Heterogenous Genetic, Clinical, and Imaging Features in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Carrying NOTCH2NLC Repeat Expansion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Repeat-Primed and Amplicon-Length PCR Analyses
2.3. Long-Read Sequencing
2.4. Clinical Assessments
2.5. Laboratory Tests
2.6. MRI Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Findings
3.2. Clinical Findings
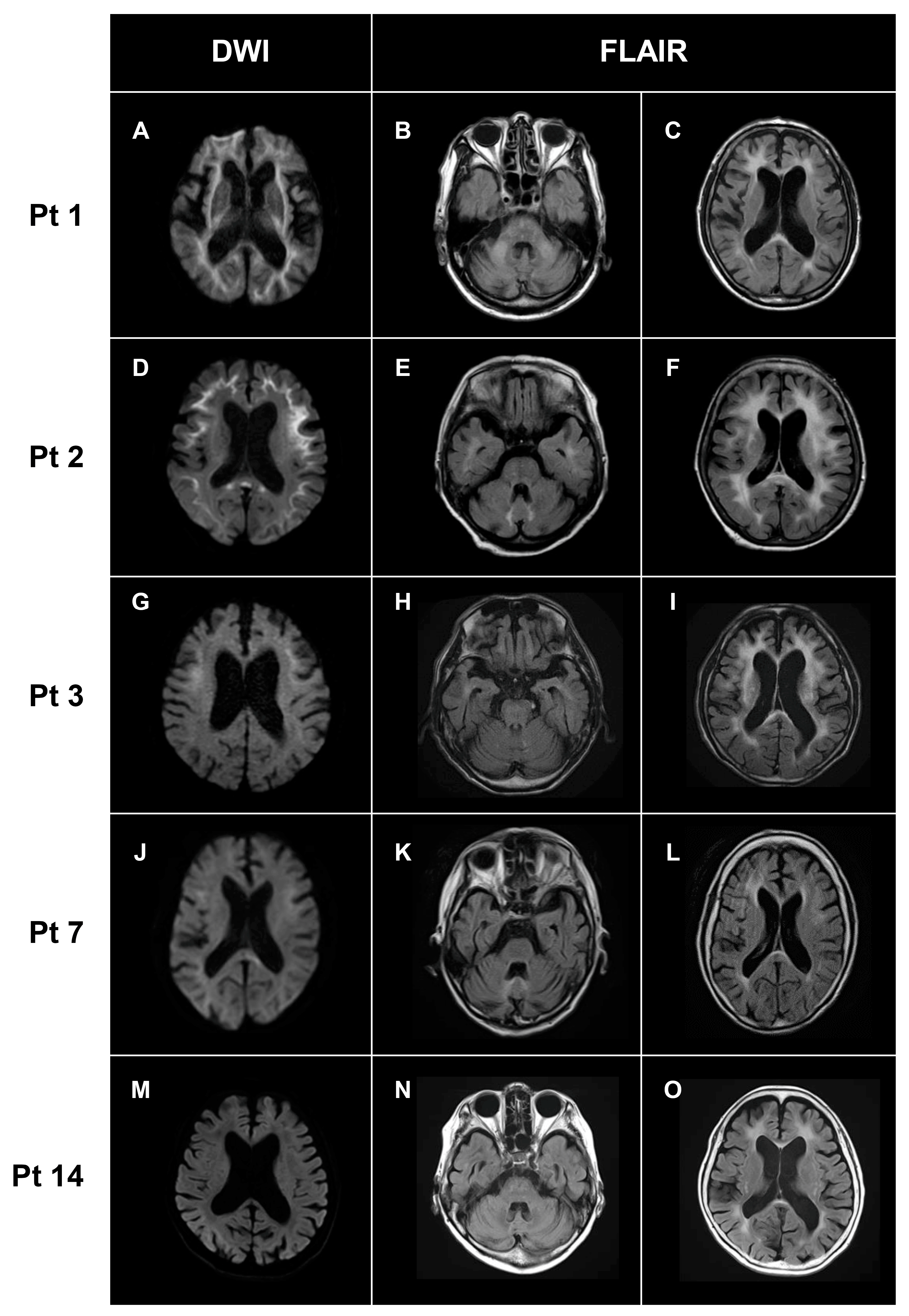
3.3. Neuroimaging Findings
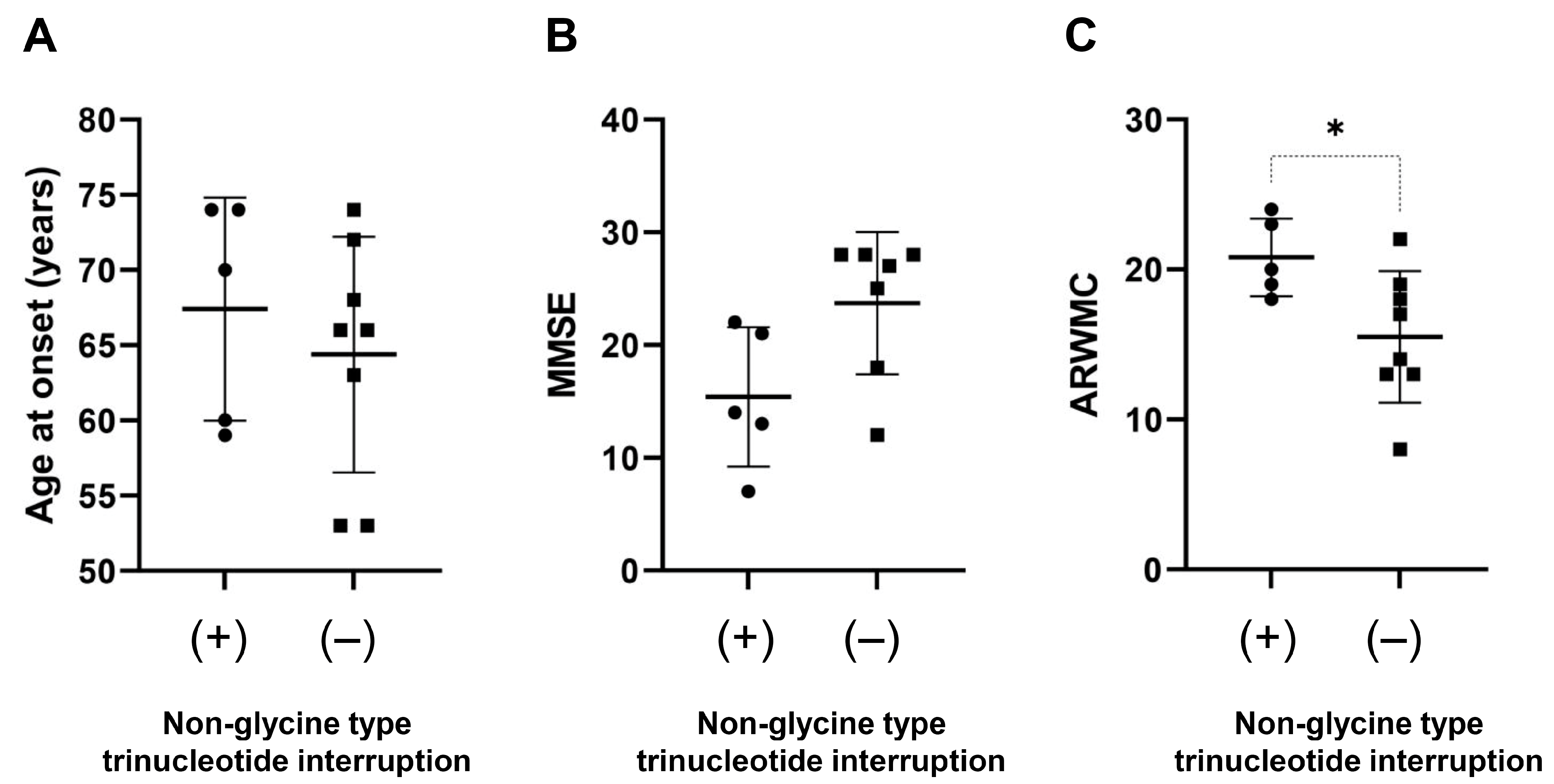
3.4. Genotype–Phenotype Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sone, J.; Mori, K.; Inagaki, T.; Katsumata, R.; Takagi, S.; Yokoi, S.; Araki, K.; Kato, T.; Nakamura, T.; Koike, H.; et al. Clinicopathological features of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease. Brain 2016, 139, 3170–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi-Fujigasaki, J. Neuronal intranuclear hyaline inclusion disease. Neuropathology 2003, 23, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, J.; Tanaka, F.; Koike, H.; Inukai, A.; Katsuno, M.; Yoshida, M.; Watanabe, H.; Sobue, G. Skin biopsy is useful for the antemortem diagnosis of neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease. Neurology 2011, 76, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiura, H.; Shibata, S.; Yoshimura, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Qu, W.; Doi, K.; Almansour, M.A.; Kikuchi, J.K.; Taira, M.; Mitsui, J.; et al. Noncoding CGG repeat expansions in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease, oculopharyngodistal myopathy and an overlapping disease. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, J.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Fujita, A.; Mizuguchi, T.; Hamanaka, K.; Mori, K.; Koike, H.; Hashiguchi, A.; Takashima, H.; Sugiyama, H.; et al. Long-read sequencing identifies GGC repeat expansions in NOTCH2NLC associated with neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Huang, W.; Zeng, S.; Jiao, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Min, H.-X.; et al. Expansion of Human-Specific GGC Repeat in Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease-Related Disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yau, W.Y.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Tucci, A.; Sivakumar, P.; Taliun, S.A.G.; Turner, C.; Efthymiou, S.; Ibáñez, K.; Sullivan, R.; et al. Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease is genetically heterogeneous. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, M.; Doi, H.; Fukai, R.; Fujita, A.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Hashiguchi, S.; Kishida, H.; Ueda, N.; Morihara, K.; Ogasawara, A.; et al. GGC Repeat Expansion of NOTCH2NLC in Adult Patients with Leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Chou, Y.T.; Chang, F.P.; Lee, W.J.; Guo, Y.C.; Chou, C.T.; Huang, H.C.; Mizuguchi, T.; Chou, C.C.; Yu, H.Y.; et al. Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease in patients with adult-onset non-vascular leukoencephalopathy. Brain 2022, 145, 3010–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gao, J.; Jiao, B.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Clinical features of NOTCH2NLC-related neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneda, T.; Kanazawa, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Baba, H.; Isami, A.; Uemura, M.; Konno, T.; Horii, A.; Ikeuchi, T.; Onodera, O. Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Presenting with Voice Tremor. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 9, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, V.; Marcolungo, L.; Maestri, S.; Alfano, M.; Lavezzari, D.; Iadarola, B.; Salviati, A.; Mariotti, B.; Botta, A.; D’apice, M.R.; et al. Characterization of FMR1 Repeat Expansion and Intragenic Variants by Indirect Sequence Capture. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 743230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Tsukie, T.; Suzuki, K.; Ihara, R.; Iwata, A.; Hara, N.; Miyashita, A.; Kuwano, R.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. Different AT(N) profiles and clinical progression classified by two different N markers using total tau and neurofilament light chain in cerebrospinal fluid. BMJ Neurol. Open 2022, 4, e000321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, L.O.; Barkhof, F.; Fazekas, F.; Bronge, L.; Augustin, M.; Sjogren, M.; Wallin, A.; Ader, H.; Leys, D.; Pantoni, L.; et al. A New Rating Scale for Age-Related White Matter Changes Applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 2001, 32, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, S.; Mizuguchi, T.; Doi, H.; Koyano, S.; Okubo, M.; Tada, M.; Shimizu, H.; Fukuda, H.; Tsuchida, N.; Uchiyama, Y.; et