Drug-Specific Global Attentional Bias in Females with Drug Use Disorder: Response Slowing Under Short but Not Long Cue Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
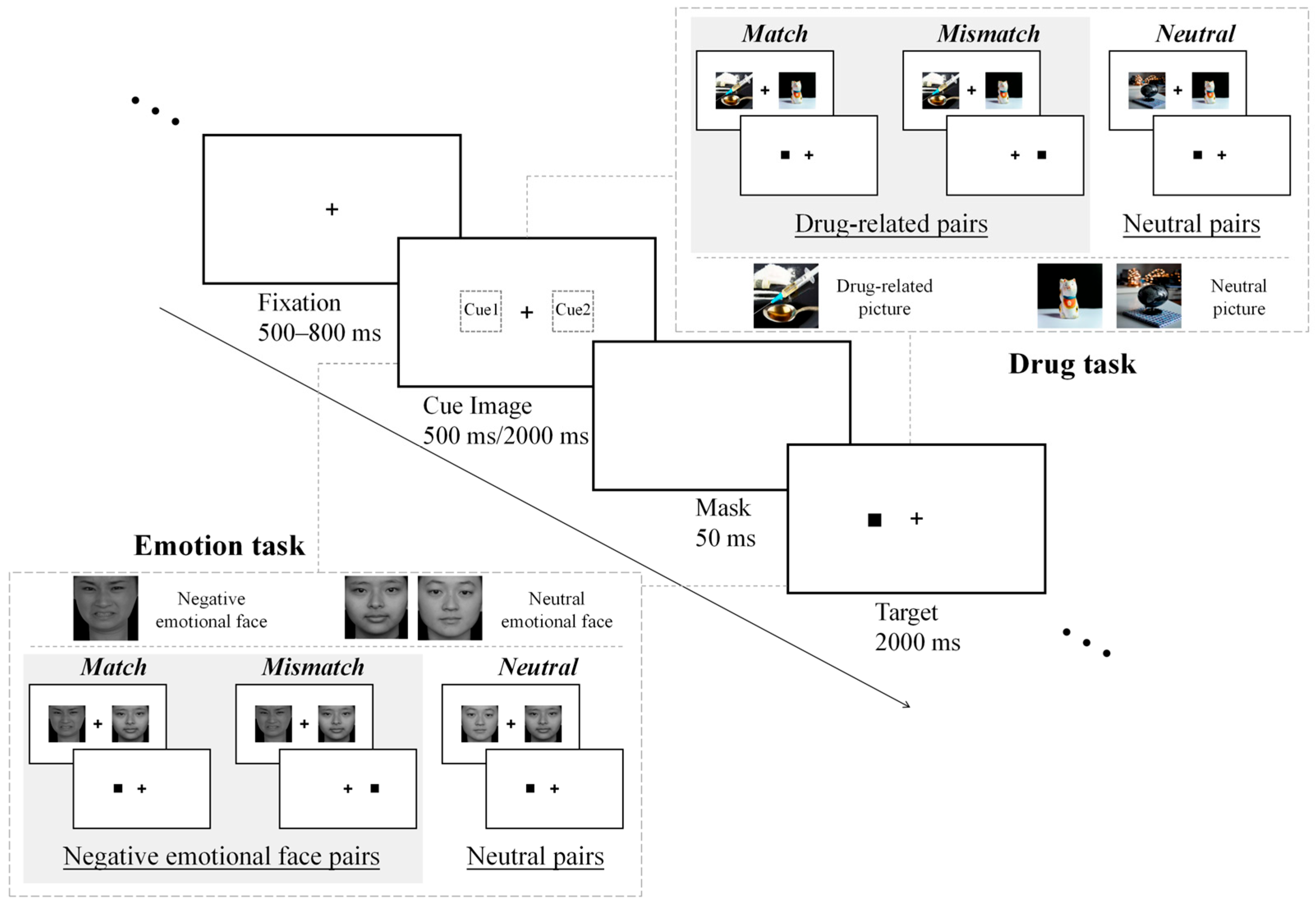
2.2. Materials and Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
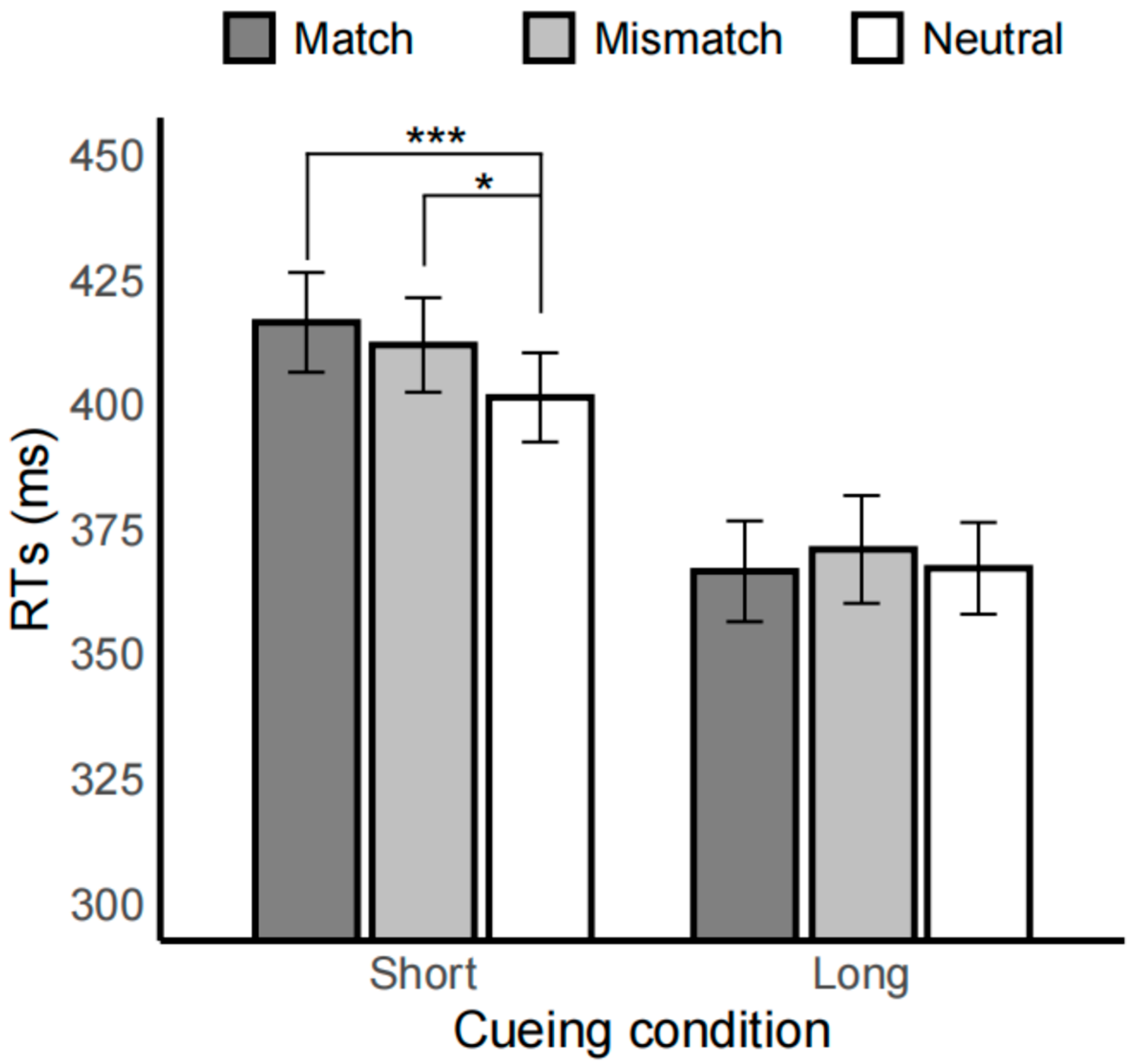
3.1. Drug Task
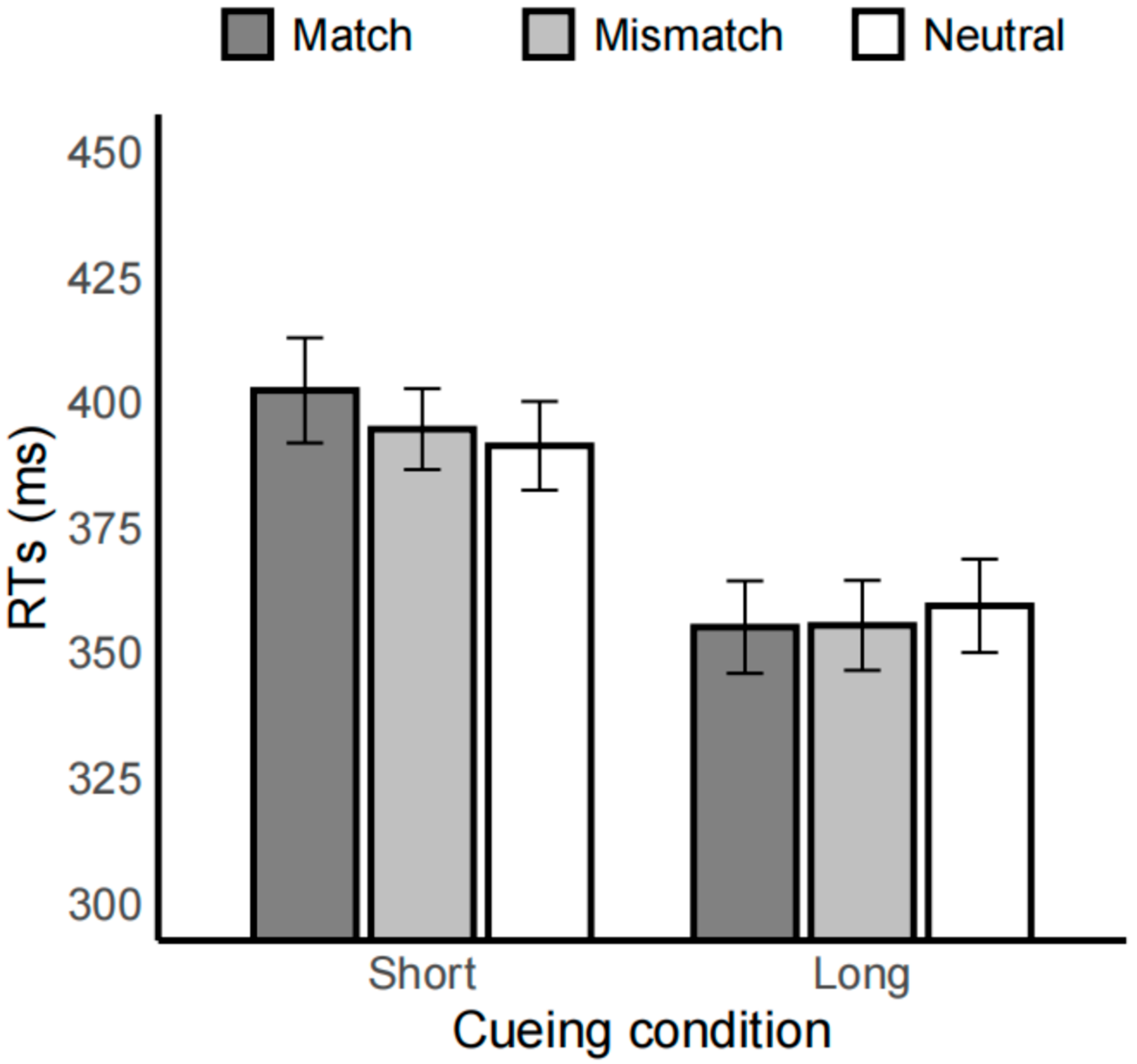
3.2. Emotion Task
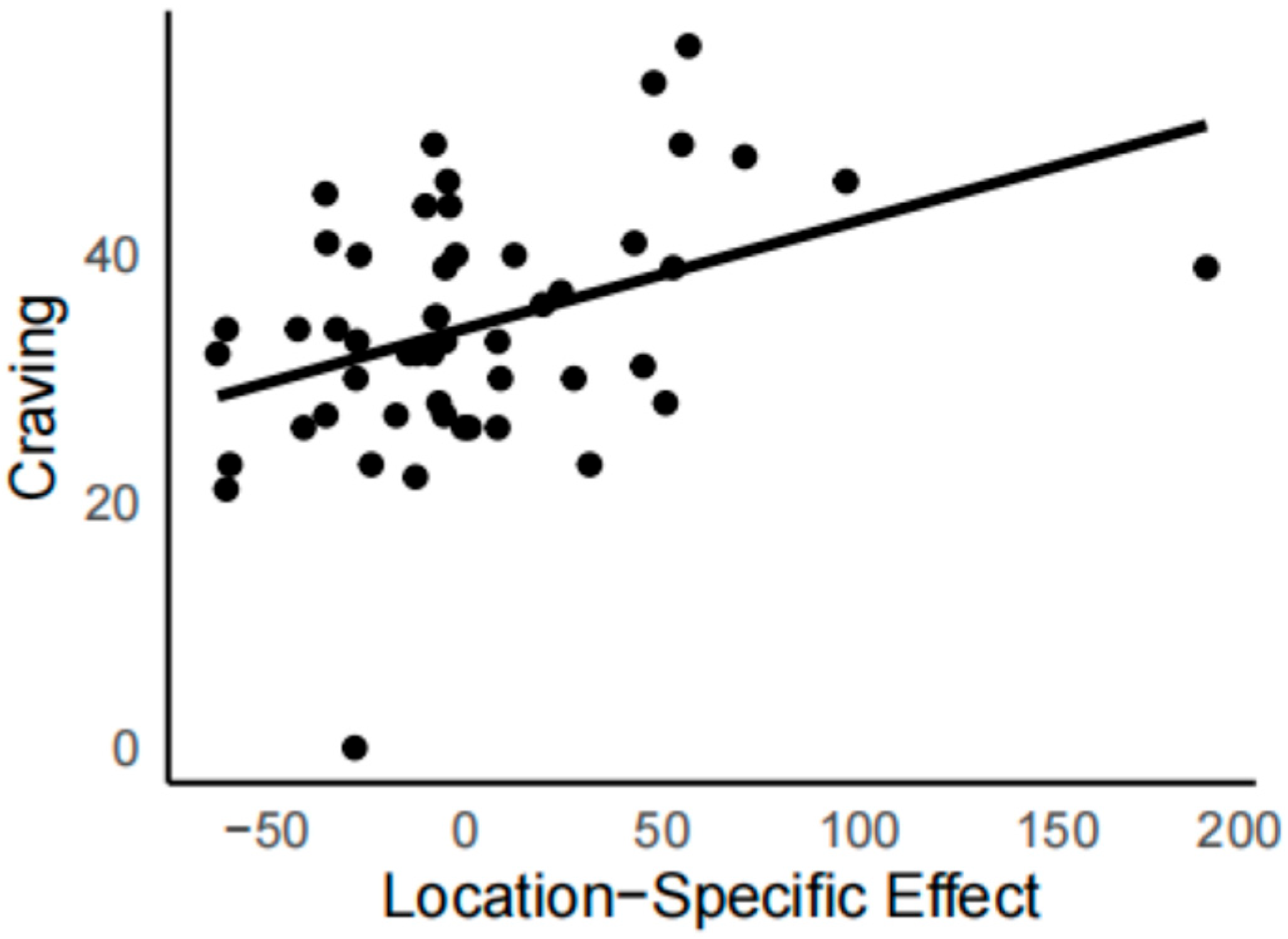
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| OCDUS | Obsessive Compulsive Drug Use Scale |
References
- Franken, I.H.A. Drug craving and addiction: Integrating psychological and neuropsychopharmacological approaches. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.; Cox, W.M. Attentional bias in addictive behaviors: A review of its development, causes, and consequences. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 97, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, X.Y.; Liang, Q.D.; Li, X.; Yang, J.M.; Yuan, J.J. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex restores attention bias to negative information in methamphetamine addicts. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 265, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.B.; Brandon, T.H.; Chassin, L. Motivational influences on cigarette smoking. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2004, 55, 463–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, V.; Garfield, J.B.B.; Mroz, K.; Campbell, S.C.; Piercy, H.; Staiger, P.K.; Lum, J.A.G.; Lubman, D.I.; Verdejo-Garcia, A. Feasibility and acceptability of approach bias modification during methamphetamine withdrawal and related methamphetamine use outcomes. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2019, 106, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrik, J.; Aston, E.R.; Kahler, C.W.; Rohsenow, D.J.; McGeary, J.E.; Knopik, V.S.; MacKillop, J. Cue-elicited increases in incentive salience for marijuana: Craving, demand, and attentional bias. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 167, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, M.; Munafò, M.R.; Franken, I.H.A. A Meta-Analytic Investigation of the Relationship Between Attentional Bias and Subjective Craving in Substance Abuse. Psychol. Bull. 2009, 135, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.; Werthmann, J.; Franken, I.; Hofmann, W.; Hogarth, L.; Roefs, A. The Role of Attentional Bias in Obesity and Addiction. Health Psychol. 2016, 35, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, S.E.; Woldorff, M.G.; Hopf, J.M.; Harris, J.A.; Heinze, H.J.; Schoenfeld, M.A. An electrophysiological dissociation of craving and stimulus-dependent attentional capture in smokers. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 16, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, K.R.; Pike, E.; Stoops, W.W.; Rush, C.R. The Magnitude of Drug Attentional Bias Is Specific to Substance Use Disorder. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2015, 29, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.; Lawn, W.; Ofori, S.; Trinci, K.; Borissova, A.; Mokrysz, C.; Petrilli, K.; Bloomfield, M.A.P.; Wall, M.B.; Freeman, T.P.; et al. The acute effects of cannabis, with and without cannabidiol, on attentional bias to cannabis related cues: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Psychopharmacology 2024, 241, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.S.; Steinberg, J.L.; Bjork, J.M.; Taylor, B.A.; Arias, A.J.; Terplan, M.; Anastasio, N.C.; Zuniga, E.A.; Lennon, M.; Cunningham, K.A.; et al. Cingulo-hippocampal effective connectivity positively correlates with drug-cue attentional bias in opioid use disorder. Psychiatry Res.-Neuroimaging 2019, 294, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaee, S.S.; Fadardi, J.S.; Cox, W.M.; Yazdi, S.A.A. Effects of Attention Control Training on Drug Abusers’ Attentional Bias and Treatment Outcome. