The Challenge of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Palsy: A Proposed Method to Identify White Matter Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.3.1. Data Correction
2.3.2. Diffusion Metrics
2.3.3. Whole Brain Tractography
2.3.4. Tractogram Extraction
Automatic Extraction
Atlas-Based Customized Extraction
- Atlas registration
- 2.
- ROI and Bundle Extraction
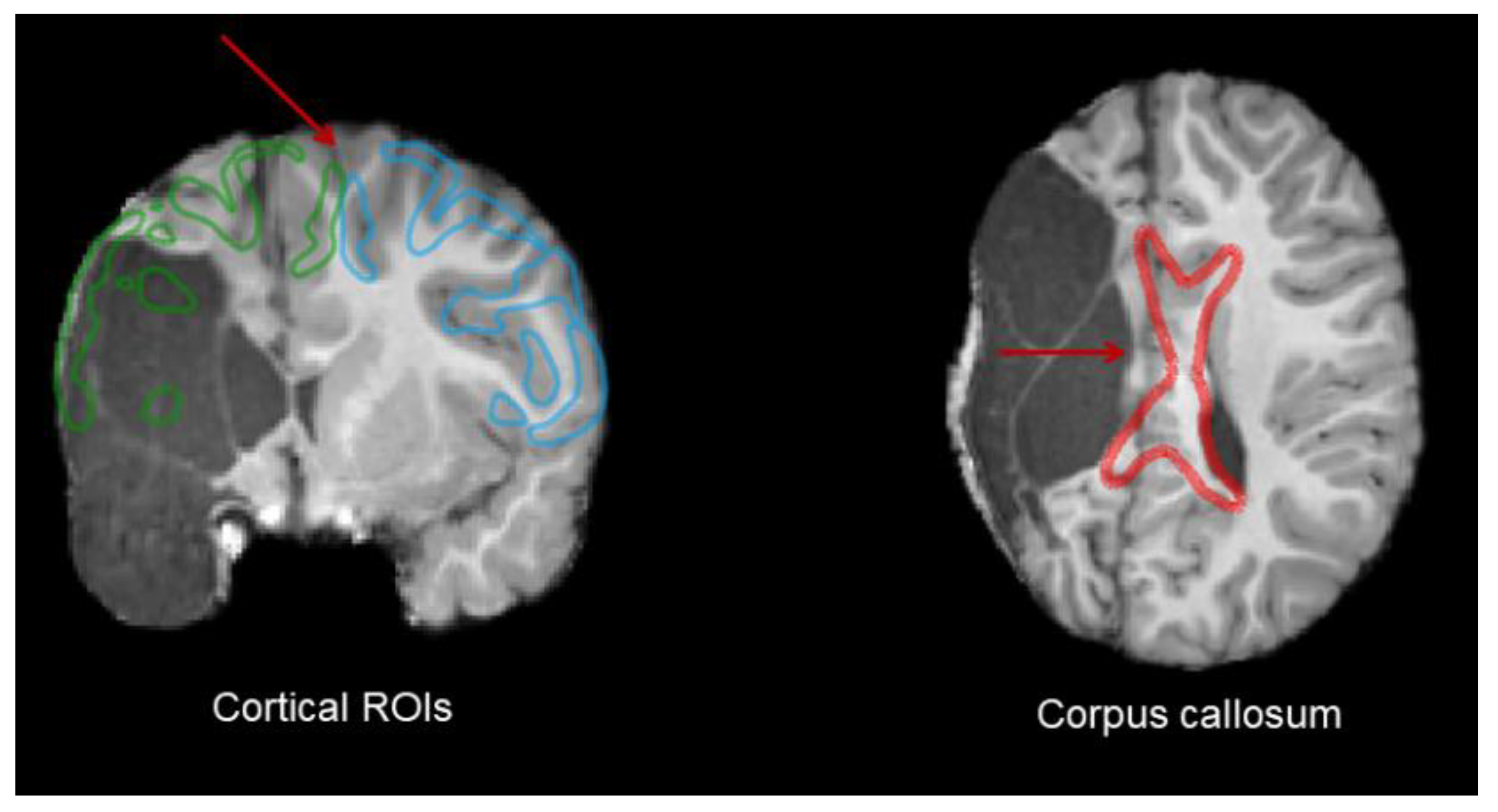
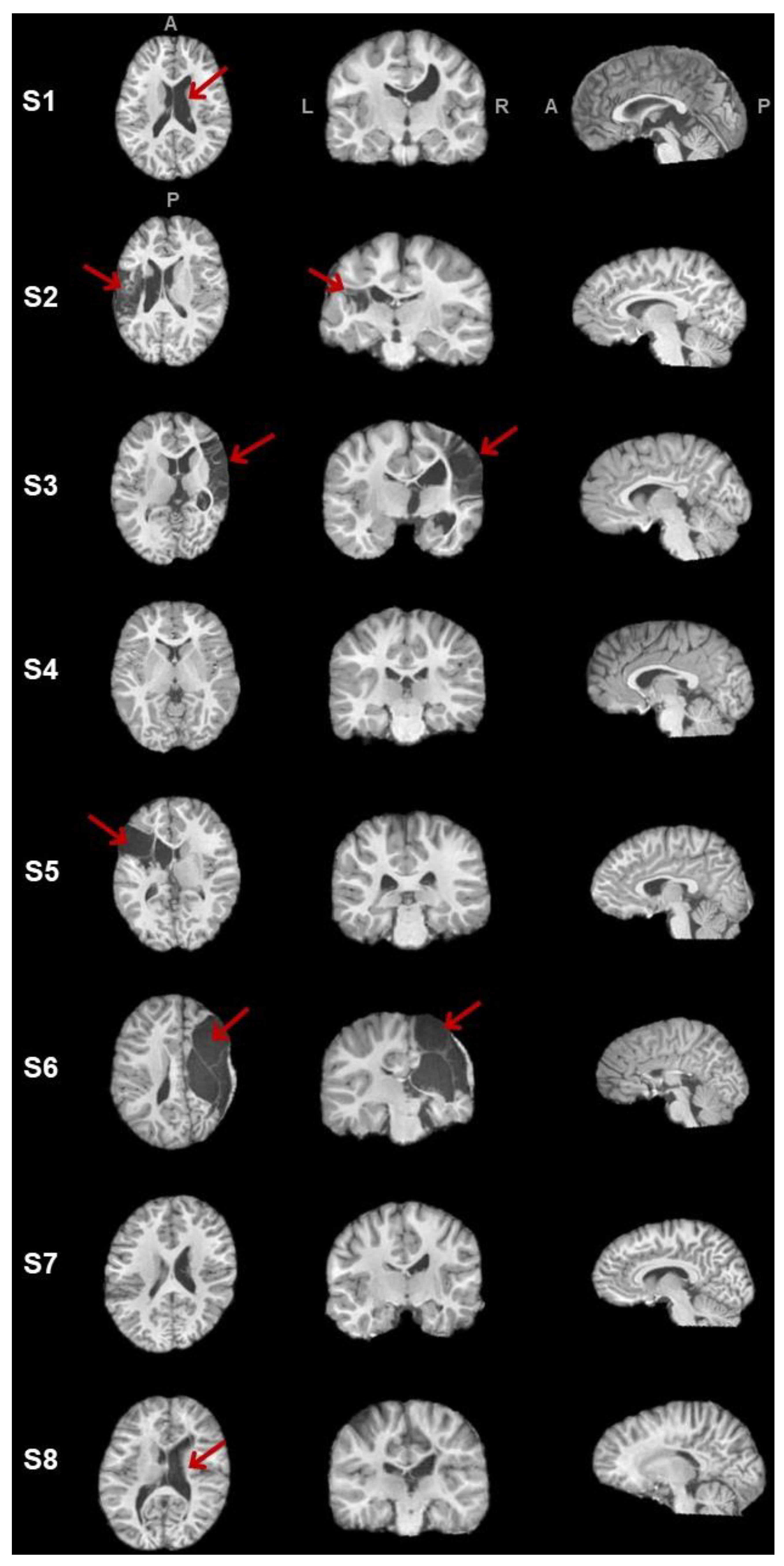
2.4. Lesion Characterization
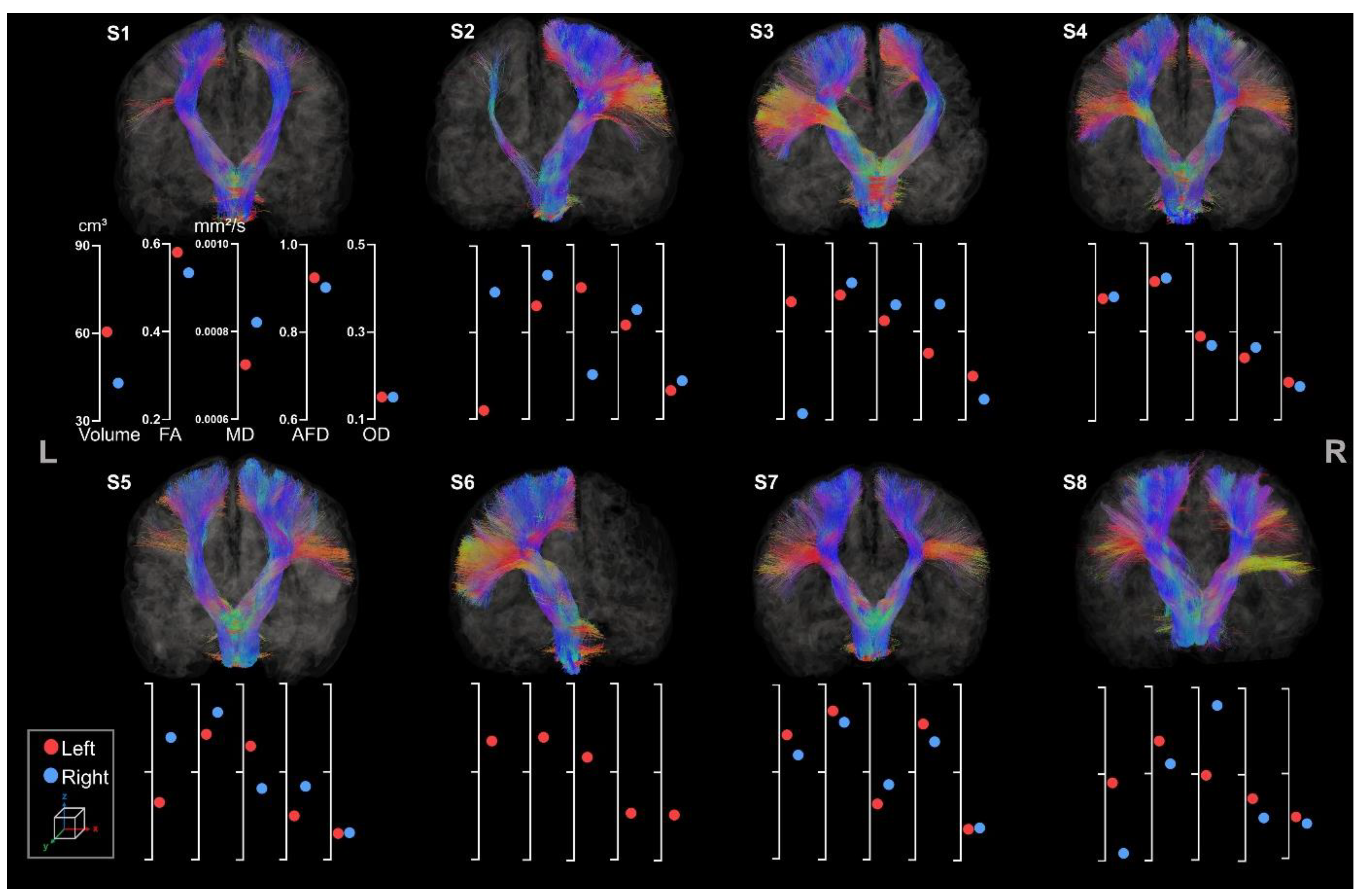
2.5. Tracometry
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Data
3.2. Automatic Tract Extraction
3.2.1. Corticospinal Tracts
3.2.2. Corpus Callosum
3.3. Atlas-Based Tracts Extraction
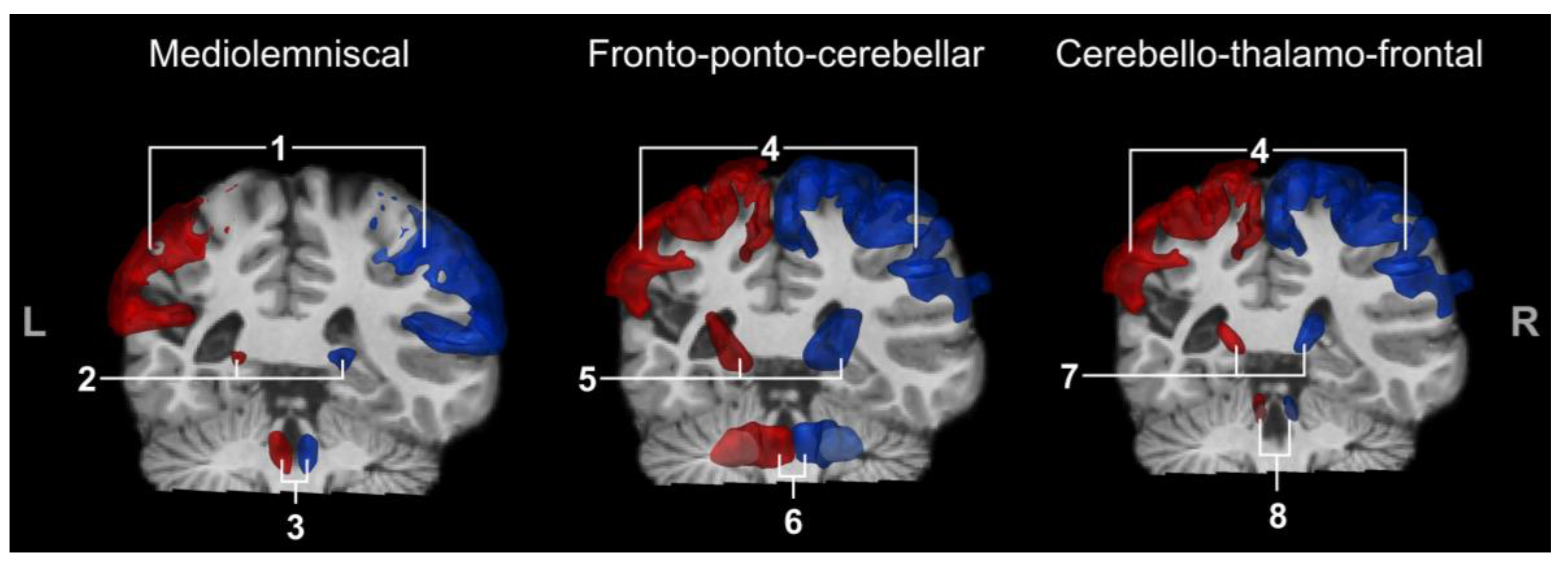
3.3.1. Medio-Lemniscal Tracts Extraction
3.3.2. Fronto-Ponto-Cerebellar Tracts
