Deficient Audiovisual Speech Perception in Schizophrenia: An ERP Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli and Paradigm
2.3. EEG Acquisition and Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
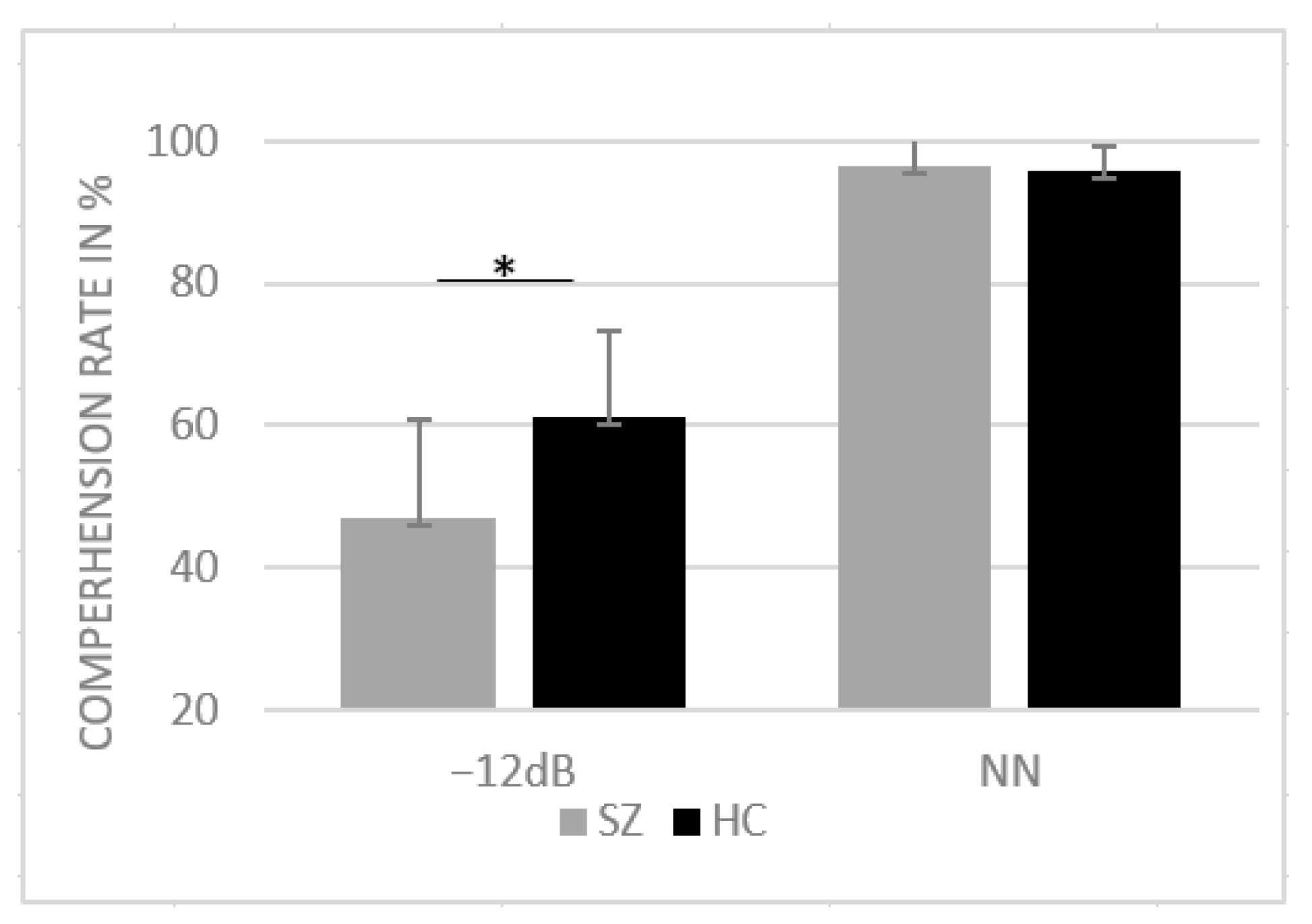
3.1. Behavioral Results
3.2. Electrophysiological Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breier, A.; Schreiber, J.L.; Dyer, J.; Pickar, D. National Institute of Mental Health longitudinal study of chronic schizophrenia: Prognosis and predictors of outcome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1991, 48, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, W.S.; McGlashan, T.H. Natural history of schizophrenia subtypes: II. Positive and negative symptoms and long-term course. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1991, 48, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekelenburg, J.J.; Vroomen, J. Neural correlates of multisensory integration of ecologically valid audiovisual events. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, E.M.; Hofer, A.; Golaszewski, S.; Siedentopf, C.; Brinkhoff, C.; Kremser, C.; Felber, S.; Fleischhacker, W.W. Brain activation patterns during a verbal fluency test—A functional MRI study in healthy volunteers and patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2004, 70, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artiges, E.; Martinot, J.; Verdys, M.; Attar-Levy, D.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio, N.; Giraud, M.; Paillère-Martinot, M. Altered hemispheric functional dominance during word generation in negative schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2000, 26, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razafimandimby, A.; Maïza, O.; Hervé, P.; Lecardeur, L.; Delamillieure, P.; Brazo, P.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Dollfus, S. Stability of functional language lateralization over time in schizophrenia patients. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 94, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurk, H.; MacDonald, J. Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature 1976, 264, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Amour, D.; De Sanctis, P.; Molholm, S.; Ritter, W.; Foxe, J.J. Seeing voices: High-density electrical mapping and source-analysis of the multisensory mismatch negativity evoked during the McGurk illusion. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, L.A.; Saint-Amour, D.; Leavitt, V.M.; Javitt, D.C.; Foxe, J.J. Do you see what I am saying? Exploring visual enhancement of speech comprehension in noisy environments. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, K.W.; Seitz, P. The use of visible speech cues for improving auditory detection of spoken sentences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumby, W.H.; Pollack, I. Visual contribution to speech intelligibility in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1954, 26, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Neural synchrony in brain disorders: Relevance for cognitive dysfunctions and pathophysiology. Neuron 2006, 52, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.E.; Baldeweg, T.; Friston, K.J. Synaptic plasticity and dysconnection in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.E.; Light, G.A.; Braff, D.L.; Ramachandran, V.S. Reduced multisensory integration in patients with schizophrenia on a target detection task. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 3128–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröhn, C.; Norgren, E.; Eriksson, L. A systematic review of the neural correlates of multisensory integration in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2022, 27, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.B.; Urrea, L.J.; Aine, C.J.; Bustillo, J.R.; Clark, V.P.; Stephen, J.M. Unisensory processing and multisensory integration in schizophrenia: A high-density electrical mapping study. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 3178–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, J.R.; Lacambre, M.; Pham, B.; Giersch, A.; Elliott, M.A. Low time resolution in schizophrenia: Lengthened windows of simultaneity for visual, auditory and bimodal stimuli. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 97, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.; Giersch, A.; Huron, C.; van Wassenhove, V. Temporal event structure and timing in schizophrenia: Preserved binding in a longer “now”. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Cai, X.; Weigl, M.; Bang, P.; Cheung, E.F.; Chan, R.C. Multisensory temporal binding window in autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 86, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balz, J.; Roa Romero, Y.; Keil, J.; Krebber, M.; Niedeggen, M.; Gallinat, J.; Senkowski, D. Beta/gamma oscillations and event-related potentials indicate aberrant multisensory processing in schizophrenia. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gelder, B.; Vroomen, J.; Annen, L.; Masthof, E.; Hodiamont, P. Audio-visual integration in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2003, 59, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, D.; Yodashkin-Porat, D.; Katz, N.; Valevski, A.; Aizenberg, D.; Sigler, M.; Weizman, A.; Kikinzon, L. Differences in audiovisual integration, as measured by McGurk phenomenon, among adult and adolescent patients with schizophrenia and age-matched healthy control groups. Compr. Psychiatry 2009, 50, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.P.; Wigton, R.L.; Joyce, D.W.; Bobin, T.; Ferragamo, C.; Wasim, N.; Lisk, S.; Shergill, S.S. Eluding the illusion? Schizophrenia, dopamine and the McGurk effect. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa Romero, Y.; Keil, J.; Balz, J.; Niedeggen, M.; Gallinat, J.; Senkowski, D. Alpha-band oscillations reflect altered multisensory processing of the McGurk illusion in schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, B.; Green, A.; Sass, K.; Kirner-Veselinovic, A.; Kircher, T. Neural integration of speech and gesture in schizophrenia: Evidence for differential processing of metaphoric gestures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 1696–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, A.; He, Y.; Straube, B. Dynamic Causal Modelling suggests impaired effective connectivity in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders during gesture-speech integration. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 216, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szycik, G.R.; Ye, Z.; Mohammadi, B.; Dillo, W.; Te Wildt, B.T.; Samii, A.; Frieling, H.; Bleich, S.; Münte, T.F. Maladaptive connectivity of Broca’s area in schizophrenia during audiovisual speech perception: An fMRI study. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szycik, G.R.; Münte, T.F.; Dillo, W.; Mohammadi, B.; Samii, A.; Emrich, H.M.; Dietrich, D.E. Audiovisual integration of speech is disturbed in schizophrenia: An fMRI study. Schizophr. Res. 2009, 110, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wassenhove, V.; Grant, K.W.; Poeppel, D. Visual speech speeds up the neural processing of auditory speech. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besle, J.; Fischer, C.; Bidet-Caulet, A.; Lecaignard, F.; Bertrand, O.; Giard, M. Visual activation and audiovisual interactions in the auditory cortex during speech perception: Intracranial recordings in humans. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14301–14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besle, J.; Fort, A.; Delpuech, C.; Giard, M. Bimodal speech: Early suppressive visual effects in human auditory cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baart, M.; Stekelenburg, J.J.; Vroomen, J. Electrophysiological evidence for speech-specific audiovisual integration. Neuropsychologia 2014, 53, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunellière, A.; Sánchez-García, C.; Ikumi, N.; Soto-Faraco, S. Visual information constrains early and late stages of spoken-word recognition in sentence context. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekelenburg, J.J.; Maes, J.P.; Van Gool, A.R.; Sitskoorn, M.; Vroomen, J. Deficient multisensory integration in schizophrenia: An event-related potential study. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 147, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkowski, D.; Moran, J.K. Early evoked brain activity underlies auditory and audiovisual speech recognition deficits in schizophrenia. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 33, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th Ed text revision); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrl, S.; Merz, J.; Burkhard, G.; Fischer, S. Mehrfachwahl-Wortschatz-Intelligenztest; MWT-B; Straube: Erlangen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, L.A.; Saint-Amour, D.; Leavitt, V.M.; Molholm, S.; Javitt, D.C.; Foxe, J.J. Impaired multisensory processing in schizophrenia: Deficits in the visual enhancement of speech comprehension under noisy environmental conditions. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 97, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgolte, A.; Roy, M.; Sinke, C.; Wiswede, D.; Stephan, M.; Bleich, S.; Münte, T.F.; Szycik, G.R. Enhanced attentional processing during speech perception in adult high-functioning autism spectrum disorder: An ERP-study. Neuropsychologia 2021, 161, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinke, C.; Neufeld, J.; Wiswede, D.; Emrich, H.M.; Bleich, S.; Münte, T.F.; Szycik, G.R. N1 enhancement in synesthesia during visual and audio–visual perception in semantic cross-modal conflict situations: An ERP study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baayen, R.H.; Piepenbrock, R.; Gulikers, L. The CELEX Lexical Database (CD-ROM); Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lin, Y.; Gao, X.; Dang, J. Correlation between audio–visual enhancement of speech in different noise environments and SNR: A combined behavioral and electrophysiological study. Neuroscience 2013, 247, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groppe, D.M.; Urbach, T.P.; Kutas, M. Mass univariate analysis of event-related brain potentials/fields I: A critical tutorial review. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, J.N.; Brederoo, S.G.; Voppel, A.E.; Sommer, I.E. Anomalies in language as a biomarker for schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2020, 33, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, P.D.; Schechter, I.; Zemon, V.; Schwartz, S.G.; Greenstein, V.C.; Gordon, J.; Schroeder, C.E.; Javitt, D.C. Dysfunction of early-stage visual processing in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogata, T.; Iidaka, T. A review of impaired visual processing and the daily visual world in patients with schizophrenia. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dondé, C.; Kantrowitz, J.T.; Medalia, A.; Saperstein, A.M.; Balla, A.; Sehatpour, P.; Martinez, A.; O’Connell, M.N.; Javitt, D.C. Early auditory processing dysfunction in schizophrenia: Mechanisms and implications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 148, 105098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, R.E.; Rapaport, J.; Mazure, C.M.; Quinlan, D.M. Selective speech perception alterations in schizophrenic patients reporting hallucinated “voices”. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlack, K.; Lee, G.; Sakuma, M.; Xie, S.; Kusnner, M.; Pepple, J.; Finer, D.L.; Hoff, A.L.; DeLisi, L.E. Language processing and memory in ill and well siblings from multiplex families affected with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 1997, 25, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cao, S.; Zhou, F.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Li, L. Masking of speech in people with first-episode schizophrenia and people with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 134, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Yang, J.; Kim, Y.; Suh, K. Abnormal speech perception in schizophrenia with auditory hallucinations. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2004, 16, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLisi, L.E.; Sakuma, M.; Kushner, M.; Finer, D.L.; Hoff, A.L.; Crow, T.J. Anomalous cerebral asymmetry and language processing in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1997, 23, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.F.; Collins, K.C.; McCarley, R.W. Reductions in the N1 and P2 auditory event-related potentials in first-hospitalized and chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2010, 36, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leicht, G.; Kirsch, V.; Giegling, I.; Karch, S.; Hantschk, I.; Möller, H.; Pogarell, O.; Hegerl, U.; Rujescu, D.; Mulert, C. Reduced early auditory evoked gamma-band response in patients with schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsma, D.; Senkowski, D.; Soto-Faraco, S.; Woldorff, M.G. The multifaceted interplay between attention and multisensory integration. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talsma, D.; Woldorff, M.G. Selective attention and multisensory integration: Multiple phases of effects on the evoked brain activity. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 1098–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hink, R.F.; Hillyard, S.A.; Benson, P.J. Event-related brain potentials and selective attention to acoustic and phonetic cues. Biol. Psychol. 1978, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näätänen, R.; Picton, T. The N1 wave of the human electric and magnetic response to sound: A review and an analysis of the component structure. Psychophysiology 1987, 24, 375–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchsbaum, M.S. Frontal lobes, basal ganglia, temporal lobes—Three sites for schizophrenia? Schizophr. Bull. 1990, 16, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, D.R.; Berman, K.F.; Illowsky, B.P. Physiological dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: III. A new cohort and evidence for a monoaminergic mechanism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1988, 45, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saykin, A.J.; Shtasel, D.L.; Gur, R.E.; Kester, D.B.; Mozley, L.H.; Stafiniak, P.; Gur, R.C. Neuropsychological deficits in neuroleptic naive patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1994, 51, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, P.J. Memory, knowledge and delusions. Br. J. Psychiatry 1991, 159, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, M.; Inui, K.; Motomura, E.; Otsuru, N.; Ushida, T.; Kakigi, R. Auditory N1 as a change-related automatic response. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 71, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowland, V.C.; Mercure, E.; Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Dick, F.; Thomas, M.S. Audio-visual speech perception: A developmental ERP investigation. Dev. Sci. 2014, 17, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baart, M.; Samuel, A.G. Early processing of auditory lexical predictions revealed by ERPs. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 585, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxe, J.J.; Yeap, S.; Snyder, A.C.; Kelly, S.P.; Thakore, J.H.; Molholm, S. The N1 auditory evoked potential component as an endophenotype for schizophrenia: High-density electrical mapping in clinically unaffected first-degree relatives, first-episode, and chronic schizophrenia patients. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 261, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.F.; Kohler, J.; Shenton, M.E.; McCarley, R.W. Deficit effect sizes and correlations of auditory event-related potentials at first hospitalization in the schizophrenia spectrum. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2020, 51, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, W.T.; Goodale, J.; Pfefferbaum, A. Auditory event-related potentials and electrodermal activity in medicated and unmedicated schizophrenics. Biol. Psychiatry 1991, 29, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, G.; Adler, J.; Schneck, M.; Armbruster, B. Influence of stimulation parameters on auditory stimulus processing in schizophrenia and major depression: An auditory evoked potential study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1990, 81, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchsbaum, M.S. The middle evoked response components and schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1977, 3, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, C.; Nageishi, Y.; Matsubayashi, M.; Omura, F.; Kishimoto, A.; Shimokochi, M. Abnormalities in event-related potentials, N100, P200, P300 and slow wave in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1991, 45, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Ford, J.M.; White, P.M.; Roth, W.T. P3 in schizophrenia is affected by stimulus modality, response requirements, medication status, and negative symptoms. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1989, 46, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahveninen, J.; Jääskeläinen, I.P.; Osipova, D.; Huttunen, M.O.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Kaprio, J.; Lönnqvist, J.; Manninen, M.; Pakarinen, S.; Therman, S.; et al. Inherited auditory-cortical dysfunction in twin pairs discordant for schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Force, R.B.; Venables, N.C.; Sponheim, S.R. An auditory processing abnormality specific to liability for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 103, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassim, F.M.; Lahooti, S.K.; Keay, E.A.; Iyyalol, R.; Rodger, J.; Albrecht, M.A.; Martin-Iverson, M.T. Dexamphetamine widens temporal and spatial binding windows in healthy participants. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023, 48, E90–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SZs (N = 20) | HCs (N = 21) | Significance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | M | SD | M | SD | |
| N (female, male) | 20 (8, 12) | 21 (9, 12) | X2(1) = 0.34, p = 0.85 | ||
| Age in years | 41.9 | 13.8 | 38.2 | 13.0 | t(39) = −0.85, p = 0.95 |
| Years of education | 10.7 (N = 19) | 1.7 | 12.4 (N = 18) | 1.2 | t(35) = 3.61, p = 0.08 |
| MWT-B | 98.6 (N = 15) | 5.3 | 106.6 (N = 19) | 4.7 | t(32) = 4.6, p < 0.001 |
| PANSS (total) | 49.5 (N = 18) | 10.0 | |||
| Positive | 11.5 (N = 18) | 3.9 | |||
| Negative | 12.2 (N = 18) | 4.8 | |||
| Illness years | 13.9 (N = 17) | 10.2 |
| SZs (N = 14) | HCs (N = 19) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NN | −12 dB | NN | −12 dB | |
| Amplitude | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) | M (SD) |
| N1 | −1.54 (1.46) | −1.29 (1.41) | −2.66 (1.46) | −1.86 (1.26) |
| P2 | 2.45 (2.0) | 2.09 (1.51) | 1.92 (2.0) | 1.62 (1.51) |
| N1-P2 | 3.99 (1.96) | 3.34 (1.82) | 4.58 (1.96) | 3.47 (1.83) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaneirad, E.; Saenger, E.; Szycik, G.R.; Čuš, A.; Möde, L.; Sinke, C.; Wiswede, D.; Bleich, S.; Borgolte, A. Deficient Audiovisual Speech Perception in Schizophrenia: An ERP Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060970
Ghaneirad E, Saenger E, Szycik GR, Čuš A, Möde L, Sinke C, Wiswede D, Bleich S, Borgolte A. Deficient Audiovisual Speech Perception in Schizophrenia: An ERP Study. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(6):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060970
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaneirad, Erfan, Ellyn Saenger, Gregor R. Szycik, Anja Čuš, Laura Möde, Christopher Sinke, Daniel Wiswede, Stefan Bleich, and Anna Borgolte. 2023. "Deficient Audiovisual Speech Perception in Schizophrenia: An ERP Study" Brain Sciences 13, no. 6: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060970
APA StyleGhaneirad, E., Saenger, E., Szycik, G. R., Čuš, A., Möde, L., Sinke, C., Wiswede, D., Bleich, S., & Borgolte, A. (2023). Deficient Audiovisual Speech Perception in Schizophrenia: An ERP Study. Brain Sciences, 13(6), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060970