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2016, 84, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.N.; Zhou, C.L.; Liu, T.Z. Effects of chronic aerobic exercise on attentional bias among women with methamphetamine addiction. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Libera, C.; Zandonai, T.; Zamboni, L.; Santandrea, E.; Sandri, M.; Lugoboni, F.; Chiamulera, C.; Chelazzi, L. Revealing Dissociable Attention Biases in Chronic Smokers Through an Individual-Differences Approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Fadardi, J.S.; Pothos, E.M. The addiction-stroop test: Theoretical considerations and procedural recommendations. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 132, 443–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtorabi, S.D.; Saleki, S.; Rahmanian, M.S.; Hadizadeh, H.; Rostami, R.; Yoonessi, A. Direct and Indirect Measures of Attention Indicate a Bias Toward Cues in Methamphetamine Users. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Zhu, D.; Xu, D.; Zhu, X.R.; Yang, S.Y. Dissociation of drug and negative emotional cue induced attentional bias in individuals with methamphetamine-use disorder. Am. J. Addict. 2024, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Li, H.Q.; Hu, B.; Li, Y.H.; Gillebert, C.R.; Mantini, D.; Liu, Q.Y. Neural Correlates of Drug-Related Attentional Bias in Heroin Dependence. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.E.; Berridge, K.C. The incentive sensitization theory of addiction: Some current issues. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankland, L.; Bradley, B.P.; Mogg, K. Time Course of Attentional Bias to Drug Cues in Opioid Dependence. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2016, 30, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, N.; Hirst, A.; de Fockert, J.W.; Viding, E. Load theory of selective attention and cognitive control. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2004, 133, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, N. Distracted and confused?: Selective attention under load. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchadell, V.; Poy, R.; Segarra, P.; Ribes-Guardiola, P.; Moltó, J. Attentional biases in abstinent patients with cocaine use disorder: Rapid orienting or delayed disengagement? Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1290890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbabaie, A.; Hatami, J.; Farhoudian, A.; Ekhtiari, H.; Khatibi, A.; Nitsche, M.A. Optimizing Electrode Montages of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Attentional Bias Modification in Early Abstinent Methamphetamine Users. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershad, A.K.; Mayo, L.M.; Van Hedger, K.; McGlone, F.; Walker, S.C.; de Wit, H. Effects of MDMA on attention to positive social cues and pleasantness of affective touch. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Jin, X.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, F.; Shen, M.W. Biased attention towards negative schematic expression in abstinent heroin abusers. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2012, 43, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhao, X. Implicit processing of heroin and emotional cues in abstinent heroin users: Early and late event-related potential effects. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2015, 41, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingelbach, K.; Rieger, J.W. Neurophysiological Basis of Emotional Face Perception and Working Memory Load in a Dual-Task MEG Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2025, 46, e70242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.E.; Schank, J.R. Aversion-associated drug and alcohol seeking in females. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 71, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, J.A.; Logsdon, M.K.; Turner, C.A.; Gonzalez, I.L.; Leonardo, N.B.; Becker, J.B. Sex differences in vulnerability to addiction. Neuropharmacology 2021, 187, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.B.; McClellan, M.L.; Reed, B.G. Sex Differences, Gender and Addiction. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, S.M.; Heller, W.; Stewart, J.L.; Silton, R.L.; Edgar, J.C.; Fisher, J.E.; Miller, G.A. Time course of attentional bias in anxiety: Emotion and gender specificity. Psychophysiology 2010, 47, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.J. Revision of the Chinese facial affective picture system. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2011, 25, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T.E.; Berridge, K.C. The Incentive-Sensitization Theory of Addiction 30 Years On. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2025, 76, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommaso, M.; Turatto, M. Testing reward-cue attentional salience: Attainment and dynamic changes. Br. J. Psychol. 2022, 113, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, P.; Naatanen, R. Foreperiod and Simple Reaction-Time. Psychol. Bull. 1981, 89, 133–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallesi, A.; McIntosh, A.R.; Stuss, D.T. Temporal preparation in aging: A functional MRI study. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 2876–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Rösler, F.; Röder, B. Early processing stages are modulated when auditory stimuli are presented at an attended moment in time:: An event-related potential study. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippen, M. Selective Permeability and Situated Cognitive Harm in Multicultural Classrooms. Topoi Int. Rev. Philos. 