Refractory Hypotension in a Late-Onset Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS) Male with m.3243 A>G Mutation: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
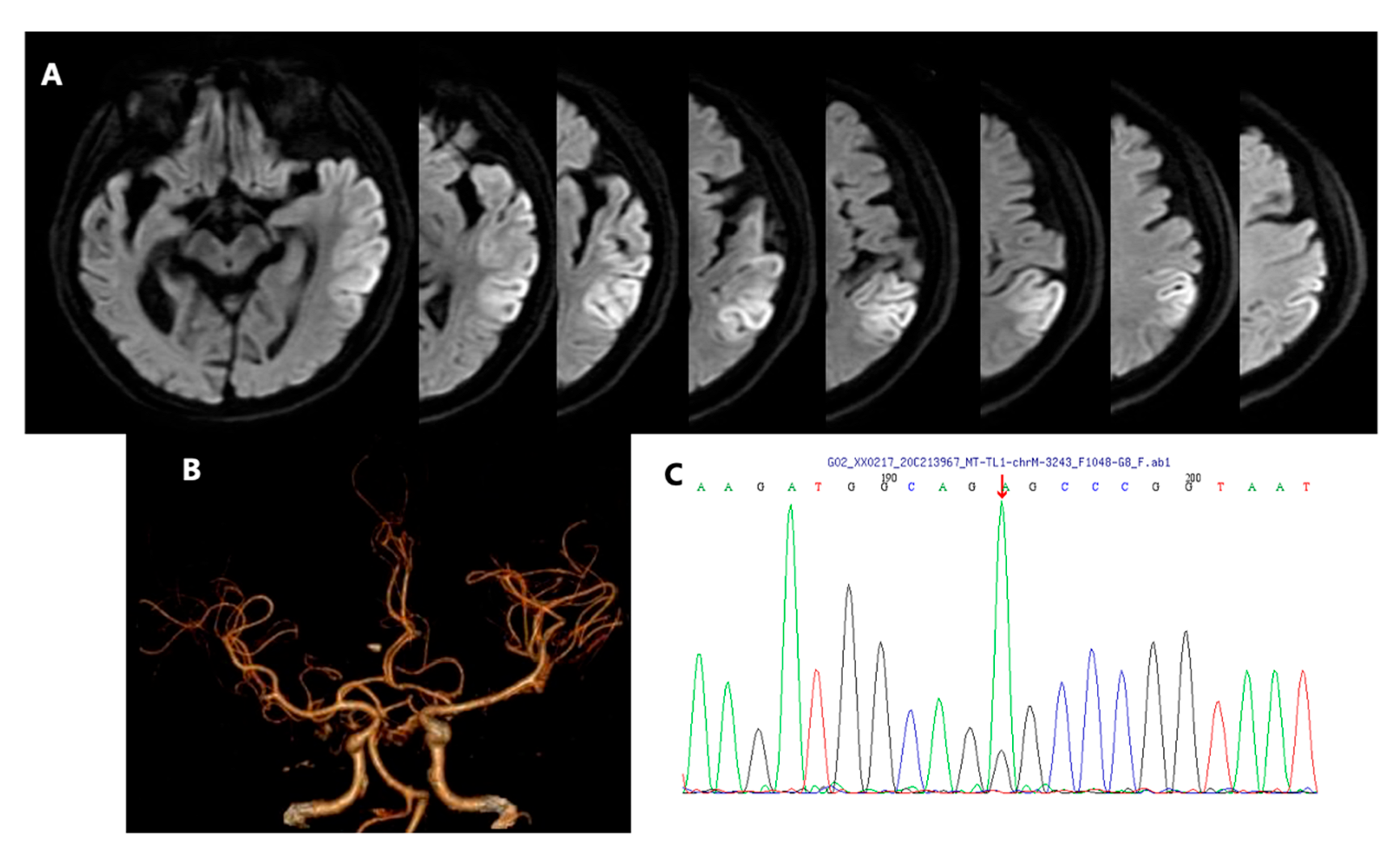
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fan, H.C.; Lee, H.F.; Yue, C.T.; Chi, C.S. Clinical Characteristics of Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-Like Episodes. Life 2021, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Horai, S.; Matsuoka, T.; Koga, Y.; Nihei, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Nonaka, I. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS): A correlative study of the clinical features and mitochondrial DNA mutation. Neurology 1992, 42, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, M.; Iizuka, T.; Nakahara, J.; Izawa, Y. Neuroimaging pattern and pathophysiology of cerebellar stroke-like lesions in MELAS with m.3243A>G mutation: A case report. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, J.P.; Pickett, S.J.; Ng, Y.S.; Alston, C.L.; Blakely, E.L.; Hardy, S.A.; Feeney, C.L.; Bright, A.A.; Schaefer, A.M.; Gorman, G.S.; et al. mtDNA heteroplasmy level and copy number indicate disease burden in m.3243A>G mitochondrial disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, N.Z.; Gorman, G.S.; Turnbull, D.M. Review: Central nervous system involvement in mitochondrial disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2017, 43, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, N.; Wilson, L.; Mann, S.; Sirrs, S.; Benavente, O. Clinical Reasoning: A complicated case of MELAS. Neurology 2016, 87, e189–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, G.S.; Schaefer, A.M.; Ng, Y.; Gomez, N.; Blakely, E.L.; Alston, C.L.; Feeney, C.; Horvath, R.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Chinnery, P.F.; et al. Prevalence of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA mutations related to adult mitochondrial disease. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, M.; Orsucci, D.; Angelini, C.; Bertini, E.; Carelli, V.; Comi, G.P.; Donati, A.; Minetti, C.; Moggio, M.; Mongini, T.; et al. The m.3243A>G mitochondrial DNA mutation and related phenotypes. A matter of gender? J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärppä, M.; Syrjälä, P.; Tolonen, U.; Majamaa, K. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with the 3243A>G mutation in mitochondrial DNA. J. Neurol. 2003, 250, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Zarrouk-Mahjoub, S. Mitochondrial vasculopathy. World J. Cardiol. 2016, 8, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Sakai, F.; Ide, T.; Miyakawa, S.; Sato, M.; Yoshii, S. Regional cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular reactivity during chronic stage of stroke-like episodes in MELAS—Implication of neurovascular cellular mechanism. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 257, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, P.; Pascual, J.M.; Anziska, Y.; Gooch, C.L.; Engelstad, K.; Jhung, S.; DiMauro, S.; De Vivo, D.C. Nerve conduction abnormalities in patients with MELAS and the A3243G mutation. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, G.; Opfer-Gehrking, T.; Offord, K.; Atkinson, E.; O’Brien, P.; Low, P. The Autonomic Symptom Profile: A new instrument to assess autonomic symptoms. Neurology 1999, 52, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.; Weimer, L.; Engelstad, K.; Linker, A.; Battista, V.; Wei, Y.; Hirano, M.; Dimauro, S.; De Vivo, D.C.; Kaufmann, P. Autonomic symptoms in carriers of the m.3243A>G mitochondrial DNA mutation. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelnik, N.; Axelrod, F.B.; Leshinsky, E.; Griebel, M.L.; Kolodny, E.H. Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathies Presenting with Features of Autonomic and Visceral Dysfunction. Pediatr. Neurol. 1996, 14, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, A. Fluid Resuscitation for Refractory Hypotension. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 621696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuka, S.; Ogawa, T.; Hashimoto, R.; Kato, H. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and management of stroke-like episodes due to MELAS. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2021, 36, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMauro, S.; Hirano, M. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathies: An update. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2005, 15, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Povalko, N.; Nishioka, J.; Katayama, K.; Kakimoto, N.; Matsuishi, T. MELAS and L-arginine therapy: Pathophysiology of stroke-like episodes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1201, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlakis, S.G.; Phillips, P.C.; DiMauro, S.; De Vivo, D.C.; Rowland, L.P. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: A distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1984, 16, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.K.; Emrick, L.; Karaa, A.; Korson, M.; Scaglia, F.; Parikh, S.; Goldstein, A. Recommendations for the Management of Strokelike Episodes in Patients with Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Strokelike Episodes. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Pavlakis, S.G. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes (MELAS): Current concepts. J. Child Neurol. 1994, 9, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoquart-Elsankari, S.; Lehmann, P.; Périn, B.; Gondry-Jouet, C.; Godefroy, O. MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging followup of a stroke-like event in a patient with MELAS. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1593–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohama, E.; Ohara, S.; Ikuta, F.; Tanaka, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Miyatake, T. Mitochondrial angiopathy in cerebral blood vessels of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Acta. Neuropathol. 1987, 74, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, M.; Yamamura, Y.; Kurihara, T.; Fukuhara, N.; Tsuruta, K.; Matsukura, S.; Hayashi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Kuriyama, M. An autopsy case of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy: Biochemical and electron microscopic studies of the brain. J. Neurol. Sci. 1988, 86, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Sakai, F.; Suzuki, N.; Hata, T.; Tsukahara, S.; Fukuda, M.; Takiyama, Y. Neuronal hyperexcitability in stroke-like episodes of MELAS syndrome. Neurology 2002, 59, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, N.Z.; Pienaar, I.S.; Reeve, A.K.; Hepplewhite, P.D.; Jaros, E.; Taylor, R.W.; Kalaria, R.N.; Turnbull, D.M. Microangiopathy in the cerebellum of patients with mitochondrial DNA disease. Brain 2012, 135, 1736–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramegna, L.L.; Cortesi, I.; Mitolo, M.; Evangelisti, S.; Talozzi, L.; Cirillo, L.; Tonon, C.; Lodi, R. Major cerebral vessels involvement in patients with MELAS syndrome: Worth a scan? A systematic review. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 48, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.S.; Lax, N.Z.; Blain, A.P.; Erskine, D.; Baker, M.R.; Polvikoski, T.; Thomas, R.H.; Morris, C.M.; Lai, M.; Whittaker, R.G.; et al. Forecasting stroke-like episodes and outcomes in mitochondrial disease. Brain 2022, 145, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hattab, A.W.; Adesina, A.M.; Jones, J.; Scaglia, F. MELAS syndrome: Clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and treatment options. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015, 116, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, P.; Engelstad, K.; Wei, Y.; Kulikova, R.; Oskoui, M.; Battista, V.; Koenigsberger, D.Y.; Pascual, J.M.; Sano, M.; Hirano, M.; et al. Protean phenotypic features of the A3243G mitochondrial DNA mutation. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.-X.; Shang, B.; Chen, W.-Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Adult-onset of mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) syndrome with hypothyroidism and psychiatric disorders. eNeurologicalSci 2017, 6, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, H.; Szczepanczyk, K.; Mirza, F.S. Late-Onset Melas with Midd: An Uncommon Age of Presentation. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2018, 4, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, A.D.; Sandhu, V.; Young, D.; Nevay, D.L.; Yeung, D.F.; Sirrs, S.; Tsang, M.Y.; Tsang, T.S.M.; Lehman, A.; Mezei, M.M.; et al. High rate of hypertension in patients with m.3243A>G MELAS mutations and POLG variants. Mitochondrion 2020, 53, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong-Nguyen, C.; Stalens, C.; Goursot, Y.; Bougouin, W.; Stojkovic, T.; Behin, A.; Mochel, F.; Berber, N.; Eymard, B.; Duboc, D.; et al. A high prevalence of arterial hypertension in patients with mitochondrial diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Sirrs, S.; Mezei, M.M.; Waters, P.J.; Mattman, A. Increased Prevalence of Hypertension in Young Adults with High Heteroplasmy Levels of the MELAS m.3243A>G Mutation. JIMD Rep. 2014, 12, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naini, A.; Kaufmann, P.; Shanske, S.; Engelstad, K.; De Vivo, D.C.; Schon, E.A. Hypocitrullinemia in patients with MELAS: An insight into the “MELAS paradox”. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 229–230, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majamaa-Voltti, K.; Majamaa, K.; Peuhkurinen, K.; Mäkikallio, T.H.; Huikuri, H.V. Cardiovascular autonomic regulation in patients with 3243A > G mitochondrial DNA mutation. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, M.; Duerr, S.; Granata, R.; Krismer, F.; Robertson, D.; Wenning, G.K. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: Pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.S.; Feeney, C.; Schaefer, A.M.; Holmes, C.E.; Hynd, P.; Alston, C.L.; Grady, J.P.; Roberts, M.; Maguire, M.; Bright, A.; et al. Pseudo-obstruction, stroke, and mitochondrial dysfunction: A lethal combination. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S.; Holmes, C.; Sharabi, Y.; Brentzel, S.; Eisenhofer, G. Plasma levels of catechols and metanephrines in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Neurology 2003, 60, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, M.; Povalko, N.; Koga, Y. Arginine therapy in mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, D.; Kruger, M.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Grimm, D. The Effects of Oral l-Arginine and l-Citrulline Supplementation on Blood Pressure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Akita, Y.; Nishioka, J.; Yatsuga, S.; Povalko, N.; Katayama, K.; Matsuishi, T. MELAS and L-arginine therapy. Mitochondrion 2007, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Akita, Y.; Nishioka, J.; Yatsuga, S.; Povalko, N.; Tanabe, Y.; Fujimoto, S.; Matsuishi, T. L-arginine improves the symptoms of strokelike episodes in MELAS. Neurology 2005, 64, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanetti, R.J.; Ng, Y.S.; Errington, L.; Blain, A.P.; McFarland, R.; Gorman, G.S. l-Arginine in Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes: A Systematic Review. Neurology 2022, 98, e2318–e2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duschek, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Reyes Del Paso, G.A.; Ettinger, U. Autonomic Cardiovascular Control and Executive Function in Chronic Hypotension. Ann. Behav. Med. 2017, 51, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Via, L.; Sanfilippo, F.; Continella, C.; Triolo, T.; Messina, A.; Robba, C.; Astuto, M.; Hernandez, G.; Noto, A. Agreement between Capillary Refill Time measured at Finger and Earlobe sites in different positions: A pilot prospective study on healthy volunteers. BMC Anesth. 2023, 23, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, J.; Maconochie, I. Capillary refill time in adults. Emerg. Med. J. 2008, 25, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.; Kelly, A.M.; Kerr, D.; Clooney, M.; Jolley, D. Impact of patient and environmental factors on capillary refill time in adults. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, E.; Ye, C.; Wu, B. Refractory Hypotension in a Late-Onset Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS) Male with m.3243 A>G Mutation: A Case Report. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071080
Wang Y, Zhang E, Ye C, Wu B. Refractory Hypotension in a Late-Onset Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS) Male with m.3243 A>G Mutation: A Case Report. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071080
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Youjie, Enhui Zhang, Chen Ye, and Bo Wu. 2023. "Refractory Hypotension in a Late-Onset Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS) Male with m.3243 A>G Mutation: A Case Report" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071080
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, E., Ye, C., & Wu, B. (2023). Refractory Hypotension in a Late-Onset Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes (MELAS) Male with m.3243 A>G Mutation: A Case Report. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071080







