Flow Diverter Device-Assisted Coiling Treatment for Cerebral Blister Aneurysm: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Description of the Tubridge FD and Endovascular Treatment
3. Results
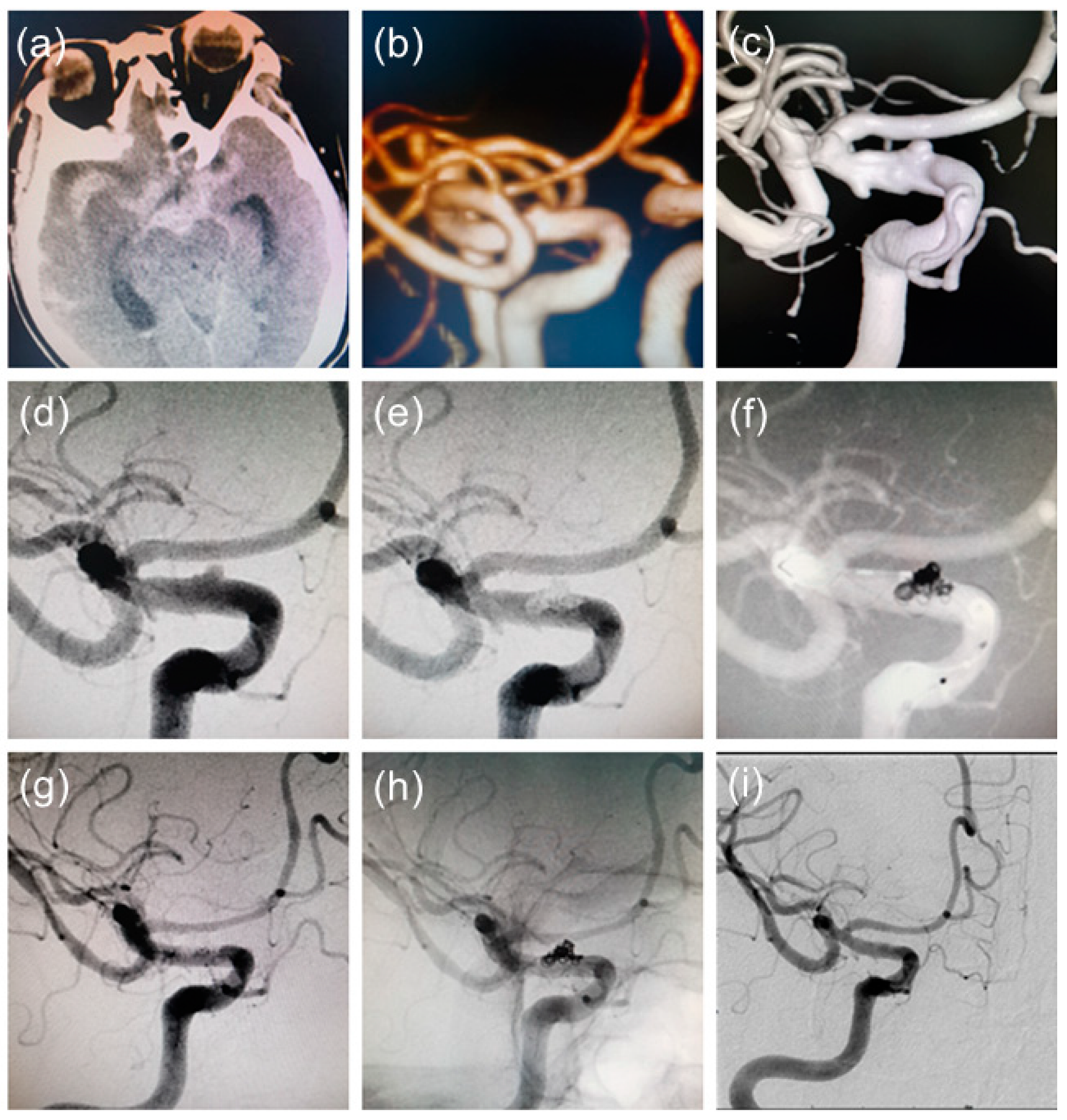
4. Typical Case
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J. Blood blister-like aneurysm with rupture point close to origin of anterior choroidal artery. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2014, 56, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, C.M.; Montemurro, N.; Lawton, M.T. Blister Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery: Microsurgical Results and Management Strategy. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchure, S.D.; Gupta, V.; Goel, G.; Gupta, A.; Jha, A. Subarachnoid hemorrhage with blister aneurysms: Endovascular management. Neurol. India 2014, 62, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çinar, C.; Oran, İ.; Bozkaya, H.; Ozgiray, E. Endovascular treatment of ruptured blister-like aneurysms with special reference to the flow-diverting strategy. Neuroradiology 2013, 55, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitz, G.W.; Sy, C.A.; Grandhi, R. Endovascular treatment of blister aneurysms. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 42, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschillo, S.; Cannizzaro, D.; Caporlingua, A.; Missori, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Treatment and Outcome of Blister-Like Aneurysms. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Gersey, Z.C.; Nuh, M.; Ghonim, H.T.; Elhammady, M.S.; Peterson, E.C. Microsurgical versus endovascular interventions for blood-blister aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: Systematic review of literature and meta-analysis on safety and efficacy. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, G.; Bain, M.; Hussain, M.S.; Moskowitz, S.; Masaryk, T.; Rasmussen, P.; Hui, F. Posterior circulation flow diversion: A single-center experience and literature review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerva, J.D.; Morton, R.P.; Levitt, M.R.; Osbun, J.W.; Ferreira, M.J.; Ghodke, B.V.; Kim, L.J. Pipeline Embolization Device as primary treatment for blister aneurysms and iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms of the internal carotid artery. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchaud, A.; Brinjikji, W.; Cloft, H.J.; Kallmes, D.F. Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Blister-Like Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Focus on Deconstructive versus Reconstructive and Flow-Diverter Treatments. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupon, E.; Garignano, G.; D’Argento, F.; Alexandre, A.; Valente, J.; Trombatore, P.; Pedicelli, A. A revised stent-retriever anchor technique to obtain the distal access through a large or giant aneurysm. Vessel. Plus 2021, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incandela, F.; Craparo, G.; Abrignani, S.; Tessitore, A.; Pitrone, A.; Caranci, F.; Arrichiello, A.; Paolucci, A. Flow diverting devices in acute ruptured blood blister aneurysms: A three centric retrospective study. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, J.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Cho, K.T.; Kim, B.H. Stent-assisted Coiling vs. Flow Diverter for Treating Blood Blister-like Aneurysms: A Proportion Meta-analysis. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2022, 32, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Takemae, T.; Sugita, K. Aneurysms protruding from the dorsal wall of the internal carotid artery. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Wang, K.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of metal coverage rate of flow diversion device on neointimal growth at side branch ostium and stented artery: An animal experiment in rabbit abdominal aorta. Neuroradiology 2012, 54, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.H.; Fang, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, Y.; Hong, B.; Liu, J. A Novel Flow Diverter (Tubridge) for the Treatment of Recurrent Aneurysms: A Single-Center Experience. Korean J Radiol. 2017, 18, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, K.; Arat, A.; Sencer, S.; Hakyemez, B.; Barburoglu, M.; Sencer, A.; İzgi, N. Treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms with flow diverter SILK stents. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Rautio, R.; Valtonen, S.; Haapanen, A. Primary treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms with stent-assisted coil embolization: Report of two cases. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, N.; Miyachi, S.; Tsukamoto, N.; Izumi, T.; Naito, T.; Haraguchi, K.; Wakabayashi, T. Endovascular coil embolization for saccular-shaped blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Kim, B.M.; Suh, S.H.; Jeon, P.; Kim, S.H.; Ihn, Y.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Sim, S.Y.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Reconstructive treatment of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms with stent and coil. Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.; Kim, J.; Suh, S.I.; Kwon, T.H.; Yoon, W. Is Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for the Treatment of Ruptured Blood Blister-Like Aneurysms of the Supraclinoid Internal Carotid Artery Effective? An Analysis of Single Institutional Experience with Pooled Data. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2021, 64, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Fang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Hong, B.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.M. Overlapped Stenting Combined with Coiling for Blood Blister-Like Aneurysms: Comparison of Low-Profile Visualized Intraluminal Support (LVIS) Stent and Non-LVIS Stent. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linfante, I.; Mayich, M.; Sonig, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Siddiqui, A.; Dabus, G. Flow diversion with Pipeline Embolic Device as treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to blister aneurysms: Dual-center experience and review of the literature. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, A.; Nappini, S.; Renieri, L.; Limbucci, N.; Ricciardi, F.; Mangiafico, S. Treatment of two blood blister-like aneurysms with flow diverter stenting. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2012, 4, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasskazoff, S.; Silvaggio, J.; Brouwer, P.A.; Kaufmann, A.; Nistor, A.; Iancu, D. Endovascular treatment of a ruptured blood blister-like aneurysm with a flow-diverting stent. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2010, 16, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princiotta, C.; Dall’olio, M.; Cirillo, L.; Leonardi, M. Staged treatment of a blood blister-like aneurysm with stent-assisted coiling followed by flow diverter in-stent insertion. A case report. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2011, 17, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Cruz, J.P.; Matouk, C.C.; Spears, J.; Marotta, T.R. The pipeline flow-diverting stent for exclusion of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with difficult morphologies. Neurosurgery 2012, 70 (Suppl. 