The Left Amygdala and Right Frontoparietal Cortex Support Emotional Adaptation Aftereffects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
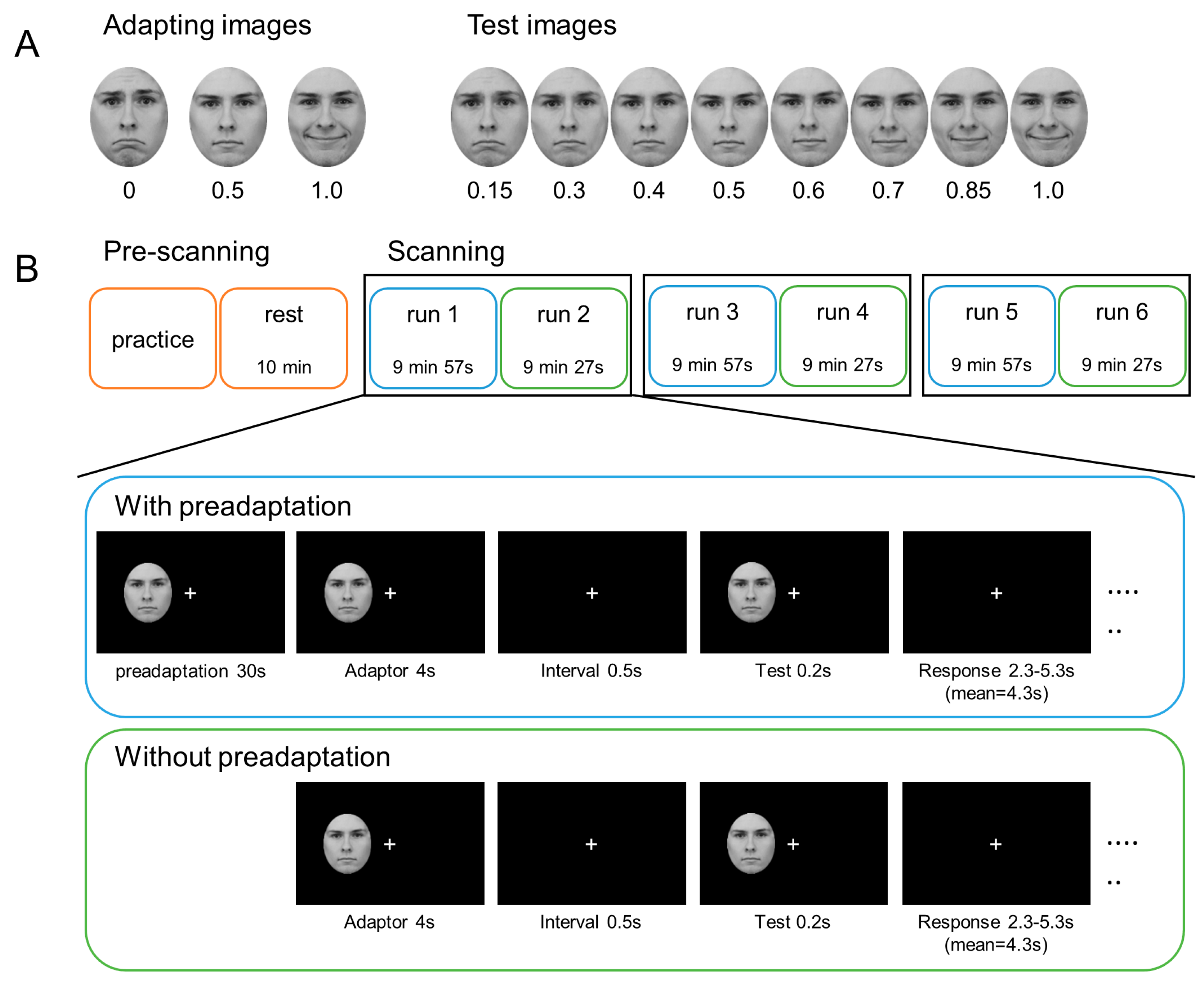
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.3.1. Pre-Scanning
2.3.2. Scanning
2.3.3. Trial Procedure
2.4. Acquisition of Imaging Data
2.5. Analysis of Behavioral Data
2.6. Image Preprocessing and Activation Analysis
2.7. ROI Analysis
3. Results
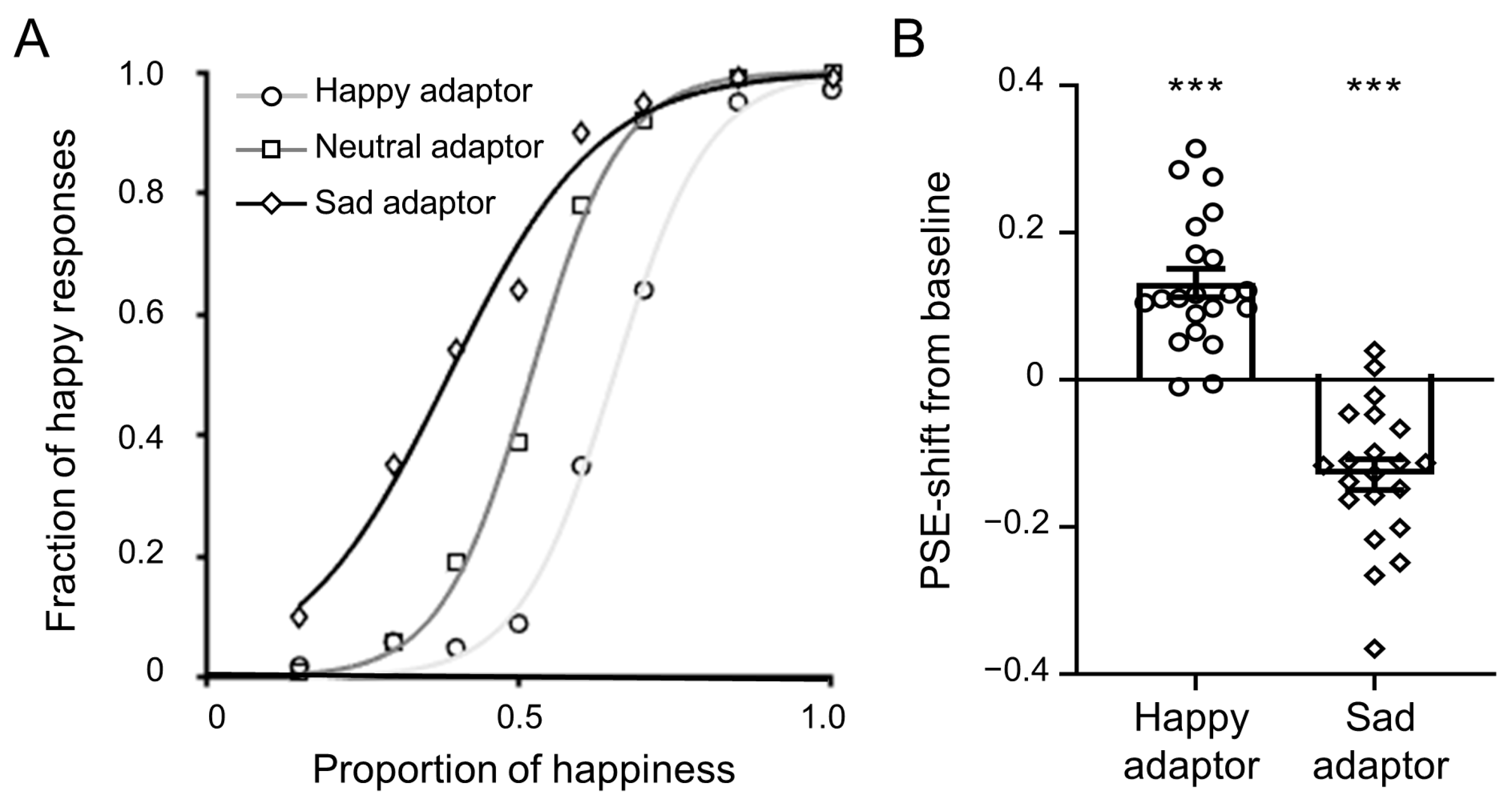
3.1. Behavioral Results
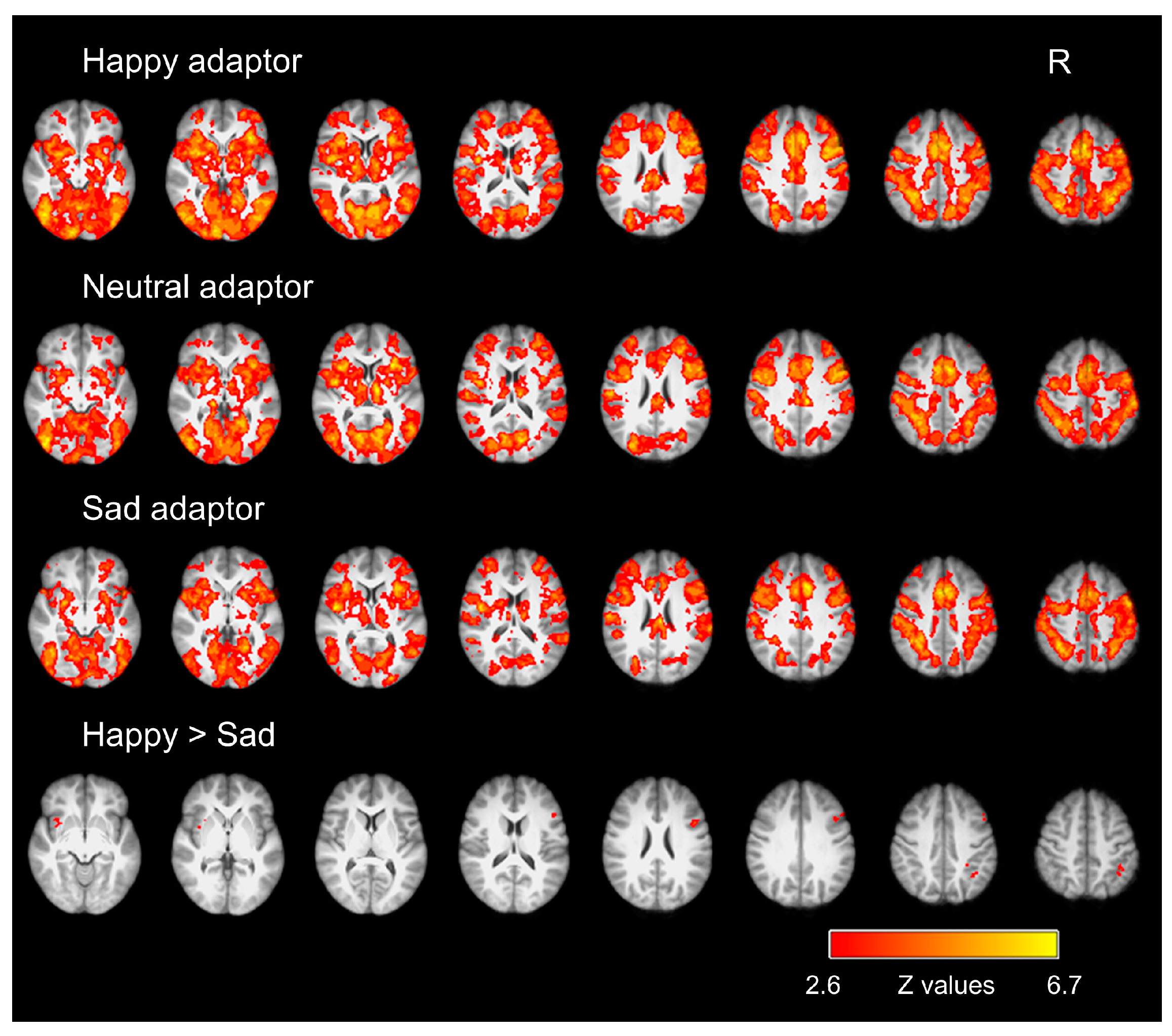
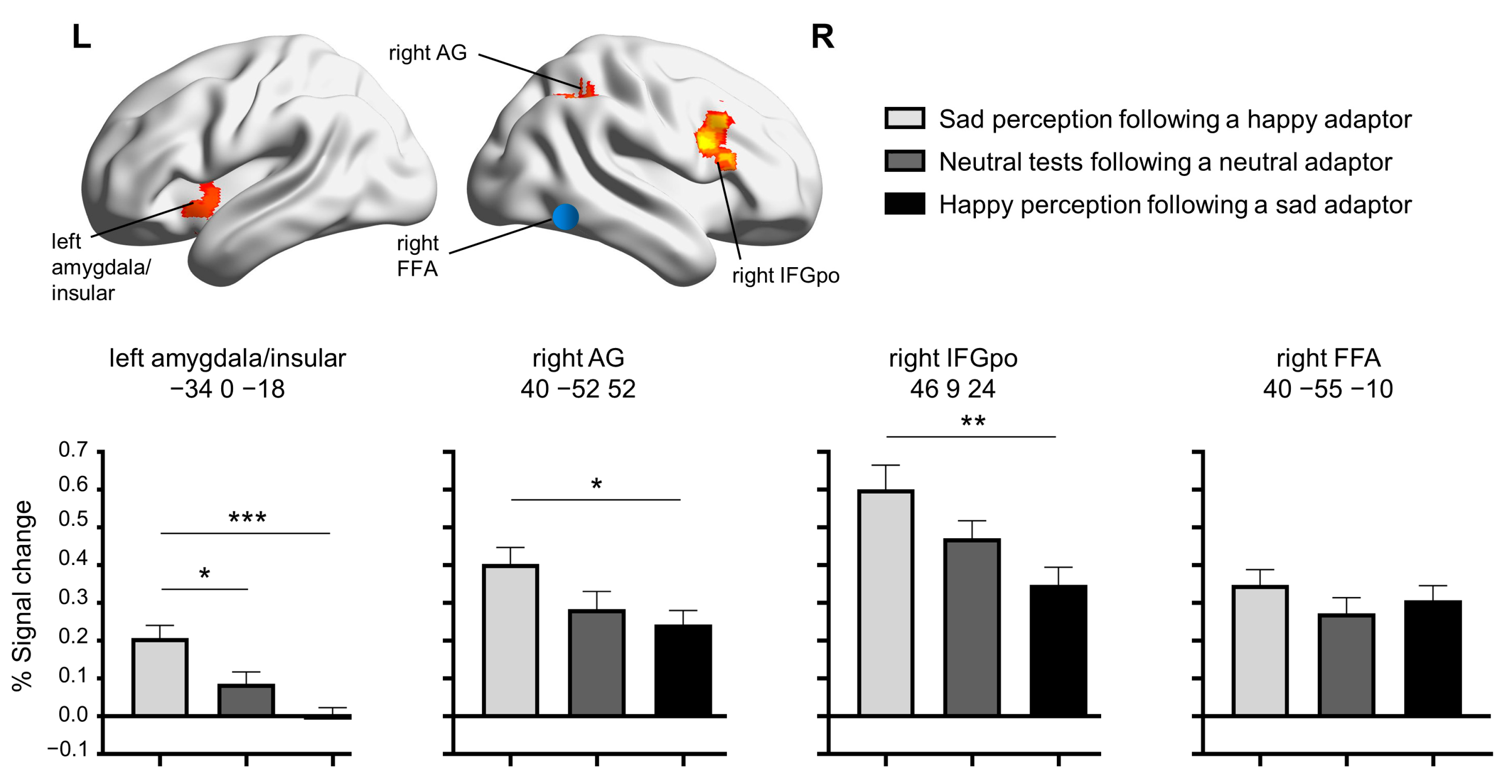
3.2. fMRI Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furl, N.; Van Rijsbergen, N.J.; Treves, A.; Dolan, R.J. Face Adaptation Aftereffects Reveal Anterior Medial Temporal Cortex Role in High Level Category Representation. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Webster, M.A.; Kaping, D.; Mizokami, Y.; Duhamel, P. Adaptation to Natural Facial Categories. Nature 2004, 428, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthoft, N.; Sha, L.; Winawer, J.; Kiani, R. Sensory and Decision-Making Processes Underlying Perceptual Adaptation. J. Vis. 2018, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, C.W.G. Perceptual Adaptation: Motion Parallels Orientation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.J.; Radner, M. Adaptation, after-Effect and Contrast in the Perception of Tilted Lines. I. Quantitative Studies. J. Exp. Psychol. 1937, 20, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huk, A.C.; Ress, D.; Heeger, D.J. Neuronal Basis of the Motion Aftereffect Reconsidered. Neuron 2001, 32, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C. Color Adaptation of Edge-Detectors in the Human Visual System. Science 1965, 149, 1115–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidenko, N.; Vu, C.Q.; Heller, N.H.; Collins, J.M. Attending to Race (or Gender) Does Not Increase Race (or Gender) Aftereffects. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.; Kloth, N.; McKone, E.; Jeffery, L.; Irons, J.; Rhodes, G. Aftereffects Support Opponent Coding of Face Gender. J. Vis. 2013, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Seriès, P.; Hancock, P.J.B.; Bednar, J.A. Similar Neural Adaptation Mechanisms Underlying Face Gender and Tilt Aftereffects. