Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
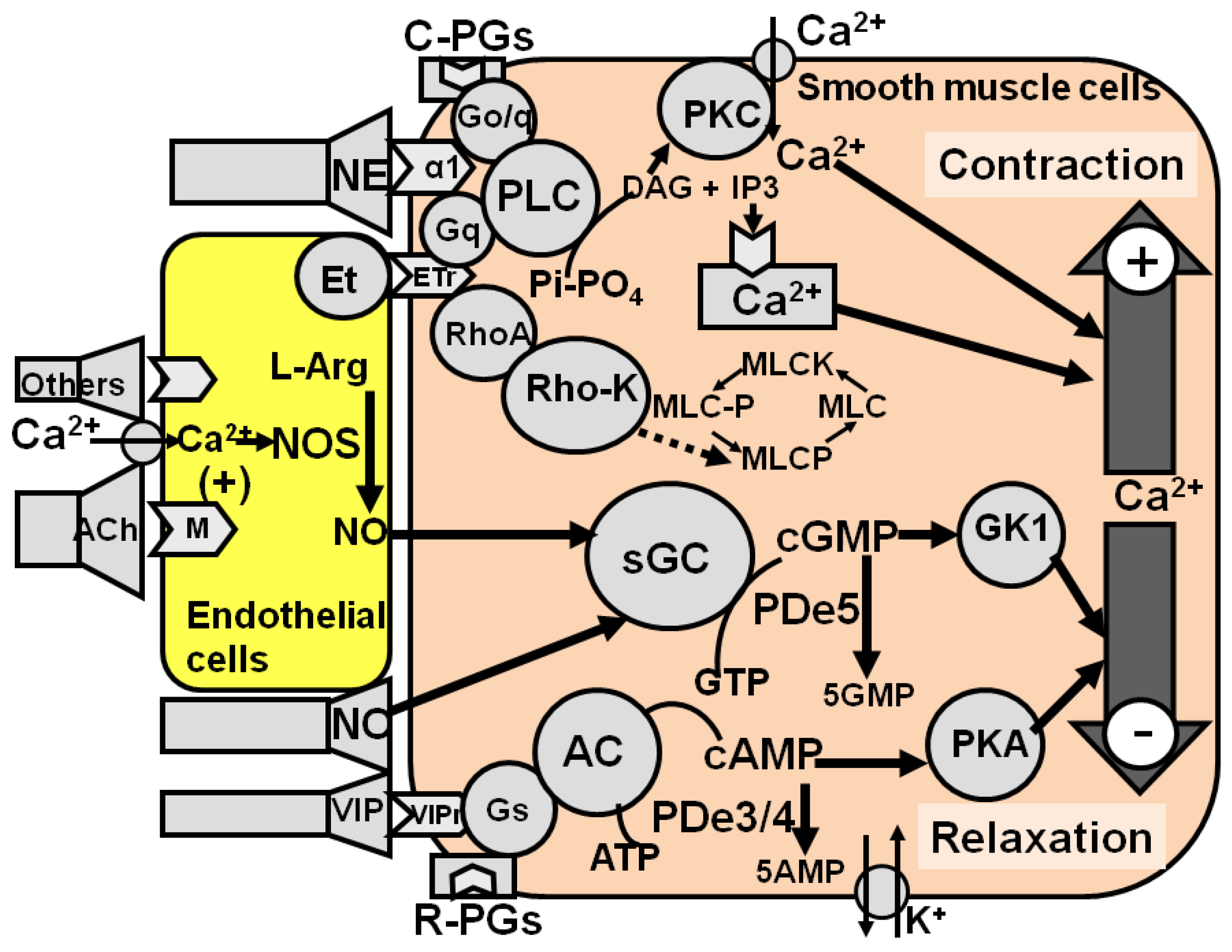
2. Neural Control of Penile Erection
3. ED Treatments
3.1. Pharmacological Strategies
3.1.1. Local Strategies
3.1.1.1. Local Treatments
3.1.1.2. PDe5
3.1.1.3. GC
3.1.1.4. Arginase
3.1.1.5. RhoA-Rho Kinase System
3.1.1.6. α1-Adrenergic Receptors
3.1.1.7. Prostanoid Receptors
3.1.1.8. PDe3/4
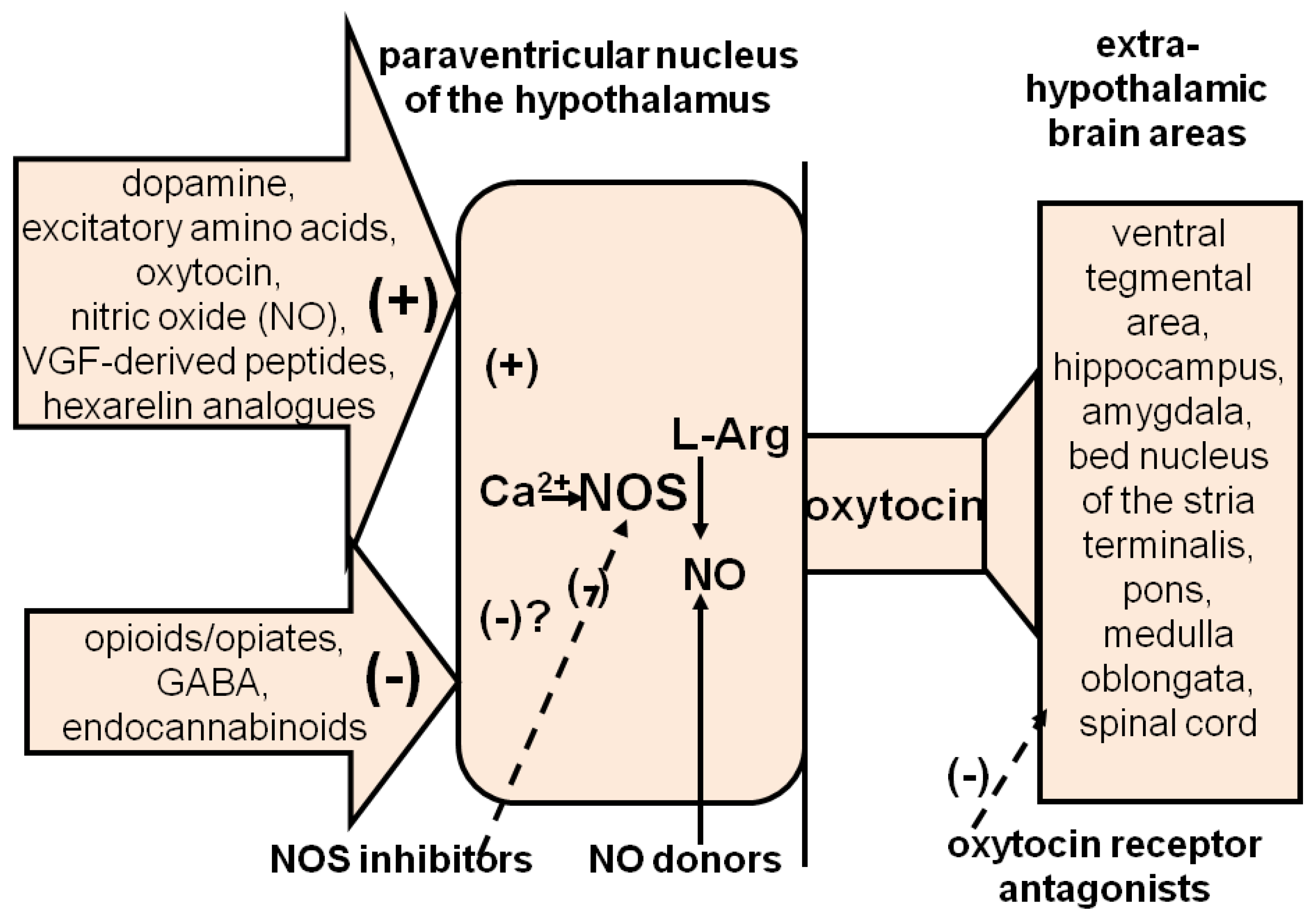
3.1.2. Central Strategies
3.1.2.1. Central Targets
3.1.2.2. Dopamine Receptors
3.1.2.3. Oxytocin Receptors
3.1.2.4. ACTH-MSH Receptors
4. Non Pharmacological Treatments of ED
4.1. Stem-Cell-, Platelet-Rich-Plasma- and Gene-Transfer-Based Therapies
4.2. Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
4.3. Botulinum Neurotoxin A
4.4. Vacuum Erection Devices
4.5. Surgical Treatment of ED
4.6. Penile Prosthesis
5. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, R.W.; Fugl-Meyer, K.S.; Bosch, R.; Fugl-Meyer, A.R.; Laumann, E.O.; Lizza, E.; Martin-Morales, A. Definitions, classification, and epidemiology of sexual dysfunction. In Sexual Medicine: Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women; Lue, T.F., Basson, R., Rosen, R., Giuliano, F., Khoury, S., Montorsi, F., Eds.; Health Publications Ltd.: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 37–72. [Google Scholar]
- Meisel, R.L.; Sachs, B.D. The physiology of male sexual behavior. In The Physiology of Reproduction; Knobil, E., Neil, J., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 3–96. [Google Scholar]
- Saenz de Tejada, I.; Angulo, J.; Cellek, S.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F.; Heaton, J.; Pickard, R.; Simonsen, U. Physiology of erectile function and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. In Sexual Medicine: Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women; Lue, T.F., Basson, R., Rosen, R., Giuliano, F., Khoury, S., Montorsi, F., Eds.; Health Publications Ltd.: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 277–343. [Google Scholar]
- Lue, T.; Tanagho, E. Physiology of erection and pharmacological management of impotence. J. Urol. 1987, 137, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, K.E.; Wagner, G. Physiology of penile erection. Physiol. Rev. 1995, 75, 191–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Neuromodulation of penile erection: An overview of the role of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. Prog. Neurobiol. 1995, 47, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.-E. Mechanisms of Penile Erection and Basis for Pharmacological Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 811–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiolas, A. Male erectile dysfunction: The chemical pharmacology of penile erection. Drugs Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2005, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.L.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Bredt, D.S.; Chang, T.S.K.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide: A physiological mediator of penile erection. Science 1992, 257, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajfer, J.; Aronson, W.J.; Bush, P.A.; Dorey, F.J.; Ignarro, L.J. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavemosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E.; Argiolas, A.; Burnett, A.; Chen, K.K.; Mills, T.M.; Steers, W.D. Future treatment targets. In Sexual Medicine: Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women; Lue, T.F., Basson, R., Rosen, R., Giuliano, F., Khoury, S., Montorsi, F., Eds.; Health Publications Ltd.: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 566–603. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, A.L.; Goldstein, I.; Andersson, K.E.; Argiolas, A.; Christ, G.; Park, K.; Xin, Z.C. Future sexual medicine physiological treatment targets. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 3269–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, E.M.; Du, J.; Lorrain, D.S.; Matuszewich, L. Extracellular dopamine in the medial preoptic area: Implications for sexual motivation and hormonal control of copulation. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 7465–7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McKenna, K.E. Central control of penile erection. Int. J. Impot. Res. 1998, 10 (Suppl. 1), S25–S34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.-K.; Chan, S.H.; Chang, L.S.; Chan, J.Y. Participation of paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus in central regulation of penile erection in the rat. J. Urol. 1997, 158, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, F.; Rampin, O. Central neural control of penile erection. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, K.E. Some proposals regarding the organization of the central nervous system control of penile erection. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, F.; Bratzu, J.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Oxytocin induces penile erection and yawning when injected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: Involvement of glutamic acid, dopamine, and nitric oxide. Horm. Behav. 2017, 96, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratzu, J.; Bharatiya, R.; Manca, E.; Cocco, C.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Sanna, F. Oxytocin induces penile erection and yawning when injected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: A microdialysis and immunohistochemical study. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 375, 112147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Central control of penile erection: A re-visitation of the role of oxytocin and its interaction with dopamine and glutamic acid in male rats. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Oxytocin, erectile function and sexual behaviour: Last discoveries and possible advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 30376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Erectile function and sexual behavior: A review of the role of nitric oxide in the central nervous system. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Sanna, F.; Argiolas, A. Dopamine, erectile function and male sexual behavior from the past to the present: A review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, L.; McKenna, K.E. A role for 5-hydroxytryptamine in descending inhibition of spinal sexual reflexes. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 88, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Dopamine and sexual behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1995, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, J.P. Central neuropharmacological agents and mechanisms in erectile dysfunction: The role of dopamine. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 24, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Central oxytocinergic neurotransmission: A drug target for the therapy of psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Curr. Drug Targets 2003, 4, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. The role of oxytocin and the paraventricular nucleus in the sexual behaviour of male mammals. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 83, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Central control of penile erection: Role of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Neuropeptides and central control of sexual behavior from the past to the present: A review. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 108, 80–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haning, H.; Niewöhner, U.; Bischoff, E. Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. Prog. Med. Chem. 2003, 41, 249–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.; Aszodi, A.; Pfeifer, A.; Alm, P.; Hofmann, F.; Ahmad, M.; Fassler, R.; Andersson, K.E. Erectile dysfunction in cyclic GMP-dependent kinase I-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitaley, K.; Wingard, C.J.; Webb, R.C.; Branam, H.; Stopper, V.S.; Lewis, R.W.; Mills, T.M. Antagonism of Rho-kinase stimulates rat penile erection via a nitric oxide-independent pathway. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, J.L.; Albersen, M.; Kutlu, O.; Gratzke, C.; Stief, C.G.; Burnett, A.L.; Lysiak, J.J.; Hedlund, P.; Bivalacqua, T.J. Inhibition of Rho-kinase improves erectile function, increases nitric oxide signaling and decreases penile apoptosis in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasker, G.F.; Pankey, E.A.; Kadowitz, P.J. Modulation of soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Physiology 2013, 28, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mónica, F.Z.; Antunes, E. Stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase for urogenital disorders. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.; Fulton, D.; Caldwell, R.W.; Romero, M.J. Arginase in the vascular endothelium: Friend or foe? Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkawy, K.S.; Lack, K.; Elbarbry, F. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Promising Arginase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Omran, G.J.; The, J.; Davis, N.F.; Bolton, D.M.; Lawrentschuk, N. Erectile dysfunction: A global review of intracavernosal injectables. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, H.; Raheem, A.A.; AbdelRahman, I.F.S.; Johnson, M.; Abdel-Raheem, T. Botulinum neurotoxin and its potential role in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2018, 6, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, F.; Joussain, C.; Denys, P. Safety and efficacy of intracavernosal injections of abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) as add on therapy to phosphosdiesterase type 5 inhibitors or prostaglandin E1 for erectile dysfunction-case studies. Toxins 2019, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sarrazin, B.; Bressolle, F.; Colson, M.H.; Bondil, P.; Saudubray, F. Efficiency and side effects of intracavernous injections of moxisylyte in impotent patients: A dose-finding study versus placebo. J. Urol. 1993, 149, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E. PDE5 inhibitors-pharmacology and clinical applications 20 years after sildenafil discovery. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2554–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrgidis, N.; Mykoniatis, I.; Haidich, A.B.; Tirta, M.; Talimtzi, P.; Kalyvianakis, D.; Ouranidis, A.; Hatzichristou, D. Effect of phosphodiesterase-type 5 inhibitors on erectile function: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; McCullough, A.R.; Jones, L.A.; Hellstrom, W.J.; Bowden, C.H.; Didonato, K.; Trask, B.; Day, W.W. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of the safety and efficacy of avanafil in subjects with erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paick, J.S.; Ahn, T.Y.; Choi, H.K.; Chung, W.S.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.W.; Min, K.S.; Moon, K.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of mirodenafil, a new oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, for treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2008, 5, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.G.; Kim, J.J. Udenafil: Efficacy and tolerability in the management of erectile dysfunction. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2013, 5, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glina, S.; Fonseca, G.N.; Bertero, E.B.; Damião, R.; Rocha, L.C.; Jardim, C.R.; Cairoli, C.E.; Teloken, C.; Torres, L.O.; Faria, G.E.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of lodenafil carbonate for oral therapy of erectile dysfunction: A phase III clinical trial. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadzoi, K.M.; Saenz de Tejada, I. Diabetes mellitus impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J. Urol. 1992, 148, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadzoi, K.M.; Kim, N.; Brown, M.L.; Goldstein, I.; Cohen, R.A.; Saenz de Tejada, I. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase products modulate corpus cavernosum smooth muscle tone. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; Cuevas, P.; Fernández, A.; Allona, A.; Moncada, I.; Martín-Morales, A.; La Fuente, J.M.; De Tejada, I.S. Enhanced thromboxane receptor-mediated responses and impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation in human corpus cavernosum from diabetic impotent men: Role of protein kinase C activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitidieri, E.; Cirino, G.; d′Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R. Pharmacology and perspectives in erectile dysfunction in man. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 208, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, M.; Uckert, S.; Waldkirch, E.; Stief, C.G.; Oelke, M.; Tsikas, D.; Sohn, M.; Jonas, U. In vitro effects of a novel class of nitric oxide (NO) donating compounds on isolated human erectile tissue. Eur. Urol. 2002, 42, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsi, J.S.; Kell, P.D.; CelleK, S.; Ralph, D.J. NCX-911, a novel nitric oxide-releasing PDE5 inhibitor relaxes rabbit corpus cavernosum in the absence of endogenous nitric oxide. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 12, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Jones, R.; Persad, R.; Angelini, G.D.; Jeremy, J.Y. Effect of sildenafil citrate and a nitric oxide donating sildenafil derivative, NCX 911, on cavernosal relaxation and superoxide formation in hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 517, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores Toque, H.A.; Priviero, F.B.; Teixeira, C.E.; Perissutti, E.; Fiorino, F.; Severino, B.; Frecentese, F.; Lorenzetti, R.; Baracat, J.S.; Santagada, V.; et al. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluations of sildenafil analogues for treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2807–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieda, N.; Hotta, Y.; Miyata, N.; Kimura, K.; Nakagawa, H. Photomanipulation of vasodilation with a blue-light-controllable nitric oxide releaser. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7085–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, H.; Ieda, N.; Hotta, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kimura, K.; Nakagawa, H. A yellowish- green-light-controllable nitric oxide donor based on N-nitrosoaminophenol applicable for photocontrolled vasodilation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, Y.; Kataoka, T.; Mori, T.; Kimura, K. Review of a potential novel approach for erectile dysfunction: Light-controllable nitric oxide donors and nanoformulations. Sex. Med. Rev. 2020, 8, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Hotta, Y.; Ieda, N.; Kataoka, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Kimura, K. Efficacy of a red-light controllable nitric oxide releaser for neurogenic erectile dysfunction: A study using a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. World J. Mens Health 2023, 41, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuku, N.P.; Unuofin, J.O.; Lebelo, S.L. Advances in nanoparticle delivery system for erectile dysfunction: An updated review. Sex. Med. 2021, 9, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasch, J.P.; Becker, E.M.; Alonso-Alija, C.; Apeler, H.; Dembowsky, K.; Feurer, A.; Gerzer, R.; Minuth, T.; Perzborn, E.; Pleiss, U.; et al. NO-independent regulatory site on soluble guanylate cyclase. Nature 2001, 410, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, A.; Stasch, J.P.; Alonso-Alija, C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Ducke, B.; Feurer, A.; Fürstner, C. NO-independent stimulators of soluble guanylate cyclase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, E.; Schramm, M.; Straub, A.; Feurer, A.; Stasch, J.P. BAY 41-2272: A stimulator of soluble guanylyl cyclase induces nitric oxide-dependent penile erection in vivo. Urology 2003, 61, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.N.; Wu, C.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Lee, F.Y.; Teng, C.M. YC-1, a novel activator of platelet guanylate cyclase. Blood 1994, 84, 4226–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, J.S.; Rees, R.W.; Hobbs, A.J.; Royle, M.; Kell, P.D.; Ralph, D.J.; Moncada, S.; Cellek, S. BAY41-2272, a novel nitric oxide independent soluble guanylate cyclase activator, relaxes human and rabbit corpus cavernosum in vitro. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, C.E.; Priviero, F.B.; Webb, R.C. Molecular mechanisms underlying rat mesenteric artery vasorelaxation induced by the nitric oxide-independent soluble guanylyl cyclase stimulators BAY 41-2272 [5-cyclopropyl-2-[1-(2-fluorobenzyl)- 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-4-ylamine] and YC-1 [3-(5′-hydroxymethyl-2′-furyl)-1-benzyl Indazole]. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasker, G.F.; Pankey, E.A.; Frink, T.J.; Zeitzer, J.R.; Walter, K.A.; Kadowitz, P.J. The sGC activator BAY 60-2770 has potent erectile activity in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H1670–H1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Estancial, C.S.; Rodrigues, R.L.; De Nucci, G.; Antunes, E.; Mónica, F.Z. Pharmacological characterisation of the relaxation induced by the soluble guanylate cyclase activator, BAY 60-2770 in rabbit corpus cavernosum. BJU Int. 2015, 116, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioni, J.D.; Nakane, M.; Hsieh, G.C.; Moreland, R.B.; Kolasa, T.; Sullivan, J.P. Activators of soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2002, 14, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, H.; Hedlund, P.; Brioni, J.D.; Sullivan, J.P.; Andersson, K.E. Nitric oxide independent activation of guanylate cyclase by YC-1 causes erectile responses in the rat. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, G.C.; O′Neill, A.B.; Moreland, R.B.; Sullivan, J.P.; Brioni, J.D. YC-1 potentiates the nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in corpus cavernosum and facilitates penile erection in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 458, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priviero, F.B.; Baracat, J.S.; Teixeira, C.E.; Claudino, M.A.; De Nucci, G.; Antunes, E. Mechanisms underlying relaxation of rabbit aorta by BAY 41-2272, a nitric oxide-independent soluble guanylate cyclase activator. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfolin, M.; Faro, R.; Araujo, E.G.; Guaraldo, A.M.; Antunes, E.; De Nucci, G. Protective effects of BAY 41-2272 (sGC stimulator) on hypertension, heart, and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by chronic L-NAME treatment in rats. J. Cardiovas. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysant, S.G. A novel approach for the treatment of hypertension with the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulating drug. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, R.W.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Toque, H.A.; Narayanan, S.P.; Caldwell, R.B. Arginase: A multifaceted enzyme important in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 641–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacchini, R.; Muniz, J.J.; Nobre, Y.T.; Cologna, A.J.; Martins, A.C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Relationship between Arginase 1 and Arginase 2 levels and genetic polymorphisms with erectile dysfunction. Nitric Oxide 2015, 51, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Wahed, A.S.A.H.; Amer, M.A.M.; Abou Mohamed, N.M.; Mobasher, M.I.; Mamdouh, H.; GamalEl Din, S.F.; ElSheemy, M.S. Serum Arginase II level can be a novel indicator for erectile dysfunction in patients with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction: A comparative study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.D.; Kim, N.N.; Traish, A.M.; Christianson, D.W. Arginase-boronic acid complex highlights a physiological role in erectile function. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, D.W. Arginase: Structure, mechanism, and physiological role in male and female sexual arousal. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minozzo, B.R.; Fernandes, D.; Beltrame, F.L. Phenolic compounds as arginase jnhibitors: New insights regarding endothelial dysfunction treatment. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moali, C.; Boucher, J.L.; Sari, M.A.; Stuehr, D.J.; Mansuy, D. Substrate specificity of NO synthases: Detailed comparison of L-arginine, homo-L-arginine, their N omega-hydroxy derivatives, and N omega-hydroxynor-L-arginine. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 10453–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.J.; Cuong, T.D.; Hung, T.M.; Ryoo, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Woo, M.H.; Choi, J.S.; Min, B.S. Arginase II inhibitory activity of phenolic compounds from Saururus chinensis. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3079–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, Y.; Zheng, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.; Uddin, J.; Park, C.; Ryu, D.G.; Kang, S.S.; Ryoo, S.; Ryter, S.W.; et al. Salvianolic acid B exerts vasoprotective effects through the modulation of heme oxygenase-1 and arginase activities. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, A.; Shin, W.; Cuong, T.D.; Min, B.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, B.H.; Ryoo, S. Arginase inhibition by piceatannol-3′-O-ß-D-glucopyranoside improves endothelial dysfunction via activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in ApoE-null mice fed a high cholesterol diet. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Park, M.; Lee, J.H.; Min, B.S.; Ryoo, S. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation through obacunone-dependent arginase inhibition restored impaired endothelial function in ApoE-null mice. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2014, 60, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudlo, M.; Demougeot, C.; Girard-Thernier, C. Arginase inhibitors: A rational approach over one century. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 475–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boydens, C.; Pauwels, B.; Vanden Daele, L.; Van de Voorde, J. Protective effect of resveratrol and quercetin on in vitro-induced diabetic mouse corpus cavernosum. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, C.J.; Azeez, T.A.; Rossetti, M.L.; Gordon, B.S.; La Favor, J.D. Long-term administration of resveratrol and MitoQ stimulates cavernosum antioxidant gene expression in a mouse castration model of erectile dysfunction. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olabiyi, A.A.; Tope-Eniola, O.S.; Oluwatuyi, A.O.; Alabi, O.; Ademola, O.G.; Oguntimehin, O.M.; AlliSmith, Y.R. Quercetin boosts nitric oxide levels and modulates the activities of arginase, acetylcholinesterase and adenosine deaminase in the corpus cavernosum of cyclosporine-treated rats. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopko, N.A.; Hannan, J.L.; Bivalacqua, T.J. Understanding and targeting the Rho kinase pathway in erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, K.A.; Ayza, M.A.; Tesfaye, B.A.; Wondafrash, D.Z.; Berhe, D.F. A systematic review on Rho-Kinase as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Res. Rep. Urol. 2020, 12, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitaley, K.; Webb, R.C.; Mills, T.M. Rho-kinase as a potential target for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Drug News Perspect. 2001, 14, 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, T.M.; Chitaley, K.; Lewis, R.W.; Webb, R.C. Nitric oxide inhibits RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling to cause penile erection. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 439, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivalacqua, T.J.; Champion, H.C.; Usta, M.F.; Cellek, S.; Chitaley, K.; Webb, R.C.; Lewis, R.L.; Mills, T.M.; Hellstrom, W.J.; Kadowitz, P.J. RhoA/Rho-kinase suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: A mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9121–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, C.E.; Ying, Z.; Webb, R.C. Proerectile effects of the Rho-kinase inhibitor (S)-(+)-2-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-5-isoquinolinyl)sulfonyl]homopiperazine (H-1152) in the rat penis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.H.; Zhao, S.T.; Meng, F.W.; Shi, B.K.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xu, Z.S. Y-27632 improves the erectile dysfunction with ageing in SD rats through adjusting the imbalance between NO and the Rho-kinase pathways. Andrologia 2007, 39, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; LoGrasso, P.V.; Defert, O.; Li, R. Rho Kinase (ROCK) inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2269–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagnini, F.; Ferazzini, M.; Grasso, M.; Blanco, S.; Croci, T. Erectile properties of the Rho-kinase inhibitor SAR407899 in diabetic animals and human isolated corpora cavernosa. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasker, G.F.; Pankey, E.A.; Allain, A.V.; Murthy, S.N.; Stasch, J.P.; Kadowitz, P.J. The selective Rho-kinase inhibitor azaindole-1 has long-lasting erectile activity in the rat. Urology 2013, 81, 465.e7–465.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Chae, M.R.; Kang, S.J.; Sung, H.H.; Han, D.H.; Chun, J.N.; Park, J.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Effects of eupatilin on the contractility of corpus cavernosal smooth muscle through nitric oxide-independent pathways. Andrology 2017, 5, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, C.E.; Jin, L.; Ying, Z.; Palmer, T.; Priviero, F.B.; Webb, R.C. Expression and functional role of the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway in rat coeliac artery. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhn, M.; Plettenburg, O.; Ivashchenko, Y.; Kannt, A.; Hofmeister, A.; Kadereit, D.; Schaefer, M.; Linz, W.; Kohlmann, M.; Herbert, J.M.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of SAR407899, a novel rho-kinase inhibitor. Hypertension 2009, 54, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wespes, E.; Rondeux, C.; Schulman, C.C. Effect of phentolamine on venous return in human erection. Brit. J. Urol. 1989, 63, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearelly, P.; Phillips, E.A.; Pan, S.; O’Brien, K.; Asher, K.; Martinez, D.; Munarriz, R. Long-term intracavernosal injection therapy: Treatment efficacy and patient satisfaction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2020, 32, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénard, F.; Lue, T.F. Self-administration in the pharmacological treatment of impotence. Drugs 1990, 39, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisidis, K.; Kalinderis, N.; Hatzimouratidis, K. Current role of local treatments for erectile dysfunction in the real-life setting. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2016, 26, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapir, R.; Bhatti, K.H.; Eliwa, A.; García-Perdomo, H.A.; Gherabi, N.; Hennessey, D.; Magri, V.; Mourmouris, P.; Ouattara, A.; Perletti, G.; et al. Effect of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on sexual function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2022, 94, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, R.A.; Anderson, R.E.; Kim, J.; Keihani, S.; Craig, J.R.; Myers, J.B.; Lenherr, S.M.; Brant, W.O.; Hotaling, J.M. Erectile dysfunction management after failed phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitor trial: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzimouratidis, K.; Salonia, A.; Adaikan, G.; Buvat, J.; Carrier, S.; El-Meliegy, A.; McCullough, A.; Torres, L.O.; Khera, M. Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction: Recommendations from the fourth international consultation for sexual medicine (ICSM 2015). J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik-Ahd, F.; Shindel, A.W. Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction in 2021 and beyond. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 49, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma-Nathan, H.; Hellstrom, W.J.; Kaiser, F.E.; Labasky, R.F.; Lue, T.F.; Nolten, W.E.; Norwood, P.C.; Peterson, C.A.; Shabsigh, R.; Tam, P.Y.; et al. Treatment of men with erectile dysfunction with transurethral alprostadil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, A.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ebiko, M.; Amano, T.; Kimura, Y.; Sakurada, S. Long-lasting effects of yohimbine on the ejaculatory function in male dogs. Biomed. Res. 2005, 5, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jabir, N.R.; Firoz, C.K.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Alsaadi, M.A.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Al-Asmari, A.I.; Alsaieedi, A.; Ahmed, B.A.; Ramu, A.K.; Tabrez, S. A literature perspective on the pharmacological applications of yohimbine. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2861–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, A.T.; Spark, R.F.; Jacobson, J.; Murray, F.T.; Geisser, M.E. Yohimbine treatment of organic erectile dysfunction in a dose-escalation trial. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2002, 14, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martin, W.J.; McIntyre, D.E. Melanocortin receptors and erectile function. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, H.A.; MacDonald, R.; Rutks, I.R.; Wilt, T.J. Trazodone for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brit. J. Urol. Int. 2003, 92, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyke, R.E. Trazodone in sexual medicine: Underused and overdosed? Sex. Med. Rev. 2020, 8, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, M.R.; Succu, S.; Cortis, L.; Argiolas, A. Extracellular dopamine increases in the paraventricular nucleus of male rats during sexual activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsma, G.; Pfaus, J.G.; Wenkstern, D.; Phillips, A.G.; Fibiger, H.C. Sexual behaviour increases dopamine transmission in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of male rats: Comparison with novelty and locomotion. Behav. Neurosci. 1992, 106, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaus, J.G.; Everitt, B.J. The psychopharmacology of sexual behavior. In Psychopharmacology: The Fourth Generation of Progress; Knobil, F.E., Kupfer, D.J., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 742–758. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, S.; Tesfaye, Y.; Thavundayil, J.X.; Thompson, T.R.; Kiely, M.E.; Vasavan Nair, N.P.; Grassino, A.; Dubrovski, B. Apomorphine: Clinical studies on erectile impotence and yawning. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Succu, S.; Argiolas, A. Dopamine agonists increase nitric oxide production in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in male rats: Correlation with penile erection and yawning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, F.; Allard, J. Dopamine and sexual function. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2001, 13 (Suppl. 3), 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoloff, P.; Schwartz, J.C. Novel dopamine receptors half a decade later. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginqrich, J.A.; Caron, M.G. Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1993, 16, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missale, C.; Nash, S.R.; Robinson, S.W.; Jaber, M.; Caron, M.G. Dopamine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 189–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.A.; Gonzalez-Burgos, G. Pathophysiologically based treatment interventions in schizophrenia. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioni, J.D.; Moreland, R.B.; Cowart, M.; Hsieh, G.C.; Stewart, A.O.; Hedlund, P.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.L.; Nakane, M.; Lynch, J.J., III; Kolasa, T.; et al. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors by ABT-724 induces penile erection in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6758–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinski, M.A.; Uchic, M.E.; Seifert, T.; Shaughnessy, T.K.; Miller, L.N.; Natane, M.; Cox, B.F.; Brioni, J.D.; Moreland, R.B. Dopamine D2, but not D4, receptor agonists are emetogenic in ferrets. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Succu, S.; Mascia, M.S.; Argiolas, A. PD-168,077, a selective dopamine D4 receptor agonist, induces penile erection when injected into the paraventricular nucleus of male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 379, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Succu, S.; Sanna, F.; Mascia, M.S.; Melis, T.; Enguehard-Gueiffier, C.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Gueiffier, A.; Argiolas, A. PIP3EA and PD168077, two selective dopamine D4 receptor agonists, induce penile erection in male rats: Site and mechanism of action in the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löber, S.; Tschammer, N.; Hübner, H.; Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A.; Gmeiner, P. The azulene framework as a novel bioisostere: Design of potent dopamine D4 receptor ligands inducing penile erection. Chem. Med. Chem. 2009, 4, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, T.A.; Allard, J.; Wayman, C.; Douglas, A.J. Dopamine-oxytocin interaction in penile erection. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner, R.S.; Nikkel, A.L.; Otte, S.; Martino, B.; Barlow, E.H.; Bhatia, P.; Stewart, A.O.; Brioni, J.D.; Decker, M.W.; Moreland, R.B. Dopamine D(4) receptor signaling in the rat paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus: Evidence of natural coupling involving immediate early gene induction and mitogen activated protein kinase phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, T.A.; Douglas, A.J. Interaction between dopamine and oxytocin in the control of sexual behaviour. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 170, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.T.; Truccone, A.; Haji-Abdi, F.; Newman, A.H.; Grundt, P.; Rice, K.C.; Husbands, S.M.; Greedy, B.M.; Enguehard-Gueiffer, C.; Gueiffer, A.; et al. Pro-erectile effects of dopamine D2-like agonists are mediated by the D3 receptor in rats and mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depoortère, R.; Bardin, L.; Rodrigues, M.; Abrial, E.; Aliaga, M.; Newman-Tancredi, A. Penile erection and yawning induced by dopamine D2-like receptor agonists in rats: Influence of strain and contribution of dopamine D2, but not D3 and D4 receptors. Behav. Pharmacol. 2009, 20, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, F.; Succu, S.; Hübner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Dopamine D2-like receptor agonists induce penile erection in male rats: Differential role of D2, D3 and D4 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, F.; Succu, S.; Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Dopamine agonist-induced penile erection and yawning: Differential role of D2 receptor subtypes and correlation with nitric oxide production in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 230, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, F.; Contini, A.; Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A. Role of dopamine D4 receptors in copulatory behavior: Studies with selective D4 agonists and antagonists. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 137, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, E.M.; Dominguez, J.M. Getting his act together: Roles of glutamate, nitric oxide, and dopamine in the medial preoptic area. Brain Res. 2006, 1126, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Bhatt, R.; Picotte, K.B.; Hull, E.M. Oxytocin in the medial preoptic area facilitates male sexual behavior in the rat. Horm. Behav. 2011, 59, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succu, S.; Sanna, F.; Melis, T.; Boi, A.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Stimulation of dopamine receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats induces penile erection and increases extra-cellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens: Involvement of central oxytocin. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Melis, T.; Cocco, C.; Succu, S.; Sanna, F.; Pillolla, G.; Boi, A.; Ferri, G.L.; Argiolas, A. Oxytocin injected into the ventral tegmental area induces penile erection and increases extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.R.; Sanna, F.; Succu, S.; Zarone, P.; Boi, A.; Argiolas, A. The role of oxytocin in the anticipatory and consummatory phases of male rat sexual behaviour. In Handbook of Oxytocin Research: Synthesis, Storage and Release, Actions and Drug Forms; Jastrow, H., Feuerbach, D., Eds.; Nova Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, M.R.; Succu, S.; Cocco, C.; Caboni, E.; Sanna, F.; Boi, A.; Ferri, G.L.; Argiolas, A. Oxytocin induces penile erection when injected into the ventral subiculum: Role of nitric oxide and glutamic acid. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succu, S.; Sanna, F.; Cocco, C.; Melis, T.; Boi, A.; Ferri, G.L.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Oxytocin induces penile erection when injected into the ventral tegmental area of male rats: Role of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succu, S.; Sanna, F.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R. Oxytocin injected into the hippocampal ventral subiculum induces penile erection in male rats by increasing glutamatergic neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arletti, R.; Bazzani, C.; Castelli, M.; Bertolini, A. Oxytocin improves male copulatory performance in rats. Horm. Behav. 