Standardizing an Experimental Murine Model of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis That Immunologically Resembles Human Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Taenia crassiceps Cysts and Inoculation
2.3. HP10 Ag-ELISA Assay
2.4. Antibody Detection
2.5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.6. Histological and Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.7. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Isolation
2.8. Proliferation Assay
2.9. C-Reactive Protein Measurement (CRP)
2.10. Behavioral Tests
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
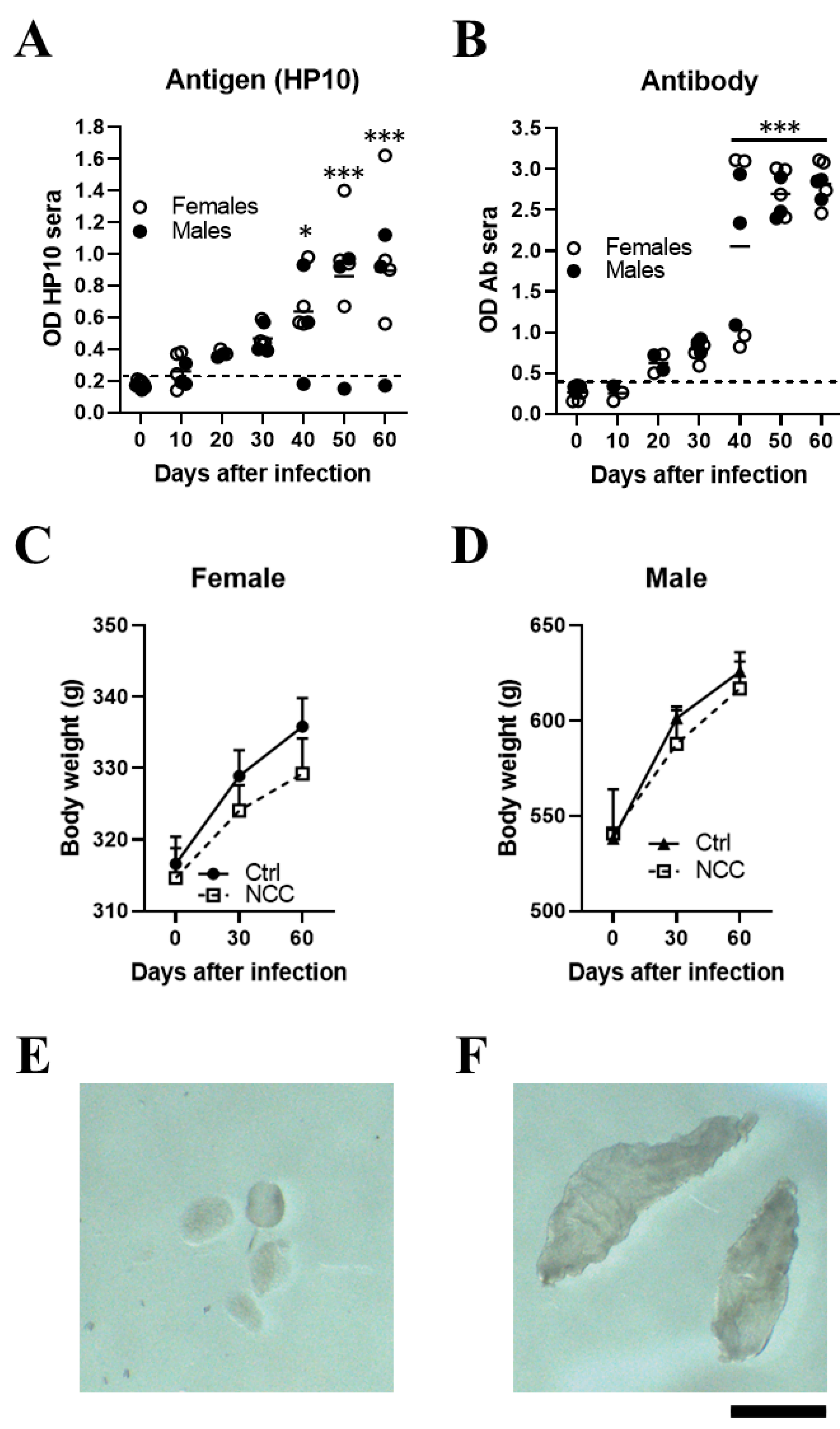
3.1. Establishment of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis and Follow-Up by HP10 Detection
3.2. Detecting Extraparenchymal Cysticerci by MRI
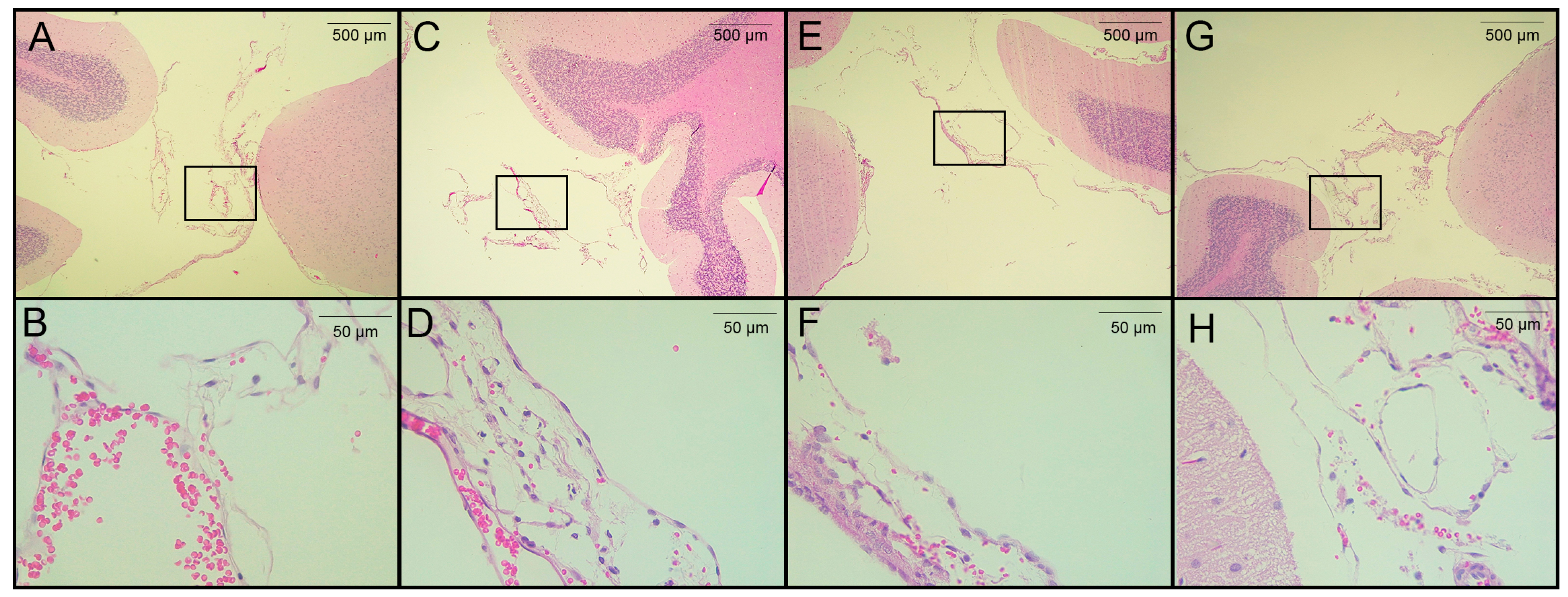
3.3. Histological Analysis
3.4. EXP-NCC Is Accompanied by Astrocyte activation Only in Female Rats
3.5. Depressed Proliferative Response in EXP-NCC
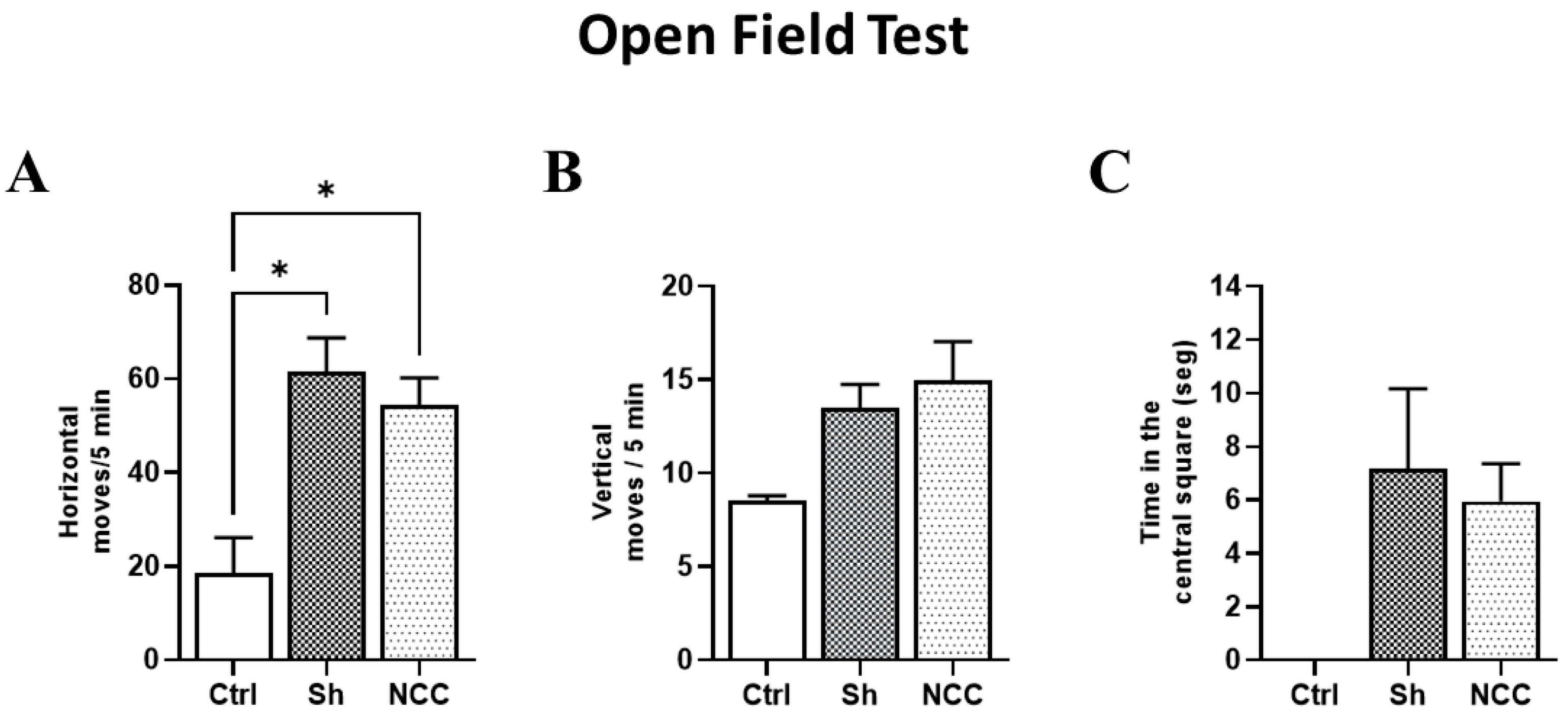
3.6. Behavior Assessment in Infected Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Rivas, R.; Flisser, A.; Norcia, L.F.; Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Carpio, A.; Romo, M.L.; Fleury, A. Neurocysticercosis in Latin America: Current epidemiological situation based on official statistics from four countries. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2022, 16, e0010652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Fleury, A.; Laclette, J.P.; Sotelo, J.; Aluja, A.; Vargas, L.; Larralde, C. Taenia solium disease in humans and pigs: An ancient parasitosis disease rooted in developing countries and emerging as a major health problem of global dimensions. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1875–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015. 2015. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/199350 (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Sierra, M.M.; Arroyo, M.; Cadena, M.; Ramírez, N.; García, F.; Taboada, D.; Galicia, A.; Govezensky, T.; Sciutto, E.; Toledo, A.; et al. Extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis: Demographic, clinicoradiological, and inflammatory features. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2017, 11, e0005646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, A.; Gomez, T.; Alvarez, I.; Meza, D.; Huerta, M.; Chavarria, A.; Carrillo Mezo, R.A.; Lloyd, C.; Dessein, A.; Preux, P.M.; et al. High prevalence of calcified silent neurocysticercosis in a rural village of Mexico. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, A.; Morales, J.; Bobes, R.J.; Dumas, M.; Yánez, O.; Piña, J.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Martínez, J.J.; Fragoso, G.; Dessein, A.; et al. An epidemiological study of familial neurocysticercosis in an endemic Mexican community. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.A.; Wiebe, S.; Zunt, J.R.; Halperin, J.J.; Gronseth, G.; Roos, K.L. Evidence-based guideline: Treatment of parenchymal neurocysticercosis: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2013, 80, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.H.; Del Brutto, O.H.; Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. Antiparasitic treatment of neurocysticercosis—The effect of cyst destruction in seizure evolution. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 76, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzle, D.; Makasi, C.; Schmidt, V.; Trevisan, C.; Van Damme, I.; Ruether, C.; Dorny, P.; Magnussen, P.; Zulu, G.; Mwape, K.E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of antiparasitic therapy for neurocysticercosis in rural Tanzania: A prospective cohort study. Infection 2023, 24, 1–13, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Sander, J.W. Historical perspective: The British contribution to the understanding of neurocysticercosis. J. Hist. Neurosci. 2019, 28, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrieta, I.; Flores, X.; Osorio, R.; Kuschick Feher, J.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Fleury, A. Natural history of extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, C.; Garcia, H.H. Current Diagnostic Criteria for Neurocysticercosis. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2021, 12, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria, A.; Fleury, A.; Bobes, R.J.; Morales, J.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto, E. A depressed peripheral cellular immune response is related to symptomatic neurocysticercosis. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, M.T.; Pretell, E.J.; Bustos, J.A.; Caballero, M.; Alfaro, M.; Kane, R.; Wilken, J.; Sullivan, C.; Fratto, T.; Garcia, H.H. Cognitive Changes and Quality of Life in Neurocysticercosis: A Longitudinal Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto, E.; Fleury, A. Inflammation in neurocysticercosis: Clinical relevance and impact on treatment decisions. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, R.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Romo, M.L.; Toledo, A.; Matus, C.; González-Hernández, I.; Jung, H.; Fleury, A. Factors Associated With Cysticidal Treatment Response in Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 59, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T.E.; O’Connell, E.M.; Hammoud, D.A.; Wetzler, L.; Ware, J.M.; Mahanty, S. Natural History of Treated Subarachnoid Neurocysticercosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, A.; Osorio, R.; Matus, C.; Martinez Lopez, Y.; Ramirez Cruz, N.; Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Arauz, A.