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaquet, E.; Rhodes, G.; Hayward, W.G. Race-Contingent Aftereffects Suggest Distinct Perceptual Norms for Different Race Faces. Vis. Cogn. 2008, 16, 734–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armann, R.; Jeffery, L.; Calder, A.J.; Rhodes, G. Race-Specific Norms for Coding Face Identity and a Functional Role for Norms. J. Vis. 2011, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Moon, S.; Iaria, G.; Barton, J. The Correlates of Subjective Perception of Identity and Expression in the Face Network: An fMRI Adaptation Study. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, L.; Rhodes, G. Insights into the Development of Face Recognition Mechanisms Revealed by Face Aftereffects: Insights into the Development of Face Recognition. Br. J. Psychol. 2011, 102, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.A.; Deroche, M.; Palmeri, T.J. Not Just the Norm: Exemplar-Based Models Also Predict Face Aftereffects. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2014, 21, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, C.; Schweinberger, S.R.; Kovács, G. Adaptor Identity Modulates Adaptation Effects in Familiar Face Identification and Their Neural Correlates. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheal, J.L.; Heisz, J.J.; Walsh, J.A.; Shedden, J.M.; Rutherford, M.D. Afterimage Induced Neural Activity during Emotional Face Perception. Brain Res. 2014, 1549, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, M.D.; Chattha, H.M.; Krysko, K.M. The Use of Aftereffects in the Study of Relationships among Emotion Categories. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2008, 34, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.L.; Benton, C.P. Anti-Expression Aftereffects Reveal Prototype-Referenced Coding of Facial Expressions. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Goldberg, M.E.; Xu, H. Auditory to Visual Cross-Modal Adaptation for Emotion: Psychophysical and Neural Correlates. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 27, bhv321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Xu, H. Adaptation Reveals That Facial Expression Averaging Occurs during Rapid Serial Presentation. J. Vis. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Fu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L. The Emotional Adaptation Aftereffect Discriminates between Individuals with High and Low Levels of Depressive Symptoms. Cogn. Emot. 2022, 36, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Burns, E.; Xu, H. Association between Autistic Traits and Emotion Adaptation to Partially Occluded Faces. Vis. Res. 2017, 133, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, G.; Burton, N.; Jeffery, L.; Read, A.; Taylor, L.; Ewing, L. Facial Expression Coding in Children and Adolescents with Autism: Reduced Adaptability but Intact Norm-Based Coding. Br. J. Psychol. 