1985, 19, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.; Gessa, G. Intraventricular oxytoxin induces yawning and penile erection in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 117, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Gessa, G.L. Oxytocin: An extremely potent inducer of penile erection and yawning in male rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 130, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Argiolas, A.; Gessa, G. Oxytocin-induced penile erection and yawning: Site of action in the brain. Brain Res. 1986, 398, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Geng, L.; Mei, L.; Osakada, T.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Kania, A.; Grinevich, V.; et al. A genetically encoded sensor measures temporal oxytocin release from different neuronal compartments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arletti, R.; Calza, L.; Giardino, L.; Benelli, A.; Cavazzuti, E.; Bertolini, A. Sexual impotence is associated with a reduced production of oxytocin and with an increased production of opioid peptides in the paraventricular nucleus of male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 233, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, A.; Bertolini, A.; Poggioli, R.; Cavazzuti, E.; Calzà, L.; Giardino, L.; Arletti, R. Nitric oxide is involved in male sexual behavior of rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 294, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, D.M.; Insel, T.R. Increased Fos Expression in Oxytocin Neurons Following Masculine Sexual Behavior. J. Neuroendocr. 1994, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijs, R.M. Intra- and extrahypothalamic vasopressin and oxytocin pathways in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1978, 192, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund-Mercier, M.; Stoeckel, M.; Palacios, J.; Pazos, A.; Reichhart, J.; Porte, A.; Richard, P. Pharmacological characteristics and anatomical distribution of [3H]oxytocin-binding sites in the wistar rat brain studied by autoradiography. Neuroscience 1987, 20, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M. Morphology of vasopressin and oxytocin neurones and their central and vascular projections. Prog. Brain Res. 1983, 60, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, M.S.; Humbert, R.; Dixen, J.; Palmisano, G.; Greenleaf, W.; Davidson, J.M. Plasma Oxytocin Increases in the Human Sexual Response. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 64, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.R.; Seckl, J.R.; Burton, S.; Checkley, S.A.; Lightman, S.L. Changes in Oxytocin and Vasopressin Secretion during Sexual Activity in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 65, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, J.S. Stimuli that cause the release of oxytocin. In Handbook of Physiology Section 7: Endocrinology; Geiger, S.R., Knobil, E., Sawyer, W.H., Greef, R., Astwood, E.B., Eds.; American Physiology Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; Volume IV, pp. 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lalu, K.; Lampelo, S.; Vanha-Perttula, T. Characterization of three aminopeptidases purified from maternal serum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 1986, 873, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbach, J.P.; Lebouille, J.L. Proteolytic conversion of arginine-vasopressin and oxytocin by brain synaptic membranes. Characterization of formed peptides and mechanisms of proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancampiano, R.; Melis, M.; Argiolas, A. Proteolytic conversion of oxytocin by brain synaptic membranes: Role of aminopeptidases and endopeptidases. Peptides 1991, 12, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancampiano, R.; Argiolas, A. Proteolytic conversion of oxytocin in vivo after microinjection in the rat hippocampus. Peptides 1993, 14, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Lange, T.; Kern, W.; McGregor, G.P.; Bickel, U.; Fehm, H.L. Sniffing neuropeptides: A transnasal approach to the human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, G.; Ludwig, M. Intranasal Oxytocin: Myths and Delusions. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, T.R. Translating oxytocin neuroscience to the cinic: A National Institute of Mental Health perspective. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walch, K.; Eder, R.; Schindler, A.; Feichtinger, W. The Effect of Single-Dose Oxytocin Application on Time to Ejaculation and Seminal Parameters in Men. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2001, 18, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burri, A.; Heinrichs, M.; Schedlowski, M.; Kruger, T.H. The acute effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on endocrine and sexual function in males. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnia, B.; Heinrichs, M.; Bergmann, W.; Jung, S.; Germann, J.; Schedlowski, M.; Hartmann, U.; Kruger, T.H. Differential effects of intranasal oxytocin on sexual experiences and partner interactions in couples. Horm. Behav. 2014, 65, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.D.; Anderson, P.S.; Ball, R.G.; Bock, M.G.; Carroll, L.; Chiu, S.H.; Clineschmidt, B.V.; Culberson, J.C.; Erb, J.M.; Evans, B.E.; et al. 1-((7,7-Dimethyl-2(S)-(2(S)-amino-4-(methylsulfonyl)butyramido)bicycle [2.2.1]-heptan-1(S)-yl)methyl)sulfonyl)-4-(2-methylphenyl)piperaz ine (L-368,899): An orally bioavailable, non-peptide oxytocin antagonist with potential utility for managing preterm labor. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterloh, I.H.; Muirhead, G.J.; Sultana, S.; Whaley, S.; van den Berg, F.; Atiee, G. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of single oral doses of a novel oxytocin receptor antagonist-cligosiban-in development for premature ejaculation: Three randomized clinical trials in healthy subjects. J. Sex. Med. 2018, 15, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Murgia, S.; Schiöth, H.B. ACTH- and α-MSH-induced grooming, stretching, yawning and penile erection in male rats: Site of action in the brain and role of melanocortin receptors. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 51, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Gessa, G.L. Behavioral effects of ACTH and MSH peptides. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1981, 4, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Donohue, T.L.; Dorsa, D.M. The opiomelanocortinergic neuronal and endocrine systems. Peptides 1982, 3, 353–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontjes, D.A.; Kirk Ways, D.; Mahaffee, D.D.; Zimmermann, C.F.; Gwynne, J.T. ACTH receptors and the effect of ACTH on adrenal organelles. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 297, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhajlani, V.; Wikberg, J.E.S. Molecular cloning and expression of the human melanocyte stimulating hormone receptor cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1992, 309, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantz, I.; Miwa, H.; Konda, Y.; Shimoto, Y.; Tashiro, T.; Watson, S.J.; Del Valle, J.; Yamada, T. Molecular cloning expression and gene localization of a fourth melanotropin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15174–15179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountjoy, K.G.; Robbins, L.S.; Mortrud, M.T.; Cone, R.D. The cloning of a family of genes that encode the melanocortin receptors. Science 1992, 257, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli-Rehfuss, L.; Mountjoy, K.G.; Robbins, L.S.; Mortrud, M.T.; Low, M.J.; Tatro, J.E.; Entwistle, M.L.; Simerly, R.; Cone, R.D. Identification of a receptor for gamma-MSH and other proopiomelanocortin peptides in the hypothalamus and limbic systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8856–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, A.N. The Melanotropins: Chemistry, Physiology and Mechanism of Action; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dorr, R.T.; Lines, R.; Levine, R.; Brooks, C.; Xiang, L.; Hruby, V.J.; Hadley, M.E. Evaluation of melanotan-II, a superpotent cyclic melanotropic peptide in a pilot phase-1 clinical study. Life Sci. 1996, 58, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, V.J.; Lu, D.; Sharma, S.D.; Castrucci, A.D.L.; Kersterson, R.A.; Al-Obeidi, F.A.; Hadley, M.E.; Cone, R.D. Cyclic lactam alpha-melanotropin analogues of Ac-Nle4-cyclo [Asp5,D-Phe7,Lys10]-alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-(4-10)-NH2 with bulky aromatic amino acids at position 7 show high antagonist potency and selectivity at specific melanocortic receptors. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 3454–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schioth, H.B.; Mutulis, F.; Muceniece, R.; Prusis, P.; Wikberg, J.E. Discovery of novel melanocortin4 receptor selective MSH analogues. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, H.; Fuciarelli, K.; Hansen, J.; Hadley, M.E.; Hruby, V.J.; Dorr, R.; Levine, N. Synthetic melanotropic peptide initiates erections in men with psychogenic erectile dysfunction: Double-blind, placebo controlled crossover study. J. Urol. 1998, 160, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergoni, A.V.; Bertolini, A.; Mutulis, F.; Wikberg, J.E.; Schioth, H.B. Differential influence of a selective melanocortin MC4 receptor antagonist (HS014) on melanocortin-induced behavioral effects in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 362, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.J.; McGowan, E.; Cashen, D.E.; Gantert, L.T.; Drisko, J.E.; Hom, G.J.; Nargund, R.; Sebhat, I.; Howard, A.D.