Parafoveal Processing of Orthography, Phonology, and Semantics during Chinese Reading: Effects of Foveal Load
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment 1
2.1. Method
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Apparatus and Procedure
2.1.3. Stimuli and Design
2.1.4. Data Analysis
2.2. Results
2.3. Discussion
3. Experiment 2
3.1. Method
3.1.1. Participants
3.1.2. Apparatus and Procedure
3.1.3. Stimuli and Design
3.1.4. Data Analysis
3.2. Results
3.3. Discussion
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rayner, K. The Perceptual Span and Peripheral Cues in Reading. Cogn. Psychol. 1975, 7, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K. Eye Movements in Reading and Information Processing: 20 Years of Research. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 372–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotter, E.R.; Angele, B.; Rayner, K. Parafoveal Processing in Reading. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2012, 74, 5–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.M.; Ferreira, F. Effects of Foveal Processing Difficulty on the Perceptual Span in Reading: Implications for Attention and Eye Movement Control. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1990, 16, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldre, A.; Andrews, S. How Does Foveal Processing Difficulty Affect Parafoveal Processing during Reading? J. Mem. Lang. 2018, 103, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yan, M. Preview Frequency Effects in Reading: Evidence from Chinese. Psychol. Res. 2022, 86, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Yan, G.; Liversedge, S.; Zang, C.; Rayner, K. Reading Spaced and Unspaced Chinese Text: Evidence From Eye Movements. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2008, 34, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Sommer, W. The Effects of Emotional Significance of Foveal Words on the Parafoveal Processing of N + 2 Words in Reading Chinese Sentences. Read. Writ. 2019, 32, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M. Visually Complex Foveal Words Increase the Amount of Parafoveal Information Acquired. Vis. Res. 2015, 111, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Xie, F.; Warrington, K. The Influence of Foveal Load on Parafoveal Processing of N + 2 during Chinese Reading. Vis. Cogn. 2023, 31, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, M.R.; Angele, B. Parafoveal Preview Effects from Word N + 1 and Word N + 2 during Reading: A Critical Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2017, 24, 666–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liversedge, S.; Bai, X.; Yan, G.; Zang, C. The Influence of Foveal Lexical Processing Load on Parafoveal Preview and Saccadic Targeting during Chinese Reading Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2019, 45, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findelsberger, E.; Hutzler, F.; Hawelka, S. Spill the Load: Mixed Evidence for a Foveal Load Effect, Reliable Evidence for a Spillover Effect in Eye-Movement Control during Reading. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2019, 81, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilev, M.R.; Yates, M.; Prueitt, E.; Slattery, T.J. Parafoveal Degradation during Reading Reduces Preview Costs Only When It Is Not Perceptually Distinct. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2021, 74, 254–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Ma, W.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Warrington, K.L.; Liversedge, S.P.; Paterson, K.B. Adult Age Differences in Parafoveal Preview Effects during Reading: Evidence from Chinese. Psychol. Aging 2021, 36, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Richter, E.M.; Shu, H.; Kliegl, R. Readers of Chinese Extract Semantic Information from Parafoveal Words. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2009, 16, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltheart, M.; Rastle, K.; Perry, C.; Langdon, R.; Ziegler, J. DRC: A Dual Route Cascaded Model of Visual Word Recognition and Reading Aloud. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 204–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balota, D.A.; Pollatsek, A.; Rayner, K. The Interaction of Contextual Constraints and Parafoveal Visual Information in Reading. Cogn. Psychol. 1985, 17, 364–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briihl, D.; Inhoff, A.W. Integrating Information across Fixations during Reading: The Use of Orthographic Bodies and of Exterior Letters. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1995, 21, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drieghe, D.; Rayner, K.; Pollatsek, A. Eye Movements and Word Skipping During Reading Revisited. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2005, 31, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.J. Eye Movement Control during Reading: Effects of Word Frequency and Orthographic Familiarity. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2008, 34, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miellet, S.; Sparrow, L. Phonological Codes Are Assembled before Word Fixation: Evidence from Boundary Paradigm in Sentence Reading. Brain Lang. 2004, 90, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.-L.; Lee, C.-Y.; Tzeng, O.J.L.; Hung, D.L.; Yen, N.-S. Use of Phonological Codes for Chinese Characters: Evidence from Processing of Parafoveal Preview When Reading Sentences. Brain Lang. 2004, 91, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K. Eye Movements and the Perceptual Span in Beginning and Skilled Readers. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1986, 41, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarriba, J.; Kambe, G.; Pollatsek, A.; Rayner, K. Semantic Codes Are Not Used in Integrating Information across Eye Fixations in Reading: Evidence from Fluent Spanish-English Bilinguals. Percept. Psychophys. 2001, 63, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.J.; Bertram, R.; Hyönä, J. Semantic Processing of Previews within Compound Words. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2008, 34, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotter, E.R. Synonyms Provide Semantic Preview Benefit in English. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 69, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotter, E.R.; Reichle, E.D.; Rayner, K. Rethinking Parafoveal Processing in Reading: Serial-Attention Models Can Explain Semantic Preview Benefit and N+2 Preview Effects. Vis. Cogn. 2014, 22, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotter, E.R.; Lee, M.; Reiderman, M.; Rayner, K. The Effect of Contextual Constraint on Parafoveal Processing in Reading. J. Mem. Lang. 2015, 83, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotter, E.R.; Jia, A. Semantic and Plausibility Preview Benefit Effects in English: Evidence from Eye Movements. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2016, 42, 1839–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotter, E.R. Reading Ahead by Hedging Our Bets on Seeing the Future. In Psychology of Learning and Motivation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 68, pp. 263–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.; Veldre, A. What Is the Most Plausible Account of the Role of Parafoveal Processing in Reading? Lang. Linguist. Compass 2019, 13, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenstein, S.; Kliegl, R. Semantic Preview Benefit during Reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2014, 40, 166–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Schotter, E.R. Semantic Preview Benefit in Reading English: The Effect of Initial Letter Capitalization. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2014, 40, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosain, R. Psycholinguistic Implications for Linguistic Relativity: A Case Study of Chinese; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Luo, Y.; Inhoff, A.W. Syllable Articulation Influences Foveal and Parafoveal Processing of Words during the Silent Reading of Chinese Sentences. J. Mem. Lang. 2014, 75, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Inhoff, A.W.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C. Use of Parafoveally Visible Characters during the Reading of Chinese Sentences. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2002, 28, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Risse, S.; Zhou, X.; Kliegl, R. Preview Fixation Duration Modulates Identical and Semantic Preview Benefit in Chinese Reading. Read. Writ. 2012, 25, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shu, H.; Miller, K.; Yan, M. Reliance on Orthography and Phonology in Reading of Chinese: A Developmental Study: Orthography and Phonology in Chinese Reading. J. Res. Read. 2018, 41, 370–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Yeon, J.; Zhou, W.; Shu, H.; Yan, M. Cross-Language Parafoveal Semantic Processing: Evidence from Korean–Chinese Bilinguals. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2016, 23, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pollatsek, A. An Integrated Model of Word Processing and Eye-Movement Control during Chinese Reading. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 127, 1139–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Reichle, E.D.; Li, X. The Effect of Word Frequency and Parafoveal Preview on Saccade Length during the Reading of Chinese. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2016, 42, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, E.D. Serial-Attention Models of Reading. In The Oxford Handbook of Eye Movements; Liversedge, S.P., Gilchrist, I., Everling, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R.; Kliegl, R. Parallel Graded Attention Models of Reading. In The Oxford Handbook of Eye Movements; Liversedge, S.P., Gilchrist, I., Everling, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.R. Applying New Design Principles to the Construction of an Illiterate E Chart. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Opt. 1978, 55, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, J.; Kenny, D.A.; Judd, C.M. Statistical Power and Optimal Design in Experiments in Which Samples of Participants Respond to Samples of Stimuli. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2014, 143, 2020–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. The Statistical Power of Abnormal-Social Psychological Research: A Review. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 1962, 65, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Brysbaert, M. SUBTLEX-CH: Chinese Word and Character Frequencies Based on Film Subtitles. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, T.J.; Angele, B.; Rayner, K. Eye Movements and Display Change Detection during Reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2011, 37, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drieghe, D.; Chan Seem, R. Parafoveal Processing of Repeated Words during Reading. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2022, 29, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baayen, R.H.; Davidson, D.J.; Bates, D.M. Mixed-Effects Modeling with Crossed Random Effects for Subjects and Items. J. Mem. Lang. 2008, 59, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, D.J.; Levy, R.; Scheepers, C.; Tily, H.J. Random Effects Structure for Confirmatory Hypothesis Testing: Keep It Maximal. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Chambers, J., Eddy, W., Härdle, W., Sheather, S., Tierney, L., Eds.; Statistics and Computing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Tian, H.; Bai, X.; Rayner, K. The Effect of Word and Character Frequency on the Eye Movements of Chinese Readers. Br. J. Psychol. 