Unique Brain Network Identification Number for Parkinson’s and Healthy Individuals Using Structural MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Scanning and Image Processing
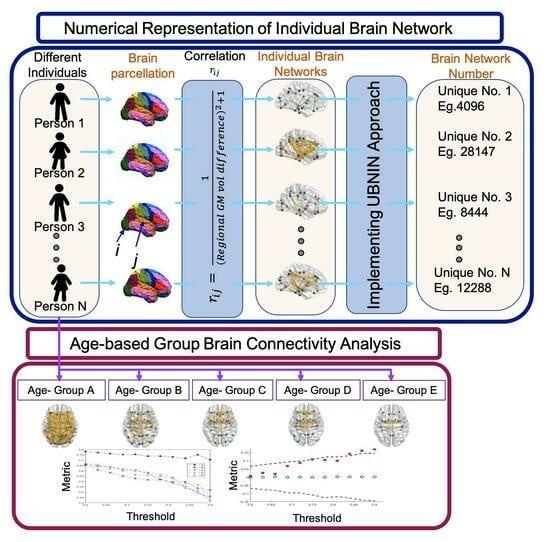
2.3. Individual Brain Network Construction
2.4. Generating Unique Brain Network Identification Number (UBNIN)
| Algorithm 1: UBNIN for an Adjacency matrix (AM) of a given network |
| N = length(AM); AM = upptriang(AM); for j = 2:N BinNode = AM(j − 1:(−1):1, j); for a = 1:length(BinNode) Val+ = 10(j−a−1)(BinNode(a)); end DECj = decimal(BinNodeVal); end temp = DEC2; power = 1; for i = 2:N−1 UBNINT = temp*(1/2power); UBNINT+ = DECi+1; power = power + 1; end |
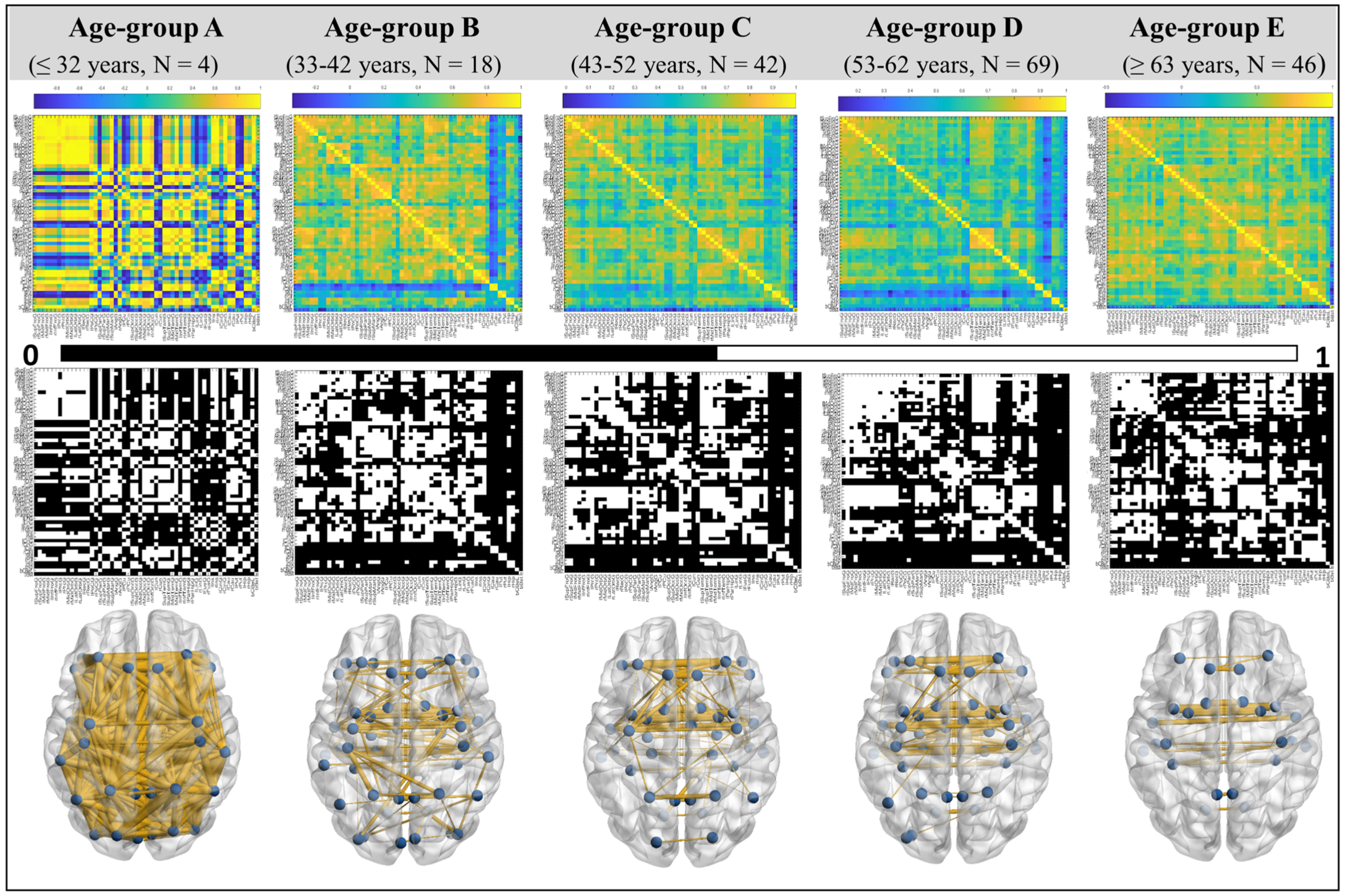
2.5. Age-Based Network Metric Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UBNIN for Individual Brain Network
3.2. Age-Based Network Metric Analysis
4. Discussions
4.1. UBNIN for Individual Brain Network
4.2. Age-Based Network Metric Analysis
4.3. Limitations and Future Scope
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Number of Nodes | UBNIN Value |
| 10 | 511.999999999985448084771633148193359375 |
| 20 | 524288 |
| 30 | 536870912 |
| 40 | 549755813888 |
| 50 | 562949953421312 |
| 100 | 633825300114114700748351602689 |
| 150 | 7.13623846352979940529142984724747568191 × 1044 |
| 200 | 8.03469022129495137770981046170581301261 × 1059 |
| 250 | 9.04625697166532776746648320380374280104 × 1074 |
| 300 | 1.01851798816724304313422284420468908053 × 1090 |
| 500 | 1.63669530394807093500659484841379957611 × 10150 |
| 800 | 3.33400721643992713703992589536062889857 × 10240 |
| 1000 | 5.35754303593133660474212524530000905281 × 10300 |
| 1020 | 5.61779104644473721165407872121570229256 × 10306 |
| 1024 | 8.98846567431157953864652595394512366809 × 10307 |
| 1025 | NaN |
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Nichols, E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Adsuar, J.C.; Ansha, M.G.; Brayne, C.; Choi, J.-Y.J.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Eeden, S.K. Incidence of Parkinson’s Disease: Variation by Age, Gender, and Race/Ethnicity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reekes, T.H.; Higginson, C.I.; Ledbetter, C.R.; Sathivadivel, N.; Zweig, R.M.; Disbrow, E.A. Sex specific cognitive differences in Parkinson disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damier, P.; Hirsch, E.C.; Agid, Y.; Graybiel, A.M. The substantia nigra of the human brain: I. Nigrosomes and the nigral matrix, a compartmental organization based on calbindin D28K immunohistochemistry. Brain 1999, 122, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Postuma, R.B.; Bloem, B.; Chan, P.; Dubois, B.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.G.; Halliday, G.M.; Hardy, J.; Lang, A.E.; et al. Time to redefine PD? Introductory statement of the MDS Task Force on the definition of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.; Wang, T.; Guggenberger, R.; Milosevic, L.; Gharabaghi, A. FiNN: A toolbox for neurophysiological network analysis. Netw. Neurosci. 