Quantification of High-Resolution Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted Vessel Wall MRI for Predicting Disease Progression in Moyamoya Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
2.2. Imaging Protocol
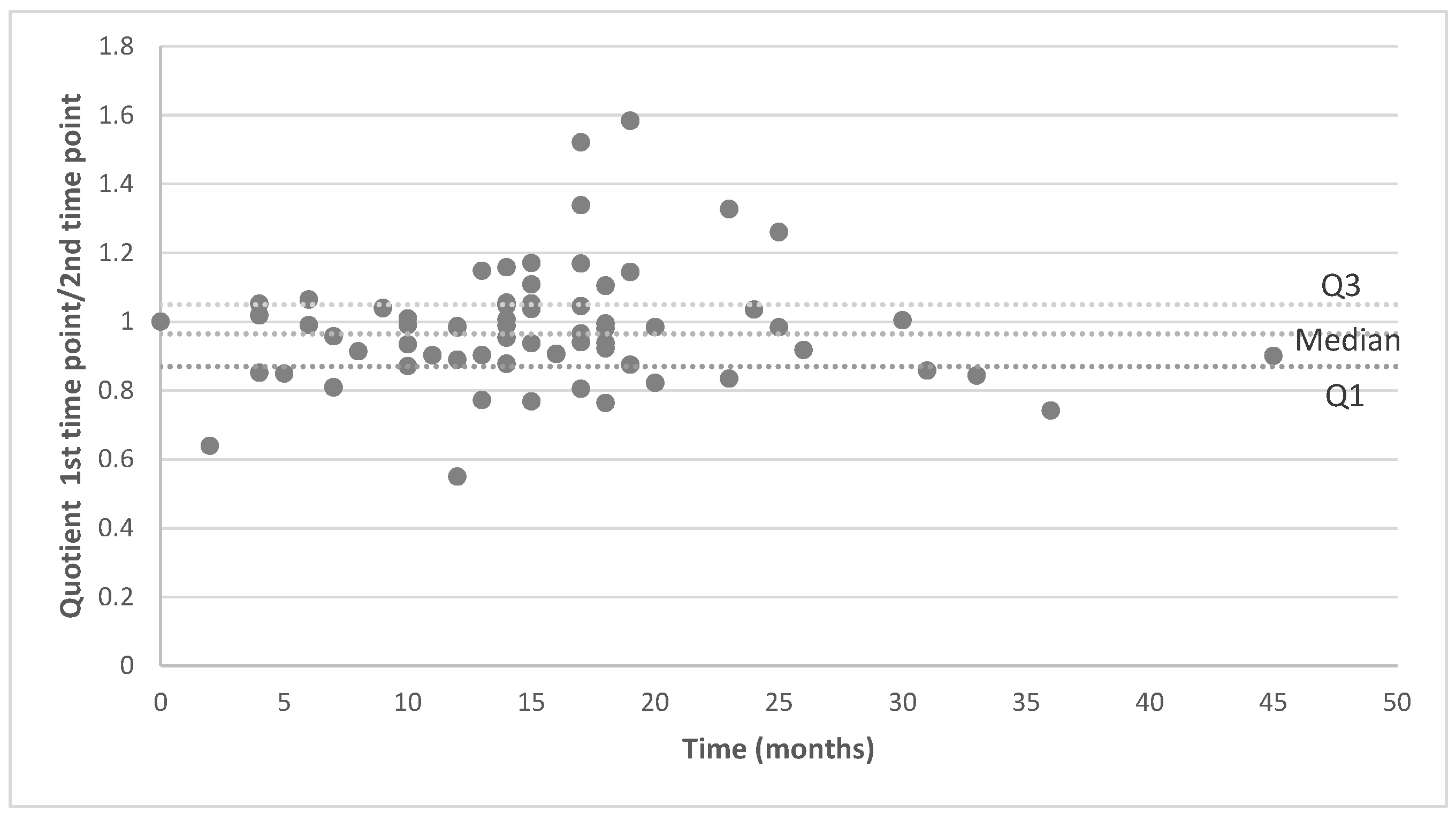
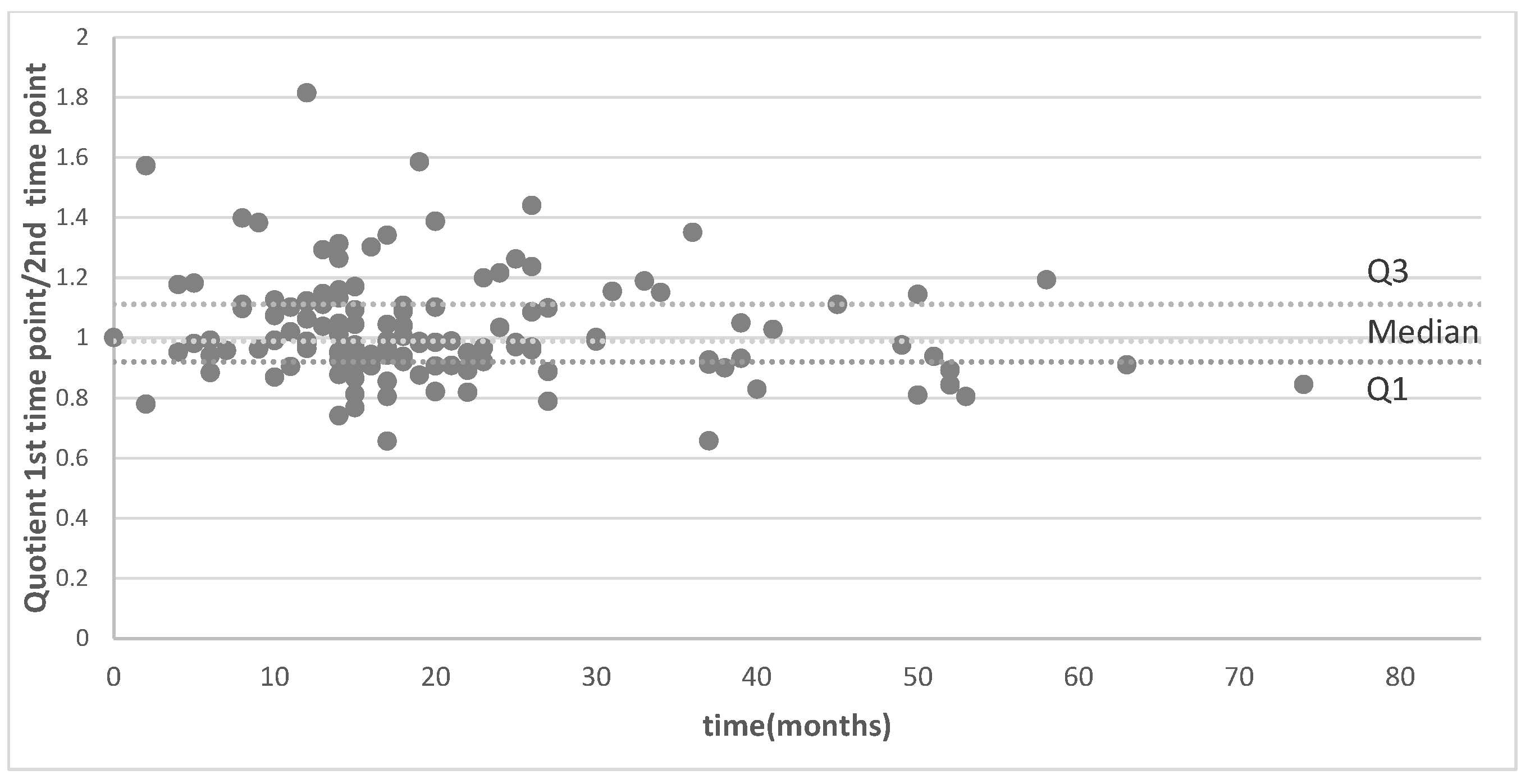
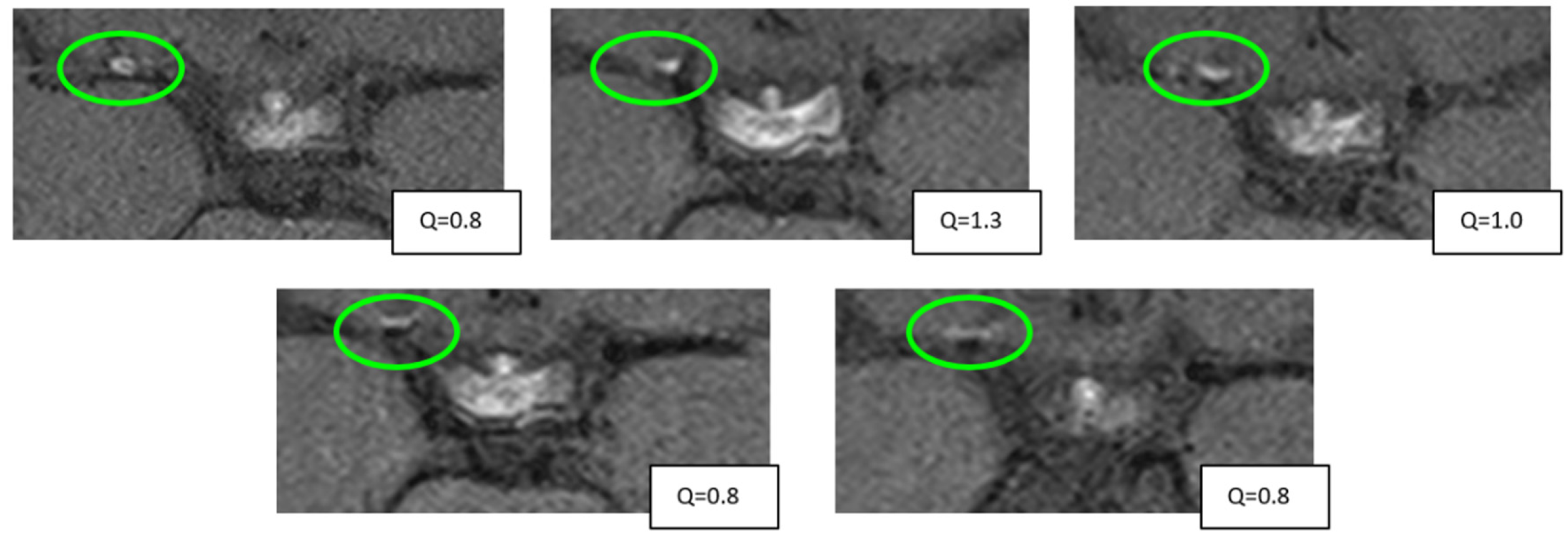
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population and Characteristics
3.2. Signal Intensity of Pituitary Stalk and White Matter of the Temporal Lobe
3.3. Analysis of MRI Performed on the Same MR Machine
3.4. Analysis of MRI Performed on Different MR Machines
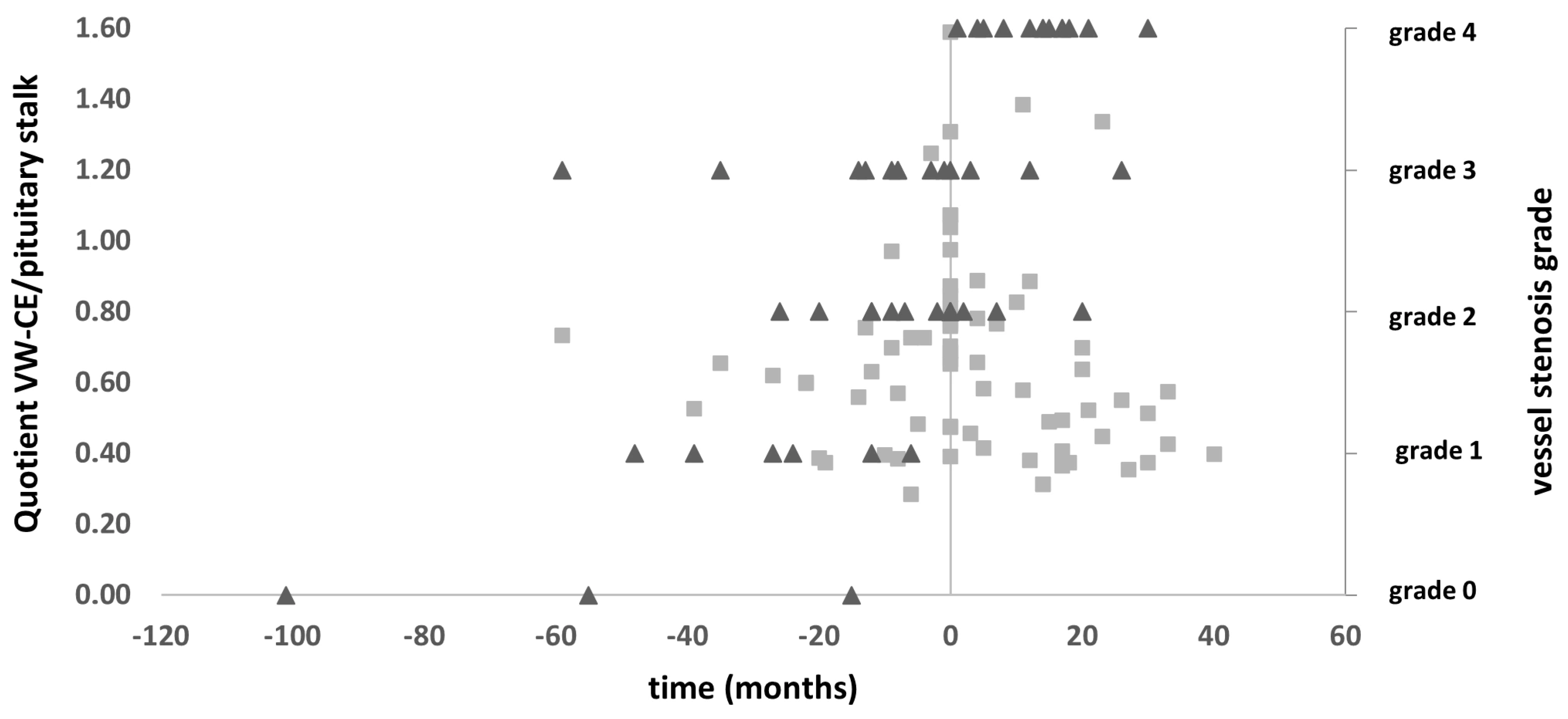
3.5. Vessel Wall CE Dynamics
3.6. Correlation with Stroke, CVR, and Angiographic Stenosis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, J.; Takaku, A. Cerebrovascular “moyamoya” disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in base of brain. Arch. Neurol. 1969, 20, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaghy, R.M.; Yasargil, G. Microangeional surgery and its techniques. Prog. Brain Res. 1968, 30, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Roder, C.; Klose, U.; Hurth, H.; Brendle, C.; Tatagiba, M.; Ernemann, U.; Khan, N.; Hauser, T.-K. Longitudinal Reproducibility of CO2-Triggered BOLD MRI for the Hemodynamic Evaluation of Adult Patients with Moyamoya Angiopathy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 50, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerweck, L.; Roder, C.; Hauser, T.-K.; Thurow, J.; Mengel, A.; Tatagiba, M.; Khan, N.; Meyer, P.T.; Ernemann, U.; Klose, U. Hemodynamic evaluation of patients with Moyamoya Angiopathy: Comparison of resting-state fMRI to breath-hold fMRI and [(15)O]water PET. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Li, M.; Liu, R.; Guan, M.; Li, R.; He, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. The Contrast Enhancement of Intracranial Arterial Wall on High-resolution MRI and Its Clinical Relevance in Patients with Moyamoya Vasculopathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Hauser, T.