Electroencephalography Based Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis in Emotional Cognitive Reappraisal Combined with Happy Music
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experiment
2.3. EEG Recording and Preprocessing
2.4. Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Behavioural Results
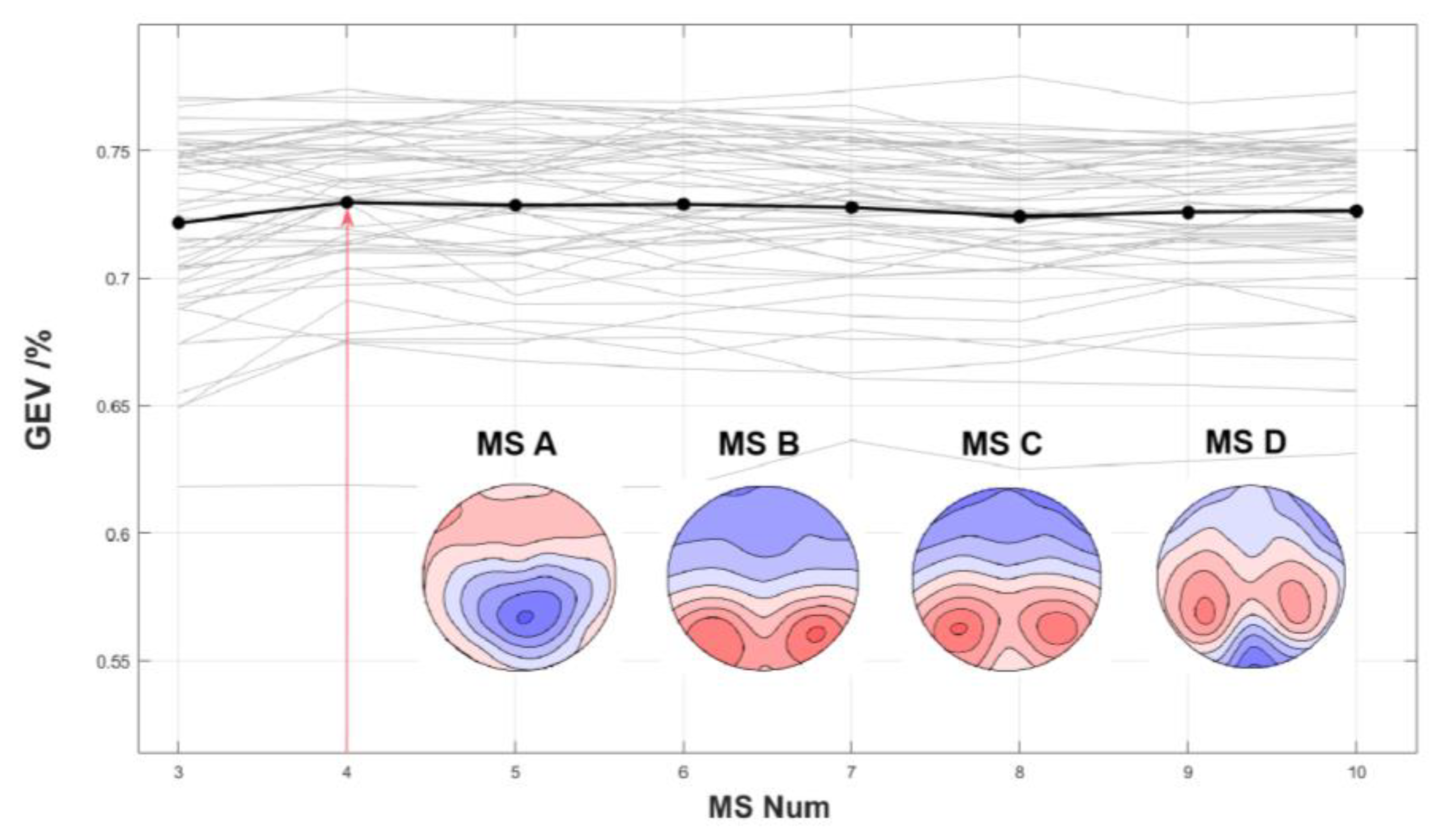
3.2. Microstate Results
3.3. Functional Conectivity Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioural Effect of Happy Music on Cognitive Reappraisal
4.2. Altered Functional Connectivity during Different Microstates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schindler, J.A. How to Live 365 Days a Year; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- John, O.P.; Gross, J.J. Individual differences in emotion regulation. In Handbook of Emotion Regulation; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 351–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, A.; Kress, L.; Stark, R. Neural correlates of immediate and prolonged effects of cognitive reappraisal and distraction on emotional experience. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradt, J.; Dileo, C.; Shim, M. Music interventions for preoperative anxiety. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD006908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Pérez, S.; Gómez-Pérez, V.; Velasco, M.C.; Perez-Campos, E.; Mayoral, E.P.C. Effects of music therapy on depression compared with psychotherapy. Arts Psychother. 2010, 37, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehaniv, C.L.; Antonova, E. Simulating and reconstructing neurodynamics with Epsilon-automata applied to electroencephalography (EEG) microstate sequences. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 November–1 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.C.; Rickard, N.S. The music USE (MUSE) questionnaire: An instrument to measure engagement in music. Music. Percept. 2012, 29, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, M.; Västfjäll, D.; Asutay, E.; Koppel, L.; Saarikallio, S. Is it me or the music? Stress reduction and the role of regulation strategies and music. Music. Sci. 2019, 2, 2059204319844161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Cera, N.; Silva, S. The “Ifs” and “Hows” of the Role of Music on the Implementation of Emotional Regulation Strategies. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, J.; Petsche, H.; Pereda, E. Interdependencies in the spontaneous EEG while listening to music. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 42, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, J.; Petsche, H. Phase synchrony analysis of EEG during music perception reveals changes in functional connectivity due to musical expertise. Signal Process. 2005, 85, 2161–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moezzi, B.; Pratti, L.M.; Hordacre, B.; Graetz, L.; Berryman, C.; Lavrencic, L.M.; Ridding, M.C.; Keage, H.A.; McDonnell, M.D.; Goldsworthy, M.R. Characterization of Young and Old Adult Brains: An EEG Functional Connectivity Analysis. Neuroscience 2019, 422, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchel, C.; Friston, K.J. Dynamic changes in effective connectivity characterized by variable parameter regression and Kalman filtering. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1998, 6, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Yan, C.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; He, Y. Characterizing dynamic functional connectivity in the resting brain using variable parameter regression and Kalman filtering approaches. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, M.G.; Bolton, T.A.W.; Van De Ville, D. The dynamic functional connectome: State-of-the-art and perspectives. NeuroImage 2017, 160, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieder, M.; Koenig, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Utsunomiya, K.