Premorbid Psychological Factors Associated with Long-Term Postoperative Headache after Microsurgery in Vestibular Schwannoma—A Retrospective Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic, Disease and Surgery Related Variables
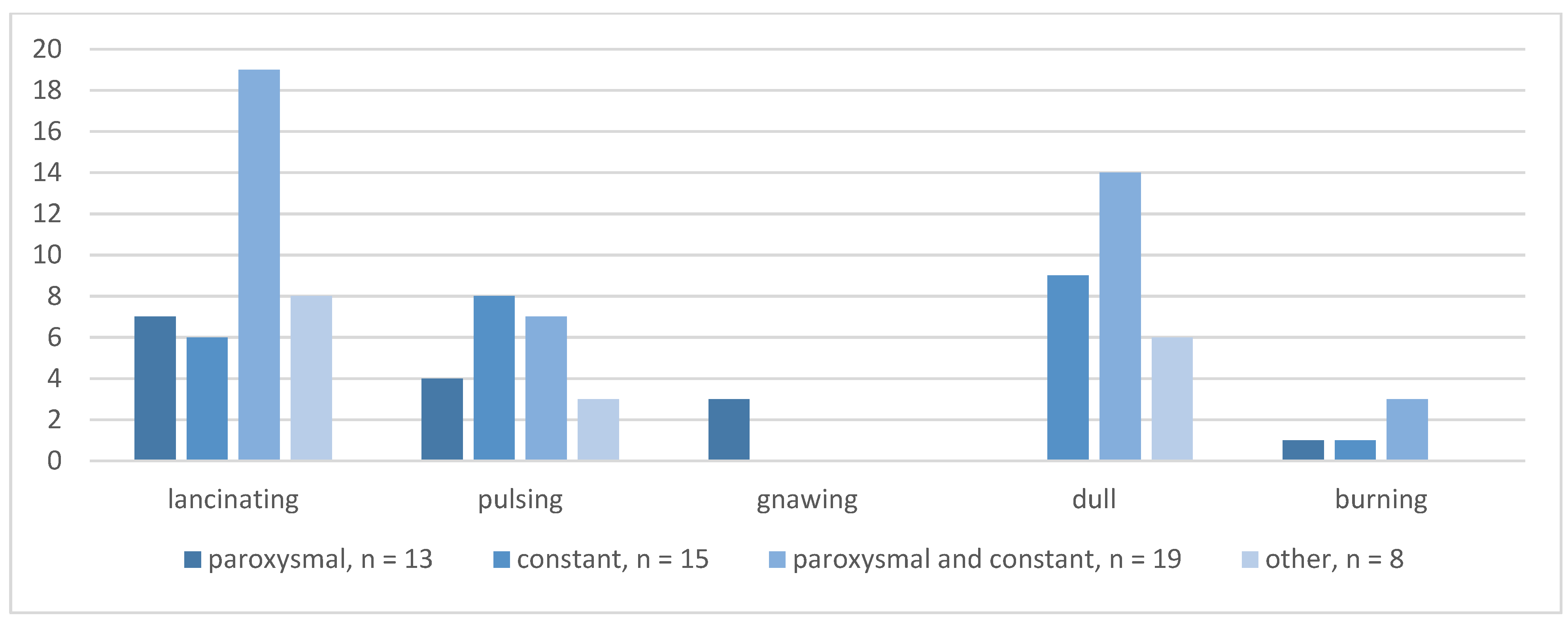
3.2. POH Characteristics
3.3. Premorbid Pain Syndromes and Premorbid Psychological Variables
3.4. Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, J.H.; Patel, N.S.; Lohse, C.M.; Tombers, N.M.; Link, M.J.; Carlson, M.L. Impact of Treatment on Vestibular Schwannoma-Symptoms: A Prospective Study Comparing Treatment Modalities. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2021, 165, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Haynes, D.S. Surgical approaches and complications in the removal of vestibular schwannomas. Otolaryngol. Clin. North. Am. 2007, 40, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samii, M.; Matthies, C. Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): The facial nerve--preservation and restitution of function. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.F.; Terry, C.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. Surgery for vestibular schwannomas: A systematic review of complications by approach. Neurosurg. Focus. 2012, 33, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, Y.; Hatayama, T.; Matsuda, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Endo, K.; Akutsu, H. Epidemiology of post-suboccipital craniotomy headache: A multicentre retrospective study. J. Perioper. Pract. 2022, 33, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levo, H.; Pyykko, I.; Blomstedt, G. Postoperative headache after surgery for vestibular schwannoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosek, A.C.; Dodick, D.W.; Ebersold, M.J.; Swanson, J.W. Headache after resection of acoustic neuroma. Headache 1999, 39, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimaaja, T.; Haanpaa, M.; Blomstedt, G.; Farkkila, M. Headaches after acoustic neuroma surgery. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, B.; Baumann, A. Headache after removal of vestibular schwannoma via the retrosigmoid approach: A long-term follow-up-study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 128, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schessel, D.A.; Nedzelski, J.M.; Rowed, D.; Feghali, J.G. Pain after surgery for acoustic neuroma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1992, 107, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.J.; Jacobowitz, O.; Post, K.D. Prevention of headache after retrosigmoid removal of acoustic tumors. Am. J. Otol. 1996, 17, 904–908. [Google Scholar]