al. Patients with biallelic GGC repeat expansions in NOTCH2NLC exhibiting a typical neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease phenotype. Genomics 2022, 114, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Ong, H.L.; Zhao, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Teo, J.X.; Foo, J.N.; Lee, H.Y.; et al. Phenotypic bases of NOTCH2NLC GGC expansion positive neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease in a Southeast Asian cohort. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Barthélemy, N.R.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; Patterson, B.W.; Gordon, B.A.; Jockel-Balsarotti, J.; Sullivan, M.; Crisp, M.J.; Kasten, T.; Kirmess, K.M.; et al. Tau Kinetics in Neurons and the Human Central Nervous System. Neuron 2018, 98, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, M.; Komatsu, H.; Sengoku, R.; Shibukawa, M.; Morimoto, S.; Matsubara, T.; Arakawa, A.; Orita, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Mitsutake, A.; et al. CSF P-Tau181 and Other Biomarkers in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease. Neurology, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Sato, N.; Kimura, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Enokizono, M.; Saito, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Kuwabara, S. MR Imaging Features of the Cerebellum in Adult-Onset Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease: 8 Cases. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2100–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, M.; Deng, J.; Pfister, V.; Grandgirard, E.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Morlet, B.; Ruffenach, F.; Negroni, L.; Koebel, P.; Jacob, H.; et al. Translation of GGC repeat expansions into a toxic polyglycine protein in NIID defines a novel class of human genetic disorders: The polyG diseases. Neuron 2021, 109, 1825–1835.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, H.; Yamaguchi, D.; Nyquist, K.; Yabuki, Y.; Miyatake, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Hamanaka, K.; Saida, K.; Koshimizu, E.; Tsuchida, N.; et al. Father-to-offspring transmission of extremely long NOTCH2NLC repeat expansions with contractions: Genetic and epigenetic profiling with long-read sequencing. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, B.; Yu, J.; Han, X.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Genetic origin of sporadic cases and RNA toxicity in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