2022, 6, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Shang, H. Grey matter abnormalities in Parkinson’s disease: A voxel-wise meta-analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, T.; Saini, J.; Gupta, C.N. Subgrouping and structural brain connectivity of Parkinson’s disease—Past studies and future directions. Neurosci. Inform. 2022, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDeligianni, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Thirion, B.; Sharp, D.J.; Ledig, C.; Leech, R.; Rueckert, D. A Framework for Inter-Subject Prediction of Functional Connectivity from Structural Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 2200–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, D.L.; Bianconi, G.; Bullmore, E.; Burgess, M.; Chung, S.; Eliassi-Rad, T.; George, D.; Kovács, I.A.; Makse, H.; Nichols, T.E.; et al. Neuroscience needs Network Science. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, T.; Saini, J.; Gupta, C.N. Sparsity Dependent Metrics Depict Alteration of Brain Network Connectivity in Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.B.; Aarsland, D.; Ginestet, C.E.; Lebedev, A.V.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Simmons, A.; Volpe, G.; Westman, E. Aberrant cerebral network topology and mild cognitive impairment in early Parkinson’s disease: Aberrant Brain Network Topology in Early PD. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 2980–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Classification of autism spectrum disorder by combining brain connectivity and deep neural network classifier. Neurocomputing 2019, 324, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettel, J.M.; Cooper, N.; Garcia, J.O.; Yeh, F.; Verstynen, T.D. White Matter Tractography and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. In eLS, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.-C.; Vettel, J.M.; Singh, A.; Poczos, B.; Grafton, S.T.; Erickson, K.I.; Tseng, W.-Y.I.; Verstynen, T.D. Quantifying Differences and Similarities in Whole-Brain White Matter Architecture Using Local Connectome Fingerprints. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Guan, X.; Guo, T.; Zeng, Q.; Ye, R.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Xuan, M.; Gu, Q.; Huang, P.; et al. Brain Atrophy and Reorganization of Structural Network in Parkinson’s Disease with Hemiparkinsonism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Cortes, J.M.; Kang, X.; Cao, J.; Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, R.; Kong, L.; Huang, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. Individual-based morphological brain network organization and its association with autistic symptoms in young children with autism spectrum disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weininger, D.; Weininger, A.; Weininger, J.L. SMILES. 2. Algorithm for generation of unique SMILES notation. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1989, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovits, I. A Compact Form of the Adjacency Matrix. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 40, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasinen, V.; Joutsa, J.; Noponen, T.; Johansson, J.; Seppänen, M. Effects of aging and gender on striatal and extrastriatal [123I]FP-CIT binding in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, T.J.; Kanaan, N.M.; Kordower, J.H. Ageing as a primary risk factor for Parkinson’s disease: Evidence from studies of non-human primates. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk-Krolikowski, K.; Tomlinson, P.; Nithi, K.; Wade-Martins, R.; Talbot, K.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Hu, M.T. The influence of age and gender on motor and non-motor features of early Parkinson’s disease: Initial findings from the Oxford Parkinson Disease Center (OPDC) discovery cohort. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G. The Relationship of Parkinson Disease with Aging. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; Naduthota, R.M.; Bharath, R.D.; Jhunjhunwala, K.; Yadav, R.; Saini, J.; Christopher, R. Imaging biomarker correlates with oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. India 2017, 65, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, G.; More, S.; Raimondo, F.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Hoffstaedter, F.; Patil, K.R. A systematic comparison of VBM pipelines and their application to age prediction. BioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattuck, D.W.; Mirza, M.; Adisetiyo, V.; Hojatkashani, C.; Salamon, G.; Narr, K.L.; Poldrack, R.A.; Bilder, R.M.; Toga, A.W. Construction of a 3D Probabilistic Atlas of Human Cortical Structures. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A Network Visualization Tool for Human Brain Connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madole, J.W.; Buchanan, C.R.; Rhemtulla, M.; Ritchie, S.J.; Bastin, M.E.; Deary, I.J.; Cox, S.R.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Strong intercorrelations among global graph-theoretic indices of structural connectivity in the human brain. NeuroImage 2023, 275, 120160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, C.R.; Bastin, M.E.; Ritchie, S.J.; Liewald, D.C.; Madole, J.W.; Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Deary, I.J.; Cox, S.R. The effect of network thresholding and weighting on structural brain networks in the UK Biobank. NeuroImage 2020, 211, 116443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E. On the use of correlation as a measure of network connectivity. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Diaz, G.; Melie-García, L.; Iturria-Medina, Y.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Hernández-González, G.; Valdés-Urrutia, L.; Galán, L.; Valdés-Sosa, P. Surface area and cortical thickness descriptors reveal different attributes of the structural human brain networks. NeuroImage 2010, 50, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, A.-S.; Xie, L.-Z.; Qian, L.; Yang, X.