3.3.3. Cerebello-Thalamo-Frontal Tracts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Shevell, M.; Dagenais, L.; Oskoui, M. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: New perspectives from a Canadian registry. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 20, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskoui, M.; Coutinho, F.; Dykeman, J.; Jetté, N.; Pringsheim, T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2006, 109 (Suppl. S109), 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mailleux, L.; Franki, I.; Emsell, L.; Peedima, M.L.; Fehrenbach, A.; Feys, H.; Ortibus, E. The relationship between neuroimaging and motor outcome in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review—Part B diffusion imaging and tractography. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 97, 103569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailleux, L.; Simon-martinez, C.; Klingels, K.; Jaspers, E. Structural Brain Damage and Upper Limb Kinematics in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.T.; Gutterman, J.; Ferre, C.L.; Chin, K.; Brandao, M.; Gordon, A.M.; Friel, K. Corpus Callosum Integrity Relates to Improvement of Upper-Extremity Function Following Intensive Rehabilitation in Children With Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2021, 35, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.; Robert, M.T.; Friel, K.M.; Gordon, A.M.; Rose, J. Relationship Between Integrity of the Corpus Callosum and Bimanual Coordination in Children With Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NINDS. Cerebral Palsy: Hope Through Research. 2013. Available online: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/hope-through-research/cerebral-palsy-hope-through-research (accessed on 18 September 2023).