-K.; Ernemann, U.; Tatagiba, M.; Khan, N.; Bender, B. Arterial wall contrast enhancement in progressive moyamoya disease. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 132, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.-Y.; Hauser, T.-K.; Haas, P.; Tellermann, J.; Hurth, H.; Ernemann, U.; Tatagiba, M.; Bender, B.; Khan, N.; Roder, C. Intensity Score of Vessel Wall Contrast Enhancement in MRI Allows Prediction of Disease Progression in Moyamoya Angiopathy. Neurosurgery 2024, 95, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Hao, F.; Zhang, L.; Peng, P.; Yuan, F.; Liu, S.; Sheng, F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Vessel wall enhancement as a predictor of arterial stenosis progression and poor outcomes in moyamoya disease. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.D.; de Havenon, A.; Kim, S.-E.; Parker, D.L.; McNally, J.S. Assessment of quantitative methods for enhancement measurement on vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of intracranial atherosclerosis. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Science, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Multiple comparison methods: Establishing guidelines for their valid application in neuropsychological research. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1994, 16, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Ma, N.; Ma, L.; Jiang, W.-J. Contrast-enhanced 3T high-resolution MR imaging in symptomatic atherosclerotic basilar artery stenosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpathiotakis, M.; Mandell, D.; Swartz, R.; Tomlinson, G.; Mikulis, D. Intracranial atherosclerotic plaque enhancement in patients with ischemic stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.S.; Klaas, J.P.; Johnson, M.P.; Benson, J.C.; Shlapak, D.; Lanzino, G.; Savastano, L.E.; Lehman, V.T. Vessel wall imaging features of Moyamoya disease in a North American population: Patterns of negative remodelling, contrast enhancement, wall thickening, and stenosis. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, J.; Zhou, D.; Ding, J.