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Fleury, A. Human Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: The Control of Inflammation Favors the Host…but Also the Parasite. Front. Immunol. 2018, 16, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, G.; Fragoso, G.; Rosetti, M.; Uribe-Figueroa, L.; Rangel-Escareño, C.; Saenz, B.; Hernández, M.; Sciutto, E.; Fleury, A. Neurocysticercosis: The effectiveness of the cysticidal treatment could be influenced by the host immunity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 203, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, G.; Gevorkian, G.; Florentino, A.; Bautista, M.A.; Espinosa, A.; Acero, G.; Díaz, G.; Fleury, A.; Pérez Osorio, I.N.; Del Rey, A.; et al. Intranasal delivery of dexamethasone efficiently controls LPS-induced murine neuroinflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 190, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.H.; Verastegui, M.R.; Arroyo, G.; Bustos, J.A.; Gilman, R.H.; Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. New animal models of neurocysticercosis can help understand epileptogenesis in neuroinfection. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1039083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sota, K.A.; Bustos, J.A.; Verastegui, M.R.; Toribio, L.; Chile, N.; Angulo, N.; Cangalaya, C.; Calcina, J.; González, A.E.; Gilman, R.H.; et al. Experimental brain infection with cysticercosis in sheep. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2022, 39, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, A.; Trejo, A.; Cisneros, H.; García-Navarrete, R.; Villalobos, N.; Hernández, M.; Villeda Hernández, J.; Hernández, B.; Rosas, G.; Bobes, R.J.; et al. Taenia solium: Development of an Experimental Model of Porcine Neurocysticercosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Zanini, M.A.; Botta, F.P.; Rodrigues, M.V.; Bazan, R.; Vulcano, L.C.; Biondi, G.F. Development of an experimental model of neurocysticercosis-induced hydrocephalus. Pilot study. Acta Cir. Bras. 2015, 30, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH. National Institutes of Health. Training Resources | OACU [Internet]. 2022. 2022. Available online: https://oacu.oir.nih.gov/training-resources (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Harrison, L.J.; Joshua, G.W.; Wright, S.H.; Parkhouse, R.M. Specific detection of circulating surface/secreted glycoproteins of viable cysticerci in Taenia saginata cysticercosis. Parasite Immunol. 1989, 11, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciutto, E.; Martínez, J.J.; Villalobos, N.M.; Hernández, M.; José, M.V.; Beltrán, C.; Rodarte, F.; Flores, I.; Bobadilla, J.R.; Fragoso, G.; et al. Limitations of current diagnostic procedures for the diagnosis of Taenia solium cysticercosis in rural pigs. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 79, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fogaroli, M.O.; Oliveira, M.A.C.; Oliveira, C.C.; Batah, S.S.; Fabro, A.T.; Vulcano, L.C.; Bazan, R.; Zanini, M.A. A Rat Model of Neurocysticercosis-Induced Hydrocephalus: Chronic Progressive Hydrocephalus with Mild Clinical Impairment. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeidi, A.; Zandi, K.; Cheok, Y.Y.; Saeidi, H.; Wong, W.F.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Yong, Y.K.; Larsson, M.; Shankar, E.M. T-cell exhaustion in chronic infections: Reversing the state of exhaustion and reinvigorating optimal protective immune responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Laforge, M.; Ouaissi, A.; Akharid, K.; Silvestre, R.; Estaquier, J. Impairment of T Cell Function in Parasitic Infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Madeira, J.C.; Trindade, G.B.; Almeida, P.H.P.; Silva, J.S.; Carregaro, V. T Lymphocyte Exhaustion During Human and Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olopade, F.E.; Shokunbi, M.T.; Sirén, A.L. The relationship between ventricular dilatation, neuropathological and neurobehavioural changes in hydrocephalic rats. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos-Silva, H.; Reciputti, B.P.; Paula, E.C.; Oliveira, A.L.; Moura, V.B.; Vinaud, M.C.; Oliveira, M.A.; Lino-Júnior, R.d.S. Experimental encephalitis caused by Taenia crassiceps cysticerci in mice. Arq. de Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2012, 70, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.I.; Mishra, B.B.; Gundra, U.M.; Mishra, P.K.; Teale, J.M. Mesocestoides corti intracranial infection as a murine model for neurocysticercosis. Parasitology 2010, 137, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verastegui, M.R.; Mejia, A.; Clark, T.; Gavidia, M.C.; Mamani, J.; Ccopa, F.; Angulo, N.; Chile, N.; Carmen, R.; Medina, R.; et al. Novel rat model for neurocysticercosis using Taenia solium. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2259–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; García, H.H. Taenia solium Cysticercosis--The lessons of history. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 359, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalid-Peralta, L.; Fleury, A.; García-Ibarra, T.M.; Hernández, M.; Parkhouse, M.; Crispín, J.C.; Voltaire-Proaño, J.; Cárdenas, G.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto., E. Human neurocysticercosis: In vivo expansion of peripheral regulatory T cells and their recruitment in the central nervous system. J. Parasitol. 