Breathing Rate as a Marker for Noise-Induced Stress in Guinea Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Measuring Movement
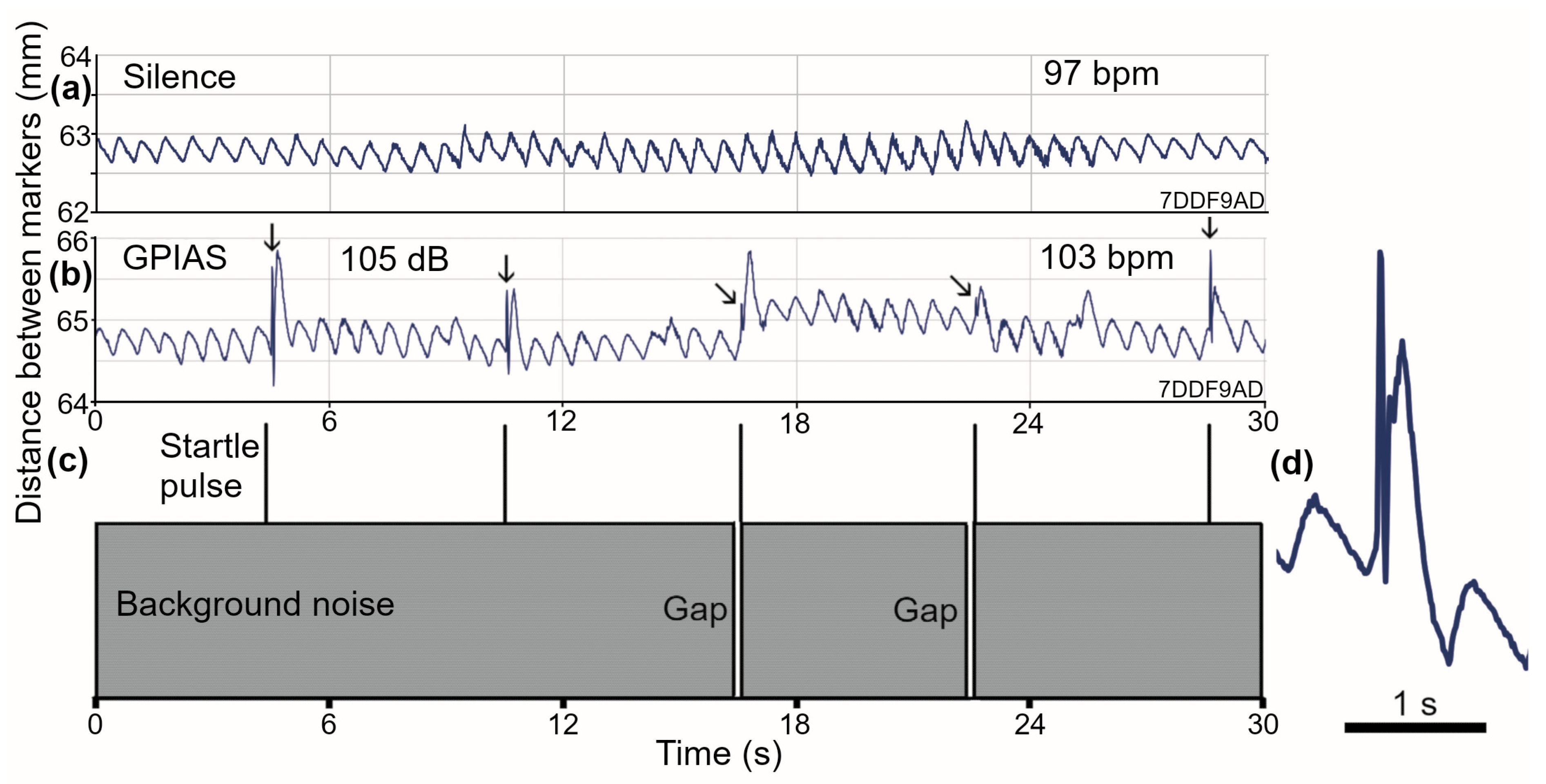
2.3. Acoustic Stimulation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
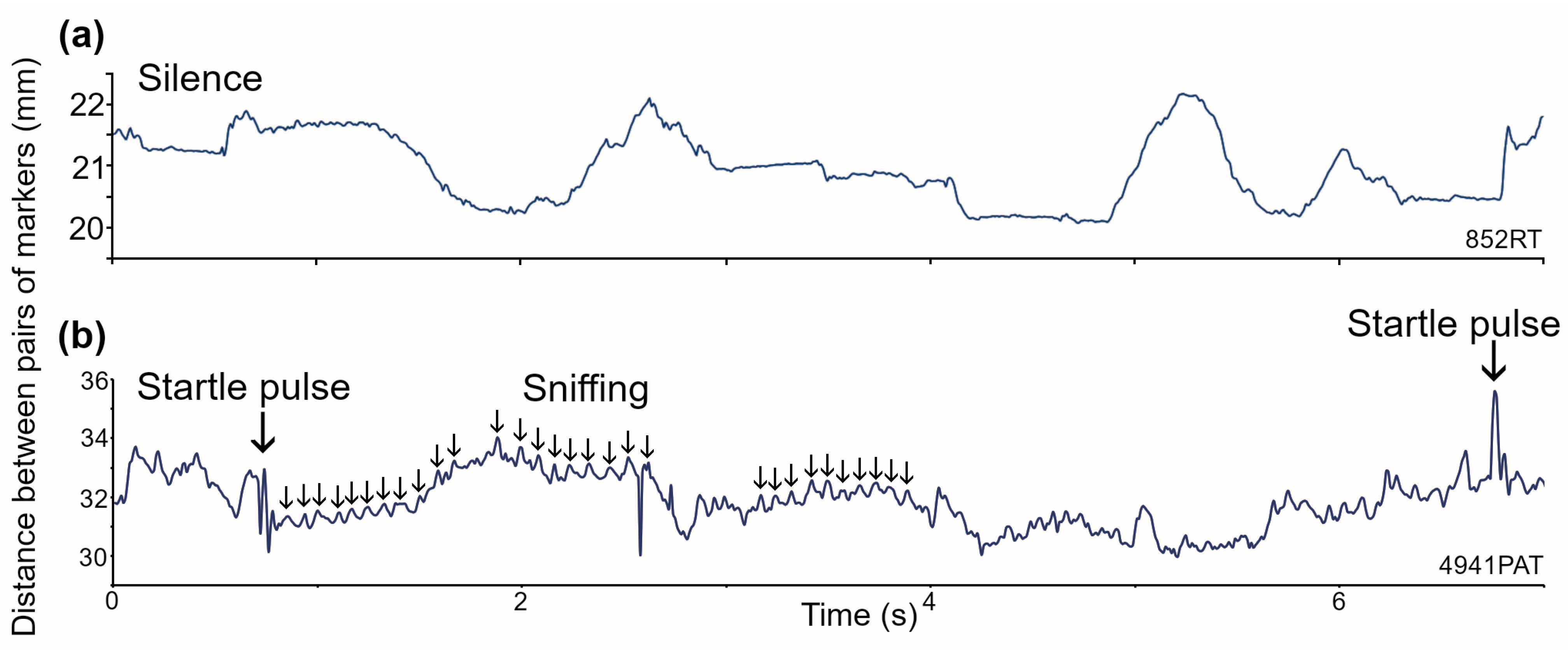
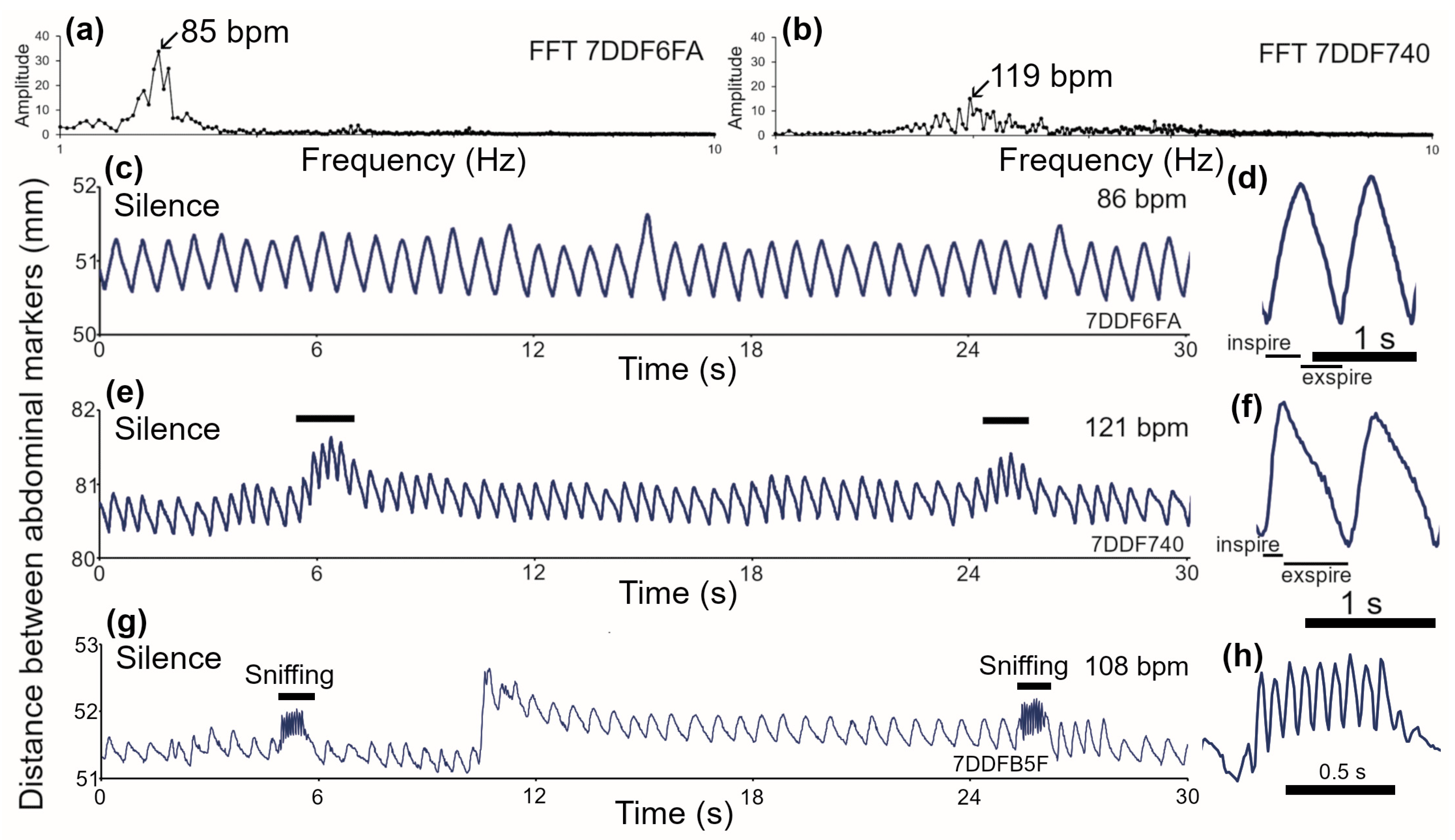
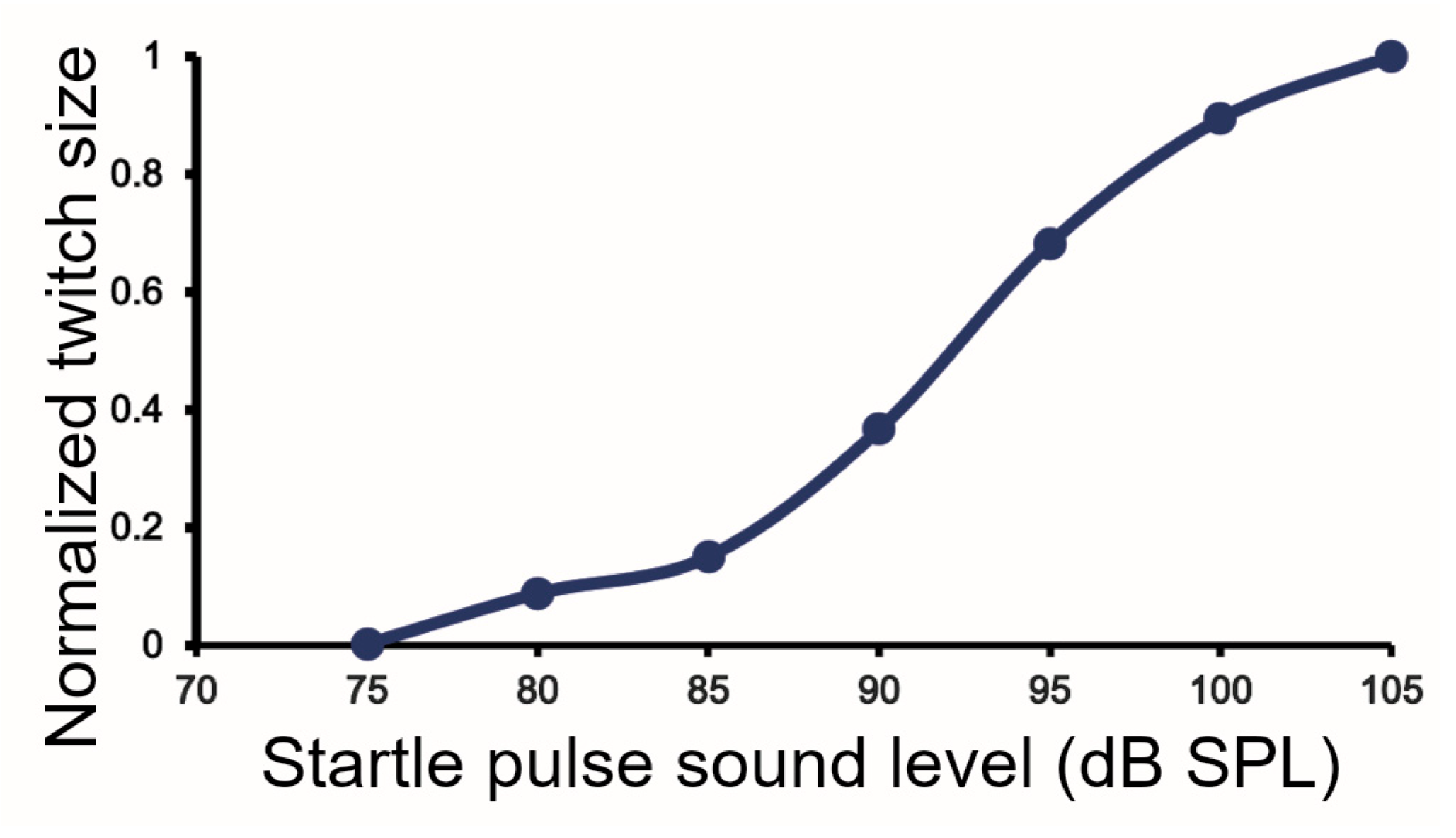
3.1. Breathing Patterns in C57BL/6J Mice
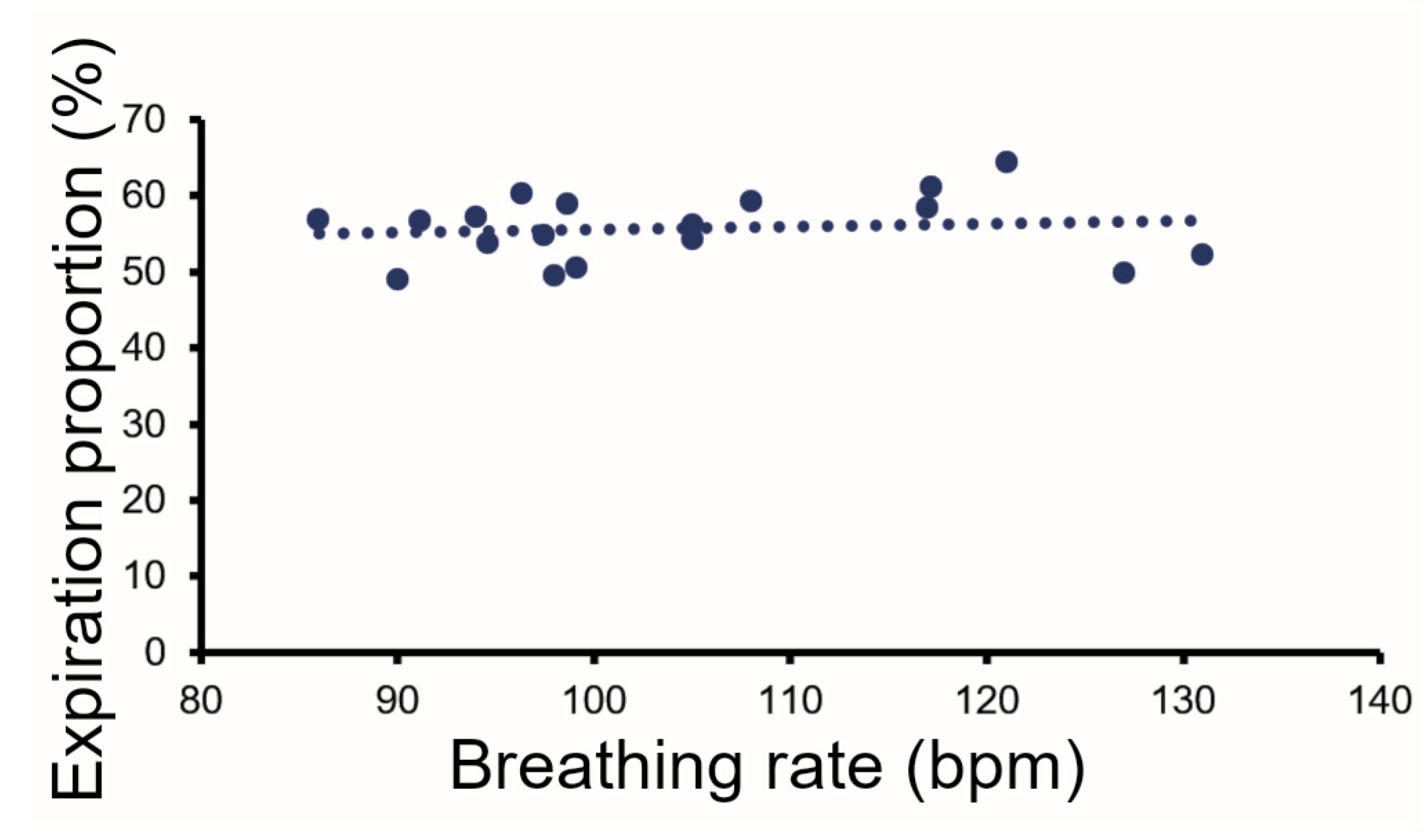
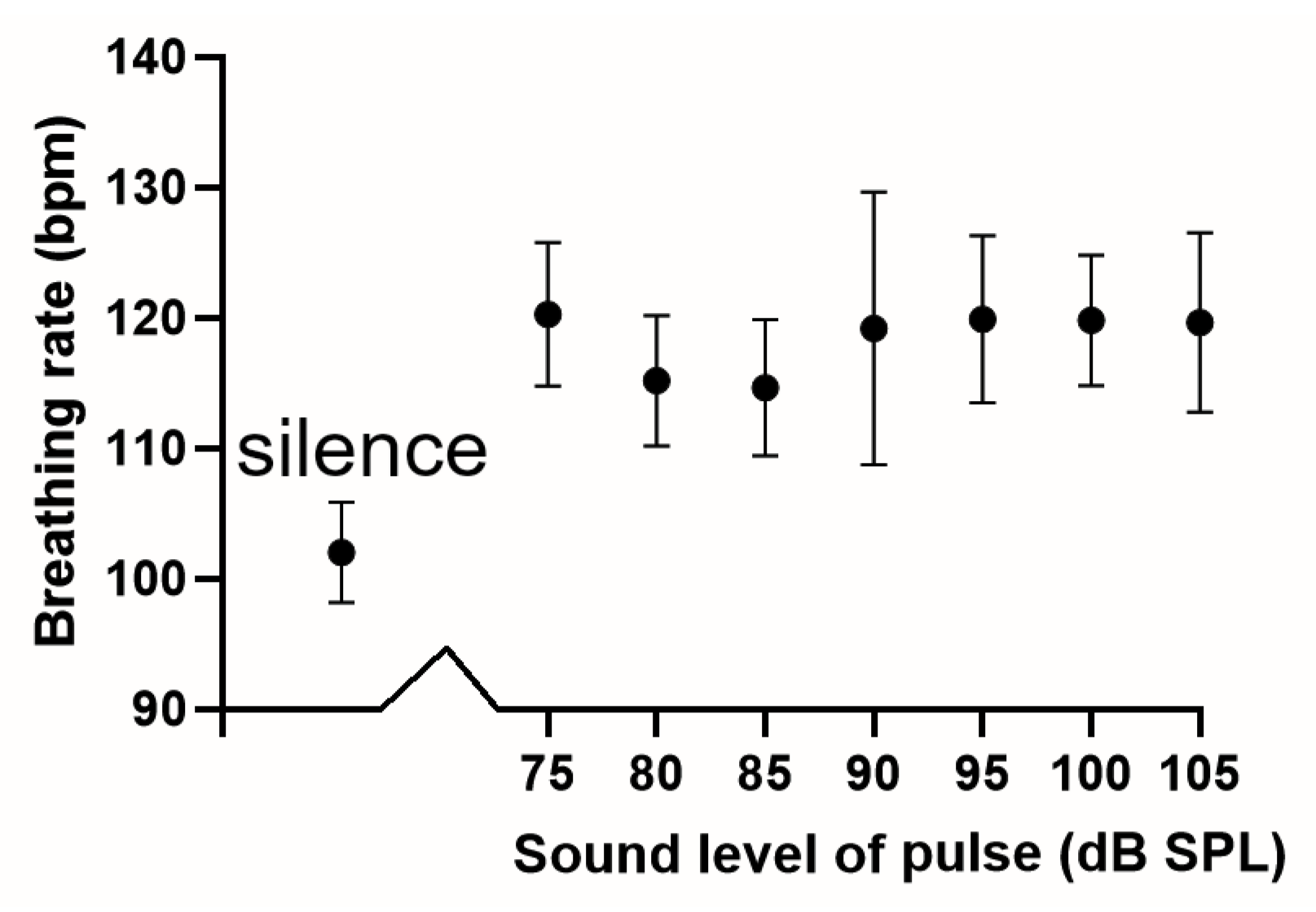
3.2. Breathing Patterns in Guinea Pigs at Rest
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBN | broadband noise |
| bpm | breaths per minute |
| dB SPL | decibels sound pressure level |
| FFT | fast Fourier transform |
| GPIAS | gap prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle |
References
- Kim, M.J.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.M.; Yu, H.J.; Park, I.; Park, S.N. Evidence of Tinnitus Development Due to Stress: An Experimental Study in Rats. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.L.; Yu, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, I.; Park, S.N. Tinnitus Generation and Behavioral Changes Caused by Chronic Stress: A Behavioral and Brain Study in a Rat Model. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Lugo, A.; Akeroyd, M.A.; Schlee, W.; Gallus, S.; Hall, D.A. Tinnitus prevalence in Europe: A multi-country cross-sectional population study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 12, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoens, V.L.; Hébert, S. Cortisol suppression and hearing thresholds in tinnitus after low-dose dexamethasone challenge. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2012, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.D.; Alrashid, M.A.; Eltabbakh, A.; Fredericks, S. The association between stress, emotional states, and tinnitus: A mini-review. Front. Aging Neurosci 2023, 15, 1131979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigi, A.; Oden, A.; Almild-Larsen, V.; Barrenas, M.L.; Holgers, K.M. Tinnitus in the general population with a focus on noise and stress: A public health study. Ear Hear. 2011, 32, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukes, E.W.; Manchaiah, V.; Allen, P.M.; Andedrsson, G.; Baguley, D.M. Exploring tinnitus heterogeneity. Prog. Brain Res. 2021, 260, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, B.; Haupt, H.; Olze, H.; Szczepek, A.J. Stress and tinnitus-from bedside to bench and back. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, L.T.; Muhlberger, A.; Langguth, B.; Scheckllmann, M. Stress Reactivity in Chronic Tinnitus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elarbed, A.; Fackrell, K.; Baguley, D.M.; Hoare, D.J. Tinnitus and stress in adults: A scoping review. Int. J. Audiol. 2021, 60, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, R.S. Patient preferences and willingness to pay for tinnitus treatments. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2012, 23, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, M.; Mazurek, B.; van Dijk, K.; Schulze, H. Too Blind to See the Elephant? Why Neuroscientists Ought to Be Interested in Tinnitus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2021, 22, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.I.; Billig, A.J.; Sedley, W.; Kumar, S.; Griffiths, T.D.; Gander, P.E. What is the role of the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus in the persistence of tinnitus? Hum Brain Mapp 2024, 45, e26627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, A.M.; Larkin, G.; Jones, A.; May, B.J. Behavioral Animal Model of the Emotional Response to Tinnitus and Hearing Loss. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2018, 19, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFerran, D.J.; Stockdale, D.J.; Holme, R.; Large, C.H.; Baguley, D.M. Why Is There No Cure for Tinnitus? Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreña, A.J.; Farley, B.J. Tinnitus-related neural activity: Theories of generation, propagation, and centralization. Hear. Res. 2013, 295, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, S.E.; Roberts, L.E.; Langguth, B. Maladaptive plasticity in tinnitus--triggers, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, R. Learning about stress: Neural, endocrine and behavioral adaptations. Stress. 2016, 19, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.A.; Defensor, E.B.; Mechanic, J.A.; Shah, P.P.; Jaime, E.A.; Robert’s, C.R.; Hutto, D.L.; Schaevitz, L.R. Retrospective Analysis of the Effects of Identification Procedures and Cage Changing by Using Data from Automated, Continuous Monitoring. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2019, 58, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, F.; Inta, D.; Palme, R.; Brandwein, C.; Pfeiffer, N.; Riva, M.A.; Gass, P.; Mallien, A.S. The impact of handling technique and handling frequency on laboratory mouse welfare is sex-specific. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, N.E.; Toth, L.A. Analytic and Interpretational Pitfalls to Measuring Fecal Corticosterone Metabolites in Laboratory Rats and Mice. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, L.; Sgoifo, A.; Trombini, M.; Landgraf, R.; Neumann, I.D.; Nalivaiko, E. Different patterns of respiration in rat lines selectively bred for high or low anxiety. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C. Measurement of the respiratory volumes of laboratory animals. Am. J. Physiol. 1947, 150, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdur, M.O.; Mead, J. Mechanics of respiration in unanesthetized guinea pigs. Am. J. Physiol. 1958, 192, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, J.M. Breathing pattern in the guinea-pig. Lab. Anim. 1974, 8, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaud, J.; Murthy, V.N. How to monitor breathing in laboratory rodents: A review of the current methods. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, C.B.; Hwang, S.K.; Mmorin, J.; Bluette, C.T.; Manickam, B.; Jiang, Z.K.; Giddabasappa, A.; Liu, C.N.; Matthew’s, K. Automated monitoring of respiratory rate as a novel humane endpoint: A refinement in mouse metastatic lung cancer models. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janke, E.; Zhang, M.; Ryu, S.E.; Bhattarai, J.P.; Schreck, M.R.; Moberly, A.H.; Luo, W.; Ding, L.; Wesson, D.W.; Ma, M. Machine learning-based clustering and classification of mouse behaviors via respiratory patterns. iScience 2022, 25, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagymáté, G.; Kiss, R.M. Application of OptiTrack motion capture systems in human movement analysis A systematic literature review. Recent Innov. Mechatron. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hockley, A.; Berger, J.I.; Palmer, A.R.; Wallace, M.N. Nitric oxide increases gain in the ventral cochlear nucleus of guinea pigs with tinnitus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 4057–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.N.; Berger, J.I.; Hockley, A.; Sumner, C.J.; Akeroyd, M.A.; Palmer, A.R.; McNaughton, P.A. Identifying tinnitus in mice by tracking the motion of body markers in response to an acoustic startle. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1452450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, M. Guinea Pigs. In Comfortable Quarters For Laboratory Animals; Liss, C., Ed.; Animal Welfare Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.I.; Coomber, B.; Shackleton, T.M.; Palmer, A.R.; Wallace, M.N. A novel behavioural approach to detecting tinnitus in the guinea pig. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 213, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraday, M.M. Rat sex and strain differences in responses to stress. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 75, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcombe, J.P.; Barnard, N.D.; Sandusky, C. Laboratory routines cause animal stress. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2004, 43, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wesson, D.W. Sniffing behavior of mice during performance in odor-guided tasks. Chem. Senses 2008, 33, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisert, J.; Golden, G.J.; Dibattista, M.; Gelperin, A. Dynamics of odor sampling strategies in mice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalivaiko, E.; Bondarenko, E.; Lidstrom, A.; Barry, R.J. Respiratory component of the orienting reflex: A novel sensitive index of sensory-induced arousal in rats. Front. Physiol. 2012, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Roy, S.; Sachdev, R.N.S.; Heck, D.H. Dynamic correlation between whisking and breathing rhythms in mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Receno, C.N.; Eassa, B.E.; Cunningham, C.N.; DeRuisseau, L.R. Young and middle-aged mouse breathing behavior during the light and dark cycles. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindry, J.C.; Ballman, C.G.; Epstein, E.E.; Seisby, J.T. Plethysmography measurements of respiratory function in conscious unrestrained mice. J. Physiol. Sci. 2016, 66, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Beig, M.I.; Baumert, M.; Trombini, M.; Mastorci, F.; Sgoifo, A.; Walker, F.R.; Day, T.A.; Nalivaiko, E. Respiratory pattern in awake rats: Effects of motor activity and of alerting stimuli. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, L.D.; Rossignoli, M.T.; Delphino-Pereira, P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Umeoka, E.H.d.L. A Comprehensive Overview on Stress Neurobiology: Basic Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, E.; Hodgson, D.M.; Nalivaiko, E. Amygdala mediates respiratory responses to sudden arousing stimuli and to restraint stress in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R951–R959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suess, W.M.; Alexander, A.B.; Smith, D.D.; Sweeney, H.W.; Marion, R.J. The effects of psychological stress on respiration: A preliminary study of anxiety and hyperventilation. Psychophysiology 1980, 17, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoka, Y.; Homma, I. Anxiety and respiratory patterns: Their relationship during mental stress and physical load. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1997, 27, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, N.; Shima, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamura, K. A central master driver of psychosocial stress responses in the rat. Science 2020, 367, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kataoka, N. A hypothalamomedullary network for physiological responses to environmental stresses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, A.E.; Slobe, B.S.; Vazquez, V.; Collins, A.C. Inbred mouse strains differ in the regulation of startle and prepulse inhibition of the startle response. Behav. Neurosci. 