers, K.; Berfelo, M.W.; Hulsman, J.A.R.J.; Myint, A.; Schwarz, M.; Vles, J. Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Refractory Epilepsy: Effects on Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Peripheral Blood. Neuroimmunomodulation 2011, 18, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Pellissier, S. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Vagus Nerve: Potential Therapeutic Implications of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, Z.; Min, L.; Deng, W.; Tan, M.; Hong, J.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Hou, J. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Reduces Neuroinflammation Through Microglia Polarization Regulation to Improve Functional Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 813472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Selden, N.R.; Aballay, A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Pediatric Patients with Epilepsy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1093574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Endogenous Cholinergic Pathway in Rat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, G.; Cai, Z.; Jiao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, A. Vagus nerve stimulation in brain diseases: Therapeutic applications and biological mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, X.; Luo, S.; Feng, Y.; Liang, F.; Shi, T.; Huang, R.; Pei, Z.; Li, Z. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Attenuates Cerebral Microinfarct and Colitis-induced Cerebral Microinfarct Aggravation in Mice. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargus, M.; Ben-Azu, B.; Landwehr, A.; Dunn, J.; Errico, J.P.; Tremblay, M.È. Mechanisms of vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of neurodevelopmental disorders: A focus on microglia and neuroinflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1527842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J. Functional and Effective Connectivity in Neuroimaging: A Synthesis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1994, 2, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiruska, P.; de Curtis, M.; Jefferys, J.G.R.; Schevon, C.A.; Schiff, S.J.; Schindler, K. Synchronization and Desynchronization in Epilepsy: Controversies and Hypotheses. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, F.; Lagarde, S.; Wendling, F.; McGonigal, A.; Jirsa, V.; Guye, M.; Bénar, C. Defining Epileptogenic Networks: Contribution of SEEG and Signal Analysis. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsi, N.M.; Yan, H.; Wong, S.M.; Yau, I.; Breitbart, S.; Go, C.; Gorodetsky, C.; Fasano, A.; Kalia, S.K.; Rutka, J.T.; et al. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates Phase-Amplitude Coupling in Thalamic Local Field Potentials. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Puligheddu, M.; Demuru, M.; Polizzi, L.; Maleci, A.; Tamburini, G.; Congia, S.; Bortolato, M.; Marrosu, F. VNS Induced Desynchronization in Gamma Bands Correlates with Positive Clinical Outcome in Temporal Lobe Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 536, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, C.; Aubert, S.; Daquin, G.; Carron, R.; Scavarda, D.; McGonigal, A.; Bartolomei, F. Responders to Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) in Refractory Epilepsy Have Reduced Interictal Cortical Synchronicity on Scalp EEG. Epilepsy Res. 2015, 113, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.E.; Wadman, W.J.; Marinazzo, D.; van Mierlo, P.; Delbeke, J.; Daelemans, S.; Sprengers, M.; Thyrion, L.; Van Lysebettens, W.; Carrette, E.; et al. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Applied with a Rapid Cycle Has More Profound Influence on Hippocampal Electrophysiology Than a Standard Cycle. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edakawa, K.; Yanagisawa, T.; Kishima, H.; Fukuma, R.; Oshino, S.; Khoo, H.M.; Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshimine, T. Detection of Epileptic Seizures Using Phase–Amplitude Coupling in Intracranial Electroencephalography. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorfer, J.B.; Nenert, R.; Shamshiri, E.; Ranuzzi, G.; Begnaud, J.; Verner, R.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Microburst Study Group. Resting-state Functional Connectivity Changes with Microburst Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy. Epilepsia Open 2025, 10, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.R.; Votaw, J.R.; Pennell, P.B.; Epstein, C.M.; Bakay, R.A.E.; Faber, T.L.; Grafton, S.T.; Hoffman, J.M. Acute Blood Flow Changes and Efficacy of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Partial Epilepsy. Neurology 1999, 52, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, F.; Bonini, F.; Vidal, E.; Trébuchon, A.; Lagarde, S.; Lambert, I.; McGonigal, A.; Scavarda, D.; Carron, R.; Benar, C.G. How Does Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Change EEG Brain Functional Connectivity? Epilepsy Res. 2016, 126, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Somayajula, S.; Shah, D.; Vooturi, S.; Panigrahi, M. Long-Term Outcome of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2025, 28, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyandi, M.; Chelvanayagam, K.; Salam, S.A.; Vadamalai, S.; Rajsekar, K.; Ramachandran, R. Significant reduction of seizure frequency in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy by vagus nerve stimulation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2025, 210, 107510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolińska, E.; Birski, M.; Hoppe, S.; Paczkowski, D.; Harat, M. Long-Term Efficacy and Quality-of-Life Changes After Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Adult Patients With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurol. 2025, 21, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, M.; Voges, B.; Chelvarajah, R.; Sen, A.; Gadže, Ž.P.; Penchet, G.; De Benedictis, A.; Fornaro, R.; Iwasaki, M.; Iijima, K.; et al. Right-Sided Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Worldwide Collection and Perspectives. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2025, 12, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner, R.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Allendorfer, J.B.; Vonck, K.; Giannicola, G. Modulation of the Thalamus by Microburst Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Feasibility Study Protocol. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1169161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrand, A.; Jacquemet, V.; Verner, R.; Owens, M.; Beaumont, E. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Parameters Evoke Differential Neuronal Responses in the Locus Coeruleus. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkawi, S.; Alsamiri, G.Y.; Halabi, M.H.; Bukhari, J.I.; Alharbi, F.; Alnafisi, F.N.; Alaslab, A.K.; Alghamdi, A.E.; Bamehriz, A.M.; Alhubayshi, M.; et al. Efficacy of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (t-VNS) in Treating Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2025, 215, 107583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. ANZ J. Surg. 2020, 90, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wrede, R.; Surges, R. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 235, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampros, M.; Vlachos, N.; Zigouris, A.; Voulgaris, S.; Alexiou, G.A. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (t-VNS) and Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Seizure 2021, 91, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbella, G.; Cocco, I.; Freri, E.; Marotta, G.; Visani, E.; Franceschetti, S.; Casazza, M. Transcutaneous Vagal Nerve Stimulatio (t-VNS): An Adjunctive Treatment Option for Refractory Epilepsy. Seizure 2018, 60, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihua, L.; Lu, S.; Liping, L.; Xiuru, W.; Hua, L.; Yuping, W. A Controlled Trial of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 39, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagara, R.; Chennareddy, S.; Reford, E.; Bhimani, A.D.; Cummins, D.D.; Downes, M.H.; Tosto, J.M.; Bederson, J.B.; Mocco, N.; Putrino, D.; et al. Complications of Implanted Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 54, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryvlin, P.; Rheims, S.; Hirsch, L.J.; Sokolov, A.; Jehi, L. Neuromodulation in Epilepsy: State-of-the-Art Approved Therapies. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touma, L.; Dansereau, B.; Chan, A.Y.; Jetté, N.; Kwon, C.; Braun, K.P.J.; Friedman, D.; Jehi, L.; Rolston, J.D.; Vadera, S.; et al. Neurostimulation in People with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis from the ILAE Surgical Therapies Commission. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1314–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneef, Z.; Skrehot, H.C. Neurostimulation in Generalized Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Scott, V.; Ugiliweneza, B.; Wang, D.; Boakye, M.; Neimat, J.; Sreenivasan, S. National Trends of Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT) and Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) for Refractory Epilepsy in Adult Patients: A Nationwide Inpatient Sample Based Propensity Score Matched Analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2024, 131, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Qu, W.; Hao, H.; Li, L. Heart-Rate Variability Indices as Predictors of the Response to Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Tan, G.; Zhu, L.-N.; Chen, D.; Xu, D.; Chu, S.-S.; Liu, L. Predictors of Seizure Reduction Outcome after Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Seizure 2019, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhani, S.I.; Abbasi, M.; Liu, Y.; Larco, J.A.; Nicolai, E.; Worrell, G.; Savastano, L. Electroencephalogram and Heart Rate Variability Features as Predictors of Responsiveness to Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Epilepsy: A Systematic Review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, K.S.; Olin, B.D.; Fisher, R.S. Ictal Tachycardia: The Head–Heart Connection. Seizure 2014, 23, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, S.; Zhao, P. Dynamical graph neural network with attention mechanism for epilepsy detection using single channel EEG. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 62, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbeaumes Jodoin, V.; Lespérance, P.; Khoa Nguyen, D.; Fournier-Gosselin, M.-P.; Richer, F. Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on pupillary function. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 98, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Sánchez, A.; Dawant, M.; Danthine, V.; Cakiroglu, I.; Santalucia, R.; Germany Morrison, E.I.; Nonclercq, A.; Tahry, R.E. VNS-Induced Dose-Dependent Pupillary Response in Refractory Epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2025, 171, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpaas, T.L.; Tcheng, T.K.; Morrell, M.J. Clinical and Electrocorticographic Response to Antiepileptic Drugs in Patients Treated with Responsive Stimulation. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 83, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cukiert, A.; Cukiert, C.M.; Burattini, J.A.; Guimaraes, R.B. Combined Neuromodulation (Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Brain Stimulation) in Patients with Refractory Generalized Epilepsy: An Observational Study. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2022, 26, 1742–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, L.J.; Mirro, E.A.; Salanova, V.; Witt, T.C.; Drees, C.N.; Brown, M.; Lee, R.W.; Sadler, T.L.; Felton, E.A.; Rutecki, P.; et al. Mesial temporal resection following long-term ambulatory intracranial EEG monitoring with a direct brain-responsive neurostimulation system. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithani, K.; Mikhail, M.; Morgan, B.R.; Wong, S.; Weil, A.G.; Deschenes, S.; Wang, S.; Bernal, B.; Guillen, M.R.; Ochi, A.; et al. Connectomic Profiling Identifies Responders to Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