- Ducic, I.; Felder, J.M., 3rd; Endara, M. Postoperative headache following acoustic neuroma resection: Occipital nerve injuries are associated with a treatable occipital neuralgia. Headache 2012, 52, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; Ji, K.; Ren, J.; Zhong, P. Functional outcome and complications after the microsurgical removal of giant vestibular schwannomas via the retrosigmoid approach: A retrospective review of 16-year experience in a single hospital. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazen, J.J.; Sisti, M.; Lam, S.M. Cranioplasty in acoustic neuroma surgery. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, C.A.; Ahern, D.K.; McKenna, M.J.; Ojemann, R.G.; Acquadro, M.A. Determinants and impact of headache after acoustic neuroma surgery. Am. J. Otol. 1994, 15, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, M.K.; Eljamel, M.S. Role of craniotomy repair in reducing postoperative headaches after a retrosigmoid approach. Neurosurgery 2010, 67, 1286–1291; discussion 91-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, N. Postoperative headache in acoustic neuroma. Headache 1995, 35, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.D.; Samy, R.N.; Nahata, A.; Zuccarello, M.; Pensak, M.L.; Golub, J.S. Reduction of bone dust with ultrasonic bone aspiration: Implications for retrosigmoid vestibular schwannoma removal. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koperer, H.; Deinsberger, W.; Jodicke, A.; Boker, D.K. Postoperative headache after the lateral suboccipital approach: Craniotomy versus craniectomy. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1999, 42, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, C.; Gokten, M.; Sezer, A.; Gezgin, İ.; Binboga, A.B.; Onay, M. Role of Craniectomy Versus Craniotomy via the Retrosigmoid Approach in Decreasing the Incidence of Postoperative Headache. Int. Surg. 2021, 106, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, M.J.; Harris, J.P.; Cueva, R.A.; Prioleau, G.; Alksne, J. Pain subsequent to resection of acoustic neuromas via suboccipital and translabyrinthine approaches. Am. J. Otol. 1996, 17, 620–624. [Google Scholar]