1), ons21–ons28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaney, K.B.; Chalouhi, N.; Viljoen, S.; Smietana, J.; Kung, D.K.; Jabbour, P.; Bulsara, K.R.; Howard, M.; Hasan, D.M. Risk of hemorrhagic complication associated with ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients on dual antiplatelet therapy. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.W.; Khan, A.S.; Barco, R.; Choulakian, A. Pipeline flow diversion of ruptured blister aneurysms of the supraclinoid carotid artery using a single-device strategy. Neurosurg Focus 2017, 42, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Vadasz, A.; Szikora, I. Treatment of ruptured blood blister aneurysms using primary flow-diverter stenting with considerations for adjunctive coiling: A single-centre experience and literature review. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2017, 23, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.D.; Taussky, P.; MacDonald, J.D.; Park, M.S. Rerupture of a Blister Aneurysm After Treatment with a Single Flow-Diverting Stent. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, E634–E638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebral, J.R.; Mut, F.; Raschi, M.; Scrivano, E.; Ceratto, R.; Lylyk, P.; Putman, C.M. Aneurysm rupture following treatment with flow-diverting stents: Computational hemodynamics analysis of treatment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Lv, X. Endovascular treatment of blood blister-like aneurysms of internal carotid artery: Stent-assisted coiling and pipeline flow diversion. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 90, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.W.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Dumont, T.M.; Levy, E.I.; Hopkins, L.N.; Lanzino, G.; Lopes, D.K.; Moftakhar, R.; Billingsley, J.T.; Welch, B.G.; et al. Feasibility and safety of pipeline embolization device in patients with ruptured carotid blister aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2014, 75, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhong, W.; Li, T.; Tan, X.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Flow Diverter-Assisted Coil Embolization of Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm Using Semi-deploying Technique. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 625203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Lin, S.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C. Treatment of Blood Blister Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery with Pipeline-Assisted Coil Embolization: A Single-Center Experience. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 882108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.B.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, P.F.; Zhao, W.Y.; Huang, Q.H.; Hong, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.M. Overlapping stents for blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 123, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, R.J.; Tutino, V.M.; Paliwal, N.; Ma, D.; Davies, J.M.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Compacting a Single Flow Diverter versus Overlapping Flow Diverters for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Computational Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, P.; Duan, G.; Zhao, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q. Safety and Efficacy of Flow Diverter Treatment for Blood Blister-Like Aneurysm: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, e79–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, E.; Piano, M.; Valvassori, L.; Quilici, L.; Pero, G.; Visconti, E.; Boccardi, E. Flow diverter devices in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A single-center experience. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 128, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.M.; Narata, A.P.; Yilmaz, H.; Bijlenga, P.; Radovanovic, I.; Schaller, K.; Lovblad, K.O.; Pereira, V.M. Blood blister-like aneurysms: Single center experience and systematic literature review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient | Age | Gender | Past Medical History | Hunt–Hess Grade | GCS Score | Location | Size (mm, Neck × Dome) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31 | Male | Hypertension, arthrolithiasis (articular gout) | 3 | 11 | Left ICA | 4.6 × 3.2 |
| 2 | 53 | Female | Hypertension | 3 | 10 | Right ICA | 3.2 × 2.3 |
| 3 | 56 | Female | Hypertension | 3 | 9 | Right ICA | 2.5 × 2.0 |
| 4 | 36 | Male | None | 2 | 15 | Left ICA | 3.4 × 2.7 |
| 5 | 45 | Female | Hypertension | 4 | 7 | Left ICA | 3.2 × 1.8 |
| 6 | 51 | Female | Hypertension | 2 | 15 | Right ICA | 2.2 × 1.7 |
| 7 | 54 | Female | Hypertension, coronary heart disease | 3 | 13 | Right ICA | 3.5 × 2.1 |
| 8 | 62 | Male | Hypertension | 3 | 13 | Right ICA | 3.8 × 2.4 |
| Patient | Tubridge FD (mm) | Admission to Treatment (h) | Pre-Operative Antiplatelet Drugs | Post-Operative Antiplatelet Drugs | Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.5 × 25 | 7 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 3 × 60 mm/1.5 × 20 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| 2 | 3.5 × 20 | 9 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 2 × 40 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| 3 | 4.0 × 20 | 7.5 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 1.5 × 40 mm/1 × 20 mm |
| 4 | 4.5 × 25 | 8 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 2 × 40 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| 5 | 3.5 × 15 | 6 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 1.5 × 40 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| 6 | 4.0 × 25 | 10 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 1.5 × 20 mm/1 × 10 mm |
| 7 | 4.0 × 20 | 9 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 2 × 40 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| 8 | 3.5 × 15 | 7.5 | Clopidogrel (300 mg) + Aspirin (300 mg) | Ticagrelor 90 mg (b.i.d.) + Aspirin 100 mg (q.d.) | 2 × 60 mm/1.5 × 20 mm |
| Patient | Raymond Roy Scale at the 2-Week Follow-Up | mRS Score at Discharge | Raymond Roy Scale at the 3-Month Follow-Up | Raymond Roy Scale at the 6-Month to 1-Year Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, W.; Tian, X.; Kang, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, E. Flow Diverter Device-Assisted Coiling Treatment for Cerebral Blister Aneurysm: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030435
Feng W, Tian X, Kang J, Han Z, Chen E. Flow Diverter Device-Assisted Coiling Treatment for Cerebral Blister Aneurysm: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030435
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Wei, Xinhua Tian, Junlong Kang, Zhaowei Han, and E Chen. 2023. "Flow Diverter Device-Assisted Coiling Treatment for Cerebral Blister Aneurysm: A Single-Center Study" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030435
APA StyleFeng, W., Tian, X., Kang, J., Han, Z., & Chen, E. (2023). Flow Diverter Device-Assisted Coiling Treatment for Cerebral Blister Aneurysm: A Single-Center Study. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030435







