Abstract
The aim of the current paper was to present important factors for keeping the basic structures of a person’s brain function, i.e., the grey and white matter, intact. Several lines of evidence have shown that motion, relation, and passion are central factors for preserving the neural system in the grey and white matter during ageing. An active lifestyle has shown to contribute to the development of the central nervous system and to contrast brain ageing. Interpersonal relationships, and interactions, have shown to contribute to complex biological factors that benefit the cognitive resilience to decline. Furthermore, the current scientific literature suggests that passion, strong interest, could be the driving factor motivating individuals to learn new things, thus influencing the development and maintenance of the neural functional network over time. The present theoretical perspective paper aims to convey several key messages: (1) brain development is critically affected by lifestyle; (2) physical training allows one to develop and maintain brain structures during ageing, and may be one of the keys for good quality of life as an older person; (3) diverse stimuli are a key factor in maintaining brain structures; (4) motion, relation, and passion are key elements for contrasting the loss of the grey and white matter of the brain.
Keywords:
grey matter; white matter; motion; physical exercises; relation; passion; interest; learning; cognitive ageing; challenges 1. Introduction
The basic elements of a person’s brain function that changes over the brain development are related to the white and grey matter of the brain [1,2]. The grey matter of the brain is composed by several biological structures, such as neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated cell axons, glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Brain white matter, instead, consists principally of long-reaching myelinated axons [3]. The color difference between these two brain structures is mainly due to the whiteness of the myelin coating the neuron axons.
Several authors have compared the brain to a computer using terminologies borrowed from information technology [4]. From such point of view, it has been sometimes simplified that the grey matter may be considered the processing unit of the brain and the white matter the wires connecting the various parts of the system. The capacity of the nervous system to adjust the organization of the brain structure and function in response to stimuli and experience is called human brain plasticity or neuroplasticity [5]. It may be argued that the neuroplasticity is the mechanism for both development and learning of new skills and knowledge. At the same time, it is the cause of pathology such as, for example, Alzheimer´s disease. This intrinsic property of the nervous system is generally retained throughout a lifespan [6] (pp. 377–378), even though a growing body of literature suggests that factors such as lifestyle and behaviors might significantly affect it [7,8,9].
The brain white matter consists of bundles of axons that are isolated with a layer of lipides (myelin) that carry electric signals between the grey areas of the brain. The myelin layer allows for a fast transmission of the electrical signals through the neuron axons. Fast and effective transmission of the electric signals from one part to another part of the brain is essential to all human cognitive functions and has been shown to be crucial for learning and memory skills [10,11]. Bartzokis [11] argues that both the production and maintenance of myelin is a key factor for typical brain functions. Myelin breakdown may, at the same time, be a causing factor to the pathology of Alzheimer´s disease and ageing. The development of the white and grey matter was studied thoroughly in an important work by Sowell and colleagues [12], examining the lifelong development of the brain structure in individuals aged 7–87 using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It has been shown that white matter is such that it grows to approx. 40 years of age and then it decreases [1,12,13]. It has been proposed that the depletion of brain white matter is possibly connected with the tendency of older adults to become cognitively and physically impaired and slower compared to younger people (see e.g., [14]).
It has been empirically shown that the number of neurons composing the grey matter steadily decline starting from the age of ten [12]. Elimination of neurons and synapses in early adulthood via the process of cortical thinning [15] and shrinkage of large neurons [16] or loss of neurons [17] are responsible for the steady decrease in grey matter while aging.
