Assessment of Diaphragm in Hemiplegic Patients after Stroke with Ultrasound and Its Correlation of Extremity Motor and Balance Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Selection
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Assessments
Ultrasonographic Assessment for Diaphragm
2.4. Assessment of Other Parameters
2.5. Sample Size Calculation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
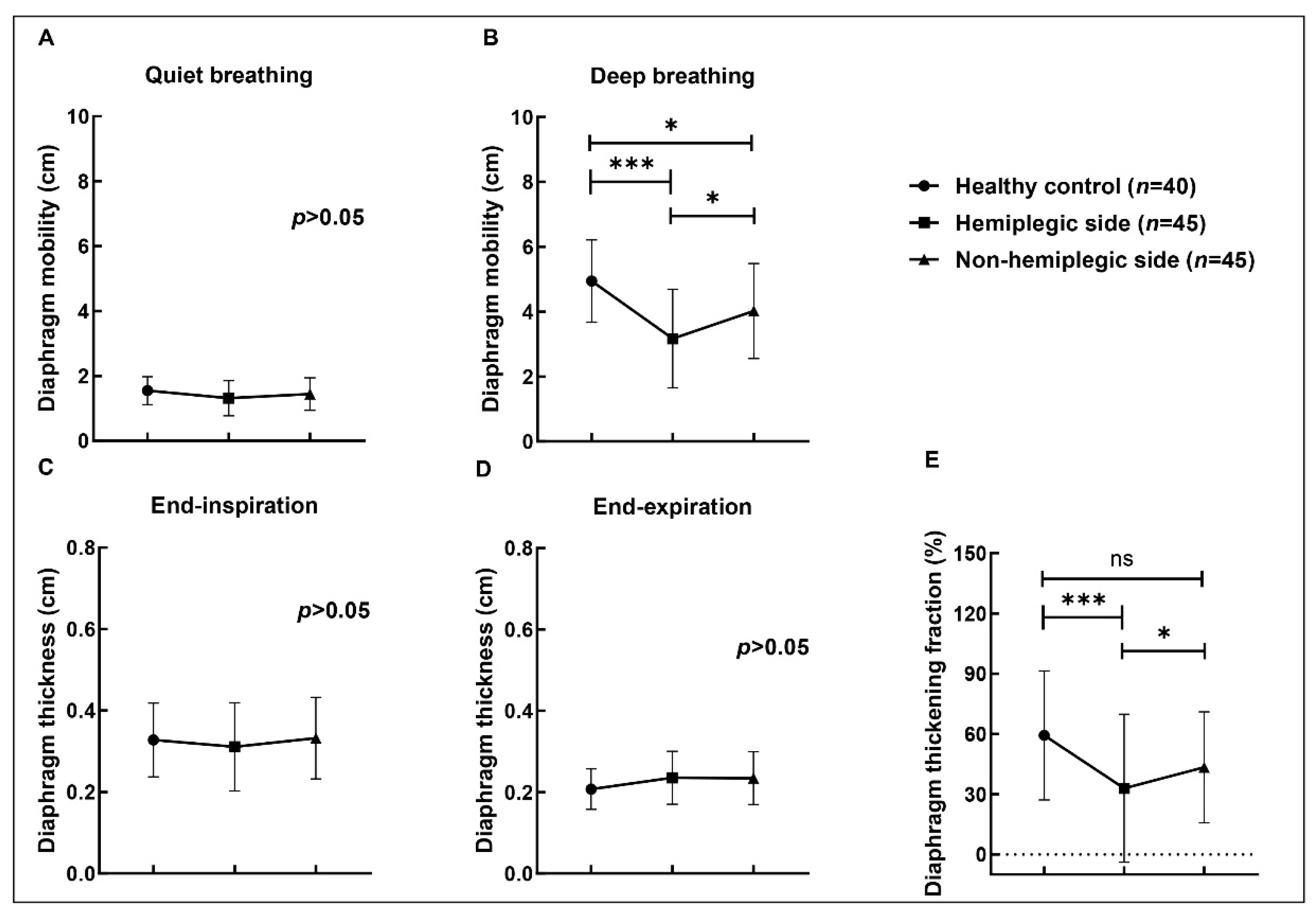
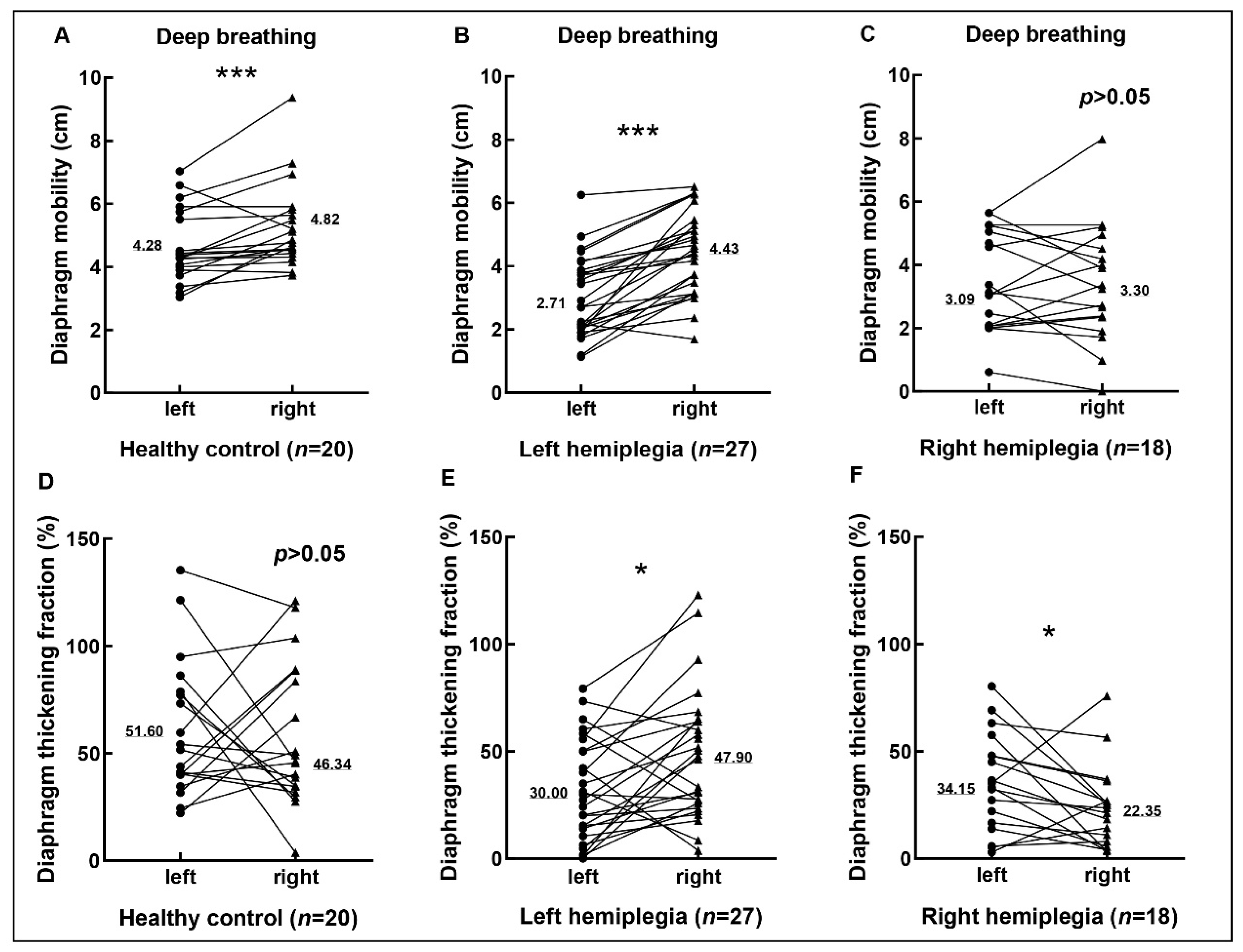
3.2. Diaphragmic Data by Ultrasonography
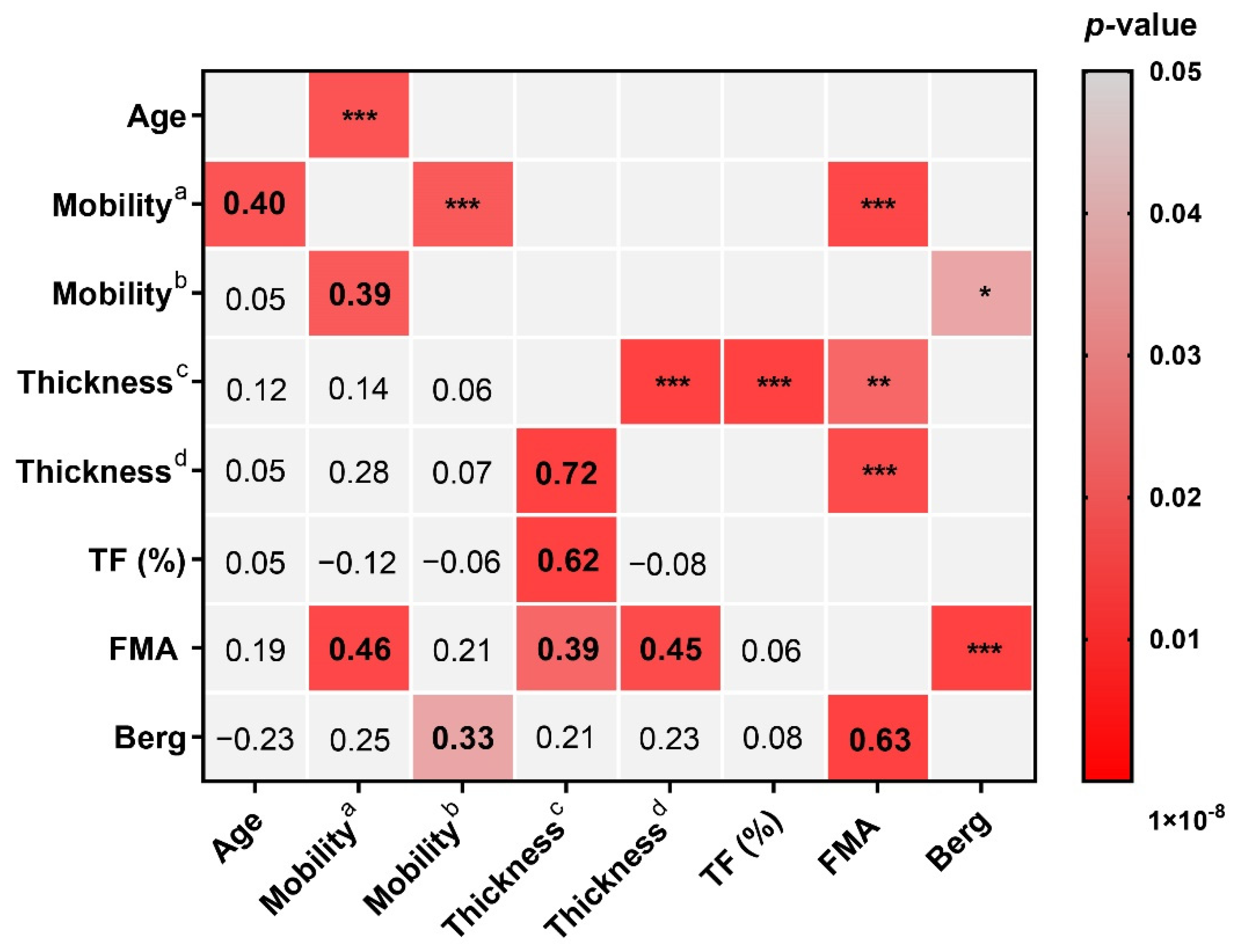
3.3. The Correlation between Diaphragm Data and Other Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Jiang, B.; Sun, H.; Ru, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China. Circulation 2017, 135, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, I. Effects of the combination of respiratory muscle training and abdominal drawing-in maneuver on respiratory muscle activity in patients with post-stroke hemiplegia: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2015, 22, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Mier, A.; Heywood, P.; Murphy, K.; Boultbee, J.; Guz, A. Diaphragmatic movement in hemiplegic patients measured by ultrasonography. Thorax 1994, 49, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminoff, M.J.; Sears, T.A. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J. Physiol. 1971, 215, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, M.; Greco, M.; Bocchino, S.; Cabrini, L.; Beccaria, P.F.; Zangrillo, A. Assessment of diaphragmatic dysfunction in the critically ill patient with ultrasound: A systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schjolberg, A.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Unlocking the locked in; a need for team approach in rehabilitation of survivors with locked-in syndrome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 125, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benditt, J.O.; Boitano, L.J. Pulmonary Issues in Patients with Chronic Neuromuscular Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, C.L.; Mohsenin, V. Respiratory complications of stroke. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 23, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandt, S.R.; Caballero, R.M.D.S.; Forgiarini, L.A., Jr.; Dias, A.S. Correlation between trunk control, respiratory muscle strength and spirometry in patients with stroke: An observational study. Physiother. Res. Int. J. Res. Clin. Phys. Ther. 2011, 16, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandevia, S.C.; Rothwell, J.C. Activation of the human diaphragm from the motor cortex. J. Physiol. 1987, 384, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskill, D.; Murphy, K.; Mier, A.; Owen, M.; Guz, A. Motor cortical representation of the diaphragm in man. J. Physiol. 1991, 443, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnevie, T.; Gravier, F.E.; Ducrocq, A.; Debeaumont, D.; Viacroze, C.; Cuvelier, A.; Muir, J.F.; Tardif, C. Exercise testing in patients with diaphragm paresis. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 248, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwal, A.; Walker, F.O.; Cartwright, M.S. Neuromuscular ultrasound for evaluation of the diaphragm. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıçoğlu, M.S.; Yurdakul, O.V.; Çelik, Y.; Aydın, T. Investigating the correlation between pulmonary function tests and ultrasonographic diaphragm measurements and the effects of respiratory exercises on these parameters in hemiplegic patients. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2022, 29, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetta, A.; Rehman, A.K.; Moxham, J.; Carr, D.H.; Polkey, M.I. Chest radiography cannot predict diaphragm function. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Li, B.; Ming, D.; Wang, W. Multislice Spiral CT Image Analysis and Meta-Analysis of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Respiratory Muscle Function. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1738205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, K.; Tsukuda, T.; Awaya, H.; Takano, K.; Koike, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Sugi, K.; Esato, K. Impaired respiratory mechanics in pulmonary emphysema: Evaluation with dynamic breathing MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999, 10, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.; Hatem, M. Quantitative analysis of diaphragm motion during fluoroscopic sniff test to assist in diagnosis of hemidiaphragm paralysis. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steier, J.; Kaul, S.; Seymour, J.; Jolley, C.; Rafferty, G.; Man, W.; Luo, Y.M.; Roughton, M.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. The value of multiple tests of respiratory muscle strength. Thorax 2007, 62, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiesshoefer, J.; Henke, C.; Herkenrath, S.D.; Randerath, W.; Brix, T.; Görlich, D.; Young, P.; Boentert, M. Noninvasive Prediction of Twitch Transdiaphragmatic Pressure: Insights from Spirometry, Diaphragm Ultrasound, and Phrenic Nerve Stimulation Studies. Respiration 2019, 98, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podnar, S.; Doorduin, J. Safety of needle electromyography of the diaphragm: Anterior lung margins in quietly breathing healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCool, F.D.; Tzelepis, G.E. Dysfunction of the diaphragm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, E.; McCool, F.D. Ultrasound evaluation of the paralyzed diaphragm. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussuges, A.; Gole, Y.; Blanc, P. Diaphragmatic motion studied by m-mode ultrasonography: Methods, reproducibility, and normal values. Chest 2009, 135, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerhill, E.M.; El-Sameed, Y.A.; Glidden, T.J.; McCool, F.D. Monitoring Recovery from Diaphragm Paralysis with Ultrasound. Chest 2008, 133, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, G.F.S.; Pellegrino, G.M.; Di Marco, F.; Imeri, G.; Brochard, L.; Goligher, E.; Centanni, S. A Review of the Ultrasound Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function in Clinical Practice. Respiration 2016, 91, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otadi, K.; Ansari, N.N.; Sharify, S.; Fakhari, Z.; Sarafraz, H.; Aria, A.; Rasouli, O. Effects of combining diaphragm training with electrical stimulation on pain, function, and balance in athletes with chronic low back pain: A randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, V.; Ferreiro, A.; Moore, T.; Fredericson, M. Core stability exercise principles. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2008, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kang, T.; Kim, B. Effects of diaphragm and deep abdominal muscle exercise on walking and balance ability in patients with hemiplegia due to stroke. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2018, 14, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.J.; Haas, M.; Moore, W.L.; Emmil, J.R.; Sipress, J.A.; Williams, A. Effects of Diaphragmatic Breathing Patterns on Balance: A Preliminary Clinical Trial. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2017, 40, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, K.J.; Atkinson, G.; Beauchamp, M.K.; Dixon, J.; Martin, D.; Rahim, S.; Harrison, S.L. Balance impairment in individuals with COPD: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Thorax 2020, 75, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Park, J.; Hwang, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Ultrasonographic Diaphragmatic Motion Analysis and Its Correlation with Pulmonary Function in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 38, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, R.Y.; Park, H.E.; Hong, J.W.; Shin, Y.B.; Yoon, J.A. Correlation of Swallowing Function with Bilateral Diaphragmatic Movement in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 43, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.W.; Jo, K.W.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Im, S. Decreased Diaphragm Excursion in Stroke Patients with Dysphagia as Assessed by M-Mode Sonography. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Cho, J.; Hwang, D.; Lee, W. Decreased Respiratory Muscle Function is Associated with Impaired Trunk Balance among Chronic Stroke Patients: A Cross-sectional Study. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 245, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verin, E.; Marie, J.; Tardif, C.; Denis, P. Spontaneous recovery of diaphragmatic strength in unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleffi-Pereira, M.; Pletsch-Assunção, R.; Cardenas, L.Z.; Santana, P.V.; Ferreira, J.G.; Iamonti, V.C.; Caruso, P.; Fernandez, A.; de Carvalho, C.R.R.; Albuquerque, A.L.P. Unilateral diaphragm paralysis: A dysfunction restricted not just to one hemidiaphragm. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supinski, G.S.; Morris, P.E.; Dhar, S.; Callahan, L.A. Diaphragm Dysfunction in Critical Illness. Chest 2018, 153, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goligher, E.C.; Laghi, F.; Detsky, M.E.; Farias, P.; Murray, A.; Brace, D.; Brochard, L.J.; Bolz, S.S.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Kavanagh, B.P.; et al. Measuring diaphragm thickness with ultrasound in mechanically ventilated patients: Feasibility, reproducibility and validity. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.E.; Paratz, J.D.; Bersten, A.D. Diaphragm and peripheral muscle thickness on ultrasound: Intra-rater reliability and variability of a methodology using non-standard recumbent positions. Respirology 2011, 16, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voyvoda, N.; Yucel, C.; Karatas, G.; Oguzulgen, I.; Oktar, S. An evaluation of diaphragmatic movements in hemiplegic patients. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wait, J.L.; Nahormek, P.A.; Yost, W.T.; Rochester, D.P. Diaphragmatic thickness-lung volume relationship in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, E.; Galeano, C.; Barbosa, N.; Forero, S.; Sunnerhagen, K.; Murphy, M. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of Fugl-Meyer Assessment of Upper Extremity in stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, L.; Korner-Bitensky, N. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale in stroke rehabilitation: A systematic review. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalá-Ripoll, J.V.; Monsalve-Naharro, J.Á.; Hernández-Fernández, F. Incidence and predictive factors of diaphragmatic dysfunction in acute stroke. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, J.G.; Morris, A.D.; Grosset, D.G.; Lees, K.R.; McMillan, N.; Bone, I. Ultrasonic evaluation of movement of the diaphragm after acute cerebral infarction. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 58, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Similowski, T.; Catalá, M.; Rancurel, G.; Derenne, J.P. Impairment of Central Motor Condudion to the Diaphragm in Stroke. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, C.M.; Mier, A.K.; Moxham, J.; Green, M. Diaphragm strength in patients with recent hemidiaphragm paralysis. Thorax 1988, 43, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerscovich, E.O.; Cronan, M.; McGahan, J.P.; Jain, K.; Jones, C.D.; McDonald, C. Ultrasonographic evaluation of diaphragmatic motion. J. Ultrasound Med. 2001, 20, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, A.H.; Rackoll, T.; Grittner, U.; Bläsing, H.; Gorsler, A.; Nabavi, D.G.; Audebert, H.J.; Klostermann, F.; Müller-Werdan, U.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; et al. Physical Fitness Training in Patients with Subacute Stroke (PHYS-STROKE): Multicentre, randomised controlled, endpoint blinded trial. BMJ 2019, 366, l5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
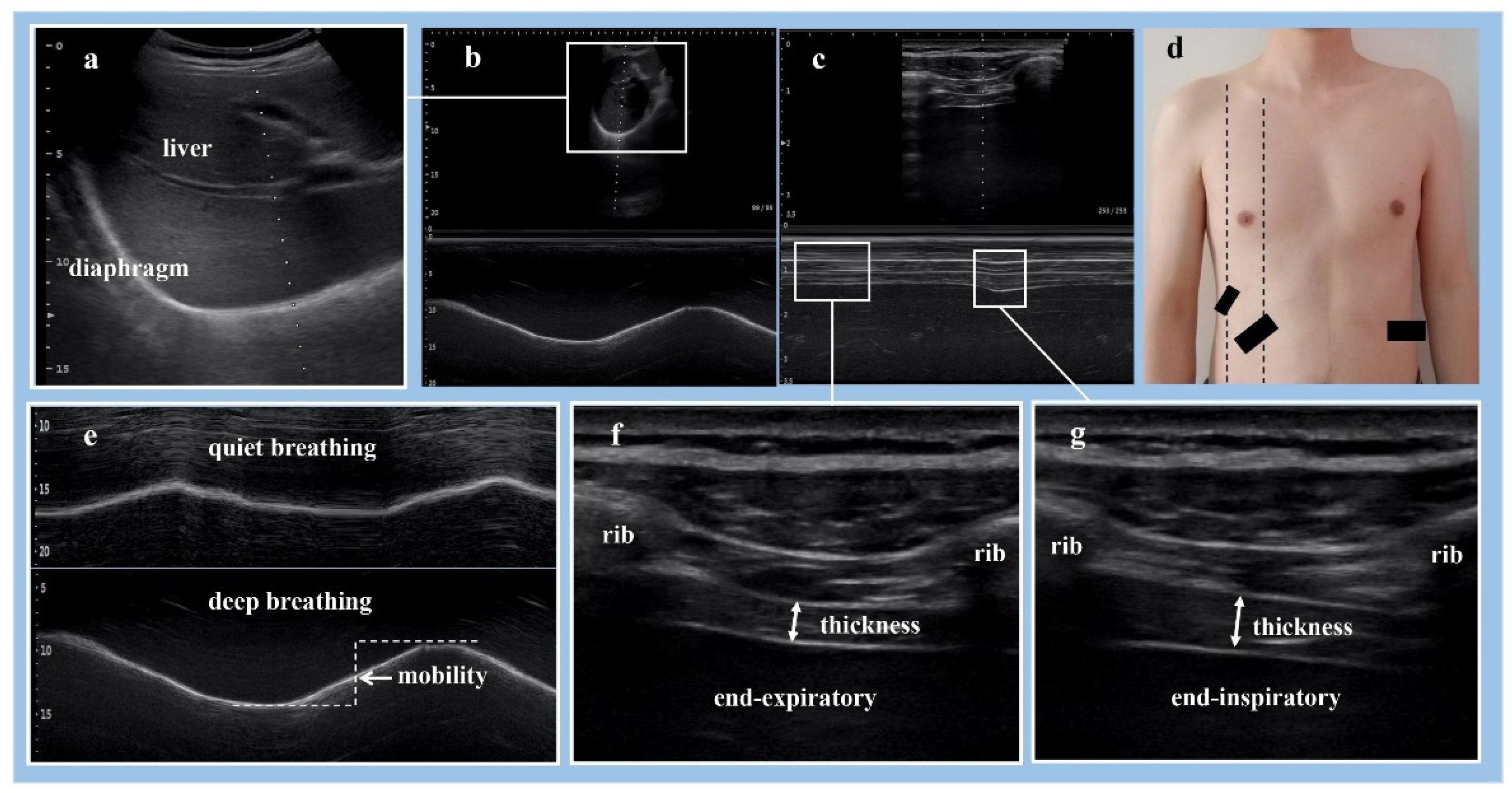
| Healthy Subjects (n = 20) | Hemiplegic Patients (n = 45) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | 0.001 *** | ||
| Male | 8 (40) | 37 (82.22) | |
| Female | 12 (60) | 8 (17.78) | |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 55.95 ± 11.75 | 61.02 ± 13.66 | 0.155 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 0.356 | ||
| Yes | 4 (20) | 14 (31.11) | |
| No | 16 (80) | 31 (68.89) | |
| Post-stroke duration, months (mean ± SD) | - | 3.33 ± 1.71 | - |
| Stroke type, n (%) | - | ||
| Ischemic | - | 29 (64.44) | |
| Hemorrhagic | - | 16 (35.56) | |
| Hemiplegic side, n (%) | - | ||
| Left | - | 27 (60) | |
| Right | - | 18 (40) | |
| Pipeline feeding, n (%) | - | ||
| Yes | - | 5 (11.11) | |
| No | - | 40 (88.89) | |
| Pulmonary infection, n (%) | - | ||
| Yes | - | 7 (15.56) | |
| No | - | 38 (84.44) | |
| Diaphragmatic dysfunction, n (%) | 0.000 *** | ||
| Yes | 1 (5) | 21 (46.67) | |
| No | 19 (95) | 24 (53.33) |
| Healthy Control (n = 40) | Hemiplegic Side (n = 45) | Non-Hemiplegic Side (n = 45) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobility (quiet breath) | 1.54 ± 0.44 | 1.31 ± 0.54 | 1.44 ± 0.50 | 0.105 |