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X.; Yang, Q.; Meng, R. High-resolution combined arterial spin labeling MR for identifying cerebral arterial stenosis induced by moyamoya disease or atherosclerosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Wu, M.; Zhou, W.; Yin, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z. High-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging provides new insights into Moyamoya disease. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1375645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, S.; Taoka, T.; Kawai, H.; Okamoto, S.; Uda, K.; Naganawa, S.; Araki, Y. Changes in Vessel Wall Enhancement Related to the Recent Neurological Symptoms in Patients with Moyamoya Disease. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuveetil, A.; Sylaja, P.; Senthilvelan, S.; Chandrasekharan, K.; Banerjee, M.; Sudhir, B.J. Vessel Wall Thickening and Enhancement in High-Resolution Intracranial Vessel Wall Imaging: A Predictor of Future Ischemic Events in Moyamoya Disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Lee, E.; Song, J. Outcomes of Bypass Surgery in Adult Moyamoya Disease by Onset Type. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2415102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acker, G.; Goerdes, S.; Schneider, U.C.; Schmiedek, P.; Czabanka, M.; Vajkoczy, P. Distinct clinical and radiographic characteristics of moyamoya disease amongst European Caucasians. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Han, C.; Sheng, F.; Cai, J. Predictors of Stroke Outcomes in Conservatively Treated Patients With Moyamoya Disease: A Follow-up MRI Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 59, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stence, N.V.; Pabst, L.L.; Hollatz, A.L.; Mirsky, D.M.; Herson, P.S.; Poisson, S.; Traystman, R.J.; Bernard, T.J. Predicting Progression of Intracranial Arteriopathies in Childhood Stroke With Vessel Wall Imaging. Stroke 2017, 48, 2274–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, S.; Cha, J.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.W.; Ki, C.-S.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, P.; Kim, J.-S.; Hong, S.