It has been proposed that the reduction in brain grey matter during the lifespan is related to the efficiency of biological systems. One of the most prominent theories attempting to explain the phenomenon is the Neural Darwinism Theory [18,19,20], according to which only those neurons that are used (activated) survive, while the others atrophy and eventually die. During the early phases of the development of the neural system—the childhood—many neurons are available and the plasticity of these neurons to create networks (and therefore to learn) is high. In this phase, the child is generally exposed to a variety of environmental stimuli and learns many basic skills, and such development is accompanied by biological and structural changes in the developing brain. However, with the formation of neural groups, the less efficient neurons and neural groups die. Only the neural groups that are linked in networks with other neural groups survive this selection, and, therefore, the brain neurons tend over time to be selected for their ability to be inter-connected despite reducing the total number of neural cells. This phenomenon could explain why grey matter is reduced over time, and why empirical functional MRI (fMRI) studies have repeatedly shown that older adults activate, to perform the same task, a larger number of neurons compared to younger people [21,22,23]. The potential principle of neurons elimination based on use is especially important in older people [24]. Older individual exhibit less behavioral and neural plasticity compared to younger individuals [25,26]. Even though the brain of most older adults shows some degree of grey matter loss over time, the size of such change greatly varies between individuals, and medically and cognitively healthier individuals have been found to display a lower degree to brain atrophy compared to less healthy individuals [27]. Such evidence has been used to argue that age alone is not the sole factor defining the development of the brain when aging. It has been experimentally observed that fine motor task and gross motor task performances correlate more in older age groups compared to young [12]. It has been proposed in the scientific literature that this could be one of the reasons why there is a higher relationship between two similar tasks when you are older than when you are younger [14]. As a smaller number of neural networks become available to perform a cognitive or motor task, the human brain uses the same networks when similar tasks are performed. Following the comparison between human brain and computers introduced before, it can be said that with increasing age, the computational power is reduced, with the result of a decline in cognitive and motor skills.
Lifestyle is one of the risk factors for cognitive impairment in normal ageing and neurodegenerative diseases [28,29]. Decreased plasticity and resilience such as in increased neurodegeneration and decreased neuroprotection is another risk factor for the development of cognitive dysfunction [29,30,31]. Research also indicates the important role of diet, endogenous metabolic factors, and emotional stimuli in aging of cognitive and motor functions [32,33,34].
Recent research shows that the most important factor in maintaining the grey and white matter is to make use of brain diverse abilities, and, therefore, to frequently electrically engage brain networks related to this activity. Among the human faculties that have been mostly studied for maintaining a healthy brain during aging are physical exercise regularly, i.e., motion [35,36,37,38], maintain strong relationships with friends or family, i.e., relation [39,40], and learn new things or acquire intellectual challenges, i.e., passion [18,19,24,41,42,43]. In the present article, we will review the evidence available in the scientific literature about the relationship between brain structural physiology development in relation to motion, relation, and passion.
2. Motion
Brain ability to adapt to internal or external conditions is often referred to as brain plasticity. This brain capability to adapt depends on the capacity of the neurons to modify connections and strength relationships between them on both a local and global level within the brain. Long-term potentiation of the efficacy of communication at the synaptic level is one of the physiological bases of training and learning. This phenomenon can be determined by both presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms, and several of these mechanisms have been identified as related to physical activity (see [44]), some examples are: calcium waves due to calcium-induced calcium release (CIRC), from the endoplasmic reticulum [45,46], retrograde transport of proteins [47], mRNA-protein complexes formation and their microtubule-mediated trafficking [48]. These proteins regulate the signaling of synapses to nervous cell nuclei and may be crucial for mediating the activity of the synapses and resulting in the gene expressions that are associated with learning and memory [44]. In line with this idea, a reduced function of the signaling proteins may be associated with brain impairment associated with cognitive problems, psychiatric conditions, and degeneration of the brain tissues [47,49]. In contrast, it has been proposed that an increase in the functions of these proteins could enhance brain function and plasticity, and physical activity may help this process [44].
Other mechanisms that have been suggested to link brain physiological development and physical activity, are brain tissue genesis in reaction to motion, such as gliogenesis, angiogenesis, and synaptogenesis [50].
Furthermore, it has been indicated that physical exercise may increase vascularization of grey matter, as well as the myelination and axonal development in white matter [51].