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Dierks, T.; Nishida, K. Discovering EEG resting state alterations of semantic dementia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Benquet, P.; Biraben, A.; Berrou, C.; Dufor, O.; Wendling, F. Dynamic reorganization of functional brain networks during picture naming. Cortex 2015, 73, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamzadeh, N.; Medvedev, A.; Azari, A.; Gandjbakhche, A.; Najafizadeh, L. Capturing dynamic patterns of task-based functional connectivity with EEG. NeuroImage 2013, 66, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Potter, T.; Nguyen, T.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic reorganization of the cortical functional brain network in affective processing and cognitive reappraisal. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 2050051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D. Brain electric microstates and cognition: The atoms of thought. In Machinery of the Mind; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear, M.D.E.; Krleza-Jeric, K.; Lemmens, T. The declaration of Helsinki. BMJ 2007, 335, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, D.; Hajcak, G. Deconstructing reappraisal: Descriptions preceding arousing pictures modulate the subsequent neural response. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2008, 20, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Electrophysiological evidence of impaired cognitive reappraisal in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: An event-related potential study. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 427, 113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.J.; Bradley, M.M.; Cuthbert, B.N. International affective picture system (IAPS): Technical manual and affective ratings. NIMH Cent. Study Emot. Atten. 1997, 1, 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, T.; Kottlow, M.; Stein, M.; Melie-Garcia, L. Ragu: A free tool for the analysis of EEG and MEG event-related scalp field data using global randomization statistics. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 938925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, X.; Tian, Z.; Liu, T.; Niu, H. EEG based dynamic functional connectivity analysis in mental workload tasks with different types of information. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Altered EEG microstate dynamics in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, D.; Ozaki, H.; Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 67, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.M.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Topographic ERP analyses: A step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr. 2008, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Stein, M.; Grieder, M.; Kottlow, M. A tutorial on data-driven methods for statistically assessing ERP topographies. Brain Topogr. 2014, 27, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, A.; Gianotti, L.R.R.; Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.; Knoch, D. Temporal characteristics of EEG microstates mediate trial-by-trial risk taking. Brain Topogr. 2017, 30, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaux, J.P.; Rodriguez, E.; Martinerie, J.; Varela, F.J. Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum. Brain Mapping. 1999, 8, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, M.; Liao, X.; Evans, A.; He, Y. GRETNA: A graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.G.; Schellenberg, E.G.; Griffith, A.T. Misery loves company: Mood-congruent emotional responding to music. Emotion 2011, 11, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, X. Vision dominates at the pre-response level and audition dominates at the response level in cross-modal interaction: Behavioral and neural evidence. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7109–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczygieł, D.; Buczny, J.; Bazińska, R. Emotion regulation and emotional information processing: The moderating effect of emotional awareness. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2012, 52, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, D.; Nisar, H.; Yap, V.V.; Tsai, C.-Y. The Effect of Music Listening on EEG Functional Connectivity of Brain: A Short-Duration and Long-Duration Study. Mathematics 2022, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmonik, C.; Brandt, A.; Anderson, J.R.; Brooks, F.; Lytle, J.; Silverman, E.; Frazier, J.T. Music listening modulates functional connectivity and information flow in the human brain. Brain Connect. 2016, 6, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisch, R. The functional neuroanatomy of reappraisal: Time matters. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.J. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, V.; Schubert, E. Background music at work: A literature review and some hypotheses. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Music Communication Science (ICoMCS2), Sydney, Australia, 3–4 December 2009; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]




| MS | rmANOVA | Multi-Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Condition | F(2, 100) = 3.803, p = 0.026 | Rea < Neu, p = 0.047 | |
| B | Condition | F(2, 100) = 3.393, p = 0.038 | Rea > Neg, p = 0.033 | |
| Group | F(1, 50) = 3.236, p = 0.043 | Music > Control | ||
| C | Condition | F(2, 100) = 3.371, p = 0.038 | Rea < Neg, p = 0.028 | |
| D | Condition | F(2, 100) = 4.830, p = 0.010 | Rea < Neg, p = 0.021 Rea < Neu, p = 0.029 | |
| Condition*Group | F(2, 100) = 3.589, p = 0.033 | Music | Rea < Neg, p = 0.017 Rea < Neu, p = 0.044 | |
| MS | Metric | rmANOVA | Multi-Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Lp | Condition | F(2, 100) = 15.061, p < 0.001 | Rea < Neg, p < 0.001 Neu < Neg, p = 0.004 | |
| Condition*Group | F(2, 100) = 11.039, p < 0.001 | Control | Rea < Neg, p < 0.001 Neu < Neg, p = 0.013 Rea < Neu, p < 0.001 | ||
| Rea | Music > Control, p = 0.033 | ||||
| C | Lp | Condition | F(2, 100) = 3.759, p = 0.027 | Rea > Neg, p = 0.048 | |
| D | Cp | Condition | F(1.731, 86.526) = 8.841, p = 0.001 | Rea > Neg, p = 0.002 | |
| Condition*Group | F(1.731, 86.526) = 8.586, p = 0.001 | Music | Rea > Neg, p < 0.001 Neu > Neg, p = 0.032 Rea > Neu, p = 0.001 | ||
| Lp | Group | F(1, 50) = 4.067, p = 0.049 | Music > Control | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, W.; Li, Y. Electroencephalography Based Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis in Emotional Cognitive Reappraisal Combined with Happy Music. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13040554
Hua W, Li Y. Electroencephalography Based Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis in Emotional Cognitive Reappraisal Combined with Happy Music. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(4):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13040554
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Wangchun, and Yingjie Li. 2023. "Electroencephalography Based Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis in Emotional Cognitive Reappraisal Combined with Happy Music" Brain Sciences 13, no. 4: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13040554
APA StyleHua, W., & Li, Y. (2023). Electroencephalography Based Microstate Functional Connectivity Analysis in Emotional Cognitive Reappraisal Combined with Happy Music. Brain Sciences, 13(4), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13040554