- Ashwal, R.S.; Russman, B.S.; Blasco, P.A.; Miller, G.; Sandler, A.; Shevell, M.; Stevenson, R.D. Practice parameter, diagnostic assessment of the child with cerebral palsy, report. Neurology 2004, 62, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of diffusion. Comptes Rendus Seances L’academie Sci. 1985, 301, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu, C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system ± a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Zhang, J. Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research. Neuron 2006, 51, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basser, P.J.; Mattiello, J.; Lebihan, D. MR Diffusion Tensor Spectroscopy and Imaging. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, F.; Peruzzo, C.; Gagliardi, C.; Maghini, P.; Colombo, P.; Servodio Iammarrone, F.; Pierpaoli, C.; Triulzi, F.; Turconi, A.C. Whole-Brain DTI Assessment of White Matter Damage in Children with Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: Evidence of Involvement beyond the Primary Target of the Anoxic Insult. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.M.; Son, S.M. Motor function outcomes of pediatric patients with hemiplegic cerebral palsy after rehabilitation treatment: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczynski, A.M.; Dukelow, S.P.; Hodge, J.A.; Carlson, H.L.; Lebel, C.; Semrau, J.A.; Kirton, A. Corticospinal tract diffusion properties and robotic visually guided reaching in children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanna, A.M.; El-toukhy, N.A.E.; Mousa, A.E.; Megahed, K.F. Does motor deficit in children with cerebral palsy correlate with diffusion tensor metrics abnormalities in thalamocortical pathways? Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyenheuft, Y.; Dricot, L.; Gilis, N.; Kuo, H.-C.; Grandin, C.; Bleyenheuft, C.; Gordon, A.M.; Friel, K.M. Capturing neuroplastic changes after bimanual intensive rehabilitation in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy: A combined DTI, TMS and fMRI pilot study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 43, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickards, T.; Sterling, C.; Taub, E.; Perkins-Hu, C.; Gauthier, L.; Graham, M.; Griffin, A.; Davis, D.; Mark, V.W.; Uswatte, G. Diffusion tensor imaging study of the response to constraint-induced movement therapy of children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy and adults with chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 95, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friel, K.M.; Ching, H.; Carmel, J.B.; Rowny, S.B.; Gordon, A.M. Improvements in hand function after intensive bimanual training are not associated with corticospinal tract dysgenesis in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Exp. Brain Res. 2014, 232, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papadelis, C.; Kaye, H.; Shore, B.; Snyder, B.; Grant, P.E.; Rotenberg, A. Maturation of Corticospinal Tracts in Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy Assessed by Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, K.M.; Emsell, L.; Leemans, A. Quantitative DTI measures. In Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Practical Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.S.; Cheung, M.M.; Chan, K.C.; Wu, E.X. B-value dependence of DTI quantitation and sensitivity in detecting neural tissue changes. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Cercignani, D.K. Twenty-five pitfalls in the analysis of diffusion MRI data. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffelt, D.; Tournier, J.D.; Rose, S.; Ridgway, G.R.; Henderson, R.; Crozier, S.; Salvado, O.; Conelly, A. Apparent Fibre Density: A novel measure for the analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3976–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descoteaux, M. High Angular Resolution Diffusion MRI: From Local Estimation to Segmentation and Tractography. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, Nice, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tournier, D.J.; Calamante, F.; Gadian, D.G.; Connelly, A. Direct estimation of the fiber orientation density function from diffusion-weighted MRI data using spherical deconvolution. NeuroImage 2004, 23, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descoteaux, M.; Deriche, R.; Knösche, T.R.; Anwander, A. Deterministic and Probabilistic Tractography Based on Complex Fibre Orientation Distributions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, S.; Pannek, K.; Pasquariello, R.; Ware, R.S.; Cioni, G.; Rose, S.E.; Boyd, R.N.; Guzzetta, A. Corticopontocerebellar Connectivity Disruption in Congenital Hemiplegia. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, H.; Pannek, K.; Boyd, R.N.; Rose, S.E. Changes in the integrity of thalamocortical connections are associated with sensorimotor deficits in children with congenital hemiplegia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palesi, F.; De Rinaldis, A.; Castellazzi, G.; Calamante, F.; Muhlert, N.; Chard, D.; Tournier, J.D.; Magenes, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A. Contralateral cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways reconstruction in humans in vivo: Implications for reciprocal cerebro-cerebellar structural connectivity in motor and non-motor areas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palesi, F.; De Rinaldis, A.; Castellazzi, G.; Calamante, F.; Muhlert, N.; Chard, D.; Tournier, J.D.; Magenes, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C. Contralateral cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways with prominent involvement of associative areas in humans in vivo. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 3369–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Schneider, T.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Alexander, D.C. NODDI: Practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnozzi, A.M.; Gal, Y.; Boyd, R.N.; Fiori, S.; Fripp, J.; Rose, S.; Dowson, N. The need for improved brain lesion segmentation techniques for children with cerebral palsy: A review. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2015, 47, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northam, G.B.; Chong, W.K.; Wyatt, J.S.; Baldeweg, T. Total Brain White Matter Is a Major Determinant of IQ in Adolescents Born Preterm. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, B.T.; Lang, E.K.; Hilderley, A.J.; Carlson, H.L. Structural connectivity of the sensorimotor network within the non-lesioned hemisphere of children with perinatal stroke. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Horber, V. The role of magnetic resonance imaging in elucidating the pathogenesis of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2007, 49, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franki, I.; Mailleux, L.; Emsell, L.; Peedima, M.L.; Fehrenbach, A.; Feys, H.; Ortibus, E. The relationship between neuroimaging and motor outcome in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review—Part A. Structural imaging. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 100, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tax, C.M.W.; Bastiani, M.; Veraart, J.; Garyfallidis, E.; Irfanoglu, M.O. What’s new and what’s next in diffusion MRI preprocessing. NeuroImage 2022, 249, 118830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theaud, G.; Houde, J.; Bor, A.; Morency, F.; Descoteaux, M. TractoFlow: A robust, efficient, and reproducible diffusion MRI pipeline leveraging Nextflow & Singularity. NeuroImage 2020, 218, 116889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Marques, P.; Alves, V.; Sousa, N. A hitchhiker’s guide to diffusion tensor imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edde, M.; Theaud, G.; Dumont, M.; Theberge, A.; Valcourt-Caron, A.; Gilbert, G.; Houde, J.