- Brooker, J.E.; Fletcher, J.M.; Dally, M.J.; Briggs, R.J.; Cousins, V.C.; Malham, G.M.; Smee, R.I.; Kennedy, R.J.; Burney, S. Factors associated with anxiety and depression in the management of acoustic neuroma patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farace, E.; Marshall, L.F. Quality of life in acoustics. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 807–808; discussion 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayam, B.; Young, R.C.; Tsuboyama, G.K. Mood disorders associated with acoustic neuromas. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 1994, 24, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ran, G.; Chen, K.; Shen, X. Preoperative Psychological Burdens in Patients with Vestibular Schwannoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2022, 131, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen, E.S.; Aaseth, K.; Grande, R.B.; Lundqvist, C.; Russell, M.B. Psychological distress, neuroticism and disability associated with secondary chronic headache in the general population—The Akershus study of chronic headache. J. Headache Pain. 2018, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Baum, A.; Holzhausen, M.; Grittner, U.; Hilgendorf, I.; Martus, P.; Altiber, A.; Evers, S.; Rolfs, A.; Kropp, P.; et al. The Rostock Headache Questionnaire (“Rokoko”)—Validation of a tool to screen and to qualify primary headaches. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2014, 82, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Koos, W.T.; Day, J.D.; Matula, C.; Levy, D.I. Neurotopographic considerations in the microsurgical treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, A.; Geyer, M.; Schumacher, J.; Brähler, E. Somatoform complaints in the German population. Z. Psychosom. Med. Psychother. 2002, 48, 38–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, A.; Brahler, E. Normative values for the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in the general German population. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 71, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, P.M.; Hell, B.; Gosling, S.D. Construct validation of a short five-factor model instrument: A self-peer study on the German adaptation of the Ten-Item Personality Inventory (TIPI-G). Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2007, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, A.; Dumkrieger, G.; Berisha, V.; Ross, K.; Chong, C.D.; Schwedt, T.J. Headache Characteristics and Psychological Factors Associated with Functional Impairment in Individuals with Persistent Posttraumatic Headache. Pain. Med. 2021, 22, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; L. Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988; Volume xxi, p. 567. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, M.L.; Tveiten, O.V.; Driscoll, C.L.; Boes, C.J.; Sullan, M.J.; Goplen, F.K.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Link, M.J. Risk factors and analysis of long-term headache in sporadic vestibular schwannoma: A multicenter cross-sectional study. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampl, C.; Thomas, H.; Tassorelli, C.; Katsarava, Z.; Lainez, J.M.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Rastenyte, D.; Ruiz de la Torre, E.; Stovner, L.J.; Steiner, T.J.; et al. Headache, depression and anxiety: Associations in the Eurolight project. J. Headache Pain. 2016, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylha, P.; Isometsa, E. The relationship of neuroticism and extraversion to symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general population. Depress. Anxiety 2006, 23, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Sánchez, C.M.; Montoro Aguilar, C.I. Migraine and Neuroticism: A Scoping Review. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meints, S.M.; Edwards, R.R. Evaluating psychosocial contributions to chronic pain outcomes. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 87 Pt B, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, L.J.; Phillips, C.; Mindell, J.A. Clinical psychology training in sleep and sleep disorders. J. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 65, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.L. Conducting Online Surveys. J. Hum. Lact. 2019, 35, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathersul, D.C.; Ruscio, A.M. Forecasting the future, remembering the past: Misrepresentations of daily emotional experience in generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2020, 44, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, M.A.; Muzzatti, B.; Bidoli, E.; Flaiban, C.; Bomben, F.; Piccinin, M.; Gipponi, K.M.; Mariutti, G.; Busato, S.; Mella, S.; et al. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) accuracy in cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 3921–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Central Tendency | p-Score POH vs. Non POH | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| POH, n = 54 | Non POH, n = 47 | ||
| male sex at birth, no. (%) | 15 (27.8) | 23 (48.9) | 0.029 |
| age at survey, mean (SD) | 54.5 (12.2) | 58.5 (11.8) | 0.039 |
| age at onset, mean (SD) | 46.3 (10.2) | 49.0 (11.7) | 0.074 |