Several lines of evidence argue in favor of the idea that a positive effect of motion on brain physiology exists [38,52]. Published research has shown that very diverse types of physical training, such as, for example, juggling training [53], mindfulness body–mind training [54], ballet dance training [55], and gymnastic training [56] can all affect brain structure in both grey and white matter. Observational studies have shown that an active lifestyle is helpful for maintaining cognitive and neurological health for all the age groups [57,58]. Greatest effects have been found for higher order processes, such as switching between tasks, working memory and cognitive inhibition [59].
It has been shown that brain white matter in children is more developed for those that exercise more [60], and elderly that exercise more maintain a higher brain functionality compared to those that are less physically active [59]. Cabeza et al. [22] found that active seniors use a larger portion of their brain to solve different tasks than seniors who are less active.
Several intervention studies have confirmed these findings. Aerobic training for six months in a sample of elderly participants (consisting of 1 h of exercise to be performed three times each week) was shown to be effective in increasing grey and white matter [59]. Another study in elderly participants found increased functionality in brain areas related to attention, and regions of the brain related to attention control [61]. The results of these studies provide strong evidence of the role of motion, that is, cardiovascular fitness training, in maintaining and enhancing the structural physiology and functionality of the central nervous system (see [52]).
Recent lines of evidence have suggested that physical exercises influence cognitive performance of elderly individuals on multiple levels, which effectively and sustainably enhance the individual cognitive reserve and show transfer to daily life activities [38]. Enhanced release of brain-derived neurotropic factor with physical activity may be of key importance in this respect [38,62,63].
3. Relation
Studies have indicated that good social relations may inhibit cognitive decline and build cognitive reverse directly and indirectly through various mechanisms [64]. A large number of social ties such as friends, family, and neighbors and their engagements, increase complexity and mental stimulation. Maintaining these relations and creating new ones requires effort and skills. Social relations may therefore enhance cognitive reverse through cognitive strategies, greater neural growth, and synaptic density, which protects against pathological processes [65,66]. Studies suggest that people with poor relationships have poor cognitive functions later in life [67,68,69]. However, there are some inconsistencies in findings as other studies have indicated no relationship between social relations and cognitive function later in life [70,71,72]. Supporting the importance of social relations to cognitive reverse, empirical studies that use magnetic resonance imaging, voxel-based morphometry, and gross stereological analysis have demonstrated that more complex and larger social networks are related to a larger volume of the orbitofrontal cortex and the amygdala. Furthermore, a greater amount of white matter lesions has been observed among people who are more socially inactive [73,74]. Furthermore, more grey matter density in brain regions, such as the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex and ventromedial prefrontal cortex, has been related to larger social networks [73].
Randomized control trials (RCT) demonstrate that social relations may enhance cognitive reverse [52,75]. Interventions that aim to increase social relations in community dwelling people have shown benefits to cognitive functions and brain volume compared to control groups [76,77,78]. Furthermore, it has been argued that interventions that aim to enhance cognitive and physical functions and have shown benefits to cognitive function, also involves social relations [77,78]. Thus, the social elements of the interventions could have contributed to the improvements in cognitive functions [70,79].
Personality traits have been shown to be associated with brain grey matter volume. Personality traits supporting human interactions as extraversion have been positively associated with the development of brain regions involved in social cognition and affective process to be associated with personality traits in young adults [80], while personality traits related to antisocial behavior have been shown to be negatively related to grey matter volume in the prefrontal cortex [81].
Based on the accumulated evidence, it is argued that good social relations are important for cognitive reverse and prevent cognitive decline [40]. However, due to methodological issues such as distinct definitions, measurements, and ambiguity in specific contributors to cognitive functions, more robust evidence (e.g., RCT studies) is needed to demonstrate causality.
4. Passion
Exercising your mind is important to maintain and establish new neural networks or stronger connections between existing neural connections [19,24]. However, keeping your mind active is not done automatically. Based on the principles of neural plasticity, the extension and formations of new synapses is a result of an active mind [24,82]. Research indicates that both younger and older adults show improvements with memory training. However, the effects seem to be quite specific [83]. Recent research demonstrates that greater involvement in serious leisure in older adults turns into greater levels of subjective well-being and harmonious passion [84].
