The McGurk Illusion: A Default Mechanism of the Auditory System
Abstract
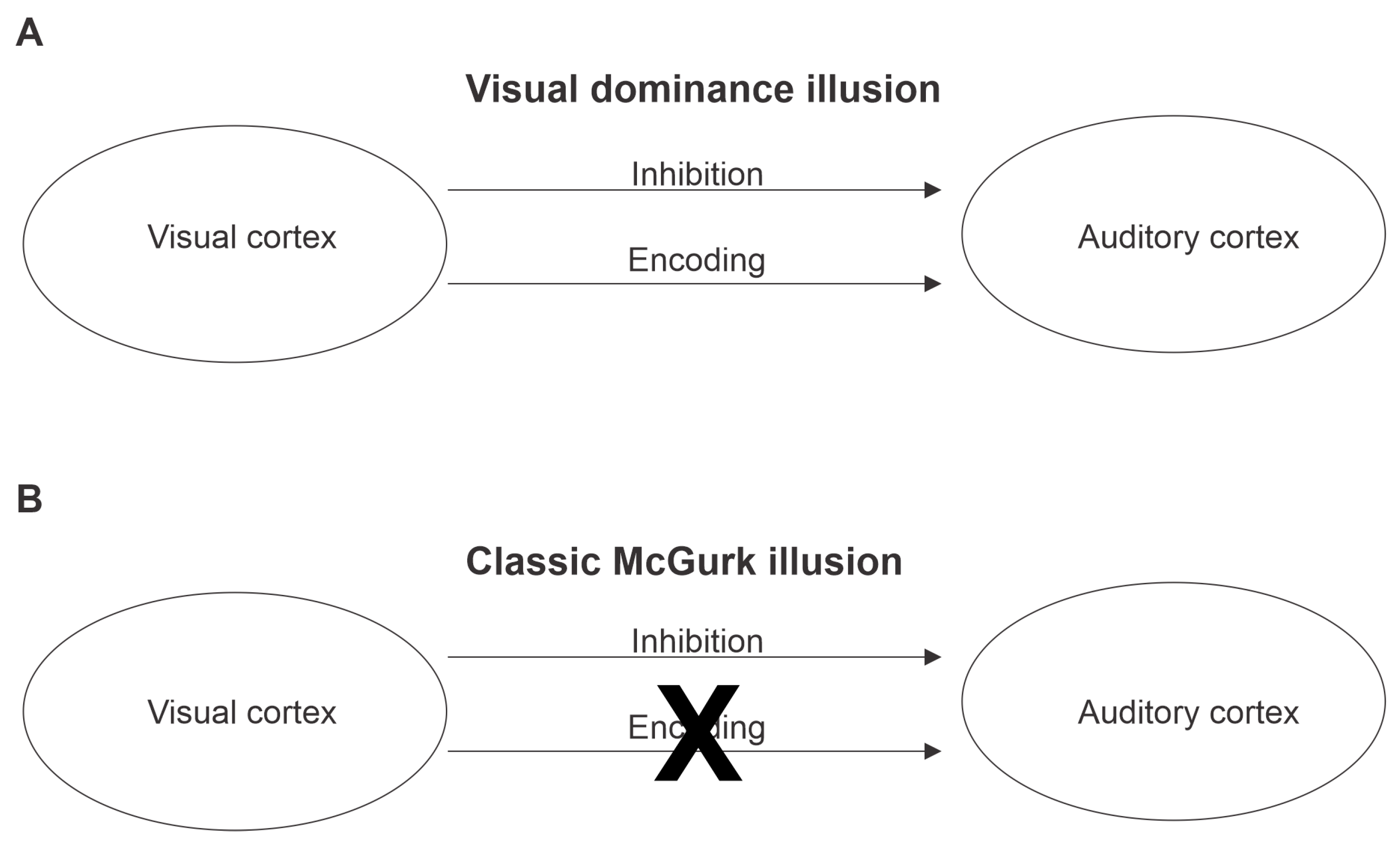
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
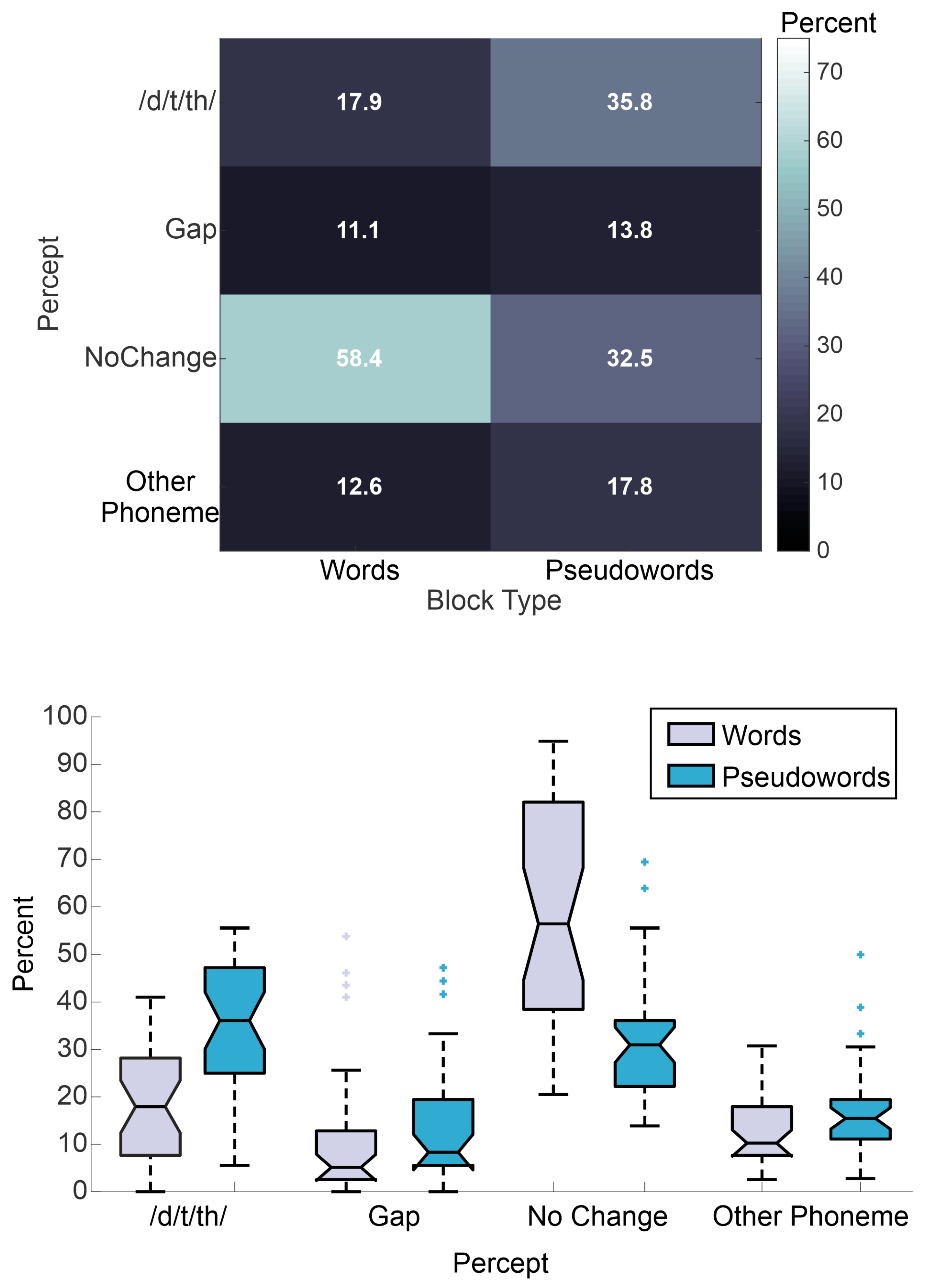
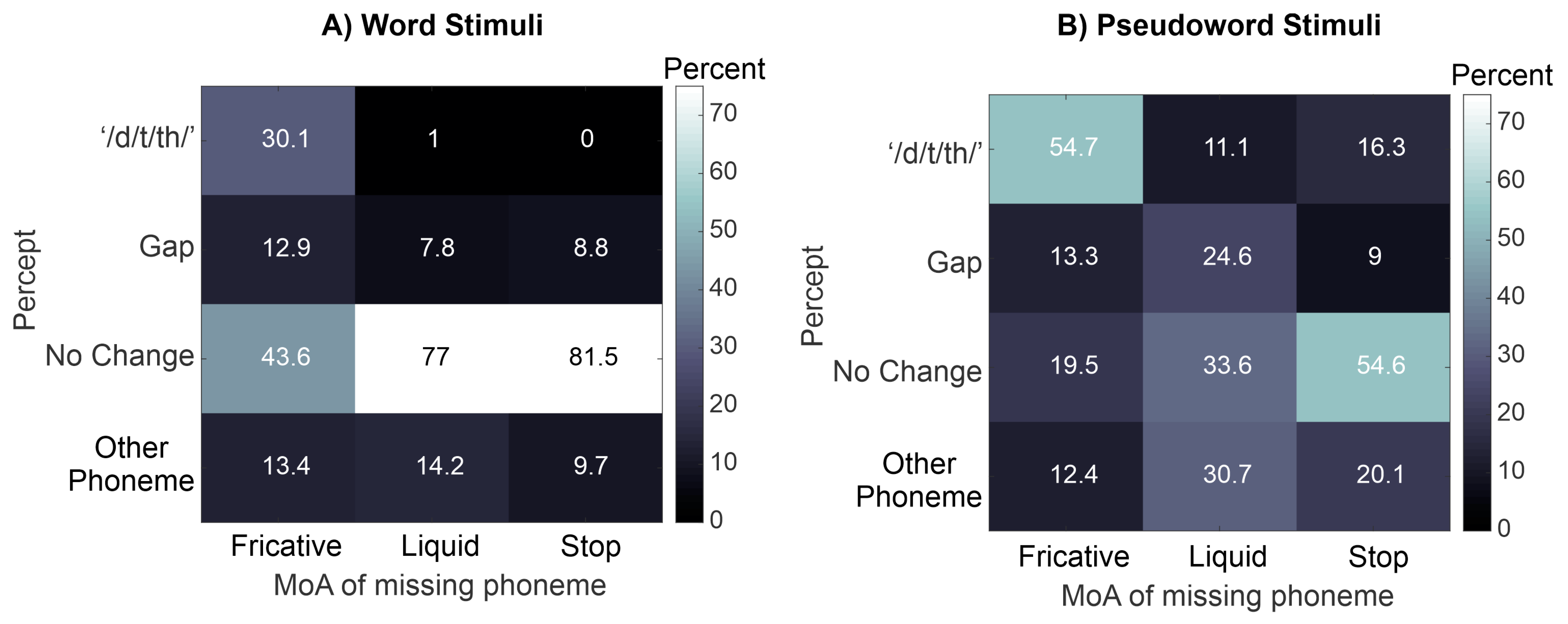
3. Results
3.1. Mixed Effects Multinomial Logistic Regression
3.2. Correlation between Auditory-Only Filling-In and McGurk Illusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGurk, H.; MacDonald, J. Hearing Lips and Seeing Voices. Nature 1976, 264, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, M.S.; Lee, K.E.; Argall, B.D.; Martin, A. Integration of Auditory and Visual Information about Objects in Superior Temporal Sulcus. Neuron 2004, 41, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, M.S.; Nath, A.R.; Pasalar, S. FMRI-Guided Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Reveals That the Superior Temporal Sulcus Is a Cortical Locus of the McGurk Effect. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 2414–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, L.C.; Zielinski, B.A.; Zielinski, J.E.V.; Liu, G.; Turkeltaub, P.E.; Leaver, A.M.; Rauschecker, J.P. Distinct Cortical Locations for Integration of Audiovisual Speech and the McGurk Effect. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, C.; Champoux, F.; Voss, P.; Bacon, B.A.; Lepore, F.; Théoret, H. Speech and Non-Speech Audio-Visual Illusions: A Developmental Study. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, R.J.; Stacey, J.E.; Cragg, L.; Stacey, P.C.; Allen, H.A. The Threshold for the McGurk Effect in Audio-Visual Noise Decreases with Development. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiyama, K.; Soshi, T.; Sakamoto, S. Enhanced Audiovisual Integration with Aging in Speech Perception: A Heightened McGurk Effect in Older Adults. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, D.; Yodashkin-Porat, D.; Katz, N.; Valevski, A.; Aizenberg, D.; Sigler, M.; Weizman, A.; Kikinzon, L. Differences in Audiovisual Integration, as Measured by McGurk Phenomenon, among Adult and Adolescent Patients with Schizophrenia and Age-Matched Healthy Control Groups. Compr. Psychiatry 2009, 50, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.G.; Backer, K.C.; Mandujano, B.; Shahin, A.J. Rethinking the Mechanisms Underlying the McGurk Illusion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 616049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, L.M.; Toscano, J.C. Rethinking the McGurk Effect as a Perceptual Illusion. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2021, 83, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engen, K.J.; Dey, A.; Sommers, M.S.; Peelle, J.E. Audiovisual Speech Perception: Moving beyond McGurk. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 152, 3216–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engen, K.J.; Xie, Z.; Chandrasekaran, B. Audiovisual Sentence Recognition Not Predicted by Susceptibility to the McGurk Effect. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2017, 79, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, K.W.; Seitz, P.-F. The Use of Visible Speech Cues for Improving Auditory Detection of Spoken Sentences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, E.A.; Fox, N.A.; van Wassenhove, V.; Knudsen, E.I. Auditory-Visual Fusion in Speech Perception in Children with Cochlear Implants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18748–18750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumby, W.H.; Pollack, I. Visual Contribution to Speech Intelligibility in Noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1954, 26, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, L.D.; Saldaña, H.M. Discrimination Tests of Visually Influenced Syllables. Percept. Psychophys. 1992, 52, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.T.; Shahin, A.J. Cross-Modal Phonetic Encoding Facilitates the McGurk Illusion and Phonemic Restoration. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 2988–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsius, A.; Paré, M.; Munhall, K.G. Forty Years After Hearing Lips and Seeing Voices: The McGurk Effect Revisited. Multisens. Res. 2018, 31, 111–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, A.J.; Backer, K.C.; Rosenblum, L.D.; Kerlin, J.R. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Cross-Modal Phonetic Encoding. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A.; Nicely, P.E. An Analysis of Perceptual Confusions Among Some English Consonants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1955, 27, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Morgan, J.L.; White, K.S. A Statistical Basis for Speech Sound Discrimination. Lang. Speech 2003, 46, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, A.J.; Miller, L.M. Multisensory Integrati3on Enhances Phonemic Restoration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.J.; Bishop, C.W.; Miller, L.M. Neural Mechanisms for Illusory Filling-in of Degraded Speech. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- Elff, M. mclogit: Multinomial Logit Models, with or without Random Effects or Overdispersion. 2021. R Package Version 0.8.7.3. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=mclogit (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Besle, J.; Fort, A.; Delpuech, C.; Giard, M.-H. Bimodal Speech: Early Suppressive Visual Effects in Human Auditory Cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wassenhove, V.; Grant, K.W.; Poeppel, D. Visual Speech Speeds up the Neural Processing of Auditory Speech. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekelenburg, J.J.; Vroomen, J. Neural Correlates of Multisensory Integration of Ecologically Valid Audiovisual Events. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, M. Auditory Event-Related Potentials (ERPs) in Audiovisual Speech Perception. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2009, 52, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatzer, H.; Shen, S.; Kerlin, J.R.; Pitt, M.A.; Shahin, A.J. Neurophysiology Underlying Influence of Stimulus Reliability on Audiovisual Integration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Duede, S.; Hanrahan, S.; Davis, T.; House, P.; Greger, B. Seeing Is Believing: Neural Representations of Visual Stimuli in Human Auditory Cortex Correlate with Illusory Auditory Perceptions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazanfar, A.A. Multisensory Integration of Dynamic Faces and Voices in Rhesus Monkey Auditory Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 25–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, C.; Petkov, C.I.; Logothetis, N.K. Visual Modulation of Neurons in Auditory Cortex. Cerebral Cortex 2008, 18, 1560–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, C.; Logothetis, N.K.; Panzeri, S. Visual Enhancement of the Information Representation in Auditory Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, G.A.; Campbell, R.; Brammer, M.J. Evidence from Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Crossmodal Binding in the Human Heteromodal Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noppeney, U.; Ostwald, D.; Werner, S. Perceptual Decisions Formed by Accumulation of Audiovisual Evidence in Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7434–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanski, L.M. Convergence of Auditory, Visual, and Somatosensory Information in Ventral Prefrontal Cortex. In The Neural Bases of Multisensory Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Romanski, L.M. Prefrontal Neuronal Responses during Audiovisual Mnemonic Processing. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.M.; D’Esposito, M. Perceptual Fusion and Stimulus Coincidence in the Cross-Modal Integration of Speech. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5884–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morís Fernández, L.; Macaluso, E.; Soto-Faraco, S. Audiovisual Integration as Conflict Resolution: The Conflict of the McGurk Illusion: The Conflict of the McGurk Illusion. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5691–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.M. Perceptual Restoration of Missing Speech Sounds. Science 1970, 167, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.M.; Hainsworth, K.R.; Brubaker, B.S.; Bashford, J.A.; Healy, E.W. Spectral Restoration of Speech: Intelligibility Is Increased by Inserting Noise in Spectral Gaps. Percept. Psychophys. 1997, 59, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, A.G. Phonemic Restoration: Insights from a New Methodology. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1981, 110, 474–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, A.G. The Role of Bottom-up Confirmation in the Phonemic Restoration Illusion. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1981, 7, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.M.; Obusek, C.J. Speech Perception and Phonemic Restorations. Percept. Psychophys. 1971, 9, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, G. The Phonemic Restoration Effect: An Insight into the Mechanisms of Speech Perception. Unpublished Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, B. When Is an Illusion Not an Illusion? An Alternative View of the Illusion Concept. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 957740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fixed Effects | ||||||
| Contrast | Effect | RRR | 95% CI (LL) | 95% CI (UL) | z | p |
| Gap vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.47 | −5.21 | <0.001 *** |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 1.53 | 1.14 | 2.04 | 2.86 | 0.004 ** | |
| No Change vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.88 | 0.69 | 1.11 | −1.09 | 0.276 |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 3.86 | 3.14 | 4.73 | 12.89 | <0.001 *** | |
| Other Phoneme vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.49 | 0.39 | 0.63 | −5.56 | <0.001 *** |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 1.41 | 1.09 | 1.83 | 2.62 | 0.009 ** | |
| Random Effects | ||||||
| Intercept (Subject ID) Co-variance Parameters | Gap~1 | NoChange~1 | Other~1 | |||
| Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | |
| Gap~1 | 1.47 | 1.21 | ||||
| No Change~1 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.01 | ||
| Other~1 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| Fixed Effects | ||||||
| Contrast | Effect | RRR | 95% CI (LL) | 95% CI (UL) | z | p |
| Gap vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.35 | −5.54 | <0.001 *** |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 1.81 | 1.26 | 2.59 | 3.22 | 0.001 ** | |
| MoA-Fricative (ref.) | ||||||
| MoA-Liquid | 11.12 | 6.02 | 20.54 | 7.69 | <0.001 *** | |
| MoA-Stop | 2.12 | 1.24 | 3.65 | 2.73 | 0.006 ** | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 1.32 | −0.45 | 0.654 | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Liquid | 1.53 | 0.30 | 7.71 | 0.52 | 0.606 | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| No Change vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.21 | −9.00 | <0.001 *** |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 4.43 | 3.35 | 5.87 | 10.42 | <0.001 *** | |
| MoA-Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| MoA-Liquid | 15.66 | 8.89 | 27.60 | 9.52 | <0.001 *** | |
| MoA-Stop | 16.83 | 11.28 | 25.10 | 13.83 | <0.001 *** | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 2.69 | 1.99 | 3.64 | 6.48 | <0.001 *** | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Liquid | 7.39 | 1.63 | 33.51 | 2.60 | 0.009 ** | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Other Phoneme vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.30 | −7.73 | <0.001 *** |
