Panax notoginseng Flower Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Epilepsy by Restoring Glutamate Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Mouse Model
2.2. Drugs and Reagents
2.3. Epileptic Kindling and Treatment
2.4. Seizure Behavior Assessment
2.5. Brain Microdialysis
2.6. HPLC–MS/MS
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PNF on Seizure Behaviors in PTZ-Kindled Mice
3.2. Effects of PNF on Cortical and Hippocampal Neurons in PTZ-Kindled Mice
3.3. Effects of PNF on Serum Inflammatory Cytokines in PTZ-Kindled Mice
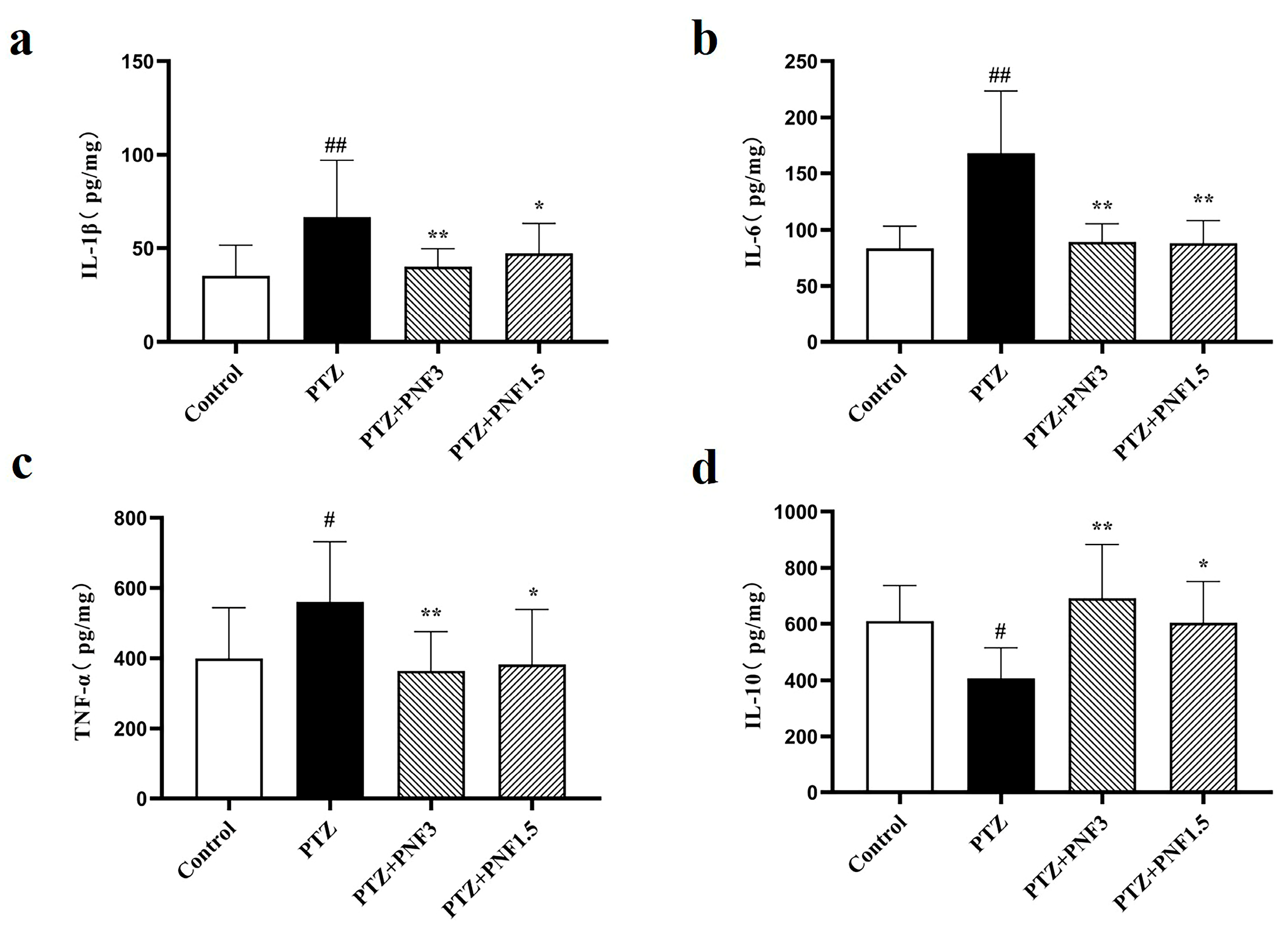
3.4. Effects of PNF on Inflammatory Cytokines in the Brain of PTZ-Kindled Mice
3.5. Effects of PNF on Hippocampal Glutamate in PTZ-Kindled Mice
3.6. Effects of PNF on Glutamate Modulating Related Proteins in the Brains of PTZ-Kindled Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thijs, R.D.; Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Trevick, S. The Epidemiology of Global Epilepsy. Neurol. Clin. 2016, 34, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Schachter, S.C. Drug treatment of epilepsy in adults. BMJ 2014, 348, g254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdillon, P.; Ren, L.; Halgren, M.; Paulk, A.C.; Salami, P.; Ulbert, I.; Fabó, D.; King, J.-R.; Sjoberg, K.M.; Eskandar, E.N.; et al. Differential cortical layer engagement during seizure initiation and spread in humans. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Wu, H.; Luan, G.; Wang, Q. The distribution and heterogeneity of excitability in focal epileptic network potentially contribute to the seizure propagation. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1137704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, F.; Jarre, G.; Pouyatos, B.; Nemoz, C.; Brauer-Krisch, E.; Muzelle, C.; Serduc, R.; Heinrich, C.; Depaulis, A. Aberrant neuronal connectivity in the cortex drives generation of seizures in rat absence epilepsy. Brain 2022, 145, 1978–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Sofroniew, M.V. Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Cheung-Hoi Yu, A. Glutamate, a Key for Astrocytes to Participate in Brain Function and Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2025, 50, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.M.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, M. Discussion on the relationship between astrocyte-regulated glutamate metabolism and epilepsy. Adv. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 53, 127–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.M.; Ma, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, M. Ginsenoside Rb1Antiepileptic effect and mechanism of therapeutic administration. Northwest J. Pharm. 2021, 36, 739–745. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Dai, Y.; Tang, M. GPCR-Gs mediates the protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on oxygen-sugar deprivation/reoxygenation-damaged astrocytes. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2024, 11, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.-Z.; Bo, T.; Ji, S.; Qiao, X.; Guo, D.-A.; Ye, M. Rapid chemical profiling of saponins in the flower buds of Panax notoginseng by integrating MCI gel column chromatography and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Xie, R.F.; Lam, W.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Cheng, Y.-C. Chemosynthesis pathway and bioactivities comparison of saponins in radix and flower of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 201, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.-B.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Hong, S.-J.; Li, P.; Li, S.-P.; Wang, Y.-T. Chemical investigation of saponins in different parts of Panax notoginseng by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2012, 17, 5836–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqubal, A.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, K.; Bhavsar, A.; Hussain, I.; Iqubal, M.K.; Kumar, R. Intranasally administered pitavastatin ameliorates pentylenetetrazol-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and cognitive dysfunction. Life Sci. 2018, 211, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 Antiepileptic effects of nasal administration on glutetrazole chronically ignited mice. Chin. J. Exp. Pharm. 