Furthermore, passion is defined as “a strong feeling toward a personally important value/preference that motivates intentions and behaviors to express that value/preference” [85] (p. 9981). An individual’s passion towards a certain theme, topic, ability, or activity is important in maintaining an active mind. Working with and practicing in the activity through deliberate practice is important, but also relatable to principles of neural plasticity (i.e., use it or lose it, repetition; [24,86]). Former studies have shown that passion is related to more deliberate practice among football players and related to better well-being and better performance among workers [85,87,88]. Based on these findings, it can be argued that passion is important in maintaining principles of neural plasticity, i.e., the passion circle (see for overview [43]). Hence repetition, use it or lose it, use it and improve it and intensity [24]. An example could be learning a second language, which is important for grey matter [37,89]. Being passionate about language and acquiring new languages could motivate the individual to spend more time practicing a second language and thus strengthen the grey matter, the neural cells, and their connections [19]. Furthermore, studies have shown that harmonious passionate individuals have more positive experiences learning a second language [90]. As a result, individuals with passion for language could engage in more deliberate practice, which is closely related to the principles of neural plasticity [24,91]. Strong interest “passion” may be considered the key factor for taking new challenges, learning new things, and the necessary amount of training and repetition needed for developing the skill or knowledge [42,43,86,92,93,94,95].
Furthermore, psychological traits associated with passion—such as grit and growth mindset—have shown to be related to the development of the grey matter in various parts of the brain [96].
It is worth noting that recent research indicates that impaired motor function, antisocial behavior, depression, and anhedonia are common prodromal presentations of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders as well as normal ageing [97,98,99,100]. It could be looked upon as a vicious circle. Less passion less motion may be promoting less relation and less well-being. Sigmundsson et al., [92] argue that passion for area, theme, and skill is a basic motivational factor together with grit and mindset. Passion gives direction to the area of interest, which could be related to the dopamine system [101], which is central in attention, learning, goal-directed behaviors, and rewards [94]. Passion may be providing the focus essential for long-term goal achievement [92] (see Figure 1).
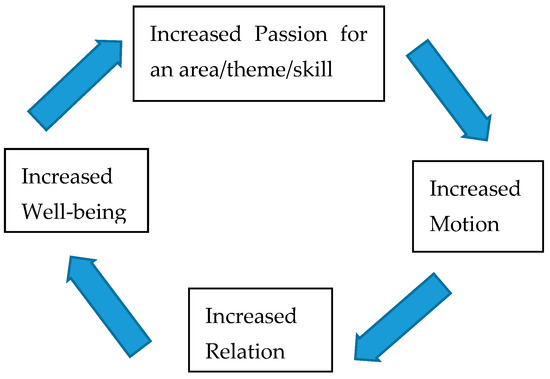
Figure 1.
Passion, motion, relation, well-being circle.
5. Limitations and Future Directions
We believe the present article summarizes quite an extensive body of literature and proposes an interesting overarching perspective on how different lifestyles and individual differences may be responsible for optimally developing and maintaining key brain structures. However, our study—due to its general and inclusive focus—does not systematically scrutinize the vast body of literature on different lifestyles and brain structure development and ageing. Future theoretical studies should attempt to summarize the existing literature in a further comprehensive and systematic manner.
Future studies should empirically test how motion, relation, and passion may be causally linked to brain development and a favorable ageing process of brain structures. These studies should attempt to obtain high-quality scientific evidence, e.g., employing RCTs.