| Block Type-Pseudoword (ref.) | ||||||
| Block Type-Word | 2.06 | 1.46 | 2.90 | 4.15 | <0.001 *** | |
| MoA-Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| MoA-Liquid | 15.00 | 8.42 | 26.71 | 9.20 | <0.001 *** | |
| MoA-Stop | 6.35 | 4.05 | 9.95 | 8.06 | <0.001 *** | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.62 | 0.91 | 0.364 | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Liquid | 2.50 | 0.53 | 11.83 | 1.15 | 0.249 | |
| Block Type-Word * MoA-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Random Effects | ||||||
| Intercept (Subject ID) Co-variance Parameters | Gap ~1 | No Change ~1 | Other ~1 | |||
| Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | |
| Gap ~1 | 1.72 | 2.63 | ||||
| No Change ~1 | 0.20 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.19 | ||
| Other ~1 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.23 |
| Fixed Effects | ||||||
| Contrast | Effect | RRR | 95% CI (LL) | 95% CI (UL) | z | p |
| Gap vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.35 | −5.56 | <0.001 *** |
| Pseudoword-Fricative (ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 11.10 | 6.01 | 20.51 | 7.69 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 2.12 | 1.23 | 3.64 | 2.72 | 0.006 ** | |
| Word-Fricative | 1.81 | 1.26 | 2.59 | 3.22 | 0.001 ** | |
| Word-Liquid | 30.69 | 6.69 | 140.67 | 4.41 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 1.32 | −0.45 | 0.653 | |
| No Change vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.21 | −9.01 | <0.001 *** |
| Pseudoword-Fricative (ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 15.65 | 8.88 | 27.58 | 9.51 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 16.82 | 11.27 | 25.09 | 13.83 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Fricative | 4.43 | 3.35 | 5.87 | 10.42 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Liquid | 513.19 | 122.58 | 2148.45 | 8.54 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 2.69 | 2.00 | 3.63 | 6.45 | <0.001 *** | |
| Other Phoneme vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.30 | −7.74 | <0.001 *** |
| Pseudoword-Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 14.99 | 8.42 | 26.69 | 9.20 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 6.35 | 4.05 | 9.95 | 8.06 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Fricative | 2.06 | 1.46 | 2.90 | 4.15 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Liquid | 77.24 | 17.76 | 335.97 | 5.80 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.62 | 0.91 | 0.364 | |
| Random Effects | ||||||
| Intercept (Subject ID) Co-variance Parameters | Gap ~1 | No Change ~1 | Other ~1 | |||
| Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | |
| Gap ~1 | 1.69 | 2.44 | ||||