-C.; Bang, O.Y. High-resolution magnetic resonance wall imaging findings of Moyamoya disease. Stroke 2014, 45, 2457–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; De Vis, J.B.; Lu, H. Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) MRI with CO2 challenge: A technical review. Neuroimage 2019, 187, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, G.; Lange, C.; Schatka, I.; Pfeifer, A.; Czabanka, M.A.; Vajkoczy, P.; Buchert, R. Brain Perfusion Imaging Under Acetazolamide Challenge for Detection of Impaired Cerebrovascular Reserve Capacity: Positive Findings with (15)O-Water PET in Patients with Negative (99m)Tc-HMPAO SPECT Findings. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Bürkle, E.; Ebner, F.H.; Tatagiba, M.; Ernemann, U.; Buck, A.; Meyer, P.T.; Khan, N. Estimation of Severity of Moyamoya Disease with [(15)O]Water-Positron Emission Tomography Compared with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Angiography. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, e75–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ge, P.; Zeng, C.; Liu, C.; Yin, Z.; Ya, X.; Zhai, Y.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Ye, X.; et al. Prognostic value of morphology and hemodynamics in moyamoya disease for long-term outcomes and disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandell, D.M.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Qiao, Y.; Hess, C.; Hui, F.; Matouk, C.; Johnson, M.; Daemen, M.; Vossough, A.; Edjlali, M.; et al. Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI: Principles and Expert Consensus Recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritanon, O.; Mataeng, S.; Apirakkan, M.; Panyaping, T. Utility of high-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging in differentiating between atherosclerotic plaques, vasculitis, and arterial dissection. Neuroradiology 2023, 65, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, K.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; An, Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, P.; Li, P.