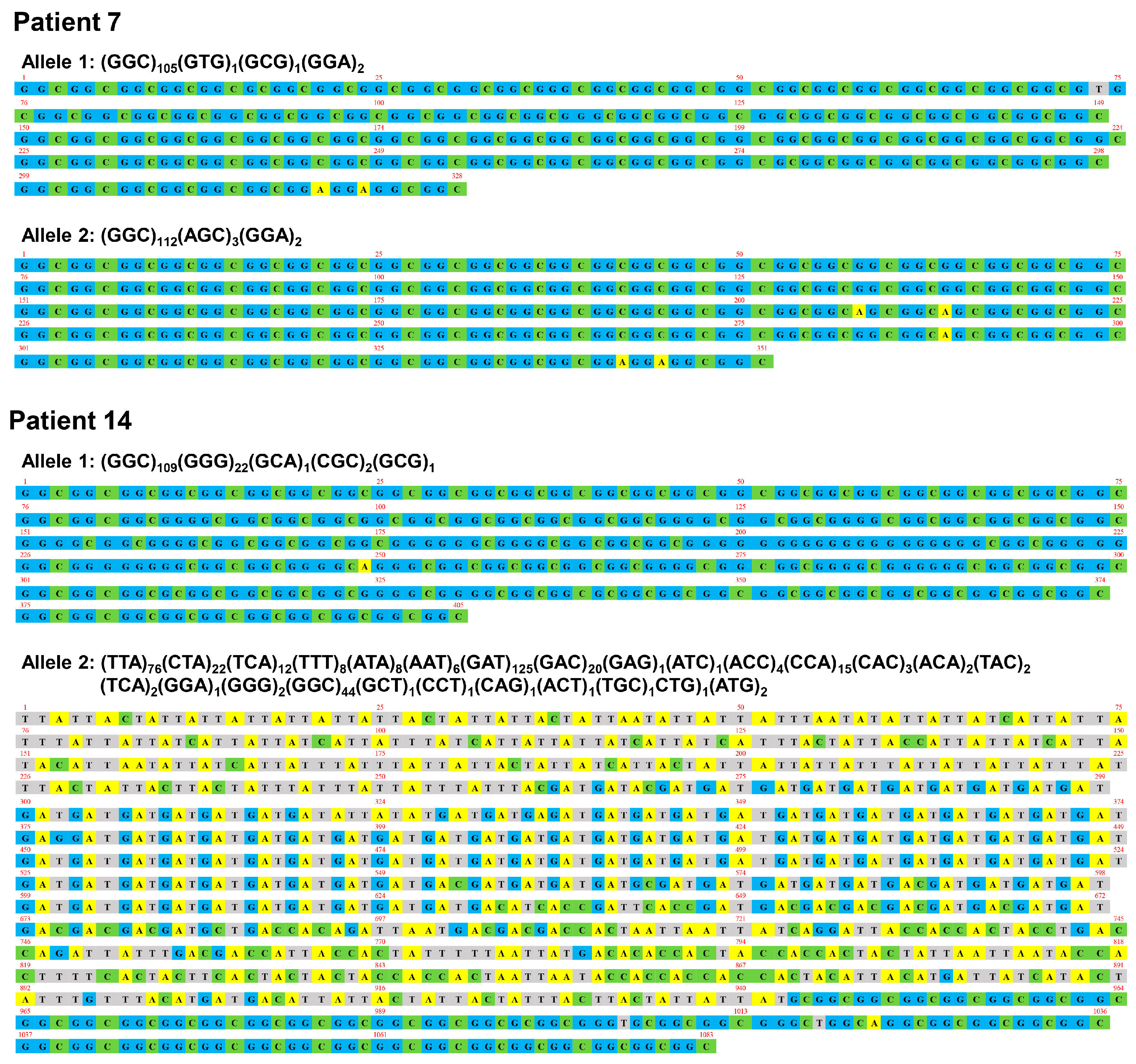
| Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4 | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | M | F | F | F | F | F | M | F | M | F | F | F | M |
| Age at onset | 70 | 53 | 74 | 66 | 68 | 53 | 50 | 74 | 59 | 66 | 60 | 63 | 72 | 60 | 74 |
| Age at examination | 77 | 66 | 78 | 68 | 72 | 55 | 78 | 78 | 69 | 72 | 74 | 71 | 78 | 63 | 84 |
| Disease duration | 7 | 13 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 28 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 10 |
| Family history | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – |
| NOTCH2NLC repeat length | |||||||||||||||
| Trinucleotide repeat size (Short allele) | 19 | 23 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 20 | N/A | 21 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 22 | 20 | N/A | 15 |
| GGC repeat size (Short allele) | 18 | 18 | 18 | 29 | 18 | 18 | N/A | 19 | 12 | 18 | 18 | 20 | 18 | N/A | 12 |
| Poly-glycine repeat size (Short allele) | 19 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 20 | N/A | 21 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 22 | 20 | N/A | 15 |
| Trinucleotide repeat size (Expanded allele) | 198 | 104 | 158 | 102 | 101 | 107 | 109/117 | 101 | 109 | 113 | 175 | 141 | 94 | 135/361 | 97 |
| GGC repeat size (Expanded allele) | 193 | 104 | 156 | 101 | 99 | 106 | 105/112 | 90 | 101 | 110 | 168 | 140 | 92 | 109/44 | 95 |
| Poly-glycine repeat size (Expanded allele) | 196 | 104 | 156 | 102 | 101 | 107 | 108/114 | 92 | 103 | 113 | 169 | 141 | 94 | 131/47 | 97 |
| GGC (%) | 97.5 | 100.0 | 98.7 | 99.0 | 98.0 | 99.1 | 96.4/95.7 | 89.0 | 93.7 | 97.3 | 96.0 | 99.3 | 97.9 | 80.0/12.2 | 97.9 |
| GGA (%) | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 1.8/1.7 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.1 | 0.0/0.3 | 2.1 |
| GGG (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 16.3/0.6 | 0.0 |
| AGC (%) | 1.5 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0/2.6 | 6.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| GAC (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0/3.6 | 0.0 |