2006, 97, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bicknell, K.; Liu, P.; Wei, W.; Rayner, K. Reading Is Fundamentally Similar across Disparate Writing Systems: A Systematic Characterization of How Words and Characters Influence Eye Movements in Chinese Reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2014, 143, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Yan, M.; Laubrock, J. Semantic Preview Benefit and Cost: Evidence from Parafoveal Fast-Priming Paradigm. Cognition 2020, 205, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B. Xian Dai Han Zi, 1st ed.; Hua Yu Jiao Xue Chu Ban She: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Kliegl, R.; Shu, H.; Pan, J.; Zhou, X. Parafoveal Load of Word N+1 Modulates Preprocessing Effectiveness of Word N+2 in Chinese Reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2010, 36, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Cutter, M.G.; Yan, G.; Bai, X.; Fu, Y.; Drieghe, D.; Liversedge, S.P. Word n + 2 Preview Effects in Three-Character Chinese Idioms and Phrases. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 1130–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.; Hawelka, S.; Schuster, S.; Hutzler, F. Foveal Processing Difficulty Does Not Affect Parafoveal Preprocessing in Young Readers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Preview Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Orthographic | Phonological | Semantic | |
| Orthographic rating | 5.6 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.2) | 1.3 (0.2) |
| Phonological rating | 1.3 (0.2) | 6.7 (0.3) | 1.3 (0.2) |
| Semantic rating | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 6.0 (0.3) |
| Measure | High Frequency | Low Frequency | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | OR | PH | SE | PSE | ID | OR | PH | SE | PSE | |
| Pretarget | ||||||||||
| FFD | 249 (51) | 253 (53) | 245 (49) | 248 (67) | 246 (48) | 265 (57) | 262 (61) | 259 (55) | 266 (62) | 266 (70) |
| GD | 271 (69) | 286 (93) | 280 (90) | 277 (94) | 286 (93) | 315 (108) | 316 (115) | 309 (96) | 319 (107) | 310 (108) |
| TT | 385 (135) | 435 (165) | 431 (210) | 437 (182) | 457 (191) | 477 (192) | 516 (201) | 530 (271) | 516 (232) | 526 (250) |
| RPD | 328 (118) | 338 (128) | 341 (136) | 322 (129) | 355 (128) | 391 (162) | 390 (160) | 400 (198) | 399 (207) | 400 (159) |
| SKIP | 0.29 (0.26) | 0.30 (0.25) | 0.31 (0.27) | 0.30 (0.28) | 0.29 (0.25) | 0.25 (0.25) | 0.26 (0.26) | 0.24 (0.25) | 0.27 (0.24) | 0.28 (0.25) |
| Target | ||||||||||
| FFD | 260 (67) | 332 (91) | 338 (92) | 332 (100) | 352 (107) | 271 (77) | 334 (94) | 336 (105) | 351 (104) | 339 (84) |
| GD | 264 (69) | 351 (101) | 364 (106) | 354 (106) | 377 (111) | 286 (89) | 358 (106) | 354 (121) | 389 (140) | 372 (106) |
| TT | 310 (132) | 404 (159) | 404 (141) | 416 (186) | 424 (180) | 347 (117) | 421 (148) | 429 (147) | 467 (257) | 447 (187) |
| RPD | 330 (158) | 425 (173) | 472 (195) | 456 (182) | 460 (206) | 401 (188) | 458 (157) | 455 (177) | 495 (202) | 486 (203) |
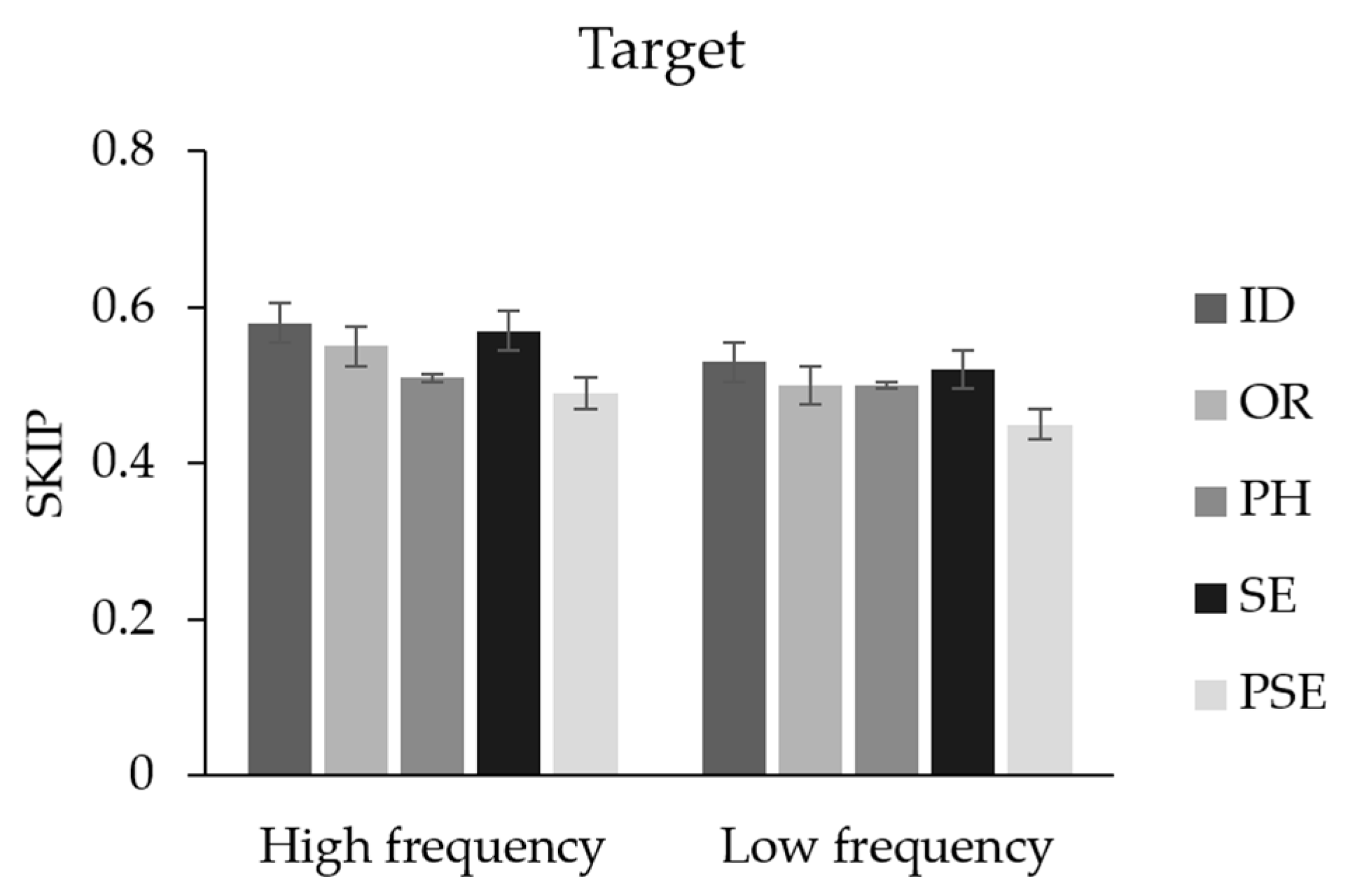
| SKIP | 0.58 (0.24) | 0.55 (0.28) | 0.51 (0.25) | 0.57 (0.25) | 0.49 (0.27) | 0.53 (0.24) | 0.50 (0.26) | 0.50 (0.26) | 0.52 (0.24) | 0.45 (0.24) |
| Fixed Effect | Word n | Word n + 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | SE | t/z | b | SE | t/z | |
| FFD | ||||||
| Intercept | 256.70 | 2.84 | 90.24 | 325.58 | 3.77 | 86.33 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 15.78 | 2.67 | 5.91 * | 4.00 | 4.51 | 0.89 |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 2.09 | 3.72 | 0.56 | 82.67 | 6.76 | 12.24 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 2.50 | 3.72 | 0.67 | 11.41 | 7.11 | 1.60 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 5.85 | 3.72 | 1.57 | 7.28 | 6.56 | 1.11 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 3.13 | 3.92 | 0.80 | 2.21 | 6.65 | 0.33 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 3.14 | 7.56 | 0.42 | −17.74 | 12.60 | −1.41 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 6.05 | 7.44 | 0.81 | −9.17 | 12.62 | −0.73 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 0.18 | 7.50 | 0.02 | −12.36 | 12.75 | −0.97 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 1.25 | 8.69 | 0.14 | −20.19 | 12.49 | −1.62 |