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Validation of Wall Enhancement as a New Imaging Biomarker of Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysm. Stroke 2019, 50, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, Y.H.; Han, B.K.; Koh, E.M.; Kim, D.K.; Do, Y.S.; Lee, W.R. Takayasu’s arteritis: Assessment of disease activity with contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texakalidis, P.; Hilditch, C.A.; Lehman, V.; Lanzino, G.; Pereira, V.M.; Brinjikji, W. Vessel Wall Imaging of Intracranial Aneurysms: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, 453–458.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, M.; Kono, S.; Sueishi, K.; Ikezaki, K. Moyamoya disease. Neuropathology 2000, 20, S61–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F. Do human intracranial arteries lack vasa vasorum? A comparative immunohistochemical study of intracranial and systemic arteries. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 96, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All Patients (n = 87) | With CE (n = 68) | Without CE (n = 19) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yo (± SD) | 42.3 ± 14.0 | 43.0 ± 14.2 | 39.3 ± 13.6 | p = 0.287 |
| Sex | p = 0.57 | |||
| 63 (72.4%) | 48 (70.6%) | 15 (78.9%) | |
| 24 (27.6%) | 20 (29.4%) | 4 (21.1%) | |
| Symptoms (on primary evaluation) | ||||
| 26 (29.9%) | 21 (30.9%) | 5 (26.3%) | p = 1.0 |
| 39 (44.8%) | 36 (52.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | p = 0.021 * |
| 7 (8.0%) | 3 (4.4%) | 4 (21.1%) | p = 0.191 |
| 11 (12.6%) | 7 (10.3%) | 4 (21.1%) | p = 1.0 |
| 4 (4.6%) | 1 (1.5%) | 3 (15.8%) | p = 0.157 |
| Suzuki grade: right/left (sum right + left, % of all) | p = 0.025 * | |||
| not affected (right/left (total, %)) | 13/21 (34, 19.5%) | 8/19 (27, 19.9%) | 5/2 (7, 18.4%) | |
| grade 1 (right/left (total, %)) | 7/7 (14, 8.5%) | 6/7 (13, 9.6%) | 1/0 (1, 2.6%) | |
| grade 2 (right/left (total, %)) | 14/13 (27, 15.5%) | 12/11 (23, 16.9%) | 2/2 (4, 10.5%) | |
| grade 3 (right/left (total, %)) | 27/21 (48, 27.6%) | 26/15 (41, 30.1%) | 1/6 (7, 18.4%) | |
| grade 4 (right/left (total, %)) | 14/9 (23, 13.2%) | 8/5 (13, 9.6%) | 6/4 (10, 26.3%) | |