-G. Large-scale cortical volume correlation networks reveal disrupted small world patterns in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 662, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farwell, L.A. Brain fingerprinting: A comprehensive tutorial review of detection of concealed information with event-related brain potentials. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2012, 6, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermens, D.F.; Russo, C.; Shan, Z.; Lagopoulos, J. Brain fingerprinting: A promising future application for predicting mental illness. Futures 2023, 152, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, T.D.; Xia, C.H.; Bassett, D.S. Personalized Neuroscience: Common and Individual-Specific Features in Functional Brain Networks. Neuron 2018, 98, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; McKeown, M.J.; Chen, X.; Wu, F. Connectivity-based Brain Parcellation for Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 70, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farras-Permanyer, L.; Mancho-Fora, N.; Montalà-Flaquer, M.; Bartrés-Faz, D.; Vaqué-Alcázar, L.; Peró-Cebollero, M.; Guàrdia-Olmos, J. Age-related changes in resting-state functional connectivity in older adults. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Kathiresan, N.; Mohan, S.; Vasileiou, G.; Singh, A.; Kaura, D.; Melhem, E.R.; Gupta, R.K.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; et al. Gender-based analysis of cortical thickness and structural connectivity in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, B. Aberrant Brain Network Efficiency in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Tremor: A Multi-Modality Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.-K.; Wu, C.; Yang, A. Age-Related Alterations in Electroencephalography Connectivity and Network Topology During n-Back Working Memory Task. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Llonch, R.; Junqué, C.; Arenaza-Urquijo, E.M.; Vidal-Piñeiro, D.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Palacios, E.M.; Domènech, S.; Salvà, A.; Bargalló, N.; Bartrés-Faz, D. Changes in whole-brain functional networks and memory performance in aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samogin, J.; Delgado, L.R.; Taberna, G.A.; Swinnen, S.P.; Mantini, D. Age-Related Differences of Frequency-Dependent Functional Connectivity in Brain Networks and Their Link to Motor Performance. Brain Connect. 2022, 12, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindle, J.V. Ageing, neurodegeneration and Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, B.; Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Age and sex differentially shape brain networks in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1907–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Eftekhari, S.-M.; Jamali-Raeufy, N.; Haghani, S.; Zeinali, H.; Roghani, M. The anti-aging protein klotho alleviates injury of nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway in 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of PKA/CaMKII/CREB signaling. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 100, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Lim, H.