2025, 44, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippen, M. Emotional Environments: Selective Permeability, Political Affordances and Normative Settings. Topoi Int. Rev. Philos. 2022, 41, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaz, M.A.; Malaker, P.; Zilverstand, A.; Moeller, S.J.; Alia-Klein, N.; Goldstein, R.Z. Attention bias modification in drug addiction: Enhancing control of subsequent habits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2012941118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Measure | Mean (Standard Deviation) |
|---|---|
| Education level (junior high school or below/senior high school) | 42/9 |
| Marital status (married/unmarried/cohabiting/divorced/separated) | 6/30/4/10/1 |
| Age | 24.71 (7.58) |
| Age at first drug use | 17.94 (3.18) |
| Mean duration of drug use | 5.51 (4.82) |
| OCDUS | 34.94 (8.65) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Tao, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Q.; Guo, W. Drug-Specific Global Attentional Bias in Females with Drug Use Disorder: Response Slowing Under Short but Not Long Cue Exposure. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101127
Wang B, Tao T, Liu J, Wang Z, Ren Q, Guo W. Drug-Specific Global Attentional Bias in Females with Drug Use Disorder: Response Slowing Under Short but Not Long Cue Exposure. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101127
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Biye, Tao Tao, Jian Liu, Zequn Wang, Qing Ren, and Wei Guo. 2025. "Drug-Specific Global Attentional Bias in Females with Drug Use Disorder: Response Slowing Under Short but Not Long Cue Exposure" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101127
APA StyleWang, B., Tao, T., Liu, J., Wang, Z., Ren, Q., & Guo, W. (2025). Drug-Specific Global Attentional Bias in Females with Drug Use Disorder: Response Slowing Under Short but Not Long Cue Exposure. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101127