2018, 109, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, M.D.; Troubridge, E.K.; Walsh, J. Visual Afterimages of Emotional Faces in High Functioning Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, N.; Jeffery, L.; Skinner, A.L.; Benton, C.P.; Rhodes, G. Nine-Year-Old Children Use Norm-Based Coding to Visually Represent Facial Expression. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2013, 39, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.W.; Yoon, K.L. Intensity Dependence in High-Level Facial Expression Adaptation Aftereffect. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, Q.; Schyns, P.G.; Kingdom, F.A.A.; Xu, H. Facial Expression Aftereffect Revealed by Adaption to Emotion-Invisible Dynamic Bubbled Faces. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vida, M.D.; Mondloch, C.J. Children’s Representations of Facial Expression and Identity: Identity-Contingent Expression Aftereffects. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2009, 104, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sou, K.L.; Xu, H. Brief Facial Emotion Aftereffect Occurs Earlier for Angry than Happy Adaptation. Vis. Res. 2019, 162, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, P.; Dayan, P.; Qian, N. Multi-Level Visual Adaptation: Dissociating Curvature and Facial-Expression Aftereffects Produced by the Same Adapting Stimuli. Vis. Res. 2012, 72, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.J.; Gray, K.L.H.; Garner, M.; Graf, E.W. High-Level Face Adaptation Without Awareness. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Hong, S.-W.; Blake, R. Adaptation Aftereffects to Facial Expressions Suppressed from Visual Awareness. J. Vis. 2010, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pell, P.J.; Richards, A. Cross-Emotion Facial Expression Aftereffects. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Burke, D. Evidence That Identity-Dependent and Identity-Independent Neural Populations Are Recruited in the Perception of Five Basic Emotional Facial Expressions. Vis. Res. 2009, 49, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fox, C.J.; Barton, J.J.S. What Is Adapted in Face Adaptation? The Neural Representations of Expression in the Human Visual System. Brain Res. 2007, 1127, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pell, P.J.; Richards, A. Overlapping Facial Expression Representations Are Identity-Dependent. Vis. Res. 