| GAT (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0/34.6 | 0.0 |
| TTA (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0/21.1 | 0.0 |
| Others (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.8/0.0 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.7/27.5 | 0.0 |
| Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4 | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical subtype | D | P | D | M | P | M | P | P | D | D | D | O | P | P | D | - |
| Cognitive decline | + | + | + | – | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | 11/15 (73%) |
| MMSE | 14 | 28 | 13 | 25 | 12 | 27 | 15 | 22 | 7 | 28 | 21 | 28 | N/A | 27 | 18 | - |
| Psychiatric symptoms | + | + | + | – | – | – | – | – | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | 7/15 (47%) |
| Consciousness disturbance | – | + | – | – | + | – | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | – | 9/15 (60%) |
| Vomiting | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | + | – | – | + | – | – | 4/15 (27%) |
| Aphasia | – | – | – | + | – | – | + | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3/15 (20%) |
| Dysarthria | – | – | + | + | – | + | - | + | – | + | + | + | – | – | + | 8/15 (53%) |
| Tremor | – | + | – | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | - | – | – | – | – | 7/15 (47%) |
| Cerebellar ataxia | + | + | + | + | - | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | 9/15 (60%) |
| Gait disturbance | + | + | + | + | - | - | – | – | + | + | + | – | – | – | + | 8/15 (53%) |
| Sensory disturbance | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | + | - | – | – | – | – | 2/15 (13%) |
| Hyporeflexia | + | + | – | + | – | – | + | + | N/A | + | + | + | – | + | + | 10/14 (71%) |
| Urinary disturbance | + | + | + | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | + | – | – | + | 7/15 (47%) |
| Muscle weakness | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | + | – | – | – | + | + | 5/15 (33%) |
| Encephalitic episodes | – | + | – | – | + | – | + | + | + | – | + | – | + | + | – | 8/15 (53%) |
| Dysphagia | + | – | + | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | 4/15 (27%) |
| Myoclonus | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1/15 (7%) |
| Constipation | + | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | 3/15 (20%) |
