The Commonality and Individuality of Human Brains When Performing Tasks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raichle, M.E. Two views of brain function. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Yetkin, F.Z.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E. The restless brain. Brain Connect 2011, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Corbetta, M.; Van Essen, D.C.; Raichle, M.E. The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas Yeo, B.T.; Krienen, F.M.; Sepulcre, J.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Lashkari, D.; Hollinshead, M.; Roffman, J.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Zöllei, L.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1125–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, R.L.; Krienen, F.M.; Castellanos, A.; Diaz, J.C.; Yeo, B.T.T. The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 2322–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, V.D.; Miller, R.; Pearlson, G.; Adalı, T. The chronnectome: Time-varying connectivity networks as the next frontier in fMRI data discovery. Neuron 2014, 84, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Tian, C.; Zeng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, R. The Relationship of Functional Connectivity of the Sensorimotor and Visual Cortical Networks Between Resting and Task States. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 592720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Greater brain activity during the resting state and the control of activation during the performance of tasks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Lee, T.M.; Kay, A.R.; Tank, D.W. Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9868–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, K.K.; Belliveau, J.W.; Chesler, D.A.; Goldberg, I.E.; Weisskoff, R.M.; Poncelet, B.P.; Kennedy, D.N.; Hoppel, B.E.; Cohen, M.S.; Turner, R. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity during primary sensory stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5675–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, E.S.; Shen, X.; Scheinost, D.; Rosenberg, M.D.; Huang, J.; Chun, M.M.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T. Functional connectome fingerprinting: Identifying individuals using patterns of brain connectivity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.; Li, J.; Orban, C.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Liu, H.; Schaefer, A.; Sun, N.; Zuo, X.-N.; Holmes, A.J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; et al. Spatial Topography of Individual-Specific Cortical Networks Predicts Human Cognition, Personality, and Emotion. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 2533–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Karbasi, A.; Barron, D.S.; Scheinost, D.; Constable, R.T. Individualized functional networks reconfigure with cognitive state. Neuroimage 2020, 206, 116233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, K.J.; Khammash, D.; Simmonite, M.; Hamlin, A.M.; Polk, T.A. Person-specific and precision neuroimaging: Current methods and future directions. Neuroimage 2022, 263, 119589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Human brain functional areas of unitary pooled activity discovered with fMRI. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Dynamic activity of human brain task-specific networks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J. A Holistic Analysis of Individual Brain Activity Revealed the Relationship of Brain Areal Activity with the Entire Brain’s Activity. Brain Sci. 2022, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.W. AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1996, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Worsley, K.J.; Poline, J.-P.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R.S.J. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1995, 2, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. Architectonic Mapping of the Human Brain beyond Brodmann. Neuron 2015, 88, 1086–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malikovic, A.; Amunts, K.; Schleicher, A.; Mohlberg, H.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Wilms, M.; Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Armstrong, E.; Zilles, K. Cytoarchitectonic analysis of the human extrastriate cortex in the region of V5/MT+: A probabilistic, stereotaxic map of area hOc5. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, M.A.; Goebel, R. Measuring structural-functional correspondence: Spatial variability of specialised brain regions after macro-anatomical alignment. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.; Detre, J.A.; Aguirre, G.K.; Cucchiara, B. Absence of changes in cortical thickness in patients with migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, E.; Gürsoy-Özdemir, Y. Occipital bending in migraine with visual aura. Headache 2021, 61, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Xia, M.; He, Y. Chronnectome fingerprinting: Identifying individuals and predicting higher cognitive functions using dynamic brain connectivity patterns. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Feczko, E.; Grayson, D.S.; Walum, H.; Nigg, J.T.; Fair, D.A. Heritability of the human connectome: A connectotyping study. Netw. Neurosci. 