| GD | ||||||
| Intercept | 298.74 | 5.42 | 55.09 | 347.64 | 4.33 | 80.28 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 35.83 | 5.25 | 6.83 * | 11.31 | 5.16 | 2.19 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 11.95 | 6.86 | 1.74 | 102.51 | 7.78 | 13.18 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −0.54 | 6.87 | −0.08 | 19.62 | 8.18 | 2.40 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 6.22 | 7.19 | 0.87 | 12.08 | 7.45 | 1.62 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 5.92 | 7.15 | 0.83 | 2.64 | 7.36 | 0.36 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −16.40 | 13.73 | −1.20 | −16.32 | 14.46 | −1.13 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −10.76 | 15.04 | −0.72 | −1.91 | 14.50 | −0.13 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −9.91 | 13.93 | −0.71 | 5.97 | 14.21 | 0.42 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −14.46 | 14.78 | −0.98 | −23.54 | 15.95 | −1.48 |
| TT | ||||||
| Intercept | 468.76 | 14.13 | 33.17 | 406.94 | 10.36 | 39.26 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 83.99 | 12.15 | 6.91 * | 29.24 | 6.36 | 4.60 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 64.59 | 12.50 | 5.17 * | 115.59 | 11.75 | 9.83 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 12.83 | 11.21 | 1.14 | 21.59 | 9.79 | 2.21 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 12.08 | 13.85 | 0.87 | 21.43 | 10.16 | 2.11 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 14.78 | 11.61 | 1.27 | −5.78 | 13.07 | −0.44 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −10.12 | 22.55 | −0.45 | −13.72 | 20.55 | −0.67 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −6.51 | 22.43 | −0.29 | 15.70 | 19.86 | 0.79 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −16.15 | 27.93 | −0.58 | −5.66 | 19.44 | −0.29 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −6.06 | 24.47 | −0.25 | −26.30 | 21.02 | −1.25 |
| RPD | ||||||
| Intercept | 366.31 | 8.62 | 42.51 | 444.40 | 11.58 | 38.38 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 61.02 | 8.67 | 7.03 * | 31.33 | 9.77 | 3.21 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 19.60 | 11.35 | 1.73 | 119.09 | 15.59 | 8.16 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 12.22 | 10.80 | 1.13 | 33.07 | 14.33 | 2.31 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 15.24 | 10.88 | 1.40 | 14.72 | 14.08 | 1.05 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 19.20 | 11.07 | 1.74 | 1.78 | 13.61 | 0.13 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −15.74 | 21.95 | −0.72 | −28.53 | 28.58 | −1.00 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −15.01 | 21.90 | −0.69 | 6.99 | 27.39 | 0.26 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −9.38 | 22.25 | −0.42 | 45.07 | 27.92 | 1.62 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −35.47 | 23.13 | −1.53 | −14.29 | 27.19 | −0.53 |
| SKIP | ||||||
| Intercept | −1.17 | 0.10 | −11.50 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 1.50 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | −0.18 | 0.00 | −3.02 * | −0.19 | 0.05 | −3.83 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.70 | −0.40 | 0.09 | −4.61 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.21 | −0.27 | 0.08 | −3.44 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.74 | −0.19 | 0.08 | −2.43 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.01 | −0.34 | 0.08 | −4.41 * |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 0.34 | 0.18 | 1.93 | −0.14 | 0.15 | −0.91 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| Preview Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Orthographic | Phonological | Semantic | |