| Biomarkers | Cutoff Value | Pt 3 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42 | 359.6 pg/mL | 764.9 | 757.4 | 521.2 |
| Aβ42/40 ratio | 0.072 | 0.125 | 0.106 | 0.095 |
| p-tau181 | 30.6 pg/mL | 65.4 | 65.6 | 69.0 |
| t-tau | 105.3 pg/mL | 179.5 | 104.0 | 116.1 |
| NfL | 2650 pg/mL | 93251 | 4430 | 7253 |
| AT(N) classification | A–T+(N)+ | A–T+(N)+ | A–T+(N)+ | |
| Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4 | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White matter lesions | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 15/15 (100%) |
| DWI high-intensity lesions in U-fibers | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | 14/15 (93%) |
| DWI high-intensity lesions in posterior lobe | + | – | + | – | + | – | + | – | + | – | + | + | – | – | - | 6/15 (44%) |
| DWI high-intensity lesions in corpus callosum | – | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | 10/15 (67%) |
| FLAIR high-intensity lesions in corpus callosum | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | – | – | – | + | 14/15 (93%) |
| Cerebellar atrophy | + | – | – | + | + | – | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | 11/15 (73%) |
| Middle cerebellar peduncle lesions | + | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | 3/15 (3%) |
| Paravermal lesions | – | + | – | – | + | – | + | + | – | – | – | + | – | – | + | 5/15 (33%) |
| ARWMC | 23 | 22 | 24 | 14 | 19 | 13 | 13 | 18 | 19 | 13 | 20 | 8 | 18 | 16 | 17 |
| Expanded GGC Repeat Number, Mean ± SD (Range) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | ||
| Clinical Symptoms | |||
| Cognitive decline | 115.7 ± 41.7 (44–194, n = 11) | 110.0 ± 20.7 (93–140, n = 4) | 0.87 |
| Hyporeflexia | 115.8 ± 42.3 (44–194, n = 10) | 113.5 ± 28.8 (93–156, n = 4) | 0.84 |
| Consciousness disturbance | 105.7 ± 34.3 (44–168, n = 9) | 127.0 ± 39.4 (95–194, n = 6) | 0.29 |
| Cerebellar ataxia | 129.9 ± 35.9 (9–194, n = 9) | 90.7 ± 24.3 (44–112, n = 6) | 0.046 * |
| Dysarthria | 120.8 ± 29.7 (90–168, n = 8) | 106.7 ± 44.5 (44–194, n = 7) | 0.48 |
| Encephalitic episodes | 101.4 ± 33.9 (4–168, n = 8) | 128.9 ± 36.3 (95–194, n = 7) | 0.13 |
| Gait disturbance | 128.6 ± 38.1 (95–194, n = 8) | 97.7 ± 28.9 (44–140, n = 7) | 0.14 |
| Tremor | 103.1 ± 7.4 (90–112, n = 7) | 123.9 ± 49.1 (44–194, n = 8) | 0.63 |