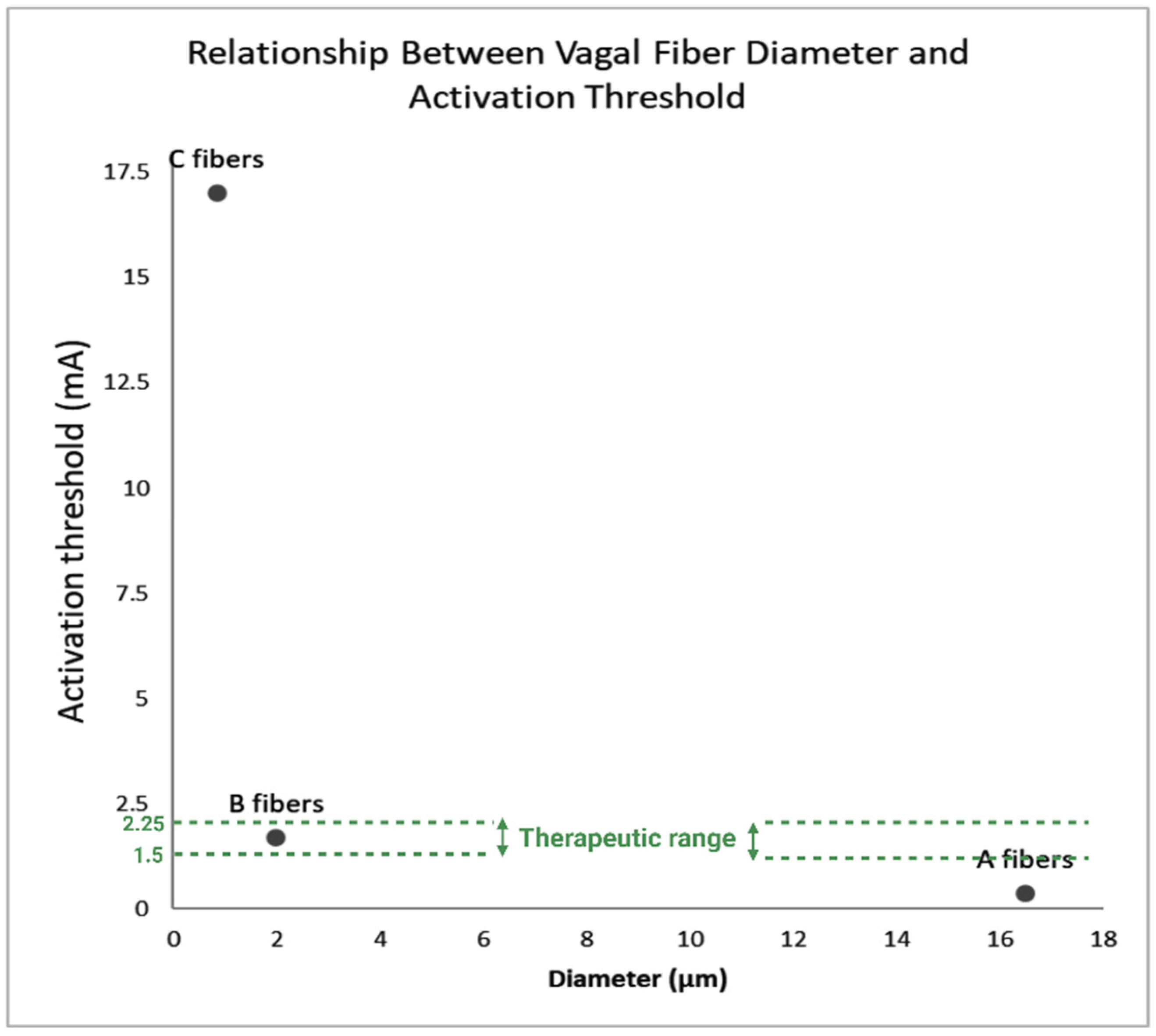
| Fiber-Specificity | VNS primarily activates myelinated A and B fibers, not unmyelinated C fibers, due to lower stimulation thresholds. These fibers mediate therapeutic effects without causing unpleasant sensations. [9,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] |
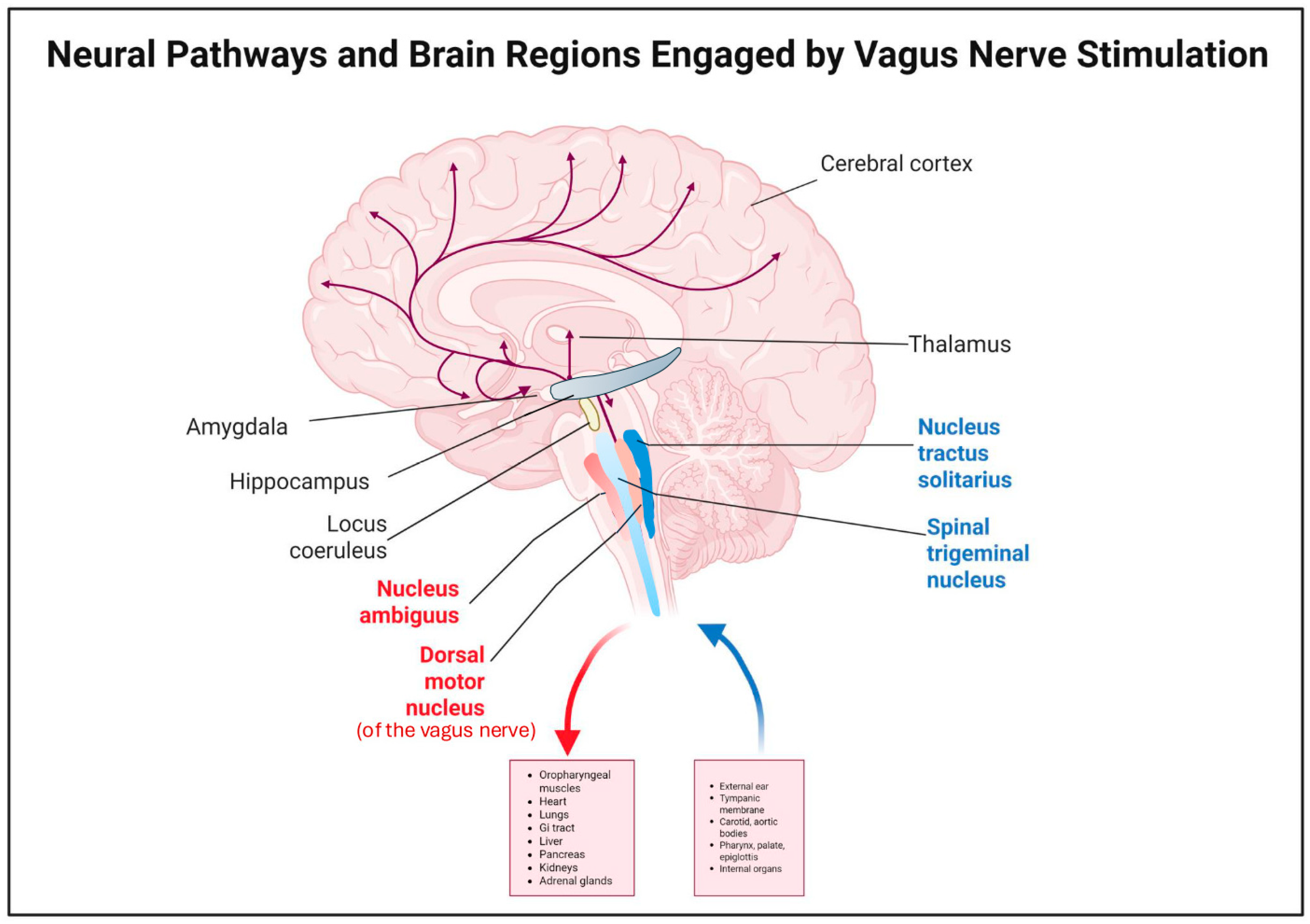
| Neural Pathway Effects | Vagus afferents project to the NTS and connected regions (LC, PN, hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala, raphe nuclei). VNS increases noradrenaline, serotonin, and GABA activity to stabilize brain function and control seizures. [16,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] |
| Anti-Inflammatory Effects | VNS activates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), increases anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β), and enhances microglial and macrophage-mediated neuroprotection. [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] |
| Feature | Standard VNS | Microburst VNS (μVNS) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Typically 20–30 Hz | 100–350 Hz (bursts) |
| Pulse pattern | Continuous or cyclical | 4–7 pulses per burst with long off periods |
| Mechanism | Broad VNS activation | Enhances locus coeruleus synchronization; targets thalamic network |
| Clinical efficacy | 50–60% patients show >50% seizure reduction | 67–80% patients show >50% seizure reduction in recent trials |
| Side effects | Voice alteration, cough, throat discomfort | Potentially reduced due to a brief burst pattern |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cocoli, K.; Curley, J.; Rohatgi, P.; Abdennadher, M. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Epilepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Approaches. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111236
Cocoli K, Curley J, Rohatgi P, Abdennadher M. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Epilepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Approaches. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111236
Chicago/Turabian StyleCocoli, Klesta, Justine Curley, Pratik Rohatgi, and Myriam Abdennadher. 2025. "Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Epilepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Approaches" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111236
APA StyleCocoli, K., Curley, J., Rohatgi, P., & Abdennadher, M. (2025). Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy for Epilepsy: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Approaches. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111236