2018, 2, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, B.; Fu, Z.; Li, S. Decomposition of individual-specific and individual-shared components from resting-state functional connectivity using a multi-task machine learning method. Neuroimage 2021, 238, 118252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.Q.R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Kong, R.; Tam, A.; Li, J.; Dhamala, E.; Zhou, J.H.; Holmes, A.J.; Yeo, B.T.T. Comparison of individualized behavioral predictions across anatomical, diffusion and functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2022, 263, 119636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domhof, J.W.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Popovych, O.V. Reliability and subject specificity of personalized whole-brain dynamical models. Neuroimage 2022, 257, 119321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, D.; Vachha, B.; Mian, A.; Faro, S.; Maheshwari, M.; Sair, H.; Petrella, J.; Pillai, J.; Welker, K. American Society of Functional Neuroradiology-Recommended fMRI Paradigm Algorithms for Presurgical Language Assessment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, E65–E73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, C.F.A.; Li, A.X.; Blumenfeld, H.; Constable, R.T.; Alkawadri, R.; Bickel, S.; Helmstaedter, C.; Meletti, S.; Bronen, R.; Warfield, S.K.; et al. Presurgical language fMRI: Clinical practices and patient outcomes in epilepsy surgical planning. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Sair, H.I.; Gujar, S.; Pillai, J.J. Language Mapping With fMRI: Current Standards and Reproducibility. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 28, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchcinski, G.; Mellerio, C.; Pallud, J.; Dezamis, E.; Turc, G.; Rigaux-Viodé, O.; Malherbe, C.; Roca, P.; Leclerc, X.; Varlet, P.; et al. Three-tesla functional MR language mapping: Comparison with direct cortical stimulation in gliomas. Neurology 2015, 84, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

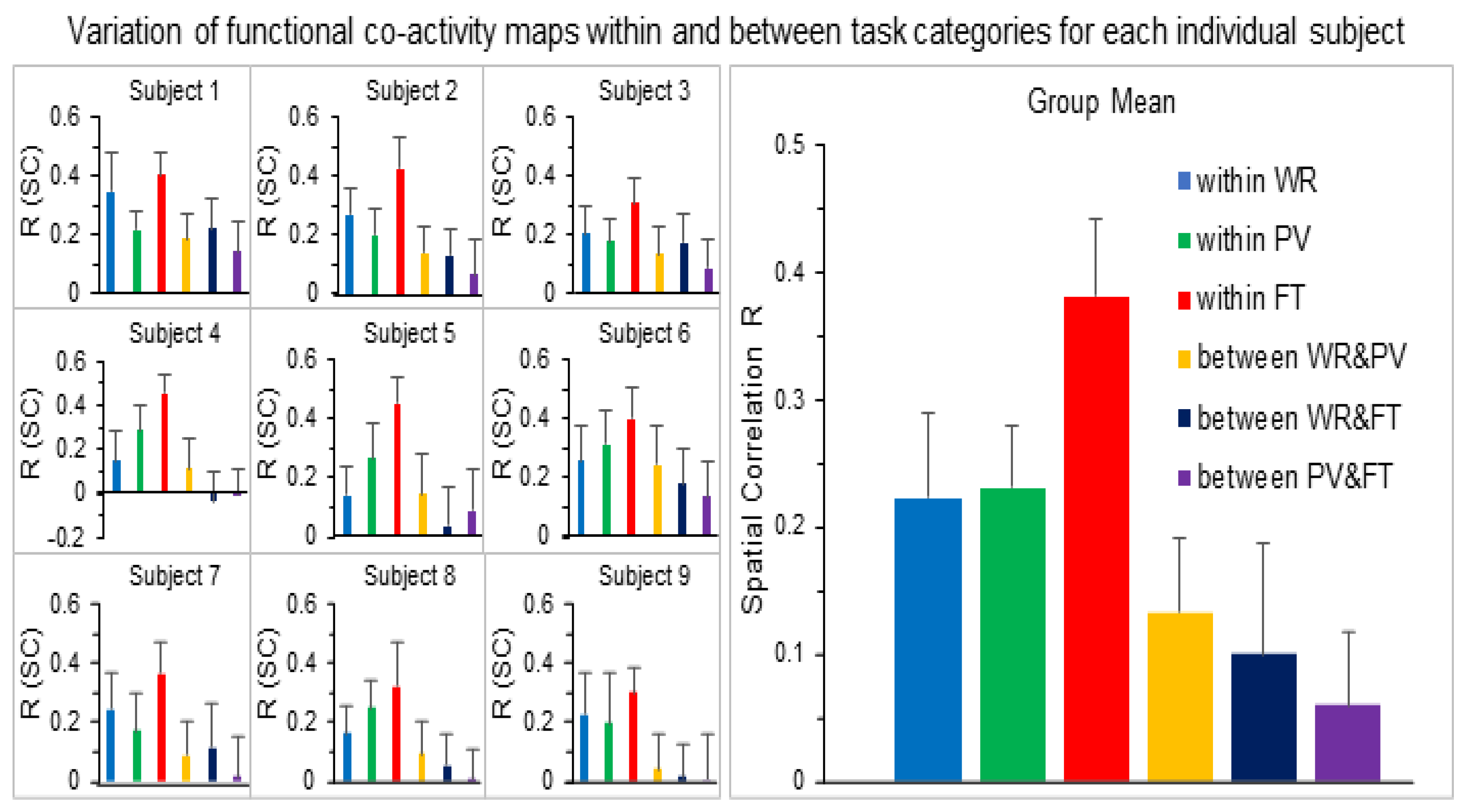

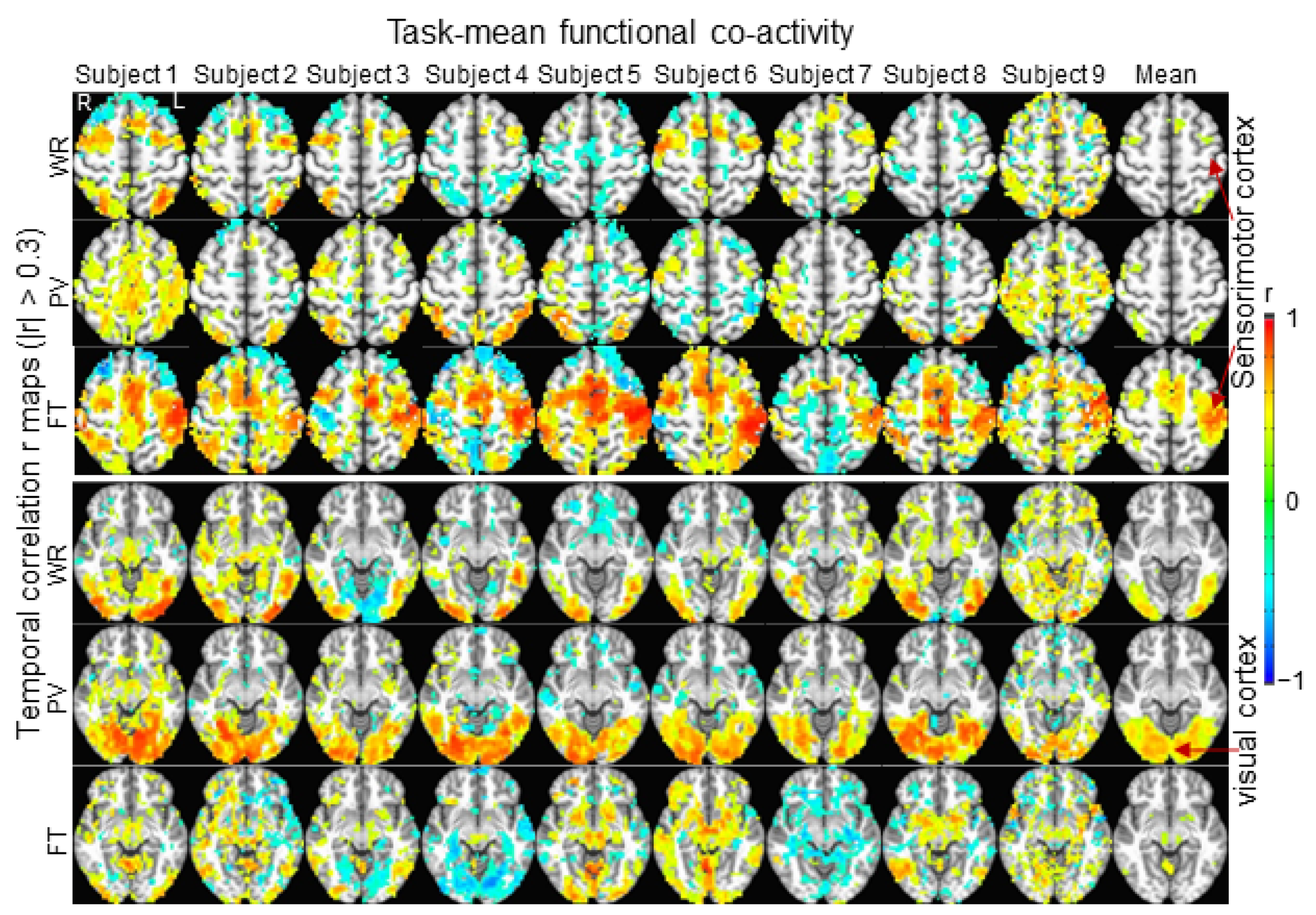
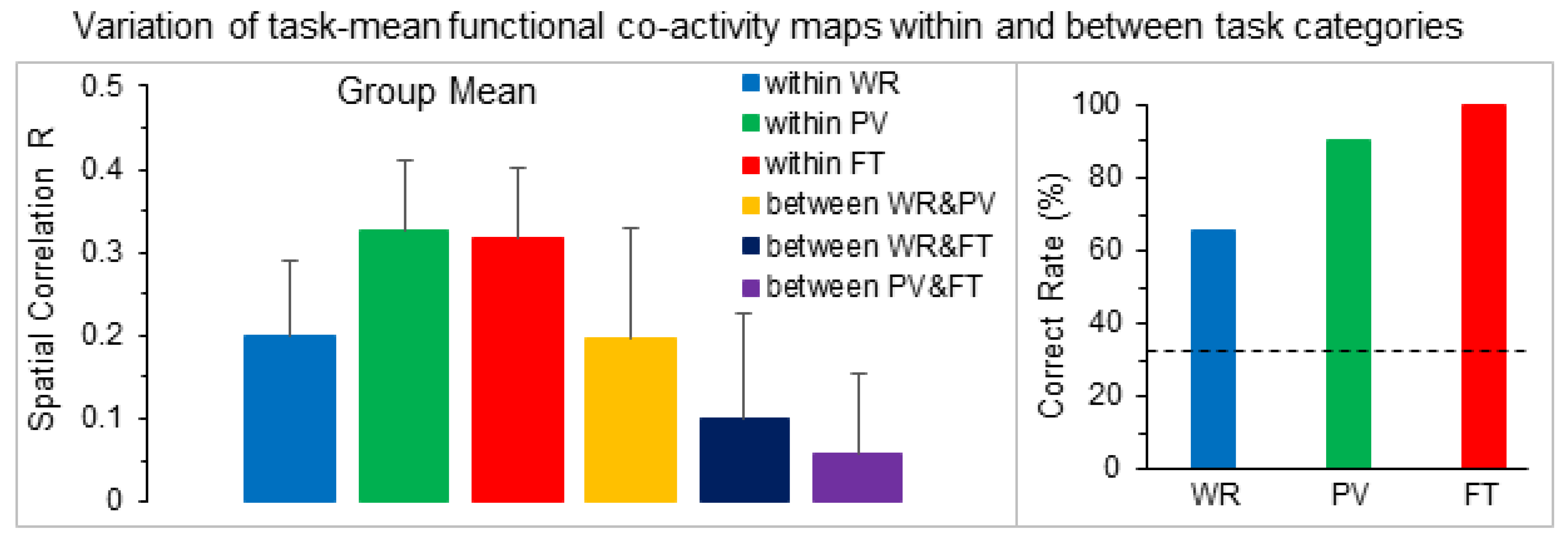
| Subject | Number of Voxels | R within WR Category | R within PV Category | R within FT Category | |||||||||
| Min | Max | MN | SD | Min | Max | MN | SD | Min | Max | MN | SD | ||
| 1 | 23,542 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 27,035 | 0.10 | 0.44 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 0.10 |
| 3 | 29,249 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.08 |
| 4 | 22,005 | −0.05 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.09 |
| 5 | 25,877 | −0.08 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.10 | −0.04 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.63 | 0.45 | 0.09 |
| 6 | 23,951 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.64 | 0.40 | 0.11 |
| 7 | 23,681 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.24 | 0.13 | −0.06 | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 0.11 |
| 8 | 26,840 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.15 |