-C.; Maltais, L.; Rheault, F.; Spagnolo, F. High-frequency longitudinal white matter diffusion- and myelin-based MRI database Reliability and variability. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 3758–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garyfallidis, E.; Brett, M.; Amirbekian, B.; Rokem, A.; Van Der Walt, S. Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2011, 62, 2296–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.-H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualization. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.; Johnson, H. Advanced Normalization Tools (ANTS). Insight J. 2009, 2, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzer, G.M.; Sochat, V.; Bauer, M.W. Singularity: Scientific containers for mobility of compute. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tommaso, C.P.; Chatzou, M.; Floden, E.W.; Barja, P.P.; Palumbo, E.; Notredame, C. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, A.R.; Cieslak, M.; Larsen, B.; Baum, G.L.; Cook, P.A.; Adebimpe, A.; Davila, D.G.; Alliott, M.A.; Jirsaraie, R.; Murtha, K.; et al. Leveraging multi-shell diffusion for studies of brain development in youth and young adulthood. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffelt, D.A.; Smith, R.E.; Ridgway, G.R.; Tournier, J.D.; Vaughan, D.N.; Rose, S.; Henderson, R.; Connelly, A. Connectivity-based fixel enhancement: Whole-brain statistical analysis of diffusion MRI measures in the presence of crossing fibres. NeuroImage 2015, 117, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Acqua, F.; Simmons, A.; Williams, S.C.; Catani, M. Can Spherical Deconvolution Provide More Information Than Fiber Orientations? Hindrance Modulated Orientational Anisotropy, a True-Tract Specific Index to Characterize White Matter Diffusion. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2464–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daducci, A.; Canales-Rodríguez, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Dyrby, T.B.; Alexander, D.C.; Thiran, J. Accelerated Microstructure Imaging via Convex Optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage 2015, 105, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, H.; Caiafa, C.F.; Wandell, B.A.; Pestilli, F. Ensemble Tractography. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, 1004692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theaud, G.; Houde, J.; Boré, A.; Rheault, F.; Morency, F.; Descoteaux, M. TractoFlow-ABS (Atlas-Based Segmentation). bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach Cuadra, M.; Duay, V.; Thiran, J.P. Atlas-based segmentation. In Handbook of Biomedical Imaging: Methodologies and Clinical Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 221–244. [Google Scholar]
- Rheault, F. Analyse et Reconstruction de Faisceaux de la Matière Blanche. Ph.D. Thesis, Computer Science. Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Garyfallidis, E.; Cote, M.-A.; Rheault, F.; Sidhu, J.; Hau, J.; Petit, L.; Fortin, D.; Cunanne, S.; Descoteaux, M. Recognition of white matter bundles using local and global streamline-based registration and clustering. NeuroImage 2018, 170, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, L.M.; Wakana, S.; Van Zijl, P.C.; Nagae-Poetscher, L.M. MRI atlas of human white matter. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1384. [Google Scholar]
- Rheault, M.; Houde, J.C.; Goyette, N.; Morency, F.; Descoteaux, M. MI-Brain, a software to handle tractograms and perform interactive virtual dissection. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Diffusion Study Group Workshop, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, J.L.; Woldorff, M.G.; PArsons, L.M.; Liotti, M.; Freitas, C.S.; Rainey, L.; Kochunov, P.V.; Nickerson, D.; Mikiten, S.A.; Fox, P.T. Automated Talairach Atlas Labels For Functional Brain Mapping. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2000, 10, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.L.; Rainey, L.H.; Summerlin, J.L.; Freitas, C.S.; Fox, P.T.; Evans, A.C.; Toga, A.W.; Mazziotta, J.C. Automated Labeling of the Human Brain: A Preliminary Report on the Development and Evaluation of a Forward-Transform Method. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1997, 5, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharif, N.B.E.A.C.; St-Onge, E.; Vogel, J.W.; Theaud, G. Surface Integration for Connectome Analysis in Age Prediction; OHBM: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garyfallidis, E.; Brett, M.; Correia, M.M.; Williams, G.B.; Nimmo-Smith, I. QuickBundles, a method for tractography simplification. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidzba, K.; Staudt, M.; Wilke, M.; Krageloh-Mann, I. Visuospatial deficits in patients with early left-hemispheric lesions and functional reorganization of language: Consequence of lesion or reorganization? Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, T.T.S. The Neurology of Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1966, 41, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Guzzetta, A.; Pannek, K.; Boyd, R. MRI Structural Connectivity, Disruption of Primary Sensorimotor Pathways, and Hand Function in Cerebral Palsy. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousineau, M. Analyse de Populations Neurodégénératives et Assurance Qualité. Master’s Thesis, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Riffert, T.W.; Schreiber, J.; Anwander, A.; Knösche, T.R. Beyond fractional anisotropy: Extraction of bundle-specific structural metrics from crossing fiber models. NeuroImage 2014, 100, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, K.; Hori, M.; Aoki, S. NODDI in clinical research. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeatman, J.D.; Dougherty, R.F.; Myall, N.J.; Wandell, B.A.; Feldman, H.M. Tract Profiles of White Matter Properties: Automating Fiber-Tract Quantification. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousineau, M.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Garyfallidis, E.; Cote, M.-A.; Morency, F.C.; Rozanski, V.; Grand’Maison, M.; Bedell, B.J.; Descoteaux, M. A test-retest study on Parkinson’s PPMI dataset yields statistically significant white matter fascicles. NeuroImage Clin 2017, 16, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichet Binette, A.; Theaud, G.; Rheault, F.; Roy, M.; Collins, L.D.; Levin, J.; Mori, H.; Hong Lee, J.; Rhys Farlow, M.; Schofield, P.; et al. Bundle specific associations between white matter microstructure and Aβ and tau pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. eLife 2021, 10, e62929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, L.B.; Rose, S.E.; Boyd, R.N. Rehabilitation and neuroplasticity in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2015, 11, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniewski, S.J.; Slaughter, J.; Lenski, M.; Haak, P. The complex aetiology of cerebral palsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2018, 14, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.; Chang, L.-C.; Nayak, A.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Botteron, K.N.; McCracken, J.; McKristry, R.C.; Rivkin, M.J.; Wang, D.J.; Rumsey, J.; et al. The diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) component of the NIH MRI study of normal brain development (PedsDTI). NeuroImage 2016, 124, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannek, K.; Boyd, R.N.; Fiori, S.; Guzzetta, A.; Rose, S.E. Assessment of the structural brain network reveals altered connectivity in children with unilateral cerebral palsy due to periventricular white matter lesions. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, I.; Roebroeck, A.; Bastiani, M.; Jansma, B.; Rubio-Gozalbo, E.; Zhang, H. Assessing Microstructural Substrates of White Matter Abnormalities: A Comparative Study Using DTI and NODDI. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Ricciardi, A.; Brownlee, W.; Kanber, B.; Prados, F.; Collorone, S.; Kaden, E.; Toosy, A.; Alexander, D.C.; Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.; et al. Comparison of Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging and Two-Compartment Spherical Mean Technique Parameter Maps in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 662855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamnes, C.K.; Roalf, D.R.; Goddings, A.; Lebel, C. Diffusion MRI of white matter microstructure development in childhood and adolescence: Methods, challenges and progress. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 33, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, C.; Deoni, S. The development of brain white matter microstructure. NeuroImage 2018, 182, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, K.G.; Rheault, F.; Petit, L.; Hansen, C.B.; Nath, V.; Yeh, F.-C.; Girard, G.; Barakovic, M.; Rafael-Patino, J.; Yu, T.; et al. Tractography dissection variability: What happens when 42 groups dissect 14 white matter bundles on the same dataset? NeuroImage 2021, 243, 118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.J.; Song, G.; Cook, P.A.; Klein, A.; Gee, J.C. A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Song, G.; Das, S.; van Strien, N.; Stone, J.R.; Gee, J.C. The ANTs cortical thickness processing pipeline. Med. Imaging 2013, 8672, 126–129. [Google Scholar]


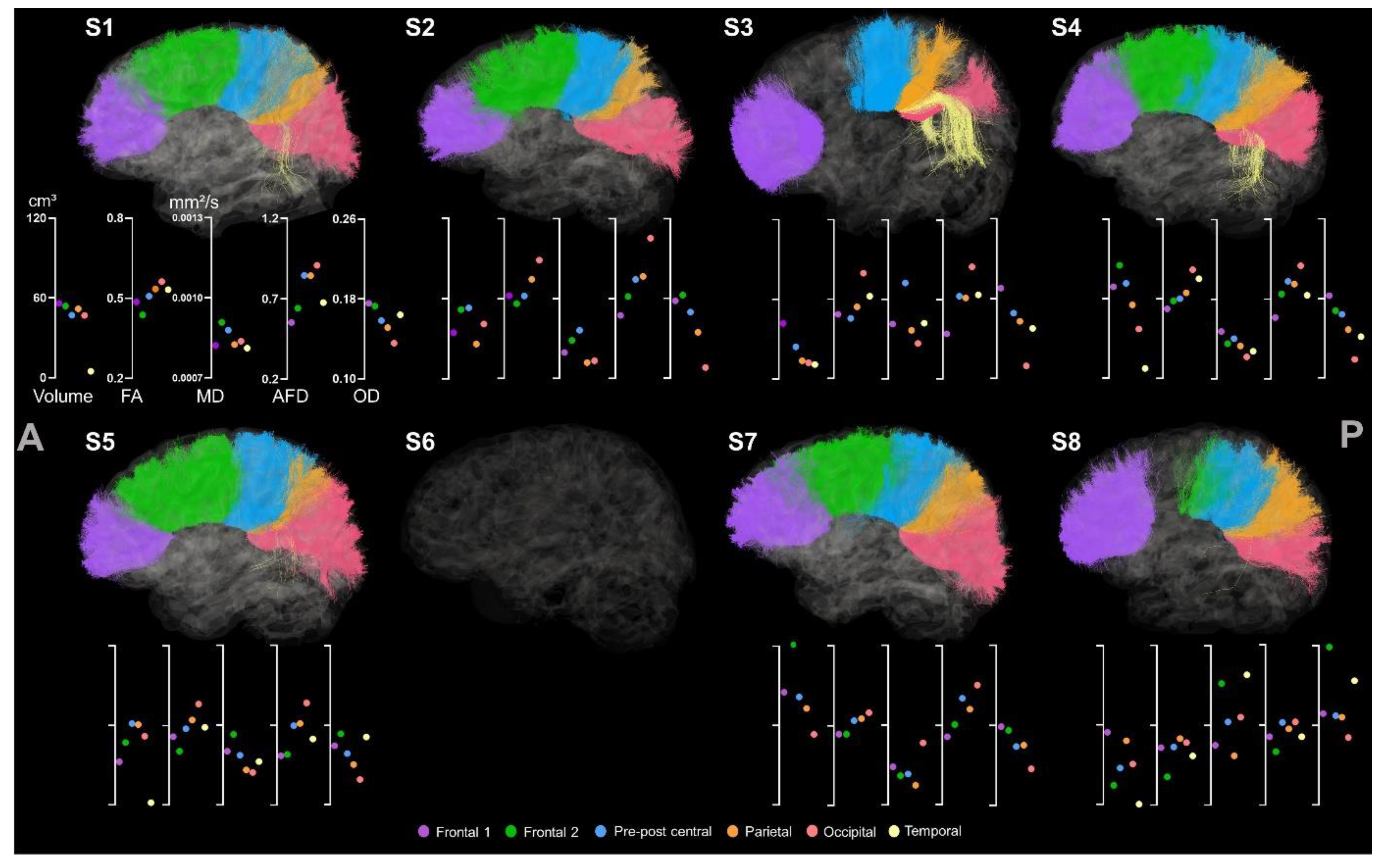
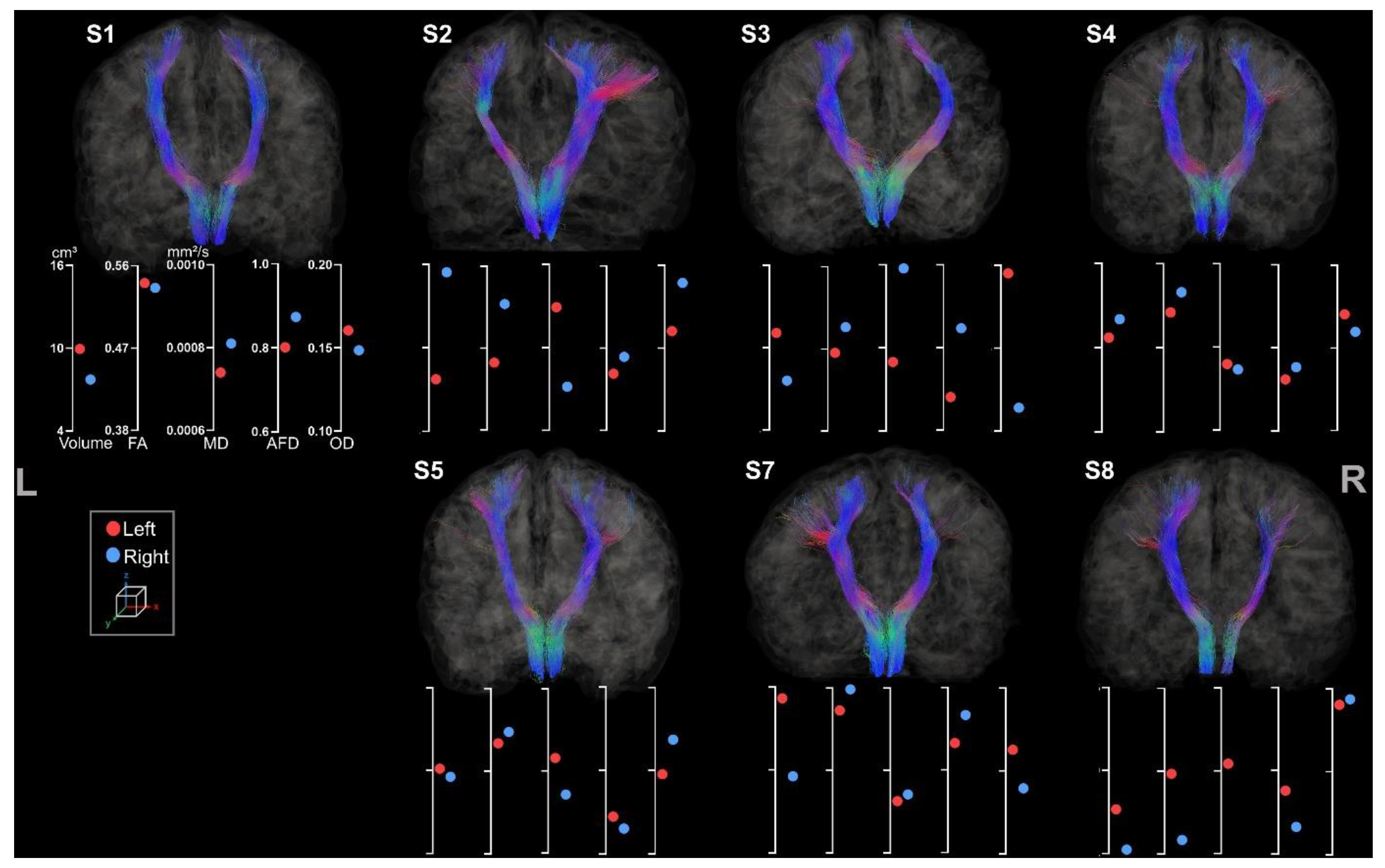
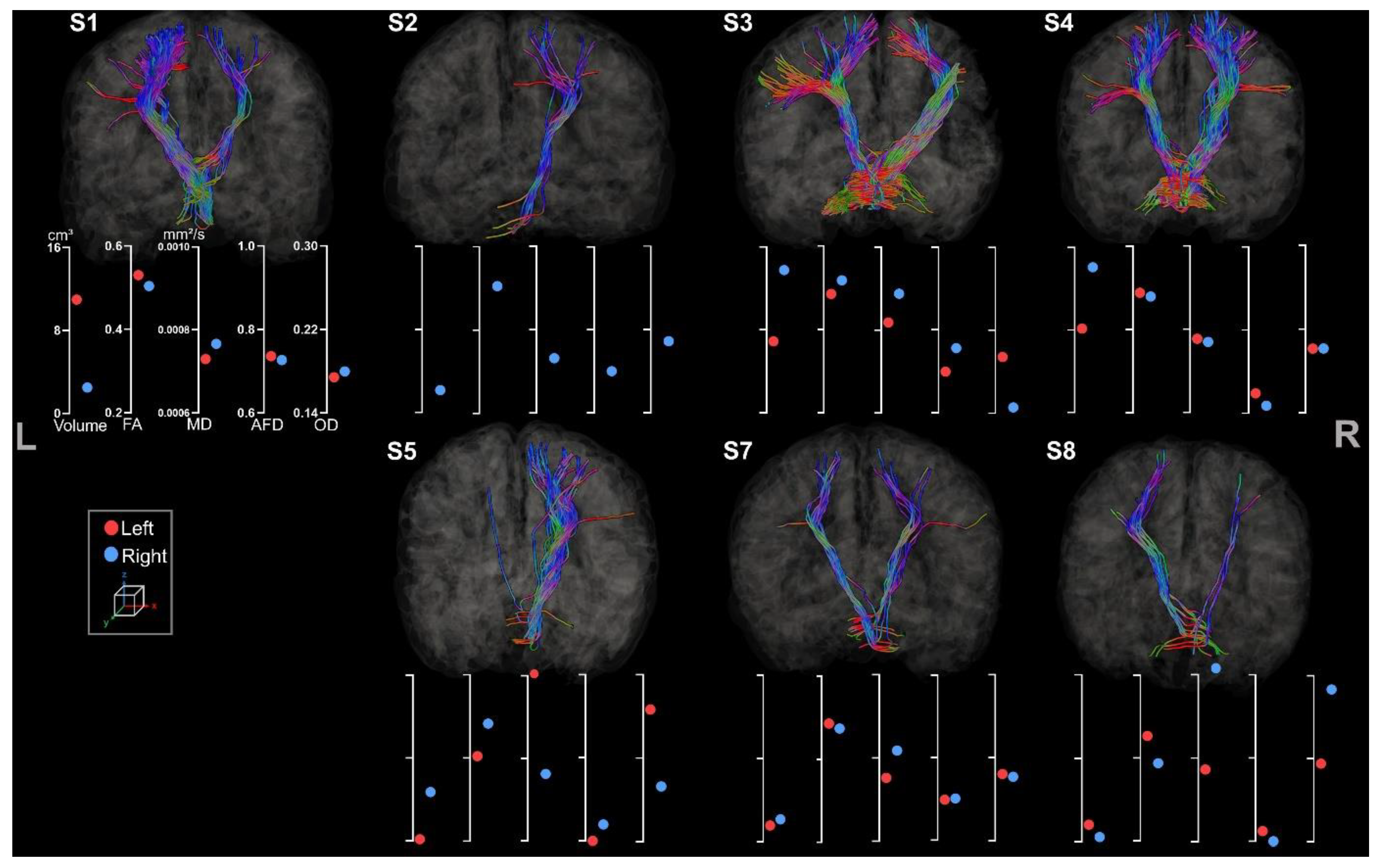

| Sex | Age | Lesion Side | Etiology | MACS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | M | 13 y, 10 m | Right | Pre- or perinatal stroke (undefined) | I |
| S2 | M | 12 y, 5 m | Left | Perinatal stroke | III |
| S3 | F | 8 y, 9 m | Right | Prenatal stroke | II |
| S4 | M | 9 y, 3 m | Right | Unknown | I |
| S5 | F | 11 y, 6 m | Left | Periventricular leukomalacia | II |
| S6 | F | 11 y, 4 m | Right | Prenatal stroke | III |
| S7 | M | 13 y, 3 m | Right | Prenatal stroke | I |
| S8 | F | 11 y, 3 m | Right | Prenatal stroke | II |
| Left Hemisphere Volume | Right Hemisphere Volume | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM | GM | WM | GM | Brain Volume | Tissues Ratio | AI | |
| S1 | 214.6 | 297 | 199.8 | 280.8 | 1166.1 | 1.06 | 0.03 |
| S2 | 145.1 | 204.7 | 232.1 | 293.8 | 1075 | 0.67 | 0.2 |
| S3 | No segmentation | ||||||
| S4 | 202.1 | 274.2 | 202.4 | 275.5 | 1131.5 | 1 | 0 |
| S5 | 152.7 | 249.7 | 215.1 | 304.8 | 1088 | 0.77 | 0.13 |
| S6 | No segmentation | ||||||
| S7 | 237.5 | 307.2 | 219.8 | 282.3 | 1217 | 1.08 | 0.04 |
| S8 | 183.9 | 239 | 165 | 225.8 | 950.9 | 1.08 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinie, O.; Karan, P.; Traverse, E.; Mercier, C.; Descoteaux, M.; Robert, M.T. The Challenge of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Palsy: A Proposed Method to Identify White Matter Pathways. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101386
Martinie O, Karan P, Traverse E, Mercier C, Descoteaux M, Robert MT. The Challenge of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Palsy: A Proposed Method to Identify White Matter Pathways. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(10):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101386
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinie, Ophélie, Philippe Karan, Elodie Traverse, Catherine Mercier, Maxime Descoteaux, and Maxime T. Robert. 2023. "The Challenge of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Palsy: A Proposed Method to Identify White Matter Pathways" Brain Sciences 13, no. 10: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101386
APA StyleMartinie, O., Karan, P., Traverse, E., Mercier, C., Descoteaux, M., & Robert, M. T. (2023). The Challenge of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Palsy: A Proposed Method to Identify White Matter Pathways. Brain Sciences, 13(10), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101386