| No Change ~1 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 0.18 | ||
| Other ~1 | 0.36 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.21 |
| Fixed Effects | ||||||
| Contrast | Effect | RRR | 95% CI (LL) | 95% CI (UL) | z | p |
| Gap vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.63 | −3.50 | <0.001 *** |
| Word-Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Fricative | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.79 | −3.21 | 0.001 ** | |
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 6.15 | 3.32 | 11.40 | 5.76 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 1.17 | 0.68 | 2.02 | 0.58 | 0.563 | |
| Word-Liquid | 17.00 | 3.70 | 78.01 | 3.64 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 1.32 | −0.45 | 0.653 | |
| No Change vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.61 | 0.40 | 0.93 | −2.32 | 0.020 * |
| Word-Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Fricative | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.30 | −10.42 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 3.53 | 2.03 | 6.14 | 4.47 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 3.79 | 2.60 | 5.54 | 6.90 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Liquid | 115.76 | 27.83 | 481.56 | 6.53 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 2.69 | 1.99 | 3.64 | 6.45 | <0.001 *** | |
| Other Phoneme vs. /d/t/th/ | Intercept | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.61 | −4.27 | <0.001 *** |
| Word- Fricative(ref.) | ||||||
| Pseudoword-Fricative | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.30 | −4.14 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Liquid | 7.27 | 4.09 | 12.93 | 6.76 | <0.001 *** | |
| Pseudoword-Stop | 3.08 | 1.97 | 4.81 | 4.94 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Liquid | 37.47 | 8.62 | 162.87 | 4.83 | <0.001 *** | |
| Word-Stop | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Syllable-2 (ref.) | ||||||
| Syllable-3 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.62 | 0.91 | 0.364 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, Z.J.; Shahin, A.J.; Bortfeld, H.; Backer, K.C. The McGurk Illusion: A Default Mechanism of the Auditory System. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030510
Iqbal ZJ, Shahin AJ, Bortfeld H, Backer KC. The McGurk Illusion: A Default Mechanism of the Auditory System. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030510
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Zunaira J., Antoine J. Shahin, Heather Bortfeld, and Kristina C. Backer. 2023. "The McGurk Illusion: A Default Mechanism of the Auditory System" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030510
APA StyleIqbal, Z. J., Shahin, A. J., Bortfeld, H., & Backer, K. C. (2023). The McGurk Illusion: A Default Mechanism of the Auditory System. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030510