| Orthographic rating | 5.3 (0.3) | 1.3 (0.3) | 1.5 (0.2) |
| Phonological rating | 1.2 (0.1) | 6.8 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) |
| Semantic rating | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.0) | 5.5 (0.3) |
| Measure | High Frequency | Low Frequency | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | OR | PH | SE | PSE | ID | OR | PH | SE | PSE | |
| Pretarget | ||||||||||
| FFD | 232 (47) | 239 (57) | 247 (65) | 241 (50) | 241 (60) | 256 (60) | 255 (54) | 256 (53) | 251 (58) | 252 (61) |
| GD | 252 (74) | 260 (96) | 271 (85) | 262 (76) | 259 (88) | 292 (100) | 291 (98) | 284 (84) | 285 (101) | 284 (106) |
| TT | 346 (119) | 375 (173) | 389 (153) | 381 (140) | 386 (163) | 426 (165) | 440 (175) | 444 (166) | 449 (196) | 442 (173) |
| RPD | 300 (103) | 310 (127) | 324 (137) | 306 (114) | 300 (117) | 352 (132) | 350 (140) | 331 (99) | 337 (152) | 331 (129) |
| Skip | 0.34 (0.27) | 0.34 (0.26) | 0.33 (0.25) | 0.34 (0.28) | 0.37 (0.26) | 0.30 (0.26) | 0.29 (0.24) | 0.32 (0.27) | 0.32 (0.26) | 0.31 (0.26) |
| Target | ||||||||||
| FFD | 259 (73) | 304 (96) | 319 (90) | 320 (102) | 310 (90) | 257 (62) | 306 (94) | 307 (85) | 297 (89) | 305 (89) |
| GD | 263 (74) | 316 (107) | 330 (104) | 329 (104) | 323 (97) | 261 (63) | 321 (104) | 319 (92) | 306 (94) | 318 (101) |
| TT | 317 (111) | 376 (154) | 379 (128) | 410 (198) | 383 (137) | 321 (119) | 383 (149) | 382 (128) | 392 (145) | 380 (127) |
| RPD | 335 (200) | 379 (150) | 416 (158) | 402 (170) | 432 (172) | 361 (174) | 456 (214) | 475 (218) | 421 (169) | 449 (177) |
| Skip | 0.54 (0.25) | 0.49 (0.24) | 0.50 (0.26) | 0.48 (0.26) | 0.49 (0.25) | 0.56 (0.25) | 0.49 (0.25) | 0.47 (0.25) | 0.48 (0.26) | 0.45 (0.25) |
| Fixed Effect | Word n | Word n + 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | SE | t/z | b | SE | t/z | |
| FFD | ||||||
| Intercept | 247.33 | 3.20 | 77.22 | 298.14 | 4.09 | 72.85 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 17.54 | 3.53 | 4.97 * | −5.14 | 3.99 | −1.29 |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 1.99 | 3.73 | 0.54 | 48.70 | 6.10 | 7.99 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 0.06 | 3.90 | 0.01 | 3.37 | 6.47 | 0.52 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −3.32 | 3.85 | −0.86 | −1.03 | 6.08 | −0.17 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −1.28 | 3.76 | −0.34 | −1.81 | 6.56 | −0.28 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −12.05 | 7.47 | −1.61 | 5.21 | 12.12 | 0.43 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −6.13 | 7.63 | −0.80 | −0.72 | 12.58 | −0.06 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −3.61 | 7.91 | −0.46 | 5.13 | 12.27 | 0.42 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −3.25 | 7.52 | −0.43 | 11.67 | 13.29 | 0.88 |
| GD | ||||||
| Intercept | 274.09 | 5.73 | 47.86 | 309.31 | 4.68 | 66.16 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 31.16 | 5.88 | 5.30 * | −4.36 | 4.57 | −0.96 |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −1.35 | 7.38 | −0.18 | 58.47 | 6.72 | 8.70 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −4.40 | 6.06 | −0.73 | 2.01 | 7.20 | 0.28 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −4.87 | 6.10 | −0.80 | −0.85 | 7.08 | −0.12 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −1.71 | 6.12 | −0.28 | 1.67 | 7.36 | 0.23 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −11.78 | 12.22 | −0.96 | 2.94 | 13.49 | 0.22 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −3.29 | 13.13 | −0.25 | −5.32 | 14.43 | −0.37 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 6.12 | 12.47 | 0.49 | 1.48 | 13.36 | 0.11 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 2.66 | 12.24 | 0.22 | 9.20 | 14.20 | 0.65 |
| TT | ||||||
