Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
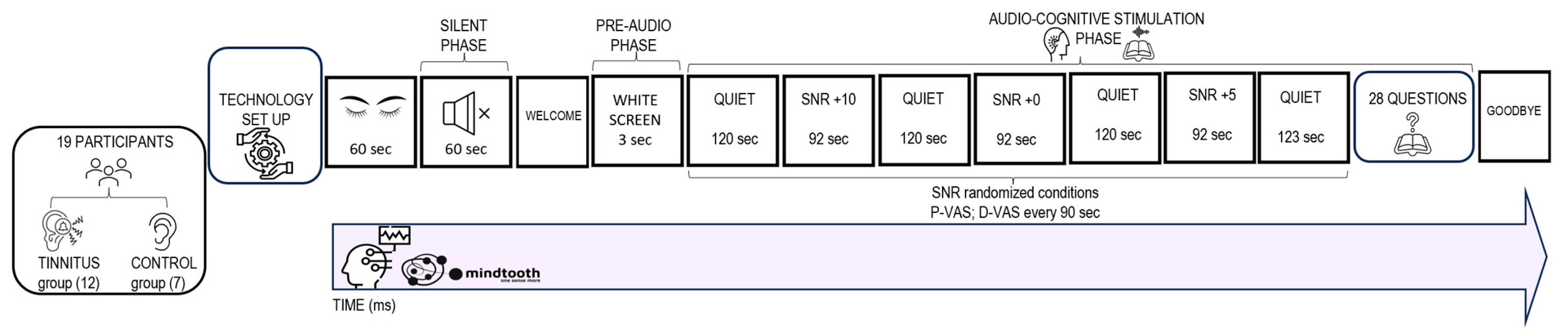
2.1. Experimental Sample
2.2. Audiological Assessment
2.3. Psychological Assessment
2.4. Electroencephalographic Assessment
2.5. Audio Cognitive Task
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
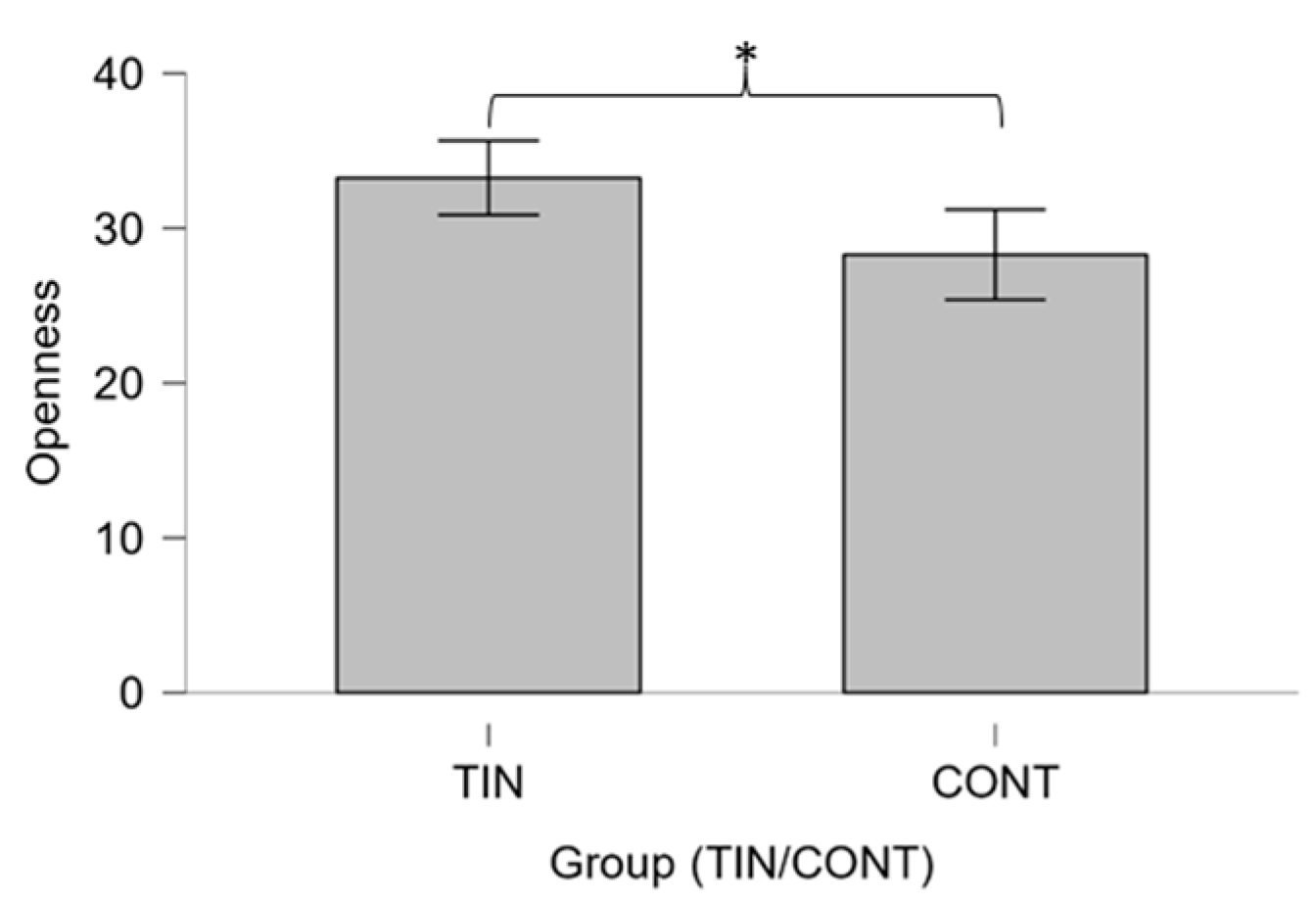
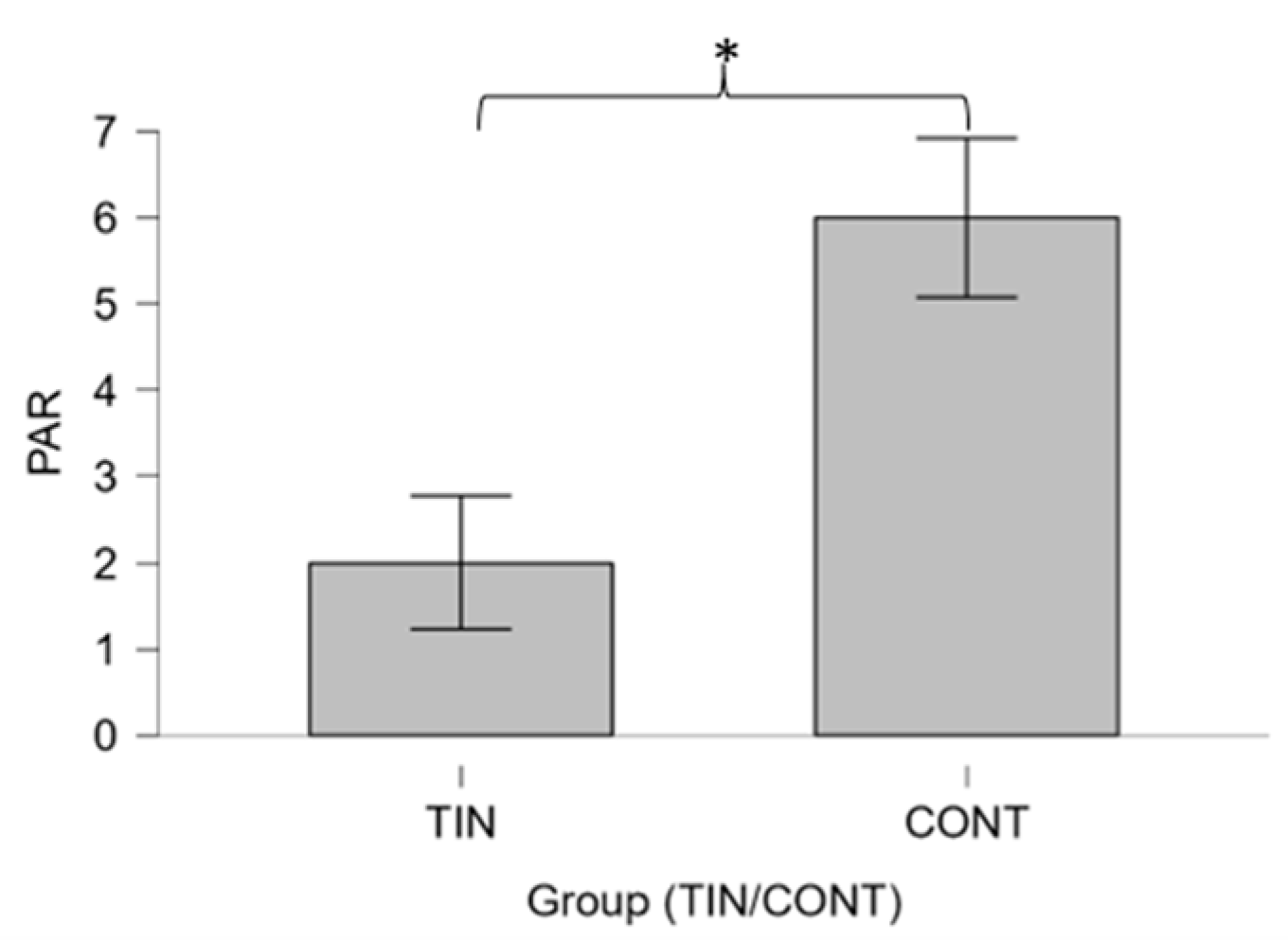
3.1. Differences between Groups
3.2. Correlation Results
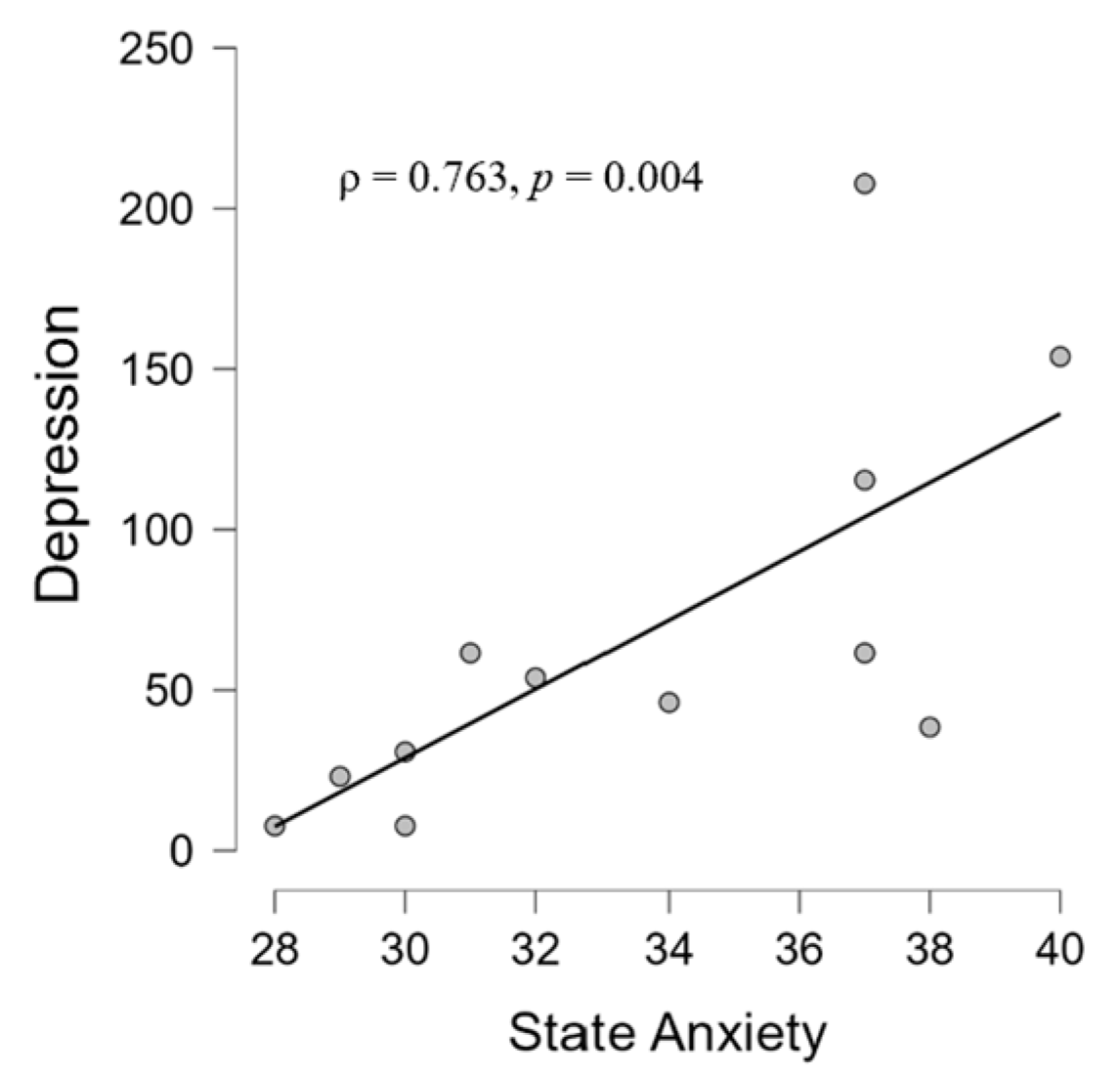
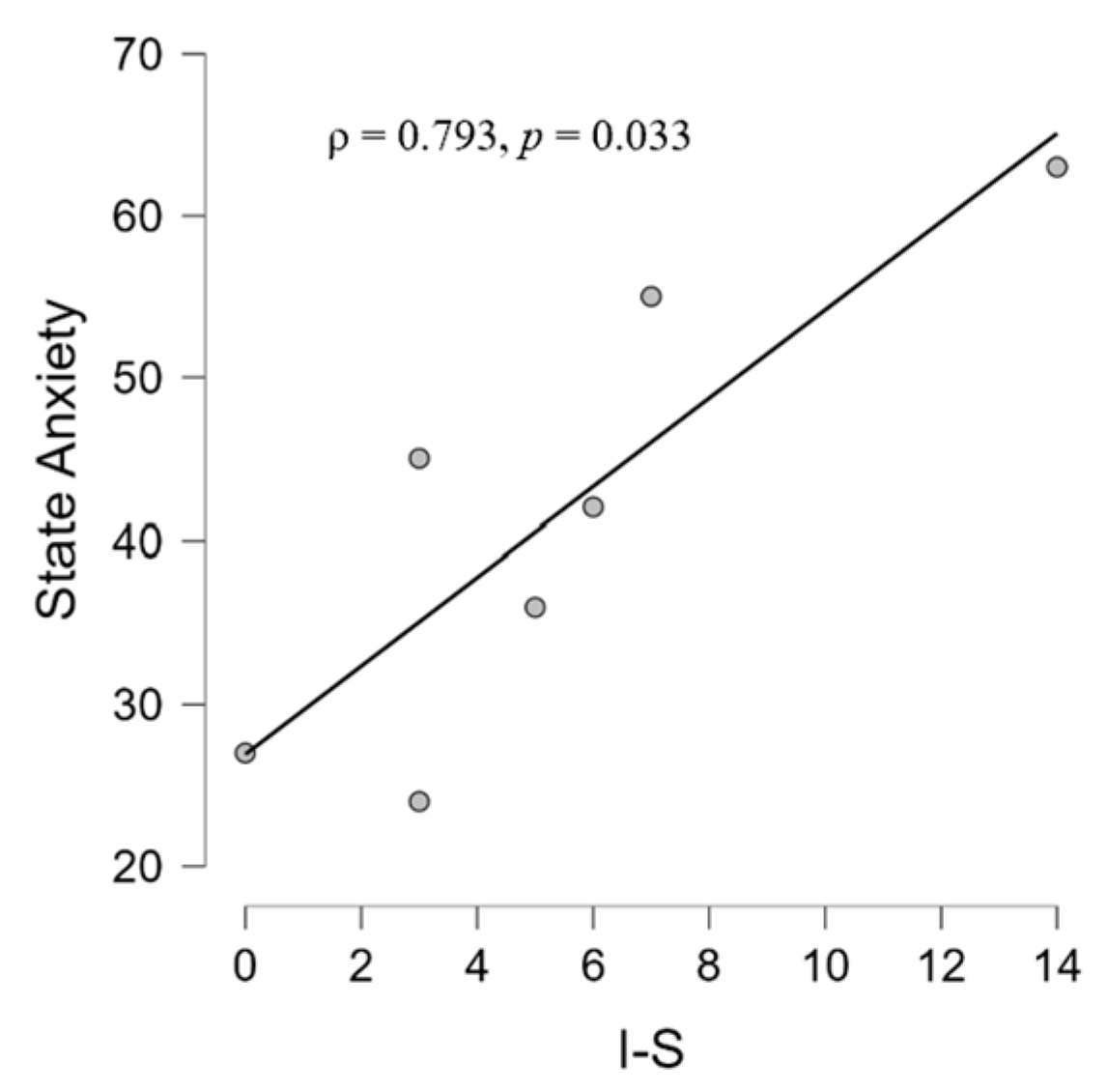
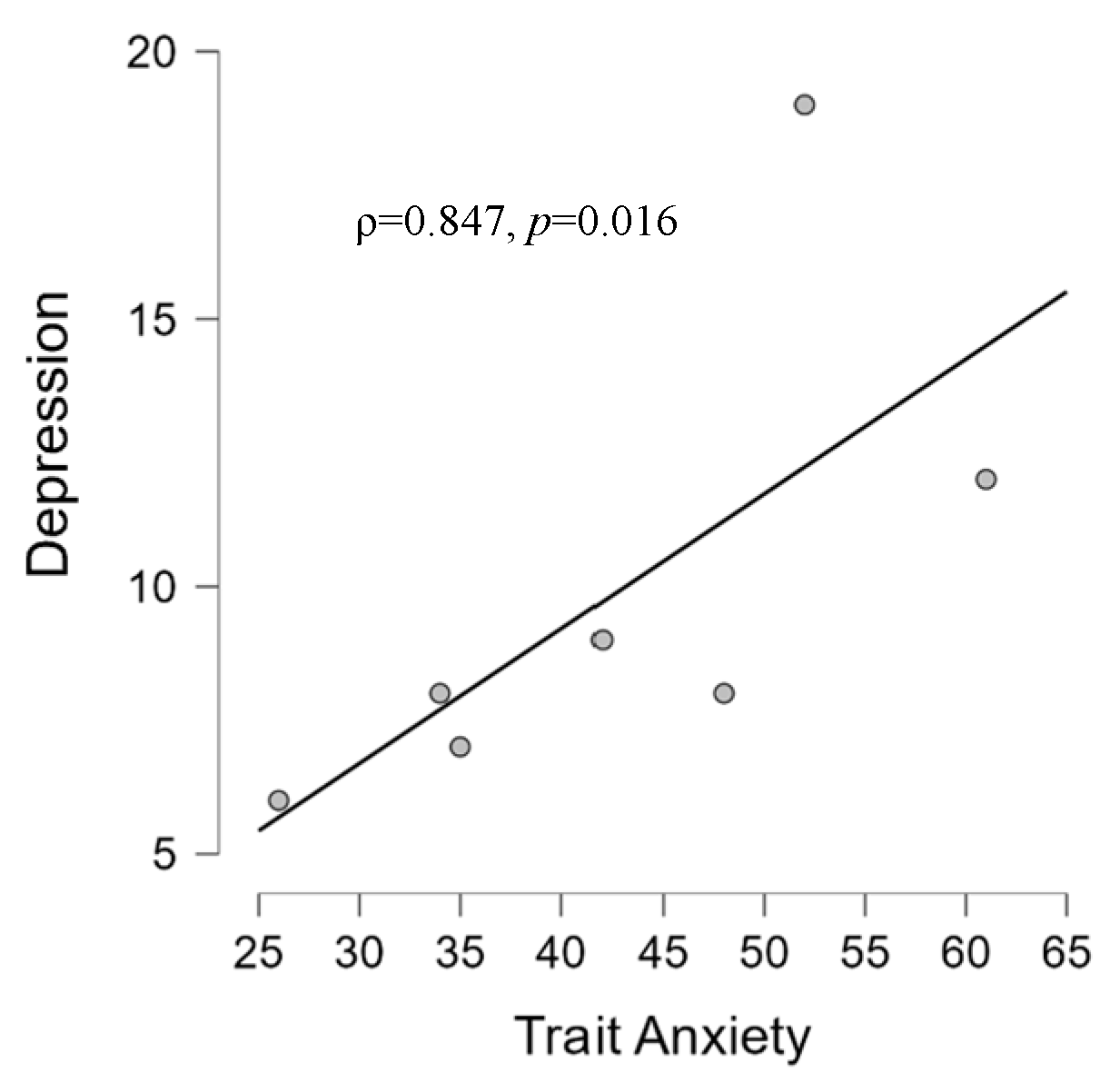
3.2.1. Psychological and Audiological Data
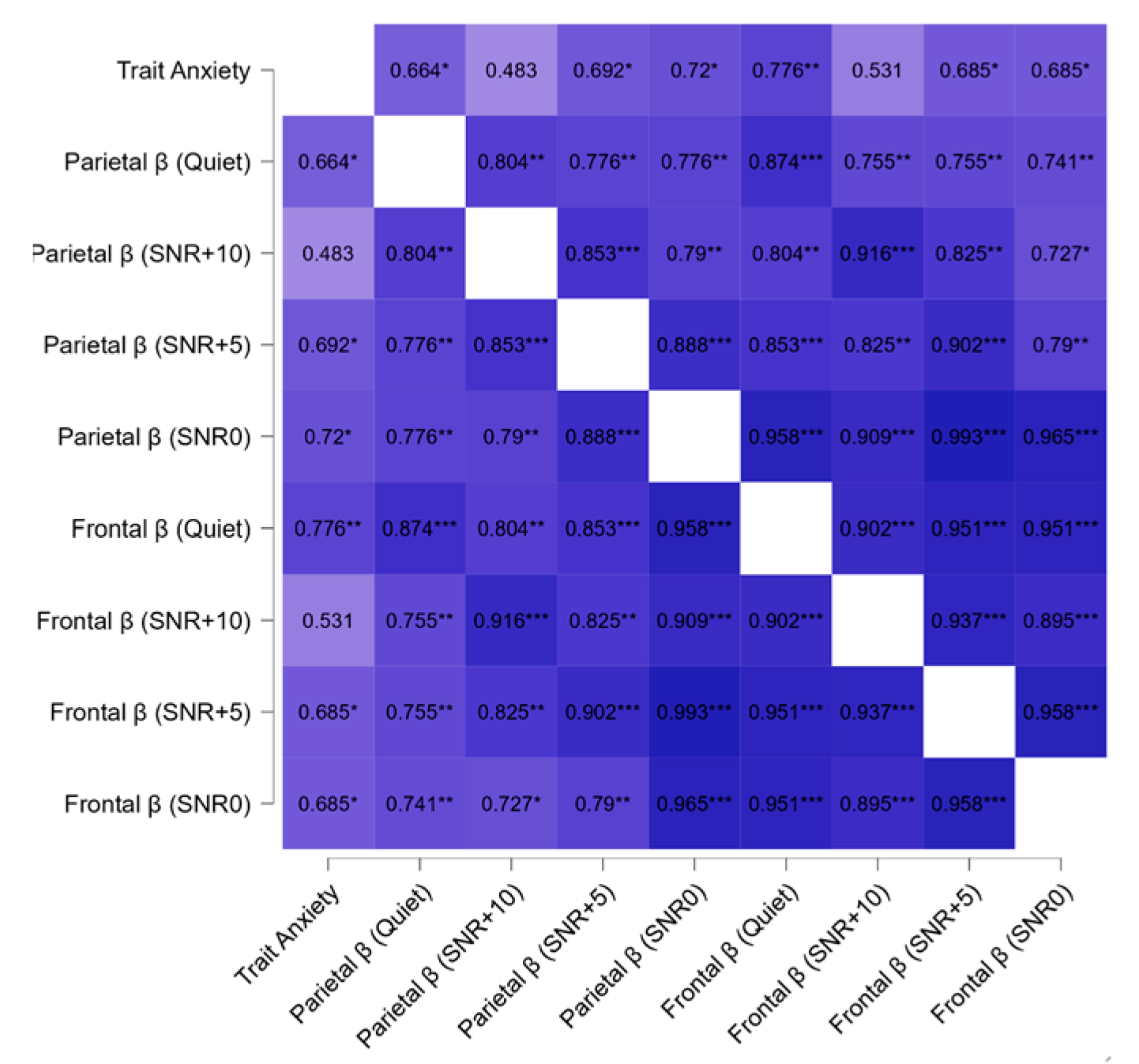
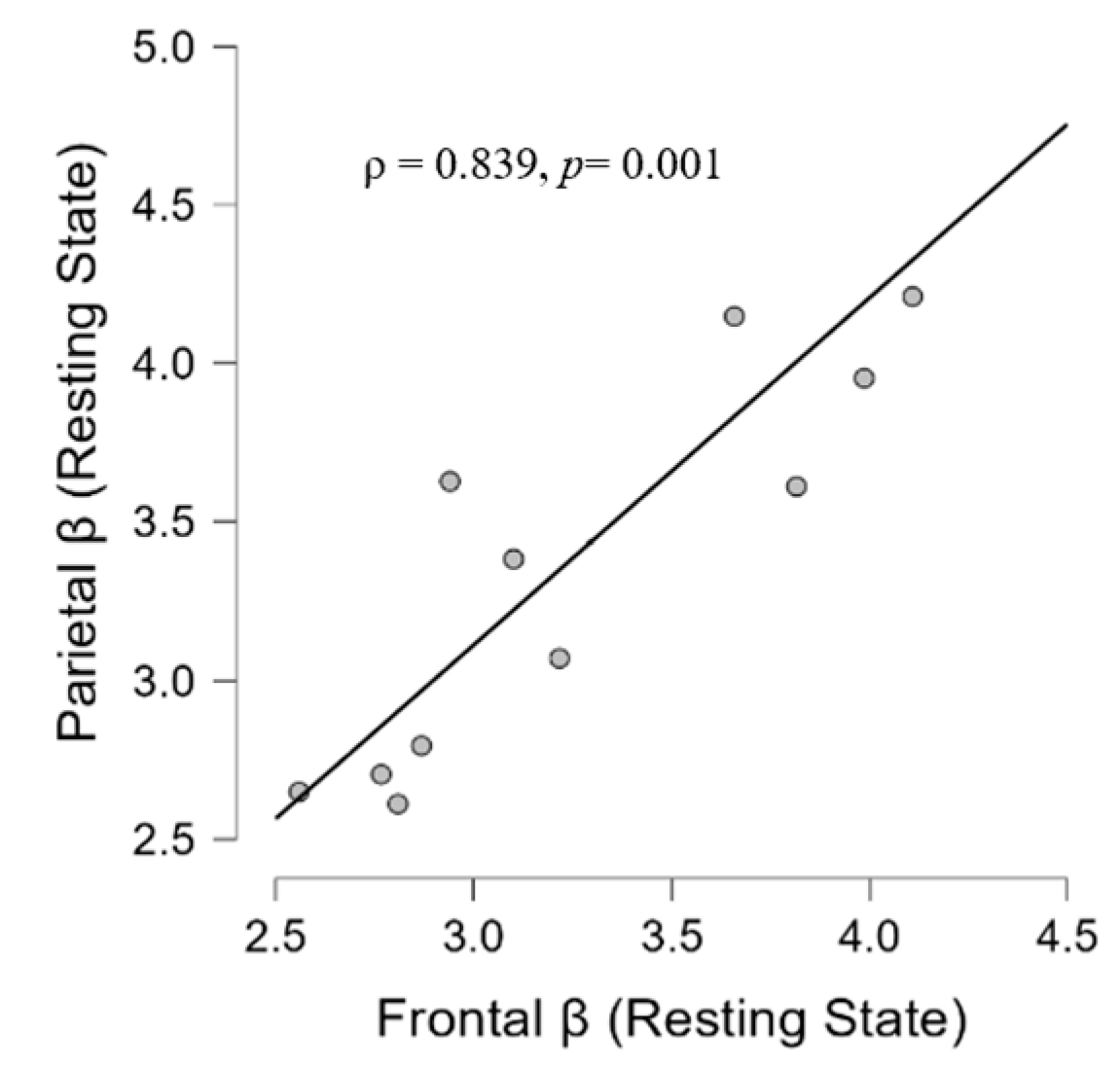
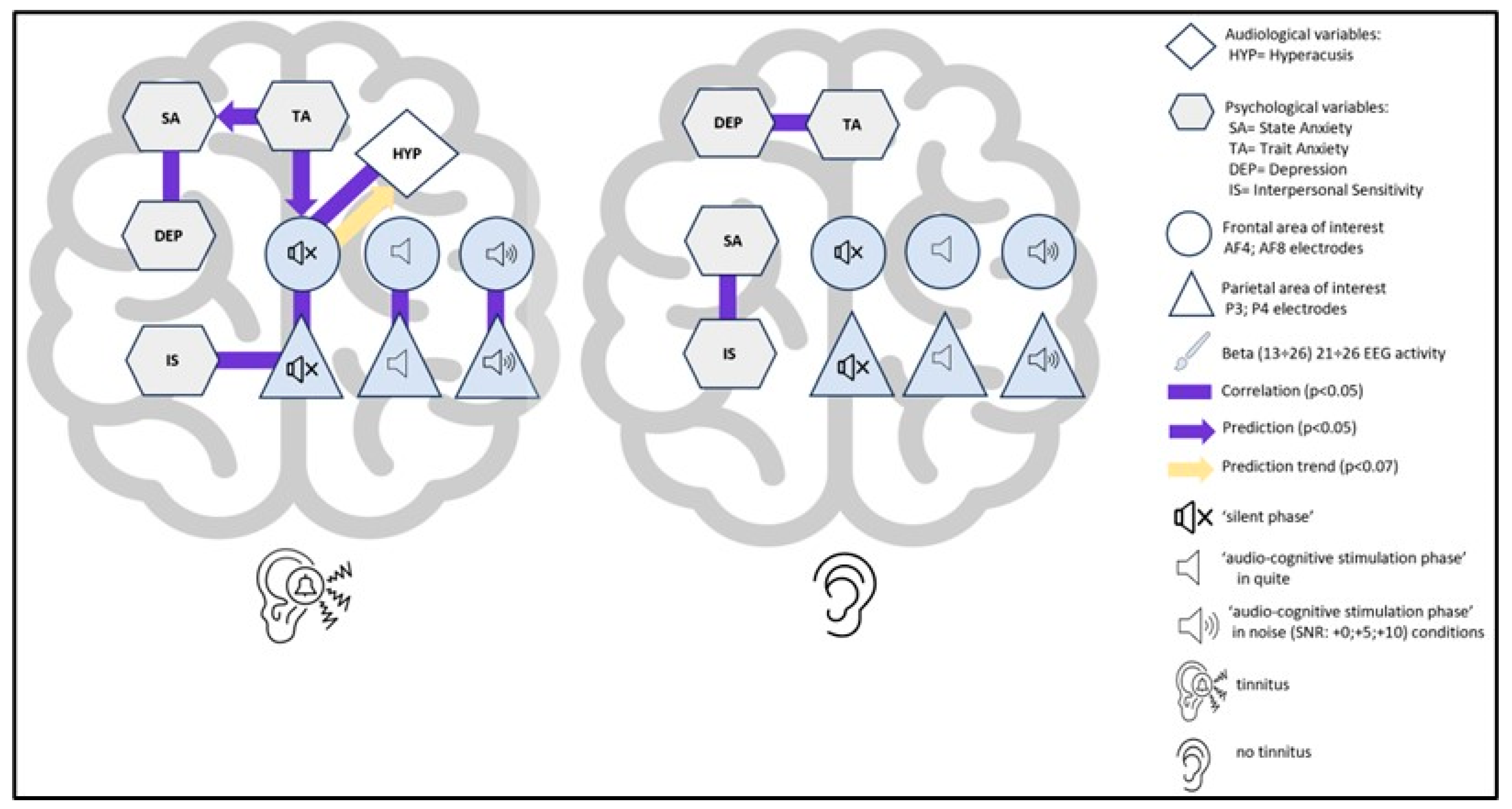
3.2.2. EEG, Psychological, and Audiological Data
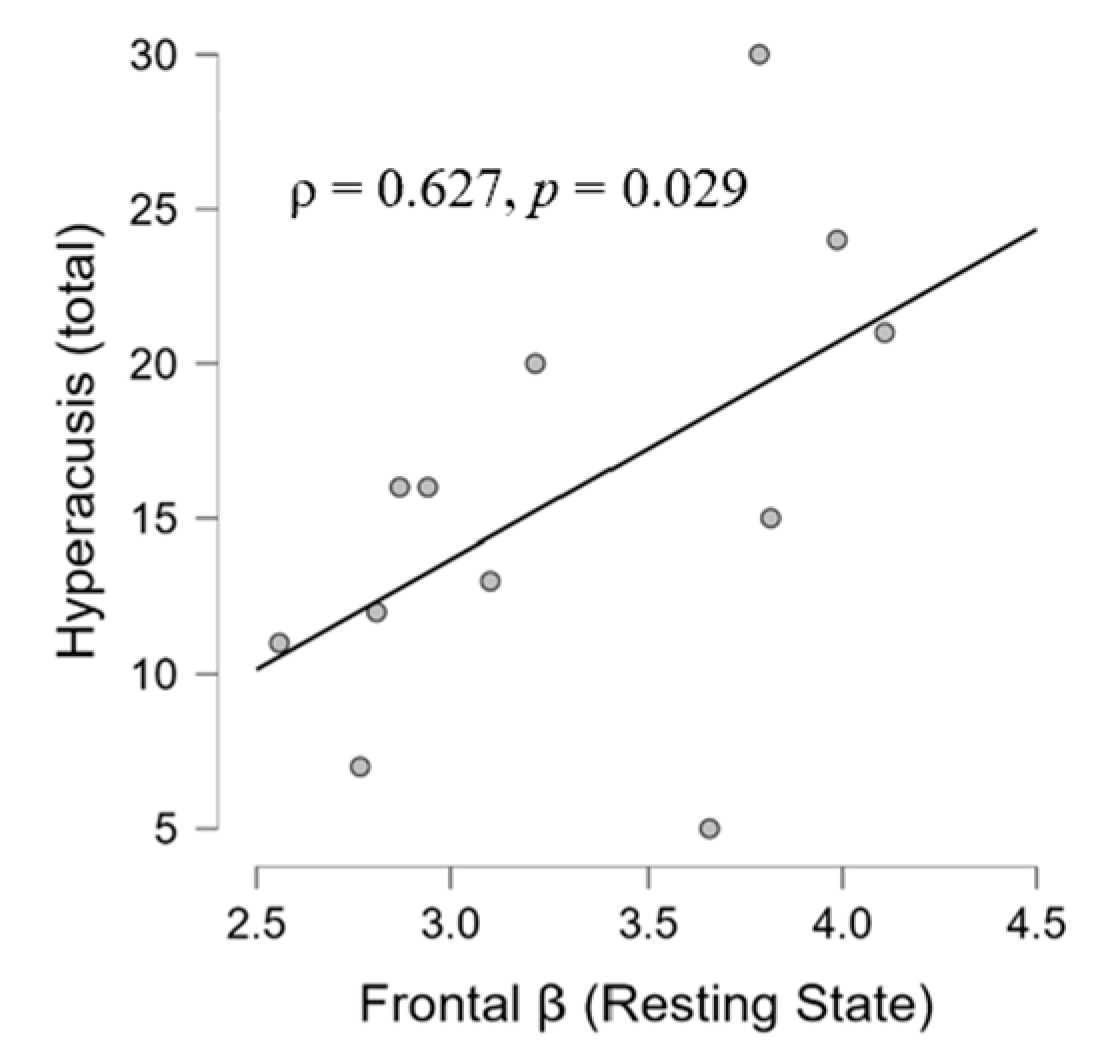
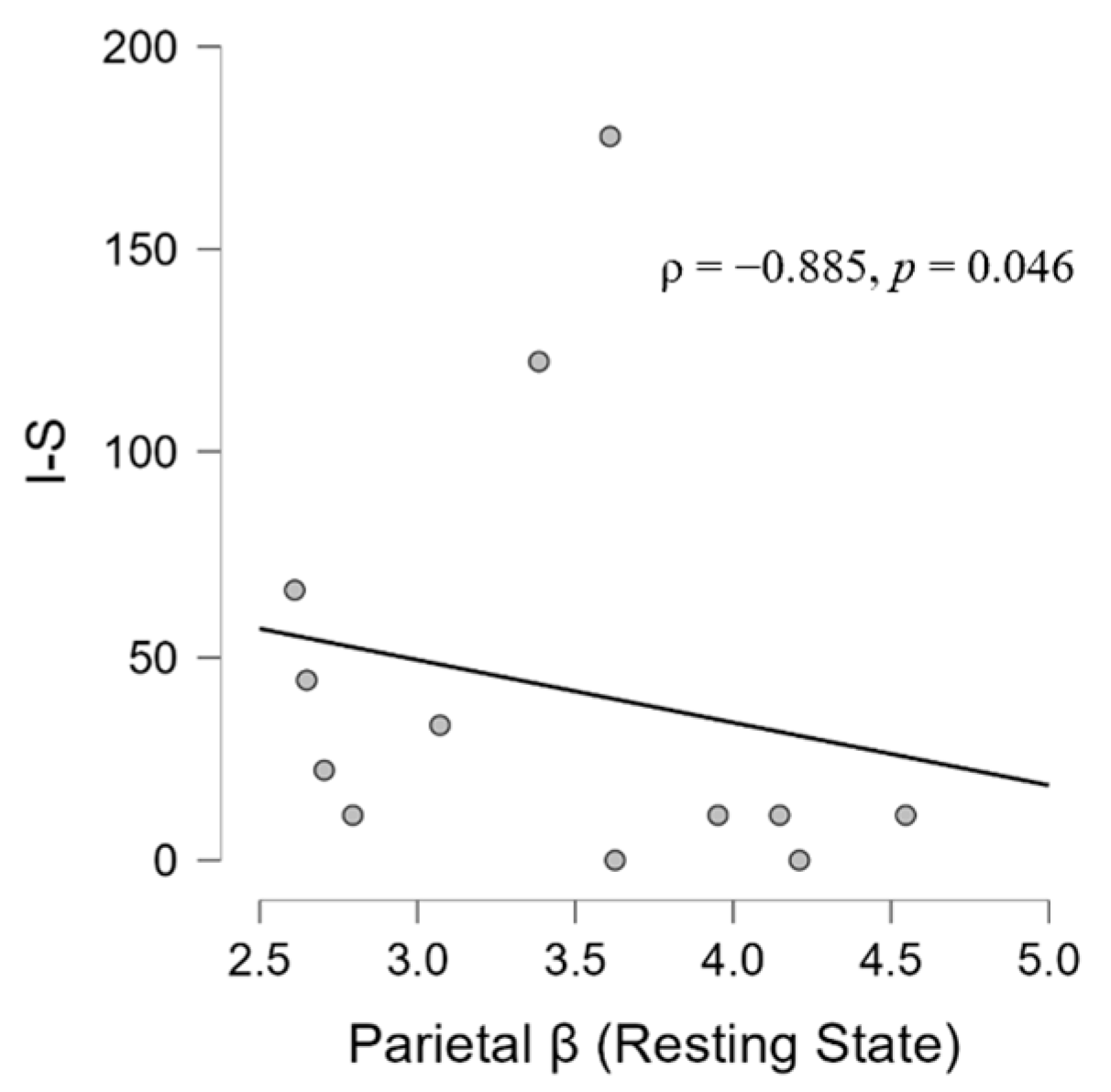
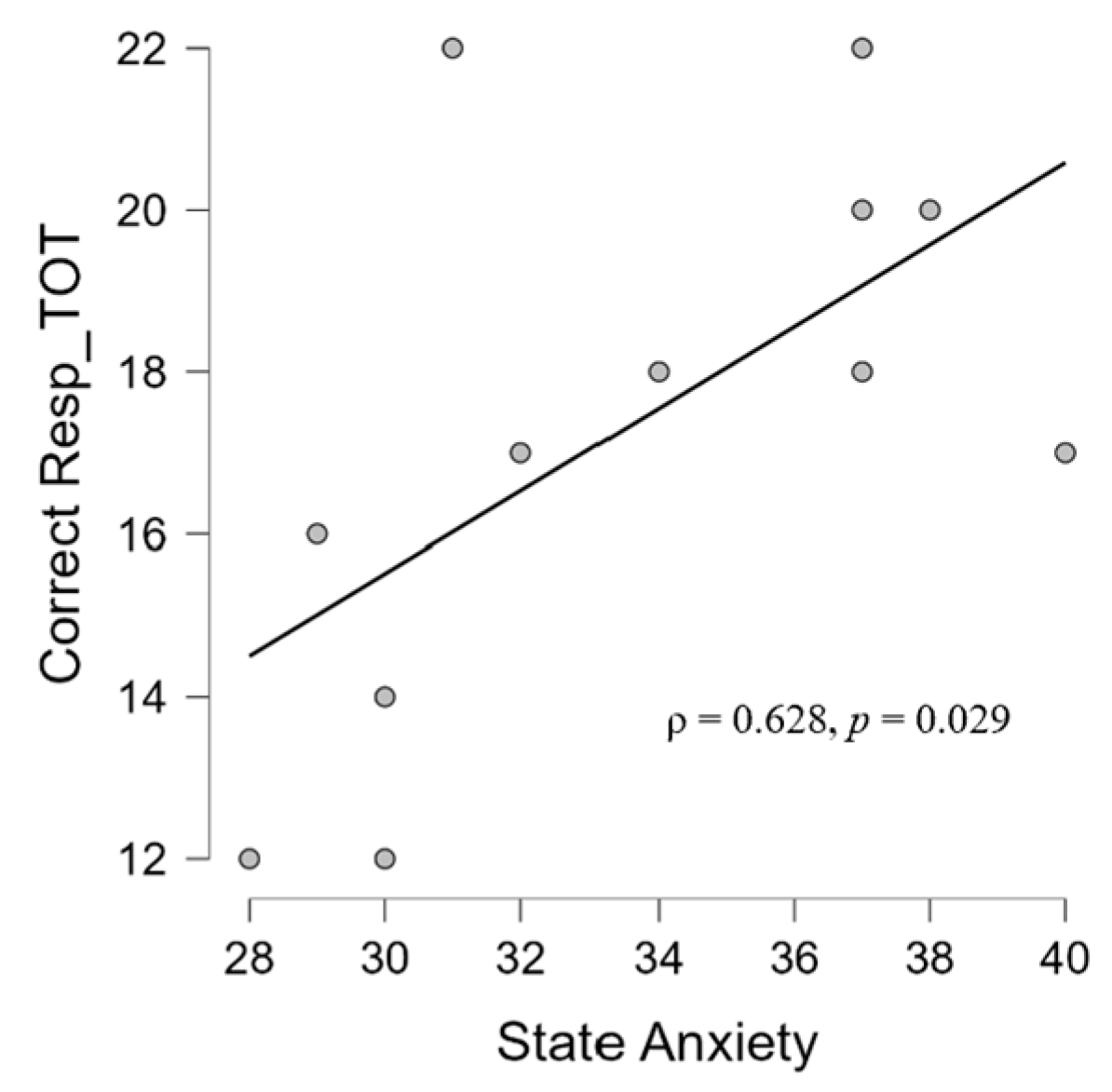
3.3. Simple Linear Regression Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences between Patients and Controls on Psychological Variables
4.2. Correlations between Psychological and Audiological Variables
4.3. Differences between Patients and Controls on Beta Band Activity
4.4. Psycho-Audio-EEG Interconnections
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elgoyhen, A.B.; Langguth, B.; De Ridder, D.; Vanneste, S. Tinnitus: Perspectives from human neuroimaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langguth, B.; Kreuzer, P.M.; Kleinjung, T.; De Ridder, D. Tinnitus. Causes and clinical management. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, D.; Schlee, W.; Vanneste, S.; Londero, A.; Weisz, N.; Kleinjung, T.; Shekhawat, G.S.; Elgoyhen, A.B.; Song, J.-J.; Andersson, G.; et al. Tinnitus and tinnitus disorder: Theoretical and operational definitions (an international multidisciplinary proposal). Prog. Brain Res. 2021, 260, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, D.M.; Hoare, D.J. Hyperacusis: Major research questions. HNO 2018, 66, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibrin, P.C.; Melo, J.J.; Marchiori, L.L. Prevalence of tinnitus complaints and probable association with hearing loss, diabetes mellitus and hypertension in elderly. Codas 2013, 25, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, M. New thinking on hearing in noise: A generalized articulation index. Sem. Hear. 2002, 23, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, T.R.; Costa, M.J.; Urnau, D.; Becker, K.T.; Schuster, L.C. recognition of speech of normal-hearing individuals with tinnitus and hyperacusis. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 15, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.P. The effect of tinnitus on some psychoacoustical abilities in individuals with normal hearing sensitivity. Int. Tinnitus J. 2014, 19, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.; Lindberg, P.; Lyttkens, L.; Melin, L. Predictors of tinnitus discomfort, adaptation and subjective loudness. Br. J. Audiol. 1990, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Shin, S.H.; Byun, S.W.; Lee, Z.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Audiological and psychological assessment of tinnitus patients with normal hearing. Front. Neurol. 2023, 13, 1102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czornik, M.; Malekshahi, A.; Mahmoud, W.; Wolpert, S.; Birbaumer, N. Psychophysiological treatment of chronic tinnitus: A review. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2022, 29, 1236–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, A.T. Expanding the biological basis of tinnitus: Crossmodal origins and the role of neuroplasticity. Hear. Res. 2003, 175, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, S.E.; Roberts, L.E.; Langguth, B. Maladaptive plasticity in tinnitus—Triggers, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallam, R.S.; Rachman, S.; Hinchcliffe, R. Psychological aspects of tinnitus. In Contributions to Medical Psychology; Rachman, S., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- Durai, M.; Searchfield, G. Anxiety and depression, personality traits relevant to tinnitus: A scoping review. Int. J. Audiol. 