| Mobility (deep breath) | 4.95 ± 1.27 | 3.17 ± 1.52 | 4.02 ± 1.47 | 0.000 *** |
| Thickness (end-inspiratory) | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 0.31 ± 0.11 | 0.33 ± 0.10 | 0.378 |
| Thickness (end-expiratory) | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.072 |
| TF (%) | 59.29 ± 32.11 | 32.95 ± 36.85 | 43.42 ± 27.62 | 0.000 *** |
| Left Side | Right Side | t/Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy control (n = 20) | ||||
| Mobility (quiet breath) | 1.48 ± 0.43 | 1.61 ± 0.45 | 1.476 | 0.156 |
| Mobility (deep breath) | 4.63 ± 1.14 | 5.26 ± 1.34 | −3.179 c | 0.001 *** |
| Thickness (end-inspiratory) | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 0.604 | 0.553 |
| Thickness (end-expiratory) | 0.20 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 1.211 | 0.241 |
| TF (%) | 60.52 ± 31.83 | 58.05 ± 33.21 | −0.16 b | 0.872 |
| Left hemiplegia patients (n = 27) | ||||
| Mobility (quiet breath) | 1.27 ± 0.50 | 1.41 ± 0.49 | −1.33 | 0.195 |
| Mobility (deep breath) | 3.01 ± 1.26 | 4.41 ± 1.30 | −4.397 b | 0.000 *** |
| Thickness (end-inspiratory) | 0.32 ± 0.12 | 0.34 ± 0.10 | −1.268 | 0.216 |
| Thickness (end-expiratory) | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | −0.27 | 0.789 |
| TF (%) | 39.26 ± 44.22 | 48.59 ± 29.74 | −2.114 b | 0.034 * |
| Right hemiplegia patients (n = 18) | ||||
| Mobility (quiet breath) | 1.48 ± 0.53 | 1.39 ± 0.60 | −0.598 | 0.558 |
| Mobility (deep breath) | 3.44 ± 1.55 | 3.40 ± 1.85 | −0.134 | 0.895 |
| Thickness (end-inspiratory) | 0.32 ± 0.10 | 0.30 ± 0.08 | −0.879 b | 0.379 |
| Thickness (end-expiratory) | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | −0.871 c | 0.384 |
| TF (%) | 35.68 ± 22.68 | 23.48 ± 19.11 | −2.243 b | 0.025 * |
| Left Hemiplegia Patients (n = 27) | Right Hemiplegia Patients (n = 18) | t/Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemiplegic side | ||||
| Mobility (deep breath) | 3.01 ± 1.26 | 3.40 ± 1.85 | −0.869 a | 0.385 |
| TF (%) | 39.26 ± 44.22 | 23.48 ± 19.11 | −1.274 a | 0.203 |
| Non-hemiplegic side | ||||
| Mobility (deep breath) | 4.41 ± 1.30 | 3.44 ± 1.55 | 2.268 | 0.028 * |
| TF (%) | 48.59 ± 29.74 | 35.68 ± 22.68 | 1.561 | 0.126 |