| grade 5 (right/left (total, %)) | 6/9 (15, 8.6%) | 5/7 (12, 8.8%) | 1/2 (3, 7.9%) | |
| grade 6 (right/left (total, %)) | 6/7 (13, 7.5%) | 3/4 (7, 5.1%) | 3/3 (6, 15.8%) | |
| Bypass status | p = 0.090 | |||
| 9 (10.3%) | 6 (8.8%) | 3 (15.8%) | |
| ||||
| unilateral | 44 (50.6%) | 35 (51.5%) | 9 (47.4%) | |
| bilateral | 34 (39.1%) | 27 (39.7%) | 7 (36.8%) | |
| ||||
| unilateral | 10 (11.5%) | 8 (11.8%) | 2 (10.5%) | |
| bilateral | 20 (23.0%) | 18 (26.4%) | 2 (10.5%) | |
| ||||
| unilateral | 3 (3.4%) | 3 (4.4%) | 0 (0%) | |
| bilateral | 1 (1.1%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goloshchapova, K.; Haas, P.; Vogl, D.; Wiggenhauser, L.; Hurth, H.; Hennersdorf, F.; Bender, B.; Hauser, T.-K.; Tatagiba, M.; Khan, N.; et al. Quantification of High-Resolution Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted Vessel Wall MRI for Predicting Disease Progression in Moyamoya Disease. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101089
Goloshchapova K, Haas P, Vogl D, Wiggenhauser L, Hurth H, Hennersdorf F, Bender B, Hauser T-K, Tatagiba M, Khan N, et al. Quantification of High-Resolution Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted Vessel Wall MRI for Predicting Disease Progression in Moyamoya Disease. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101089
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoloshchapova, Kateryna, Patrick Haas, Daniel Vogl, Lucas Wiggenhauser, Helene Hurth, Florian Hennersdorf, Benjamin Bender, Till-Karsten Hauser, Marcos Tatagiba, Nadia Khan, and et al. 2025. "Quantification of High-Resolution Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted Vessel Wall MRI for Predicting Disease Progression in Moyamoya Disease" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101089
APA StyleGoloshchapova, K., Haas, P., Vogl, D., Wiggenhauser, L., Hurth, H., Hennersdorf, F., Bender, B., Hauser, T.-K., Tatagiba, M., Khan, N., & Roder, C. (2025). Quantification of High-Resolution Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted Vessel Wall MRI for Predicting Disease Progression in Moyamoya Disease. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101089






