E46K α-Synuclein Mutation Fails to Promote Neurite Outgrowth by Not Inducing Cdc42EP2 Expression, Unlike Wild-Type or A53T α-Synuclein in SK-N-SH Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. SK-N-SH Cell Differentiation
2.3. Gene Transfection
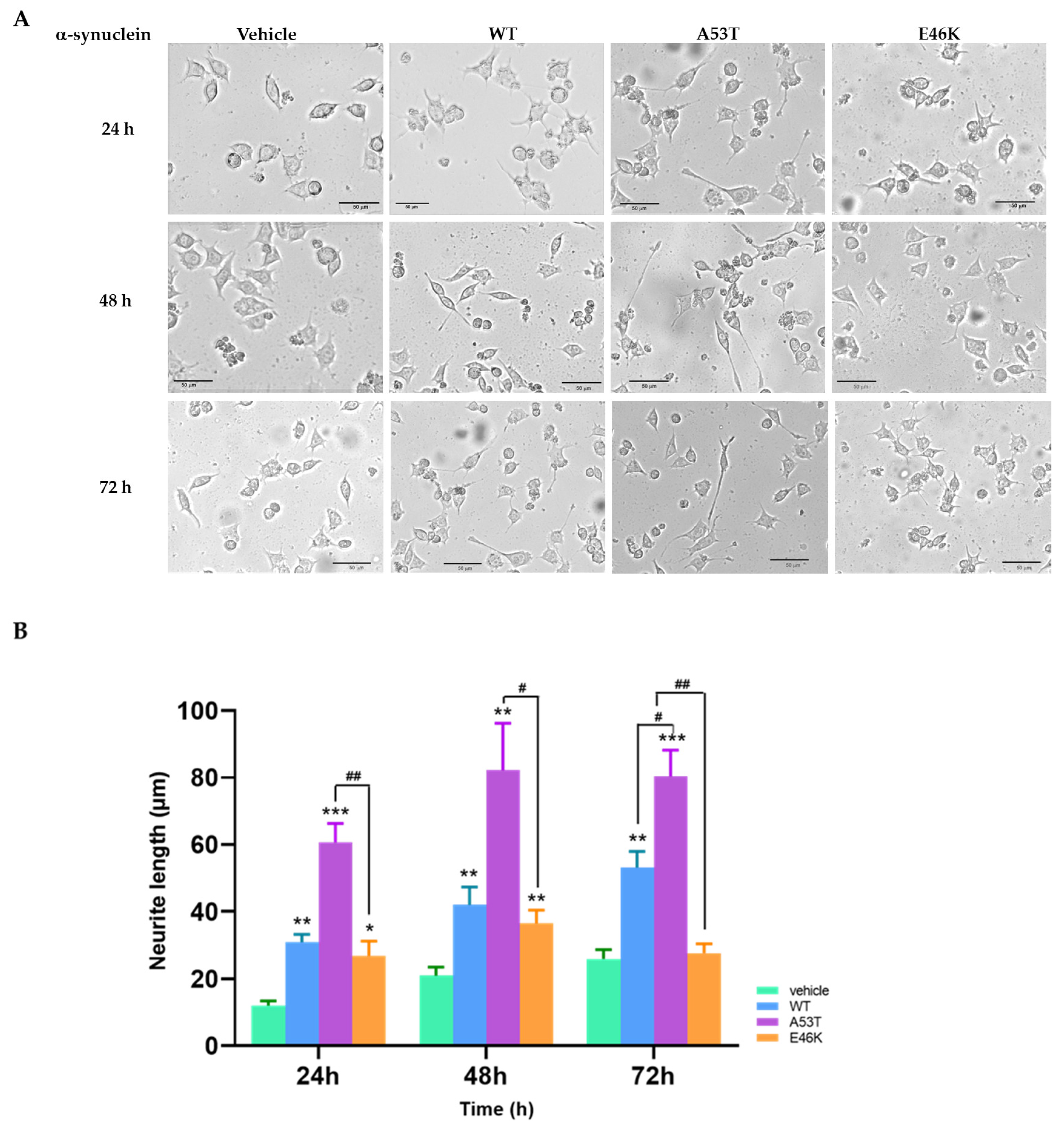
2.4. Neurite Outgrowth Measurement
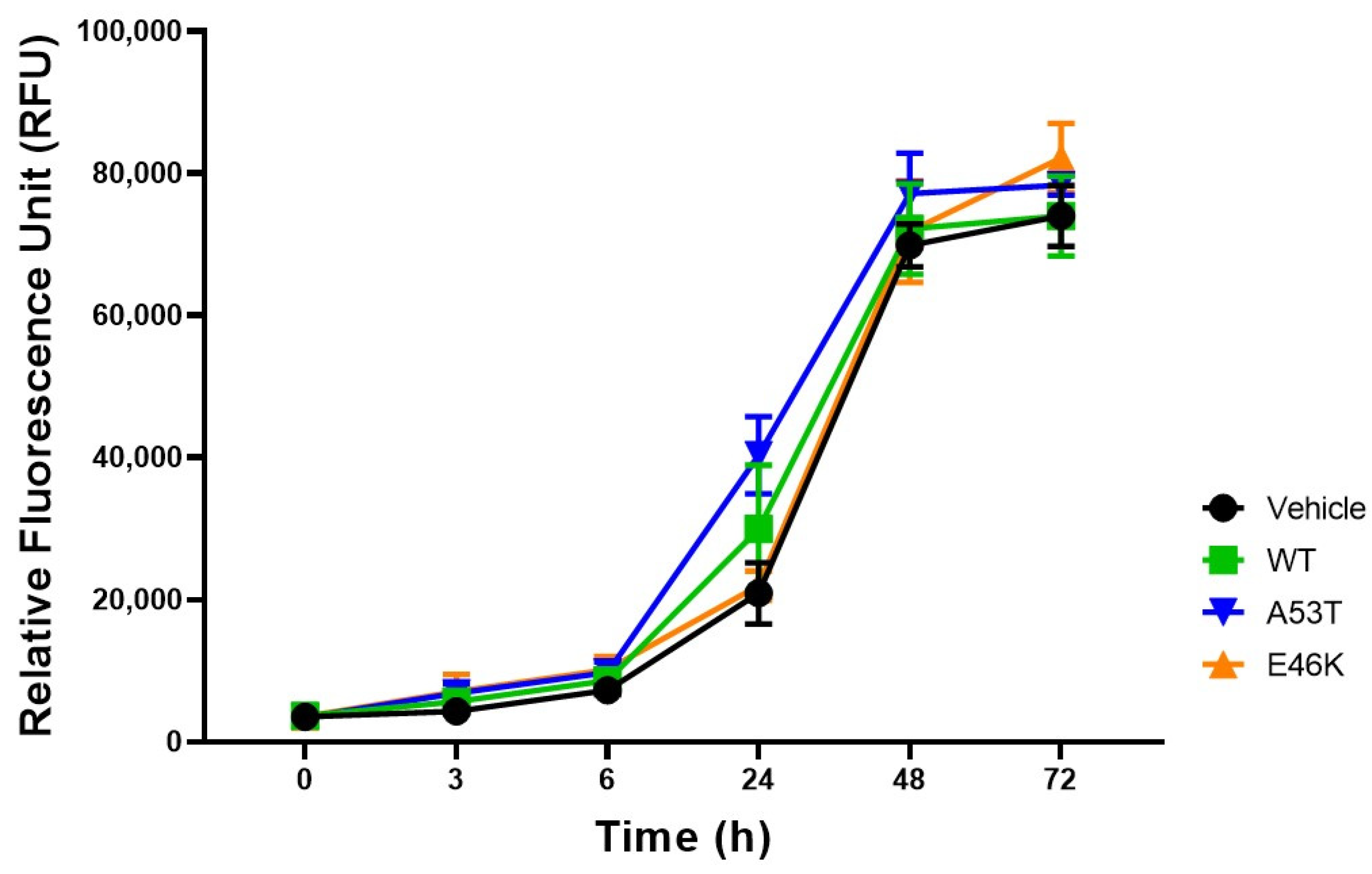
2.5. Cell Viability and Proliferation Evaluation
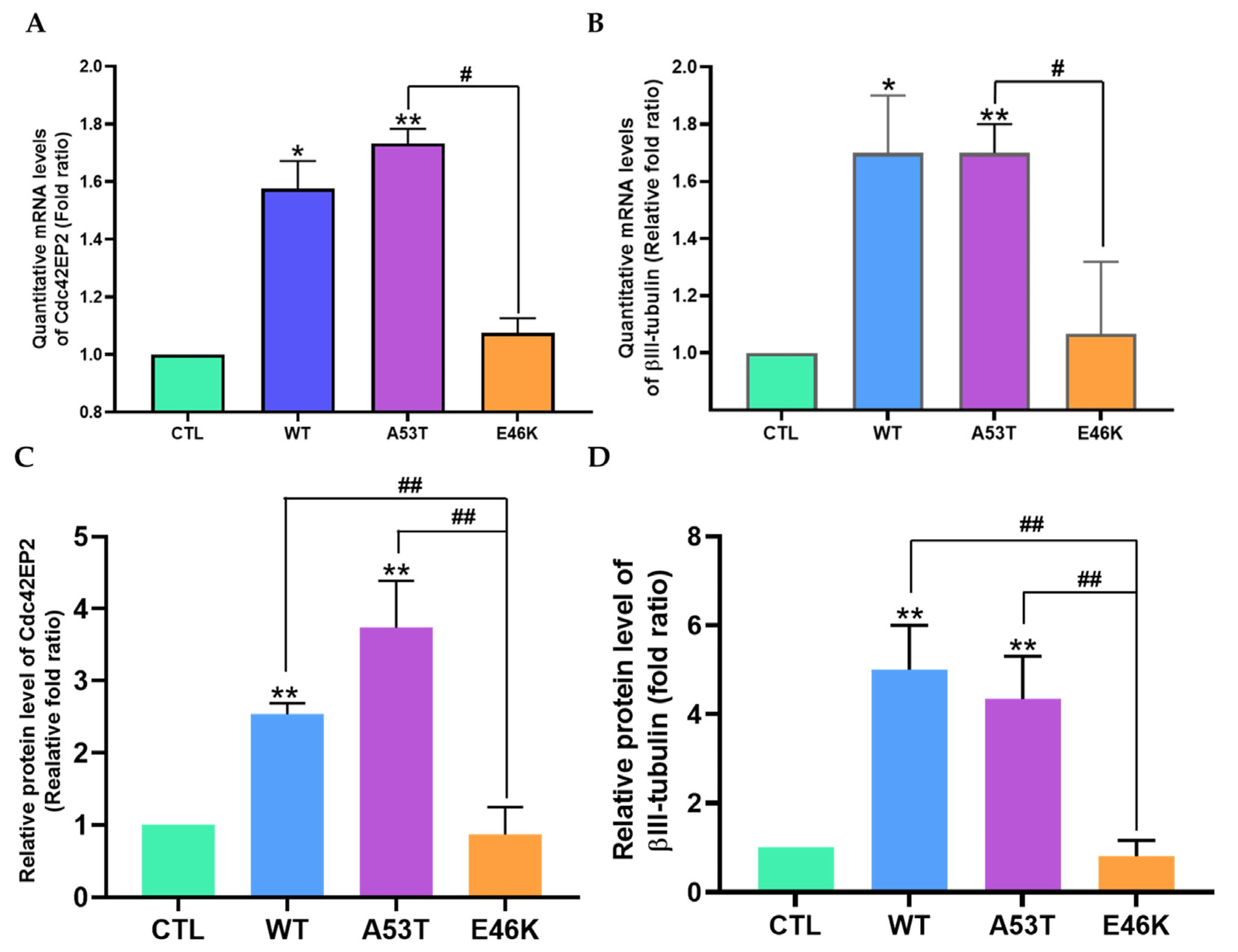
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
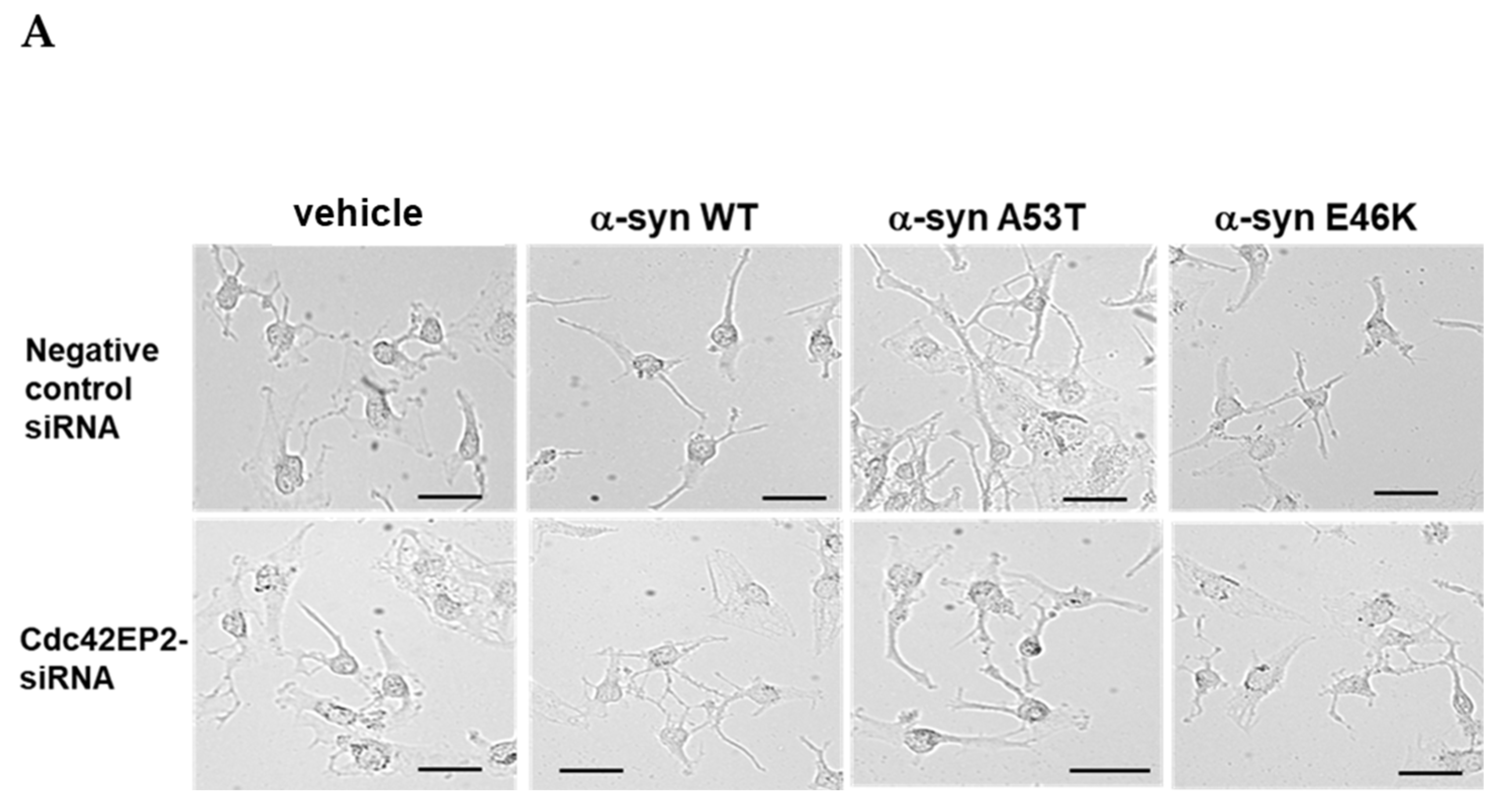
2.9. Knock-Down with Small Interference RNA (siRNA) Transfection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. E46K α-Syn Mutant Overexpression Attenuated Neurite Outgrowth
3.2. Proliferation of E46K Mutant α-Syn Transfected SK-N-SH Cells
3.3. Cdc42EP2 Negatively Regulated Neurite Outgrowth by Downregulating βIII-Tubulin in E46K α-Syn Transfectants
3.4. α-Syn-Induced Cdc42EP2 Expression Regulated Neurite Outgrowth in SK-N-SH Cells
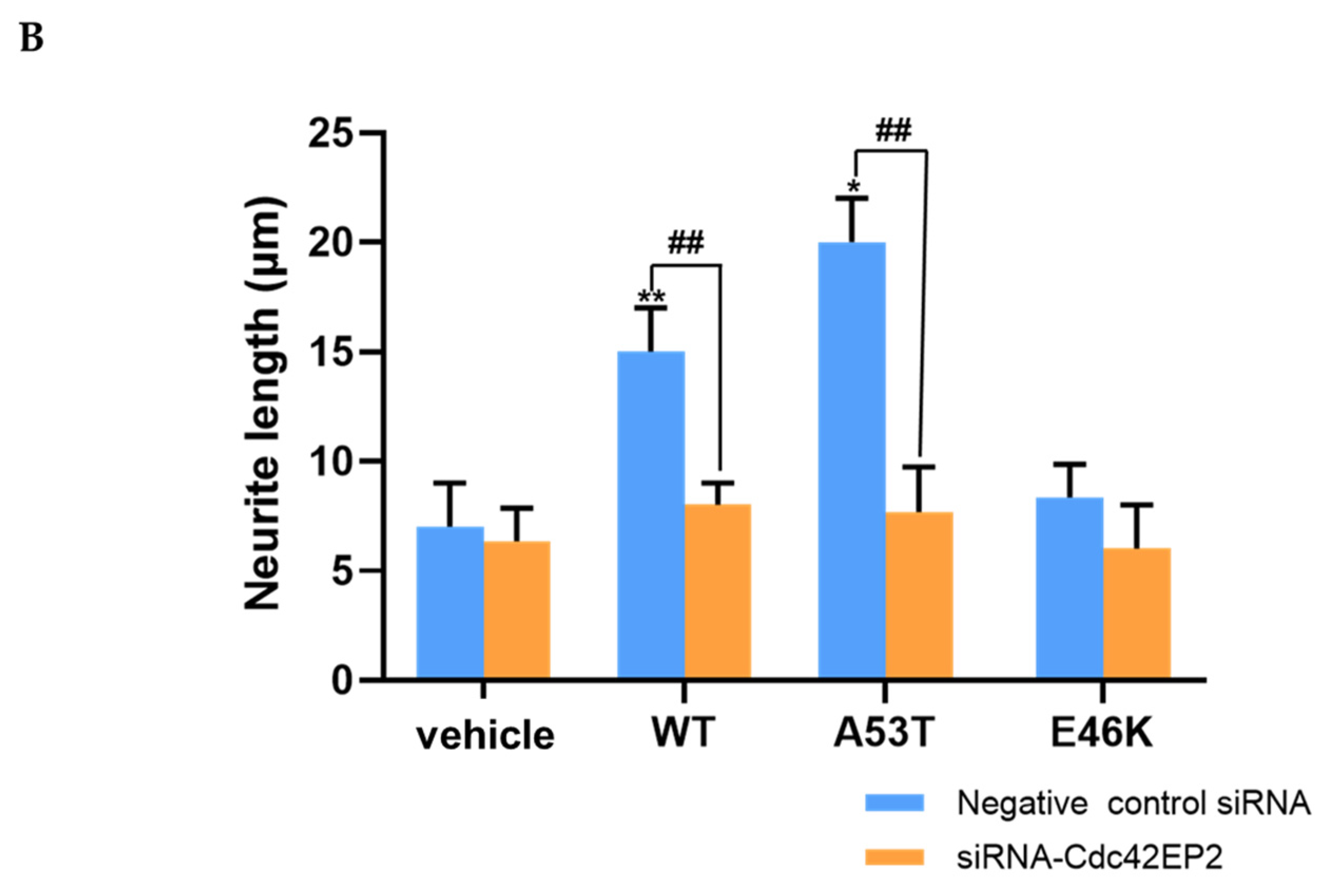
3.5. Cdc42EP2 Knockdown Abrogated α-Syn-Induced Neurite Outgrowth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, S.; Raymick, J.; Imam, S. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies against Parkinson’s Disease: Recent Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, M.T. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Vélez, G.E.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Parkinson’s Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 44, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morato Torres, C.A.; Wassouf, Z.; Zafar, F.; Sastre, D.; Outeiro, T.F.; Schüle, B. The Role of Alpha-Synuclein and Other Parkinson’s Genes in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stykel, M.G.; Humphries, K.M.; Kamski-Hennekam, E.; Buchner-Duby, B.; Porte-Trachsel, N.; Ryan, T.; Coackley, C.L.; Bamm, V.V.; Harauz, G.; Ryan, S.D. α-Synuclein mutation impairs processing of endomembrane compartments and promotes exocytosis and seeding of α-synuclein pathology. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, A.; Wersinger, C.; Moussa, C.E.; Vernier, P. The role of alpha-synuclein in both neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1035, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryskalin, L.; Busceti, C.L.; Limanaqi, F.; Biagioni, F.; Gambardella, S.; Fornai, F. A Focus on the Beneficial Effects of Alpha Synuclein and a Re-Appraisal of Synucleinopathies. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Regensburger, M.; Schreglmann, S.; Boyer, L.; Prots, I.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Zhao, C.; Winkler, J.; Masliah, E.; et al. Role of α-synuclein in adult neurogenesis and neuronal maturation in the dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16906–16916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.; Im, H. alpha-Synuclein modulates neurite outgrowth by interacting with SPTBN1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxreiter, F.; Nuber, S.; Kandasamy, M.; Klucken, J.; Aigner, R.; Burgmayer, R.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Riess, O.; Winkler, J.; Winner, B. Changes in adult olfactory bulb neurogenesis in mice expressing the A30P mutant form of alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Uéda, K.; Chan, P.; Yu, S. Alpha-synuclein promotes early neurite outgrowth in cultured primary neurons. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreglmann, S.R.; Regensburger, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Xiang, W.; Winkler, J.; Winner, B. The temporal expression pattern of alpha-synuclein modulates olfactory neurogenesis in transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. α-Synuclein Promotes Maturation of Immature Juxtaglomerular Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, V. Force: A messenger of axon outgrowth. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 140, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.P.; Matias, I.; Araujo, A.P.B.; Garcia, M.N.; Barros-Aragão, F.G.Q.; Alves-Leon, S.V.; de Souza, J.M.; Foguel, D.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Braga, C.; et al. α-synuclein oligomers enhance astrocyte-induced synapse formation through TGF-β1 signaling in a Parkinson’s disease model. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, R.; Sawada, H.; Kawamoto, Y.; Uemura, K.; Shibasaki, H.; Shimohama, S. BDNF is induced by wild-type alpha-synuclein but not by the two mutants, A30P or A53T, in glioma cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartelli, D.; Aliverti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Santambrogio, C.; Ragg, E.M.; Casagrande, F.V.; Cantele, F.; Beltramone, S.; Marangon, J.; De Gregorio, C.; et al. α-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, M.; Grigoletto, J.; Abd-Elhadi, S.; Glickstein, H.; Friedman, A.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Sharon, R. A role for α-Synuclein in axon growth and its implications in corticostriatal glutamatergic plasticity in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wan, W.; Ma, Z. An unexpected improvement in spatial learning and memory ability in alpha-synuclein A53T transgenic mice. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Villalba, A.; Sirerol-Piquer, M.S.; Belenguer, G.; Soriano-Cantón, R.; Muñoz-Manchado, A.B.; Villadiego, J.; Alarcón-Arís, D.; Soria, F.N.; Dehay, B.; Bezard, E.; et al. Synaptic Regulator α-Synuclein in Dopaminergic Fibers Is Essentially Required for the Maintenance of Subependymal Neural Stem Cells. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Lopez, E.; Vidyadhara, D.J.; Liberia, T.; Meller, S.J.; Harmon, L.E.; Hsu, R.M.; Spence, N.; Brennan, B.; Han, K.; Yücel, B.; et al. α-Synuclein Pathology and Reduced Neurogenesis in the Olfactory System Affect Olfaction in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenouchi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Hsu, L.J.; Mackowski, B.; Rockenstein, E.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. Reduced neuritic outgrowth and cell adhesion in neuronal cells transfected with human alpha-synuclein. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2001, 17, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzetti, S.; Calogero, A.M.; Pezzoli, G.; Cappelletti, G. Cross-talk between α-synuclein and the microtubule cytoskeleton in neurodegeneration. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 359, 114251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebauer, L.; Schneider, Y.; Drobny, A.; Plötz, S.; Koudelka, T.; Tholey, A.; Prots, I.; Winner, B.; Zunke, F.; Winkler, J.; et al. Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachetzki, J.C.; Grimm, T.; Schlachetzki, Z.; Ben Abdallah, N.M.; Ettle, B.; Vöhringer, P.; Ferger, B.; Winner, B.; Nuber, S.; Winkler, J. Dopaminergic lesioning impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis by distinct modification of α-synuclein. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Guo, C. E46K Mutation of α-Synuclein Preorganizes the Intramolecular Interactions Crucial for Aggregation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 4803–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, D.R.; Li, B.; Sun, C.; Fan, W.; Zhou, K.; Hughes, M.P.; Sawaya, M.R.; Jiang, L.; Eisenberg, D.S. The α-synuclein hereditary mutation E46K unlocks a more stable, pathogenic fibril structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3592–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regensburger, M.; Schreglmann, S.R.; Stoll, S.; Rockenstein, E.; Loskarn, S.; Xiang, W.; Masliah, E.; Winner, B. Oligomer-prone E57K-mutant alpha-synuclein exacerbates integration deficit of adult hippocampal newborn neurons in transgenic mice. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targett, I.L.; Crompton, L.A.; Conway, M.E.; Craig, T.J. Differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells using retinoic acid and BDNF: A model for neuronal and synaptic differentiation in neurodegeneration. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2024, 60, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Shin, K.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Park, C.H.; Chang, K.A.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, D.; Suh, Y.H. Alpha-synuclein induces migration of BV-2 microglial cells by up-regulation of CD44 and MT1-MMP. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemberton, K.; Mersman, B.; Xu, F. Using ImageJ to Assess Neurite Outgrowth in Mammalian Cell Cultures: Research Data Quantification Exercises in Undergraduate Neuroscience Lab. J. Undergrad. Neurosci. Educ. 2018, 16, A186–A194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres-Espín, A.; Santos, D.; González-Pérez, F.; del Valle, J.; Navarro, X. Neurite-J: An image-J plug-in for axonal growth analysis in organotypic cultures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 236, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Luk, K.C.; Patel, T.P.; Tanik, S.A.; Riddle, D.M.; Stieber, A.; Meaney, D.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 2011, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Han, C.; Jiang, H.; Ma, K.; Guo, S.; Xia, Y.; Wan, F.; Huang, J.; Xiong, N.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 4 Inhibition Reduces Rotenone-Induced Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation via Autophagy in SH-SY5Y Cells. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.A.; Falomir-Lockhart, L.J.; Botelho, M.G.; Lin, K.H.; Wales, P.; Koch, J.C.; Gerhardt, E.; Taschenberger, H.; Outeiro, T.F.; Lingor, P.; et al. Elevated α-synuclein caused by SNCA gene triplication impairs neuronal differentiation and maturation in Parkinson’s patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Zou, Y.; Qin, Q.; Qu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. α-Synuclein induces Th17 differentiation and impairs the function and stability of Tregs by promoting RORC transcription in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 108, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prots, I.; Veber, V.; Brey, S.; Campioni, S.; Buder, K.; Riek, R.; Böhm, K.J.; Winner, B. α-Synuclein oligomers impair neuronal microtubule-kinesin interplay. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21742–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.C.; Bitow, F.; Haack, J.; d’Hedouville, Z.; Zhang, J.N.; Tönges, L.; Michel, U.; Oliveira, L.M.; Jovin, T.M.; Liman, J.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein affects neurite morphology, autophagy, vesicle transport and axonal degeneration in CNS neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, V.; Dolt, K.S.; Alcaide-Corral, C.J.; Walton, T.; Lucatelli, C.; Mashimo, T.; Tavares, A.A.S.; Kunath, T. In vivo(18)F-DOPA PET imaging identifies a dopaminergic deficit in a rat model with a G51D alpha-synuclein mutation. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1095761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.H.C.; Martinez-Valbuena, I.; So, R.W.L.; Mehra, S.; Silver, N.R.G.; Mao, A.; Stuart, E.; Schmitt-Ulms, C.; Hyman, B.T.; Ingelsson, M.; et al. The G51D SNCA mutation generates a slowly progressive alpha-synuclein strain in early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Sheveleva, A.; Tuna, F.; Willison, K.R.; Ying, L. Acetylation Rather than H50Q Mutation Impacts the Kinetics of Cu(II) Binding to alpha-Synuclein. Chemphyschem 2021, 22, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.Q.; Yuan, Y.H.; Chu, S.F.; Li, G.H.; Chen, N.H. E46K