6. Conclusions
The key message in this theoretical perspective article is that we can have an effect on our brain development and ageing. In this context, it is important that our brain functions are continuously trained. Motion (physical exercise), relation (social interactions), and passion (learning new things) are key elements for contrasting the loss of the grey and white matter of the brain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: H.S., S.G.; Writing-original draft preparation, H.S., B.H.D., S.G.; writing—review and editing, H.S., S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Giorgio, A.; Santelli, L.; Tomassini, V.; Bosnell, R.; Smith, S.; De Stefano, N.; Johansen-Berg, H. Age-related changes in grey and white matter structure throughout adulthood. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R.; Albert, M.; Belleville, S.; Craik, F.I.M.; Duarte, A.; Grady, C.L.; Lindenberger, U.; Nyberg, L.; Park, D.C.; Reuter-Lorenz, P.A.; et al. Maintenance, reserve and compensation: The cognitive neuroscience of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principles of Neural Science; Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; Siegelbaum, S.; Hudspeth, A.J.; Mack, S. (Eds.) McGraw-hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 4, pp. 1227–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Shagrir, O. Why we view the brain as a computer. Synthese 2006, 153, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Yin, X.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Evans, A.C.; Jiang, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. The Plasticity of Brain Gray Matter and White Matter following Lower Limb Amputation. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 823185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Amedi, A.; Fregni, F.; Merabet, L.B. The plastic human brain cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci 2005, 28, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaynman, S.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Revenge of the “sit”: How lifestyle impacts neuronal and cognitive health through molecular systems that interface energy metabolism with neuronal plasticity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falck, R.S.; Davis, J.C.; Liu-Ambrose, T. What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C. Lifestyle modulators of neuroplasticity: How physical activity, mental engagement, and diet promote cognitive health during aging. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 3589271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmithorst, V.J.; Wilke, M.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Holland, S.K. Cognitive functions correlate with white matter architecture in a normal pediatric population: A diffusion tensor MRI study. Hum. Brainmapping 2005, 26, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzokis, G. Age-related myelin breakdown: A developmental model of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowell, E.R.; Peterson, B.S.; Thompson, P.M.; Welcome, S.E.; Henkenius, A.L.; Toga, A.W. Mapping cortical change across the human life span. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Grossman, R.I.; Babb, J.S.; Rabin, M.L.; Mannon, L.J.; Kolson, D.L. Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: Volumetric MR imaging analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leversen, J.S.; Haga, M.; Sigmundsson, H. From children to adults: Motor performance across the life-span. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, S.J.; Monk, C.S.; Nelson, C.A. Mechanisms of postnatal neurobiological development: Implications for human development. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2001, 19, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Morrison, J.H.; Rosene, D.L.; Hyman, B.T. Are neurons lost from the primate cerebral cortex during normal aging? Cereb. Cortex 1998, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, E.; Luiten, P.G. Cerebral microvascular pathology in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 575–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, G.M. Neural Darwinism: The Theory of Neuronal Group Selection; Basic Books; American Psychological Association (APA): Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Edelman, G.M. Bright Air, Brilliant Fire: On the Matter of the Mind; Basic books; American Psychological Association (APA): Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Edelman, G.M. Neural Darwinism: Selection and reentrant signaling in higher brain function. Neuron 1993, 10, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R. Hemispheric Asymmetry Reduction in Older Adults: The HAROLD Model. Psych Aging 2002, 17, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R.; Anderson, N.D.; Locantore, J.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Aging Gracefully: Compensatory Brain Activity in High-Performing Older Adults. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.S. Compensatory mechanisms in the aging motor system. Ageing Res. Rev. 2006, 5, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.A.; Jones, T.A. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: Implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes, P.B. Theoretical Propositions of Life-Span Developmental Psychology. Dev. Psych. 