| time since surgery in months, mean (SD) | 121.6 (109.3) | 139.7 (95.6) | 0.096 |
| Koos, no. (%) | 0.222 | ||
| 1 | 8 (14.8) | 5 (10.6) | |
| 2 | 14 (25.9) | 10 (21.3) | |
| 3 | 20 (37.0) | 14 (29.8) | |
| 4 | 9 (16.7) | 13 (27.7) | |
| missing | 2 (3.7) | 5 (10.6) | |
| facial nerve paresis, no. (%) | 12 (22.2) | 15 (31.9) | 0.267 |
| missing | 1 (1.9) | 1 (2.1) | |
| hearing loss after surgery, no. (%) | 27 (50.0) | 28 (59.6) | 0.335 |
| craniectomy, no. (%) | 23 (42.6) | 30 (63.8) | 0.095 |
| missing | 10 (18.5) | 4 (8.5) | |
| positioning during surgery, no. (%) | 0.654 | ||
| semi-sitting | 37 (68.5) | 34 (72.3) | |
| supine | 8 (17.0) | 8 (17.0) | |
| missing | 5 (10.6) | 5 (10.6) | |
| Variable * | Group | p-Score POH vs. Non POH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| premorbid pain syndromes | POH, n = 24 (44.4%) | Non POH, n = 6 (12.8%) | <0.001 |
| chronic back pain | 11 | 2 | - |
| headache | 17 | 2 | - |
| face pain | 2 | 0 | - |
| knee pain | 1 | 0 | - |
| stomach and bowel problems | 4 | 1 | - |
| premorbid mental ailments | POH, n = 25 (46.3%) | Non POH, n = 8 (17.0%) | <0.001 |
| difficulty falling asleep/ problems sleeping through the night | 20 | 4 | - |
| physical exhaustion | 3 | 2 | - |
| panic attacks | 3 | 1 | - |
| rumination | 3 | 0 | - |
| psychosomatic stomach pain | 0 | 1 | - |
| suicide attempt | 1 | 0 | - |
| premorbid psychological diagnosis | POH, n = 15 (27.8%) | Non POH, n = 7 (14.9%) | 0.106 |
| Major Depression | 11 | 2 | - |
| Burnout | 2 | 2 | - |
| acute stress disorder | 3 | 0 | - |
| anxiety disorder | 1 | 1 | - |
| posttraumatic stress disorder | 0 | 2 | - |
| premorbid headache syndromes | POH, n = 21 (38.9%) | Non POH, n = 10 (21.3%) | 0.048 |
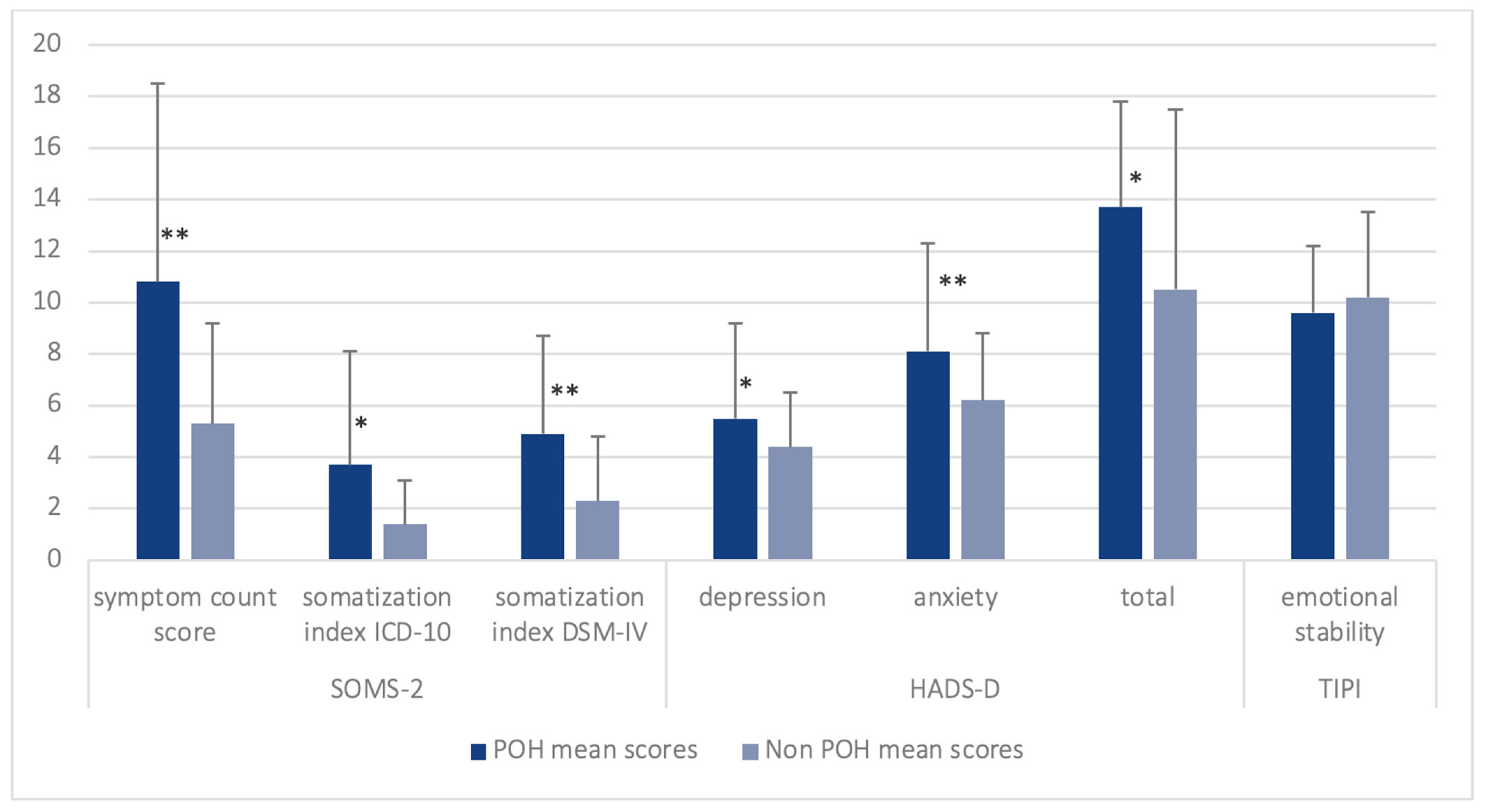
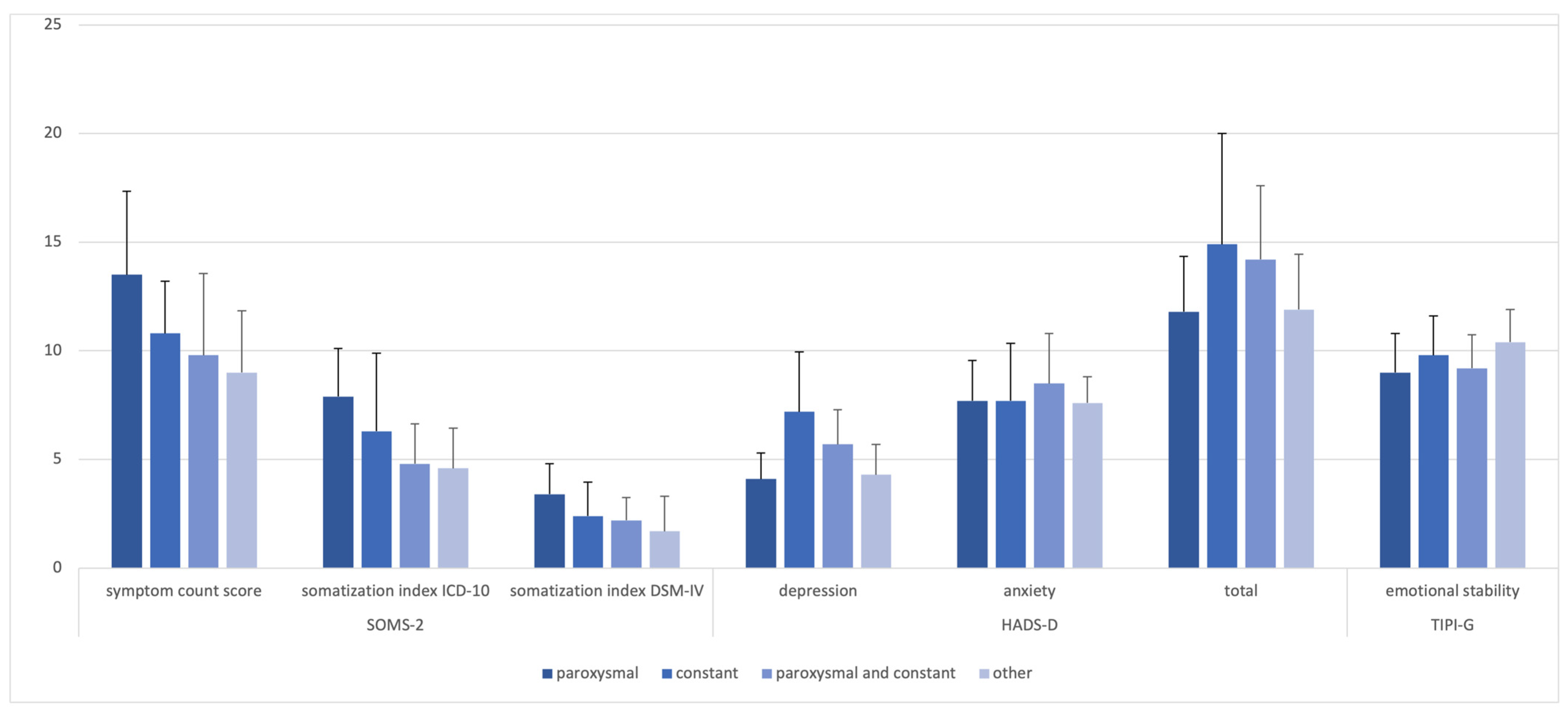
| Central Tendency | p Value POH vs. Non POH | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| POH, n = 54 | Non POH, n = 47 | ||
| SOMS-2 | |||
| symptom count score, mean (SD) | 10.9 (8.0) | 5.6 (3.8) | <0.001 |
| somatization Index ICD-10, mean (SD) | 2.5 (2.5) | 1.3 (1.3) | 0.016 |
| somatization Index DSM-IV, mean (SD) | 5.9 (4.8) | 2.9 (2.5) | 0.001 |
| HADS-D | |||
| depression, mean (SD) | 5.6 (3.9) | 3.9 (2.2) | 0.034 |
| anxiety, mean (SD) | 7.9 (4.3) | 5.8 (2.7) | 0.014 |
| total score, mean (SD) | 13.5 (7.3) | 9.8 (4.2) | 0.008 |
| TIPI-G | |||
| emotional stability, mean (SD) | 9.6 (3.3) | 10.3 (2.5) | 0.383 |
| Model 1: Demographics and Procedural Characteristics | Model 2: Psychological Measures | Model 3: Stepwise Regression | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.93 (1.90) | −1.89 (1.46) | −1.58 (1.20) |