2012, 98, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce-Sillas, A.; Álvarez-Luquín, D.D.; Cárdenas, G.; Casanova-Hernández, D.; Fragoso, G.; Hernández, M.; Proaño-Narváez, J.V.; García-Vázquez, F.; Fleury, A.; Sciutto, E.; et al. Interleukin 10 and dendritic cells are the main suppression mediators of regulatory T cells in human neurocysticercosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 183, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Baca, M.; De la Cruz, V.; Lemus, L.; Lamoyi, E. Depressed T-cell proliferation associated with susceptibility to experimental Taenia crassiceps infection. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Lara-García, J.; Arroyo, M.; Fleury, A. Relevance of 3D magnetic resonance imaging sequences in diagnosing basal subarachnoid neurocysticercosis. Acta Trop. 2015, 152, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, O.E.; Omobowale, T.O.; Abatan, M.O. Neurocognitive domains and neuropathological changes in experimental infection with Trypanosoma brucei brucei in Wistar rats. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, R.J.; Roth, K.A.; Carroll, B.J. Acute and chronic stress effects on open field activity in the rat: Implications for a model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1981, 5, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa-Cerón, A.; Méndez, A.; Hernández-Aceves, J.; Juárez-González, J.C.; Villalobos, N.; Hernández, M.; Díaz, G.; Soto, P.; Concha, L.; Pérez-Osorio, I.N.; et al. Standardizing an Experimental Murine Model of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis That Immunologically Resembles Human Infection. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071021
Espinosa-Cerón A, Méndez A, Hernández-Aceves J, Juárez-González JC, Villalobos N, Hernández M, Díaz G, Soto P, Concha L, Pérez-Osorio IN, et al. Standardizing an Experimental Murine Model of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis That Immunologically Resembles Human Infection. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(7):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071021
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa-Cerón, Alejandro, Alejandro Méndez, Juan Hernández-Aceves, Juan C. Juárez-González, Nelly Villalobos, Marisela Hernández, Georgina Díaz, Paola Soto, Luis Concha, Iván N. Pérez-Osorio, and et al. 2023. "Standardizing an Experimental Murine Model of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis That Immunologically Resembles Human Infection" Brain Sciences 13, no. 7: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071021
APA StyleEspinosa-Cerón, A., Méndez, A., Hernández-Aceves, J., Juárez-González, J. C., Villalobos, N., Hernández, M., Díaz, G., Soto, P., Concha, L., Pérez-Osorio, I. N., Ortiz-Retana, J. J., Bobes, R. J., Parkhouse, R. M., Hamamoto Filho, P. T., Fragoso, G., & Sciutto, E. (2023). Standardizing an Experimental Murine Model of Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis That Immunologically Resembles Human Infection. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13071021