1987, 2, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.N.; Barnes, C.A. Neural plasticity in the ageing brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosc. 2006, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, S.M.; Pham, D.L.; Kraut, M.A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Davatzikos, C. Longitudinal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies of Older Adults: A Shrinking Brain. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3295–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the etiological links behind neurodegenerative diseases: Inflammatory cytokines and bioactive kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onchev, G. Changes in Psychopathology and Mental Health Resilience. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 676492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of Special Issue ‘Dissecting Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Diseases: Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection’. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, M.; Badesso, S.; Lorenzo, E.; Guruceaga, E.; Pérez-Mediavilla, A.; García-Osta, A.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M. Identifying the Main Functional Pathways Associated with Cognitive Resilience to Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepsomali, P.; Coxon, C. Inflammation and diet: Focus on mental and cognitive health. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. Off. Organ Wroc. Med. Univ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, D.; Tuka, B.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L.; Telegdy, G. Memory enhancement with kynurenic acid and its mechanisms in neurotransmission. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Cardellicchio, P.; Di Fazio, C.; Nazzi, C.; Fracasso, A.; Borgomaneri, S. The Influence of Vicarious Fear-Learning in “Infecting” Reactive Action Inhibition. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 946263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Sommerlad, A.; Orgeta, V.; Costafreda, S.G.; Huntley, J.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet 2017, 390, 2673–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation. Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Joyner, M.J.; Jack, C.R. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Brain Volumes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, F.; Hamacher, D.; Schega, L.; Müller, N.G. Thinking while moving or moving while thinking–concepts of motor-cognitive training for cognitive performance enhancement. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.S.; Landis, K.R.; Umberson, D. Social relationships and health. Science 1988, 241, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P. The Compassionate Mind; Robinson: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zatorre, R.J. Predispositions and plasticity in music and speech learning: Neural correlates and implications. Science 2013, 342, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Haga, M.; Hermundsdottir, F. The passion scale: Aspects of reliability and validity of a new 8-item scale assessing passion. New Ideas Psychol. 2020, 56, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Haga, M.; Hermundsdottir, F. Passion, grit and mindset in young adults: Exploring the relationship and gender differences. New Ideas Psychol. 2020, 59, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liegro, C.M.; Schiera, G.; Proia, P.; Di Liegro, I. Physical activity and brain health. Genes 2019, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.F.Y.; Lim, W.L.; Ch’ng, T.H. Activity-dependent synapse to nucleus signaling. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 138, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bading, H. Nuclear calcium signalling in the regulation of brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Damas, A.; Saura, C.A. Synapse-to-nucleus signaling in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Liegro, C.M.; Schiera, G.; Di Liegro, I. Regulation of mRNA transport, localization and translation in the nervous system of mammals. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcello, E.; Di Luca, M.; Gardoni, F. Synapse-to-nucleus communication: From developmental disorders to Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayes, J.; Harasym, D.; Turco, C.V.; Locke, M.B.; Nelson, A.J. Exercise-induced neuroplasticity: A mechanistic model and prospects for promoting plasticity. Neurosci. 2019, 25, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Fields, R.D.; Johansen-Berg, H. Plasticity in gray and white: Neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-X.; Xu, W.; Pei, J.-J. Leisure activities, cognition and dementia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganski, B.; Gaser, C.; Busch, V.; Schuierer, G.; Bogdahn, U.; May, A. Changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature 2004, 427, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Y.; Lu, Q.; Fan, M.; Yang, Y.; Posner, M.I. Mechanisms of white matter changes induced by meditation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10570–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänggi, J.; Koeneke, S.; Bezzola, L.; Jäncke, L. Structural neuroplasticity in the sensorimotor network of professional female ballet dancers. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Lu, M.; Song, Z.; Wang, J. Long-term intensive training induced brain structural changes in world class gymnasts. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddock, L.; Voss, M.W.; Kramer, A.F. Physical activity and fitness effects on cognition and brain health in children and older adults. Kinesiol. Rev. 2012, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.F.; Colcombe, S. Fitness effects on the cognitive function of older adults: A meta-analytic study—Revisited. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 13, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colcombe, S.J.; Erickson, K.I.; Scalf, P.E.; Kim, J.S.; Prakash, R.; McAuley, E.; Elavsky, S.; Marquez, D.X.; Hu, L.; Kramer, A.F. Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddock-Heyman, L.; Erickson, K.I.; Kienzler, C.; Drollette, E.S.; Raine, L.B.; Kao, S.C.; Bensken, J.; Weisshappel, R.; Castelli, D.M.; Hillman, C.H.; et al. Physical activity increases white matter microstructure in children. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colcombe, S.J.; Kramer, A.F.; Erickson, K.I.; Scalf, P.; McAuley, E.; Cohen, N.J.; Webb, A.; Jerome, G.J.; Marquez, D.X.; Elavsky, S. Cardiovascular fitness, cortical plasticity, and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3316–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaepen, K.; Goekint, M.; Heyman, E.M.; Meeusen, R. Neuroplasticity—Exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 765–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, G.G.; Almondes, K.M.D. Exercise-dependent BDNF as a modulatory factor for the executive processing of individuals in course of cognitive decline. A systematic review. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.E.; Duff, H.; Kelly, S.; McHugh Power, J.E.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A.; Loughrey, D.G. The impact of social activities, social networks, social support and social relationships on the cognitive functioning of healthy older adults: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Tang, Y.; Arnold, S.E.; Wilson, R.S. The effect of social networks on the relation between Alzheimer’s disease pathology and level of cognitive function in old people: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratiglioni, L.; Paillard-Borg, S.; Winblad, B. An active and socially integrated lifestyle in late life might protect against dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, L.L.; Mendes de Leon, C.F.; Wilson, R.S.; Bienias, J.L.; Evans, D.A. Social resources and cognitive decline in a population of older African Americans and whites. Neurology 2004, 63, 2322–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Hamer, M.; McMunn, A.; Steptoe, A. Social Isolation and Loneliness: Relationships With Cognitive Function During 4 Years of Follow-up in the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Psychosom. Med. 2013, 75, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunzunegui, M.-V.; Alvarado, B.E.; Del Ser, T.; Otero, A. Social Networks, Social Integration, and Social Engagement Determine Cognitive Decline in Community-Dwelling Spanish Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2003, 58, S93–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsen, M.J.; Smits, C.H.M.; van Tilburg, T.; Knipscheer, K.C.P.M.; Deeg, D.J.H. Activity in Older Adults: Cause or Consequence of Cognitive Functioning? A Longitudinal Study on Everyday Activities and Cognitive Performance in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2002, 57, P153–P162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.; Hardy, R.; Wadsworth, M.E.J. Does active leisure protect cognition? Evidence from a national birth cohort. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 56, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, T.E.; Lusignolo, T.M.; Albert, M.; Berkman, L. Social relationships, social support, and patterns of cognitive aging in healthy, high-functioning older adults: MacArthur Studies of Successful Aging. Health Psychol. 2001, 20, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickart, K.C.; Wright, C.I.; Dautoff, R.J.; Dickerson, B.C.; Barrett, L.F. Amygdala volume and social network size in humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Joo, W.; Youm, Y.; Chey, J. Social brain volume is associated with in-degree social network size among older adults. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaffe, K.; Hoang, T. Nonpharmacologic Treatment and Prevention Strategies for Dementia. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, H.H.; Kadowaki, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Sekikawa, A.; Ueshima, H. Cognitive Impairment as a Strong Predictor of Incident Disability in Specific ADL-IADL Tasks Among Community-Dwelling Elders: The Azuchi Study. Gerontologist 2005, 45, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, J.A.; Ding, D.; Borenstein, A.R.; DeCarli, C.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chu, S. Changes in Brain Volume and Cognition in a Randomized Trial of Exercise and Social Interaction in a Community-Based Sample of Non-Demented Chinese Elders. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 30, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkala, K.H.; Routasalo, P.; Kautiainen, H.; Sintonen, H.; Tilvis, R.S. Effects of Socially Stimulating Group Intervention on Lonely, Older People’s Cognition: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 19, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toepoel, V. Ageing, Leisure, and Social Connectedness: How could Leisure Help Reduce Social Isolation of Older People? Soc. Indic. Res. 2013, 113, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Huo, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Long, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, L.; et al. Relationship between personality and gray matter volume in healthy young adults: A voxel-based morphometric study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, A.; Lencz, T.; Bihrle, S.; LaCasse, L.; Colletti, P. Reduced prefrontal gray matter volume and reduced autonomic activity in antisocial personality disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, M.; Pedersen, A.V.; Sigmundsson, H. Interrelationship among selected measures of motor skills. Child Care Health Dev. 2008, 34, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, A.S.; Bäkman, L. Long-Term Maintenance of Gains From Memory Training in Older Adults: Two 3½Year Follow-up Studies. J. Gerontol. 1993, 48, P233–P237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doistua, J.; Lazcano, I.; Madariaga, A. Serious Leisure and Passion in University Programs for Seniors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachimowicz, J.M.; Wihler, A.; Bailey, E.R.; Galinsky, A.D. Why grit requires perseverance and passion to positively predict performance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9980–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Trana, L.; Polman, R.; Haga, M. What is trained develops! theoretical perspective on skill learning. Sports 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verner-Filion, J.; Vallerand, R.J.; Amiot, C.E.; Mocanu, I. The two roads from passion to sport performance and psychological well-being: The mediating role of need satisfaction, deliberate practice, and achievement goals. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2017, 30, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T.; Hill, A.P.; Appleton, P.R.; Vallerand, R.J.; Standage, M. The psychology of passion: A meta-analytical review of a decade of research on intrapersonal outcomes. Motiv. Emot. 2015, 39, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling, R.; Amprosi, M.; Kremmel, B.; Bsteh, G.; Eberharter, K.; Zehentner, M.; Steiger, R.; Tuovinen, N.; Gizewski, E.R.; Benke, T.; et al. Second language learning induces grey matter volume increase in people with multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Vallerand, R.J.; Padilla, A.M. On the Role of Passion in Second Language Learning and Flourishing. J. Happiness Stud. 2021, 22, 2761–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, R.J.; Salvy, S.J.; Mageau, G.A.; Elliot, A.J.; Denis, P.L.; Grouzet, F.M.; Blanchard, C. On the role of passion in performance. J. Personal. 2007, 75, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Haga, M.; Elnes, M.; Dybendal, B.H.; Hermundsdottir, F. Motivational Factors Are Varying across Age Groups and Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmundsson, H. Passion, grit and mindset in the ages 14 to 77: Exploring relationship and gender differences. New Ideas Psychol. 2021, 60, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Guðnason, S.; Jóhannsdóttir, S. Passion, grit and mindset: Exploring gender differences. New Ideas Psychol. 2021, 63, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Dybendal, B.H.; Loftesnes, J.M.; Olafsson, B.; Grassini, S. Passion a key for success: Exploring motivational factors in football players. New Ideas Psychol. 2022, 65, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, X.; He, M.; Gong, Q. Neuroanatomical correlates of grit: Growth mindset mediates the association between gray matter structure and trait grit in late adolescence. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Fabius, J.H.; Moravkova, K.; Fracasso, A.; Borgomaneri, S. The neurobiological correlates of gaze perception in healthy individuals and neurologic patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. Recent advances in the study of the comorbidity of depressive and anxiety disorders. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Yang, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q. Aberrant Structure MRI in Parkinson’s Disease and Comorbidity with Depression Based on Multinomial Tensor Regression Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Spekker, E.; Szabó, Á.; Polyák, H.; Vécsei, L. Modelling the neurodevelopmental pathogenesis in neuropsychiatric disorders. Bioactive kynurenines and their analogues as neuroprotective agents—in celebration of 80th birthday of Professor Peter Riederer. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, C.A.; McCaul, M.E.; Wong, D.F.; Oswald, L.M.; Zhou, Y.; Brasic, J.; Kuwabara, H.; Kumar, A.; Alexander, M.; Ye, W.; et al. Sex differences in striatal dopamine release in healthy adults. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).