| sex at birth | 0.95 (0.53) | - | - |
| age at onset | −0.04 (0.03) | −0.51 (0.03) * | |
| tumor size (Koos) | −0.20 (0.27) | - | - |
| positioning during surgery | 0.03 (0.73) | - | - |
| time since treatment (months) | −0.003 (0.003) | - | - |
| preexisting headache | 0.45 (0.40) | - | |
| premorbid mental ailments | - | 1.16 (0.68) | 1.85 (0.69) * |
| premorbid chronic pain syndromes | - | 1.45 (0.67) * | 1.55 (0.68) * |
| symptom count score † | - | 0.48 (0.41) | - |
| emotional stability | - | 0.41 (0.10) | - |
| HADS-D Depression | HADS-D Anxiety | HADS-D Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 14.80 (3.50) | 13.01 (3.00) | 27.89 (2.50) |
| sex at birth | −2.26 (1.12) * | - | - |
| age at onset | - | - | - |
| time since sugery (months) | - | - | - |
| premorbid mental ailments | - | - | - |
| premorbid chronic pain syndromes | - | - | - |
| symptom count score † | - | 1.29 (0.60) * | - |
| emotional stability | −0.54 (0.15) ** | −0.80 (0.15) ** | −1.48 (0.25) ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, M.; Rampp, S.; Scheer, M.; Strauss, C.; Prell, J.; Schönfeld, R.; Leplow, B. Premorbid Psychological Factors Associated with Long-Term Postoperative Headache after Microsurgery in Vestibular Schwannoma—A Retrospective Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081171
Thomas M, Rampp S, Scheer M, Strauss C, Prell J, Schönfeld R, Leplow B. Premorbid Psychological Factors Associated with Long-Term Postoperative Headache after Microsurgery in Vestibular Schwannoma—A Retrospective Pilot Study. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(8):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081171
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Mareike, Stefan Rampp, Maximilian Scheer, Christian Strauss, Julian Prell, Robby Schönfeld, and Bernd Leplow. 2023. "Premorbid Psychological Factors Associated with Long-Term Postoperative Headache after Microsurgery in Vestibular Schwannoma—A Retrospective Pilot Study" Brain Sciences 13, no. 8: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081171
APA StyleThomas, M., Rampp, S., Scheer, M., Strauss, C., Prell, J., Schönfeld, R., & Leplow, B. (2023). Premorbid Psychological Factors Associated with Long-Term Postoperative Headache after Microsurgery in Vestibular Schwannoma—A Retrospective Pilot Study. Brain Sciences, 13(8), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081171