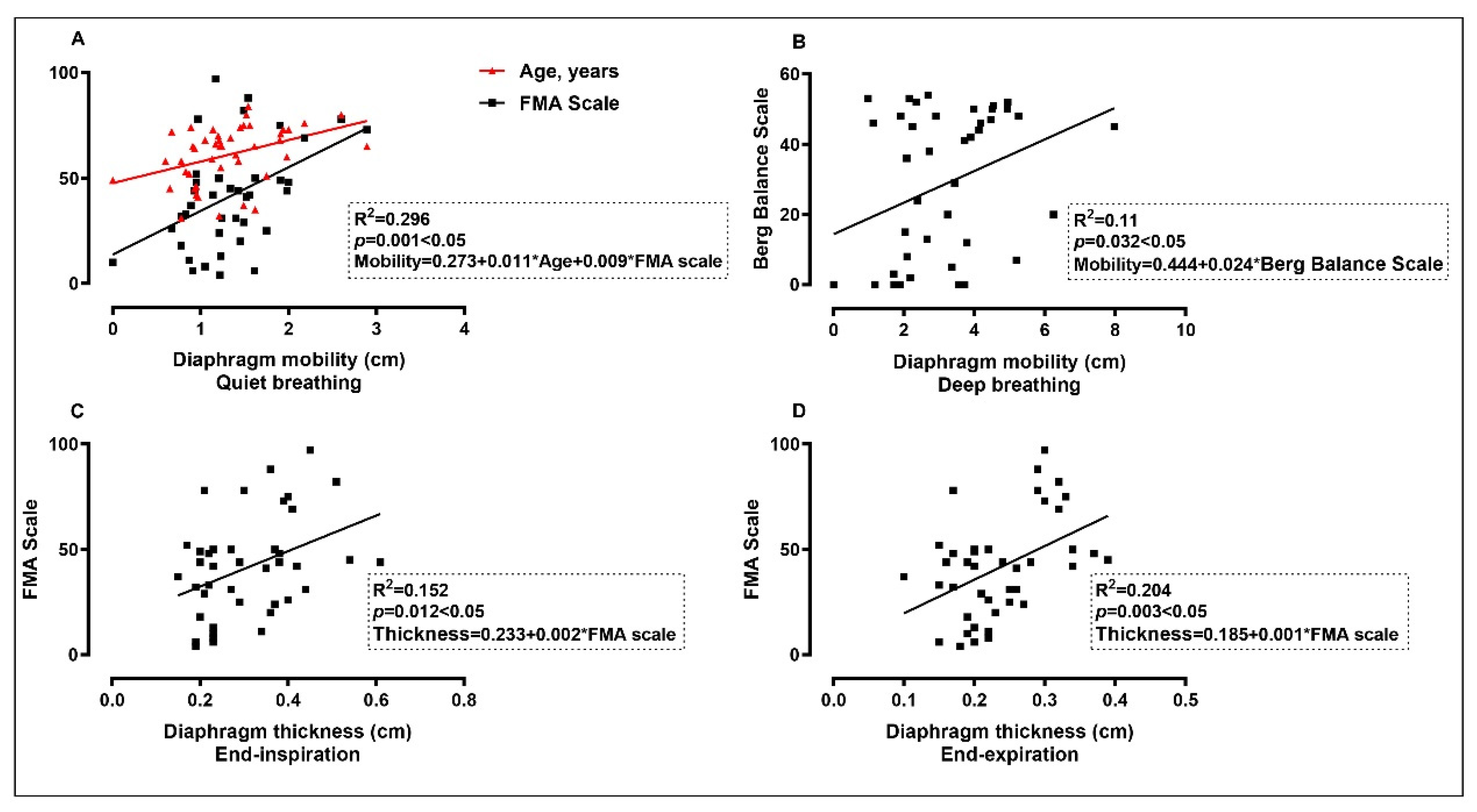
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | R | Collinearity Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Predictors | b | SE | β | Tolerance | VIF | |||
| 1 a | constant | 0.273 | 0.334 | 0.818 | 0.418 | 0.544 | |||
| Age | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.293 | 2.116 | 0.041 | 0.996 | 1.036 | ||
| FMA | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.407 | 2.938 | 0.006 | 0.996 | 1.036 | ||
| 2 b | constant | 2.444 | 0.389 | 6.290 | 0.000 | 0.331 | |||
| Berg | 0.024 | 0.011 | 0.331 | 2.221 | 0.032 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 3 c | constant | 0.233 | 0.032 | 7.169 | 0.000 | 0.390 | |||
| FMA | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.390 | 2.648 | 0.012 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 4 d | constant | 0.185 | 0.019 | 9.741 | 0.000 | 0.452 | |||
| FMA | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.452 | 3.164 | 0.003 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Qu, Q.; Deng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Fu, C.; Jia, J. Assessment of Diaphragm in Hemiplegic Patients after Stroke with Ultrasound and Its Correlation of Extremity Motor and Balance Function. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070882
Liu X, Qu Q, Deng P, Zhao Y, Liu C, Fu C, Jia J. Assessment of Diaphragm in Hemiplegic Patients after Stroke with Ultrasound and Its Correlation of Extremity Motor and Balance Function. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(7):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoman, Qingming Qu, Panmo Deng, Yuehua Zhao, Chenghong Liu, Conghui Fu, and Jie Jia. 2022. "Assessment of Diaphragm in Hemiplegic Patients after Stroke with Ultrasound and Its Correlation of Extremity Motor and Balance Function" Brain Sciences 12, no. 7: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070882
APA StyleLiu, X., Qu, Q., Deng, P., Zhao, Y., Liu, C., Fu, C., & Jia, J. (2022). Assessment of Diaphragm in Hemiplegic Patients after Stroke with Ultrasound and Its Correlation of Extremity Motor and Balance Function. Brain Sciences, 12(7), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070882