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.; et al. Activation of melanocortin MC(4) receptors increases erectile activity in rats ex copula. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 454, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Mauri, A.; Gessa, G.L. Paraventricular nucleus lesion prevents yawning and penile erection induced by apomorphine and oxytocin, but not by ACTH in rats. Brain Res. 1987, 421, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Vargiu, L.; Gessa, G.L. d(CH2)5Tyr(Me)-[Orn8]vasotocin, a potent oxytocin antagonist, antagonizes penile erection and yawning induced by oxytocin and apomorphine, but not by ACTH-(1–24). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 134, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizusawa, H.; Hedlund, P.; Andersson, K.E. alpha-Melanocyte stimulating hormone and oxytocin induced penile erections, and intracavernous pressure increases in the rat. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemulapalli, R.; Kurowski, S.; Salisbury, B.; Parker, E.; Davis, H. Activation of central melanocortin receptors by MT-II increases cavernosal pressure in rabbits by the neuronal release of NO. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Semple, E.; Shalabi, F.; Hill, J.W. Oxytocin neurons enable melanocortin regulation of male sexual function in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6310–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.E.; Earle, D.C.; Rosen, R.C.; Willett, M.S.; Molinoff, P.B. Double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of the safety, pharmacokinetic properties and pharmacodynamic effects of intranasal PT-141, a melanocortin receptor agonist, in healthy males and patients with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P. PT-141–Palatin. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2004, 5, 456–462. [Google Scholar]
- King, S.H.; Mayorov, A.V.; Balse-Srinivasan, P.; Hruby, V.J.; Vanderah, T.W.; Wessells, H. Melanocortin receptors, melanotropic peptides and penile erecton. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Ückert, S.; Bannowsky, A.; Albrecht, K.; Kuczyk, M.A. Melanocortin receptor agonists in the treatment of male and female sexual dysfunctions: Results from basic research and clinical studies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2014, 23, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, B.A.; Amer, T.; Fraser, M. Melanotan-induced priapism: A hard-earned tan. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e227644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, C.W.; Lopategui, D.M.; Cordon, B.H. Melanotan tanning injection: A rare cause of priapism. Sex. Med. 2021, 9, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; Xin, Z.C.; Dai, J.; Lue, T.F. Commonly used mesenchymal stem cell markers and tracking labels: Limitations and challenges. Histol. Histopathol. 2013, 28, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Jenkins, L.; Albersen, M.; Corona, G.; Isidori, A.M.; Goldfarb, S.; Maggi, M.; Nelson, C.J.; Parish, S.; Salonia, A.; et al. Erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiou, R. Stem-cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2017, 28 (Suppl. 1), S81–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, S.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Sikka, S.C.; Hellstrom, W.J. Advances in stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, X.; Ouyang, X.; Fang, J.; Huang, X.; Wei, H. Transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved erectile dysfunction induced by cavernous nerve injury. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6354–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; Chang, M.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, W.H.; Wu, C.C.; Yeh, S.D. Revisiting the regenerative therapeutic advances towards erectile dysfunction. Cells 2020, 9, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.S.; Li, Y.Q.; Deng, Z.Q.; Liu, G.H. Progress and prospect of stem cell therapy for diabetic erectile dysfunction. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 2000–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakpahan, C.; Ibrahim, R.; William, W.; Faizah, Z.; Juniastuti, J.; Lusida, M.I.; Oceandy, D. Stem cell therapy and diabetic erectile dysfunction: A critical review. World J. Stem Cells 2021, 13, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siregar, S.; Novesar, A.R.; Mustafa, A. Application of stem cell in human erectile dysfunction-a systematic review. Res. Rep. Urol. 2022, 14, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, M.M.; Rai, B.P.; Webb, W.R.; Madaan, S. Is there a role for stem cell therapy in erectile dysfunction secondary to cavernous nerve injury? Network meta-analysis from animal studies and human trials. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 17562872221086999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, B.; Wang, T. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus through the attenuation of ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yao, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, M. Effects of stem cell-derived exosome therapy on erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta- analysis of preclinical studies. Sex. Med. 2023, 11, qfac019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Sun, X.; Bian, J.; Wu, R.; Guan, X.; Ouyang, B.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Luo, D.; Atala, A.; et al. Correction of diabetic erectile dysfunction with adipose derived stem cells modified with the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in a rodent diabetic model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Nie, P.; Yang, W.; Guo, R.; Ding, D.; Liang, R.; Wei, B.; Wei, H. An EPO-loaded multifunctional hydrogel synergizing with adipose-derived stem cells restores neurogenic erectile function via enhancing nerve regeneration and penile rehabilitation. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokeshwar, S.D.; Patel, P.; Shah, S.M.; Ramasamy, R. A systematic review of human trials using stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2020, 8, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; von Schwarz, E.R. Stem-cell therapy for erectile dysfunction: A review of clinical outcomes. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2021, 33, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Cakir, O.O.; Satchi, M.; Fallara, G.; Pang, K.H.; European Society for Sexual Medicine Scientific Collaboration and Partnership. The current role and implications of stem cell therapy in erectile dysfunction: A transformation from caterpillar to butterfly is required. Eur. Urol. Focus 2023, 9, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melman, A.; Bar-Chama, N.; McCullough, A.; Davies, K.; Christ, G.J. hMaxi-K gene transfer in males with erectile dysfunction: Results of the first human trial. Hum. Gene Ther. 2006, 17, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melman, A.; Biggs, G.; Davies, K.; Zhao, W.; Tar, M.T.; Christ, G.J. Gene transfer with a vector expressing Maxi-K from a smooth muscle-specific promoter restores erectile function in the aging rat. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, G.J.; Andersson, K.E.; Williams, K.; Zhao, W.; D′Agostino, R., Jr.; Kaplan, J.; Aboushwareb, T.; Yoo, J.; Calenda, G.; Davies, K.P.; et al. Smooth-muscle- specific gene transfer with the human maxi-k channel improves erectile function and enhances sexual behavior in atherosclerotic cynomolgus monkeys. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; He, W.; Qin, G.; Luo, J.; Xiao, M. Transplantation KCNMA1 modified bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cell therapy for diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction. Andrologia 2014, 46, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, Y.; Appel, B.; Jacob, G.; Massarwi, O.; Gruenwald, I. Can low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy improve erectile function? A 6-month follow-up pilot study in patients with organic erectile dysfunction. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Tan, K.; Yang, Y.; Yong, S.; Yu, X. Effect of low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave on the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Mens Health 2019, 13, 1557988319846749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Shindel, A.W.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Cellular signaling pathways modulated by low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2019, 31, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunckhorst, O.; Wells, L.; Teeling, F.; Muir, G.; Muneer, A.; Ahmed, K. A systematic review of the long-term efficacy of low-intensity shockwave therapy for vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pu, J.