2016, 55, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.A.; Henshaw, H.; Akeroyd, M.A.; Adams, B.; Hoare, D.J. Associations between subjective tinnitus and cognitive performance: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Trends Hear. 2020, 24, 2331216520918416E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronlein, T.; Langguth, B.; Pregler, M.; Kreuzer, P.M.; Wetter, T.C.; Schecklmann, M. Insomnia in patients with chronic tinnitus: Cognitive and emotional distress as moderator variables. J. Psychosom. Res. 2016, 83, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, B.; Böcking, B.; Dobel, C.; Rose, M.; Brüggemann, P. Tinnitus and Influencing Comorbidities. Laryngorhinootologie 2023, 102, S50–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Munster, J.J.; Van der Valk, W.H.; Stegeman, I.; Lieftink, A.F.; Smit, A.L. The relationship of tinnitus distress with personality traits: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Tinnitus-associated cognitive and psychological impairments: A comprehensive review meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1275560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Gallus, S.; Hall, D.A.; Kleinjung, T.; Langguth, B.; Maruotti, A.; Meyer, M.; Norena, A.; Probst, T.; Pryss, R.C. Editorial: Towards an Understanding of Tinnitus Heterogeneity. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, D.; McFerran, D.; Hall, D. Tinnitus. Lancet 2013, 382, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, L.; Handscomb, L.; Hoare, D.J.; Hall, D.A. A scientific cognitive-behavioral model of tinnitus: Novel conceptualizations of tinnitus distress. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): Mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 8, 221–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czornik, M.; Birbaumer, N.; Braun, C.; Hautzinger, M.; Wolpert, S.; Löwenheim, H.; Malekshahi, A. Neural substrates of tinnitus severity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 181, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, G.; McKenna, L. The role of cognition in tinnitus. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126 (Suppl. S556), 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, R.S.; McKenna, L.; Shurlock, L. Tinnitus impairs cognitive efficiency. Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.; Hoare, D.J.; Hall, D.A. The consequences of tinnitus and tinnitus severity on cognition: A review of the behavioural evidence. Hear. Res. 2016, 332, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegg-Quinn, S.; Bennett, R.J.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Baguley, D.M. The impact of tinnitus upon cognition in adults: A systematic review. Int. J. Audiol. 2016, 55, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, D.E.; Broadbent, M.H.; Jones, J.L. Performance correlates of self-reported cognitive failure and of obsessionality. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1986, 25, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, G.; Bakhsh, R.; Johansson, L.; Kaldo, V.; Carlbring, P. Stroop facilitation in tinnitus patients: An experiment conducted via the world wide web. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2005, 8, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevis, K.J.; McLachlan, N.M.; Wilson, S.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of psychological functioning in chronic tinnitus. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2018, 60, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houdayer, E.; Teggi, R.; Velikova, S.; Gonzalez-Rosa, J.J.; Bussi, M.; Comi, G.; Leocani, L. Involvement of cortico-subcortical circuits in normoacousic chronic tinnitus: A source localization EEG study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlee, W.; Hartmann, T.; Langguth, B.; Weisz, N. Abnormal resting-state cortical coupling in chronic tinnitus. BMC Neurosci. 2009, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecklmann, M.; Landgrebe, M.; Langguth, B. Phenotypic characteristics of hyperacusis in tinnitus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.A.; Akrofi, K.; Carpenter-Thompson, J.R.; Husain, F.T. Default mode, dorsal attention and auditory resting state networks exhibit differential functional connectivity in tinnitus and hearing loss. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, M.D.; Krasnow, B.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, G.G.; Slobodskoj-Plusnin, J.Y.; Bocharov, A.V.; Pylkova, L.V. The default mode network and EEG alpha oscillations: An independent component analysis. Brain Res. 2011, 1402, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Betzel, R.F.; Cohen, J.R.; Damoiseaux, J.S.; De Brigard, F.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fornito, A.; Gratton, C.; Gordon, E.M.; Laird, A.R.; et al. Controversies and progress on standardization of large-scale brain network nomenclature. Netw. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 864–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmelpfennig, J.; Topczewski, J.; Zajkowski, W.; Jankowiak-Siuda, K. The role of the salience network in cognitive and affective deficits. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1133367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, S.; Steward, T.; Harrison, B.J.; Jamieson, A.J.; Davey, C.G.; Agathos, J.A.; Moffat, B.A.; Glarin, R.K.; Felmingham, K.L. Subcortical contributions to salience network functioning during negative emotional processing. NeuroImage 2023, 270, 119964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; He, H.; Ma, W.; Liu, D.; Huang, M.; Dong, L.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Luo, C.; Yao, D. Functional integration between salience and central executive networks: A role for action video game experience. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 9803165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, Y. Abnormal Functional Connectivity within Default Mode Network and Salience Network Related to Tinnitus Severity. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2023, 24, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, D.; Vanneste, S.; Song, J.-J.; Adhia, D. Tinnitus and the triple network model: A perspective. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 15, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.T.; Schmidt, S.A. Using resting state functional connectivity to unravel networks of tinnitus. Hear. Res. 2014, 307, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesford, Q.K.; Simpson, S.L.; Burdette, J.H.; Hayasaka, S.; Laurienti, P.J. The brain as a complex system: Using network science as a tool for understanding the brain. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V. Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: A unifying triple network model. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 483–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, T.P.; Bressler, S.L. Neurocognitive networks: Findings, models, and theory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 2232–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Attanasio, G.; Fattapposta, F.; Locuratolo, N.; Mannarelli, D.; Filipo, R. An electrophysiological approach to tinnitus interpretation. Int. Tinnitus J. 2012, 17, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjamian, P. The application of electro- and magneto-encephalography in tinnitus research—Methods and interpretations. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasoda-Mohan, A.; Vanneste, S. The Electrophysiological Explorations in Tinnitus Over the Decades Using EEG and MEG. In Textbook of Tinnitus; Schlee, W., Langguth, B., De Ridder, D., Vanneste, S., Kleinjung, T., Møller, A.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Aricò, P.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Mancini, P. Two are better than one: Differences in cortical EEG patterns during auditory and visual verbal working memory processing between Unilateral and Bilateral Cochlear Implanted children. Hear. Res. 2024, 446, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Mancini, P. Gamma-Band Modulation in Parietal Area as the Electroencephalographic Signature for Performance in Auditory–Verbal Working Memory: An Exploratory Pilot Study in Hearing and Unilateral Cochlear Implant Children. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Mancini, P.; Greco, A.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Leone, C.A.; Grassia, R.; Di Nardo, W.; Di Cesare, T.; Rossi, F.; et al. ‘Musical effort’ and ‘musical pleasantness’: A pilot study on the neurophysiological correlates of classical music listening in adults normal hearing and unilateral cochlear implant users. Hear. Balance Commun. 2022, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Giorgi, A.; Vozzi, A.; Leone, C.A.; Grassia, R.; Di Nardo, W.; Di Cesare, T.; Fetoni, A.R.; Freni, F.; et al. Music in noise recognition: An EEG study of listening effort in cochlear implant users and normal hearing controls. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Giorgi, A.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Scorpecci, A.; Giannantonio, S.; De Lucia, A.; Garofalo, S.; Grassia, R.; Leone, C.A.; Longo, P.; et al. Higher right hemisphere gamma band lateralization and suggestion of a sensitive period for vocal auditory emotional stimuli recognition in unilateral cochlear implant children: An EEG study. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 608156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG frequency bands in psychiatric disorders: A review of resting state studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlenko, V.B.; Chernyi, S.V.; Goubkina, D.G. EEG Correlates of Anxiety and Emotional Stability in Adult Healthy Subjects. Neurophysiology 2009, 41, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.K.; Fries, P. Beta-band oscillations—Signaling the status quo? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, G.G. Motivation, emotion, and their inhibitory control mirrored in brain oscillations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, M.N.; Jayakkumar, S.; Chong, E.; Yeow, C.H. A wearable, EEG-based massage headband for anxiety alleviation. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 3557–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, E.; Correa, Á.; Sanabria, D.; Jung, T.P. Tonic EEG dynamics during psychomotor vigilance task. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2013; pp. 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciaraffa, N.; Di Flumeri, G.; Germano, D.; Giorgi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Borghini, G.; Vozzi, A.; Ronca, V.; Varga, R.; van Gasteren, M.; et al. Validation of a Light EEG-Based Measure for Real-Time Stress Monitoring during Realistic Driving. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Di Flumeri, G.; Babiloni, F. Neurophysiological Signals Processing. In Industrial Neuroscience in Aviation: Evaluation of Mental States in Aviation Personnel; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 83–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Martinez-Levy, A.C.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Aricò, P.; Capotorto, R.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Di Flumeri, G. Wearable Technologies for Electrodermal and Cardiac Activity measurements: A Comparison between Fitbit Sense, Empatica E4 and Shimmer GSR3+. Sensors 2023, 23, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhollebeke, G.; De Smet, S.; De Raedt, R.; Baeken, C.; van Mierlo, P.; Vanderhasselt, M.A. The neural correlates of psychosocial stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of spectral analysis EEG studies. Neurobiol. Stress. 2022, 18, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakakis, G.; Grigoriadis, D.; Giannakaki, K.; Simantiraki, O.; Roniotis, A.; Tsiknakis, M. Review on psychological stress detection using biosignals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 13, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanok, N.A.; Jones, N.A. EEG Asymmetry Characteristics in Relation to Childhood Anxiety Subtypes: A Dimensional Approach. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2024, 55, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, J.J.; Roberts, L.E. The neuroscience of tinnitus. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, D.; Elgoyhen, A.B.; Romo, R.; Langguth, B. Phantom percepts: Tinnitus and pain as persisting aversive memory networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8075–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.T. Neural networks of tinnitus in humans: Elucidating severity and habituation. Hear. Res. 2016, 334, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.D.; Alrashid, M.A.; Eltabbakh, A.; Fredericks, S. The association between stress, emotional states, and tinnitus: A mini-review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1131979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepek, A.J.; Mazurek, B. Neurobiology of Stress-Induced Tinnitus. In The Behavioral Neuroscience of Tinnitus. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Searchfield, G.D., Zhang, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.T.; Khan, R.A. Review and Perspective on Brain Bases of Tinnitus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2023, 24, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanting, C.P.; De Kleine, E.; Van Dijk, P. Neural activity underlying tinnitus generation: Results from PET and fMRI. Hear. Res. 2009, 255, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Giliberto, G.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Attanasio, G. Listening Effort in Tinnitus: A Pilot Study Employing a Light EEG Headset and Skin Conductance Assessment during the Listening to a Continuous Speech Stimulus under Different SNR Conditions. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.W.; Jacobson, G.P.; Spitzer, J.B. Development of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzani, D.; Genovese, E.; Marrara, A.; Gherpelli, C.; Pingani, L.; Forghieri, M.; Rigatelli, M.; Guadagnin, T.; Arslan, E. Validity of the Italian adaptation of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory; focus on quality of life and psychological distress in tinnitus-sufferers. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2008, 28, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moschen, R.; Fioretti, A.; Eibenstein, A.; Natalini, E.; Cuda, D.; Chiarella, G.; Rumpold, G.; Riedl, D. Validation of the Italian Tinnitus Questionnaire Short Form (TQ 12-I) as a Brief Test for the Assessment of Tinnitus-Related Distress: Results of a Cross-Sectional Multicenter-Study. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfa, S.; Dubal, S.; Veuillet, E.; Perez-Diaz, F.; Jouvent, R.; Collet, L. Psychometric Normalization of a Hyperacusis Questionnaire. ORL 2002, 64, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, J.A. Pathophysiology of tinnitus: A special case—Hyperacusis and a proposed treatment. Am. J. Otol. 1987, 8, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jüris, L.; Andersson, G.; Larsen, H.C.; Ekselius, L. Psychiatric comorbidity and personality traits in patients with hyperacusis. Int. J. Audiol. 2013, 52, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaesing, L.; Kroener-Herwig, B. Self-reported and behavioral sound avoidance in tinnitus and hyperacusis subjects, and association with anxiety ratings. Int. J. Audiol. 2012, 51, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendesen, E.; Kılıç, S.; Erbil, N.; Aydın, Ö.; Turkyilmaz, D. An Exploratory Study of the Effect of Tinnitus on Listening Effort Using EEG and Pupillometry. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 169, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallam, R.S.; Jakes, S.C.; Hinchcliffe, R. Cognitive variables in tinnitus annoyance. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1988, 27, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretti, A.; Tortorella, F.; Masedu, F.; Valenti, M.; Fusetti, M.; Pavaci, S. Validity of the Italian version of Khalfa’s questionnaire on hyperacusis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2015, 35, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Prunas, A.; Sarno, I.; Preti, E.; Madeddu, F.; Perugini, M. Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the SCL-90-R: A study on a large community sample. Eur. Psychiatry 2012, 27, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derogatis, L.R. Symptom Checklist-90-R: Administration, Scoring and Procedures Manual, 3rd ed.; National Computer Systems: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bersani, F.S.; Salviati, M.; Terlizzi, S.; Melcore, C.; Panico, R.; Romano, G.F.; Valeriani, G.; Altissimi, G.; Mazzei, F.; Testugini, V.; et al. Tinnitus: Clinical experience of the psychosomatic connection. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory: A Comprehensive Bibliography; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrabissi, L.; Santinello, M. Verifica Della Validità Dello STAI Forma Y di Spielberger; Verification of the validity of the STA; Giunti Organizzazioni Speciali: Tuscany, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparre, D.; Pepe, I.; Laera, D.; Abbatantuono, C.; De Caro, M.F.; Taurino, A.; D’erasmo, D.; Fanizzi, P.; Antonucci, L.A.; Pantaleo, A.; et al. Cognitive Functioning and Psychosomatic Syndromes in a Subjective Tinnitus Sample. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1256291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Cartocci, G.; Mancini, P. School wellbeing and psychological characteristics of online learning in families of children with and without hearing loss during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol. Sch. 2022, 60, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zou, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. The electrophysiology correlation of the cognitive bias in anxiety under uncertainty. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, M.W. A cognitive approach to trait anxiety. Eur. J. Pers. 2000, 14, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeter, M.; Kindt, M. High trait anxiety: A challenge for disrupting fear memory reconsolidation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, G.; Peluso, A.M.; Capestro, M.; Miglietta, M. An Italian Version of the 10-Item Big Five Inventory: An Application to Hedonic and Utilitarian Shopping Values. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 76, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammstedt, B.; John, O.P. Measuring Personality in One Minute or Less: A 10-Item Short Version of the Big Five Inventory in English and German. J. Res. Pers. 2007, 41, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Praamstra, P. The five percent electrode system for high-resolution EEG and ERP measurements. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Colosimo, A.; Babiloni, F. A new regression-based method for the eye blinks artifacts correction in the EEG signal, without using any EOG channel. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 3187–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, C.; Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. Eeglab—An Open Source Matlab Toolbox for Electrophysiological Research. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 58, 000010151520134182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, J.; Kikumoto, A.; Mayr, U. EEG Decoding Reveals the Strength and Temporal Dynamics of Goal-Relevant Representations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrandies, W. Global field power and topographic similarity. Brain Topogr. 1990, 3, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Giorgi, A.; Germano, D.; Ronca, V.; Vozzi, A.; Borghini, G.; Tamborra, L.; Simonetti, I.; Capotorto, R.; Ferrara, S.; et al. A Neuroergonomic Approach Fostered by Wearable EEG for the Multimodal Assessment of Drivers Trainees. Sensors 2023, 23, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.G.; De Martino, M.; Mancuso, A.; Iaconetta, G.; Manara, R.; Elia, A.; Laudanna, A.; Di Salle, F.; Esposito, F. Semantics-weighted lexical surprisal modeling of naturalistic functional MRI time-series during spoken narrative listening. Neuroimage 2020, 222, 117281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Nasta, C.; Giorgi, A.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Mancini, P. Neurophysiological Verbal Working Memory Patterns in Children: Searching for a Benchmark of Modality Differences in Audio/Video Stimuli Processing. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 4158580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrini, M.; Cutugno, F.; Maturi, P.; Prosser, S.; Leoni, F.A.; Arslan, E. Bisyllabic words for speech audiometry: A new italian material. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 1993, 13, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cartocci, G.; Scorpecci, A.; Borghini, G.; Maglione, A.G.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Giannantonio, S.; Giorgi, A.; Malerba, P.; Rossi, D.; Modica, E.; et al. EEG rhythms lateralization patterns in children with unilateral hearing loss are different from the patterns of normal hearing controls during speech-in-noise listening. Hear. Res. 2019, 379, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanasio, G.; Cartocci, G.; Covelli, E.; Ambrosetti, E.; Martinelli, V.; Zaccone, M.; Ponzanetti, A.; Gueli, N.; Filipo, R.; Cacciafesta, M. The Mozart effect in patients suffering from tinnitus. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samp). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether One of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger Than the Other. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1947, 13, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.S.; Armaan, A.; Antony, A.S. A comparison of regression models for prediction of graduate admissions. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Science (ICCIDS), Chennai, India, 21–23 February 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; Gogtay, N. Biostatistics Series Module 6: Correlation and Linear Regression. Indian J. Dermatol. 2016, 61, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinstäuber, M.; Weise, C.; Andersson, G.; Probst, T. Personality traits predict and moderate the outcome of Internet-based cognitive behavioural therapy for chronic tinnitus. Int. J. Audiol. 2018, 57, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langguth, B.; Kleinjung, T.; Fischer, B.; Hajak, G.; Eichhammer, P.S.P.G.; Sand, P.G. Tinnitus severity, depression, and the big five personality traits. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 166, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucci, S.; Geocze, L.; Abranches, D.C.; Antúnez, A.E.A.; Penido, N.D.O. Systematic review of evidence on the association between personality and tinnitus. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 80, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strumila, R.; Lengvenytė, A.; Vainutienė, V.; Lesinskas, E. The role of questioning environment, personality traits, depressive and anxiety symptoms in tinnitus severity perception. Psychiatr. Q. 2017, 88, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmaryono, I.; Wijayanti, D.; Maharani, H.R. Number of Response Options, Reliability, Validity, and Potential Bias in the Use of the Likert Scale Education and Social Science Research: A Literature Review. Int. J. Educ. Methodol. 2022, 8, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Bernieri, F.J. (Eds.) Interpersonal Sensitivity: Theory and Measurement; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q. How Interpersonal Sensitivity Affects Depression under the COVID-19 Lockdown among College Students in South China: A Moderated Mediation Model. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2023, 16, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, J.M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Lin, H.W. Relationships between tinnitus and the prevalence of anxiety and depression. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, A.; Forti, S.; Ambrosetti, U.; Bo, L.D. Questionnaires to evaluate anxiety and depressive levels in tinnitus patients. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2009, 140, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, K.A.; Olatunji, B.O. Specificity of trait anxiety in anxiety and depression: Meta-analysis of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 82, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.C.; Chung, K.K.H.; Jhuo, R.A. The relationships among working memory, state anxiety, and academic performance in Chinese undergraduates with SLD. Read. Writ. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, D.; Jahangir, N.; Khizar, U.; John, H.; Ilyas, Z. Impact of anxiety on self-esteem, self-concept and academic achievement among adolescent. Elem. Educ. Online 2021, 20, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar]
- El-Anzi, F.O. Academic achievement and its relationship with anxiety, self-esteem, optimism, and pessimism in Kuwaiti students. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2005, 33, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Osińska, K.; Kaźmierczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, H.; Wierzchowska, M.; Matuszewska, I. Cortical activity in tinnitus patients and its modification by phonostimulation. Clinics 2013, 68, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazami-Goudarzi, M.; Michels, L.; Weisz, N.; Jeanmonod, D. Temporo-insular enhancement of EEG low and high frequencies in patients with chronic tinnitus. QEEG study of chronic tinnitus patients. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanneste, S.; van de Heyning, M.; De Ridder, D. The neural network of phantom sound changes over time: A comparison between recent-onset and chronic tinnitus patients. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderlund, G.; Sikström, S.; Smart, A. Listen to the noise: Noise is beneficial for cognitive performance in ADHD. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, A.; Avitable, M.J.; Goldstein, B. Quantitative electroencephalography power analysis in subjective idiopathic tinnitus patients: A clinical paradigm shift in the understanding of tinnitus, an electrophysiological correlate. Int. Tinnitus J. 2006, 12, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.H.; Byun, S.W.; Lee, Z.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.Y. Clinical Findings That Differentiate Co-Occurrence of Hyperacusis and Tinnitus from Tinnitus Alone. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, J.; Brzezicka, A.; Gola, M.; Wróbel, A. Beta band oscillations engagement in human alertness process. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 85, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropotov, J.D. Quantitative EEG, Event-Related Potentials and Neurotherapy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vozzi, A.; Martinez Levy, A.; Ronca, V.; Giorgi, A.; Ferrara, S.; Mancini, M.; Capotorto, R.; Cherubino, P.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; et al. Time-Dependent Analysis of Human Neurophysiological Activities during an Ecological Olfactory Experience. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, W.R.; Johnson, M.C.; Borkovec, T.D. Worry: An electrocortical analysis. Adv. Behav. Res. Ther. 1986, 8, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.; Ironson, G.; Scafidi, F.; Nawrocki, T.; Goncalves, A.; Burman, I.; Picken, J.; Fox, N.; Schanberg, S.; Kuhn, C. Massage therapy reduces anxiety and enhances EEG pattern of alertness and math computations. Int. J. Neurosci. 1996, 86, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, G.D.; Benson, H.; Friedman, R. Topographic EEG mapping of the relaxation response. Biofeedback Self-Regul. 1996, 21, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzello, S.J.; Landers, D.M. State anxiety reduction and exercise: Does hemispheric activation reflect such changes? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunyé, T.T.; Patterson, J.E.; Wooten, T.; Hussey, E.K. A critical review of cranial electrotherapy stimulation for neuromodulation in clinical and non-clinical samples. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 625321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, G.; Giorgi, A.; Ronca, V.; Mezzadri, L.; Capotorto, R.; Aricò, P.; Di Flumeri, G.; Babiloni, F. Cooperation and mental states neurophysiological assessment for pilots’ training and expertise evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Workshop on Technologies for Defense and Security (TechDefense), Rome, Italy, 20–22 November 2023; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Cao, F. The associations of interpersonal sensitivity with mental distress and trait aggression in early adulthood: A prospective cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 272, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langguth, B.; de Ridder, D.; Schlee, W.; Kleinjung, T. Tinnitus: Clinical Insights in Its Pathophysiology—A Perspective. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, E.C.; Sandoval, X.C.R.; Simeone, C.N.; Tidball, G.; Lea, J.; Westerberg, B.D. Systematic review and network meta-analysis of cognitive and/or behavioral therapies (CBT) for tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrenechea, F.V. Efficacy of neurofeedback as a treatment for people with subjective tinnitus in reducing the symptom and related consequences: A systematic review from 2010 to 2020. Acta Otorrinolaringol. 2023, 74, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| P | G | Age | Tinnitus Onset | M/B | Description of Perceived Sound/Noise | Current Situations of Occurrence | Tinnitus-Reducing act./sit. | Perception during the Task | THI | Tinnitus Severity | TQ-12 | HYP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T | 57.597 | 2 months ago | M | Loud high-pitched whistle | Before sleeping | Being with people; listening to music | yes | 14 | mil | 8 | 13 |
| 2 | T | 59.526 | 5–6 years ago | B | Water brook | Always | Watching TV | yes | 14 | mil | 7 | 7 |
| 3 | T | 47.715 | 2 years ago, being alone in the house in the night | B | High-pitched but slight whistling; sound ‘as of ambulance’. | In silence | Everyday life because he does street work | no | 20 | mod | 11 | 15 |
| 4 | T | 26.926 | End of June 2022 | B | Ambulance sound; Tibetan bells; candy frizz | At work (switchboard operator in a pizzeria) | Nothing | no | 32 | mod | 13 | 11 |
| 5 | T | 61.192 | 2 years ago, at the end of the lockdown for COVID-19 | B | Pulsating whistle | Before sleeping | Listening to music; working and focusing attention on something | no | 14 | mil | 4 | 30 |
| 6 | T | 47.096 | First period in 2000, from 2019 strong perception | B | As of a power plan in operation; electrical circuit | Always | Nothing | no | 48 | mod | 5 | 16 |
| 7 | T | 42.359 | October 2022 in conjunction with strong emotional stress | M | Vigilant whistle. | Always | Nothing | no | 26 | mod | 5 | 24 |
| 8 | T | 55.397 | Post COVID-19 infection | B | It appeared as an itchy and muffled sensation, then turned into … | Always early in the morning and before sleep | During the day the tinnitus is not felt | no | 18 | mod | 2 | 5 |
| 9 | T | 54.301 | June 2022 after a severe cold | M | Ear plugged; violin string shrill | The evening before sleeping, in the silence | If distracted the patient reports feeling better | no | 17 | mod | 9 | 16 |
| 10 | T | 58.444 | 2–3 years ago | B | Buzzing as a refrigerator | The evening before sleeping; watching TV | Distracted by cooking; by work | yes | 15 | mil | 14 | 21 |
| 11 | T | 31.814 | 8–9 years ago, worked at airport on runways | B | Left whistle; bilateral pulsating sound very annoying | In the silence | Listening to music; playing PC with headphones | no | 11 | mil | 8 | 12 |
| 12 | T | 26.630 | 2.5 years ago | B | Hissing, high frequency, like brake on rails | In the evening before falling asleep; tired | Sounds; white noise (use of dedicated APPs) | yes | 12 | mil | 11 | 20 |
| 13 | C | 29.225 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | C | 61.485 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | C | 33.521 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | C | 70.918 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 17 | C | 41.39 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 18 | C | 32.162 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | C | 55.504 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inguscio, B.M.S.; Rossi, D.; Giliberto, G.; Vozzi, A.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Greco, A.; Attanasio, G.; Cartocci, G. Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060570
Inguscio BMS, Rossi D, Giliberto G, Vozzi A, Borghini G, Babiloni F, Greco A, Attanasio G, Cartocci G. Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(6):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060570
Chicago/Turabian StyleInguscio, Bianca Maria Serena, Dario Rossi, Giovanna Giliberto, Alessia Vozzi, Gianluca Borghini, Fabio Babiloni, Antonio Greco, Giuseppe Attanasio, and Giulia Cartocci. 2024. "Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band" Brain Sciences 14, no. 6: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060570
APA StyleInguscio, B. M. S., Rossi, D., Giliberto, G., Vozzi, A., Borghini, G., Babiloni, F., Greco, A., Attanasio, G., & Cartocci, G. (2024). Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band. Brain Sciences, 14(6), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14060570