| Urinary dysfunction | 138.4 ± 36.6 (95–194, n = 7) | 93.0 ± 20.8 (44–110, n = 8) | 0.01 * |
| Psychiatric symptoms | 114.9 ± 47.8 (44–194, n = 7) | 113.6 ± 26.9 (90–168, n = 8) | 0.89 |
| MRI findings | |||
| Cerebellar atrophy | 109.0 ± 39.8 (44–193, n = 11) | 128.0 ± 24.1 (106–156, n = 4) | 0.13 |
| DWI high-intensity lesions in corpus callosum | 112.7 ± 40.9 (44–193, n = 10) | 116.8 ± 29.7 (90–156, n = 5) | 0.93 |
| DWI high-intensity lesions in posterior lobe | 129.5 ± 40.5 (99–193, n = 6) | 103.8 ± 31.8 (44–156, n = 9) | 0.19 |
| Paravermal lesion | 100.0 ± 8.5 (90–112, n = 5) | 121.1 ± 43.3 (44–193, n = 10) | 0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fitrah, Y.A.; Higuchi, Y.; Hara, N.; Tokutake, T.; Kanazawa, M.; Sanpei, K.; Taneda, T.; Nakajima, A.; Koide, S.; Tsuboguchi, S.; et al. Heterogenous Genetic, Clinical, and Imaging Features in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Carrying NOTCH2NLC Repeat Expansion. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060955
Fitrah YA, Higuchi Y, Hara N, Tokutake T, Kanazawa M, Sanpei K, Taneda T, Nakajima A, Koide S, Tsuboguchi S, et al. Heterogenous Genetic, Clinical, and Imaging Features in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Carrying NOTCH2NLC Repeat Expansion. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(6):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060955
Chicago/Turabian StyleFitrah, Yusran Ady, Yo Higuchi, Norikazu Hara, Takayoshi Tokutake, Masato Kanazawa, Kazuhiro Sanpei, Tomone Taneda, Akihiko Nakajima, Shin Koide, Shintaro Tsuboguchi, and et al. 2023. "Heterogenous Genetic, Clinical, and Imaging Features in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Carrying NOTCH2NLC Repeat Expansion" Brain Sciences 13, no. 6: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060955
APA StyleFitrah, Y. A., Higuchi, Y., Hara, N., Tokutake, T., Kanazawa, M., Sanpei, K., Taneda, T., Nakajima, A., Koide, S., Tsuboguchi, S., Watanabe, M., Fukumoto, J., Ando, S., Sato, T., Iwafuchi, Y., Sato, A., Hayashi, H., Ishiguro, T., Takeda, H., ... Ikeuchi, T. (2023). Heterogenous Genetic, Clinical, and Imaging Features in Patients with Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease Carrying NOTCH2NLC Repeat Expansion. Brain Sciences, 13(6), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060955