2013, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.L.; Benton, C.P. The Expressions of Strangers: Our Identity-Independent Representation of Facial Expression. J. Vis. 2012, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, S.; Shinomori, K. The Output of Human Expression System Measured by Visual Adaptation and Its Implication for the Computer Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2009 Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Xiamen, China, 11–14 October 2009; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, J.E.; Mighall, H.K.; Almeida, R.A.; Bell, J.; Badcock, D.R. Rapidly Acquired Shape and Face Aftereffects Are Retinotopic and Local in Origin. Vis. Res. 2012, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dayan, P.; Lipkin, R.M.; Qian, N. Adaptation across the Cortical Hierarchy: Low-Level Curve Adaptation Affects High-Level Facial-Expression Judgments. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3374–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baart, M.; Vroomen, J. Recalibration of Vocal Affect by a Dynamic Face. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izen, S.C.; Lapp, H.E.; Harris, D.A.; Hunter, R.G.; Ciaramitaro, V.M. Seeing a Face in a Crowd of Emotional Voices: Changes in Perception and Cortisol in Response to Emotional Information across the Senses. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izen, S.C.; Ciaramitaro, V.M. A Crowd of Emotional Voices Influences the Perception of Emotional Faces: Using Adaptation, Stimulus Salience, and Attention to Probe Audio-Visual Interactions for Emotional Stimuli. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2020, 82, 3973–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, A.; Bestelmeyer, P.E.G. Evidence for a Supra-Modal Representation of Emotion from Cross-Modal Adaptation. Cognition 2015, 134, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuk, V.G.; Schweinberger, S.R. Adaptation Aftereffects in Vocal Emotion Perception Elicited by Expressive Faces and Voices. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.; Latinus, M.; Noguchi, T.; Garrod, O.; Crabbe, F.; Belin, P. Crossmodal Adaptation in Right Posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus during Face–Voice Emotional Integration. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6813–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furl, N.; Van Rijsbergen, N.J.; Treves, A.; Friston, K.J.; Dolan, R.J. Experience-Dependent Coding of Facial Expression in Superior Temporal Sulcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13485–13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Quantitative Methods in Psychology: A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; reprint; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-8058-0283-2. [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield, R.C. The Assessment and Analysis of Handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, D.; Flykt, A.; Öhman, A. The Karolinska Directed Emotional Faces—KDEF; CD ROM from Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Psychology section, Karolinska Institutet: Stockholm, Sweden, 1998; ISBN 91-630-7164-9. [Google Scholar]
- Swe, D.C.; Burton, N.S.; Rhodes, G. Are Expression Aftereffects Fully Explained by Tilt Adaptation? J. Vis. 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.M. Optimal Experimental Design for Event-Related fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 8, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Fast Robust Automated Brain Extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. A Global Optimisation Method for Robust Affine Registration of Brain Images. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. Non-Linear Optimisation; FMRIB Centre: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. Non-Linear Registration Aka Spatial Normalisation; FMRIB Centre: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Worsley, K.J. Statistical Analysis of Activation Images. In Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Introduction to Methods; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; Volume 14, pp. 251–270. ISBN 978-0-19-263071-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cziraki, C.; Greenlee, M.W.; Kovács, G. Neural Correlates of High-Level Adaptation-Related Aftereffects. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.; Walther, C.; Schweinberger, S.R.; Kovács, G. Dissociating the Neural Bases of Repetition-Priming and Adaptation in the Human Brain for Faces. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 2727–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kanwisher, N.; McDermott, J.; Chun, M.M. The Fusiform Face Area: A Module in Human Extrastriate Cortex Specialized for Face Perception. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4302–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, J.A.; Turner, B.O.; Ashby, F.G.; Poldrack, R.A. Deconvolving BOLD Activation in Event-Related Designs for Multivoxel Pattern Classification Analyses. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2636–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Montaser-Kouhsari, L.; Xu, H. Effects of Face Feature and Contour Crowding in Facial Expression Adaptation. Vis. Res. 2014, 105, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matsumiya, K. Seeing a Haptically Explored Face: Visual Facial-Expression Aftereffect From Haptic Adaptation to a Face. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 2088–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, D.; Aleman, A.; Kahn, R.S. Lateralization of Amygdala Activation: A Systematic Review of Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 45, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.C.; Nimmo-Smith, I.; Lawrence, A.D. Functional Neuroanatomy of Emotions: A Meta-Analysis. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 3, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Peng, S.; Luo, Y.; Gong, G. Facial Expression Recognition: A Meta-Analytic Review of Theoretical Models and Neuroimaging Evidence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 820–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dricu, M.; Frühholz, S. A Neurocognitive Model of Perceptual Decision-making on Emotional Signals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1532–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquoine, P.G. Contributions of the Insula to Cognition and Emotion. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogolla, N. The Insular Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R580–R586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Nomi, J.S.; Hébert-Seropian, B.; Ghaziri, J.; Boucher, O. Structure and Function of the Human Insula. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Uddin, L.Q. Saliency, Switching, Attention and Control: A Network Model of Insula Function. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, W.W.; Menon, V.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Keller, J.; Glover, G.H.; Kenna, H.; Reiss, A.L.; Greicius, M.D. Dissociable Intrinsic Connectivity Networks for Salience Processing and Executive Control. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Padmanabhan, A.; Gross, J.J.; Menon, V. Development of Human Emotion Circuits Investigated Using a Big-Data Analytic Approach: Stability, Reliability, and Robustness. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7155–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Oruc, I.; Fox, C.J.; Barton, J.J.S. Factors Contributing to the Adaptation Aftereffects of Facial Expression. Brain Res. 2008, 1191, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minemoto, K.; Ueda, Y.; Yoshikawa, S. The Aftereffect of the Ensemble Average of Facial Expressions on Subsequent Facial Expression Recognition. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2022, 84, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbi, M.; Keysers, C. Inferior Frontal Gyrus Activity Triggers Anterior Insula Response to Emotional Facial Expressions. Emotion 2008, 8, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Iidaka, T.; Kakehi, K.; Tsukiura, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Maeda, Y.; Matsue, Y. Frontal Lobe Networks for Effective Processing of Ambiguously Expressed Emotions in Humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 348, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uono, S.; Sato, W.; Kochiyama, T.; Sawada, R.; Kubota, Y.; Yoshimura, S.; Toichi, M. Neural Substrates of the Ability to Recognize Facial Expressions: A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2016, 12, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Monte, O.; Krueger, F.; Solomon, J.M.; Schintu, S.; Knutson, K.M.; Strenziok, M.; Pardini, M.; Leopold, A.; Raymont, V.; Grafman, J. A Voxel-Based Lesion Study on Facial Emotion Recognition after Penetrating Brain Injury. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, C.H.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, K.; Fu, X. Reexamining the Neural Network Involved in Perception of Facial Expression: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnici, H.M.; Richter, F.R.; Yazar, Y.; Simons, J.S. Multimodal Feature Integration in the Angular Gyrus during Episodic and Semantic Retrieval. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5462–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, G.F.; Lambon Ralph, M.A.; Simons, J.S. A Unifying Account of Angular Gyrus Contributions to Episodic and Semantic Cognition. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghier, M.L. The Angular Gyrus: Multiple Functions and Multiple Subdivisions. Neuroscientist 2013, 19, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghier, M.L. Multiple Functions of the Angular Gyrus at High Temporal Resolution. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 7–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, G.F.; Tibon, R. Dual-Axes of Functional Organisation across Lateral Parietal Cortex: The Angular Gyrus Forms Part of a Multi-Modal Buffering System. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas Yeo, B.T.; Krienen, F.