| Intercept | 4.04 | 1.19 | 34.05 | 373.44 | 7.45 | 50.16 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 6.54 | 1.07 | 6.12 * | −3.28 | 6.52 | −0.50 |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 2.91 | 1.04 | 2.80 * | 64.45 | 10.15 | 6.35 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 8.33 | 1.10 | 0.76 | 2.16 | 12.21 | 0.18 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −6.08 | 9.80 | 0.00 | 2.23 | 9.71 | 0.23 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 3.99 | 1.01 | 0.39 | −19.31 | 12.06 | −1.60 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −2.45 | 1.96 | −1.25 | −7.89 | 20.09 | −0.39 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −1.48 | 1.96 | −0.76 | −7.25 | 20.84 | −0.35 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −8.87 | 2.00 | −0.44 | −2.08 | 19.42 | −0.11 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −1.12 | 2.08 | −0.54 | 12.04 | 27.68 | 0.44 |
| RPD | ||||||
| Intercept | 324.09 | 7.71 | 42.01 | 411.43 | 8.25 | 49.86 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | 31.84 | 7.24 | 4.40 * | 41.94 | 9.46 | 4.44 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −12.59 | 10.11 | −1.25 | 94.82 | 13.61 | 6.97 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −15.42 | 9.16 | −1.68 | 17.78 | 13.45 | 1.32 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −13.93 | 8.70 | −1.60 | −5.37 | 14.14 | −0.38 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −5.14 | 8.80 | −0.58 | 25.62 | 13.76 | 1.86 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −22.03 | 18.81 | −1.17 | −9.66 | 26.37 | −0.37 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | −6.30 | 18.62 | −0.34 | −41.06 | 28.57 | −1.44 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 17.17 | 17.40 | 0.99 | −28.97 | 28.21 | −1.03 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 0.86 | 17.53 | 0.05 | 3.55 | 25.56 | 0.14 |
| SKIP | ||||||
| Intercept | −0.90 | 0.10 | −9.32 | −0.01 | 0.06 | −0.23 |
| Frequency (High vs. Low) | −0.24 | 0.07 | −3.63 * | −0.05 | 0.05 | −0.93 |
| Preview (PSE vs. ID) | 0.14 | 0.09 | 1.61 | −0.39 | 0.08 | −4.96 * |
| Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 0.16 | 0.09 | 1.76 | −0.11 | 0.08 | −1.33 |
| Preview (PSE vs. PH) | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.88 | −0.10 | 0.08 | −1.35 |
| Preview (PSE vs. SE) | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.92 | −0.08 | 0.08 | −0.96 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. ID) | −0.06 | 0.18 | −0.34 | −0.30 | 0.16 | −1.88 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. OR) | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.28 | −0.19 | 0.15 | −1.27 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. PH) | −0.22 | 0.17 | −1.28 | −0.04 | 0.16 | −0.23 |
| Frequency × Preview (PSE vs. SE) | −0.10 | 0.18 | −0.58 | −0.16 | 0.15 | −1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Kang, L.; Chen, W.; Xie, F.; Warrington, K.L. Parafoveal Processing of Orthography, Phonology, and Semantics during Chinese Reading: Effects of Foveal Load. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050512
Zhang L, Kang L, Chen W, Xie F, Warrington KL. Parafoveal Processing of Orthography, Phonology, and Semantics during Chinese Reading: Effects of Foveal Load. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(5):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050512
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Liangyue Kang, Wanying Chen, Fang Xie, and Kayleigh L. Warrington. 2024. "Parafoveal Processing of Orthography, Phonology, and Semantics during Chinese Reading: Effects of Foveal Load" Brain Sciences 14, no. 5: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050512
APA StyleZhang, L., Kang, L., Chen, W., Xie, F., & Warrington, K. L. (2024). Parafoveal Processing of Orthography, Phonology, and Semantics during Chinese Reading: Effects of Foveal Load. Brain Sciences, 14(5), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14050512