2022, 28, 65–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barker-Haliski, M.; White, H.S. Glutamatergic Mechanisms Associated with Seizures and Epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, P.; Xu, R.; Meng, K.; Liao, S.; Jia, P.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, C. Insights into the development of pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptic seizures from dynamic metabolomic changes. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 2441–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.; Jha, S. Innate immune activation and neuroinflammatory pathways in Epilepsy. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2025, 84, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yan, M.; Rengarajan, T.; Feng, X. Amomum tsaoko fruit extract exerts anticonvulsant effects through suppression of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in a pentylenetetrazol kindling model of epilepsy in mice. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaye Kandeda, A.; Okomolo Moto, F.C.; Mbomo Ayissi, R.E.; Omam, J.P.O.; Ojong, L.; Bum, E.N. Pergularia daemia hydro-ethanolic extract protects against pentylenetetrazole kindling-induced seizures, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, M.; Ou, S.; Sun, L.; Qian, K.; Kuang, H.; Wu, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides ameliorate epileptogenesis, cognitive impairment, and neuroinflammation in a pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling mouse model. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1336122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sands, C.D.; Tang, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neural damage in the brain of mice via regulating the dysfunction of microglia and astrocytes. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyashkin, G.; Blinova, E.; Grigoryan, M.; Parshenkov, M.; Skovorodko, P.; Ius, V.; Lebed, A.; Shegay, P.; Kaprin, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Myricetin on PTZ-Induced Seizures in Mice: Evaluation of Oxidation, Neuroinflammation and Metabolism, and Apoptosis in the Hippocampus. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8914–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller Guzzo, E.F.; Rosa, G.; Lourenço de Lima, A.M.D.; Padilha, R.; Coitinho, A. Piroxicam reduced the intensity of epileptic seizures in a kindling seizure model. Neurol. Res. 2024, 46, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.S.; Ankar, A.; Cokley, J.; Muscal, E.; Riviello, J.J.; Lai, Y. Combined Systemic Immunotherapy and Intrathecal Dexamethasone in Febrile Infection Related Epilepsy Syndrome. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2025, 12, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.M.; Eldin, H.E.S.; Abdelsameea, A.A.; Abdelnour, H.M.; Alabiad, M.A.; Elkholy, M.R.; Aboregela, A.M. Betahistine Attenuates Seizures, Neurodegeneration, Apoptosis, and Gliosis in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus in a Mouse Model of Epilepsy: A Histological, Immunohistochemical, and Biochemical Study. Microsc. Microanal. 2022, 28, 1734–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Matsabisa, M.; Tang, M. Panax notoginseng Flower Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Epilepsy by Restoring Glutamate Homeostasis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101110
Zhao Y, Zhu F, Xie J, Wang Y, Matsabisa M, Tang M. Panax notoginseng Flower Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Epilepsy by Restoring Glutamate Homeostasis. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101110
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yang, Feiya Zhu, Jiayu Xie, Yiting Wang, Motlalepula Matsabisa, and Minke Tang. 2025. "Panax notoginseng Flower Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Epilepsy by Restoring Glutamate Homeostasis" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101110
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhu, F., Xie, J., Wang, Y., Matsabisa, M., & Tang, M. (2025). Panax notoginseng Flower Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Epilepsy by Restoring Glutamate Homeostasis. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101110