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Lashkari, D.; Hollinshead, M.; Roffman, J.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Zöllei, L.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The Organization of the Human Cerebral Cortex Estimated by Intrinsic Functional Connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1125–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, S.; Dosenbach, N.U.F. The Frontoparietal Network: Function, Electrophysiology, and Importance of Individual Precision Mapping. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.W.; Repovš, G.; Anticevic, A. The Frontoparietal Control System: A Central Role in Mental Health. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreng, R.N.; Sepulcre, J.; Turner, G.R.; Stevens, W.D.; Schacter, D.L. Intrinsic Architecture Underlying the Relations among the Default, Dorsal Attention, and Frontoparietal Control Networks of the Human Brain. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.E.; Badcock, D.R. On the Hierarchical Inheritance of Aftereffects in the Visual System. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, K.N.; Silvers, J.A.; Buhle, J.T. Functional Imaging Studies of Emotion Regulation: A Synthetic Review and Evolving Model of the Cognitive Control of Emotion: Functional Imaging Studies of Emotion Regulation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1251, E1–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielscher, A.; Pessoa, L. Neural Correlates of Perceptual Choice and Decision Making during Fear–Disgust Discrimination. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Fu, R.; Li, H.; Jiang, N.; Li, A.; Yang, J.; Mei, L. The Left Amygdala and Right Frontoparietal Cortex Support Emotional Adaptation Aftereffects. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030257
Su X, Fu R, Li H, Jiang N, Li A, Yang J, Mei L. The Left Amygdala and Right Frontoparietal Cortex Support Emotional Adaptation Aftereffects. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xinqi, Ruilin Fu, Huiling Li, Nan Jiang, Aqian Li, Jingyu Yang, and Leilei Mei. 2024. "The Left Amygdala and Right Frontoparietal Cortex Support Emotional Adaptation Aftereffects" Brain Sciences 14, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030257
APA StyleSu, X., Fu, R., Li, H., Jiang, N., Li, A., Yang, J., & Mei, L. (2024). The Left Amygdala and Right Frontoparietal Cortex Support Emotional Adaptation Aftereffects. Brain Sciences, 14(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030257