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z. Effects of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy on erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2022, 32, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, R.; Natale, C.; Hellstrom, W.J.G. Reviewing the evidence for shockwave- and cell-based regenerative therapies in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2021, 13, 17562872211002059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschler, S.C.; Harhaus, L.; Schoenle, P.; Boecker, A.; Kneser, U.; Bergmeister, K.D. Ultrasound and shock-wave stimulation to promote axonal regeneration following nerve surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usta, M.F.; Gabrielson, A.T.; Bivalacqua, T.J. Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of erectile dysfunction following radical prostatectomy: A critical review. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2019, 31, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shaer, W.; Ghanem, H.; Diab, T.; Abo-Taleb, A.; Kandeel, W. Intra-cavernous injection of BOTOX® (50 and 100 Units) for treatment of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction: Randomized controlled trial. Andrology 2021, 9, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, F.; Denys, P.; Joussain, C. Effectiveness and safety of intracavernosal incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) 100 U as an add-on therapy to standard pharmacological treatment for difficult-to-treat erectile dysfunction: A case series. Toxins 2022, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, I.F.S.; Raheem, A.A.; Elkhiat, Y.; Aburahma, A.A.; Abdel-Raheem, T.; Ghanem, H. Safety and efficacy of botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of erectile dysfunction refractory to phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Andrology 2022, 10, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, F.; Joussain, C.; Denys, P.; Laurin, M.; Behr-Roussel, D.; Assaly, R. Intracavernosal onabotulinumtoxina exerts a synergistic pro-erectile effect when combined with sildenafil in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Sex. Med. 2022, 19, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, O. Surgical Device. U.S. Patent 1,225,341, 18 May 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Witherington, R. Vacuum constriction device for management of erectile impotence. J. Urol. 1989, 141, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, L.W.; Munarriz, R.; Wang, R.; Morey, A.; Levine, L. External mechanical devices and vascular surgery for erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 1579–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederichs, W.; Kaula, N.F.; Lue, T.F.; Tanagho, E.A. The effect of subatmospheric pressure on the simian penis. J. Urol. 1989, 142, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, R. The science of vacuum erectile device in penile rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Lin, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Luo, A.; Berardinelli, F.; Dai, Y.; Wang, R. Molecular mechanisms of vacuum therapy in penile rehabilitation: A novel animal study. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, N.; Moore, K.T. Vacuum devices in erectile dysfunction: Indications and efficacy. Brit. J. Urol. 1998, 82, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; McGahan, J.P.; Stone, A.R.; White, R.D. The hemodynamics of vacuum constriction erections: Assessment by color Doppler ultrasound. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welliver, R.C., Jr.; Mechlin, C.; Goodwin, B.; Alukal, J.P.; McCullough, A.R. A pilot study to determine penile oxygen saturation before and after vacuum therapy in patients with erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadig, P.W.; Ware, J.C.; Blumoff, R. Noninvasive device to produce and maintain an erection-like state. Urology 1986, 27, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrfeld, T.; Lee, D.I. The role of vacuum erection devices in penile rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2009, 21, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidi, A.A.; Becher, E.F.; Zhang, G.; Lewis, J.H. Patient acceptance of and satisfaction with an external negative pressure device for impotence. J. Urol. 1990, 144, 1154–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.W.; Witherington, R. External vacuum therapy for erectile dysfunction: Use and results. World J. Urol. 1997, 15, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodansky, H.J. Treatment of male erectile dysfunction using the active vacuum assist device. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, S.; Aydos, K.; Kosar, A.; Anafarta, K. Treating erectile dysfunction with a vacuum tumescence device: A retrospective analysis of acceptance and satisfaction. Br. J. Urol. 1995, 76, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.L.; Yang, Y.; Fu, F.D.; Wu, C.J.; Qin, F.; Yuan, J.H. Optimal pressure in penile rehabilitation with a vacuum erection device: Evidence based on a rat model. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shauly, O.; Gould, D.J.; Patel, K.M. Emerging nonsurgical and surgical techniques to treat erectile dysfunction: A systematic review of treatment options and published outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2019, 72, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsar, H.; Metin, A.; Sozduyar, N.; Salih, M.; Gulsoy, U. Erectile dysfunction due to venous incompetence treated by dorsal vein ligation. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 1992, 24, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Hassouna, M.M.; Elhilali, M.M. Long-term results of penile venous ligation for corporeal venous occlusive dysfunction. Can. J. Surg. 1995, 38, 537–541. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.U.; Dean, R.C.; Carrion, R.; Bochinski, D.; Lue, T.F. Crural ligation for primary erectile dysfunction: A case series. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 2064–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, Y.; Gruenwald, I.; Gedalia, U.; Nassar, S.; Engel, A.; Har-Shai, Y. Evaluation of penile revascularization for erectile dysfunction: A 10-year follow-up. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Munarriz, R. Penile microvascular arterial bypass surgery: Indications, outcomes, and complications. Sci. World. J. 2010, 10, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, B.; Bastuba, M.; Goldstein, I. Penile revascularization—Contemporary update. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.D.; Lee, W.J.; Yang, S.C.; Lin, P.C.; Tai, H.C.; Hsieh, J.T.; Liu, S.P.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, M.F. Safety and six-month durability of angioplasty for isolated penile artery stenoses in patients with erectile dysfunction: A first-in-man study. EuroIntervention 2014, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.D.; Owen, R.C.; White, G.S.; Elkelany, O.O.; Rahnema, C.D. Endovascular treatment of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Asian J. Androl. 2015, 17, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munarriz, R.; Uberoi, J.; Fantini, G.; Martinez, D.; Lee, C. Microvascular arterial bypass surgery: Long-term outcomes using validated instruments. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, H.G.; Kliot, M.; Lange, P.H.; Ellis, W.J.; Takayama, T.K.; Yang, C.C. Two-year outcome of unilateral sural nerve interposition graft after radical prostatectomy. Urology 2006, 68, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, M.; Tasaki, I.; Kitamura, R.; Yakabe, A.; Hayashi, M.; Matsuya, F.; Miyaguchi, T.; Tsuruta, J. Cavernous nerve graft reconstruction using an autologous nerve guide to restore potency. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, G.R.; Borden, L.S., Jr.; Backous, D.D.; Bayles, S.W.; Corman, J.M. Erectile function following unilateral cavernosal nerve replacement. Can. J. Urol. 2008, 15, 3990–3993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.A.; Avellino, A.M.; Shurtleff, D.; Lendvay, T.S. Reinnervating the penis in spina bifida patients in the United States: Ilioinguinal-to-dorsal-penile neurorrhaphy in two cases. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Trindade, J.C.; Viterbo, F.; Petean Trindade, A.; Fávaro, W.J.; Trindade-Filho, J.C.S. Long-term follow-up of treatment of erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy using nerve grafts and end-to-side somatic-autonomic neurorraphy: A new technique. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, E.B.; Antunes, D.L. Surgical treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2015, 3, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, Z.; Mirza, M. Post-prostatectomy erectile dysfunction: Contemporary approaches from a US perspective. Res. Rep. Urol. 2014, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skoufias, S.; Sturny, M.; Fraga-Silva, R.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Stergiopoulos, N.; Adamakis, I.; Constantinides, C.A. Novel concept enabling an old idea: A flexible electrode array to treat neurogenic erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2018, 15, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, F.B.; Bradley, W.E.; Timm, G.W. Management of erectile impotence: Use of implantable inflatable prosthesis. Urology 1973, 2, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabalin, J.N.; Kuo, J.C. Long-term followup of and patient satisfaction with the Dynaflex self-contained inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1997, 158, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.K.; Delk, J.R.; Salem, E.A.; Cleves, M.A. Long-term survival of inflatable penile prostheses: Single surgical group experience with 2384 first-time implants spanning two decades. J. Sex. Med. 2007, 4 Pt 1, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, J.; Tremeaux, J.C.; Faix, A.; Pierrevelcin, J.; Staerman, F. Erectile function and sexual satisfaction before and after penile prosthesis implantation in radical prostatectomy patients: A comparison with patients with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E. Penile prosthesis implant: Scientific advances and technological innovations over the last four decades. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2017, 6, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Wu, B.R.; Xiang, P.; Xiao, J.; Hu, X.C. Management of male erectile dysfunction: From the past to the future. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1148834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montorsi, F.; Rigatti, P.; Carmignani, G.; Corbu, C.; Campo, B.; Ordesi, G.; Breda, G.; Silvestre, P.; Giammusso, B.; Morgia, G.; et al. AMS three-piece inflatable implants for erectile dysfunction: A long-term multi-institutional study in 200 consecutive patients. Eur. Urol. 2000, 37, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Croce, G.; Schifano, N.; Pescatori, E.; Caraceni, E.; Colombo, F.; Bettocchi, C.; Carrino, M.; Vitarelli, A.; Pozza, D.; Fiordelise, S.; et al. Which patient may benefit the most from penile prosthesis implantation? Andrology 2022, 10, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Najari, B.B.; Davison, W.L.; Al Hussein Al Awamlh, B.; Zhao, F.; Paduch, D.A.; Mulhall, J.P.; Chughtai, B.; Lee, R.K. Trends in the utilization of penile prostheses in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in the United States. J. Sex. Med. 2015, 12, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, T.P.; Rajanahally, S.; Hellstrom, W.J.G.; Hsieh, T.C.; Raheem, O.A. Global trends in prevalence, treatments, and costs of penile prosthesis for erectile dysfunction in men. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuszak, A.W.; Lentz, A.C.; Farooq, A.; Jones, L.; Bella, A.J. Technological improvements in three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis design over the past 40 years. J. Sex. Med. 2015, 12 (Suppl. 7), 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E. A review of current and emerging therapeutic options for erectile dysfunction. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, T.; Layon, A.J. Clinical applications of nitric oxide. Chest 1996, 110, 506–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Serefoglu, E.C. An update on the drug safety of treating erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretta, N.; De Rocco Ponce, M.; Minicuci, N.; De Santis, I.; Palego, P.; Garolla, A.; Foresta, C. Efficacy of penile low-intensity shockwave treatment for erectile dysfunction: Correlation with the severity of cavernous artery disease. Asian J. Androl. 2021, 23, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mechanism Involved | Molecular Targets | Classes of Drugs | Clinically Relevant Drugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facilitation of cavernous smooth muscle relaxation | NO–cGMP signaling pathway, neurotransmitter/ neuropeptide/autacoid receptors, adenylate cyclase/cAMP signaling pathway, Ca2+ channels, K+ channels | PDe 5 inhibitors, NO donors, guanylate cyclase activators, Pde-resistant cGMP analogues, NO-independent GC stimulators and activators, arginase inhibitors, PDe3/4 inhibitors, contracting prostaglandins, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). | Sildenafil Vardenafil Tadalafil Avenafil Prostaglandin E1 Alprostadil Papaverine |
| Inhibition of cavernous smooth muscle contraction | adrenergic α1-receptors, endothelin receptors, RhoA/Rho kinase system | adrenergic α1-antagonists, endothelin receptor antagonists, RhoA/Rho Kinase inhibitors, botulinum neurotoxin A | Phentolamine Phenoxybenzamine Moxisylite Botulinum neurotoxin A |
| Mechanism Involved | Molecular Targets | Classes of Drugs | Clinically Relevant Drugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased activity of neurotransmitters/neuropeptides/autacoids that facilitate erectile function | Neurotransmitter/ neuropeptide/autacoid receptors, second messengers, etc. | Dopamine agonists, excitatory amino acid agonists, oxytocin agonists, nitric oxide donors, melanocortin receptor agonists, hexarelin analogues, VGF analogues | Apomorphine, melanotan II, PT-141 |
| Decreased activity of neurotransmitters/neuropeptides/autacoids that inhibit erectile function | Neurotransmitter /neuropeptide/ autacoid receptors, second messengers, etc. | α2-antagonists, opioid antagonists, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) antagonists, cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists, serotonin antagonists | Yohimbine, trazodone |
| Dopamine Receptor Family | Receptor Subtypes | Transduction Mechanisms | Effect on Penile Erection |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D1 | Increased activity of AC–cAMP signalling pathway, increased PIP2 turnover, increased Ca2+ mobilitation | None |
| D5 | |||
| D2 | D2s–D2l | Decreased activity of AC–cAMP signalling pathway, increased K+ channel activation, increased voltage-gated Ca2+ channel activation | Facilitatory |
| D3 | None | ||
| D4 | Facilitatory |
| α-MSH | Ac-Ser-Tyr-Ser-Met-Glu-His-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-ValNH2 |
| MT-II | Ac-Nle4-cyclo[Asp5-His6-D-Phe7-Arg8-Trp9-LysNH210]α-MSH(4–10) |
| PT-141 | Ac-Nle4-cyclo[Asp5-His6-D-Phe7-Arg8-Trp9-LysOH10]α-MSH(4–10) |
| SHU-9119 | Ac-Nle4-cyclo[Asp5, His6, D-Nal(2′)7, Arg8-Trp9-LysNH210]α-MSH(4–10) |
| HS024 | (cyclo[AcCys3-Nle4-Arg5-His6-D-Nal7-Arg8-Trp9-Lys10-CysNH211]α-MSH(3-11) |
| THIQ | (N-[(3R)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinium-3-ylcarbonyl]-(1R)-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-2- |
| [4-cyclohexyl-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1ylmethyl)piperidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethylamine |
| Strategy | Mechanism of Action | Preclinical Evidence | Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intracavernous, normal or modified stem cells obtained from numerous tissues | Erectile function is recovered by restoring the activity of endothelial and smooth muscle cells, and nerves in penile cavernous and vascular tissues | Yes, in rodent models of ED, mainly diabetes, vascular, nerve injuries and aging models | Yes, in patients with ED of different etiology, mainly diabetes and prostatectomy |
| Platelet-enriched plasma | Erectile function is recovered by restoring the activity of endothelial and smooth muscle cells, and nerves in penile cavernous and vascular tissues | Yes, in rodent models of ED, mainly diabetes, vascular, nerve injuries and aging models | Yes, in patients with ED of different etiology, mainly diabetes and prostatectomy |
| Gene transfer | Erectile function is potentiated by inserting genes that facilitate relaxation in cavernous smooth muscle tissues | Yes, in rodent models of aging and in a monkey model of atherosclerotic ED | Yes, but only preliminary clinical data (Phase 1) are available in patients with ED of different etiology |
| Intracavernous botulinum neurotoxin A | Erection is obtained by a relaxation of cavernous smooth muscle by a still unknown mechanism, possibly mediated by the block of the release of mediators that keep cavernous smooth muscle contracted | Yes, in rodent models of ED, mainly hypertension model | Yes, in patients with ED of different etiology, mainly vascular, selected for penile prosthesis implant |
| Strategy | Mechanism of Action | Preclinical Evidence | Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular surgery with or without stent | Revascularitation by eliminating focal arterial blocks mainly in the inferior epigastric artery | Yes, in rodent models of ED, mainly vascular | Yes, in patients with vascular ED caused focal arterial damage, mainly of the inferior epigastric arthery |
| Venous ligation or embolization | Blockage of venous branches to reduce venous outflow from the penis during erection | Yes, in rodents models of ED, mainly aging | Yes, in patients with cavernous venous occlusive dysfunction |
| Neuronal gafts | Reconstruction of pelvic nerves and/or reunion of damaged/truncated pelvic nerve axons to the penis | Yes, in rodent models of ED, mainly penile nerve trauma and/or crash | Yes, in patients with pelvic nerve damage, mainly after pelvic/penile trauma and radical prostatectomy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argiolas, A.; Argiolas, F.M.; Argiolas, G.; Melis, M.R. Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050802
Argiolas A, Argiolas FM, Argiolas G, Melis MR. Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(5):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050802
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgiolas, Antonio, Francesco Mario Argiolas, Giacomo Argiolas, and Maria Rosaria Melis. 2023. "Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies" Brain Sciences 13, no. 5: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050802
APA StyleArgiolas, A., Argiolas, F. M., Argiolas, G., & Melis, M. R. (2023). Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Sciences, 13(5), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050802