Mutant α-Synuclein Is Degraded by Both Proteasome and Macroautophagy Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Íñigo-Marco, I.; Valencia, M.; Larrea, L.; Bugallo, R.; Martínez-Goikoetxea, M.; Zuriguel, I.; Arrasate, M. E46K α-synuclein pathological mutation causes cell-autonomous toxicity without altering protein turnover or aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8274–E8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.Q.; Yuan, Y.H.; Gao, Y.N.; Huang, J.Y.; Ma, K.L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Guo, X.F.; Chen, N.H. Overexpression of human E46K mutant α-synuclein impairs macroautophagy via inactivation of JNK1-Bcl-2 pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.R.; Geghman, K.D.; Tapias, V.; Sew, T.; Dail, M.K.; Li, C.; Greenamyre, J.T. Expression of human E46K-mutated α-synuclein in BAC-transgenic rats replicates early-stage Parkinson’s disease features and enhances vulnerability to mitochondrial impairment. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 240, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.J.; Pervaiz, N.; Abbasi, A.A. The Parkinson Disease gene SNCA: Evolutionary and structural insights with pathological implication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažeković, A.; Jerčić, K.G.; Borovečki, F. SNCA 3’ UTR Genetic Variants in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, D.S.; Pirone, D.M.; Burbelo, P.D. A new family of Cdc42 effector proteins, CEPs, function in fibroblast and epithelial cell shape changes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, A.J.; Calvo, F. The Borg family of Cdc42 effector proteins Cdc42EP1-5. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, F.; Ma, J.; Xu, C. Cyclic stretch-induced the cytoskeleton rearrangement and gene expression of cytoskeletal regulators in human periodontal ligament cells. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnack, C.; Danzer, K.M.; Hengerer, B.; Gillardon, F. Protein array analysis of oligomerization-induced changes in alpha-synuclein protein-protein interactions points to an interference with Cdc42 effector proteins. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yue, C.; Chen, J.; Tian, C.; Yang, D.; Xing, L.; Liu, H.; Jin, Y. Class III β-Tubulin in Colorectal Cancer: Tissue Distribution and Clinical Analysis of Chinese Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3915–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Casacuberta, I.; Vilas, D.; Pont-Sunyer, C.; Tobías, E.; Cantó-Santos, J.; Valls-Roca, L.; García-García, F.J.; Garrabou, G.; Grau-Junyent, J.M.; Martí, M.J.; et al. Neuronal induction and bioenergetics characterization of human forearm adipose stem cells from Parkinson’s disease patients and healthy controls. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Kim, S. E46K α-Synuclein Mutation Fails to Promote Neurite Outgrowth by Not Inducing Cdc42EP2 Expression, Unlike Wild-Type or A53T α-Synuclein in SK-N-SH Cells. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15010009
Jung H, Kim S. E46K α-Synuclein Mutation Fails to Promote Neurite Outgrowth by Not Inducing Cdc42EP2 Expression, Unlike Wild-Type or A53T α-Synuclein in SK-N-SH Cells. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Hyunja, and Seonghan Kim. 2025. "E46K α-Synuclein Mutation Fails to Promote Neurite Outgrowth by Not Inducing Cdc42EP2 Expression, Unlike Wild-Type or A53T α-Synuclein in SK-N-SH Cells" Brain Sciences 15, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15010009
APA StyleJung, H., & Kim, S. (2025). E46K α-Synuclein Mutation Fails to Promote Neurite Outgrowth by Not Inducing Cdc42EP2 Expression, Unlike Wild-Type or A53T α-Synuclein in SK-N-SH Cells. Brain Sciences, 15(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15010009