| 9 | 25,528 | −0.01 | 0.48 | 0.23 | 0.14 | −0.10 | 0.54 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.09 |
| MN | 25,301 | 0.02 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.10 |
| SD | 2229 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Subject | Number of voxels | R between WR and PV | R between WR and FT | R between PV and FT | |||||||||
| Min | Max | MN | SD | Min | Max | MN | SD | Min | Max | MN | SD | ||
| 1 | 23,542 | −0.03 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.10 | −0.05 | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 27,035 | −0.07 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.09 | −0.10 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.09 | −0.27 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| 3 | 29,249 | −0.09 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 0.09 | −0.00 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 0.10 | −0.10 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 22,005 | −0.20 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.13 | −0.28 | 0.25 | −0.04 | 0.14 | −0.22 | 0.21 | −0.00 | 0.12 |
| 5 | 25,877 | −0.16 | 0.43 | 0.15 | 0.14 | −0.26 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.13 | −0.22 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| 6 | 23,951 | −0.07 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.13 | −0.06 | 0.49 | 0.18 | 0.12 | −0.10 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| 7 | 23,681 | −0.16 | 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.11 | −0.27 | 0.47 | 0.12 | 0.15 | −0.28 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| 8 | 26,840 | −0.18 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.11 | −0.20 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.10 | −0.23 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.10 |
| 9 | 25,528 | −0.23 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.12 | −0.18 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.11 | −0.39 | 0.35 | −0.00 | 0.16 |
| MN | 25,301 | −0.13 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.11 | −0.15 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.12 | −0.20 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| SD | 2229 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J. The Commonality and Individuality of Human Brains When Performing Tasks. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14020125
Huang J. The Commonality and Individuality of Human Brains When Performing Tasks. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jie. 2024. "The Commonality and Individuality of Human Brains When Performing Tasks" Brain Sciences 14, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14020125
APA StyleHuang, J. (2024). The Commonality and Individuality of Human Brains When Performing Tasks. Brain Sciences, 14(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14020125