1997, 111, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dampney, R.A. Central mechanisms regulating coordinated cardiovascular and respiratory function during stress and arousal. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R429–R443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohn, F.; Novello, M.; van der Giessen, R.S.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Pel, J.J.M.; Bosman, L.W.J. The integrated brain network that controls respiration. eLife 2023, 12, e83654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.; Colgan, D.D.; Klee, D.; Hanes, D.; Oken, B.S. Patterns of Respiration Rate Reactivity in Response to a Cognitive Stressor Associate With Self-Reported Mental Health Outcomes. Psychol. Rep. 2025, 128, 1517–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, T.R.A.; Weng, H.Y.; Mitra, V.; Imhoff-Smith, T.P.; Azemi, E.; Goldman, R.I.; Rosenkranz, M.A.; Wu, S.; Chen, A.; Davidson, R.J. Slower respiration rate is associated with higher self-reported well-being after wellness training. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, D.E.; Chhean, D.; Pich, V.; Hofmann, S.G.; Barlow, D.H. Tinnitus among Cambodian refugees: Relationship to PTSD severity. J. Trauma. Stress. 2006, 19, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; An, S.Y.; Sim, S.; Park, B.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.K.; Choi, H.G. Analysis of the prevalence and associated risk factors of tinnitus in adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, B.; Doge, J.; O’Brien, K.; Bohnert, A.; Lackner, K.J.; Beutel, M.E.; Michal, M.; Munzel, T.; Wild, P.S.; Pfeiffer, N.; et al. Tinnitus and Its Relation to Depression, Anxiety, and Stress-A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Herrera, A.; Wurbel, H.; Voelkl, B. Evidence of HARKing in mouse behavioural tests of anxiety. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 231744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boecking, B.; Rose, M.; Brueggemann, P.; Mazurek, B. Two birds with one stone.-Addressing depressive symptoms, emotional tension and worry improves tinnitus-related distress and affective pain perceptions in patients with chronic tinnitus. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.N.; Palmer, A.R. Neural Plasticity in Tinnitus Mechanisms. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wallace, M.N.; Berger, J.I.; Sumner, C.J.; Palmer, A.R.; Akeroyd, M.A.; McNaughton, P.A. Breathing Rate as a Marker for Noise-Induced Stress in Guinea Pigs. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111152
Wallace MN, Berger JI, Sumner CJ, Palmer AR, Akeroyd MA, McNaughton PA. Breathing Rate as a Marker for Noise-Induced Stress in Guinea Pigs. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111152
Chicago/Turabian StyleWallace, Mark N., Joel I. Berger, Christian J. Sumner, Alan R. Palmer, Michael A. Akeroyd, and Peter A. McNaughton. 2025. "Breathing Rate as a Marker for Noise-Induced Stress in Guinea Pigs" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111152
APA StyleWallace, M. N., Berger, J. I., Sumner, C. J., Palmer, A. R., Akeroyd, M. A., & McNaughton, P. A. (2025). Breathing Rate as a Marker for Noise-Induced Stress in Guinea Pigs. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111152