-S.; Kawasaki, I.; Shim, Y.-H.; Vaikath, N.N.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Anti-aging treatments slow propagation of synucleinopathy by restoring lysosomal function. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1849–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Su, Y.; Xu, B.; Chhetri, J.K.; Chan, P. Age as a risk factor for orthostatic hypotension induced by the levodopa challenge test in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Results from a single-center trial. Medicine 2023, 102, e33161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlskog, J.E. Seniors with Parkinson’s Disease: Initial Medical Treatment. J. Clin. Neurol. 2010, 6, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filippi, M.; Basaia, S.; Sarasso, E.; Stojkovic, T.; Stankovic, I.; Fontana, A.; Tomic, A.; Piramide, N.; Stefanova, E.; Markovic, V.; et al. Longitudinal brain connectivity changes and clinical evolution in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 26, 5429–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, H.; Kumarnsit, E.; Chatpun, S. Age-Related Alterations in EEG Network Connectivity in Healthy Aging. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


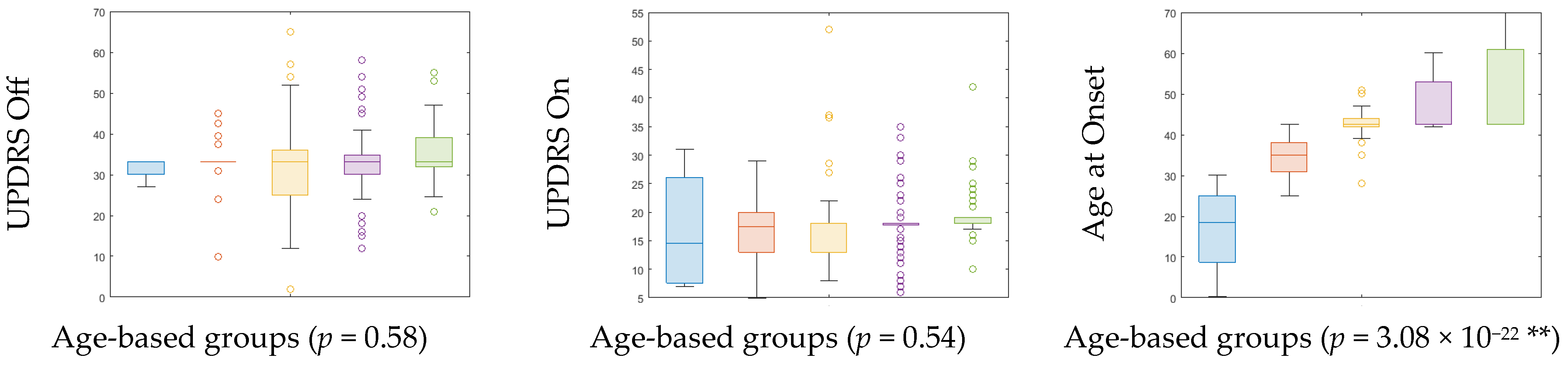


| Age-Cohort (Age Range) | Count | Gender (Male:Female) | UPDRS off (Mean ± SD) | UPDRS on (Mean ± SD) | H&Y (Median) | Age at Onset (Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | HC | PD | HC | |||||
| A (≤32) | 4 | 5 | 3:1 | 5:0 | 31.69 ± 2.71 | 16.75 ± 9.91 | 2 | 16.83 ± 10.67 |
| B (33–42) | 18 | 14 | 11:7 | 7:7 | 32.94 ± 7.13 | 16.67 ± 6.16 | 2 | 35.19 ± 4.69 |
| C (43–52) | 42 | 23 | 28:14 | 19:4 | 32.33 ± 11.11 | 17.78 ± 8.15 | 2 | 42.83 ± 4.29 |
| D (53–62) | 69 | 22 | 56:13 | 16:6 | 32.79 ± 8.76 | 17.70 ± 5.37 | 2 | 47.47 ± 6.26 |
| E (≥63) | 46 | 6 | 36:10 | 5:1 | 35.17 ± 6.97 | 19.30 ± 4.78 | 2 | 51.54 ± 9.88 |
| p-value | 0.58 | 0.54 | 3.08 × 10−22 ** | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samantaray, T.; Gupta, U.; Saini, J.; Gupta, C.N. Unique Brain Network Identification Number for Parkinson’s and Healthy Individuals Using Structural MRI. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091297
Samantaray T, Gupta U, Saini J, Gupta CN. Unique Brain Network Identification Number for Parkinson’s and Healthy Individuals Using Structural MRI. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(9):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091297
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamantaray, Tanmayee, Utsav Gupta, Jitender Saini, and Cota Navin Gupta. 2023. "Unique Brain Network Identification Number for Parkinson’s and Healthy Individuals Using Structural MRI" Brain Sciences 13, no. 9: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091297
APA StyleSamantaray, T., Gupta, U., Saini, J., & Gupta, C. N. (2023). Unique Brain Network Identification Number for Parkinson’s and Healthy Individuals Using Structural MRI. Brain Sciences, 13(9), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13091297